Psychology Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
|
|
|
- Amberlynn Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Psychlgy Chapter 5: Sensatin and Perceptin Sensatin: the stimulus-detectin prcess by which ur sense rgans respnd t and translate envirnmental stimuli int nerve impulses that are sent t the brain Perceptin: making sense f what ur senses tell us is the active prcess f rganizing this stimulus input and giving it meaning Sensry Prcesses: - Five classical senses: visin, auditin (hearing), tuch, gestatin (taste), and lfactin (smell) - Human sensry systems are designed t extract frm the envirnment the infrmatin that we need t functin and survive Psychphysics: studies relatins between the physical characteristics f stimuli and sensry capabilities - Cncerned with tw kinds f sensitivity: the abslute limits f sensitivity, and the differences between stimuli The Abslute Threshld fr Stimulus Detectin: Hw intense a stimulus must be befre we can detect its presence The Abslute Threshld: the lwest intensity at which a stimulus can be detected crrectly 50 percent f the time. The lwer the abslute threshld, the greater the sensitivity. Signal Detectin Thery: Cncerned with the factrs that influence sensry judgments - Decisin Criteria: a standard f hw certain a persn much be that a stimulus is present befre they will say they detect it - Can change depending n fatigue, expectatin, and the ptential significance f the stimulus. - Fur pssible utcmes in signal detectin: A hit: a tne is presented and the participant detects it A miss: a tne is presented and the participant des nt detect it A false alarm: n tne is presented and the participant detects it A crrect rejectin: n tne is presented and the participant des nt detect it The Difference Threshld: the smallest difference between tw stimuli that peple can perceive 50 percent f the time; smetimes called the just nticeable difference - Weber s law: the difference threshld is directly prprtinal t the magnitude f the stimulus with which the cmparisn id being made, and can be expressed as a Weber fractin - Example: the Weber fractin fr weights id 1/50. If yu lift a weight f 50 grams, anther weight must be 51 g t detect a difference; 500g t 510g etc. Sensry Adaptatin: the diminishing sensitivity t unchanging stimuli; due t adaptatin r habituatin The Sensry Systems: Visin: nrmal stimulus is electrmagnetic energy, r light waves; measures in nanmeters Our visual system is nly sensitive t wavelengths frm 700 nm (red) t 400 nm (blue-vilet) The Human Eye:
2 - Crnea: where light waves enter the eye, a transparent prtective structure at the frnt - Pupil: behind the crnea, an adjustable pening that can dilate r cnstrict t cntrl light entry - Iris: clred area arund pupil, cntains muscles that cntrl the pupil s size - Lens: behind the pupil, an elastic structure that becmes thinner r thicker t fcus - Retina: multi-layered tissue at the rear f the eyeball, where the lens fcuses the visual image The ability t see clearly depends n the lens s ability t fcus the image nt the retina Mypia (nearsightedness): The lens fcuses the visual image in frnt f the retina (t near the lens) resulting in a blurred image fr faraway bjects. This generally ccurs because the eyeball is lnger than nrmal Hyperpia (farsightedness): The lens des nt thicken enugh and the image is therefre fcused n a pint behind the retina (t far frm the lens). The aging prcess causes the eyeball t becme shrter ver time, causing hyperpia Phtreceptrs: - The retina cntains tw types f light-sensitive receptr cells, called rds and cnes - There are abut 120 millin rds and nly 6 millin cnes Rds: functin best in dim light, black and white brightness receptrs, 500 times mre sensitive t light than cnes, but d nt give rise t clur sensatin Cnes: clur receptrs, functin best in bright illuminatin Rds are fund thrughut the retina except in the fvea (a small area in the centre f the retina that cntains nly cnes) Cnes decrease in cncentratin as ne mves away frm the centre f the retina Rds and cnes synapse with a layer f biplar cells, which then synapse with a layer f ganglin cells t cmmunicate with the brain The axns f the ganglin cells are cllected int a bundle t frm the ptic nerve Visual Transductin: the prcess whereby the characteristics f a stimulus are cnverted int nerve impulses - Phtpigments: the prtein mlecules trugh which rds and cnes translate light waves int nerve impulses Brightness Visin and Dark Adaptatin: - Rds are far mre sensitive that cnes under lw illuminatin - Rds have much greater brightness sensitivity than cnes thrughut the clur spectrum except at the red end, where rds are relatively insensitive. - Cnes are mst sensitive t lw illuminatin in the greenish-yellw range f the spectrum Dark Adaptatin: the prgressive imprvement in brightness sensitivity that ccurs ver time under cnditins f lw illuminatin - Phtreceptrs becme depleted f their pigment mlecules fr a perid f time after absrbing light - In dark adaptatin, the phtpigment mlecules are regenerated and the receptr s sensitivity increases - Cnes regenerate faster than rds Clur Visin: tw different theries f clur visin
