Customised Charts. Size 20"x30" Laminated & Mounted Framed on Board. College Logo & Name
|
|
|
- Madison Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Customised Charts Size 20"x30" Laminated & Mounted Framed on Board Rs. 1350/- Each 4 20 College Logo & Name 30
2 MICROBIOLOGY SLIDES, CHARTS & MODELS List No. 8 w.e.f. 1st Dec SLIDES 1 BACTERIA TUBERCULOSIS 2 BACTERIA SYPHILIS 3 BACTERIA TYPHOID 4 BACTERIA LEPTOSPIRA 5 BACTERIA TETENUS 6 BACTERIA DIPTHERIA 7 BACTERIA MYOBACERIUM TUBERCULOSIS IN TISSUE 8 BACTERIA CHOLERA 9 BACTERIA NOCARDIA 10 BACTERIA GONOCOCCI 11 BACTERIA PNEUMOCOCCI 12 BACTERIA HELICOBACTER PYLORI 13 BACTERIA BACTERIAL CELL STRUCTURE 14 ENTOMO MOSQUITO AEDES 15 FUNGI ASPERGILLUS 16 FUNGI CANDIDA 17 HELMINTH WUCHERIA BANCROFTI (FILARIA) 18 HELMINTH ASCARIS LUMBRICOIDES 19 HELMINTH STRONGYLOIDESSTERCORALIS 20 MIXED BACTERIA 21 COCCI 22 BACILLI 23 ESCEROCJOA COLI 24 BACILLUS SUBTILLIS 25 BACILLUS MEGATERIUM 26 MYOBACERIUM TUBERCULOSIS IN TISSUE 27 RHIZOBIUM IN ROOT NODULE 28 VIBRIO 29 SPIRLLUM 30 STAPHYLOCOCCUS EPIDERMIS 31 STREPTOCOCCUS LACTIS 32 GRAM-POSITIVE 33 GRAM NEGATIVE 34 STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS 35 STREPTOCOCCI POSITIVE 36 STREPTOCOCCI NEGATIVE MICROSCOPIC IMPORTED U.S.A (SET of 50) IN AVAILABLE IN SETS ONLY 37 STREPTOCCUS PNEUMONIAE 38 STREPTOCCUS GRAMPOSITIVE 39 STREPTOCCUS NONMOTILE 40 STREPTOCCUS ENCAPSULATED LANCET-SHAPED COCCI 41 STREPTOCCUS FECALIS 42 CORYNBACTERIUM DIPHTHERIAE 43 CORYNBACTERIUM DIPHTHERIAE GRAM STAIN 44 GRAM STAIN BACILLUS ANTHRACIS 45 LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES GRAM STAIN 46 NEISSERIA GONORHOEAE 47 NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS 48 E.COLI GRAM STAIN 49 SALMONELLA TYPHI 50 BACTERIA CONJUGATION IMP 20 See Pg. No. 5
3 MICROBIOLOGY CHARTS Charts Laminated and attached with durable strips Charts Laminated Framed on NU-Board Introduction to Microbiology MB 1 MB 2 MB 3 Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Classification of medically important bacterial families. Classification of medically important virus families. Normal Flora MB 4 Normal flora in Human Body (Skin, Eye, Mouth and nose, G. E. Tract, vagina) Pathogenicity of Microorganisms MB 5 MB 6 Bacterial Pathogens Id50 v /s LD50, Adhesion to host cell membranes, Action of exotoxins, Koch s postulates. Types of viral pathogenesis, Dissemination of virus to secondary sites in the body, Mother-to-infant. Diagnostic Microbiology MB 7 MB 8 MB 9 MB 10 Laboratory techniques in diagnosis of microbial diseases. Effect of sensitivity and specificity of a test on the presence of false-positives and false-negatives. Steps in Gram stain method. Tests commonly used in identifying bacteria. Immunologic detection of microorganisms. Detection of Microbial DNA or RNA Vaccines And Antibiotics MB 11 MB 12 MB 13 MB 14 MB 15 Bacterial Vaccines (DTaP, Childhood immunization) Formulation of Some of the vaccines. VIRAL VACCINES Candidates for hepatitis immunization. HBsAg = hepatitis B surface antigen. DNA VACCINES produce antigen needed to generate immunity. MHC = Major histocompatibility complex. Summary of therapeutic applications of selected antiviral agents. Bacterial Structure, Growth And Metabolism MB 16 MB 17 MB 18 Bacterial cell & Bacterial cell walls. Comparison of gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial cell. Synthesis of a bacterial cell wall. Bacterial Genetics MB 19 Bacterial growth. MB 20 Bacterial genome & Bacterial replication MB 21 Visual detection of bacteriophage by the plaque method. MB 22 Gene Transfer - A. Conjugation, B. Transduction, C. Transformation. MB 23 Gene Regulation - A. Negative control (repression) B. Positive control (catabolite activation) Staphylococci MB 24 MB 25 Staphylococci - Staphylococcus Aureus, Infections & Causes of Diseases Staphylococcus species (Summary of stapholcoccal disease.) MB 25 Staphylococcus species (Stapholococcal disease.) 2
4 Dbios MICROBIOLOGY CHARTS Charts Laminated and attached with durable strips Charts Laminated Framed on NU-Board Streptococci MB 26 MB 27 Gram-positive Rods MB 28 MB 29 MB 30 Neisseriae MB 31 Gastrointestinal Gram-negative Rods Gram-negative Rods Clostridia and other Anaerobic Rods Spirochetes Mycoplasma Chlamydiae Mycobacteria And Actinomycetes Rickettsiae Streptococcus pyogenes. Streptococcus species (Summary of streptococcal disease) Corynebacteria species (Summary of Corynebacterium diphtheriae disease). Bacillus species (Summary of anthrax disease) Listeria species & Life cycle Neisseria species (Summary of neisseria diseases). MB 32 Escherichia species & Salmonella species. MB 33 Campylobacter species (Summary of campylobacter disease). MB 34 Mechanism of shigella infection causing diarrhea & Shigella disease. MB 35 Vibrio & Yersinia species. MB 36 Helicobacter disease & Infection. MB 37 Infection by Haemophilus influenzae & species. MB 38 Bordetella pertussis & Disease MB 39 Legionella species (Summary of legionella disease). MB 40 Pseudomonas species & infection of ear. MB 41 Brucell species & Transmission MB 42 Francisella species (Summary of francisella species). MB 43 Epidemiology & pathogenesis of plague. MB 44 Bubo characteristic of infection due to yersinia pestis & species. MB 45 MB 46 MB 47 MB 48 MB 49 MB 50 MB 51 MB 52 MB 53 MB 54 MB 55 MB 56 MB 57 MB 58 Toxic & degradative enzymes produced by clostridium perfringens. ET=enterotoxin. Mechanism of botulinum toxin. AcCoA = acetyl CoA. & Tetanus toxin. Clostridium species (Summary of clostridial disease). Clinical stages of untreated syphilis. Clinical stages of untreated Lyme disease. Treponema & Borrelia species. Leptospira species (Summary of Leptospira species) Mycoplasma species (Summary of mycoplasma disease). Reproduction cycle of Chlamydia. Chlamydia species (Summary of Chlamydia disease). Mycobacteria classification, T.B. & Progressive of active T.B. Infection. Mantoux skin test for T.B. Mycobacterium species (Summary of mycobacterium disease). Classification, micrograph, Spotted fevers & Rickettsia disease. Fungi MB 59 MB 60 MB 61 MB 62 Protozoa Helminths Viruses Classification of pathogenic fungi. Cutaneous & subcutaneous mycoses. Systemic mycoses. Opportunistic