Psychologists who specialize in considering the ways in which the biological structures and functions of the body affect behavior are known as.
|
|
|
- Joseph Chester Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test Bank Understanding Psychology 12th Edition Feldman Completed download: Chapter 03 Neuroscience and Behavior Multiple Choice Questions 1. Psychologists who specialize in considering the ways in which the biological structures and functions of the body affect behavior are known as. genetic psychologists biopsychologists evolutionary psychologists clinical neuropsychologists APA Outcome: 1.1 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-1 Topic: Neurons 3-1
2 2. Alison has developed an interest in the ways in which the biological structures and functions of the body affect behavior. She will most likely become a(n): genetic psychologist. behavioral neuroscientist. evolutionary psychologist. clinical neuropsychologist. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-1 Topic: Neurons 3-2
3 3. The basic elements of the nervous system are called: axons. glial cells. neurons. neurotransmitters. APA Outcome: 1.1 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurons 3-3
4 4. As many as neurons throughout the body are involved in the control of behavior. 1 billion 1 trillion 5 million 50 million Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurons 3-4
5 5. Neurons are physically held in place by. axons glial cells dendrites myelin cells Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurons 3-5
6 6. Which of the following is NOT one of the functions of glial cells? They nourish nerve cells. They communicate messages within the nervous system. They help repair damage that might occur to neurons. They provide nourishment to neurons. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: How Neurons Fire 3-6
7 7. A cluster of fibers at one end of a neuron that receives messages from other neurons is called: axon. terminal button. glial fiber. dendrite. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Nervous System 3-7
8 8. Compare your forearm, palm, wrist, and fingers to a neuron. In such an analogy, the dendrites would be your: forearm. fingers. wrist. palm. Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Nervous System 3-8
9 9. An axon is a: neuron's cell body. cluster of fibers at one end of a neuron. support cell in the nervous system. long, slim, tube-like structure extending from a neuron. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Nervous System 3-9
10 10. Which of the following structures is especially important for carrying messages received by the dendrites to other neurons? Neurotransmitter Synapse Axon Glial cell Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Nervous System 3-10
11 11. Terminal buttons are found at the end of: neurotransmitters. dendrites. axons. glial cells. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Nervous System 3-11
12 12. Which of the following sequences correctly arranges nervous system structures from the most general to the most specific? Neuron axon terminal button Neuron terminal button axon Axon terminal button neuron Axon neuron terminal button Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Nervous System 3-12
13 13. Dendrite is to axon what is to. receiving; sending sending; receiving reuptake; action potential action potential; reuptake Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: How Neurons Fire 3-13
14 14. Compare your forearm, palm, knuckles, and fingers to a neuron. In such an analogy, the axon would be your: forearm. fingers. palm. knuckles. Bloom's: Apply Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: How Neurons Fire 3-14
15 15. Which of the following sequences accurately reflects the route followed by nerve impulses when one neuron communicates with another? Dendrite axon cell body Dendrite cell body axon Cell body axon dendrite Axon dendrite cell body Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-15
16 16. Electrical wires are generally protected by a tube of plastic. A similar insulating function is performed in the nervous system by the: myelin sheath. glial cells. terminal buttons. synapse. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-16
17 17. is a protective coat of fat and protein that wraps around the axon. Myelin sheath Glial cell Dendrite Synapse Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-17
18 18. You cannot fire a gun softly, or flush a toilet halfway. Like an action potential, gun fire and a toilet's flush follow the law. incremental transformation graded action all-or-none intensity of stimulus Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: How Neurons Fire 3-18
19 19. The rule that neurons are either on or off is known as the law. intensity of stimulus graded action all-or-none incremental transformational Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: How Neurons Fire 3-19
20 20. The state in which there is a negative electrical charge of about -70 millivolts within a neuron is known as the state. triggering terminal optimum resting Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Speed of Transmission 3-20
21 21. Regarding action potentials, which of the following statements is TRUE? As the impulse travels along the axon, the movement of ions causes a change in charge from positive to neutral in successive sections of the axon. The action potential moves from one end of the axon to the other like a flame moving along a fuse. After the impulse has passed through a particular section of the axon, negative ions are pumped out of that section, and its charge returns to positive while the action potential continues to move along the axon. Just after an action potential has passed through a section of the axon, a neuron can fire again immediately if it receives appropriate stimulation. Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Speed of Transmission 3-21
22 22. As an action potential occurs, the neuron's electrical charge: changes from negative to neutral. changes from positive to neutral. changes from negative to positive. changes from positive to negative. Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Speed of Transmission 3-22
