Brief Definitive Report
|
|
|
- Evelyn Wilfred Russell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brief Definitive Report ANALYSIS OF RESTRICTION FRAGMENT LENGTH POLYMORPHISM IN LYMPHOKINE GENES OF NORMAL AND AUTOIMMUNE MICE BY GUNTHER RICHTER, ZHIHAI QIN, TIBOR DIAMANTSTEIN, AND THOMAS BLANKENSTEIN From the Freie Universitat Berlin, Klinikum Steglitz, Institut fur Immunologie, 1000 Berlin 45, Federal Republic of Germany The genetic origin for the lupus-like disease in (NZB x NZW)F1, MRL/lpr or BxSB mice is largely unknown (reviewed in reference 1). The mice develop symptoms such as generalized B cell hyperactivation, early IgM to IgG class switch, or functional abnormalities in the CD4+ T cell subpopulation indicating the potential involvement oflymphokines in the pathogenesis ofthe disease. This assumption is supported by findings such as decreased IL-2 and IL-2 receptor expression in (NZB x NZW)F1, MRL/lpr and BxSB mice (2), abnormal IL-1 transcripts (3), increased IL-4 expression (4), spontaneous transcription of IFN--y (5), and increased TNFa activity in MRL/lpr mice (6). In contrast, TNFa production was found to be decreased in NZW and (NZB x NZW)F, mice (7). The authors proposed that decreased TNFet production might be related to a mutation in the TNF-a gene as demonstrated by RFLP analysis. Moreover, administration of TNFa partially abolished the development of the disease. Altogether, the participation of lymphokines in autoimmunity suggested to analyze lymphokine genes at the genetic level. First, we sought to reevaluate the relevance of the TNFa polymorphism in NZB by determining the frequency of this allele in a large number of laboratory and wild mice and found that the TNFa allele ofnzw is inherited in most normal inbred strains and wild mice arguing against an involvement of the NZW TNFa gene as a causal agent in the development of lupus in (NZB x NZW)Fi hybrids. Second, we searched for polymorphisms in other lymphokine or lymphokine receptor genes whose expression seems to be abnormal in autoimmune mice. As judged from the RFLP analysis, the genes encoding IL-la, IL-2, IL-2 receptor a chain, IL-4, IL-5, and IFN-y seem to be normal in autoimmune strains. Materials and Methods The sources of (C57BL/6 x DBA/2)k',, BALB/c, C3H, DBA/2, BxSB, MRL/lpr, NZW, NZB, MOLF/EI (Mus musculus molossinus), CAST/EI (Mus musculus castaneus), Mus musculus musculus, Mus spretoides (4A), Mus spicilegus (4B), Mus spretus, Mus ceroicolor, Mus cookii, Mus caroli, Mus pyromys sazicola (plathythrix), and Mus coelomys pahari, and of Lewis rat have been described (8, 9). Preparation of liver DNA and Southern blot analysis have been described This work was supported by a grant from the German-Israeli Foundation for Scientific Research and Development. This work contains part of the doctoral thesis of G. Richter. Address correspondence to Tibor Diamantstein, Institut fur Immunologie, Hindenburgdamm 27, 1000 Berlin 45, FRG. J. Exp. MED. The Rockefeller University Press " /89/10/1439/05 $ Volume 170 October
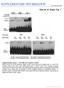
2 1440 RICHTER ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT (9). As nick-translated probes, purified fragments carrying the following lymphokine cdna regions were used : TNFa, 1.0-kb Sal I fragment of psvd2-3 mtnf (10) ; IL-la, 1.0-kb Bam HI fragment ofpil (11); IL-2, 0.8-kb Sal I full-length cdna ofpsupdol-il-2 (Blankenstein, T, unpublished); IL-4, 0.5-kb Bgl II fragment of pxeril-4 (Blankenstein, T, unpublished) ; IL-2 receptor a chain : 0.95-kb Hind III-Rsa I fragment ofpmil2r2 (12) ; IL-5 : 0.5-kb Bam HI-Acc I fragment of psp6k-mtrf23 (13) ; IFN-.y, 0.6-kb Pst I fragment of pat153 MIFN G (Fiers, W., unpublished). Results Barn HI-digested liver DNA of a large number of autoimmune, normal laboratory mice and murine rodents representing the phylogenetical distance between house mice and the rat were analyzed by Southern blots using the TNFa probe (Fig. 1, a and b). A 10.5-kb Barn HI fragment lights up in NZB, DBA/2, BALB/c, and the heterozygous (C57BL/6 x DBA/2)Fl. After longer exposure, an additional 1.5-kb fragment appears in these mice. The 12-kb Barn HI allele present in NZW is also inherited in MRL/lpr, BxSB, C3H, (C57BL/6 x DBA/2)FI, MOLF/EI (inbred M. m. molossinus), CAST/El (inbred M. m. castaneus), and in outbred M. m. musculus, M. spretoides, M. spicilegus, M. spretus and M. caroli. The phylogenetically more distantly related M. ceroicolor, M. cookii, M. c. pahari, M. p. saxicola, and the rat exhibit TNFa-specific bands of different size. The complete lack of allelic forms within the wild mice species and the frequent occurrence of the 12-kb Barn HI band indicate the strong evolutionary constraint ofthe TNFci gene (9). The allele represented by the 12-kb band in NZW is inherited in most laboratory and wild mice, arguing against a defect TNFa gene in NZW mice based on this polymorphism (7). Additionally, no polymorphism could be detected when NZW and other autoimmune mice were compared with normal inbred strains in Eco RI digests and hybridized FIGURE 1. Southern blot analysis of indicated animals with the TNFa probe. (a) Normal and autoimmune laboratory strain and (b) wild mice including rat DNA digested with Barn HI ; (c) DNA of laboratory strains digested with Eco RI.
