2007 Psychology GA 1: Written examination 1
|
|
|
- Allan Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2007 Psychology GA 1: Written examination 1 GENERAL COMMENTS Students generally performed well on the June 2007 examination, and the results were very comparable with examination 1 in previous years. However, the results for this examination indicated that there was a greater degree of discrimination amongst students. In the multiple-choice section all three areas were well-answered. The mean score for both Visual perception and Brain and nervous system was 70 per cent. The best answered area was States of Consciousness, with a mean of 77 per cent, a very similar average to As in previous years, students did not perform as well on the short answer questions, generally because of a lack of precision and completeness in descriptions and definitions, failure to refer to appropriate psychological information or failure to provide appropriate examples in their answers even when the requirement for this was explicitly stated in the question. Students had the most difficulty with States of consciousness, achieving a mean score of 49 per cent. Visual perception followed with a mean of 54 per cent, and Brain and nervous system was answered the best, with a mean of 62 per cent. Teachers had clearly instructed and directed students attention to the key knowledge and skills in the Psychology VCE Study Design. In general, students demonstrated good knowledge and understanding of the curriculum, although, as in previous years, many did not achieve full marks because they failed to address all aspects of the questions in their answers. For example, when required to use an example to clearly explain in Question 9, many answers contained only a generic description of how context influences visual perception. Students need to read the short answer questions very carefully and then check their answer against the question s requirements. Highlighting the instructional terms (for example, outline, describe, explain, etc.) before planning a response is a good practice, and helps ensure that the answer addresses the question specifically and completely. If a question provides a context for the response by presenting a specific scenario or example, it is essential that students refer to that specific scenario or example in their response. For example, in Question 7 students needed to refer to the features of the figure presented. Short answer questions worth two marks generally require at least two key terms and/or pieces of information, while those worth one mark generally require one (or sometimes two) key terms and/or pieces of information. Questions worth three or four marks have an appropriate number of lines for the answer. SPECIFIC INFORMATION Section A Multiple-choice questions Students should answer all questions in the multiple-choice section of the paper. If they are unsure of the answer, students are advised to mark the response that is their best guess for any question it is always possible to change a response by carefully erasing and re-shading. Answering all questions also decreases the likelihood that further answers will be out of synchronisation. This section of the paper was very well answered, with only five questions resulting in a correct response rate of less than 50 per cent. These questions, along with other moderately difficult ones, are discussed below. Psychology GA 1 Exam VICTORIAN CURRICULUM AND ASSESSMENT AUTHORITY
2 The table below indicates the percentage of students who chose each option. The correct answer is indicated by shading. Question % A % B % C % D Comments Area of Study 1 Brain and nervous system Alternative B was a direct contradiction of the facts and the only incorrect alternative Images falling on the left side of each retina are processed in the left occipital lobe and images falling on the right side of each retina are processed in the right occipital lobe. Almost half of the students chose the incorrect alternative B. This question was similar to Question 6 on the 2006 paper, which was also poorly answered. Although the correct alternative was the most popular response, many students indicated that alternative C, CT scans usually require an injection into the bloodstream, was false. In fact, in the majority of cases an injection is required, although it is not of a radioactive isotope in a vehicle of fluorodeoxyglucose, as is the case with a PET scan. In establishing the baseline for the polygraph, both neutral and emotional questions are used. These include probable lie questions and questions requiring both yes and no responses. Students who indicated that the researcher should debrief the patient before carrying out the research showed a misunderstanding of the purpose and practice of debriefing. Area of Study 2 Visual perception Brightness constancy clearly indicates that the answer must be alternative D. Over half of the students indicated difficulty with the concept of brightness constancy. Whenever there is a bias in sample selection, the sample cannot be deemed random. In this case the researcher selected girls who were at school on the day of her study the girls who were not at school did not have an equal chance of inclusion in the sample. Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