mycoses:- Condidiasis, Cryptococcosis, Aspergillus, Mucormycosis, pneumocystis. MB 63 A. Life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica. B. Photomicrographs of tropozoite and cyst forms. MB 64 Intestinal protozoal infections. MB 65 Urogenital tract infections. MB 66 Blood and tissue protozoal infections. MB 67 Life cycle of Leishmania. MB 68 MB 69 MB 70 MB 71 MB 72 MB 73 MB 74 MB 75 MB 76 Cestodes infection. Trematodes Infection. Nematode infection. Intestinal nematode infections. General structure, Classification families. Replication cycle of VIRUSES. Replication of DNA VIRUS Mechanism of RNA virus genome replication. Effects of Viral infection on Host cell. Nonenveloped DNA Viruses MB 77 MB 78 MB 79 MB 80 Classification of Non enveloped DNA viruses. Relationship between steps in the development of a skin wart and the Life Cycle of papilloma virus. Adenovirus infection. Replication of B19 parvovirus. Enveloped DNA Viruses MB 81 MB 82 MB 83 MB 84 MB 85 MB 86 Classification of enveloped DNA viruses. Structure & Replication of herpes viruses. Primary & Recurrent herpes simplex infections. Time course of varicella (chickenpox) in children. In adults, the disease shows a longer time course and is more severe. Properties of common herpes virus infection. Time course of smallpox. Hepatitis B & Hepatitis D (delta) Viruses MB 87 Classification of major viral agents causing hepatitis. [Note: Hepatitis D is a defective virus and is classified in its own floating genus. Hepatitis A, C, and E are discussed.] MB 88 Replication & Hepatitis B Virus. MB 89 Typical course of hepatitis B virus infection. A. Acute infection. B. Chronic infection. MB 90 Structure of hepatitis D & consequences of HDV infection. 3
5 MICROBIOLOGY CHARTS MB 98 The HIV Replication cycle. MB 103 Schematic representation of pathogenesis of rabies infection. Charts Laminated and attached with durable strips Charts Laminated Framed on NU-Board Positive-strand RNA Viruses MB 91 Classification of positive-strand RNA viruses. MB 92 Polio virus infection & CNS invasion. MB 93 Pathogenesis of the common cold showing stages from infection to recovery. MB 94 Pathology or rubella virus infection. MB 95 Summary of hepatitis A, B, and C. Retroviruses and AIDS MB 96 MB 97 MB 98 MB 99 MB 100 MB 101 Negative-strand RNA Viruses Double-stranded RNA Viruses: The Reoviridae Unconventional Infectious Agents Diseases 4 Classification of retroviruses that cause disease in humans. Structure of HIV virus HIV replication cycle. Common modes of transmission of HIV. Pathogenesis of HIV. Typical time course of HIV infection. MB 102 Classification of negative-strand RNA viruses. MB 103 A. Schematic representation of pathogenesis of rabies infection. B. Wildlife rabies in the United States. MB 104 Influenza virus. A. Electron micrograph. B. Schematic drawing showing envelope proteins-called H and N spikesthat protrude from the surface. MB 105 Time course of influenza A virus infection & Measel virus. MB 106 Structure of Rotavirus. A. Electron micrograph. B. Schematic drawing. MB 107 MB 108 MB 109 MB 110 MB 111 MB 112 MB 113 MB 114 MB 115 MB 116 MB 117 MB 118 MB 119 Mechanism for multiplication of infections prior agents. Characteristics of sexually transmitted diseases (STD): Bacterial pathogens. Characteristics of sexually transmitted diseases: Fungi, Protozoa, and viruses. Disease summary of some major organisms causing bacterial food poisoning. Disease summary of urinary tract infections. Characteristics of organisms causing bacterial meningitis. Characteristics of hepatitis. [ ALT = alanine aminotransferase.] Characteristics of community-acquired pneumonia. Characteristics of atypical pneumonia. Examples of bacteria and viruses that cause diseases of the eye. Opportunistic infections of HIV - Bacteria & Fungi Opportunistic infections of Viruses Sinusitis (Bacterial) & otitis media
6 MICROBIOLOGY CHARTS Charts Laminated and attached with durable strips Charts Laminated Framed on NU-Board CH-1901 CH-1902 CH-1903 CH-1904 CH-1905 CH-1906 CH-1907 CH-1908 CH-1909 CH-1910 CH-1911 CH-1912 CH-1913 CH-1914 CH-1915 CH-1916 CH-1917 CH-1918 CH-1919 CH-1920 CH-1921 CH-1922 CH-1923 CH-1924 CH-1925 L.C. Enterobius vermicularis (thread or pin worm) L.C. Trichuris trichiura (whip worm) L.C. Ascaris lumbricoides (round worm) L.C. Ancylostoma duodenale (hook worm) L.C. Strongyloides stercoralis L.C. Trichinella spiralis L.C. Wuchereria bancrofti (filariasis) L.C. Brugia malayi L.C. Loa loa (eye worm) L.C. Onchocerca volvulus (blinding worm) L.C. Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm) L.C. Taenia solium (pork tape worm) L.C. Taenia saginata (beef tape worm) L.C. Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tape worm) L.C. Hymenolepis diminuta (rat tape worm) L.C. Diphyllobothrium latum (fish tape worm) L.C. of such tape worm - sparganosis L.C. Echinococcus granulosus (dog tape worm) L.C. Enchinococcus multilocularis L.C. Schistosoma species (blood fluke) L.C. Clonorchis sinensis, (oriental liver fluke) L.C. Opisthorchis felineus, (cat liver fluke) L.C. Fasciola hepatica (sheep liver fluke) L.C. Fasciolopsis buski L.C. Heterophyes heterophyes CH-1926 CH-1927 CH-1928 CH-1929 CH-1930 CH-1931 CH-1932 CH-1933 CH-1934 CH-1935 CH-1936 CH-1937 CH-1938 CH-1939 CH-1940 CH-1941 CH-1942 CH-1943 CH-1944 CH-1945 CH-1946 CH-1947 L.C. Metagonimius yokogawai L.C. Paragonimius westermani (lung fluke) L.C. Isospora belli (causing coccidiosis in humans) L.C. Cryptosporidium parvum L.C. Cyclospora cayetanensis L.C. Sarcocystis hominis L.C. Microsporidia L.C. Entamoeba histolytica (causing amoebiasis) L.C. Giardia intestinalis (g. lamblia) L.C. Chilomastix mesnili L.C. Balantidium coli L.C. Toxoplasma gondii L.C. Malaria parasite L.C. and morphology of Leishmania Morphological stages of the Trypanosomatidae Trypanosomiasis (african type : sleeping sickness) (1) L.C. in insect (2) L.C. in humans Trypanosomiasis (s. american : chagas' disease) (1) L.C. in insect (2) L.C. in humans Toxocara canis - (dog round worm) Toxocara cati (cat round worm) Gnathostoma spiningerum - morphology & life cycle Cutaneous larva migrans (creeping eruption) Trichomonas species MICROBIOLOGY IMP. CHARTS Size 18"x24"Approx Otherwise mentioned Laminated framed on Board IMP 13 IMP 14 IMP 15 IMP 16 IMP 17 IMP 18 IMP 20 IMP 22 IMP 23 IMP 24 IMP 25 IMP 26 IMP 27 IMP 28 IMP 29 UNDERSTANDING AIDS LIFE (39"X19") ASCOMYCETES BASIDIOMYCETES ZYGOMYCETES BACTERIA VIRUS (SET OF 3) WATER BORNE PATHOGENS MICROBIOLOGY CAREER POSTER MICROBIOLOGY FOOD POISONING MECHANISM OF GENE TRANSFER BACTERIA CULTURE RESOURCE (21"X34") HUMAN MICRO ANATOMY POSTER (27"X38") DRUGS POSTER SERIES (17"X22")(SET OF 8) DANGEROUS DRUGS (30"X48") MICROBIOLOGICAL CHART (25"X35") VIRUS - I 5