23 23. are specialized neurons that fire not only when a person enacts a particular behavior, but also when a person simply observes another individual carrying out the same behavior. Pharyngeal motor neuron Mirror neurons Ventral cord motor neuron Amphid neurons Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Mirror Neurons 3-23
24 24. Regarding mirror neurons, which of the following statements is ACCURATE? Mirror neurons are involved in face recognition and language acquisition, but not in empathy. Mirror neurons are involved in empathy and face recognition, but not in language acquisition. Mirror neurons are involved in empathy, language acquisition, and face recognition. Mirror neurons are involved in empathy and language acquisition, but not in face recognition. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Mirror Neurons 3-24
25 25. A synapse is a: chemical. signal. joint. gap. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Synapse 3-25
26 26. is the space between two neurons where the axon of a sending neuron communicates with the dendrites of a receiving neuron by using chemical messages. Synapse Terminal button Axon Cell body Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Synapse 3-26
27 27. Which of the following statements regarding inhibitory messages is TRUE? Inhibitory messages always increase the likelihood that a receiving neuron will fire. Inhibitory messages decrease the likelihood that a receiving neuron will fire. The dendrites of a neuron cannot receive both excitatory and inhibitory messages simultaneously. Inhibitory messages make it more likely that an action potential will travel down its axon. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-27
28 28. The reabsorption of neurotransmitters by a terminal button is termed as: recycling. reassertion. reuptake. reuse. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-28
29 29. Which neurotransmitter is described INCORRECTLY? Acetylcholine transmits messages related to skeletal muscles GABA an excitatory neurotransmitter inhibited by alcohol or tranquilizers Serotonin helps regulate sleep and mood Glutamate plays a role in memory Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-29
30 30. The neurotransmitter dopamine is involved in: the brain's effort to deal with pain. Alzheimer's disease. the regulation of sleep, eating, mood, and pain. movement, attention, and learning. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-30
31 31. Which neurotransmitter is CORRECTLY matched with a psychological function? Relief of pain glutamate Regulates mood acetylcholine Facilitates learning dopamine Contributes to memory serotonin Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-31
32 32. Which disorder is CORRECTLY paired with an associated neurotransmitter? Parkinson's disease: dopamine Depression: glutamate Schizophrenia: serotonin Alzheimer's disease: endorphins Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-32
33 33. Inhibitory is to excitatory what is to. glutamate; GABA glutamate; acetylcholine GABA; glutamate endorphins; GABA Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-33
34 34. Which expression below most closely approximates the number of neural connections in the brain? 10 quadrillion 1 million 1 billion 1 trillion Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Central Nervous System 3-34
35 35. The nervous system is divided into the and the nervous systems. primary; secondary somatic; autonomic sympathetic; parasympathetic central; peripheral Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Central Nervous System 3-35
36 36. The brain and the spinal cord constitute the nervous system. central peripheral extraneous parasympathetic APA Outcome: 1.1 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Central Nervous System 3-36
37 37. is an automatic, involuntary response to an incoming stimulus. Action potential Intuition Instinct Reflex Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Nervous System 3-37
38 38. The is the main means for transmitting messages between the brain and the body. cortex medulla axon spinal cord Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Difficult Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Nervous System 3-38
39 39. Which of the following is TRUE of the spinal cord's control of behavior? The spinal cord cannot control any behaviors without the help of the brain. The spinal cord is not involved in reflexes. The spinal cord can control some simple reflexes without the brain's help. The spinal cord can control relatively complex behavior without the brain's help. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Nervous System 3-39
40 40. The central nervous system is composed of. The peripheral nervous system comprises. the somatic and autonomic nervous systems; the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems the somatic and autonomic nervous systems; the brain and the spinal cord the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems; the somatic and autonomic nervous systems the brain and the spinal cord; the somatic and autonomic nervous systems Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Central Nervous System 3-40
41 41. Sensory is to motor what is to. efferent; afferent afferent; efferent afferent; interneuron interneuron; efferent Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-41
42 42. communicate information in the opposite direction, from the brain and nervous system to muscles and glands. Mirror neurons Amphid neurons Motor neurons Autoneurons Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-42
43 43. The two major divisions of the peripheral nervous system are the and divisions. somatic; autonomic sympathetic; parasympathetic afferent; efferent sensory; motor Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-43
44 44. is the part of the peripheral nervous system that specializes in the control of voluntary movements and the communication of information to and from the sense organs. Somatic division Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Autonomic division Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-44