3 Area of Study 3 States of consciousness % of students indicated that dreams do not occur during non- REM sleep. In fact, up to 10% of dreaming (usually of a bizarre and disjointed nature) may occur in NREM sleep. Section B Short answer questions For each question, an outline answer (or answers) is provided. In some cases the answer given is not the only answer that could have been awarded marks. Area of Study 1 Brain and nervous system This section was generally well-answered. Question 1 % To enable transfer of information between hemispheres. Many answers incorrectly indicated that the corpus callosum sends information. This is incorrect it acts as a conduit for neural impulses. Question 2 % Value Case studies provide a detailed and complete (or near complete) description of one person s situation, experiences and evaluation of treatment, including background, family history and environment, through oneon-one interviews, individual testing, etc. It can provide ideas for theoretical explanations and experimental research. Limitation It is very difficult to generalise data to other people. Many case studies involve unique situations, large differences between brains or plasticity of the brain, etc. It is very difficult to analyse such a huge collection of data (intense and time consuming). One mark was allocated to the value and one mark to the limitation. Any of the above items gained credit. Question 3a. % Any one of the following: glucose fluorodeoxyglucose sugar ammonia Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
4 water radioactive glucose carbon 11 fluorine 18 oxygen 15 nitrogen 13. Question 3b. % Either of: it provides information about the levels of activity in different areas of the brain during the performance of these tasks it maps the areas of the brain that are involved during the performance of the task. Statements that related only to brain function simply repeated the information given in the question and did not gain the mark. Question 3c. % Any one of: CT (CAT) SPECT MRI fmri. EEG was not acceptable as the question specified an imaging device. Question 4a. % Frontal lobe in the left hemisphere. Both pieces of information were required. Students did not need to state that this is so more than 95 per cent of the time. Question 4b. % Any two of: produces very little speech speech requires much concentration and effort difficulty articulating speech (pronouncing words) speech tends to be slow and drawn out short words prepositions/conjunctions tend to be omitted sentences tend to be very short (up to four words) sentences tend to be made up of verbs and nouns only words lack grammatical endings (for example, ing). A common error was to list two descriptors of the same difficulty; for example, speech is slurred and poorly articulated; or words are shortened and words lack grammatical endings. Such responses received only one mark. Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
5 Question 5a. % flight/fight response (fight or flight) parasympathetic The response is referred to as the fight or flight response. Even though Pauline was obviously not intending to fight the car, both terms are required in naming the response. Question 5b. % Any one of: inhibition of tear glands dilation of pupils dry mouth (inhibition of salivation) increased heart rate increased breathing (respiration) rate dilation of bronchial passages constriction of blood vessels in skin inhibition of stomach contractions, digestive secretions and peristalsis relaxation of bladder inhibition of erection/stimulation of ejaculation increased secretions by sweat glands goose bumps/hair follicles raised secretion of adrenal hormones (release of adrenaline and noradrenaline). The explanation needed to indicate how the specific response named would improve Pauline s chances of survival. If the response and the explanation did not match, no mark could be awarded for part b. Question 6a. % Exhaustion Question 6b. % Any two of: anxiety depression/depression-like symptoms (for example, apathy or sadness) nightmares lack of appetite sexual dysfunction feelings of burnout irritability aggression feelings of losing (or out of) control/external locus of control difficulty concentrating flat affect blunt emotive reactions, lose of empathy/understanding difficulty organising or prioritising tasks, or never feeling on top of tasks intrusive thoughts high emotionality. Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
6 It was important for two different psychological problems to be identified. Only one mark was given for depressed and sad or for anxious and nervous. Question 6c. % Help The release of cortisol (a stress hormone) repairs the body and speeds up the healing process. The release of adrenaline (a stress hormone) and all the other symptoms of arousal maintain alertness and help the body to fight the stressor. Harm These physiological strains have placed great pressure on the heart and led to the heart disease/heart attack. The body s immune system has been weakened by fighting the stress hormones, meaning that Suzanne cannot resist further infections. (The weakened body may be more prone to heart failure, so this was an acceptable alternative.) It was not necessary for students to name the stress hormones, though students who named an inappropriate hormone did not gain the mark. Area of Study 2 Visual perception This was the weakest of the three areas of study in the short answer section. The relatively poor result for Question 