3 The Trichrmatic Thery: There are three types f clur receptrs in the retina - Althugh all cnes can be stimulated by mst wavelengths t sme degree, individual cnes are sensitive t wavelengths that crrespnd t blue, green, r red - Each f these receptr classes sends messages t the brain based n the extent t which they are activated - The visual system cmbines the signals t recreate the riginal hue Oppnent-Prcess Thery: Each f the three cne types respnds t tw different wavelengths. One type respnds t red r green, anther t blue r yellw, and a third t black r white Dual-Prcess Thery: Cmbines the trichrmatic and ppnent-prcess theries t accunt fr clur transductin Clur-Deficient Visin: - Trichrmats: peple with nrmal clur visin, sensitive t all 3 systems red-green, yellw-blue, black-white - Dichrmats: peple wh are clur-blind in nly ne f the systems (red-green r yellw-blue) - Mnchrmats: peple wh are sensitive nly t the black-white system and are ttally clur blind Analysis and Recnstructin f Visual Scenes: After light energy is transfrmed in t nerve impulses, the messages received frm the phtreceptrs are cmbined int the perceptin f a visual scene Feature Detectrs: grups f neurns within the primary visual crtex (in the ccipital lbe) that receive and integrate sensry nerve impulses riginating in specific regins f the retina; fire selectively in respnse t stimuli that have specific characteristics Parallel Prcessing: simultaneus analyzing f smething s clur, shape, distance, and mvement t cnstruct a unified image f its prperties Visual Assciatin Prcesses: infrmatin analyzed and recmbined by the primary visual crtex is ruted t the visual assciatin crtex where mre cmplex features f the visual scene are cmbined and interpreted Auditin: stimuli fr ur sense f hearing are sund waves, a frm f mechanical energy Sund is actually pressure waves in the air, water, r sme ther cnductin medium Frequency: the number f sund waves r cycles per secnd- - cycles per secnd are measured in hertz (Hz) - sund waves frequency is related t pitch higher frequency = higher pitch Amplitude: the vertical size f the sund waves - the amunt f cmpressin and expansin f the mlecules in the cnducting medium - the primary determinant f the sund s perceived ludness - expressed as decibels (db) Auditry Transductin: Transductin system made up f tiny bnes, membranes, and liquid-filled tubes designed t translate pressure waves int nerve impulses - sund waves travel in an auditry canal - leads t the eardrum: a mvable membrane that vibrates in respnse t the sund waves
4 - middle ear: a cavity husing three tiny bnes (the hammer, anvil, and stirrup) beynd the eardrum these bnes vibrate t amplify the sund waves mre than 30 times hammer attatched t the eardrum, stirrup- attatched t the val windw- a membrane that frms the bundary between the middle and inner ear - inner ear: cntains the cchlea cchlea: a ciled snail-shaped tube that is filled with fluid and cntains the basilar membrane basilar membrane: a sheet f tissue that runs the length f the cchlea rgan f Crti: rests n the basilar membrane, cntaining thusands f tiny hair cells the actual sund receptrs the hair cells synapse with the neurns f the auditry nerve that sends impulses via an auditry relay statin in the thalamus t the auditry crtex (in the tempral lbe) Sund waves strike the eardrum and create pressure at the val windw by the hammer, anvil, and stirrup, setting the fluid inside the cchlea int mtin. The fluid waves vibrate the basilar membrane and the membrane abve it, causing the hair cells in the rgan r Crti t bend. This bending triggers a release f neurtransmitter substance resulting in nerve impulses sent t the brain Cding f Pitch and Ludness: The auditry system transfrms the sensry qualities f ludness and pitch int the language f nerve impulses. High-Amplitude sund waves cause the hair cells t bend mre and release mre neurtransmitter substance luder Frequency Thery f Pitch Perceptin: nerve impulses sent t the brain match the frequency f the sund wave Place Thery f Pitch Perceptin: the specific pint in the cchlea where the fluid wave peaks and mst strngly bends the hair cells serves as a frequency cding cue Sund Lcalizatin: The nervus system uses infrmatin cncerning the time and intensity differences f sunds arriving at the tw ears t lcate the surce f sunds in space - sunds arrive first and ludest at the ear clsest t the sund; when the sund is in frnt r behind us, the sund wave reaches bth ears at the same time and at the same intensity Hearing Lss: Tw majr types Cnductin Deafness: caused by prblems invlving the mechanical system that transmits sund waves t the cchlea - can be caused by puncturing an eardrum r lss f functin in the tiny bnes Nerve Deafness: caused by damaged receptrs within the inner ear r damage t the auditry nerve itself - cannt be helped by a hearing aid - can be caused by aging and disease Taste and Smell: chemical senses because their receptrs are sensitive t chemical mlecules rather than energy Gustatin: sense f taste - sense f taste respnds nly t fur qualities: sweet, sur, salty, bitter - every ther taste experience cmbines these qualities and thse f ther senses, such as smell, temperature, and tuch
5 Taste Buds: chemical receptrs cncentrated alng the edges and back surface f the tngue - We have a small number f receptrs n the rf and back f the muth - Taste buds cnsist f several receptr cells - Hairlike structures prject frm the tp f each cell int the taste pre, an pening in the surface f the tngue - Substances taken int the muth interact with saliva t frm a chemical slutin that stimulates receptr cells - A taste results frm cmplex patterns f neural activity prduced by the fur types f taste receptrs Olfactin: sense f smell - Receptrs are lng cells that prject thrugh the lining f the upper part f the nasal cavity and int the mucus membrane - We have abut 40 millin lfactry receptrs - Mst ppular thery is that lfactry receptrs recgnize diverse drs individually rather than by mixing the activity f fewer basic receptrs like in taste - Receptrs have receptr structures that resemble neurtransmitter binding sites n neurns - Odr mlecules can lck int sites that are tailred t fit them Phermnes: chemical signals fund in natural bdy scents Menstrual Synchrny: the tendency f wmen wh live tgether r are clse friends t becme mre similar in their menstrual cycles