PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT. Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof
|
|
|
- Cornelius Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof
2 Definition Clinical symptoms: Pathogenesis: Etiology: Neurodegenerative syndrome with chronic, progressive course (hypokinetic-hyperrigid/tremordominant) Degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopamine neurons Idiopathic vs. symptomatic forms Involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action even when supported; with a propensity to bend the trunk forward [...], the senses and the intellects being uninjured. James Parkinson (1817) 2
3 Milestones in research History 1817: J. Parkinson Essay on the Shaking Palsy 1873: Charcot Description of the clinical picture and and first attempts at treatment 1919: Trétiakoff Discovery of cell degeneration in the substantia nigra as anatomical substrate 1957: Carlsson Discovery of dopamine deficiency in the striatum as biochemical substrate (Nobel Prize 2000) 1979: Davis Research into the pathological mechanism using the MPTP model Ongoing: Research into genetic and neuroprotective factors 3
4 Milestones in therapy Drug therapy History 1946: First synthetic anticholinergics 1961: Birkmayer & Hornykiewicz Clinical use of L-dopa 1969: Schwab Discovery of the antiparkinson effect of amantadine 1963: Birkmayer Clinical use of L-dopa + decarboxylase inhibitor 1974: Calne Introduction of dopamine agonists 1975: Birkmayer Use of MAO-B inhibitors 1997: Introduction of COMT inhibitors to clinical treatment 4
5 6 Epidemiology Facts Epidemiology In Europe the age-correlated prevalence (per 100,000 inhabitants) is 1.6 (Europarkinson Study, 1997) Roughly 1% of all over-65s are affected Roughly 25% of Parkinson patients remain undiagnosed Average life expectancy is slightly reduced
6 Age-specific incidence of new cases of Epidemiology Incidence (per 100,000 inhabitants) USA Iceland Japan Estonia Finland Age 7
7 Risk factors Epidemiology Age Positive family history Possible: Poisoning with herbicides, pesticides, heavy metals Doubtful: Personality Living in the countryside Possible protective factors: Consumption of tea and coffee Nicotine 9
8 Cell degeneration in the substantia nigra Pathogenesis healthy Schneider E.: Diagnostik und Therapie des M. Parkinson [Diagnosis and treatment of ], de Gruyter,
9 Genetic causes Pathogenesis PARK 1 Locus: Chromosome 4q21 Gene product: α-synuclein (Polymeropoulos et al., 1997) PARK 2 Locus: Chromosome 6q25 Gene product: Unknown (Kitada et al., 1998) PARK 3 Locus: Chromosome 2p13 Gene product: Unknown (Gasser et al., 1998) 4, 4, PARK 4, PARK
10 Lewy bodies Microscopic findings Pathogenesis By kind permission of Prof. H. Braak Center for Morphology, Frankfurt University Hospital Copyright by MedWeb, UK 12
11 Lewy bodies Pathoanatomical cascade model Pathogenesis Stages of Lewy body formation: I. Dorsal vagal nucleus/olfactory bulb II. Brain stem/reticular formation III.Basal prosencephalon/ amygdala/substantia nigra IV.Mesocortex V. Neocortex association areas VI.Neocortex sensory and motor areas (Braak et al., 2002) presymptomatic symptomatic I II III IV V VI 13
12 14 Oxidative stress Pathogenesis Disturbed cell homeostasis through: inefficient detoxification impaired mitochondrial function Results: increased radical formation reduced ATP production DNA damage
13 L-Dopa metabolites in the brain L-Dopa DDC MAO-B Dopamine COMT DOPAC COMT HVA 3-MT MAO-B
14 Core structures of the basal ganglia Pathophysiology Caudate nucleus & putamen Thalamus Caudate nucleus Striatum Putamen Thalamus Globus pallidus Globus pallidus Substantia nigra Tail of the caudate nucleus Substantia nigra Subthalamic nucleus 16
15 17 Basal ganglia loops Physiological state Pathophysiology Glutamate Dopamine