45 45. Somatic is to autonomic what is to. involuntary; voluntary voluntary; involuntary excitation; rest rest; excitation Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-45
46 46. The part of the autonomic division of the nervous system that acts to prepare the body for action in stressful situations, engaging all the organism's resources to respond to a threat is known as the. somatic division sympathetic division parasympathetic division apathetic division Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-46
47 47. The "fight-or-flight" response is associated with the division. somatic sympathetic parasympathetic apathetic Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-47
48 48. The part of the autonomic division of the nervous system that acts to calm the body after an emergency has ended is known as the division. somatic sympathetic parasympathetic apathetic Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-48
49 49. The division also directs the body to store energy for use in emergencies. somatic sympathetic parasympathetic apathetic Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-49
50 50. Which of the following situations is most likely to involve the action of the parasympathetic nervous system? Brooke's finger accidentally grazes the hot iron; she immediately jerks her hand away. After mistaking her roommate for a thief, Callum relaxes after having a glass of water. Walking toward her car in a deserted parking lot one night, Danica is surprised by a strange man appearing from nowhere. Peyton is preparing to go to bed and is alarmed to see a stranger at her window. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Peripheral Nervous System 3-50
51 51. With respect to its potential basis in nervous system activity, "voodoo death" has been attributed to: an overactive sympathetic nervous system. an overactive parasympathetic nervous system. the cessation of sympathetic nervous system responses. an understimulated central nervous system. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Autonomic Division 3-51
52 52. Izzy sees a leopard in her backyard. Her pupils are dilated and her heart is pounding; her breathing is shallow and rapid. Her nervous system is active. parasympathetic sympathetic apathetic somatic Bloom's: Apply Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Autonomic Division 3-52
53 53. Which of the following terms best describes the organization of the nervous system today? Linear Recursive Hierarchical Random Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Evolutionary Foundations of Nervous System 3-53
54 54. The branch of psychology that seeks to identify behavior patterns that are a result of our genetic inheritance from our ancestors is known as. social psychology health psychology clinical psychology evolutionary psychology Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Evolutionary Foundations of Nervous System 3-54
55 55. Evolutionary psychologists have spawned a new and increasingly influential field known as: social psychology. health psychology. molecular genetics. behavioral genetics. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Evolutionary Foundations of Nervous System 3-55
56 56. The study of the effects of heredity on how people conduct themselves is known as. behavioral genetics classical genetics development genetics molecular genetics Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Evolutionary Foundations of Nervous System 3-56
57 57. Dr. Schilling is investigating the potential genetic basis of antisocial personality disorder by examining the relative prevalence of the disorder among either identical or fraternal twins, raised either together or in different families. Dr. Schilling is best described as a. behavioral geneticist classical geneticist development geneticist molecular geneticist APA Outcome: 4.2 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Discuss the functions of the nervous system's main divisions. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Evolutionary Foundations of Nervous System 3-57
58 58. Which of the following statements best expresses the relationship between the nervous system and the endocrine system? They operate entirely independently. The endocrine system is part of the central nervous system. The endocrine system influences and is influenced by the central nervous system. The central nervous system is one part of the endocrine system. Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-58
59 59. A key component of the endocrine system is the tiny gland, which is found near and regulated by the in the brain. adrenal; hippocampus pituitary; hippocampus adrenal; hypothalamus pituitary; hypothalamus Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-59
60 60. The gland is a major component of the endocrine system which secretes hormones that control growth and other parts of the endocrine system. esophageal apocrine parotid pituitary Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-60
61 61. The gland has sometimes been called the "master gland" because it controls the functioning of the rest of the endocrine system. pituitary esophageal apocrine parotid Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-61
62 62. The hormone oxytocin has been implicated in each of the following behaviors EXCEPT the: urge to nurse newborn infants. desire to seek or respond to potential sexual partners. development of trust in others. tendency to produce violent, dangerous behavior. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-62
63 63. Which of the following glands or structures is CORRECTLY matched with the hormone it produces? Pineal gland; insulin Pancreas; serotonin Medulla; melatonin Pituitary gland; oxytocin Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-63
64 64. Which of the following hormones is CORRECTLY matched with its function? Aldosterone regulates daily rhythms Erythropoietin regulates the sodium and potassium balance in the blood Adipokines regulate the production of red blood cells Steroids bulk up one's muscles Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-64