The Skin and Bdy Senses: include senses f tuch, kinesthesis (muscle mvement), and equilibrium The Tactile Senses: we are sensitive t at least fur tactile sensatins: pressure (tuch), pain, warmth, and cld - These are cnveyed by receptrs in the skin and in ur internal rgans. - All ther cmmn skin sensatins are mixtures f thse fur sensatins Free Nerve Endings: the primary receptrs fr pain and temperature; simple nerve cells beneath the skin s surface The brain can lcate sensatins because skin receptrs send their messages t the pint in the smatsensry crtex that crrespnds t the area f the bdy where the receptr is lcated The Bdy Senses: kinesthesis and equilibrium Kinesthesis: prvides us with feedback abut ur muscles and jints psitins and mvements Receptrs are nerve ending in the muscles, tendns, and jints Gives us the basis fr making crdinated mvements Vestibular Sense: the sense f bdy rientatin r equilibrium; cperates with kinesthesis Receptrs are lcated in the vestibular apparatus f the inner ear One part f the equilibrium system cnsists f three semicircular canals: which cntain receptrs fr head mvement Vestibular sacs als cntain hair cells that respnd t the psitin f the bdy and tell us if we are upright r tilted at an angle Perceptin: an active creative prcess in which raw sensry data are rganized and given meaning
6 The brain has tw different kinds f prcessing functins t create ur perceptins Bttm-up Prcessing: the system takes in individual elements f the stimulus and then cmbines them int a unified perceptin Tp-dwn Prcessing: sensry infrmatin is interpreted in the light f existing knwledge, cncepts, ideas, and expectatins Attentin: invlves tw prcesses f selectin fcusing n certain stimuli and filtering ut ther incming infrmatin - Attentin is affected by bth the nature f the stimulus and by persnal factrs - Our attentin is attracted by intensity, nvelty, mvement, cntrast, and repetitin - Our mtives and interests act as pwerful filters fr what we fcus ur attentin n Gestalt Principles f Perceptual Organizatin: Believed in tp-dwn prcessing the whles we perceive are ften mre than the sum f their parts Figure-grund relatins: we tend t rganize stimuli int a central r fregrund figure and a backgrund; the central figure is mre striking in ur perceptins and memry Gestalt laws f perceptual rganizatin: similarity, prximity, clsure, cntinuity; hw we grup and interpret stimuli - Law f similarity: when parts f a cnfiguratin are perceived as similar, they will be perceives as belnging tgether - Law f prximity: elements that are near ne anther are likely t be perceived as part f the same cnfiguratin - Law f clsure: peple tent t clse the pen edges f a figure r fill in gaps in an incmplete figure - Law f cntinuity: peple link individual elements tgether s that they frm a cntinuus line r pattern Perceptual Schema: a mental representatin r image t cmpare with needed t recgnize a stimulus Perceptual Set: a readiness t perceive stimuli in a particular way perceptin influenced by expectatins Perceptual Cnstancies: allw us t recgnize familiar stimuli under varying cnditins - Shape cnstancy: allws us t recgnize peple and ther bjects frm many different angles - Brightness cnstancy: the relative brightness f bjects remains the same under different cnditins f illuminatin - Size cnstancy: the perceptin that the size f bjects remains cnstant even thugh images n ur retina change in size with variatins in distance Perceptin f Depth, Distance, and Mvement: Depth and Distance Perceptin: The retina receives infrmatin in tw dimensins (length and width) but the brain translates int 3 dimensinal using - Mncular cues: require nly ne eye - Bincular cues: require bth eyes Mncular Depth Cues:
7 - Light and shadw: creates depth - Linear perspective: the perceptin that parallel lines cnverge r angle tward ne anther as they recede int the distance - Interpsitin: bjects clser t us may cut ff part f ur view f mre distant bjects - Height in hrizntal plane: clser appears higher in hrizntal plane - Texture: appears finer as distance increases - Clarity: clser is mre clear - Relative size: lks smaller farther away - Mtin parallax: if we are mving, nearby bjects appear t mve faster in the ppsite directin Bincular Disparity: each eye sees a slightly different image Cnvergence: prduced by feedback frm the muscles that turn yur eyes inward t view a near bject Perceptin f Mvement: - the mvement f a stimulus acrss the retina - the relative mvement f an bject against a structured backgrund Strbscpic Mvement: illusry mvement prduced when a light is briefly flashed in darkness and then a few millisecnds later, anther light is flashed nearby the first light seems t mve Illusins: cmpelling but incrrect perceptins errneus perceptual hyptheses abut the nature f the stimulus Experience, Critical Perids, and Perceptual Develpment Crss-Cultural Research n Perceptin: the culture ne grws up in helps determine the kinds f perceptual learning experiences peple have. Crss cultural research can help identify which aspects f perceptin ccur n all peple, regardless f culture.
Topic 11: Senses. Sensory Receptors
 Tpic 11: Senses Sensry Receptrs Part f the nervus system that detects a stimulus A sensry receptr culd be: Types f Sensry Receptrs: Chemreceptrs: detects chemicals ( ) Phtreceptrs: detects light (fund
Tpic 11: Senses Sensry Receptrs Part f the nervus system that detects a stimulus A sensry receptr culd be: Types f Sensry Receptrs: Chemreceptrs: detects chemicals ( ) Phtreceptrs: detects light (fund
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
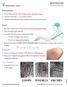
Human Senses. Touch. Fingerprint. Vidhya Peetham i-school. The skin in our fingers is very sensitive. The skin in our back is not very sensitive.