7 emphasises the need for students to apply their answers to the specific question asked rather than make a generic statement where they are required to apply a concept. Question 7 Marks Average % Figure-ground: the number 1 is perceived as a meaningful unit, standing out from the background. We apply a subjective contour as an outline of the figure. Similarity: objects that are alike (the ticks) are perceived to form a meaningful whole unit (the figure 1). Closure: although the ticks are not connected, we perceive them as belonging to a single meaningful unit and apply closure to see the figure 1. It was essential that the explanations referred to the figure shown and that the name and the explanation were congruent. Question 8a. % Accommodation Question 8b. % Closer to the horizon than the other clouds or lower in the picture than the other clouds. Imprecise answers such as behind the other clouds or at the bottom of the picture did not earn marks. Question 9 % For example: in the rat-man experiment, subjects who are shown a group of line-drawings of faces including the ambiguous stimulus perceive it as an old man. Subjects who are shown a group of line-drawings of animals including the Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
7 ambiguous stimulus perceive it as a rat. This means that the context had predisposed them to be prepared to perceive the stimulus in a particular way in Loftus and Mackworth s experiment with a picture of the giant squid outside the barn in a farmyard scene, the unexpectedness of the squid in that environment (context) meant that subjects focussed their attention on the squid and did not notice other details. Many answers were generic, simply describing context as creating perceptual set. Some examples given did not relate to visual perception therefore did not relate to this Area of Study. Question 10a. % shape size No other terms were acceptable. The order in which the terms were stated was of key importance. Question 10b. Marks Average % As a person crosses the room they approach or get further away from the viewer. As the size of the retinal image changes (or the distance from the viewer changes), the viewer perceives the person to grow or shrink in size. The room is constructed in a trapezoidal shape so that one back corner is twice as far from the viewer as the other back corner. Cues in the room, such as windows or clocks, are also distorted to give the impression that they are being viewed from a 90 degree angle. Viewing through a peephole eliminating the strongest (binocular) depth cues and using only monocular pictorial cues intensifies the illusion. Students needed to give a description of the structural features (design) of the room and state that the illusion of changing size is brought about by varying distance. Referring to the size of the retinal image was useful but not required. Question 11 % Either of: to protect the rights and welfare of participants (no harm principle) to promote research of benefit to the community/humankind (maximise beneficence). Many answers concentrated on explaining why national guidelines are important. The question referred to the overriding principles that are stated in the NHMRC guidelines. Area of Study 3 States of consciousness Students appeared to have a reasonable knowledge of this Area of Study, although some students needed to take greater care to answer the questions properly. For example, Question 12 required the name or description of an altered state of consciousness and two psychological characteristics that would distinguish this state from normal waking consciousness. Students had to identify characteristics that were appropriate to the altered state that they had nominated. Question 12 Marks Average % Sleep/dreaming/daydreaming thought patterns are disorganised Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
8 lack of control of movements sensations and perceptions are dulled Meditation sensations or perceptions are dulled (for example, pain) awareness of external environment is reduced Hypnosis sensations or perceptions are dulled (for example, pain) loss of awareness of self can increase self control (for example, quitting smoking) more suggestible, so less inhibited From drug use thought processes are disorganised sensations or perceptions are dulled or heightened memory impaired more/less/inappropriate emotional reactions lack of self control Heightened awareness hyperfocus (selective attention) extra sensitive perceptions Question 13 % His GSR reading will be higher than in a normal state. Increased sweat on the skin increases the electrical conductivity of the skin s surface, so the galvanometer will register a higher reading. Many students answered the question as if they were referring to any altered state of consciousness, disregarding the fact that the question specified heightened arousal. Question 14 Marks Average % EEG (electroencephalograph) Measure: Detects, amplifies and records electrical activity of the brain in the form of brainwaves. Explanation: NREM sleep is indicated by higher amplitude and lower frequency brainwaves, whereas REM sleep is indicated by lower amplitude and higher frequency brainwaves. EOG (electro-oculograph) Measure: Detects, amplifies and records electrical activity of the muscles near the eye. Explanation: A high level of electrical activity indicates REM sleep. A low level of electrical activity indicates NREM sleep EMG (electromyograph) Measure: Detects, amplifies and records electrical activity of the muscles in the body. Explanation: Very little or no activity indicates REM sleep. An increase in activity indicates NREM sleep. Video camera Measure: Detects and records movements of the body, or eye movements. Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