65 65. Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding hormone replacement therapy as a treatment for menopausal symptoms? It is used less frequently now than in the past. It is the only treatment that does not have any side effects. Its benefits outweigh its risks. It has become increasingly popular. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-65
66 66. Your friend is considering using steroids to increase muscle mass. You would warn him that steroid abuse can lead to: violent, dangerous behavior. obesity. autism. Type II diabetes. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 3-66
67 67. Which of the following is NOT a brain-scanning technique? Electroencephalogram (EEG) Electromyogram (EMG) Positron emission tomography (PET) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) APA Outcome: 2.2 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Endocrine System 3-67
68 68. Which brain-scanning technique below is CORRECTLY matched with its description? EEG records the brain's electrical activity with electrodes PET causes a momentary interruption of the brain's electrical activity fmri traces biochemical activity in the brain TMS produces a graph of electrical wave patterns APA Outcome: 2.2 Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 3-68
69 69. Which brain-scanning technique below is INCORRECTLY matched with its diagnostic use? EEG facilitates the diagnosis of epilepsy and learning disorders PET may help identify brain tumors fmri improves diagnosis of strokes and multiple sclerosis TMS facilitates the diagnosis of nervous system disorders such as Alzheimer's disease Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 3-69
70 70. Brent is taking part in an experiment in the cognitive neuroscience lab on campus. Silently, he reads rapid sequences of words flashed on a computer screen. Simultaneously, the electrical activity of his brain is recorded through skull electrodes. The brain-scanning technique used in this study is: fmri. PET. EEG. TMS. APA Outcome: 2.2 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 3-70
71 71. The newest brain-scanning technique which is popularly used is: PET. EEG. TMS. fmri. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 3-71
72 72. Marisol is trying a new treatment for severe depression. Brief magnetic pulses are sent through her brain. Marisol is undergoing: optogenetic therapy. transcranial magnetic stimulation. positron emission tomography. functional magnetic resonance imaging. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 3-72
73 73. Soon, it may be possible to view the activity of individual neural circuits, due to the emerging field of: optogenetics. synaptic reflectance. neurogenetics. transcranial magnetic stimulation. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 3-73
74 74. Which of the following structures is NOT part of the brain's central core? Hippocampus Cerebellum Pons Reticular formation Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Structure 3-74
75 75. The hindbrain includes each of the following structures EXCEPT the: medulla. thalamus. pons. cerebellum. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Structure 3-75
76 76. The part of the brain closest to the spinal cord is the ; it is important for functions such as. cerebellum; maintaining body temperature cerebellum; heart rate and respiration medulla; maintaining body temperature medulla; heart rate and respiration Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Structure 3-76
77 77. The pons serves to: regulate arousal. relay sensory information to the brain's association areas. integrate movement between the left and right halves of the body. consolidate memories. Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Structure 3-77
78 78. The part of the brain that controls bodily balance is the. hypothalamus thalamus reticular formation cerebellum Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-78
79 79. Yves has been drinking. He has difficulty walking a straight line when asked to do so by a police officer. Apparently, Yves' is functioning poorly. thalamus cerebellum corpus callosum reticular formation APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-79
80 80. The part of the brain extending from the medulla through the pons and made up of groups of nerve cells that can immediately activate other parts of the brain to produce general bodily arousal is known as the. reticular formation thalamus cerebellum limbic system Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-80
81 81. The thalamus may be likened to a(n): amplifier. receiver. filter. relay station. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-81
82 82. The is the part of the brain that is located in the middle of the central core and acts primarily to relay information about the senses. thalamus cerebellum hypothalamus amygdala Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-82
83 83. The is a tiny part of the brain that maintains homeostasis and produces and regulates vital behavior such as eating, drinking, and sexual behavior. medulla cerebellum amygdala hypothalamus Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-83
84 84. Pizza! Beer! Sex! Our motivation or drive for such things is based on the activity of the brain region known as the: hypothalamus. thalamus. hippocampus. amygdala. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-84
85 85. The maintains a steady internal environment for the body. thalamus amygdala hypothalamus hippocampus Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-85
86 86. The in the brain contributes to the body's maintenance of a steady internal physiological state called. thalamus; homeostasis hypothalamus; homeostasis hippocampus; equilibrium thalamus; equilibrium Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-86
87 87. The limbic system contains which of the following structures? Amygdala Pons Thalamus Corpus callosum Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 3-87
88 88. The structures of the jointly control a variety of basic functions relating to emotions and self-preservation such as eating, aggression, and reproduction. central core of the brain endocrine system limbic system cerebral cortex Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the limbic system's key structures and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Limbic System 3-88