3 RICHTER ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT 1441 FIGURE 2. DNA of autoimmune and normal laboratory mice were hybridized in Southern blots to indicated lymphokine or lymphokine receptor, probes. Probes and restriction enzyme used are indicated below and to the left, respectively. Size marker in all experiments was X Hind III-digested DNA. Fragment size is given in kilobases. (1) NZB, (2) NZW, (3) MRL/Ipr, (4) BxSB, (5) C3H, (6) BALB/c, (7) (C57BL/6 x DBA/2)FI. to the TNFa probe (Fig. 1 c). Next, we searched for RFLPs in other lymphokine or lymphokine receptor genes of autoimmune mice in comparison to normal mice. Barn HI- and Eco RI-digested DNA were hybridized in Southern blots to the ILla, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IFN-y, and IL-2 receptor probes (Fig. 2). For IL-2 only the Eco RI Southern blot is shown. No polymorphism could be observed in either of IL-2, IL-2 receptor, IL-5, or IFN-y loci. BALB/c shows a Bam HI polymorphism in the IL-la gene, NZW exhibits an IL-4 polymorphism for Eco RI. Discussion The purpose ofthis investigation was to assess the potential genetically determined involvement of lymphokine genes in the pathogenesis of lupus-like disease on the basis of RFLP analysis. Similar studies have been performed concerning the Ig heavy chain V, TCR Vc,-, and Vp-genes and the IL-6 locus without obvious success to demonstrate a correlation betwlen disease and certain alleles or haplotypes (9, 14-16).
4 1442 RICHTER ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT Based on the finding that a dominant gene closely linked to the MHC complex of NZW mice is one of the factors responsible for autoimmunity in (NZB x NZW)F1 hybrids (16), it was proposed that a mutated TNFa gene represented by a Barn HI polymorphism and therefrom resulting low TNFci expression may be involved in the pathogenesis in (NZB x NZW)Fj mice (7). The TNFa gene has been located within the MHC complex (17). In contrast, the lupus gene or closely linked genes in NZW have been mapped by genetic analysis -10 cmorgan apart from the MHC locus (16). Therefore, it seemed necessary to analyze whether this TNFa polymorphism is found exclusively in NZW mice. RFLP analysis in a large number of inbred strains and wild mice showed that only BALB/c, DBA/2, and NZB possess the apparent normal TNFa gene, whereas 11 other mice have inherited the same allele as NZW mice. Furthermore, both allelic forms do not seem to result from a larger mutation since no polymorphism could be detected upon Eco RI digests. These results argue against an involvement of the NZW TNFot gene in the pathogenesis of (NZB x NZW)Fi hybrids. This is supported by the recent finding of Boswell et al. who found increased TNFot expression in MRL/lpr mice (6). MRL/lpr exhibit the same restriction site pattern for the TNFci gene as NZW mice (Fig. 1). The general B cell hyperactivation, increased numbers of lymphokine-secreting T cell populations, and a number of studies describing deregulated lymphokine expression in autoimmune mice indicate that lymphokines may be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune mice. We therefore extended the RFLP analysis to other lymphokine genes of autoimmune mice in comparison to normal mice. As previously shown for IL-6 (9), no polymorphism could be detected in the loci containing IL-2, the IL-2 receptor, IL-5, and IFN-y genes. Allelic forms were identified in the IL-lac gene of BALB/c and in the IL-4 gene ofnzw. The IL-4 allele in NZW is also inherited in MOLF/EI, the inbred M. m. molossinus (unpublished observation). Together, our results do not support the involvement of lymphokine genes as primary agent in the development ofthe lupus-like disease. The possible significance of an Eco RI RFLP in the IL-3 locus unique to NZB and NZW mice (unpublished observation) remains to be elucidated. Summary Analysis of RFLP has been employed in lymphokine genes of autoimmune and normal mice. No polymorphism could be detected in the loci containing IL-2, IL-2 receptor, IL-5, and IFN-y in NZB, NZW BxSB, and MRL/lpr mice when compared with normal mice. Allelic forms were identified in the IL-1a gene of BALB/c and in the IL-4 gene ofnzw The frequency of the Barn HI RFLP in the TNFa gene of NZW which has been proposed to be associated with the development of autoimmune disease in (NZB x NZW)Fj mice has been analyzed in a number of different inbred strains and in wild mice. Since the same allele is inherited in most autoimmune, healthy laboratory and wild mice the TNFa gene does not seem to be one of the causal agents that contributes to the development of autoimmunity in (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. We are grateful to W Fiers for kindly providing IL-2, IL-4, TNFa, and IFN-y probes ;U. Gubler for the IL-la probe ; and T Honjo for IL-5 and IL-2 receptor probes. We thank S. VoO for preparation of the manuscript. Received for publication 9 May 1989 and in revised form 10 July 1989.