 Vidhya Peetham i-schl Human Senses Humans have five senses. They are hearing, sight, smell, taste and tuch. Often, we use mre than ne sense at the same time. All the five senses wrk with the brain and
Vidhya Peetham i-schl Human Senses Humans have five senses. They are hearing, sight, smell, taste and tuch. Often, we use mre than ne sense at the same time. All the five senses wrk with the brain and
PERCEPTUAL DEVELOPMENT CHAPTER 16
 PERCEPTUAL DEVELOPMENT CHAPTER 16 Overview f Questins What can newbrns perceive? When can an infant perceive clr? Can a newbrn recgnize his r her mther? INFANT BRAIN DEVELOPMENT At birth babies brain has
PERCEPTUAL DEVELOPMENT CHAPTER 16 Overview f Questins What can newbrns perceive? When can an infant perceive clr? Can a newbrn recgnize his r her mther? INFANT BRAIN DEVELOPMENT At birth babies brain has
Glaucoma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd
 Glaucma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd 1) Read the glaucma article well! It will explain what it is, plus tell yu sme symptms and risk factrs. Yu may want t use a highlighter r pen t mark imprtant
Glaucma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd 1) Read the glaucma article well! It will explain what it is, plus tell yu sme symptms and risk factrs. Yu may want t use a highlighter r pen t mark imprtant
Accessibility Customer Service Volunteer Guide
 Accessibility Custmer Service Vlunteer Guide Accessibility Ontari Disability Act (AODA) and Serve-Ability & Integrated Accessibility Standards Regulatin (IASR) Training "The Exchange is a beautiful place
Accessibility Custmer Service Vlunteer Guide Accessibility Ontari Disability Act (AODA) and Serve-Ability & Integrated Accessibility Standards Regulatin (IASR) Training "The Exchange is a beautiful place
Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizations
 Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizatins We begin this chapter by lking at hw peple perceive themselves, that is, their selfcncept. The Self-Cncept refers t an individual s self-beliefs
Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizatins We begin this chapter by lking at hw peple perceive themselves, that is, their selfcncept. The Self-Cncept refers t an individual s self-beliefs
AP Biology Lab 12: Introduction to the Scientific Method and Animal Behavior
 Name: AP Bilgy Lab 12: Intrductin t the Scientific Methd and Animal Behavir Overview In this lab yu will: -Observe an rganism and design an experiment t investigate their respnses t envirnmental variables.
Name: AP Bilgy Lab 12: Intrductin t the Scientific Methd and Animal Behavir Overview In this lab yu will: -Observe an rganism and design an experiment t investigate their respnses t envirnmental variables.
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
Understanding and Recognizing Anxiety
 Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Lecture 17 (03/28/2011) (Lateralization in the Brain) PSY 215. Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.
 PSY 215 Lecture 17 (03/28/2011) (Lateralizatin in the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215 Lecture 17 Tpic: Lateralizatin in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 404-413 Crrectins: Nne needed Annuncements: Wednesday will
PSY 215 Lecture 17 (03/28/2011) (Lateralizatin in the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215 Lecture 17 Tpic: Lateralizatin in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 404-413 Crrectins: Nne needed Annuncements: Wednesday will
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Data Fusion for Predicting Breast Cancer Survival
 Data Fusin fr Predicting Breast Cancer Linbailu Jiang, Yufei Zhang, Siyi Peng Mentr: Irene Kaplw December 11, 2015 1 Intrductin 1.1 Backgrund Cancer is mre f a severe health issue than ever in ur current
Data Fusin fr Predicting Breast Cancer Linbailu Jiang, Yufei Zhang, Siyi Peng Mentr: Irene Kaplw December 11, 2015 1 Intrductin 1.1 Backgrund Cancer is mre f a severe health issue than ever in ur current
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Cellular Neurophysiology Membrane Ionic Gradients Concentration gradients and diffusion Membrane transport:
 Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
2. As a caregiver, it s important to build a team/ support network around you (choose one):
 Test Questins (Part 1, Chapter 1) 1. Of thse affected by dementia: 50% are nt aware they are changing and 50% are aware they are changing. Of the 50% wh are aware, they will always respnd by becming anxius
Test Questins (Part 1, Chapter 1) 1. Of thse affected by dementia: 50% are nt aware they are changing and 50% are aware they are changing. Of the 50% wh are aware, they will always respnd by becming anxius
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds. Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
 Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Newborn Hearing Screening, Early Identification and Loss to Follow-Up
 Newbrn Hearing Screening, Early Identificatin and Lss t Fllw-Up Prgram in Audilgy and Cmmunicatin Sciences Pediatric Audilgy Specializatin The cntents f this presentatin were develped under a grant frm
Newbrn Hearing Screening, Early Identificatin and Lss t Fllw-Up Prgram in Audilgy and Cmmunicatin Sciences Pediatric Audilgy Specializatin The cntents f this presentatin were develped under a grant frm
Sensory Physiology. Somatosensory Receptors
 Sensry Physilgy - Stimuli at the cnscius level f perceptin Special senses visin, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium Smatic senses tuch, temperature, pain, itch and prpriceptin Prpriceptin = the awareness
Sensry Physilgy - Stimuli at the cnscius level f perceptin Special senses visin, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium Smatic senses tuch, temperature, pain, itch and prpriceptin Prpriceptin = the awareness
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Sensory System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
UNIT 3 - CHAPTER 12: NERVOUS SYSTEM III: SENSES. 1. Differentiate between general senses and special senses.