7 MICROBIOLOGY MODELS AM 123 L.C. Toxoplasma gondii AM 127 Phlebtomus argentipes (SANDFLY) various stages of development. AM 128 ANAEMIA KALA-AZAR AM 130 L.C. of Leishmania tropica (SAND FLY) AM 131 L.C. of Plasmodium vivax AM 133 L.C. of Anopheles AM 146 L.C. of Ancylostoma duodenale (HOOK WORM) AM 149 L.C. of Enterobius vermicularis AM 151 L.C. of Ascaris lumbricoides (ROUND WORM) AM 152 L.C. of Woucheria bancrofti (FILARIA) AM 153 L.C. of a Culex AM 154 L.C. of a N Ades (STEGOMYIA) AM 155 L.C. of a Mansonioides AM 156 L.C. Strongyloides stercoralis AM 157 L.C. Trichuris trichiura (whip worm) AM 158 L.C. Taenia saginata (beef tape worm) AM 159 L.C. Entamoeba histolytica (causing amoebiasis) AM 160 L.C. Taenia solium (pork tape worm) AM 161 L. C. of a Giardia intestinalis (G. Lamblia) AM 163 L.C. of Balantidium coil AM 164 L.C. Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm) AM 165 L.C. Fasciola hepatica (sheep liver fluke) AM 166 L.C. Echinococcus granulosus (dog tape worm) MB 301 Herpes Simplex virus MB 302 Adeno virus MB 303 Hepititis B Virus MB 304 Polio Virus MB 305 Influenza Virus MB 306 HIV Virus MB 307 Rhabdo Virus MB 308 Bacteriophage MB 309 Cultivation of Virus in Egg MB 310 Rota Virus MB 311 Cytamegalo Virus etc. MB 312 Helical Structure of Virus MB 313 Hepatitis C MB 314 Corona Virus MB 315 Arena Virus MB 316 Bacteria Structure MB 317 Bacteria Three Types AM 123 AM 156 MB 305 MB 307 6
8 SCIENTIST/MEDICAL PROFESSIONAL PORTRAITS FAMOUS NOBEL PRIZE WINNERS IN MEDICAL FIELD Size: 12"X18" Laminated Mounted on Board Size: 16 x21" Laminated Mounted on Board Size: 20 x26 Laminated Mounted on Board SCIENTIST PORTRAITS Year Name Field 2011 Beutler, Hoffman, Steinman Innate Immunity & adaptive immunity 1997 STANLEY B. PRUSINER Prions 1996 PETER C. DOHERTY Cell mediated immune defense ROLF M. ZINKERNAGEL Cell mediated immune defense JOSEPH E. MURRAY Cell transplantation in the treatment of human disease E. DONNALL THOMAS Cell transplantation in the treatment of human disease J. MICHAEL BISHOP Cellular origin of retroviral oncogenes HAROLD E. VARMUS Cellular origin of retroviral oncogenes SUSUMU TONEGAWA Generation of antibody diversity NIELS K. JERNE, Development and control of the immune system 1984 GEORGES J.F. KOHLER Development and control of the immune system 1984 CÉSAR MILSTEIN Development and control of the immune system 1983 BARBARA MC CLINTOCK Mobile genetic elements (transposons) WERNER ARBER, Restriction enzymes 1978 DANIEL NATHANS Restriction enzymes 1978 HAMILTON O. SMITH Restriction enzymes 1968 W. HOLLEY, H. G. KHORANA, NIRENBERG Genetic code and its function in protein synthesis PEYTON ROUS Tumor inducing viruses 1965 F. JACOB, A. LWOFF, J. MONOD Genetic control of enzyme and virus synthesis. (Set of 3) 1959 SEVERO OCHOA Biological synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid ARTHUR KORNBERG Biological synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid GEORGE WELLS BEADLE Genes act by regulating definite chemical events 1958 EDWARD LAWRIE TATUM Genes act by regulating definite chemical events 1958 JOSHUA LEDERBERG The organization of the genetic material of bacteria J. F. ENDERS, WELLER, ROBBINS Ability of poliomyelitis viruses to grow in cultures of various types of tissue SELMAN ABRAHAM WAKSMAN Streptomycin, against tuberculosis MAX THEILER Yellow fever and how to combat it FLEMING, BORIS CHAIN, H. FLOREY Penicillin and its curative effect in various infectious diseases KARL LANDSTEINER Human blood groups ILYA ILYICH METCHNIKOV Work on immunity PAUL EHRLICH Work on immunity CHARLES LOUIS ALPHONSE LAVERAN Malarial parasite ROBERT KOCH Investigations in relation to tuberculosis SIR RONALD ROSS Life cycle of Plasmodium in mosquito EMIL ADOLF VON BEHRING Serum therapy, especially its application against diphtheria. Digital Charts Size: 12"x18" Set of 60 Overhead Transparency Laminated Mounted on Board in One Volume These Microscopic Structures (1000X Magnification) were produced from original examinations & data furnished by bacteriological experts. ZYGOMYCETES 1. ASEXUAL PHASE 2. SEXUAL PHASE 3. EXAMPLES ASCOMYCETES 1. ASEXUAL PHASE 2. SEXUAL PHASE 3. EXAMPLES BASIDIOMYCETES 1. POLYPORE FUNGI 2. GILL FUNGI 3. EXAMPLES WATER BORNE PATHOGENS 1. ENTOMEBA HISTOLYTICA 2. GIARDIA LAMBLIA 3. CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM 4. SCHISTO SOMES 5. VIBRIO CHOLERAE 6. SALMONELLA TYPHI 7. SHIGELLA SPP. 8. CAMPYLOBACTER 9. LEGIONELLA SPP. 10. ESCHERICHIA COLI 11. HEPATITIS A+B 12. NORWALK & NORWALK LIKE VIRUS 13. ROTAVIRUSES MICROBIAL FOOD POISONING 1. SALMONELLA SPP. 2. CAMPYLOBACTER JEJUNI 3. VIBRIO PARAHAEMOLYTICUS 5. STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS 6. ESCHERICHIA COLI 7. CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM 8. BACILLUS CEREUS 9. CLOSTRIDIUM PERTRINGEUS 10. LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES 11. NORWALK & LIKE VIRUS 12 ROTAVIRUSES Small Size 12 x18 Midium Size 16 x21 Large (Set of 3) BACTERIA 1. SINGLE SPHERES 2. SPHERES IN PAIRS 3. SPHERES IN CHAINS 4. SPHERES IN CLUSTERS 5. SINGLE ROD 6. RODS WITH FLAGELLA 7. RODS WITH SPORES 8. RODS WITH CAPSULES 9. RODS IN CHAINS WITH SPORES 10. ACTIRIOMYCETES 11. CURVED RODS 12. SPIRALS 13. SPIRAL WITH FLAGELLA 14. SPIROCHETES VIRUS-STRUCTURE 1. ADENOVIRUS 2. T.M.V 3. INFLUENZA 4. HIV 5. SMALL POX 6. BATERIOPHAGE P22 (Set of 3) us : desh@dbios.org Mob
9 MICROBIOLOGY MODELS AM 146 AM 152 AM 154 AM 157 AM 158 AM 160 AM 161 AM 163 AM 164
1. Parasitology Protozoa 4
 Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS
 COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
FOOD BORNE INFECTIONS
 Food Poisoning Food poisoning Advisory commitee on Microbiological safety of food (ACMSF, UK) has defined food poisoning as : An acute illness with gastrointestinal or neurological manifestation affecting
Food Poisoning Food poisoning Advisory commitee on Microbiological safety of food (ACMSF, UK) has defined food poisoning as : An acute illness with gastrointestinal or neurological manifestation affecting
स क ष मज व ववज ञ न ववभ ग DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY व.एम.एम.स ए व सफदरज ग अस पत ल VMMC & SAFDARJUNG HOSPITAL नई ददल ल ११००२९ NEW DELHI
 स क ष मज व ववज ञ न ववभ ग DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY व.एम.एम.स ए व सफदरज ग अस पत ल VMMC & SAFDARJUNG HOSPITAL नई ददल ल ११००२९ NEW DELHI 110029 Teaching Schedule for MBBS 4thSemester (January June 2017)
स क ष मज व ववज ञ न ववभ ग DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY व.एम.एम.स ए व सफदरज ग अस पत ल VMMC & SAFDARJUNG HOSPITAL नई ददल ल ११००२९ NEW DELHI 110029 Teaching Schedule for MBBS 4thSemester (January June 2017)
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM)
 HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 39, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 39, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 38, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 38, 2018 (Notification
STUDY PLAN II year students 2nd semester 1 Class
 STUDY PLAN II year students 2nd semester 1 Class 1. Pyogenic cocci. Staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus species, differentiation of staphylococci. Pathogenicity factors and toxins. Characteristics of
STUDY PLAN II year students 2nd semester 1 Class 1. Pyogenic cocci. Staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus species, differentiation of staphylococci. Pathogenicity factors and toxins. Characteristics of
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 33, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 33, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 49, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 49, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 22, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 22, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 50, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 50, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 3, 2019 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 3, 2019 (Notification
Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases
 Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases Abdominal pain Entamoeba histolytica (amebic colitis, liver infection) Giardia lamblia Cryptosporidium Intestinal helminths (Ascaris, Strongyloides) Anisakis (symptoms
Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases Abdominal pain Entamoeba histolytica (amebic colitis, liver infection) Giardia lamblia Cryptosporidium Intestinal helminths (Ascaris, Strongyloides) Anisakis (symptoms
Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
 Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Unofficial translation No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Unofficial translation No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory. 11 April 2013
 Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
Parasite Life Cycles. Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou. Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo
 Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year )
 BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705
![February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705](/thumbs/80/81975511.jpg) February 2009 [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks Answer All questions. I. Essays: (2x15=30) 1. Define hypersensitivity. Classify Hypersensitivity. Discuss in
February 2009 [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks Answer All questions. I. Essays: (2x15=30) 1. Define hypersensitivity. Classify Hypersensitivity. Discuss in
SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester FRIDAY. MICROBIOLOGY Lecture (Head Building) 11:00-12:30
 SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester Lectures -Head Building, Friday 11:00-12:30 Seminars/Practical Lessons-Lab.Room Instutute of Microbiology and Immunology, Friday 13:00-15:30
SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester Lectures -Head Building, Friday 11:00-12:30 Seminars/Practical Lessons-Lab.Room Instutute of Microbiology and Immunology, Friday 13:00-15:30
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
MICROBIOLOGY BACTERIOLOGY III semester
 MICROBIOLOGY 2016-17 BACTERIOLOGY III semester 07. 10. 2016. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial properties. Bacterial structures (capsule, cell wall). Pathogenicity and
MICROBIOLOGY 2016-17 BACTERIOLOGY III semester 07. 10. 2016. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial properties. Bacterial structures (capsule, cell wall). Pathogenicity and
Department of Microbiology, IMS, BHU Teaching schedule B.D.S. 4 th Semester 2 nd Year (2017 Batch) Session
 Department of Microbiology, IMS, BHU Teaching schedule B.D.S. 4 th Semester 2 nd Year (2017 Batch) 2018-19 Session Date Topic Name of Faculty members/ Senior Resident* 02.01.2019 Viridans group of Streptococci
Department of Microbiology, IMS, BHU Teaching schedule B.D.S. 4 th Semester 2 nd Year (2017 Batch) 2018-19 Session Date Topic Name of Faculty members/ Senior Resident* 02.01.2019 Viridans group of Streptococci
4. The most common cause of traveller s diarrheoa is a. Rotavirus b. E coli c. Shigella d. Giardia e. Salmonella
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
Pathogens of the Digestive System
 Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
Bacteriology Virology Mycology Parasitology Immunology Pathology Epidemiology. Microbe alternate terms Germs, microorganisms, pathogens, agents, bugs
 1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations
 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE OUTBREAK MANUAL New Jersey s Public Health Response Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations June 2013 Public Health Emergency Response Capability Requirements as stated
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE OUTBREAK MANUAL New Jersey s Public Health Response Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations June 2013 Public Health Emergency Response Capability Requirements as stated
1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE?
 1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY. lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, hookworm. Human Parasitology (Code: ) Guideline
 HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland N.B. Unofficial translation. Legally valid only in Finnish and Swedish
 Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland N.B. Unofficial translation. Legally valid only in Finnish and Swedish No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 was repealed
Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland N.B. Unofficial translation. Legally valid only in Finnish and Swedish No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 was repealed
MUST KNOW QUESTIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY
 MUST KNOW QUESTIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY Systemic Bacteriology Chapter 1. Staphylococcus Name various virulence factors ( Enzymes & Toxins) of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA Catalase & Coagulase test Lesions caused
MUST KNOW QUESTIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY Systemic Bacteriology Chapter 1. Staphylococcus Name various virulence factors ( Enzymes & Toxins) of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA Catalase & Coagulase test Lesions caused
The German Law on Prevention and Control of Communicable Diseases (Infektionsschutzgesetz)- Surveillance System. Michael H. Kramer
 The German Law on Prevention and Control of Communicable Diseases (Infektionsschutzgesetz)- Surveillance System VHPB - Meeting, Berlin, Germany, 13-14 October 2003 Michael H. Kramer Federal Ministry of
The German Law on Prevention and Control of Communicable Diseases (Infektionsschutzgesetz)- Surveillance System VHPB - Meeting, Berlin, Germany, 13-14 October 2003 Michael H. Kramer Federal Ministry of
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 15 / Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 Chapter 15 / Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 1 2 The removal of plasmids reduces virulence in which of the following organisms? a. Clostridium tetani b. Escherichia coli c. Staphylococcus aureus d. Streptococcus mutans e. Clostridium botulinum 3
1 2 The removal of plasmids reduces virulence in which of the following organisms? a. Clostridium tetani b. Escherichia coli c. Staphylococcus aureus d. Streptococcus mutans e. Clostridium botulinum 3
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE
 INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites TYPICAL
 APPENDIX 9.1 Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites COMMON FOODBORNE S CAUSED BY BACTERIA Bacillus cereus food poisoning diarrheal Bacillus
APPENDIX 9.1 Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites COMMON FOODBORNE S CAUSED BY BACTERIA Bacillus cereus food poisoning diarrheal Bacillus
Epidemiology. Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Human Reservoir :
 Lecture ( 3 ) Dr. Ismail I. Daood Epidemiology Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Infectious disease is disease that is caused the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host's
Lecture ( 3 ) Dr. Ismail I. Daood Epidemiology Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Infectious disease is disease that is caused the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host's
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology
 NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
SOUTH EASTERN KENYA UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION 2015/2016 FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF PUBLIC HEALTH
 SOUTH EASTERN KENYA UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION 2015/2016 FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF PUBLIC HEALTH HPH 102: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY DATE: 7/12/2015 TIME:10:30-12:30PM INSTRUCTIONS
SOUTH EASTERN KENYA UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION 2015/2016 FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF PUBLIC HEALTH HPH 102: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY DATE: 7/12/2015 TIME:10:30-12:30PM INSTRUCTIONS
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE. 1. Type of cell. 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
"Wanted Poster" Diseases
 "Wanted Poster" Diseases Part One - Choosing a Disease Listed below are several bacteria and the disease they cause. Pick any one bacteria/disease to research. It is highly recommended that you pick a
"Wanted Poster" Diseases Part One - Choosing a Disease Listed below are several bacteria and the disease they cause. Pick any one bacteria/disease to research. It is highly recommended that you pick a
Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease:
 Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY
 LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY 1. General characteristics of piogenic cocci. 2. Staphylococcus, staphylococcus species, differentiation signs of staphylococci. Factor
LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY 1. General characteristics of piogenic cocci. 2. Staphylococcus, staphylococcus species, differentiation signs of staphylococci. Factor
M O L E C U L A R G E N E T I C S
 MOLECULAR GENETICS ADVANTAGES OF MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular genetics is a dynamic and transformative area of diagnostics, leading to insights in research and treatment in many disease states that are
MOLECULAR GENETICS ADVANTAGES OF MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular genetics is a dynamic and transformative area of diagnostics, leading to insights in research and treatment in many disease states that are
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Chapter 15. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
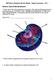 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
Overview IMPORTANCE CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS
 IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
Microbiology Final. 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea?
 Microbiology Final 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea? - EAEC* 2) Ab toxin A is stand for : - active* 3) Differentiate between staphylococcus and streptococcus : - catalase test* 4) Microsporum
Microbiology Final 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea? - EAEC* 2) Ab toxin A is stand for : - active* 3) Differentiate between staphylococcus and streptococcus : - catalase test* 4) Microsporum
KOMAR UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KUST) Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016
 Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
GI Micro Lab. B- After that the stool sample should be cultured on different types of media
 GI Micro Lab A- Stool sample is taken and added to Selenite broth to: - 1- Inhibit growth of normal flora bacteria 2- Enhance growth of pathogenic bacteria B- After that the stool sample should be cultured
GI Micro Lab A- Stool sample is taken and added to Selenite broth to: - 1- Inhibit growth of normal flora bacteria 2- Enhance growth of pathogenic bacteria B- After that the stool sample should be cultured
Lectures. Experiments. General introduction 3. Introduction to Medical Protozoa 0.5. Lobosea (amoebae) 3 3. Flagellates 3 3.
 Teaching outline of Human Parasitology (Use for international students) Department of Human Parasitology Hainan Medical College Teaching Target Human Parasitology is the study of those species of the animal
Teaching outline of Human Parasitology (Use for international students) Department of Human Parasitology Hainan Medical College Teaching Target Human Parasitology is the study of those species of the animal
PHAR 6724: Introduction to the Immune System and Infectious Disease
 PHAR 6724: Introduction to the Immune System and Infectious Disease Course Syllabus Spring 2018 3.1 Credits This course adheres to the items listed in the College of Pharmacy Central Syllabus: https://docs.google.com/a/umn.edu/document/d/1artq5e1rbzxe8letwo7be8k8snzaegmmz_qcw8yj-ii/edit?pli=1
PHAR 6724: Introduction to the Immune System and Infectious Disease Course Syllabus Spring 2018 3.1 Credits This course adheres to the items listed in the College of Pharmacy Central Syllabus: https://docs.google.com/a/umn.edu/document/d/1artq5e1rbzxe8letwo7be8k8snzaegmmz_qcw8yj-ii/edit?pli=1
GOYAL BROTHERS PRAKASHAN
 Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? IMPORTANT NOTES 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? IMPORTANT NOTES 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1
 Influenza influenza Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1 Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis stomach flu gastroenteritides gastroenterities food poisoning campylobacter colitis gastroenterocolitis gastrointestinal
Influenza influenza Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1 Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis stomach flu gastroenteritides gastroenterities food poisoning campylobacter colitis gastroenterocolitis gastrointestinal
Interpretation At-a-Glance Bacteriology. Parasitology
 Patient: EMILY TET DOB: December 31, 1980 ex: F MN: 0001558266 Order Number: M9301014 Completed: January 31, 2019 eceived: January 30, 2019 Collected: January 30, 2019 Test Office Test POD Test MD, DO,
Patient: EMILY TET DOB: December 31, 1980 ex: F MN: 0001558266 Order Number: M9301014 Completed: January 31, 2019 eceived: January 30, 2019 Collected: January 30, 2019 Test Office Test POD Test MD, DO,
Storage conditions. roomtemperature or incubator at 36 C. Other: 2-8 C Blood: roomtemperature or incubator at. A.s.a.p. max 24h. A.s.a.p.
 Extract Vademecum Department of Medical Microbiology Status: Code: Version: Approval date: Geldig MMB-PR-04/1 1 Juni 2017 Name request Specimen Material needed Transport Bacteriology Bacterial culture
Extract Vademecum Department of Medical Microbiology Status: Code: Version: Approval date: Geldig MMB-PR-04/1 1 Juni 2017 Name request Specimen Material needed Transport Bacteriology Bacterial culture
DISEASE PREVENTION & ANTIMICROBIAL USE REDUCTION: IMPACT OF VACCINATION
 DISEASE PREVENTION & ANTIMICROBIAL USE REDUCTION: IMPACT OF VACCINATION Anwar Hoosen Department of Medical microbiology University of Pretoria & Tswane Academic Division, NHLS 1 VACCINE ACHIEVEMENTS At
DISEASE PREVENTION & ANTIMICROBIAL USE REDUCTION: IMPACT OF VACCINATION Anwar Hoosen Department of Medical microbiology University of Pretoria & Tswane Academic Division, NHLS 1 VACCINE ACHIEVEMENTS At
YR 2 IMMUNOLOGY/MICROBIOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- September 18, 1998.
 YR 2 IMMUNOLOGY/MICROBIOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- September 18, 1998. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-60. 1. A 28 year old prostitute is complaining of a whitish vaginal discharge. Vaginal examination
YR 2 IMMUNOLOGY/MICROBIOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- September 18, 1998. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-60. 1. A 28 year old prostitute is complaining of a whitish vaginal discharge. Vaginal examination
INFECTIOUS DISEASE. Page 2
 Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Chapter 13. Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology
 Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Study Guide. Medical Parasitology. 3 rd. YEAR MEDICINE. Dr. Abdulkader M. D. Tonkal Head of Medical Parasitology department ACADEMIC YEAR
 Study Guide Medical Parasitology 3 rd. YEAR MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 2008 Dr. Abdulkader M. D. Tonkal Head of Medical Parasitology department 1428 ه 27/1 بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Table of content I. FACULTY
Study Guide Medical Parasitology 3 rd. YEAR MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 2008 Dr. Abdulkader M. D. Tonkal Head of Medical Parasitology department 1428 ه 27/1 بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Table of content I. FACULTY
Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio
 Labquality EQAS Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio Clinically relevant external quality assessment program for microbiology Bacterial serology Bacteriology Mycology Parasitology Preanalytics Virology Labquality
Labquality EQAS Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio Clinically relevant external quality assessment program for microbiology Bacterial serology Bacteriology Mycology Parasitology Preanalytics Virology Labquality
1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution. 2) know the mechanisms of host immune responses to viral infections
 VIROLOGY A The course aims to provide the student with the cognitive and methodological tools necessary to: 1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution 2) know the
VIROLOGY A The course aims to provide the student with the cognitive and methodological tools necessary to: 1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution 2) know the
Fiscal Note for Permanent Rule Changes for North Carolina Division of Public Health
 Fiscal Note for Permanent Rule Changes for North Carolina Division of Public Health Agency: Dept. Of Health and Human Services, Division of Public Health, Epidemiology Section, Communicable Disease Branch
Fiscal Note for Permanent Rule Changes for North Carolina Division of Public Health Agency: Dept. Of Health and Human Services, Division of Public Health, Epidemiology Section, Communicable Disease Branch
Potential Reimbursement CPT Codes
 BioFire FilmArray Blood Culture Identification (BCID) Panel Medicare All targets (n) 87150 n x * *BioFire BCID Panel is comprised of 27 total targets. The number of targets allowed for reimbursement may
BioFire FilmArray Blood Culture Identification (BCID) Panel Medicare All targets (n) 87150 n x * *BioFire BCID Panel is comprised of 27 total targets. The number of targets allowed for reimbursement may
SYLLABUS. The Pathology of Infectious Diseases (PATH-217)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: The Pathology of Infectious Diseases (PATH-217) 3 units, 44 hrs. (4 hrs. lecture/week) The course is a study
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: The Pathology of Infectious Diseases (PATH-217) 3 units, 44 hrs. (4 hrs. lecture/week) The course is a study
INFECTIOUS DISEASES CONTAGIOUS DISEASES COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity. 2 nd Lecture
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 2 nd Lecture Preferred Portal of Entry Just because a pathogen enters your body it does not mean it s going to cause disease. pathogens - preferred portal of entry
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 2 nd Lecture Preferred Portal of Entry Just because a pathogen enters your body it does not mean it s going to cause disease. pathogens - preferred portal of entry
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE
 NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping
 Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping Bioterrorism Preparedness: A Conference for Senior Practitioners and Professionals Dr. Arnold N. Weinberg Professor of Medicine
Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping Bioterrorism Preparedness: A Conference for Senior Practitioners and Professionals Dr. Arnold N. Weinberg Professor of Medicine
CHAPTER 515. COMMUNICABLE DISEASE AND INJURY REPORTING EFFECTIVE 9/12/2014
 TITLE 310. CHAPTER 515. COMMUNICABLE DISEASE AND INJURY REPORTING EFFECTIVE 9/12/2014 310:515-1-1. Purpose The rules in this Chapter implement the Communicable Diseases Reporting Regulations, 63 O.S. 1981,
TITLE 310. CHAPTER 515. COMMUNICABLE DISEASE AND INJURY REPORTING EFFECTIVE 9/12/2014 310:515-1-1. Purpose The rules in this Chapter implement the Communicable Diseases Reporting Regulations, 63 O.S. 1981,
co URSE Medical Microbiology 3 COURSE CODE MMB310S
 @ セ M オセ M セ セ M@ - @ M セ M セ @ -- M --- @ M POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES Department of Health Sciences セ BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES -- ----- - QU ALIFICATION: ALIFICATION
@ セ M オセ M セ セ M@ - @ M セ M セ @ -- M --- @ M POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES Department of Health Sciences セ BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES -- ----- - QU ALIFICATION: ALIFICATION
Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Department of Civil Engineering. Zerihun Alemayehu
 CHAPTER 2 WATER QUALITY AND HEALTH Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Department of Civil Engineering Water Treatment Zerihun Alemayehu Some Water Facts Body composition Body, 65% water; blood, 83%; bones,
CHAPTER 2 WATER QUALITY AND HEALTH Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Department of Civil Engineering Water Treatment Zerihun Alemayehu Some Water Facts Body composition Body, 65% water; blood, 83%; bones,
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
The Chain of Infection
 The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
risk factors, 125 superimposed on chronic idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease, vasculitis, 127, 129
 Subject Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS enteropathy/colopathy, 153 See also Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), 153 156 Actinomycosis, 2, 79 88 appendix in, 89 Acute infectious-type colitis,
Subject Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS enteropathy/colopathy, 153 See also Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), 153 156 Actinomycosis, 2, 79 88 appendix in, 89 Acute infectious-type colitis,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine)
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
Immune System. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Immune System Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the bacteria is the cause of pneumonia? a. staphylococci c. Treponema
Class: Date: Immune System Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the bacteria is the cause of pneumonia? a. staphylococci c. Treponema
Patient: Ima Sample. Accession: Shiloh Rd, Ste 101. Collected: 2/10/2018. Received: 2/12/2018 Alpharetta GA
 GI-MAP TM DNA Stool Analysis Patient: Ima Sample Accession: 20180212-0001 5895 Shiloh Rd, Ste 101 Collected: 2/10/2018 Received: 2/12/2018 Alpharetta GA 30005 877-485-5336 DOB: 7/11/1981 Completed: Ordered
GI-MAP TM DNA Stool Analysis Patient: Ima Sample Accession: 20180212-0001 5895 Shiloh Rd, Ste 101 Collected: 2/10/2018 Received: 2/12/2018 Alpharetta GA 30005 877-485-5336 DOB: 7/11/1981 Completed: Ordered
Parasitology third year
 Quality Assurance Unit Tanta University Faculty of Medicine Department of Parasitology Course Specifications Parasitology third year 011-01 Course Specifications: parasitology third Year, 011-01 Parasitology
Quality Assurance Unit Tanta University Faculty of Medicine Department of Parasitology Course Specifications Parasitology third year 011-01 Course Specifications: parasitology third Year, 011-01 Parasitology
Boston MRC Introduction to Biological Hazards Response
 Boston MRC Introduction to Biological Hazards Response Julien Farland MS, RBP Director of Biological Safety Boston Public Health Commission March 25, 2015 Objectives Describe the types and classes of biological
Boston MRC Introduction to Biological Hazards Response Julien Farland MS, RBP Director of Biological Safety Boston Public Health Commission March 25, 2015 Objectives Describe the types and classes of biological
Welcome to Parasitic. Fall 2008
 Welcome to Parasitic Diseases Fall 2008 Dickson Despommier, Ph.D. Charles Knirsch, MPH, MD Josh Stillman, MD Parasite Any organism that takes metabolic advantage of another organism Viruses Rickettsiae
Welcome to Parasitic Diseases Fall 2008 Dickson Despommier, Ph.D. Charles Knirsch, MPH, MD Josh Stillman, MD Parasite Any organism that takes metabolic advantage of another organism Viruses Rickettsiae
Introduction to Medical Parasitology
 Introduction to Medical Parasitology Lecture I Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Suggested Textbooks 1. Cheesbrough (2009), District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries.
Introduction to Medical Parasitology Lecture I Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Suggested Textbooks 1. Cheesbrough (2009), District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries.
Patient: Ima Sample. Accession: Shiloh Rd, Ste 101. Collected: 9/4/2018. Received: 9/6/2018 Alpharetta GA
 GI-MAP TM DNA Stool Analysis Patient: Ima Sample Accession: 20180906-0001 5895 Shiloh Rd, Ste 101 Collected: 9/4/2018 Received: 9/6/2018 Alpharetta GA 30005 877-485-5336 DOB: 9/1/2009 Completed: 9/6/2018
GI-MAP TM DNA Stool Analysis Patient: Ima Sample Accession: 20180906-0001 5895 Shiloh Rd, Ste 101 Collected: 9/4/2018 Received: 9/6/2018 Alpharetta GA 30005 877-485-5336 DOB: 9/1/2009 Completed: 9/6/2018
Manitoba Monthly Surveillance Unit Report
 Manitoba Monthly Surveillance Unit Report Reported up to June 30, 2012 Highlights: 1. Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms Together Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Clostridium difficile
Manitoba Monthly Surveillance Unit Report Reported up to June 30, 2012 Highlights: 1. Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms Together Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Clostridium difficile
1/29/2013. Viruses and Bacteria. Infectious Disease. Pathogens cause disease by: Chapters 16 and 17
 Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Biology. Chapter 19. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 19 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea 19.1 What Are Viruses? Viruses: noncellular infectious agents Consists of a protein coat around a core of
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 19 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea 19.1 What Are Viruses? Viruses: noncellular infectious agents Consists of a protein coat around a core of
The Nematodes (Round worms)
 The Nematodes (Round worms) - Small, round, elongated, Non-segmented worms with body cavity. They have separate sexes, usually don t need an I.H and do not multiply in human host because eggs don t hatch
The Nematodes (Round worms) - Small, round, elongated, Non-segmented worms with body cavity. They have separate sexes, usually don t need an I.H and do not multiply in human host because eggs don t hatch
Overview of Microbiology. James D. Dick, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Quiz Student:
 Quiz 5 080911 Student: 1. The enveloped viruses typically obtain their envelope A. from the host plasma membrane. B. as they exit the host. C. from a newly constructed viral-derived membrane. D. from the
Quiz 5 080911 Student: 1. The enveloped viruses typically obtain their envelope A. from the host plasma membrane. B. as they exit the host. C. from a newly constructed viral-derived membrane. D. from the
Biology. Slide 1 of 30. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
EDUCATIONAL AIDS FOR COMMUNITY MEDICINE
 Dbios List No. 7 w.e.f. Jan 1, 2016 EDUCATIONAL AIDS FOR COMMUNITY MEDICINE (P.S.M. DEPTT.) Customised Charts Size 20"x30" Laminated & Mounted Framed on Board Rs. 1350/- Each 4 20 College Logo & Name 30
Dbios List No. 7 w.e.f. Jan 1, 2016 EDUCATIONAL AIDS FOR COMMUNITY MEDICINE (P.S.M. DEPTT.) Customised Charts Size 20"x30" Laminated & Mounted Framed on Board Rs. 1350/- Each 4 20 College Logo & Name 30
Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan
 Parasitoses Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan Epidemiology for clinicians JMAJ 48(3): 148 154, 2005 Yoshiya SATO Professor, University of the Ryukyus Abstract: The recent profile of parasitic diseases
Parasitoses Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan Epidemiology for clinicians JMAJ 48(3): 148 154, 2005 Yoshiya SATO Professor, University of the Ryukyus Abstract: The recent profile of parasitic diseases
Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Manuel R. Amieva, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Infectious Diseases Department of Microbiology & Immunology Stanford University School of Medicine Sharon
Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Manuel R. Amieva, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Infectious Diseases Department of Microbiology & Immunology Stanford University School of Medicine Sharon
Protozoans and Helminthes
 Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