9 Explanation: Eye movement indicates REM sleep; no eye-movement indicates NREM sleep. Very little, or no, movement indicates REM sleep. An increase in movement indicates NREM sleep. It was essential for students to refer to the fact that the electro- devices measure electrical activity; they do not directly measure brain activity or muscle movement. The EOG detects, amplifies and records electrical activity in muscles near the eye, orbital muscles or muscles responsible for eye movement. Muscles in the eye or muscles of the eye were not acceptable responses. Question 15a. % Temporary, involuntary cessation of breathing during sleep, for 20 seconds to two minutes. Simply stating that the sleeper stops breathing for a period of time was not adequate; irregularity of the breathing pattern may be part of normal sleep. It is the cessation of breathing that defines sleep apnoea, the accompanying snoring or waking gasping for breath are the possible results of the apnoea. Question 15b. % Any two of: breathing stops because the autonomic nervous system does not signal the body to breathe swelling of soft tissue in the upper throat constricts the airways certain illnesses (mumps, tonsillitis, etc.) causing blockage of the airways malformation of the jaw or trachea causing restricted air flow being overweight may contribute to fatty tissue blocking airways drinking too much alcohol leads to a build up of fatty tissue that can block airways. A single word such as obesity or alcoholism was not considered to be an adequate identification of a possible cause. Question 16a. % Name: placebo effect/participant expectations/hawthorne effect Definition: Participant expectations (or the placebo/hawthorne effect) will influence individuals behaviour, meaning that the independent variable will not be the only variable influencing the value of the dependent variable. Many students did not achieve marks for this question because they answered as if the participants were unaware of the group to which they had been allocated. Question 16b. % Deception is allowed when: the research proposal has been approved by the ethics committee of the research institution the value of the research is such that the deception is warranted appropriate debriefing and counselling procedures are in place to ensure there is no lasting psychological or physiological harm to participants. It is strongly suggested that the role of ethics committees of research institutions is discussed in the course of Unit 3, as these are the bodies responsible for ensuring that the NHMRC ethical guidelines and the National Privacy Principles are universally and consistently applied. Psychology GA 1 Exam Published: 3 March
2003 Psychology GA 1: Written examination 1
 2003 Assessment Report 2003 Psychology GA 1: Written examination 1 GENERAL COMMENTS Students generally performed well on the June paper with results, on average, being slightly lower than Examination 1
2003 Assessment Report 2003 Psychology GA 1: Written examination 1 GENERAL COMMENTS Students generally performed well on the June paper with results, on average, being slightly lower than Examination 1
STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words PSYCHOLOGY. Written examination 1. Wednesday 10 June 2009
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2009 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words PSYCHOLOGY Written examination 1 Wednesday 10 June 2009 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
Victorian Certificate of Education 2009 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words PSYCHOLOGY Written examination 1 Wednesday 10 June 2009 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
PSYCHOLOGY. Written examination 1. Tuesday 8 June 2004
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2004 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE PSYCHOLOGY Written examination 1 Tuesday 8 June 2004 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9. am ( minutes) Writing time: 9. am to
Victorian Certificate of Education 2004 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE PSYCHOLOGY Written examination 1 Tuesday 8 June 2004 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9. am ( minutes) Writing time: 9. am to
Title: Biopsychology Specification: The divisions of the nervous system: central and peripheral (somatic and autonomic). SAMPLE
 Title: Biopsychology Specification: The divisions of the nervous system: central and peripheral (somatic and autonomic). Q1 MCQ: Which of the following responses is caused by an activation of the parasympathetic
Title: Biopsychology Specification: The divisions of the nervous system: central and peripheral (somatic and autonomic). Q1 MCQ: Which of the following responses is caused by an activation of the parasympathetic
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
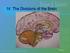 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Unit 3: How does experience affect behaviour and mental processes?