89 89. Darnell underwent surgery to control his severe epilepsy. However, Darnell cannot form new memories of his experiences now, although he does remember past events. Most likely, the surgery destroyed a portion of the in Darnell's brain. amygdala striatum medulla hippocampus APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Identify the limbic system's key structures and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Limbic System 3-89
90 90. The is referred to as the "new brain." hindbrain limbic system cerebral cortex central core Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-90
91 91. Which of the following sequences correctly identifies the orders of the lobes of the cortex, from anterior to posterior? Frontal temporal and parietal posterior Occipital temporal and parietal frontal Frontal occipital temporal and parietal Frontal temporal and parietal occipital Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-91
92 92. In which lobe is the motor area located? Occipital Frontal Parietal Temporal Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-92
93 93. The area is part of the cortex that is largely responsible for the body's voluntary movement. attribution sensory motor association Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-93
94 94. In a neurophysiological investigation, a monkey makes an involuntary gesture when a portion of its brain is electrically stimulated. The area of the brain that was most likely stimulated is the: parietal lobe. frontal lobe. temporal lobe. occipital lobe. APA Outcome: 1.1 Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-94
95 95. The area is the site in the brain of the tissue that corresponds to each of the senses, with the degree of sensitivity related to the amount of tissue. attribution sensory motor association Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-95
96 96. The somatosensory area is to the auditory area what the lobe is to the lobe. temporal; parietal parietal; occipital occipital; parietal parietal; temporal Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-96
97 97. The visual area in the cortex is located in the. frontal lobe occipital lobe temporal lobe parietal lobe APA Outcome: 1.1 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-97
98 98. The brain injury suffered by 19th-century railroad worker Phineas Gage allowed psychologists to learn about the functions of the brain's: association areas. central core. limbic system. sensory areas. APA Outcome: 1.1 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-98
99 99. The areas are considered to be the site of higher mental processes such as thinking, language, memory, and speech. sensory attribution motor association APA Outcome: 1.1 Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-99
100 100. Which of the following is NOT an executive function? Recalling information Setting goals Controlling impulses Making judgments APA Outcome: 1.1 Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-100
101 101. Violet's speech is slow and labored; however, she can understand others' speech. Violet has: Broca's aphasia. Wernicke's aphasia. dyslexia. dyscalculia. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-101
102 102. Warren suffers from Wernicke's aphasia. Which of the following difficulties will he experience? Warren will experience an inability to recognize faces. Warren will have difficulty recognizing objects visually. Warren will have trouble producing fluent speech. Warren will experience difficulty understanding language. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 3-102
103 103. The process by which the brain reorganizes itself throughout development is termed: neuroformation. neuroplasticity. neuroadaptation. neuromutability. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Define plasticity and describe the brain's capacity for recovery and repair. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Neuroplasticity 3-103
104 104. is the creation of new neurons. Neurogenesis Neuroadaptation Neuromutability Neuropathy Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Define plasticity and describe the brain's capacity for recovery and repair. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Neuroplasticity 3-104
105 105. Neurogenesis is especially evident in brain areas related to learning and memory. Based on this statement, you might expect neurogenesis to be particularly prevalent in the brain's: thalamus. cerebellum. hippocampus. hypothalamus. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Specialization of Hemispheres 3-105
106 106. Which of the following is TRUE about the brain? New research has confirmed that no new brain cells are created after childhood. The interconnections between neurons become less complex throughout life. Specific experience can modify the way in which information is processed. The brain does not have the ability to shift functions to different locations in cases of surgery. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Specialization of Hemispheres 3-106
107 107. The use of stem cells in research and treatment remains controversial because stem cells come from: nonhuman species. aborted fetuses. genetic engineering in the laboratory. paid adult donors. Bloom's: Understand Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Biofeedback 3-107
108 108. Which of the following statements is most accurate in the context of lateralization of language? It is most likely left-lateralized. It is most likely right-lateralized. The control of language is shared equally between the hemispheres. The lateralization of language varies dramatically from one person to another. APA Outcome: 1.1 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-3 Topic: Split Brain 3-108
109 109. Trevor is scratching his head, trying desperately to solve a verbal analogy as part of a standardized entrance examination; Sienna, meanwhile, is giving an oral presentation in a political science class. Of the brain's hemispheres, Trevor's hemisphere is most active; Sienna's hemisphere is most active. right; right left; left right; left left; right Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-3 Topic: Split Brain 3-109