16 18 Basal ganglia loops State in Pathophysiology Glutamate Dopamine
17 20 Development of symptoms Pathophysiology Cell death in the substantia nigra Dopamine deficiency in the striatum Neurotransmitter imbalance Dopamine deficiency vs. glutamate hyperactivity Dysfunction of the basal ganglia loops
18 22 Main symptoms Symptoms Bradykinesia Rigor Tremor Postural instability
19 Clinical diagnostic criteria (at least three must be satisfied) Diagnosis Unilateral onset of the Resting tremor and/or at least two of the main symptoms Progressive course Very good response to L-dopa L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia and fluctuations in efficacy No atypical signs Gerlach, Reichmann & Riederer, Springer Verlag,
20 Accompanying symptoms Symptoms Vegetative Post-encephalitic seborrhea (seborrhea) Sialorrhea Digestive disturbances Disturbed micturition and potency Orthostatic hypotension Disturbed thermoregulation Psychopathological Depression Bradyphrenia Dementia 23
21 Exclusion criteria for Differential diagnosis Acute onset Oculogyric crises/gaze palsy Remission Neuroleptics Cerebellar symptoms Babinski s sign positive Early signs of dementia or autonomic dysfunction No response to L-dopa Gerlach, Reichmann & Riederer, Springer Verlag,
22 Parkinson Plus syndrome I Differential diagnosis Multisystem atrophy Cerebellar symptoms (disturbances of equilibrium, unsteady gait, coordination disturbances) or Autonomic disturbances (drop in blood pressure, bladder disorders, impotence) Progressive supranuclear gaze palsy Postural instability as an early symptom Vertical gaze palsy (upwards or downwards) Unsteady gait Symmetrical symptoms No resting tremor 35
23 Parkinson Plus syndrome II Lewy body dementia Early development of dementia Fluctuating psychotic symptoms Agitation Paradoxical neuroleptic sensitivity Differential diagnosis Corticobasal degeneration Dystonia (mainly flexion dystonia of the arm) Irregular, unilateral tremor Alien limb phenomenon Cortical sensitivity disturbances Pyramidal tract signs 36
24 37 Secondary (symptomatic) parkinsonism Differential diagnosis Drug-induced: Toxic in origin: Other etiology: Neuroleptics Antihypertensives Antiemetics Cerebral calcium-channel blockers Reversible Carbon monoxide Lead Manganese Cyanide Methanol MPTP Not progressive Metabolic Postencephalitic Traumatic Compressive Treatable
25 Therapeutic options Drug therapy Treatment L-Dopa therapy/dopamine agonists Dopamine replacement Glutamate antagonist (amantadine) Inhibition of glutamatergic hyperactivity MAO-B inhibitors Central inhibition of dopamine breakdown COMT inhibitors Peripheral inhibition of L-dopa breakdown 38
26 39 Points of attack of drug therapies Treatment Dopamine agonists Phenylalanine Tyrosine Dopamine (DA) Glutamate antagonist Amantadine sulfate MAO-B inhibitor Glu Presynapse Glial cell
27 Therapeutic options Deep brain stimulation Treatment Hyperstimulation (120 Hz) in affected regions of the brain: Subthalamic nucleus Globus pallidus Thalamus Symptom and drug reduction Tremor Hypo-/hyperkinesia L-Dopa-sparing effect Invasive, reversible 40
28 41 Therapeutic options Transplantation Treatment TRANSPLANTATION Decrease in dopaminergic input in the striatum Dopaminergic reinnervation of the striatum
29 OTHER MOVEMENT DISORDERS
30 Movement disorders Hyperkinetic Chorea Ballism Tremor Myoclonus Tics dystonia Hypokinetic Parkinsonism: PD and All Parkinsonian Syndromes
31 DYSTONIA Dystonia is defined as a syndrome of sustained muscle contractions, frequently causing twisting movements and postures (Fahn 1987). Agonist and antagonist muscles contract simultaneously to produce the abnormal postures of dystonia. Dystonic movements may be slow and continuous, or fast and brief.