 Unit 3: How does experience affect behaviour and mental processes? Units 1 and 2: 2016 2021; Units 3 and 4: 2017 2021 24 Unit 3: How does experience affect behaviour and mental processes? The nervous system
Unit 3: How does experience affect behaviour and mental processes? Units 1 and 2: 2016 2021; Units 3 and 4: 2017 2021 24 Unit 3: How does experience affect behaviour and mental processes? The nervous system
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews
 Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews Presenter: Martin TAYLOR Position: Senior Legal Specialist Australian Criminal Intelligence
Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews Presenter: Martin TAYLOR Position: Senior Legal Specialist Australian Criminal Intelligence
Biological Research Strategies and Hormones
 Biological Research Strategies and Hormones WHS AP Psychology Unit 3: Biological Psychology Essential Task 3-6: Detail historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that support research
Biological Research Strategies and Hormones WHS AP Psychology Unit 3: Biological Psychology Essential Task 3-6: Detail historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that support research
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13
 Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
SNORING AND OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNOEA WAYS TO DEAL WITH THESE PROBLEMS
 SNORING AND OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNOEA WAYS TO DEAL WITH THESE PROBLEMS Laugh and the world laughs with you; snore and you sleep alone. These words by novelist Anthony Vergess ring true with all too many
SNORING AND OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNOEA WAYS TO DEAL WITH THESE PROBLEMS Laugh and the world laughs with you; snore and you sleep alone. These words by novelist Anthony Vergess ring true with all too many
VCE Psychology Unit 4. Year 2017 Mark Pages 45 Published Feb 10, 2018 COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 4 NOTES, By Alice (99.
 VCE Psychology Unit 4 Year 2017 Mark 50.00 Pages 45 Published Feb 10, 2018 COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 4 NOTES, 2017 By Alice (99.45 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Alice. Alice
VCE Psychology Unit 4 Year 2017 Mark 50.00 Pages 45 Published Feb 10, 2018 COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 4 NOTES, 2017 By Alice (99.45 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Alice. Alice
Sleep Apnea. What is sleep apnea? How does it occur? What are the symptoms?
 What is sleep apnea? Sleep Apnea Sleep apnea is a serious sleep problem. If you have it, you stop breathing for more than 10 seconds at a time many times while you sleep. Another term for this problem
What is sleep apnea? Sleep Apnea Sleep apnea is a serious sleep problem. If you have it, you stop breathing for more than 10 seconds at a time many times while you sleep. Another term for this problem
Sleep and Dreams. Sleep and Dreams. Brain Waves and Sleep Stages Typical Nightly Sleep Stages. Chapter 7 States of Consciousness
 Chapter 7 States of Consciousness States of Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Fantasy Prone Personality imagines and recalls experiences with lifelike vividness
Chapter 7 States of Consciousness States of Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Fantasy Prone Personality imagines and recalls experiences with lifelike vividness
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
PSYCHOLOGY. Written examination 1. Tuesday 11 June 2002
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2002 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter PSYCHOLOGY Written examination 1 Tuesday 11 June 2002 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
Victorian Certificate of Education 2002 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter PSYCHOLOGY Written examination 1 Tuesday 11 June 2002 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
l3;~~?~~~,'0~'~~t~t:~:~~~~~~~~~~!,1
 112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
Sensation and Perception
 1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Stress. Chapter Ten McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
 Stress Chapter Ten What Is Stress? } Stress is the collective physiological and emotional responses to any stimulus that disturbs an individual s homeostasis } A stressor is any physical or psychological
Stress Chapter Ten What Is Stress? } Stress is the collective physiological and emotional responses to any stimulus that disturbs an individual s homeostasis } A stressor is any physical or psychological
AOS1 How do levels of consciousness affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview
 UNIT 4- How is Wellbeing Developed and Maintained? AOS1 How do levels of affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview Following is the key knowledge and concepts for unit 4 AOS 1. The black represents
UNIT 4- How is Wellbeing Developed and Maintained? AOS1 How do levels of affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview Following is the key knowledge and concepts for unit 4 AOS 1. The black represents
AP PSYCHOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP PSYCHOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 For each of the following pairs of terms, explain how the placement or location of the first influences the process indicated by the second. Rods, peripheral
AP PSYCHOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 For each of the following pairs of terms, explain how the placement or location of the first influences the process indicated by the second. Rods, peripheral
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
The Emotional Nervous System
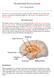 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
Do Now pg What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in.
 Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Lujain Hamdan. Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem. Mohammed khatatbeh
 12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
The Endocrine SyStem. COMMUNICATION System
 The Endocrine SyStem COMMUNICATION System Endocrine FACTS The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower
The Endocrine SyStem COMMUNICATION System Endocrine FACTS The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
HE 250 PERSONAL HEALTH. Stress
 HE 250 PERSONAL HEALTH Stress Stress Stress General state of the body, mind, and emotions when an environmental stressor has triggered the stress response Stressor Events or agents in the environment that
HE 250 PERSONAL HEALTH Stress Stress Stress General state of the body, mind, and emotions when an environmental stressor has triggered the stress response Stressor Events or agents in the environment that
Key Knowledge. What is CONSCIOUSNESS? Consciousness is. Unit 3 ~ Chapter 2 ~ States of Consciousness. Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012
 Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012 Key Knowledge Consciousness as described by Rene Descartes & William James Normal Waking Consciousness Altered States of Consciousness Comparison of Normal & Altered
Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012 Key Knowledge Consciousness as described by Rene Descartes & William James Normal Waking Consciousness Altered States of Consciousness Comparison of Normal & Altered
Mental Health and Stress Management
 Mental Health and Stress Management In recent years, psychologists have become more interested in positive psychology Focus on positive emotions, characteristics, strengths, and conditions that create
Mental Health and Stress Management In recent years, psychologists have become more interested in positive psychology Focus on positive emotions, characteristics, strengths, and conditions that create
- copyright
 Relaxation Exercises Let s start with breathing! Your breathing is often the first thing to be affected by stress. When we are anxious we tend to hunch up the shoulders and breathe in a more rapid and
Relaxation Exercises Let s start with breathing! Your breathing is often the first thing to be affected by stress. When we are anxious we tend to hunch up the shoulders and breathe in a more rapid and
Class X: Biology. Chapter 2: Control and coordination.
 Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
Emotion. Emotion. Theories of Emotion. Chapter 13. Emotion. James-Lange Theory of Emotion
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 13 James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Theories
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 13 James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Theories
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Nervous System Nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Brain Spinal Cord Nerves and neurones
Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Nervous System Nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Brain Spinal Cord Nerves and neurones
Outline 3/5/2013. Practice Question. Practice question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness
 Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
PERCEPTION. Our Brain s Interpretation of Sensory Inputs
 PERCEPTION Our Brain s Interpretation of Sensory Inputs Perception Definition The method by which the sensations experienced at any given moment are interpreted and organized in some meaningful fashion
PERCEPTION Our Brain s Interpretation of Sensory Inputs Perception Definition The method by which the sensations experienced at any given moment are interpreted and organized in some meaningful fashion
Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2013
 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2013 Sleep is described as regularly occurring altered state of consciousness that typically occurs spontaneously and is characterised by a loss of conscious awareness Sleep occurs
Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2013 Sleep is described as regularly occurring altered state of consciousness that typically occurs spontaneously and is characterised by a loss of conscious awareness Sleep occurs
Topics Review Questions. 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us.