110 110. Kate has suffered damage to the right side of her brain. Which of the following processes is LEAST likely to be affected? Achieving feng shui in her living room by rearranging the couch and the TV Balancing her checkbook Reading that look on her boyfriend's face Thinking that a new song on the radio is really catchy APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-3 Topic: Split Brain 3-110
111 111. The hemispheres of the brain are connected by a bundle of fibers called the: corpus callosum. corpus cerebellum. central sulcus. cerebral cortex. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-3 Topic: Split Brain 3-111
112 112. Ramona is a woman. Stefan is a man. Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding potential differences in the corpus callosum between these two individuals? Stefan's corpus callosum is probably the same size as Ramona's. Ramona's corpus callosum is larger than Stefan's. Ramona's corpus callosum is slightly smaller than Stefan's. Stefan's corpus callosum is much larger than Ramona's. Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-3 Topic: Split Brain 3-112
113 113. Which of the following generalizations is probably most accurate regarding potential gender differences in the lateralization of language? No gender differences in the lateralization of language have been found. Language is more strongly left-lateralized among females than among males. Language is more strongly left-lateralized among males than among females. The lateralization of language is variable from one person to another. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-3 Topic: Split Brain 3-113
114 114. People whose corpus callosum has been surgically cut to stop seizures are called. deep-brain patients dual brain patients split-brain patients bicameral patients Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-4 Topic: Split Brain 3-114
115 115. Mrs. Simon has learned to lessen the pain associated with her migraine headaches by voluntarily relaxing specific muscles and reducing her blood pressure. This example illustrates: deep-brain stimulation. biofeedback. split-brain control. transcranial stimulation. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Explain what split-brain research reveals about the functions of the brain's two hemispheres. Learning Outcome: 9-4 Topic: Split Brain Worksheet Questions 116. The myelin sheath is an insulating coat of fat and protein wrapped around an axon. Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurons 3-115
116 117. According to the all-or-none law, neurons are either on or off. Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurons 118. At the cellular level, our ability to empathize with others may reflect the activity of mirror neurons. Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Mirror Neurons 119. Inhibitory message is a chemical message that prevents or decreases the likelihood that a receiving neuron will fire. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Describe how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 120. After a long run, Aaron sometimes experiences a feeling of euphoria, a "runners' high," reflecting the activity of neurotransmitters called endorphins. Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Describe how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells. Learning Outcome: 7-3 Topic: Neurotransmitters 3-116
117 121. Afferent neurons transmit information from the perimeter of the body to the central nervous system. Difficulty: Difficult Learning Objective: Describe how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Neurotransmitters 122. The somatic nervous system regulates voluntary movement; in contrast, the autonomic nervous system underlies involuntary movement. Learning Objective: Describe how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Nervous System 123. Arif's heart rate and respiration are slowing, and his dilated pupils are contracting. His parasympathetic nervous system has become active. Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Nervous System 124. Evolutionary psychology is the branch of psychology that seeks to identify how behavior is influenced and produced by our genetic inheritance from our ancestors
118 Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the key neurotransmitters and their functions and describe their known or suspected roles in behavior as well as in illnesses. Learning Outcome: 8-1 Topic: Nervous System 125. The tiny pituitary gland is known as the "master gland." Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Describe the function of the endocrine system. Learning Outcome: 8-2 Topic: Endocrine System 126. A technique called EEG (electroencephalogram) records the brain's electrical activity through electrodes. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 127. Wilma has been experiencing memory difficulties, and her doctor is concerned that Wilma may have a brain tumor. He recommends a(n) PET (positron emission tomography) to confirm his diagnosis. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Name the techniques used to map and study the brain. Learning Outcome: 9-1 Topic: Brain Imaging 128. Extending from the medulla, through the midbrain, into the forebrain is the reticular formation, which serves to regulate general bodily arousal
119 Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 129. Information travels from our sensory receptors to the thalamus in the brain, which relays it to higher association areas. Learning Objective: Identify the brain's levels, structures, and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Brain Function 130. The amygdala and hippocampus are found within the brain's limbic system. Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Identify the limbic system's key structures and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Limbic System 131. Epileptics have sometimes had portions of their limbic system removed. Subsequent memory problems may reflect damage to the hippocampus. Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the limbic system's key structures and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Limbic System 132. The cortex has four major sections called lobes