32 Dystonia may be classified by age of onset, distribution and etiology. By region of distribution, dystonia is subdivided into focal, segmental, hemi-body, and generalized dystonia. Childhood-onset dystonia may begin in a body part, presenting as focal dystonia, but typically becomes generalized, especially if the underlying cause is a genetically-based or metabolic disorder
33
34 CHOREA Chorea, from the Greek word meaning dance, describes involuntary, random, abrupt, rapid, arrhythmic, unsustained movements and twitches that seem to flow from one body part to another. The timing, direction, and distribution of choreic movements varies from moment to moment, and cannot be predicted by an observer.
35 chorea
36 ATHETOSIS Athetosis, meaning no fixed position, describes a pattern of continuous writhing movements. First coined by Hammond in 1871, the original description of athetosis was an inability to retain the fingers and toes in any position in which they may be placed. Athetosis is often linked with chorea, as in choreoathetosis, to give a sense of its continuous, writhing, twisting aspect. Athetoid movements affect the limbs, especially distally, but also the trunk and cranial structures.
37 MYOCLONUS Myoclonic jerks are sudden, brief muscle contractions that produce a simple quick movement. Myoclonic jerks may be repetitive and rhythmic or random and unpredictable. Myoclonus may occur at rest, with postureholding, directed movement ( action myoclonus ), or be triggered by external stimuli ( reflex myoclonus ), whether auditory, visual or tactile.
38 Myoclonus may be classified on the basis of 1. its distribution:focal, segmental, multifocal, or generalized or 2. site of origin: cortex, brain stem, spinal cord
39 PARKINSONISM and OTHER MOVEMENT DISORDERS n HEMIFACIAL SPASM: involuntary tonic or clonic contraction of muscles innervated by 7th cranial nerve Idiopathic / vascular compression of facial nerve treatment: BTX-A pharmacologic agents
40 TREMOR Tremor is a regular, rhythmic oscillation of one or more body parts produced by alternating or synchronous contractions of opposing muscles. Phenomenologically, tremors are classified according to two main categories: 1. tremors at rest and 2. tremors with action.
41 Rest tremors occur when the affected body part is in complete repose, and fully supported. The classical tremor of parkinsonism is a tremor at rest. Action tremors occur with voluntary muscle contractions, and are subdivided into postural, kinetic, task- or positionspecific, and isometric tremors
42
43 TICS Tics are repetitive, stereotyped movements or phonations that occur abruptly against a background of normal motor activity and behavior. Most tics are simple movements, such as an abrupt stereotyped ocular deviation, blink, facial grimace, or shoulder shrug. Complex tics consist of coordinated patterns of sequential movement. Tics are purposeless movements that are often preceded by an inner urge or tension that is relieved by allowing the movement to occur.