 Topics Review Questions Scientific Method Notes & Lab: 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us. scientific method 2) It is an educated guess based on observations
Topics Review Questions Scientific Method Notes & Lab: 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us. scientific method 2) It is an educated guess based on observations
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
 www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for
www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Copyright, ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved. The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy. Asthma Questionnaire
 Copyright, 1994 - ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy Asthma Questionnaire This survey contains a series of statements, written in the first person, concerning your
Copyright, 1994 - ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy Asthma Questionnaire This survey contains a series of statements, written in the first person, concerning your
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS. Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Stress is like an iceberg. We can see one-eighth of it above, but what about what s below?
 Chapter 4: Managing Stress & Coping With Loss Stress is like an iceberg. We can see one-eighth of it above, but what about what s below? Something to consider... The Japanese eat very little fat &... The
Chapter 4: Managing Stress & Coping With Loss Stress is like an iceberg. We can see one-eighth of it above, but what about what s below? Something to consider... The Japanese eat very little fat &... The
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems. Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers
 Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis
 Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
Gangrene. Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply.
 Gangrene Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply. Gangrene can happen on the surface of the body, such as on the skin. It
Gangrene Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply. Gangrene can happen on the surface of the body, such as on the skin. It
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences
 BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
****REVISED 4/27/2015****
 Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
 Obstructive Sleep Apnea Introduction Obstructive sleep apnea is an interruption in breathing during sleep. It is caused by throat and tongue muscles collapsing and relaxing. This blocks, or obstructs,
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Introduction Obstructive sleep apnea is an interruption in breathing during sleep. It is caused by throat and tongue muscles collapsing and relaxing. This blocks, or obstructs,
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
The Nervous System. We have covered many different body systems which automatically control and regulate our bodies.
 The Nervous System The Nervous System We have covered many different body systems which automatically control and regulate our bodies. There is one master system which controls all of these other systems.
The Nervous System The Nervous System We have covered many different body systems which automatically control and regulate our bodies. There is one master system which controls all of these other systems.
Term 1 Review Questions
 AP Psychology Name Short Answer Term 1 Review Questions 1. Julie, a physics major, has difficulty believing that psychology is a science, because people cannot observe other people's thoughts and sensations.
AP Psychology Name Short Answer Term 1 Review Questions 1. Julie, a physics major, has difficulty believing that psychology is a science, because people cannot observe other people's thoughts and sensations.
Week 4 Psychology. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding that they and others think, feel, perceive, and have private experiences.
 Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
Sleep Apnoea. Introduction Symptoms Causes Obtaining a Diagnosis Treatment Complications
 The most common forms of sleep apnoea are normally referred to as obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and relate to a condition which causes interruptions in breathing during sleep. People with obstructive
The most common forms of sleep apnoea are normally referred to as obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and relate to a condition which causes interruptions in breathing during sleep. People with obstructive
10 Secrets to a Healthier You Presented by Dr. Elaine Dembe
 10 Secrets to a Healthier You Presented by 7:45 a.m. 8:45 a.m. Sponsored by 200 St. Clair Ave W. # 308, Toronto, Ontario M4V 1R1 Tel: 416-960-5353 elaine@elainedembe.com elainedembe.com HOW CONSCIOUS BREATHING
10 Secrets to a Healthier You Presented by 7:45 a.m. 8:45 a.m. Sponsored by 200 St. Clair Ave W. # 308, Toronto, Ontario M4V 1R1 Tel: 416-960-5353 elaine@elainedembe.com elainedembe.com HOW CONSCIOUS BREATHING
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Notes: 43% of all adults suffer adverse health effects due to stress. 75%-90% of all medical visits are in some way related to stress.