5 RICHTER ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT 1443 References.. 1. Theofilopoulos, A. N., and F. J. Dixon Murin e models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv. Immunol. 37: Altmann, A., A. N. Theofilopoulos, R. Weiner, D. H. Katz, and F. J. Dixon Analysi s of T cell function in autoimmune murine strains. J Exp. Med. 154 : Boswell, J. M., M. A. Yui, S. Endres, D. W. Burt, and V. E. Kelly Novel and 4. enhanced IL 1 gene expression in autoimmune mice with lupus. J. Immunol. 141 :118. Schauer, U B cell growth factor activity in supernatants of MRL-lpr/lpr derived T cell hybridomas. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 72 : Murray, L., and C. Martens The abnormal T lymphocytes in lpr mice transcribe interferon-,y and tumor necrosis factor-a genes spontaneously in vivo. Eur. J Immunol. 19 : Boswell, J. M., M. A. Yui, D. W. Burt, and V. E. Kelley Increased Tumor Necrosis Factor and IL 1 (3 gene expression in the kidneys of mice with lupus nephritis.) Immunol. 141 : Jacob, C. O., and H. O. McDevitt Tumor necrosis factor-a in murine autoimmune `lupus' nephritis. Nature (Lond). 331: Blankenstein, Th., F. Bonhomme, and U. Krawinkel Evolution of pseudogenes in the immunoglobulin VH gene family of the mouse. Immunogenetics. 26 : Qin, Z., G. Richter, T. Diamantstein, and Th. Blankenstein Structure and evolution of mouse interleukin 6 gene. Mol. Immunol. In press. 10. Fransen, L., R. Muller, A. Marmenout,J. Tavernier, J. van der Heyden, E. Kawashima, A. Chollet, R. Tizard, H. van Heuverswyn, A. van Vliet, M. R Ruysschaert, and W. Fiers Molecular cloning of mouse tumor necrosis factor cdna and its eucaryotic expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 13 : Lomedico, P. T., U. Gubler, C. P. Heilman, M. Dukovich, J. G. Giri, Y E. Pan, K. Collier, R. Semionow, A. O. Chua, and S. B. Mizel Cloning and expression of murine interleukin 1 cdna in Escherichia coli. Nature (Loud.) 312: Shimizu, A., S. Kondo, S. Takeda, J. Yodoi, N. Ishida, H. Sabe, H. Osawa, T. Diamantstein, T. Nikaido, and T. Honjo Nucleotide sequence ofmouse IL 2 receptor cdna and its comparison with the human IL 2 receptor sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 13 : Kinashi, T., N. Harada, E. Severinson, T. Tanabe, P Sideras, M. Konishi, C. Azuma, A. Tominaga, S. Bergstedt-Lindquist, M. Takahashi, F. Matsuda, Y Yaoita, K. Takatsu, and T. Honjo Cloning of complementary DNA encoding T-cell replacing factor and identity with B-cell growth factor II. Nature (Loud.). 324 : Kofler, R., R. M. Perlmutter, D. J. Noonan, F. J. Dixon, and A. N. Theofilopoulus Ig heavy chain variable region gene complex of lupus mice exhibit normal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Exp. Med. 162 : Singer, P. A., R. J. McEvilly, R. S. Balderas, F. J. Dixon, and A. N. Theofilopoulos Tcell receptor a-chain variable-region haplotypes ofnormal and autoimmune laboratory mouse strains. Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA. 85: Kotzin, B. L., and E. Palmer The contribution ofnzw genes to lupus-like disease 17. in (NZB x NZW)F, mice. J. Exp. Med. 165 :1237. Muller, U.,V. Jongeneel, S. A. Nespasov, K. E Lindahl, and M. Steinmetz Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin genes map close to H-2D in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Nature (Lond). 325 :265.
J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: collagen disease, genetic polymorphism, MRL mice, recombinant inbred strains, Cd72. MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr MRL/ lpr
 Online publication June 24, 2009 1, 2 1 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 11 16 collagen disease, genetic polymorphism, MRL mice, recombinant inbred strains, Cd72 SNPs case-control study MHC Fcγ NO MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr
Online publication June 24, 2009 1, 2 1 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 11 16 collagen disease, genetic polymorphism, MRL mice, recombinant inbred strains, Cd72 SNPs case-control study MHC Fcγ NO MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
Single cell studies on the role of B-cell stimulatory factor 1 in
 Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 84, pp. 1389-1393, March 1987 Immunology Single cell studies on the role of B-cell stimulatory factor 1 in B-cell activation (cytokines/hapten-gelatin fractionation/t-cell
Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 84, pp. 1389-1393, March 1987 Immunology Single cell studies on the role of B-cell stimulatory factor 1 in B-cell activation (cytokines/hapten-gelatin fractionation/t-cell
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a group of genes that governs tumor and tissue transplantation between individuals of a species.