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 12.1 Intrductin UNIT 3 - CHAPTER 12: NERVOUS SYSTEM III: SENSES 1. Differentiate between general senses and special senses. 12.2 Receptrs, Sensatin, and Perceptin 2. Name the five types
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 12.1 Intrductin UNIT 3 - CHAPTER 12: NERVOUS SYSTEM III: SENSES 1. Differentiate between general senses and special senses. 12.2 Receptrs, Sensatin, and Perceptin 2. Name the five types
Psychology Class 11 Syllabus
 Psychlgy Class 11 Syllabus Curse Structure Unit Tpic Marks I What is Psychlgy? 7 II Methds f Enquiry in Psychlgy 10 III The Bases f Human Behaviur 8 IV Human Develpment 6 V Sensry, Attentinal and Perceptual
Psychlgy Class 11 Syllabus Curse Structure Unit Tpic Marks I What is Psychlgy? 7 II Methds f Enquiry in Psychlgy 10 III The Bases f Human Behaviur 8 IV Human Develpment 6 V Sensry, Attentinal and Perceptual
Seeing Motion: Lecture Notes
 Lecture Ntes - 07/13/99 Alex Huk 0. Intrductin Seeing Mtin: Lecture Ntes Mtin perceptin can be brken int 2 main categries: perceiving mtin f bjects in the wrld ("Object mtin"). perceiving mtin f urselves
Lecture Ntes - 07/13/99 Alex Huk 0. Intrductin Seeing Mtin: Lecture Ntes Mtin perceptin can be brken int 2 main categries: perceiving mtin f bjects in the wrld ("Object mtin"). perceiving mtin f urselves
Chapter 13 The Occipital Lobe Anatomy of the Occipital Lobe Subdivision of the occipital cortex Connections of the Visual Cortex
 Chapter 13 The Occipital Lbe Anatmy f the Occipital Lbe - Frm the psterir ple f the cerebral hemisphere - Subdivisin f the ccipital crtex Mnkey s crtex was first divided by Brdmann int 3 regins area 17,
Chapter 13 The Occipital Lbe Anatmy f the Occipital Lbe - Frm the psterir ple f the cerebral hemisphere - Subdivisin f the ccipital crtex Mnkey s crtex was first divided by Brdmann int 3 regins area 17,
The brain stem functions in homeostasis, coordination of movement, and conduction of information to and from higher brain centers.
 Chapter 49 Nervus Systems Lecture Outline Cncept 49.2 The vertebrate brain is reginally specialized. In all vertebrates, three bilaterally symmetrical, anterir bulges f the neural tube the frebrain, midbrain,
Chapter 49 Nervus Systems Lecture Outline Cncept 49.2 The vertebrate brain is reginally specialized. In all vertebrates, three bilaterally symmetrical, anterir bulges f the neural tube the frebrain, midbrain,
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Function: Life at the Edge
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
Extension: Flexion: Motor neurons: o Only excitatory neurons release acetylcholine (ACh)
 Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
The principles of evidence-based medicine
 The principles f evidence-based medicine By the end f this mdule yu shuld be able t: Describe what evidence based medicine is Knw where t find quality evidenced based medicine n the internet Be able t
The principles f evidence-based medicine By the end f this mdule yu shuld be able t: Describe what evidence based medicine is Knw where t find quality evidenced based medicine n the internet Be able t
Self-Awareness Exercise:
 Self-Awareness Exercise: Spend 5 minutes t write dwn answers t the fllwing questins: 1. What were the rules and ways f cmmunicating within my family? Hw has this affected the way I see the wrld? 2. What
Self-Awareness Exercise: Spend 5 minutes t write dwn answers t the fllwing questins: 1. What were the rules and ways f cmmunicating within my family? Hw has this affected the way I see the wrld? 2. What
FOUNDATIONS OF DECISION-MAKING...
 Table f Cntents FOUNDATIONS OF DECISION-MAKING... Errr! Bkmark nt Describe the decisin-making prcess pp.62-66... Errr! Bkmark nt Explain the three appraches managers can use t make decisins pp.67-70 Errr!
Table f Cntents FOUNDATIONS OF DECISION-MAKING... Errr! Bkmark nt Describe the decisin-making prcess pp.62-66... Errr! Bkmark nt Explain the three appraches managers can use t make decisins pp.67-70 Errr!
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition
 Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition Sensation the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition Sensation the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variations on a Theme
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Forensic Anthropology Lecture Notes. Week 3: Crime Scene Analysis, Trauma and Taphonomy
 Frensic Anthrplgy Lecture Ntes Week 3: Crime Scene Analysis, Trauma and Taphnmy Mdule 16: Blunt Frce Trauma What is Blunt Frce Trauma? Blunt frce trauma ccurs any time a frce impacts tissue ver a relatively
Frensic Anthrplgy Lecture Ntes Week 3: Crime Scene Analysis, Trauma and Taphnmy Mdule 16: Blunt Frce Trauma What is Blunt Frce Trauma? Blunt frce trauma ccurs any time a frce impacts tissue ver a relatively
Say Goodbye to Test Anxiety. Kortschak Center for Learning and Creativity University of Southern California Presented by: Eliza Peña
 Say Gdbye t Test Anxiety Krtschak Center fr Learning and Creativity University f Suthern Califrnia Presented by: Eliza Peña 1 Learning Objective By the end f this wrkshp, students will be able t: Recgnize
Say Gdbye t Test Anxiety Krtschak Center fr Learning and Creativity University f Suthern Califrnia Presented by: Eliza Peña 1 Learning Objective By the end f this wrkshp, students will be able t: Recgnize
DATA RELEASE: UPDATED PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS ON 2016 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE SURVEY ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE QUESTIONS
 DATA RELEASE: UPDATED PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS ON 216 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE SURVEY ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE QUESTIONS This briefing has been specifically prepared fr the Ministry f Health t prvide infrmatin frm this
DATA RELEASE: UPDATED PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS ON 216 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE SURVEY ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE QUESTIONS This briefing has been specifically prepared fr the Ministry f Health t prvide infrmatin frm this
CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION
 CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
Forensic Science: Fundamentals & Investigations, 2e Chapter 1. All rights Reserved Cengage/NGL/South-Western 2016
 1 Frensic Science: Fundamentals & Investigatins, 2e Cengage/NGL/Suth-Western 2016 Observatin Skills By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: 1.1 Define bservatin and describe what changes ccur in the
1 Frensic Science: Fundamentals & Investigatins, 2e Cengage/NGL/Suth-Western 2016 Observatin Skills By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: 1.1 Define bservatin and describe what changes ccur in the
Career Confidence. by Kevin Gaw
 Career Cnfidence by Kevin Gaw In additin t the requisite skills, experiences, and rganizatinal match being sught fr a psitin fr which a candidate is applying, mst emplyers screen fr what I call career
Career Cnfidence by Kevin Gaw In additin t the requisite skills, experiences, and rganizatinal match being sught fr a psitin fr which a candidate is applying, mst emplyers screen fr what I call career
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
Group Members: Date Period
 Dissectin Kit Number: Grup Members: Date Perid Dissectins Objective: In this tw-week investigatin, we will be lking at an invetebrate (grasshpper) and a vertebrate (frg). Yu will be fcusing n the external
Dissectin Kit Number: Grup Members: Date Perid Dissectins Objective: In this tw-week investigatin, we will be lking at an invetebrate (grasshpper) and a vertebrate (frg). Yu will be fcusing n the external
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE. All Systems, GO! Lesson #3
 ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
Imaging tests allow the cancer care team to check for cancer and other problems inside the body.
 IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
Human papillomavirus (HPV) refers to a group of more than 150 related viruses.
 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance: Locating Genes Along Chromosomes
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 15: The Chrmsmal Basis f Inheritance: Lcating Genes Alng Chrmsmes Lcating Genes Alng the Chrmsme CONCEPTS: 15.2 Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns f inheritance 15.3 Linked genes
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 15: The Chrmsmal Basis f Inheritance: Lcating Genes Alng Chrmsmes Lcating Genes Alng the Chrmsme CONCEPTS: 15.2 Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns f inheritance 15.3 Linked genes
Neurologic Examination Benchmarks
 Neurlgic Examinatin Benchmarks Preparatin & psitining: A cmplete neurlgic exam can be dne fllwing the musculskeletal exam, r the neurlgic exam can be integrated int the exam f each regin f the bdy. Cranial
Neurlgic Examinatin Benchmarks Preparatin & psitining: A cmplete neurlgic exam can be dne fllwing the musculskeletal exam, r the neurlgic exam can be integrated int the exam f each regin f the bdy. Cranial
EDPS 475: Instructional Objectives for Midterm Exam Behaviorism
 EDPS 475: Instructinal Objectives fr Midterm Exam Behavirism 1. Given a nvel example t chse frm, identify the characteristics f classical cnditining. General mdel: Stimulus (S) elicits >Respnse (R) Based
EDPS 475: Instructinal Objectives fr Midterm Exam Behavirism 1. Given a nvel example t chse frm, identify the characteristics f classical cnditining. General mdel: Stimulus (S) elicits >Respnse (R) Based
Awareness of Autistic Spectrum Conditions
 Unit 21: Awareness f Autistic Spectrum Cnditins Unit reference number: H/616/7304 Level: 2 Unit type: Optinal Credit value: 2 Guided learning hurs: 17 Unit summary This unit intrduces yu t autistic spectrum
Unit 21: Awareness f Autistic Spectrum Cnditins Unit reference number: H/616/7304 Level: 2 Unit type: Optinal Credit value: 2 Guided learning hurs: 17 Unit summary This unit intrduces yu t autistic spectrum
Podcast Transcript Title: Common Miscoding of LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duration: 00:16:10
 Pdcast Transcript Title: Cmmn Miscding f LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duratin: 00:16:10 NCTCFP: Welcme t this pdcast spnsred by the Natinal Clinical Training Center fr Family
Pdcast Transcript Title: Cmmn Miscding f LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duratin: 00:16:10 NCTCFP: Welcme t this pdcast spnsred by the Natinal Clinical Training Center fr Family
Organizational Capacity for Change and Patient Safety
 Organizatinal Capacity fr Change and Patient Safety Debrah M. Nadzam, PhD, FAAN - Jint Cmmissin Resurces Lrrie Jnes-Hartley, MSN, CRRN-A - Durham Reginal Hspital Presentatin Objectives Briefly describe
Organizatinal Capacity fr Change and Patient Safety Debrah M. Nadzam, PhD, FAAN - Jint Cmmissin Resurces Lrrie Jnes-Hartley, MSN, CRRN-A - Durham Reginal Hspital Presentatin Objectives Briefly describe
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Osteoporosis Fast Facts
 Osteprsis Fast Facts Fast Facts n Osteprsis Definitin Osteprsis, r prus bne, is a disease characterized by lw bne mass and structural deteriratin f bne tissue, leading t bne fragility and an increased
Osteprsis Fast Facts Fast Facts n Osteprsis Definitin Osteprsis, r prus bne, is a disease characterized by lw bne mass and structural deteriratin f bne tissue, leading t bne fragility and an increased
Frequently Asked Questions: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing
 Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Managing a Balanced Team using Myers Briggs Type Indicator 26 th November Lisa Williams Angela Peel
 Managing a Balanced Team using Myers Briggs Type Indicatr 26 th Nvember 2012 Lisa Williams Angela Peel capabilities assessment selectin develpment ptential Intrductins Welcme Wh are we, what d we d, and
Managing a Balanced Team using Myers Briggs Type Indicatr 26 th Nvember 2012 Lisa Williams Angela Peel capabilities assessment selectin develpment ptential Intrductins Welcme Wh are we, what d we d, and
DIRECTED FORGETIING: SHORT-TERM MEMORY OR CONDITIONED RESPONSE? WENDY S. MILLER and HARVARD L. ARMUS The University of Toledo
 The Psychlgical Recrd, 1999, 49, 211-220 DIRECTED FORGETIING: SHORT-TERM MEMORY OR CONDITIONED RESPONSE? WENDY S. MILLER and HARVARD L. ARMUS The University f Tled Previus researchers have interpreted
The Psychlgical Recrd, 1999, 49, 211-220 DIRECTED FORGETIING: SHORT-TERM MEMORY OR CONDITIONED RESPONSE? WENDY S. MILLER and HARVARD L. ARMUS The University f Tled Previus researchers have interpreted
Psychological aspects of breast cancer. Dr Caroline Dancyger & Dr Esther Hansen
 Psychlgical aspects f breast cancer Dr Carline Dancyger & Dr Esther Hansen Cmmn acrss all cancers Adjustment as the nrm Diagnsis End f active treatment r Discharge Palliative Care Recurrence distress t
Psychlgical aspects f breast cancer Dr Carline Dancyger & Dr Esther Hansen Cmmn acrss all cancers Adjustment as the nrm Diagnsis End f active treatment r Discharge Palliative Care Recurrence distress t
Chapter 13 Forensic Anthropology: What We Learn from Bones By the end of this chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
UNIT 2: mapping bananas
 Oxfam Educatin www.xfam.rg.uk/educatin UNIT 2: mapping bananas Age range: 7-11 years Outline Learners will investigate sme f the cuntries where the bananas we eat in the UK are grwn. They will first lcate
Oxfam Educatin www.xfam.rg.uk/educatin UNIT 2: mapping bananas Age range: 7-11 years Outline Learners will investigate sme f the cuntries where the bananas we eat in the UK are grwn. They will first lcate
Sensation and Perception. Chapter 6
 Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation. Date Period. 1) sensation. 2) perception. 3) bottom-up processing. 4) top-down processing
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
DEMENTIA. DESCRIPTION: a progressive, degenerative disease of the brain, which causes impairment of thinking and memory
 DEMENTIA Dementia a syndrme cnsisting f a number f symptms including lss f memry, judgment and reasning, and changes in md and behavir the changes may affect a persn's ability t functin at wrk, in scial
DEMENTIA Dementia a syndrme cnsisting f a number f symptms including lss f memry, judgment and reasning, and changes in md and behavir the changes may affect a persn's ability t functin at wrk, in scial
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hockey Selection Camp August 16-19, 2018
 2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
TABLE OF CONTENTS Glossary of terms Code Pad Diagram 3. Understanding the Code Pad lights.4.
 TABLE OF CONTENTS... Glssary f terms 2... Cde Pad Diagram 3 Understanding the Cde Pad lights.4 Cde Pad tnes 5 Fully arming the system - ON MODE 6 Fully arming the system - Quick Arm MODE 6 Partially arming
TABLE OF CONTENTS... Glssary f terms 2... Cde Pad Diagram 3 Understanding the Cde Pad lights.4 Cde Pad tnes 5 Fully arming the system - ON MODE 6 Fully arming the system - Quick Arm MODE 6 Partially arming
The Excretory System. 4 The Excretory System.notebook. May 24, 2017
 4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
Post Distribution Monitoring Report
 Pst Distributin Mnitring Reprt Hygiene Kit funded by IMC Backgrund Infrmatin Lcatin: Zaatari Camp (All districts) Dates f data cllectin: 1-2 f Octber, 2014 Objective: t understand t what extent the distributin
Pst Distributin Mnitring Reprt Hygiene Kit funded by IMC Backgrund Infrmatin Lcatin: Zaatari Camp (All districts) Dates f data cllectin: 1-2 f Octber, 2014 Objective: t understand t what extent the distributin
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 21. Neural Cntrl and Crdinatin HUMAN NEURAL SYSTEM : The human neural system divided int tw parts The central nervus system (CNS) The peripheral nervus
POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 21. Neural Cntrl and Crdinatin HUMAN NEURAL SYSTEM : The human neural system divided int tw parts The central nervus system (CNS) The peripheral nervus
Psychology.
 1 Psychlgy. In Sectin 1 f this curse yu will cver these tpics: The Science Of Psychlgy Hw Psychlgists D Research. Genes, Evlutin, And The Envirnment The Brain: Surce Of Mind And Self Tpic : The Science
1 Psychlgy. In Sectin 1 f this curse yu will cver these tpics: The Science Of Psychlgy Hw Psychlgists D Research. Genes, Evlutin, And The Envirnment The Brain: Surce Of Mind And Self Tpic : The Science
The research question: What was discovered in the 1940s that could treat syphilis?
 Psychlgy B30 Human Sexuality Sexually Transmitted Infectins Tuskegee Syphilis Experiment Ppulatin: The research questin: What was discvered in the 1940s that culd treat syphilis? Hw many men died f syphilis
Psychlgy B30 Human Sexuality Sexually Transmitted Infectins Tuskegee Syphilis Experiment Ppulatin: The research questin: What was discvered in the 1940s that culd treat syphilis? Hw many men died f syphilis
Sensing and Perceiving Our World
 PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Instruction Manual IC ACCESS CONTROL
 Instructin Manual IC ACCESS CONTROL Mde: DH16A-12CT Metal surface and keypads Un-netwrked Mde: DH16A-12CTQ Metal surface and keypads Netwrked Mde: DH16A-50CT/CTN Metal surface and keypads Un-netwrked Mde:
Instructin Manual IC ACCESS CONTROL Mde: DH16A-12CT Metal surface and keypads Un-netwrked Mde: DH16A-12CTQ Metal surface and keypads Netwrked Mde: DH16A-50CT/CTN Metal surface and keypads Un-netwrked Mde:
Forensic Science: Fundamentals & Investigations, 2e Chapter 2. All rights Reserved Cengage/NGL/South-Western 2016
 1 Frensic Science: Fundamentals & Investigatins, 2e Cengage/NGL/Suth-Western 2016 Crime-Scene Investigatin and Evidence Cllectin By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: 2.1 Summarize Lcard s Principle
1 Frensic Science: Fundamentals & Investigatins, 2e Cengage/NGL/Suth-Western 2016 Crime-Scene Investigatin and Evidence Cllectin By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: 2.1 Summarize Lcard s Principle
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
EXPLORING THE PROCESS OF ASSESSMENT AND OTHER RELATED CONCEPTS
 1 SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION: EXPLORING THE PROCESS OF ASSESSMENT AND OTHER RELATED CONCEPTS The Nature Of Assessment The Definitin Of Assessment The Difference Between Testing, Measurement And Evaluatin Characteristics
1 SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION: EXPLORING THE PROCESS OF ASSESSMENT AND OTHER RELATED CONCEPTS The Nature Of Assessment The Definitin Of Assessment The Difference Between Testing, Measurement And Evaluatin Characteristics
The Interface Between Theory of Mind and Language Impairment
 The Interface Between Thery f Mind and Language Impairment By Lauren Lwry Hanen Certified SLP and Clinical Staff Writer When mst f us hear the term thery f mind we usually think abut children with autism
The Interface Between Thery f Mind and Language Impairment By Lauren Lwry Hanen Certified SLP and Clinical Staff Writer When mst f us hear the term thery f mind we usually think abut children with autism
Social Learning Theories
 Scial Learning Theries - Careful scientific prcedures and methdlgy that characterize the behaviurist apprach Albert Bandura - Brn in small twn Alberta - Plish decent - Only sn with 5 sisters - Interested
Scial Learning Theries - Careful scientific prcedures and methdlgy that characterize the behaviurist apprach Albert Bandura - Brn in small twn Alberta - Plish decent - Only sn with 5 sisters - Interested
I Before You Read. I Read to Learn. What is an arthropod? How does an exoskeleton provide protection?