44 n WILSON S DISEASE curable movement disorder AR, on chr 13q14.3 (Cu transporting ATPase) failure to excrete Cu --- systemic Cu poisoning n intestinal absorption is normal n reduced biliary excretion n result: increased Cu excretion in urine initially Cu accumulates in liver then in brain, eye, kidney, bones and blood tissues. Symptoms: ages of year clinical types: 1. Akinetic-rigid syndrome 2. Generalized dystonic syndrome 3. Tremor+ ataxia+ dysarthria: pseudosclerotic
45 n n n n n n n n Diagnosis: 24 hr urine cu excretion liver biopsy MRI genetic study Treatment of Wilson D-penicillamine + pyridoxine trientine Zinc n BAL? n LIVER TRANSPLANTATION
46 HUNTINGTON S DISEASE n AD, chorea + dementia n genetic defect: excessive trinucleotide repeat of CAG n defected protein called huntingtin n no established therapy n symptomatic treatment SYDENHAM S CHOREA n beta hemolytic streptococcus induced autoimmune disorder n between ages of 5-15 years n outcome is favorable n prophylactic penicillin therapy prevents recurrences
Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y
 Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y Educational Objectives Improved history taking in patients with movement disorders. Develop a systematic approach to observing and describing
Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y Educational Objectives Improved history taking in patients with movement disorders. Develop a systematic approach to observing and describing
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology
 Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview
 Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
An approach to movement disorders. Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London
 An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective. Dr John Coyle
 Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Parkinson s Disease. Sirilak yimcharoen
 Parkinson s Disease Sirilak yimcharoen EPIDEMIOLOGY ~1% of people over 55 years Age range 35 85 years peak age of onset is in the early 60s ~5% of cases characterized by an earlier age of onset (typically
Parkinson s Disease Sirilak yimcharoen EPIDEMIOLOGY ~1% of people over 55 years Age range 35 85 years peak age of onset is in the early 60s ~5% of cases characterized by an earlier age of onset (typically
Phenomenology of Movement Disorders
 Phenomenology of Movement Disorders Raja Mehanna MD Anatomical reasoning Anatomical reasoning Phenomenological reasoning Abnormal movement Hypokinetic Hyperkinetic Ataxia Video 1 But there is a tremor!
Phenomenology of Movement Disorders Raja Mehanna MD Anatomical reasoning Anatomical reasoning Phenomenological reasoning Abnormal movement Hypokinetic Hyperkinetic Ataxia Video 1 But there is a tremor!
Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161,
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Overview. Overview. Parkinson s disease. Secondary Parkinsonism. Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits
 Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders
 Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Dr Donald Grosset Consultant Neurologist - Honorary Professor Institute of Neurological Sciences - Glasgow University Hypokinetic Parkinson's Disease
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Dr Donald Grosset Consultant Neurologist - Honorary Professor Institute of Neurological Sciences - Glasgow University Hypokinetic Parkinson's Disease
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Movement disorders in childhood: assessment and diagnosis. Lucinda Carr
 Movement disorders in childhood: assessment and diagnosis Lucinda Carr Movement disorders in childhood: Assessment Classification Causes Diagnosis Presentation of movement disorders in childhood: Concerns
Movement disorders in childhood: assessment and diagnosis Lucinda Carr Movement disorders in childhood: Assessment Classification Causes Diagnosis Presentation of movement disorders in childhood: Concerns
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Extrapyramidal Motor System. Basal Ganglia or Striatum. Basal Ganglia or Striatum 3/3/2010
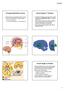 Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Margo J Nell Dept Pharmacology
 Margo J Nell Dept Pharmacology 1 The extra pyramidal system Separation of cortico-spinal system (pyramidal system, (PS)) from the basal ganglia (extra pyramidal motor system (EPS)) because they produce
Margo J Nell Dept Pharmacology 1 The extra pyramidal system Separation of cortico-spinal system (pyramidal system, (PS)) from the basal ganglia (extra pyramidal motor system (EPS)) because they produce
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
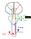 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
Movement disorders. Dr Rick Leventer Royal Children s Hospital
 Movement disorders Dr Rick Leventer Royal Children s Hospital richard.leventer@rch.org.au Movement disorders! conditions that affect the speed, fluency, quality, and ease of movement! usually affect TONE
Movement disorders Dr Rick Leventer Royal Children s Hospital richard.leventer@rch.org.au Movement disorders! conditions that affect the speed, fluency, quality, and ease of movement! usually affect TONE
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease. SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease
 Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Movement Disorders. Eric Kraus, MD! Neurology!