 Immunology Dr. John J. Haddad Chapter 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a group of genes that governs tumor and tissue transplantation between individuals
Immunology Dr. John J. Haddad Chapter 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a group of genes that governs tumor and tissue transplantation between individuals
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antigen processing: How are
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antigen processing: How are
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii. Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza
 Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
Autoimmune disease, including lacrimal gland inflammation,
 Th1 Versus Th2 Immune Responses in Autoimmune Lacrimal Gland Disease in MRL/Mp Mice Douglas A. Jabs, 1,2 Bella Lee, 1 Judith A. Whittum Hudson, 3 and Robert A. Prendergast 1 PURPOSE. In MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr
Th1 Versus Th2 Immune Responses in Autoimmune Lacrimal Gland Disease in MRL/Mp Mice Douglas A. Jabs, 1,2 Bella Lee, 1 Judith A. Whittum Hudson, 3 and Robert A. Prendergast 1 PURPOSE. In MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr
Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens
 Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
Antibodies and T Cell Receptor Genetics Generation of Antigen Receptor Diversity
 Antibodies and T Cell Receptor Genetics 2008 Peter Burrows 4-6529 peterb@uab.edu Generation of Antigen Receptor Diversity Survival requires B and T cell receptor diversity to respond to the diversity of
Antibodies and T Cell Receptor Genetics 2008 Peter Burrows 4-6529 peterb@uab.edu Generation of Antigen Receptor Diversity Survival requires B and T cell receptor diversity to respond to the diversity of
Course Title Form Hours subject
 Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
outbred colonies are stocks inbred colonies are strains 3/22/2012 Mouse strains 2.500
 Nomenclature for rodents Stock vs strain outbred colonies are stocks Kai Õkva inbred colonies are strains Outbred nomenclature First three letters reveal place where stock is maintained (Kuo) Followed
Nomenclature for rodents Stock vs strain outbred colonies are stocks Kai Õkva inbred colonies are strains Outbred nomenclature First three letters reveal place where stock is maintained (Kuo) Followed
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
Differential regulation of interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 gene
 Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 87, pp. 5283-5287, July 1990 Immunology Differential regulation of interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 gene expression: A comparison of T-cell gene induction by anti-cd3 antibody
Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 87, pp. 5283-5287, July 1990 Immunology Differential regulation of interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 gene expression: A comparison of T-cell gene induction by anti-cd3 antibody
Histocompatibility antigens
 Histocompatibility antigens Tuesday 09 November 2010 Telegraph UK Livers grown in the laboratory could eventually solve organ transplant shortage. Made-to-measure organs for transplantation are a step
Histocompatibility antigens Tuesday 09 November 2010 Telegraph UK Livers grown in the laboratory could eventually solve organ transplant shortage. Made-to-measure organs for transplantation are a step
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) - MHC molecules were initially discovered during studies aimed
CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) - MHC molecules were initially discovered during studies aimed
Association mapping (qualitative) Association scan, quantitative. Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall. Association scan, qualitative
 Association mapping (qualitative) Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Fig. 11.26 Association scan, qualitative Association scan, quantitative osteoarthritis controls χ 2 test C s G s 141 47
Association mapping (qualitative) Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Fig. 11.26 Association scan, qualitative Association scan, quantitative osteoarthritis controls χ 2 test C s G s 141 47
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH
 SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase
 6866 Med Genet 1991; 28: 686-690 Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene as an aid to the diagnosis of phenylketonuria L Kalaydjieva, B Dworniczak, C Aulehla-Scholz,M Devoto, G Romeo, M
6866 Med Genet 1991; 28: 686-690 Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene as an aid to the diagnosis of phenylketonuria L Kalaydjieva, B Dworniczak, C Aulehla-Scholz,M Devoto, G Romeo, M
LYMPHOCYTES & IMMUNOGLOBULINS. Dr Mere Kende, Lecturer SMHS
 LYMPHOCYTES & IMMUNOGLOBULINS Dr Mere Kende, Lecturer SMHS Immunity Immune- protection against dangers of non-self/invader eg organism 3 components of immune system 1 st line: skin/mucosa/cilia/hair/saliva/fatty
LYMPHOCYTES & IMMUNOGLOBULINS Dr Mere Kende, Lecturer SMHS Immunity Immune- protection against dangers of non-self/invader eg organism 3 components of immune system 1 st line: skin/mucosa/cilia/hair/saliva/fatty
HLA and antigen presentation. Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol
 HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
HLA and antigen presentation. Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol
 HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
Bachelor of Chinese Medicine ( ) AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
 Bachelor of Chinese Medicine (2002 2003) BCM II Dr. EYT Chan February 6, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 134 UPB AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES 1. Introduction Diseases may be the consequence of an aberrant immune response,
Bachelor of Chinese Medicine (2002 2003) BCM II Dr. EYT Chan February 6, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 134 UPB AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES 1. Introduction Diseases may be the consequence of an aberrant immune response,
The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SINGLE CHOICE. 5. The gamma invariant chain binds to this molecule during its intracytoplasmic transport. A TCR B BCR C MHC II D MHC I E FcγR
 A Name: Group: SINGLE CHOICE 1. Which is the most important ligand of TLR5? A endospore B flagellin C polysaccharide capsule D DNA E pilus 2. The antibody-binding site is formed primarily by... A the constant
A Name: Group: SINGLE CHOICE 1. Which is the most important ligand of TLR5? A endospore B flagellin C polysaccharide capsule D DNA E pilus 2. The antibody-binding site is formed primarily by... A the constant
Normal GC initiation then collapse; normal mutation and 10. Constitutive signalling leads to spontaneous GC in PP, even BCR -/- 19
 S1 Genetic modifications affecting germinal-centre formation and function Gene Compartment GC Phenotype Ref LTα, LTβ, TNF, Organ Disorganized lymphoid architecture in spleens; poor 1 TNFRI, LTβR architecture
S1 Genetic modifications affecting germinal-centre formation and function Gene Compartment GC Phenotype Ref LTα, LTβ, TNF, Organ Disorganized lymphoid architecture in spleens; poor 1 TNFRI, LTβR architecture
The Major Histocompatibility Complex
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex Today we will discuss the MHC The study of MHC is necessary to understand how an immune response is generated. And these are the extra notes with respect to slides
The Major Histocompatibility Complex Today we will discuss the MHC The study of MHC is necessary to understand how an immune response is generated. And these are the extra notes with respect to slides
Two categories of immune response. immune response. infection. (adaptive) Later immune response. immune response
 Ivana FELLNEROVÁ E-mail: fellneri@hotmail.com, mob. 732154801 Basic immunogenetic terminology innate and adaptive immunity specificity and polymorphism immunoglobuline gene superfamily immunogenetics MHC
Ivana FELLNEROVÁ E-mail: fellneri@hotmail.com, mob. 732154801 Basic immunogenetic terminology innate and adaptive immunity specificity and polymorphism immunoglobuline gene superfamily immunogenetics MHC
Basic Immunology. Lecture 5 th and 6 th Recognition by MHC. Antigen presentation and MHC restriction
 Basic Immunology Lecture 5 th and 6 th Recognition by MHC. Antigen presentation and MHC restriction Molecular structure of MHC, subclasses, genetics, functions. Antigen presentation and MHC restriction.