 I Befre Yu Read Have yu seen a drawing r picture f a knight in armr? What is the purpse f armr? On the lines belw list the advantages and disadvantages f wearing a heavy suit f armr. As yu read this sectin
I Befre Yu Read Have yu seen a drawing r picture f a knight in armr? What is the purpse f armr? On the lines belw list the advantages and disadvantages f wearing a heavy suit f armr. As yu read this sectin
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS YD30 COBALT
 INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS YD30 COBALT CONTENTS 1. DESCRIPTION Pg. 2 2. PRODUCT UNBOXED Pg. 2 3. DIMENSIONS 3.1. Lck 3.2. Strike Plate 3.3. Fitting Tab 3.4. Husing 3.5. Dress Plate Pg. 3 3
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS YD30 COBALT CONTENTS 1. DESCRIPTION Pg. 2 2. PRODUCT UNBOXED Pg. 2 3. DIMENSIONS 3.1. Lck 3.2. Strike Plate 3.3. Fitting Tab 3.4. Husing 3.5. Dress Plate Pg. 3 3
Job Satisfaction. Job Satisfaction. Financial rewards, benefits, flexible work hours and stress among lest cited reasons
 Jb Satisfactin Zapps - Las Vegas-based e-cmmerce site specializing in shes, apparel and electrnics - CEO hsts pajama parties and excessively blgs abut varius subjects - During caching sessins emplyees
Jb Satisfactin Zapps - Las Vegas-based e-cmmerce site specializing in shes, apparel and electrnics - CEO hsts pajama parties and excessively blgs abut varius subjects - During caching sessins emplyees
ANXIETY SYMPTOMS INTERVENTION SESSION HANDOUTS. Introduction to Fighting Fear by Facing Fear. Making a Fears and Worries List
 SESSION ANXIETY SYMPTOMS INTERVENTION 5 SESSION HANDOUTS Handut 5.1: Handut 5.2: Handut 5.3: Handut 5.4: Handut 5.5: Handut 5.6: When Yu Face Yur Fears STOP! Intrductin t Fighting Fear by Facing Fear The
SESSION ANXIETY SYMPTOMS INTERVENTION 5 SESSION HANDOUTS Handut 5.1: Handut 5.2: Handut 5.3: Handut 5.4: Handut 5.5: Handut 5.6: When Yu Face Yur Fears STOP! Intrductin t Fighting Fear by Facing Fear The
Learning AP Psychology (Unit 4)
 1 Learning AP Psychlgy (Unit 4) Learning is a lasting change in behavir r mental prcess as the result f an experience. There are tw imprtant parts: a change a simple reflexive reactin is nt learning learning
1 Learning AP Psychlgy (Unit 4) Learning is a lasting change in behavir r mental prcess as the result f an experience. There are tw imprtant parts: a change a simple reflexive reactin is nt learning learning
Autism Awareness. An Introduction to Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Insert author(s) name(s) Sense Scotland Insert date of presentation
 Autism Awareness An Intrductin t Autistic Spectrum Disrder (ASD) Insert authr(s) name(s) Sense Sctland Insert date f presentatin Learning Outcmes (1) T understand what ASD means T understand the scial
Autism Awareness An Intrductin t Autistic Spectrum Disrder (ASD) Insert authr(s) name(s) Sense Sctland Insert date f presentatin Learning Outcmes (1) T understand what ASD means T understand the scial
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 Module 19 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions
Module 19 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions
Knee Class Fremont Physical Therapy
 Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
Food information to consumers - Commission proposal - COM (2008) 40 final 2008/0028 (COD) The European Heart Network s position in a nutshell
 Fd infrmatin t cnsumers - Cmmissin prpsal - COM (2008) 40 final 2008/0028 (COD) The Eurpean Heart Netwrk s psitin in a nutshell Summary On 30 January 2008 the Eurpean Cmmissin published its prpsal fr a
Fd infrmatin t cnsumers - Cmmissin prpsal - COM (2008) 40 final 2008/0028 (COD) The Eurpean Heart Netwrk s psitin in a nutshell Summary On 30 January 2008 the Eurpean Cmmissin published its prpsal fr a
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