 Movement Disorders Eric Kraus, MD! Neurology! Classify Bradykinesia! Tic! Myoclonus! Tremor! Dystonia! Athetosis! Chorea! Ballismus! Case 1 This 64 year-old female has had progression of a tremor over
Movement Disorders Eric Kraus, MD! Neurology! Classify Bradykinesia! Tic! Myoclonus! Tremor! Dystonia! Athetosis! Chorea! Ballismus! Case 1 This 64 year-old female has had progression of a tremor over
Involuntary Movements in Children and Adolescents: Is it Seizure, Tic or Something Else?
 Involuntary Movements in Children and Adolescents: Is it Seizure, Tic or Something Else? California Association of Nurse Practitioners Monterey, March 22, 2013 Julie Sprague-McRae, MS, RN, PPCNP-BC Ruth
Involuntary Movements in Children and Adolescents: Is it Seizure, Tic or Something Else? California Association of Nurse Practitioners Monterey, March 22, 2013 Julie Sprague-McRae, MS, RN, PPCNP-BC Ruth
Parts of the motor circuits
 MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease
 Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy"
 Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson s Disease. Prevalence. Mark S. Baron, M.D. Cardinal Features. Clinical Characteristics. Not Just a Movement Disorder
 Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Chapter 8. Parkinsonism. M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University.
 Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity. Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS
 Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
PARKINSON S PRIMER. Dr. Kathryn Giles MD, MSc, FRCPC Cambridge, Ontario, Canada
 PARKINSON S PRIMER Dr. Kathryn Giles MD, MSc, FRCPC Cambridge, Ontario, Canada COPYRIGHT 2017 BY SEA COURSES INC. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
PARKINSON S PRIMER Dr. Kathryn Giles MD, MSc, FRCPC Cambridge, Ontario, Canada COPYRIGHT 2017 BY SEA COURSES INC. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
MOVEMENT DISORDERS UPDATE H. MURRAY TODD, M.D., F.A.A.N.
 MOVEMENT DISORDERS UPDATE H. MURRAY TODD, M.D., F.A.A.N. Movement Disorders Hypokinesia : decreased voluntary and automatic movements Hyperkinesia : excessive movements HYPOKINESIAS Parkinson s disease
MOVEMENT DISORDERS UPDATE H. MURRAY TODD, M.D., F.A.A.N. Movement Disorders Hypokinesia : decreased voluntary and automatic movements Hyperkinesia : excessive movements HYPOKINESIAS Parkinson s disease
Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders
 Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders Mini Medical School October 25, 2018 Heather Rigby, MD, FRCPC 2014 MFMER slide-1 2014 MFMER slide-2 Basal Ganglia Dysfunction - Movement Disorders
Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders Mini Medical School October 25, 2018 Heather Rigby, MD, FRCPC 2014 MFMER slide-1 2014 MFMER slide-2 Basal Ganglia Dysfunction - Movement Disorders
STEADY YOUR APPROACH TO TREMOR (OVERVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS)
 STEADY YOUR APPROACH TO TREMOR (OVERVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS) Karen M. Thomas D.O. Diplomate, ABPN Director of Movement Disorders Program Director of Comprehensive Parkinson s Disease Program Sentara
STEADY YOUR APPROACH TO TREMOR (OVERVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS) Karen M. Thomas D.O. Diplomate, ABPN Director of Movement Disorders Program Director of Comprehensive Parkinson s Disease Program Sentara
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Parkinson Disease. Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC. Presented by: Ontario s Geriatric Steering Committee
 Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
An Approach to Patients with Movement Disorders
 An Approach to Patients with Movement Disorders Joaquim Ferreira, MD, PhD Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics Faculty of Medicine University of Lisbon EDUCATIONAL TOOLS MDS video library
An Approach to Patients with Movement Disorders Joaquim Ferreira, MD, PhD Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics Faculty of Medicine University of Lisbon EDUCATIONAL TOOLS MDS video library
Dystonia: Title. A real pain in the neck. in All the Wrong Places
 Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Parkinson's Disease. Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology
 Parkinson's Disease Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology 18 February 2002 Parkinson Disease Neurological disease affecting over four million patients
Parkinson's Disease Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology 18 February 2002 Parkinson Disease Neurological disease affecting over four million patients
Hypokinetic Movement Disorders
 Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Ariane Park, MD, MPH Assistant Professor-Clinical Division of Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Hypokinetic movement disorders Diminished voluntary
Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Ariane Park, MD, MPH Assistant Professor-Clinical Division of Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Hypokinetic movement disorders Diminished voluntary
Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Movement Disorder Department
 Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Movement Disorder Department Hyperkinetic movement disorders Increase in muscle movements causing involuntary motion Tremor Dystonia
Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Movement Disorder Department Hyperkinetic movement disorders Increase in muscle movements causing involuntary motion Tremor Dystonia
Shake It Off: Recognizing & Treating Movement Disorders
 Ooi Phaik Yee Annual scientific meeting College of Medicine, Academy of Medicine of Malaysia 12 th November 2017 Shake It Off: Recognizing & Treating Movement Disorders MOVEMENT DISORDER A group of symptoms
Ooi Phaik Yee Annual scientific meeting College of Medicine, Academy of Medicine of Malaysia 12 th November 2017 Shake It Off: Recognizing & Treating Movement Disorders MOVEMENT DISORDER A group of symptoms
Parkinson s Disease Update. Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Movement disorder neurologist Providence St. Vincent s
 Parkinson s Disease Update Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Movement disorder neurologist Providence St. Vincent s What is a movement disorder? Neurological disorders that affect ability to move by causing
Parkinson s Disease Update Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Movement disorder neurologist Providence St. Vincent s What is a movement disorder? Neurological disorders that affect ability to move by causing
10/13/2017. Disclosures. Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders. Deep Brain Stimulation: Objectives.
 Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Update on Parkinson s disease and other Movement Disorders October 2018
 Update on Parkinson s disease and other Movement Disorders October 2018 DR. JONATHAN EVANS CONSULTANT IN NEUROLOGY QUEEN S MEDICAL CENTRE NOTTINGHAM Disclosures: Honoraria UCB, Britannia, Allergan, AbbVie
Update on Parkinson s disease and other Movement Disorders October 2018 DR. JONATHAN EVANS CONSULTANT IN NEUROLOGY QUEEN S MEDICAL CENTRE NOTTINGHAM Disclosures: Honoraria UCB, Britannia, Allergan, AbbVie
Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE
 Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Course Participant will: 1. Be familiar with the pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease (PD) 2. Understand clinical
Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Course Participant will: 1. Be familiar with the pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease (PD) 2. Understand clinical
Parkinson's Disease KP Update
 Parkinson's Disease KP Update Andrew Imbus, PA-C Neurology, Movement Disorders Kaiser Permanente, Los Angeles Medical Center No disclosures "I often say now I don't have any choice whether or not I have
Parkinson's Disease KP Update Andrew Imbus, PA-C Neurology, Movement Disorders Kaiser Permanente, Los Angeles Medical Center No disclosures "I often say now I don't have any choice whether or not I have
Parkinson s Disease Initial Clinical and Diagnostic Evaluation. J. Timothy Greenamyre, MD, PhD
 Parkinson s Disease Initial Clinical and Diagnostic Evaluation J. Timothy Greenamyre, MD, PhD Involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action and even when supported
Parkinson s Disease Initial Clinical and Diagnostic Evaluation J. Timothy Greenamyre, MD, PhD Involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action and even when supported
ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging. Dr. Olav E. Krigolson Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE
 ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging Dr. Olav E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE The Basal Ganglia Primary motor cortex Execution of movement
ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging Dr. Olav E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE The Basal Ganglia Primary motor cortex Execution of movement
Semivoluntary movement (=unvoluntary)
 EXTRAPYRAMIDAL DISORDERS = Movement disorders = Degenerative disease 1 4 types of movements: Voluntary movement Semivoluntary movement (=unvoluntary) Involuntary movement Automatic movement 2 3 Movement
EXTRAPYRAMIDAL DISORDERS = Movement disorders = Degenerative disease 1 4 types of movements: Voluntary movement Semivoluntary movement (=unvoluntary) Involuntary movement Automatic movement 2 3 Movement
Dr Barry Snow. Neurologist Auckland District Health Board
 Dr Barry Snow Neurologist Auckland District Health Board Dystonia and Parkinson s disease Barry Snow Gowers 1888: Tetanoid chorea Dystonia a movement disorder characterized by sustained or intermittent
Dr Barry Snow Neurologist Auckland District Health Board Dystonia and Parkinson s disease Barry Snow Gowers 1888: Tetanoid chorea Dystonia a movement disorder characterized by sustained or intermittent
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies. Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai
 Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai 1 Scope Modality of treatment Pathophysiology of PD and dopamine metabolism Drugs Are there
Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai 1 Scope Modality of treatment Pathophysiology of PD and dopamine metabolism Drugs Are there
Childhood Movement Disorders Alessandro Capuano, MD, PhD Federica Graziola, MD
 Childhood Movement Disorders Alessandro Capuano, MD, PhD Federica Graziola, MD Movement Disorders Center Department of Neuroscience Bambino Gesù Pediatric Hospital, Rome Two categories: Approach to diagnosis
Childhood Movement Disorders Alessandro Capuano, MD, PhD Federica Graziola, MD Movement Disorders Center Department of Neuroscience Bambino Gesù Pediatric Hospital, Rome Two categories: Approach to diagnosis
Parkinson s Disease: initial diagnosis, initial treatment & non-motor features. J. Timothy Greenamyre, MD, PhD
 Parkinson s Disease: initial diagnosis, initial treatment & non-motor features J. Timothy Greenamyre, MD, PhD Involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action and even
Parkinson s Disease: initial diagnosis, initial treatment & non-motor features J. Timothy Greenamyre, MD, PhD Involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action and even
PARKINSON S DISEASE. Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons 5/11/16 CARDINAL FEATURES OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Parkinson s disease
 5/11/16 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease Prevalence increases with age (starts 40s60s) Seen in all ethnic groups, M:F about 1.5:1 Second most common neurodegenerative disease Genetics role greater
5/11/16 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease Prevalence increases with age (starts 40s60s) Seen in all ethnic groups, M:F about 1.5:1 Second most common neurodegenerative disease Genetics role greater
Evaluation and Management of Parkinson s Disease in the Older Patient
 Evaluation and Management of Parkinson s Disease in the Older Patient David A. Hinkle, MD, PhD Comprehensive Movement Disorders Clinic Pittsburgh Institute for Neurodegenerative Diseases University of
Evaluation and Management of Parkinson s Disease in the Older Patient David A. Hinkle, MD, PhD Comprehensive Movement Disorders Clinic Pittsburgh Institute for Neurodegenerative Diseases University of
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Tremor. Mario Zappia. Università degli Studi di Catania
 Tremor Mario Zappia Università degli Studi di Catania Tremor: Definition Rhythmical, Involuntary, Oscillatory movement of a body part Classification of Dyskinesias Based on Rhythmicity Rhythmical Dyskinesias:
Tremor Mario Zappia Università degli Studi di Catania Tremor: Definition Rhythmical, Involuntary, Oscillatory movement of a body part Classification of Dyskinesias Based on Rhythmicity Rhythmical Dyskinesias:
Tremor What is tremor? What causes tremor? What are the characteristics of tremor? What are the different categories of tremor?