Basic Immunology Lecture 5 th and 6 th Recognition by MHC. Antigen presentation and MHC restriction Molecular structure of MHC, subclasses, genetics, functions. Antigen presentation and MHC restriction.
Dissection of Genetic Mechanisms Governing the Expression of Serum Retroviral gp70 Implicated in Murine Lupus Nephritis
 This information is current as of September 5, 2018. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Dissection of Genetic Mechanisms Governing the Expression of Serum Retroviral gp70 Implicated in Murine
This information is current as of September 5, 2018. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Dissection of Genetic Mechanisms Governing the Expression of Serum Retroviral gp70 Implicated in Murine
Brief Definitive Report
 Brief Definitive Report HUMAN T CELL LEUKEMIA/LYMPHOMA VIRUS I INFECTION AND SUBSEQUENT CLONING OF NORMAL HUMAN B CELLS Direct Responsiveness of Cloned Cells to Recombinant Interleukin 2 by Differentiation
Brief Definitive Report HUMAN T CELL LEUKEMIA/LYMPHOMA VIRUS I INFECTION AND SUBSEQUENT CLONING OF NORMAL HUMAN B CELLS Direct Responsiveness of Cloned Cells to Recombinant Interleukin 2 by Differentiation
Review Article Role of MHC-Linked Susceptibility Genes in the Pathogenesis of Human and Murine Lupus
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 584374, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2012/584374 Review Article Role of MHC-Linked Susceptibility Genes in the Pathogenesis of Human and Murine Lupus
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 584374, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2012/584374 Review Article Role of MHC-Linked Susceptibility Genes in the Pathogenesis of Human and Murine Lupus
Variation in the HindlII Restriction Fragments of DNA from the Chinese Tian Tan Strain of Vaccinia Virus
 J. gen. irol. (1985), 66, 1819-1823. Printed in Great Britain 1819 Key words: vaccinia virus~vaccine~restriction Jragrnent variation ariation in the Hindl Restriction Fragments of DNA from the Chinese
J. gen. irol. (1985), 66, 1819-1823. Printed in Great Britain 1819 Key words: vaccinia virus~vaccine~restriction Jragrnent variation ariation in the Hindl Restriction Fragments of DNA from the Chinese
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Genes
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Genes Topic 4 The Major Histocompatibility Complex Outline of Lectures The immunological reasons for transplant rejection How the MHC was discovered using inbred
The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Genes Topic 4 The Major Histocompatibility Complex Outline of Lectures The immunological reasons for transplant rejection How the MHC was discovered using inbred
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) and T Cell Receptors
 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) and T Cell Receptors Historical Background Genes in the MHC were first identified as being important genes in rejection of transplanted tissues Genes within the MHC
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) and T Cell Receptors Historical Background Genes in the MHC were first identified as being important genes in rejection of transplanted tissues Genes within the MHC
Immunopathogenesis of SLE and Rationale for Biologic Therapy
 Immunopathogenesis of SLE and Rationale for Biologic Therapy Peter Lipsky, MD Editor, Arthritis Research and Therapy Bethesda, MD Environmental Triggers, Gender, and Genetic Factors Contribute to SLE Pathogenesis
Immunopathogenesis of SLE and Rationale for Biologic Therapy Peter Lipsky, MD Editor, Arthritis Research and Therapy Bethesda, MD Environmental Triggers, Gender, and Genetic Factors Contribute to SLE Pathogenesis
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 08; 30 March 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P351-C1 / P352-D1 PKD1-PKD2 P351-C1 lot C1-0914: as compared to the previous version B2 lot B2-0511 one target probe has been removed and three reference probes have been replaced.
SALSA MLPA probemix P351-C1 / P352-D1 PKD1-PKD2 P351-C1 lot C1-0914: as compared to the previous version B2 lot B2-0511 one target probe has been removed and three reference probes have been replaced.