120 Learning Objective: Identify the limbic system's key structures and functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Limbic System 133. The somatosensory area in the parietal lobe encompasses specific locations associated with the ability to perceive touch and pressure in a particular area of the body. Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 134. New neurons are created even during adulthood, in a process called neurogenesis. Learning Objective: Identify the major areas of the cerebral cortex and their functions. Learning Outcome: 9-2 Topic: Cerebral Cortex 135. Vance has learned to voluntarily control the activation of his autonomic nervous system as part of the treatment for an anxiety disorder. This is an example of biofeedback. APA Outcome: 1.3 Bloom's: Apply Learning Objective: Define plasticity and describe the brain's capacity for recovery and repair. Learning Outcome: 9-4 Topic: Biofeedback Essay Questions 3-120
121 136. Draw a typical neuron and label its major parts accurately. Briefly describe the functions of the parts labeled on your diagram. The drawing should contain: (a) dendrites, which should appear as clusters of branchlike extensions from the cell body; (b) the cell body, which should appear as a roundish structure in the center of the diagram; (c) the axon, which should appear as a long tube extending from the cell body; and (d) myelin, which should appear bracketing portions of the axon. The diagram should also include a terminal button, a bulblike ending to the axon. The function of the following structures should be described. Dendrites receive information from other neurons. Axon sends message to another neuron. Myelin insulates one axon from another and speeds neural transmission. APA Outcome: 1.1 Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Neurons 137. Write a note on mirror neurons. Mirror neurons are neurons that fire not only when a person enacts a particular behavior but also when a person simply observes another individual carrying out the same behavior. Mirror neurons may help explain how (and why) humans have the capacity to understand others' intentions. Specifically, mirror neurons may fire when we view someone doing something, helping us to predict what their goals are and what they may do next. The discovery of mirror neurons suggests that the capacity of even young children to imitate others may be an inborn behavior. Furthermore, mirror neurons may be at the root of empathy those feelings of concern, compassion, and sympathy for others and even the development of language in humans. APA Outcome: 1.1 Bloom's: Understand Learning Objective: Identify the parts of a neuron, and explain how they transmit information. Learning Outcome: 7-2 Topic: Mirror Neurons 3-121
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy
 Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain
 General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test
 AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Copyright 2017 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 1
 1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Biological Psychology
 Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
The Nervous System. The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.
 The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
Structure of the Cortex
 Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems. Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers
 Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain
 Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior
 Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Biological Basis of Behavior. Chapter 2
 Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Neuroscience. Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior.
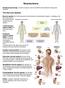 Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
2) All of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviour can be traced to the activity of the a. neurons. b. ganglia. c. genes. d. nerve fibres.
 Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Psychology study guide chapter 2
 Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
18. The visual cortex is located in the: A) occipital lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) frontal lobe. D) parietal lobe.
 Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Week 2 Psychology. The Brain and Behavior
 Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Vocabulary. Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold
 Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Biology and Behavior CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 2 Biology and Behavior CHAPTER OUTLINE Biological psychology studies the cells, genes, and organs of the body, and the physical and chemical changes involved in behavior and mental processes. I.
CHAPTER 2 Biology and Behavior CHAPTER OUTLINE Biological psychology studies the cells, genes, and organs of the body, and the physical and chemical changes involved in behavior and mental processes. I.
I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission
 I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Objectives: Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. Describe
I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Objectives: Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. Describe
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1
 Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems. Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers
 Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON
 UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Why does the writer above love running so much? One of the reasons. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure. Reader s Guide. Exploring Psychology
 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
Biological Psychology. Phrenology (Franz Gall) branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
 Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