 Tremor What is tremor? Tremor is an unintentional, somewhat rhythmic, muscle movement involving to-and-fro movements (oscillations) of one or more parts of the body. It is the most common of all involuntary
Tremor What is tremor? Tremor is an unintentional, somewhat rhythmic, muscle movement involving to-and-fro movements (oscillations) of one or more parts of the body. It is the most common of all involuntary
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Biological Psych Frontal Lobes
 Biological Psych Frontal Lobes Frontal lobe What is it? Home to personality? Lesions: wide variety symptoms More than any part of brain Involved in: motor function problem solving spontaneity memory language
Biological Psych Frontal Lobes Frontal lobe What is it? Home to personality? Lesions: wide variety symptoms More than any part of brain Involved in: motor function problem solving spontaneity memory language
Parkinson s Disease. Patients will ask you. 8/14/2015. Objectives
 Parkinson s Disease Jean Van Kingsley MS, FNP-BC Objectives Describe the pathophysiolgy of PD. Review clinical charachteristics of PD. Identify management strategies, to maximize functional status. Recognize
Parkinson s Disease Jean Van Kingsley MS, FNP-BC Objectives Describe the pathophysiolgy of PD. Review clinical charachteristics of PD. Identify management strategies, to maximize functional status. Recognize
Types of involuntary movements
 Tremor Types of involuntary movements Dystonia Chorea Myoclonus Tics Tremor Rhythmic shaking of muscles that produces an oscillating movement Parkinsonian tremor Rest tremor > posture > kinetic Re-emergent
Tremor Types of involuntary movements Dystonia Chorea Myoclonus Tics Tremor Rhythmic shaking of muscles that produces an oscillating movement Parkinsonian tremor Rest tremor > posture > kinetic Re-emergent
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Atypical parkinsonism
 Atypical parkinsonism Wassilios Meissner Service de neurologie et CMR atrophie multisystématisée, CHU de Bordeaux Institut des Maladies Neurodégénératives, Université Bordeaux 2, CNRS UMR 5293 Parkinsonism?
Atypical parkinsonism Wassilios Meissner Service de neurologie et CMR atrophie multisystématisée, CHU de Bordeaux Institut des Maladies Neurodégénératives, Université Bordeaux 2, CNRS UMR 5293 Parkinsonism?
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Table of Contents. Preface... xi. Part I: Introduction to Movement Disorders
 Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Connections of basal ganglia
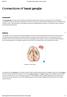 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
A Parkinson s Disease and related disorders
 A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
M. Carranza M. R. Snyder J. Davenport Shaw T. A. Zesiewicz. Parkinson s Disease. A Guide to Medical Treatment
 M. Carranza M. R. Snyder J. Davenport Shaw T. A. Zesiewicz Parkinson s Disease A Guide to Medical Treatment SEEd srl. All rights reserved Piazza Carlo Emanuele II, 19 10123 Torino, Italy Tel. 011.566.02.58
M. Carranza M. R. Snyder J. Davenport Shaw T. A. Zesiewicz Parkinson s Disease A Guide to Medical Treatment SEEd srl. All rights reserved Piazza Carlo Emanuele II, 19 10123 Torino, Italy Tel. 011.566.02.58
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
10th Medicine Review Course st July Prakash Kumar
 10th Medicine Review Course 2018 21 st July 2018 Drug Therapy for Parkinson's disease Prakash Kumar National Neuroscience Institute Singapore General Hospital Sengkang General Hospital Singhealth Duke-NUS
10th Medicine Review Course 2018 21 st July 2018 Drug Therapy for Parkinson's disease Prakash Kumar National Neuroscience Institute Singapore General Hospital Sengkang General Hospital Singhealth Duke-NUS
8/28/2017. Behind the Scenes of Parkinson s Disease
 BEHIND THE SCENCES IN Parkinson s Disease Behind the Scenes of Parkinson s Disease Anna Marie Wellins DNP, ANP C Objectives Describe prevalence of Parkinson's disease (PD) Describe the hallmark pathologic
BEHIND THE SCENCES IN Parkinson s Disease Behind the Scenes of Parkinson s Disease Anna Marie Wellins DNP, ANP C Objectives Describe prevalence of Parkinson's disease (PD) Describe the hallmark pathologic