VARIATION IN THE MAJOR URINARY PROTEIN MULTIGENE FAMILY IN WILD-DERIVED MICE ABSTRACT
 Copyright 0 1985 by the Genetics Society of America VARIATION IN THE MAJOR URINARY PROTEIN MULTIGENE FAMILY IN WILD-DERIVED MICE BONNIE M. SAMPSELL AND WILLIAM A. HELD Department of Cell and Tumor Biology,
Copyright 0 1985 by the Genetics Society of America VARIATION IN THE MAJOR URINARY PROTEIN MULTIGENE FAMILY IN WILD-DERIVED MICE BONNIE M. SAMPSELL AND WILLIAM A. HELD Department of Cell and Tumor Biology,
heterozygous murine cell line
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 82, pp. 6600-6604, October 1985 Genetics Retroviral insertional mutagenesis of a target allele in a heterozygous murine cell line (proviral insertion/12-microglobulin gene/viral
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 82, pp. 6600-6604, October 1985 Genetics Retroviral insertional mutagenesis of a target allele in a heterozygous murine cell line (proviral insertion/12-microglobulin gene/viral
Supplementary note: Comparison of deletion variants identified in this study and four earlier studies
 Supplementary note: Comparison of deletion variants identified in this study and four earlier studies Here we compare the results of this study to potentially overlapping results from four earlier studies
Supplementary note: Comparison of deletion variants identified in this study and four earlier studies Here we compare the results of this study to potentially overlapping results from four earlier studies
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
T cell Receptor. Chapter 9. Comparison of TCR αβ T cells
 Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
IMMUNOGENETICS AND TRANSPLANTATION
 IMMUNOGENETICS AND TRANSPLANTATION WHAT S THE MHC GOT TO DO WITH TRANSPLANTATION? We have learned that the molecules of Class I and II MHC are involved in presenting antigenic peptides to the receptors
IMMUNOGENETICS AND TRANSPLANTATION WHAT S THE MHC GOT TO DO WITH TRANSPLANTATION? We have learned that the molecules of Class I and II MHC are involved in presenting antigenic peptides to the receptors
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Mon, Wed, Fri 11:00 AM-12:00 PM. Owen, Judy, Jenni Punt, and Sharon Stranford Kuby-Immunology, 7th. Edition. W.H. Freeman and Co., New York.
 Course Title: Course Number: Immunology Biol-341/541 Semester: Fall 2013 Location: HS 268 Time: Instructor: 8:00-9:30 AM Tue/Thur Dr. Colleen M. McDermott Office: Nursing Ed 101 (424-1217) E-mail*: mcdermot@uwosh.edu
Course Title: Course Number: Immunology Biol-341/541 Semester: Fall 2013 Location: HS 268 Time: Instructor: 8:00-9:30 AM Tue/Thur Dr. Colleen M. McDermott Office: Nursing Ed 101 (424-1217) E-mail*: mcdermot@uwosh.edu
Self-tolerance. Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens. Central Tolerance. Peripheral tolerance
 Autoimmunity Self-tolerance Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens Central Tolerance Peripheral tolerance Factors Regulating Immune Response Antigen availability Properties
Autoimmunity Self-tolerance Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens Central Tolerance Peripheral tolerance Factors Regulating Immune Response Antigen availability Properties
Chapter 17. Synthesis
 Chapter 17. Synthesis In this chapter I begin by describing three types of suppressor T cells called Ts1, Ts2, Ts3, two kinds of helper T cells called Th1 and Th2 cells, and an intriguing aspect of serum
Chapter 17. Synthesis In this chapter I begin by describing three types of suppressor T cells called Ts1, Ts2, Ts3, two kinds of helper T cells called Th1 and Th2 cells, and an intriguing aspect of serum
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. FOCiS. Lecture outline. Regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
A Proposal Concept of a Polygene Network in Systemic Vasculitis: Lessons from MRL Mouse Models Masato Nose 1
 Allergology International. 2007;56:79-86 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.r-0-10 REVIEW ARTICLE A Proposal Concept of a Polygene Network in Systemic Vasculitis: Lessons from MRL Mouse Models Masato Nose 1 ABSTRACT
Allergology International. 2007;56:79-86 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.r-0-10 REVIEW ARTICLE A Proposal Concept of a Polygene Network in Systemic Vasculitis: Lessons from MRL Mouse Models Masato Nose 1 ABSTRACT
Recent Developments in Immune Network Theory including a concept for an HIV Vaccine. Geoffrey W. Hoffmann
 Recent Developments in Immune Network Theory including a concept for an HIV Vaccine Geoffrey W. Hoffmann Network Immunology Inc. 3311 Quesnel Drive Vancouver, B.C. Canada V6S 1Z7 and Department of Physics
Recent Developments in Immune Network Theory including a concept for an HIV Vaccine Geoffrey W. Hoffmann Network Immunology Inc. 3311 Quesnel Drive Vancouver, B.C. Canada V6S 1Z7 and Department of Physics
The Human Immunoglobulin Heavy Variable Genes
 IMGT Locus on Focus Exp Clin Immunogenet 1999;16:36 60 Received: September 25, 1998 The Human Immunoglobulin Heavy Variable Genes Nathalie Pallarès a Sophie Lefebvre a Valérie Contet a Fumihiko Matsuda
IMGT Locus on Focus Exp Clin Immunogenet 1999;16:36 60 Received: September 25, 1998 The Human Immunoglobulin Heavy Variable Genes Nathalie Pallarès a Sophie Lefebvre a Valérie Contet a Fumihiko Matsuda
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
SEX. Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection. Sex: Sources of Genotypic Variation. Genetic Variation
 Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection Sex: Sources of Genotypic Variation Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin Genetic Variation If there is no genetic variation, neither
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection Sex: Sources of Genotypic Variation Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin Genetic Variation If there is no genetic variation, neither