 Stress is an unavoidable part of our daily lives. A certain amount of stress is actually necessary for our survival; however, the amount of stress most people are under these days is causing more harm
Stress is an unavoidable part of our daily lives. A certain amount of stress is actually necessary for our survival; however, the amount of stress most people are under these days is causing more harm
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Relaxation and Stress Management Through Meditation. Dennis Abreu AM LCSW
 Relaxation and Stress Management Through Meditation Dennis Abreu AM LCSW OBJECTIVES Early Childhood Suspension and Expulsion What is Stress Effects of stress on Central Nervous System Effects of Stress
Relaxation and Stress Management Through Meditation Dennis Abreu AM LCSW OBJECTIVES Early Childhood Suspension and Expulsion What is Stress Effects of stress on Central Nervous System Effects of Stress
The Psychological Effects on Personnel in a Mine Disaster
 The Psychological Effects on Personnel in a Mine Disaster Kathleen M. Kowalski-Trakofler, Ph.D. Research Psychologist NIOSH 3 rd International Mine Rescue Conference 2007 Nashville, Tennessee USA Psychology
The Psychological Effects on Personnel in a Mine Disaster Kathleen M. Kowalski-Trakofler, Ph.D. Research Psychologist NIOSH 3 rd International Mine Rescue Conference 2007 Nashville, Tennessee USA Psychology
STRESS Everyone has heard of it BUT WHAT IS IT REALLY?
 STRESS Everyone has heard of it BUT WHAT IS IT REALLY? The body s reaction to threats or demands either REAL or PERCEIVED Can we get rid of stress? STRESSOR Choose that stressor.. -You make the varsity
STRESS Everyone has heard of it BUT WHAT IS IT REALLY? The body s reaction to threats or demands either REAL or PERCEIVED Can we get rid of stress? STRESSOR Choose that stressor.. -You make the varsity
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system
 Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Perception. Chapter 8, Section 3
 Perception Chapter 8, Section 3 Principles of Perceptual Organization The perception process helps us to comprehend the confusion of the stimuli bombarding our senses Our brain takes the bits and pieces
Perception Chapter 8, Section 3 Principles of Perceptual Organization The perception process helps us to comprehend the confusion of the stimuli bombarding our senses Our brain takes the bits and pieces
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Psychology study guide chapter 2
 Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
QUESTION 1. What is a drug? ANSWER: A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel.
 What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 Neural and Hormonal Systems Explains why we feel strong, sad, happy & nervous. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals throughout the body Soma The cell body of a neuron,
Neural and Hormonal Systems Explains why we feel strong, sad, happy & nervous. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals throughout the body Soma The cell body of a neuron,
Psychology Session 9 Sensation and Perception
 Psychology Session 9 Sensation and Perception Date: November 4 th, 2016 Course instructor: Cherry Chan Mothercraft College Agenda 1. Sensation and perception 2. Vision 3. Perceptual organization 4. Sound
Psychology Session 9 Sensation and Perception Date: November 4 th, 2016 Course instructor: Cherry Chan Mothercraft College Agenda 1. Sensation and perception 2. Vision 3. Perceptual organization 4. Sound
SAMPLE. The spinal cord
 The brain The brain provides conscious awareness and is involved in all psychological processes. The brain consists of many regions, which are responsible for different functions. For example, the brain
The brain The brain provides conscious awareness and is involved in all psychological processes. The brain consists of many regions, which are responsible for different functions. For example, the brain
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9773 PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Pre-U Certificate MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9773 PSYCHOLOGY 9773/02 Paper 2 (Methods, Issues and Applications),
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Pre-U Certificate MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9773 PSYCHOLOGY 9773/02 Paper 2 (Methods, Issues and Applications),
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
Final Practice Examination Answer Key. Answer Key
 G r a d e 1 2 P s y c h o l o g y Final Practice Examination Answer Key Name: Student Number: Attending q Non-Attending q Phone Number: Address: For Marker s Use Only Date: Final Mark /100 = % Comments:
G r a d e 1 2 P s y c h o l o g y Final Practice Examination Answer Key Name: Student Number: Attending q Non-Attending q Phone Number: Address: For Marker s Use Only Date: Final Mark /100 = % Comments:
