Japanese Journal of Radiology Diffusional kurtosis imaging of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis:preliminary clinical experience
|
|
|
- Byron Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Japanese Journal of Radiology Diffusional kurtosis imaging of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis:preliminary clinical experience --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Keywords: Corresponding Author: RMED-0R Diffusional kurtosis imaging of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis:preliminary clinical experience Original Article Diffusional kurtosis, MRI, DKI, non-gaussian, multiple sclerosis, normal-appearing white matter Mariko Yoshida Juntendo University School of Medicine Tokyo, JAPAN Corresponding Author Secondary Information: Corresponding Author's Institution: Juntendo University School of Medicine Corresponding Author's Secondary Institution: First Author: Mariko Yoshida First Author Secondary Information: Order of Authors: Mariko Yoshida Masaaki Hori Kazumasa Yokoyama Issa Fukunaga Michimasa Suzuki Koji Kamagata Keigo Shimoji Atsushi Nakanishi Nobutaka Hattori Yoshitaka Masutani Shigeki Aoki Order of Authors Secondary Information: Abstract: Purpose. We evaluated diffusional changes in normal-appearing white matter (NAWM) regions remote from multiple sclerosis (MS) plaques by using diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) to investigate the non-gaussian behavior of water diffusion. Materials and methods. Participants were MS patients and age-matched healthy volunteers. DKI was performed on a -T MR imager. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and diffusional kurtosis (DK) maps were computed. Regions of interest (ROIs) were compared in cerebral regions, including the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobe white matter (WM) in controls and NAWM in MS patients. Results The mean FA of all ROIs was 0.±0.0 (SD) (controls) or 0.±0.09 (MS group) (P =0.0). Mean ADC was 0.± mm /s (controls) or 0.0± mm /s (MS group). The mean DK of all ROIs was 0.±0.00 (controls) or 0.±0.0 (MS group) (P = 0.00). Analysis of individual ROIs revealed significant differences in DK in ROIs between normal WM and NAWM, but significant Powered by Editorial Manager and Preprint Manager from Aries Systems Corporation
2 differences in ADC and FA in only one ROI each. Conclusion DKI may provide a new sensitive indicator for detecting tissue damage in MS patients in addition to conventional diffusional evaluations such as diffusion tensor imaging. Powered by Editorial Manager and Preprint Manager from Aries Systems Corporation
3 Title Page w/ ALL Author Contact Info. Diffusional kurtosis imaging of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis:preliminary clinical experience Mariko Yoshida(Corresponding Author) Masaaki Hori Kazumasa Yokoyama Issa Fukunaga Michimasa Suzuki Koji Kamagata Keigo Shimoji Atsushi Nakanishi Nobutaka Hattori Yoshitaka Masutani Shigeki Aoki M. Yoshida M. Hori M. Suzuki K. Kamagata K. Shimoji A. Nakanishi S. Aoki Department of Radiology, Juntendo University School of Medicine, -- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo -, Japan Tel. +---; Fax K. Yokoyama N. Hattori Department of Neurology, Juntendo University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan I. Fukunaga Graduate School of Health Promotion Science, Tokyo Metropolitan University, Tokyo, Japan Y. Masutani Division of Radiology, and Biomedical Engineering, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
4 *Manuscript (must not contain any author information) Click here to view linked References INTRODUCTION In multiple sclerosis (MS), diffusion analysis of water molecules using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a quantitative technique for providing more specific microstructural changes than conventional MRI. It allows the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in the tissues to be calculated. The ADC reflects the microscopic Brownian motion of water molecules. It has been reported very sensitive to the occult tissue damage of MS and described abnormalities of diffusion MRI metrics in the normal-appearing white matter (NAWM) outside plaques of MS patients and in MS the ADC in the NAWM was elevated -. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) provides a mathematical description of the magnitude and directional dependency (anisotropy) of the movement of water molecules in three-dimensional space. It produce indices of fractional anisotropy (FA) and ADC in three-dimensional direction separately. Recent studies have shown that DTI can quantify the extent and pathological severity of structural changes occurring within MS plaques and in the NAWM -. Moreover, previous investigators have noted reduced FA and elevated ADCs in both MS plaques and NAWM, with higher ADCs in the plaques
5 than in the NAWM, 9-. Diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) is an emerging MRI technique that provides information on non-gaussian water diffusion in tissues,. DKI can provide a diffusional non-gaussianity called diffusional kurtosis (DK) as well as the standard DTI metrics such as FA and ADC. An advantage of DK over FA is that because DK does not rely on spatially oriented tissue structures, it can be used to evaluate both gray and white matter (WM). Moreover, unlike DTI, DKI is not affected by crossing fiber tracts. We evaluated diffusional changes in the NAWM regions remote from MS plaques by using DKI in a clinically appropriate setting. METHODS Subjects The subjects were MS patients ( men and women; mean age,.±. SD years) and healthy volunteers ( men and women, mean age.±.9 years) with no history of neurological disease. Informed consent was obtained from all patients and volunteers. The local ethical committee approved this study. All of the MS patients had relapsing remitting MS, defined according to standard
6 criteria - ; the median Expanded Disability Status Scale at study entry was.(range, 0 to.0), and the mean disease duration was 9.±. years. Imaging protocol Our data for diffusion metrics were acquired on a -T magnetic resonance scanner (Achieva; Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands) with an -channel-array SENSE head coil. After conventional imaging sequences had been taken, including T- and T-weighted images and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images, DKI was acquired with single shot, spin-echo echo planar imaging (EPI) sequence, following repetition time/echo time, 000/0 ms; number of signals acquired: one; section thickness: mm, 0 slices; field of view: mm; matrix: ; imaging time: approximately min; and six diffusion weighting (b) values (0, 00, 000, 00, 000, and 00 s/mm ), with diffusion encoding in directions for every b value. Gradient length (δ) was kept at.ms, and the time between the two leading edges of the diffusion gradient (Δ) was kept at 9. ms. A b value of 00 s/mm was used as a reference value for consistency with recent reports,. Diffusion metrics
7 B0 distortion correction was applied to all diffusion data on the magnetic resonance imager. DKI data were transferred to an offline workstation. Diffusion metric maps were calculated by using the free software dtv II. FZR (Image Computing and Analysis Laboratory, Department of Radiology, The University of Tokyo Hospital, Japan). FA and ADC maps and color maps with -directional (x, y, z) information using a conventional mono-exponential model were obtained, as were DK maps. Regions of interest (ROIs) were determined in NAWM in the MS group and normal WM in the control group, and the values of FA, ADC, and DK (also known as mean DK or mean kurtosis, defined as the average of the kurtosis over all possible diffusion directions. ) were compared in these regions. The DKI pulse sequence and processing algorithm have been described previously,. Briefly, this technique uses a diffusion-sensitizing pulse sequence and the signal intensity data are fitted to the functional form, 9 : [A] where S 0 is the signal intensity for b = 0, D app is the ADC, and K app is the apparent diffusional kurtosis(adk). The Stejskal-Tanner sequence 0 defined that b-value is given
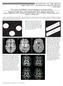
8 by b= (γδg) (Δ-δ/), where γ is the nuclear spin gyromagnetic ratio, g is the diffusion time, Δ and δ were given above (Imaging protocol). Parametric maps of the ADK and ADC were created by fitting the image signal intensities on a voxel-by-voxel basis to Eq. [A], as described elsewhere, 9. The conventional DTI data are calculated by using information at the b value, 000. Image analysis First, we checked the MS patients plaques on the FLAIR images and T-weighted echo-planar images. The ROIs were placed on NAWM in the MS group by using the T-weighted echo-planar images or color maps. Particular care was taken to avoid contamination by MS plaques close to the NAWM (Fig. ). None of the ROIs were in the MS plaques and peripheral plaques. ROIs were also drawn in matching regions in the WM of the age-matched controls. FA, ADC, and DKI were calculated by using the free software dtv II FZR. All of the ROIs were fixed at the same size, 9 voxels (total: mm ); each voxel is interpolated mm isotropic voxel with cubic shape. The size of ROIs was decided as large as possible in order not to deviate from all WM regions. The ROIs were consisted of 0 bilateral areas ; the frontal lobe WM, the parietal lobe
9 WM, superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF), corona radiata, the peripheral WM of anterior horn of lateral ventricle and posterior horn of lateral ventricle, anterior limb of internal capsule (ALIC), posterior limb of internal capsule (PLIC), the occipital lobe WM, and the temporal lobe WM, and the ROIs on the corpus callosum that were not bilateral ; the genu (GCC), the anterior (ACC), the posterior (PCC), and the splenium (SCC). Statistical analysis The Mann Whitney test was performed to assess for differences in the averaged values of FA, ADC, and DK between the patients and healthy control subjects using IBM SPSS Statistics software (version 9.0, SPSS, Chicago, IL). P < 0.0 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. For comparison of the individual ROIs in the normal WM and NAWM, Mann Whitney U-tests with Bonferroni correction were performed to compare the averaged FA, ADC, and DK values between MS patients and normal controls. P < 0.0 (with Bonferroni correction, P < 0.00) was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
10 RESULTS Analysis of mean values of FA, ADC, and DK in all ROIs The mean values and standard deviations (SD) are shown on the table.. The mean FA for all ROIs was 0.±0.0 SD in the control group and 0.±0.09 in the MS group. The mean ADC was 0.±0.0 0 mm /s in the control group and 0.0±0.0 0 mm /s in the MS group. The mean DK of all ROIs was 0.±0.00 in the control group and 0.±0.0 in the MS group. Significant differences in mean FA (P =0.0), and particularly in DK (P = 0.00), were observed between normal WM and NAWM. ADC values were non-significantly higher in the MS group than in the control group (P = 0.9). These analyses are summarized in the Fig.. Analysis of individual ROIs in normal WM and NAWM Mann Whitney U-tests revealed marked differences (P < 0.0) in FA in ROIs (right parietal lobe WM, left temporal lobe WM, PCC, and SCC) between the control and MS groups. Marked differences (P < 0.0) in ADC were observed in ROIs (right SLF, temporal lobe WM bilaterally, PCC, and SCC) between the control and MS
11 groups. Marked differences (P < 0.0) in DK were observed in ROIs (right SLF, temporal lobe WM bilaterally, left frontal lobe WM, PCC, and SCC) between the control and MS groups. Bonferroni correction revealed significant differences ( P < 0.00) in FA in one ROI (right parietal lobe WM) between normal WM and NAWM. Significant differences in ADC were observed in one ROI (left temporal lobe WM) between the control and MS groups. Significant differences in DK were observed in ROIs (right SLF, left temporal lobe WM, and SCC) between the control and MS groups. DISCUSSION MS is an autoimmune-mediated disease of the central nervous system; its lesions are characterized by inflammation, edema, demyelination, remyelination, axonal damage, gliosis, or a combination of these features -. Recently these findings are known as neurodegenerative phenomena. Neuronal/axonal damage and gray matter and WM atrophy play an important role in disease progression,. Conventional MRI is the primary imaging modality that supports the clinical diagnosis of MS,, and quantitative analysis especially using histogram have been reported -0.
12 However, it is limited to low pathological specificity and quantitative evaluation of the WM outside visible lesions on T-weighted images or FLAIR. Therefore, it cannot be used to evaluate diffuse damage in the NAWM and the association of this damage with clinical status. DTI is a quantitative technique that can be used to overcome these limitations. Recent studies have found that DTI can reveal subtle damage in the NAWM of MS patients,. DTI studies have shown that MS plaques and NAWM have significantly higher average ADCs and significantly lower average FAs than healthy WM and that NAWM injury becomes more pronounced with increasing disease duration and clinical disability,,. However, DTI presupposes a Gaussian approximation of the diffusion displacement in an unrestricted environment, where diffusion properly restricted by barriers of cell membranes, axon sheaths and water compartments and so on. DTI cannot be used to measure non-gaussian diffusion; moreover, it may not predict accurate values at dense intersections of fiber tracts. In contrast, DKI can be used to quantify non-gaussian diffusion and is a more sensitive indicator of diffusional heterogeneity, 9,. Diffusional non-gaussianity may arise from diffusion barriers such as cell membranes, axon sheaths, 9
13 myelin layers and organelles, and water compartments. DKI can be regarded as an indicator of microstructural complexity and can be used to investigate abnormalities in tissues with isotropic structure, i.e. gray matter as well as WM. It has already been shown that the DKI method can be used to detect changes in tissue microstructure between healthy subjects and patients with white matter lesions, during normal human aging, rodent brain maturation, in staging of cerebral gliomas, after mild brain injury 9, 0, in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, in cerebral infarction, and in lung/small airway disease. Histological studies in MS have revealed pathological damage in WM areas that have appeared normal on conventional MRI. This damage consists of astrogliosis, microglial activation, vascular hyalinization, blood brain-barrier breakdown, reduced myelin density, and axonal loss. Our results showed that DKI could detect abnormalities in NAWM that could not be imaged by conventional MRI. Differences in DK between NAWM and normal WM were more pronounced than those in FA or ADC. Our results suggest that DKI is sensitive to microstructural changes associated with the above pathology by quantifying diffusional 0
14 non-gaussianity. DK is thought to be sensitive to slow diffusional movement under restricted environment, which may be mainly determined by microstructure. As a consequence of our results, DKI can provide the additional information and be a more precise biomarker of tissue damage in NAWM in MS patients compared to DTI (FA and ADC). More sensitive evaluation of NAWM could have indications in predicting clinical status and as a tool for monitoring the responses of MS patients to medications. The limitations of our study included that the small number of patients and a possible need to further optimize the protocol used for data acquisition with DKI. Normalization of DK data would be needed if this technique were to be compared with others, such as DTI and q-space imaging. Our study was an ROI study and it could therefore be considered subjective and assessment for small area of WM. More types of statistical analysis (e.g., of the automatic ROI setting or the use of histogram analysis, 9 ) are considered, and we need to attempt tract-specific analysis of the WM in MS. This study focused on comparison between normal WM and NAWM. It is necessary for us to assess lesions including some types of plaques in MS in order to know their elaborate pathological changes. Moreover, studies of the correlation between clinical findings (e.g.,
15 cognitive function or clinical stages) and imaging data will be needed. Other limitation is that we used only mean DK. Recently the studies of directional DK, i.e. axial and radial kurtosis, have been reported, 9,,. Such directional DK analysis may provide more precise microstructural information regarding the brain tissue, 9. However, mean DK, the directionally averaged kurtosis, has been shown to be useful in some reports such as glioma and acute cerebral infarction and so on,, 9, 0. In MS, there has been no study using mean DK. So it is important that we report these preliminary results, because this study was able to demonstrate the clinical potential of DKI for assessing NAWM in MS patients. Conclusion DKI has been demonstrated to be a sensitive quantitative indicator in addition to conventional diffusional evaluations such as DTI. DKI can provide new information about NAWM changes in MS by detecting of subtle changes in brain tissue microstructure. Acknowledgment This study is partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (Comprehensive Brain Science Network) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan.
16 REFERENCES. Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 00; : -.. Rocca MA, Cercignani M, Iannucci G, Comi G, Filippi M. Weekly diffusion-weighted imaging of normal-appearing white matter in MS. Neurology 000; : -.. Cercignani M, Iannucci G, Filippi M. Diffusion-weighted imaging in multiple sclerosis. Ital J Neurol Sci 999; 0: S-9.. Horsfield MA, Lai M, Webb SL, Barker GJ, Tofts PS, Turner R, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficients in benign and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 99; : Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR Biomed 99; : -.. Guo AC, MacFall JR, Provenzale JM. Multiple sclerosis: diffusion tensor MR imaging for evaluation of normal-appearing white matter. Radiology 00; : 9-.. Filippi M, Agosta F. Imaging biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 00; : 0-.. Rovaris M, Agosta F, Pagani E, Filippi M. Diffusion tensor MR imaging. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 009; 9: Werring DJ, Brassat D, Droogan AG, Clark CA, Symms MR, Barker GJ, et al. The pathogenesis of lesions and normal-appearing white matter changes in multiple sclerosis: a serial diffusion MRI study. Brain 000; ( Pt ): Castriota Scanderbeg A, Tomaiuolo F, Sabatini U, Nocentini U, Grasso MG, Caltagirone C. Demyelinating plaques in relapsing-remitting and secondary-progressive multiple sclerosis: assessment with diffusion MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 000; : -.
17 Tsuchiya K, Hachiya J, Maehara T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in multiple sclerosis: comparison with contrast-enhanced study. Eur J Radiol 999; : -9.. Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 00; : -0.. Lu H, Jensen JH, Ramani A, Helpern JA. Three-dimensional characterization of non-gaussian water diffusion in humans using diffusion kurtosis imaging. NMR Biomed 00; 9: -.. Hori M, Fukunaga I, Masutani Y, Taoka T, Kamagata K, Suzuki Y, et al. Visualizing Non-Gaussian Diffusion: Clinical Application of q-space Imaging and Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging of the Brain and Spine. Magn Reson Med Sci 0; : (in press).. McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 00; 0: -.. Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 00 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 0; 9: Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G, Filippi M, Hartung HP, Kappos L, et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 00 revisions to the "McDonald Criteria". Ann Neurol 00; : 0-.. Kurtzke JF. A new scale for evaluating disability in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 9; : Jensen JH, Helpern JA. MRI quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed 00; : Stejeskal EO, Tanner JE. Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dipendent field gradient. J Chem Phys 9; : -9.
18 McFarlin DE, McFarland HF. Multiple sclerosis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 9; 0: -.. McFarlin DE, McFarland HF. Multiple sclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 9; 0: -.. Rodriguez M, Siva A, Ward J, Stolp-Smith K, O'Brien P, Kurland L. Impairment, disability, and handicap in multiple sclerosis: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Neurology 99; : -.. Vigeveno RM, Wiebenga OT, Wattjes MP, Geurts JJ, Barkhof F. Shifting imaging targets in multiple sclerosis: from inflammation to neurodegeneration. J Magn Reson Imaging 0; : -9.. Geurts JJ, Stys PK, Minagar A, Amor S, Zivadinov R. Gray matter pathology in (chronic) MS: modern views on an early observation. J Neurol Sci 009; : -0.. Fazekas F, Barkhof F, Filippi M, Grossman RI, Li DK, McDonald WI, et al. The contribution of magnetic resonance imaging to the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 999; : -.. Barkhof F, van Walderveen M. Characterization of tissue damage in multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 999; : -.. Miki Y, Grossman RI, Udupa JK, van Buchem MA, Wei L, Phillips MD, et al. Differences between relapsing-remitting and chronic progressive multiple sclerosis as determined with quantitative MR imaging. Radiology 999; 0: Miki Y, Grossman RI, Udupa JK, Wei L, Polansky M, Mannon LJ, et al. Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: longitudinal analysis of MR images--lack of correlation between changes in T lesion volume and clinical findings. Radiology 999; : Phillips MD, Grossman RI, Miki Y, Wei L, Kolson DL, van Buchem MA, et al. Comparison of T lesion volume and magnetization transfer ratio histogram analysis and of atrophy
19 and measures of lesion burden in patients with multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 99; 9: Werring DJ, Clark CA, Barker GJ, Thompson AJ, Miller DH. Diffusion tensor imaging of lesions and normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 999; : -.. Bammer R, Augustin M, Strasser-Fuchs S, Seifert T, Kapeller P, Stollberger R, et al. Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging for characterizing diffuse and focal white matter abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Med 000; : -9.. Abdallah CG, Tang CY, Mathew SJ, Martinez J, Hof PR, Perera TD, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in studying white matter complexity: a gap junction hypothesis. Neurosci Lett 00; : -.. Lazar M, Jensen JH, Xuan L, Helpern JA. Estimation of the orientation distribution function from diffusional kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 00; 0: -.. Iraji A, Davoodi-Bojd E, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Hossein-Zadeh GA, Jiang Q. Diffusion kurtosis imaging discriminates patients with white matter lesions from healthy subjects. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 0; 0: Falangola MF, Jensen JH, Babb JS, Hu C, Castellanos FX, Di Martino A, et al. Age-related non-gaussian diffusion patterns in the prefrontal brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 00; : -0.. Cheung MM, Hui ES, Chan KC, Helpern JA, Qi L, Wu EX. Does diffusion kurtosis imaging lead to better neural tissue characterization? A rodent brain maturation study. Neuroimage 009; : -9.. Raab P, Hattingen E, Franz K, Zanella FE, Lanfermann H. Cerebral gliomas: diffusional kurtosis imaging analysis of microstructural differences. Radiology 00; : -.
20 Grossman EJ, Ge Y, Jensen JH, Babb JS, Miles L, Reaume J, et al. Thalamus and Cognitive Impairment in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study. J Neurotrauma Zhuo J, Xu S, Proctor JL, Mullins RJ, Simon JZ, Fiskum G, et al. Diffusion kurtosis as an in vivo imaging marker for reactive astrogliosis in traumatic brain injury. Neuroimage 0; 9: -.. Helpern JA, Adisetiyo V, Falangola MF, Hu C, Di Martino A, Williams K, et al. Preliminary evidence of altered gray and white matter microstructural development in the frontal lobe of adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a diffusional kurtosis imaging study. J Magn Reson Imaging 0; : -.. Hori M, Aoki S, Fukunaga I, Suzuki Y, Masutani Y. A new diffusion metric, diffusion kurtosis imaging, used in the serial examination of a patient with stroke. Acta Radiol Sh Rep 0; :.. Trampel R, Jensen JH, Lee RF, Kamenetskiy I, McGuinness G, Johnson G. Diffusional kurtosis imaging in the lung using hyperpolarized He. Magn Reson Med 00; : -.. Allen IV, McQuaid S, Mirakhur M, Nevin G. Pathological abnormalities in the normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Sci 00; : -.
21 Figure FA ADC DK controls 0.±0.0 0.±0.0 0.±0.00 MS patients 0.± ±0.0 0.±0.0 Table. The averages and standard deviations (SD) of fractional anisotropy (FA), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), and diffusional kurtosis (DK) values for all the ROIs. ( 0 - mm /s)
22 frontal lobe WM corona radiata SLF GCC parietal lobe WM anterior horn WM ALIC ACC PCC SCC posterior horn WM PLIC temporal lobe WM occipital lobe WM Fig.. Examples of the drawing of regions of interest. Particular care was taken to avoid contamination by plaques close to the normal-appearing white matter. Abbreviation: white matter(wm), anterior limb of internal capsule(alic), posterior limb of internal capsule(plic), superior longitudinal fasciculus(slf), genu of corpus callosum(gcc), anterior corpus callosum(acc), posterior corpus callosum(pcc), splenium of corpus callosum(scc).
23 Average FA or DK Average ADC( 0 - mm /s) **P=.00 *P=.9 *P=.0 Fig.. Averages of fractional anisotropy (FA), diffusional kurtosis (DK), and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in control and multiple sclerosis (MS) groups. Significant differences in FA and DK were observed between the control and MS groups.
24 Acknowledgement Acknowledgment This study is partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (Comprehensive Brain Science Network) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan.
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging: An Emerging Technique for Evaluating the Microstructural Environment of the Brain
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review Steven et al. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging of the Brain Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Andrew J. Steven 1 Jiachen Zhuo Elias R. Melhem Steven
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review Steven et al. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging of the Brain Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Andrew J. Steven 1 Jiachen Zhuo Elias R. Melhem Steven
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Parameters of diffusional kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction in different brain regions
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 933-938, 2016 Parameters of diffusional kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction in different brain regions YUE LIN GUO 1, SU JUAN LI 1,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 933-938, 2016 Parameters of diffusional kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction in different brain regions YUE LIN GUO 1, SU JUAN LI 1,
Published July 31, 2014 as /ajnr.A4050
 Published July 31, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4050 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuromyelitis Optica: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study T.M. Doring, F.C.R. Lopes, T.T.A. Kubo, G. Tukamoto, M.C. Kimura, R.M. Strecker,
Published July 31, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4050 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuromyelitis Optica: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study T.M. Doring, F.C.R. Lopes, T.T.A. Kubo, G. Tukamoto, M.C. Kimura, R.M. Strecker,
During human aging, the brain exhibits both macro- and
 Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Quantitative divusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging, cerebral atrophy, and disability in multiple sclerosis
 318 Division of Clinical Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK M Wilson X Lin B P Turner L D Blumhardt Division of Academic Radiology P S Morgan
318 Division of Clinical Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK M Wilson X Lin B P Turner L D Blumhardt Division of Academic Radiology P S Morgan
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Stroke Assessment With Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging
 Stroke Assessment With Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Edward S. Hui, PhD; Els Fieremans, PhD; Jens H. Jensen, PhD; Ali Tabesh, PhD; Wuwei Feng, MD, MS; Leonardo Bonilha, MD, PhD; Maria V. Spampinato, MD;
Stroke Assessment With Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Edward S. Hui, PhD; Els Fieremans, PhD; Jens H. Jensen, PhD; Ali Tabesh, PhD; Wuwei Feng, MD, MS; Leonardo Bonilha, MD, PhD; Maria V. Spampinato, MD;
Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1803 1808, November/December 1999 Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Marco Bozzali, Maria A. Rocca, Giuseppe Iannucci,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1803 1808, November/December 1999 Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Marco Bozzali, Maria A. Rocca, Giuseppe Iannucci,
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis. Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
Neuroradiology Original Research
 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. imaging (MRI) provides
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Bas Jasperse, MD; Arjan Minneboo, MD; Vincent de Groot, MD; Nynke F. Kalkers, MD, PhD; Paul E.
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Bas Jasperse, MD; Arjan Minneboo, MD; Vincent de Groot, MD; Nynke F. Kalkers, MD, PhD; Paul E.
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic?
 Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Overview. Fundamentals of functional MRI. Task related versus resting state functional imaging for sensorimotor mapping
 Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
ADC evaluations of the hippocampus and amygdala in multiple sclerosis
 Neurology Asia 2014; 19(4) : 387 391 ADC evaluations of the hippocampus and amygdala in multiple sclerosis 1 Mikail Inal, 1 Birsen Unal Daphan, 1 Yasemin Karadeniz Bilgili, 2 Yakup Turkel, 3 Ibrahim Kala
Neurology Asia 2014; 19(4) : 387 391 ADC evaluations of the hippocampus and amygdala in multiple sclerosis 1 Mikail Inal, 1 Birsen Unal Daphan, 1 Yasemin Karadeniz Bilgili, 2 Yakup Turkel, 3 Ibrahim Kala
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:821 827, May 1999 Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Maria A. Rocca,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:821 827, May 1999 Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Maria A. Rocca,
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry
 2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury
 Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients. SDM (39) 221 Left superior longitudinal
 Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography
 Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Assessment of Brain White Matter Maturation During the First Postnatal Year
 DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
The potential role of novel diffusion imaging techniques in the understanding and treatment of epilepsy
 Review Article The potential role of novel diffusion imaging techniques in the understanding and treatment of epilepsy Gavin P. Winston 1,2 1 Epilepsy Society MRI Unit, Chesham Lane, Chalfont St Peter,
Review Article The potential role of novel diffusion imaging techniques in the understanding and treatment of epilepsy Gavin P. Winston 1,2 1 Epilepsy Society MRI Unit, Chesham Lane, Chalfont St Peter,
Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine are potentially catastrophic.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
Heidi M. Feldman, MD, PhD,* Jason D. Yeatman, BA, Eliana S. Lee, BS,* Laura H. F. Barde, PhD,* Shayna Gaman-Bean, MD*
 Review Article Diffusion Tensor Imaging: A Review for Pediatric Researchers and Clinicians Heidi M. Feldman, MD, PhD,* Jason D. Yeatman, BA, Eliana S. Lee, BS,* Laura H. F. Barde, PhD,* Shayna Gaman-Bean,
Review Article Diffusion Tensor Imaging: A Review for Pediatric Researchers and Clinicians Heidi M. Feldman, MD, PhD,* Jason D. Yeatman, BA, Eliana S. Lee, BS,* Laura H. F. Barde, PhD,* Shayna Gaman-Bean,
NEURO. Keywords Idiopathic NPH. Lumboperitoneal shunt. Q-space imaging. Axon diameter. Diffusion MRI
 Eur Radiol (2016) 26:2992 2998 DOI 10.1007/s00330-015-4162-9 NEURO Prospective estimation of mean axon diameter and extra-axonal space of the posterior limb of the internal capsule in patients with idiopathic
Eur Radiol (2016) 26:2992 2998 DOI 10.1007/s00330-015-4162-9 NEURO Prospective estimation of mean axon diameter and extra-axonal space of the posterior limb of the internal capsule in patients with idiopathic
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Normal-Appearing Brain T1 Relaxation Time Predicts Disability in Early Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Normal-Appearing Brain T1 Relaxation Time Predicts Disability in Early Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Francesco Manfredonia, MD; Olga Ciccarelli, PhD; Zhaleh Khaleeli, MRCP;
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Normal-Appearing Brain T1 Relaxation Time Predicts Disability in Early Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Francesco Manfredonia, MD; Olga Ciccarelli, PhD; Zhaleh Khaleeli, MRCP;
Axial Diffusivity of the Corona Radiata Correlated With Ventricular Size in Adult Hydrocephalus
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Cauley and Cataltepe Imaging Adult Hydrocephalus Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Keith A Cauley Oguz Cataltepe 2 Cauley KA,
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Cauley and Cataltepe Imaging Adult Hydrocephalus Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Keith A Cauley Oguz Cataltepe 2 Cauley KA,
Massimo Filippi * 1. Introduction
 Journal of the Neurological Sciences 206 (2003) 157 164 www.elsevier.com/locate/jns MRI clinical correlations in the primary progressive course of MS: new insights into the disease pathophysiology from
Journal of the Neurological Sciences 206 (2003) 157 164 www.elsevier.com/locate/jns MRI clinical correlations in the primary progressive course of MS: new insights into the disease pathophysiology from
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Stefan Ropele, Siegried Strasser-Fuchs, Michael Augustin, Rudolf Stollberger, Christian Enzinger, Hans-Peter Hartung, and Franz Fazekas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1885 1891, November/December 2000 A Comparison of Magnetization Transfer Ratio, Magnetization Transfer Rate, and the Native Relaxation Time of Water Protons Related to Relapsing-remitting
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1885 1891, November/December 2000 A Comparison of Magnetization Transfer Ratio, Magnetization Transfer Rate, and the Native Relaxation Time of Water Protons Related to Relapsing-remitting
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Magnetization Transfer and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:267 272, February 2002 Magnetization Transfer and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Matilde Inglese, Fabrizio Salvi, Giuseppe Iannucci, Gian Luigi
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:267 272, February 2002 Magnetization Transfer and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Matilde Inglese, Fabrizio Salvi, Giuseppe Iannucci, Gian Luigi
Mild traumatic brain injury is one of the most significant
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Cognitive Impairment in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Longitudinal Diffusional Kurtosis and Perfusion Imaging Study E.J. Grossman, J.H. Jensen, J.S. Babb, Q. Chen, A. Tabesh, E.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Cognitive Impairment in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Longitudinal Diffusional Kurtosis and Perfusion Imaging Study E.J. Grossman, J.H. Jensen, J.S. Babb, Q. Chen, A. Tabesh, E.
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER. Multiple Sclerosis: A serious and unpredictable neurological disease
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER Multiple Sclerosis: A serious and unpredictable neurological disease Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that still
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER Multiple Sclerosis: A serious and unpredictable neurological disease Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that still
MRI of Pathological Aging Brain
 MRI of Pathological Aging Brain Yukio Miki Department of Radiology, Osaka City University A variety of pathological changes occur in the brain with aging, and many of these changes can be identified by
MRI of Pathological Aging Brain Yukio Miki Department of Radiology, Osaka City University A variety of pathological changes occur in the brain with aging, and many of these changes can be identified by
Diffusion tensor imaging of the infant brain: From technical problems to neuroscientific breakthroughs Jessica Dubois
 Diffusion tensor imaging of the infant brain: From technical problems to neuroscientific breakthroughs Jessica Dubois L. Hertz-Pannier, G. Dehaene-Lambertz, J.F. Mangin, D. Le Bihan Inserm U56, U663; NeuroSpin
Diffusion tensor imaging of the infant brain: From technical problems to neuroscientific breakthroughs Jessica Dubois L. Hertz-Pannier, G. Dehaene-Lambertz, J.F. Mangin, D. Le Bihan Inserm U56, U663; NeuroSpin
Injuries of neural tracts in a patient with CADASIL: a diffusion tensor imaging study
 Jang and Seo BMC Neurology (2015) 15:176 DOI 10.1186/s12883-015-0434-x CASE REPORT Open Access Injuries of neural tracts in a patient with CADASIL: a diffusion tensor imaging study Sung Ho Jang and You
Jang and Seo BMC Neurology (2015) 15:176 DOI 10.1186/s12883-015-0434-x CASE REPORT Open Access Injuries of neural tracts in a patient with CADASIL: a diffusion tensor imaging study Sung Ho Jang and You
Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update
 MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update Poster No.: C-0285 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Valls Masot, A. M. Quiles Granado, J. Puig Alcántara, L. RamióTorrentà,
MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update Poster No.: C-0285 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Valls Masot, A. M. Quiles Granado, J. Puig Alcántara, L. RamióTorrentà,
Cognitive Impairment and Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Normal Appearing White Matter in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, March: 265-271, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Cognitive Impairment and Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Normal Appearing White Matter in Multiple Sclerosis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, March: 265-271, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Cognitive Impairment and Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Normal Appearing White Matter in Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) generally begins in the second-tothird
 Published October 22, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1776 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.S. Vishwas T. Chitnis R. Pienaar B.C. Healy P.E. Grant Tract-Based Analysis of Callosal, Projection, and Association Pathways in Pediatric
Published October 22, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1776 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.S. Vishwas T. Chitnis R. Pienaar B.C. Healy P.E. Grant Tract-Based Analysis of Callosal, Projection, and Association Pathways in Pediatric
The new Global Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score (MSSS) correlates with axonal but not glial biomarkers
 The new Global Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score (MSSS) correlates with axonal but not glial biomarkers A. Petzold M.J. Eikelenboom G. Keir C.H. Polman B.M.J. Uitdehaag E.J. Thompson G. Giovannoni 04.08.2005
The new Global Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score (MSSS) correlates with axonal but not glial biomarkers A. Petzold M.J. Eikelenboom G. Keir C.H. Polman B.M.J. Uitdehaag E.J. Thompson G. Giovannoni 04.08.2005
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging
 Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy: Insights into the Pathology and Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis.
 Chapter 10 (pp 139-167) of Multiple Sclerosis 2 - Blue Books of Practical Neurology, vol. 27. J.H Noseworthy, W.I. McDonald (eds.). Elsevier Science (USA), 2003. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy:
Chapter 10 (pp 139-167) of Multiple Sclerosis 2 - Blue Books of Practical Neurology, vol. 27. J.H Noseworthy, W.I. McDonald (eds.). Elsevier Science (USA), 2003. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy:
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!!
 Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology
 Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1939 1945, November/December 1999 Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images Alex Rovira, Juli Alonso,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1939 1945, November/December 1999 Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images Alex Rovira, Juli Alonso,
Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension pathogenesis?: Diffusion weighted MR imaging study
 Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity
 Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Stereotactic Diffusion Tensor Tractography For Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Web Training Modules Module 13: MR Imaging for Brain Injuries
 Web Training Modules Module 13: MR Imaging for Brain Injuries 1 Introduction... 4 Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries... 5 Structural MRI... 5 Diffusion Tensor Imaging... 6 Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging... 11 Functional
Web Training Modules Module 13: MR Imaging for Brain Injuries 1 Introduction... 4 Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries... 5 Structural MRI... 5 Diffusion Tensor Imaging... 6 Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging... 11 Functional
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
Spatiotemporal dynamics of diffusional kurtosis, mean diffusivity and perfusion changes in experimental stroke
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Spatiotemporal dynamics of diffusional kurtosis, mean diffusivity and perfusion changes in experimental stroke
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Spatiotemporal dynamics of diffusional kurtosis, mean diffusivity and perfusion changes in experimental stroke
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Quantitative Neuroimaging- Gray and white matter Alteration in Multiple Sclerosis. Lior Or-Bach Instructors: Prof. Anat Achiron Dr.
 Quantitative Neuroimaging- Gray and white matter Alteration in Multiple Sclerosis Lior Or-Bach Instructors: Prof. Anat Achiron Dr. Shmulik Miron INTRODUCTION Multiple Sclerosis general background Gray
Quantitative Neuroimaging- Gray and white matter Alteration in Multiple Sclerosis Lior Or-Bach Instructors: Prof. Anat Achiron Dr. Shmulik Miron INTRODUCTION Multiple Sclerosis general background Gray
Published May 14, 2015 as /ajnr.A4311
 Published May 14, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4311 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Mean Diffusional Kurtosis in Patients with Glioma: Initial Results with a Fast Imaging Method in a Clinical Setting A. Tietze,
Published May 14, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4311 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Mean Diffusional Kurtosis in Patients with Glioma: Initial Results with a Fast Imaging Method in a Clinical Setting A. Tietze,
Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT
 Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT ? Spectrum of Neurocognitive disorders The adult literature on HIV related CNS damage supports a spectrum
Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT ? Spectrum of Neurocognitive disorders The adult literature on HIV related CNS damage supports a spectrum
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is considered an inflammatory autoimmune
 REVIEW ARTICLE Multiple Sclerosis: The Role of MR Imaging Y. Ge SUMMARY: MR offers by far the most sensitive technique for detecting multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions and has proved to be an important paraclinical
REVIEW ARTICLE Multiple Sclerosis: The Role of MR Imaging Y. Ge SUMMARY: MR offers by far the most sensitive technique for detecting multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions and has proved to be an important paraclinical
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note
 High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
Clinical Correlations of Brain Lesion Distribution in Multiple Sclerosis
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 29:768 773 (2009) Original Research Clinical Correlations of Brain Lesion Distribution in Multiple Sclerosis M.M. Vellinga, MD, 1 * J.J.G. Geurts, PhD, 2,3 E. Rostrup,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 29:768 773 (2009) Original Research Clinical Correlations of Brain Lesion Distribution in Multiple Sclerosis M.M. Vellinga, MD, 1 * J.J.G. Geurts, PhD, 2,3 E. Rostrup,
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling chronic demyelinating disease
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
A nimal experiments and post-mortem examinations have
 PAPER A prospective study of secondary degeneration following subcortical infarction using diffusion tensor imaging Zhijian Liang, Jinsheng Zeng, Sirun Liu, Xueying Ling, Anding Xu, Jian Yu, Li Ling...
PAPER A prospective study of secondary degeneration following subcortical infarction using diffusion tensor imaging Zhijian Liang, Jinsheng Zeng, Sirun Liu, Xueying Ling, Anding Xu, Jian Yu, Li Ling...
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 19:6 18 (2004) Invited Review Clinical Applications of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Qian Dong, MD, Robert C. Welsh, PhD,* Thomas L. Chenevert, PhD, Ruth C. Carlos, MD,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 19:6 18 (2004) Invited Review Clinical Applications of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Qian Dong, MD, Robert C. Welsh, PhD,* Thomas L. Chenevert, PhD, Ruth C. Carlos, MD,
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Keywords: Multiple Sclerosis; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Diffuse. Introduction. Abstract Objective
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Diffuse Weighted Imaging and Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery Sequences of MRI in Brain Multiple Sclerosis Plaques Detection How to Cite This Article: Nafisi-Moghadam
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Diffuse Weighted Imaging and Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery Sequences of MRI in Brain Multiple Sclerosis Plaques Detection How to Cite This Article: Nafisi-Moghadam
Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
 Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1394 Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of the brain Tractography analysis with application in healthy individuals
Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1394 Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of the brain Tractography analysis with application in healthy individuals
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
Imaging of Demyelinating Processes
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXI, nº 82, pág. 81-88, Abr.-Jun., 2009 Imaging of Demyelinating Processes Alice Boyd Smith, MD Chief, Neuroradiology - Department of Radiologic Pathology, Armed Forces
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXI, nº 82, pág. 81-88, Abr.-Jun., 2009 Imaging of Demyelinating Processes Alice Boyd Smith, MD Chief, Neuroradiology - Department of Radiologic Pathology, Armed Forces
Cortical hypoperfusion in Parkinson's disease assessed with arterial spin labeling MRI
 Cortical hypoperfusion in Parkinson's disease assessed with arterial spin labeling MRI Poster No.: C-0609 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Aoki, K. Kamagata, Y. Motoi, K. Kamiya,
Cortical hypoperfusion in Parkinson's disease assessed with arterial spin labeling MRI Poster No.: C-0609 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Aoki, K. Kamagata, Y. Motoi, K. Kamiya,
Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Magnetization Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Clinical Changes in Patients With Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Magnetization Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Clinical Changes in Patients With Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Celia Oreja-Guevara, MD; Arnaud Charil, MSc; Domenico
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Magnetization Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Clinical Changes in Patients With Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Celia Oreja-Guevara, MD; Arnaud Charil, MSc; Domenico
Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
Introduction to Brain Imaging
 Introduction to Brain Imaging Human Brain Imaging NEUR 570 & BIC lecture series September 9, 2013 Petra Schweinhardt, MD PhD Montreal Neurological Institute McGill University Montreal, Canada Various techniques
Introduction to Brain Imaging Human Brain Imaging NEUR 570 & BIC lecture series September 9, 2013 Petra Schweinhardt, MD PhD Montreal Neurological Institute McGill University Montreal, Canada Various techniques
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS
 Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Extremely preterm infants are at high risk of brain injury
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.L.Y. Cheong D.K. Thompson H.X. Wang R.W. Hunt P.J. Anderson T.E. Inder L.W. Doyle Abnormal White Matter Signal on MR Imaging Is Related to Abnormal Tissue Microstructure BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.L.Y. Cheong D.K. Thompson H.X. Wang R.W. Hunt P.J. Anderson T.E. Inder L.W. Doyle Abnormal White Matter Signal on MR Imaging Is Related to Abnormal Tissue Microstructure BACKGROUND
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is a major consequence
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
Diffusion Tensor Imaging 12/06/2013
 12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