Biphasic increase in circulating and renal TNF-a in MRL-lpr mice with differing regulatory mechanisms
 Kidney International, Vol. 47 (1995), pp. 122 13 Biphasic increase in circulating and renal TNF-a in MRL-lpr mice with differing regulatory mechanisms HITsHI YOKOYAMA,1 BURKHARD KREFT, and Viciu RUBIN
Kidney International, Vol. 47 (1995), pp. 122 13 Biphasic increase in circulating and renal TNF-a in MRL-lpr mice with differing regulatory mechanisms HITsHI YOKOYAMA,1 BURKHARD KREFT, and Viciu RUBIN
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
 Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Topic (Final-03): Immunologic Tolerance and Autoimmunity-Part II
 Topic (Final-03): Immunologic Tolerance and Autoimmunity-Part II MECHANISMS OF AUTOIMMUNITY The possibility that an individual s immune system may react against autologous antigens and cause tissue injury
Topic (Final-03): Immunologic Tolerance and Autoimmunity-Part II MECHANISMS OF AUTOIMMUNITY The possibility that an individual s immune system may react against autologous antigens and cause tissue injury
somatic cell hybrids (DNA polymorphism/multigene family/hormonally responsive genes/southern blot analysis)
 Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 79, pp. 1220-1224, February 1982 Genetics Mapping the structural genes coding for the major urinary proteins in the mouse: Combined use of recombinant inbred strains and
Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 79, pp. 1220-1224, February 1982 Genetics Mapping the structural genes coding for the major urinary proteins in the mouse: Combined use of recombinant inbred strains and
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection
 T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
Antigen Recognition by T cells
 Antigen Recognition by T cells TCR only recognize foreign Ags displayed on cell surface These Ags can derive from pathogens, which replicate within cells or from pathogens or their products that cells
Antigen Recognition by T cells TCR only recognize foreign Ags displayed on cell surface These Ags can derive from pathogens, which replicate within cells or from pathogens or their products that cells
The Adaptive Immune Response. T-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
Brief DeNnitive Report
 Published Online: 1 July, 1981 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.154.1.199 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 25, 2018 Brief DeNnitive Report VIRUS-SPECIFIC INTERFERON ACTION Protection of Newborn
Published Online: 1 July, 1981 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.154.1.199 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 25, 2018 Brief DeNnitive Report VIRUS-SPECIFIC INTERFERON ACTION Protection of Newborn
IMMUNOGENETICS AND INTRODUCTION TO TRANSPLANTATION
 IMMUNOGENETICS AND INTRODUCTION TO TRANSPLANTATION WHAT S THE MHC GOT TO DO WITH TRANSPLANTATION? We have learned that Class I and II MHC are involved in presenting antigenic peptides to the receptors
IMMUNOGENETICS AND INTRODUCTION TO TRANSPLANTATION WHAT S THE MHC GOT TO DO WITH TRANSPLANTATION? We have learned that Class I and II MHC are involved in presenting antigenic peptides to the receptors
Chapter 5. Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors
 Chapter 5 Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors Structural variation in Ig constant regions Isotype: different class of Ig Heavy-chain C regions are encoded in separate genes Initially, only two of
Chapter 5 Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors Structural variation in Ig constant regions Isotype: different class of Ig Heavy-chain C regions are encoded in separate genes Initially, only two of
Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis Biol 405 Molecular Medicine PKU a history In 1934 Følling identified a clinical condition - imbecillitas phenylpyruvica. Mental retardation associated with this
Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis Biol 405 Molecular Medicine PKU a history In 1934 Følling identified a clinical condition - imbecillitas phenylpyruvica. Mental retardation associated with this
The Generation of Specific Immunity
 The Generation of Specific Immunity Antibody structure! Antibodies classified by specificity (antigen, binding site) and class (general structure, function)! Differences in variable regions produce different
The Generation of Specific Immunity Antibody structure! Antibodies classified by specificity (antigen, binding site) and class (general structure, function)! Differences in variable regions produce different
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
P450I I E 1 Gene : Dra I. Human Cytochrome Polymorphism and
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1992, 168, 113-117 Human Cytochrome Polymorphism and P450I I E 1 Gene : Dra I Susceptibility to Cancer FUMIYUKI VEMATSUHIDEAKI KIKUCHI*, MASAKICHI MOTOMIYA j', TATSUYA ABE j', CHIKASHI
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1992, 168, 113-117 Human Cytochrome Polymorphism and P450I I E 1 Gene : Dra I Susceptibility to Cancer FUMIYUKI VEMATSUHIDEAKI KIKUCHI*, MASAKICHI MOTOMIYA j', TATSUYA ABE j', CHIKASHI
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes ~ 4.6 -
 Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
alveolar macrophages (AMs) after 24 hours of in vitro culture in complete medium
 Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Post-meiotic transcription of phosphoglycerate-kinase 2 in mouse testes
 Bioscience Reports 5, 1087-1091 (i985) 1087 Printed in Great Britain Post-meiotic transcription of phosphoglycerate-kinase 2 in mouse testes Robert P. ERICKSON I, Alan M. MICHELSON 2, Michael P. ROSENBERG
Bioscience Reports 5, 1087-1091 (i985) 1087 Printed in Great Britain Post-meiotic transcription of phosphoglycerate-kinase 2 in mouse testes Robert P. ERICKSON I, Alan M. MICHELSON 2, Michael P. ROSENBERG
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Brief Definitive Report
 Brief Definitive Report HUMAN TCR-,y+/S', CD8+ T LYMPHOCYTES RECOGNIZE TETANUS TOXOID IN AN MHC-RESTRICTED FASHION BY DANUTA KOZBOR,* GIORGIO TRINCHIERI,* DIMITRI S. MONOS,$ MASAHARU ISOBE,* GIANDOMENICO
Brief Definitive Report HUMAN TCR-,y+/S', CD8+ T LYMPHOCYTES RECOGNIZE TETANUS TOXOID IN AN MHC-RESTRICTED FASHION BY DANUTA KOZBOR,* GIORGIO TRINCHIERI,* DIMITRI S. MONOS,$ MASAHARU ISOBE,* GIANDOMENICO
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Amplification of Rearranged c-abl Oncogenes in CML Blast Crisis
 Breakpoints on Chromosomes 9 and 22 in Philadelphia Chromosome-positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Amplification of Rearranged c-abl Oncogenes in CML Blast Crisis Steven J. Collins Department ofmedicine,
Breakpoints on Chromosomes 9 and 22 in Philadelphia Chromosome-positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Amplification of Rearranged c-abl Oncogenes in CML Blast Crisis Steven J. Collins Department ofmedicine,
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
CHAPTER 18: Immune System
 CHAPTER 18: Immune System 1. What are four characteristics of the specific immune system? a. b. c. d. 2. List the two main types of defense mechanisms and briefly describe features of each. 3. Give examples
CHAPTER 18: Immune System 1. What are four characteristics of the specific immune system? a. b. c. d. 2. List the two main types of defense mechanisms and briefly describe features of each. 3. Give examples
Generation of antibody diversity October 18, Ram Savan
 Generation of antibody diversity October 18, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #10 Slide 1 of 30 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 : Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
Generation of antibody diversity October 18, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #10 Slide 1 of 30 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 : Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
Brief Definitive Report
 Published Online: 1 May, 1988 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.167.5.1749 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 6, 2019 Brief Definitive Report VIRUS-TRIGGERED IMMUNE SUPPRESSION IN MICE CAUSED
Published Online: 1 May, 1988 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.167.5.1749 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 6, 2019 Brief Definitive Report VIRUS-TRIGGERED IMMUNE SUPPRESSION IN MICE CAUSED
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
IMGT Collier de Perles: the New Look for IgSF and MhcSF in IMGT
 IMGT Collier de Perles: the New Look for IgSF and MhcSF in IMGT Quentin Kaas and Marie-Paule Lefranc Laboratoire d ImmunoGénétique Moléculaire Université Montpellier, UPR CNRS 1142, IGH Institut Universitaire
IMGT Collier de Perles: the New Look for IgSF and MhcSF in IMGT Quentin Kaas and Marie-Paule Lefranc Laboratoire d ImmunoGénétique Moléculaire Université Montpellier, UPR CNRS 1142, IGH Institut Universitaire
Chapter 11. How Genes Are Controlled. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
[Some people are Rh positive and some are Rh negative whether they have the D antigen on the surface of their cells or not].
![[Some people are Rh positive and some are Rh negative whether they have the D antigen on the surface of their cells or not]. [Some people are Rh positive and some are Rh negative whether they have the D antigen on the surface of their cells or not].](/thumbs/95/122584877.jpg) Few things to add to agglutination subject: When you agglutinate red blood cells (hemagglutination) you cross link the antigens that are present on two adjacent red blood cells, and of course red blood
Few things to add to agglutination subject: When you agglutinate red blood cells (hemagglutination) you cross link the antigens that are present on two adjacent red blood cells, and of course red blood
The MHC and Transplantation Brendan Clark. Transplant Immunology, St James s University Hospital, Leeds, UK
 The MHC and Transplantation Brendan Clark Transplant Immunology, St James s University Hospital, Leeds, UK Blood Groups Immunofluorescent staining has revealed blood group substance in the cell membranes
The MHC and Transplantation Brendan Clark Transplant Immunology, St James s University Hospital, Leeds, UK Blood Groups Immunofluorescent staining has revealed blood group substance in the cell membranes
,8 Genes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients
 Anti-Ro(SSA) Autoantibodies Are Associated with T Cell Receptor,8 Genes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Mark Barton Frank,* Robert McArthur,*** John B. Harley,*** and Atsushi Fujisaku* *Arthritis
Anti-Ro(SSA) Autoantibodies Are Associated with T Cell Receptor,8 Genes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Mark Barton Frank,* Robert McArthur,*** John B. Harley,*** and Atsushi Fujisaku* *Arthritis
Systemic autoimmune nephritogenic components induce CSF-1 and TNF-c in MRL kidneys
 Kidney International, Vol. (997), pp. 99 CELL BIOLOGY - IMMUNOLOGY -_PATHOLOGY Systemic autoimmune nephritogenic components induce CSF- and TNF-c in MRL kidneys TAKASHI WADA, TAKERO NAITO, ROBERT C. GRIFFITHS,
Kidney International, Vol. (997), pp. 99 CELL BIOLOGY - IMMUNOLOGY -_PATHOLOGY Systemic autoimmune nephritogenic components induce CSF- and TNF-c in MRL kidneys TAKASHI WADA, TAKERO NAITO, ROBERT C. GRIFFITHS,
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Class I Ag processing. TAP= transporters associated with antigen processing Transport peptides into ER
 Antigen processing Class I Ag processing TAP= transporters associated with antigen processing Transport peptides into ER Proteosome degrades cytosolic proteins Large, multi-subunit complex Degrades foreign
Antigen processing Class I Ag processing TAP= transporters associated with antigen processing Transport peptides into ER Proteosome degrades cytosolic proteins Large, multi-subunit complex Degrades foreign
