Infection/Disease Control HEPATITIS CONTROL PROGRAM
|
|
|
- Prosper Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPERATING PROCEDURE NO Florida State Hospital Chattahoochee, Florida July 8, 2009 Infection/Disease Control HEPATITIS CONTROL PROGRAM 1. Purpose: To establish consistent surveillance, reporting, control and prevention practices for hepatitis. 2. Policy: Florida State Hospital shall have an effective Hepatitis Control Program that will enable the early detection of hepatitis and prevent disease transmission from one person to another. 3. Training Requirements: All Florida State Hospital employees will be trained on this operating procedure upon hire into the position during Worksite Education and by their supervisor each time the operating procedure is revised. 4. Reference: a. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals. b. Section 60K-5.031(2) of the State Personnel Rules of the Career Service System. c. Control of Communicable Diseases in Man, by the American Public Health Association. d. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Protection Against Viral Hepatitis: Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report Recommendations and Reports, February 9, 1990, Volume 39, No. RR-2. e. 29 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part Occupational Exposure to Bloodborne Pathogens Federal Register. f. Florida Administrative Code 38I-20, Safety and Health Standards g. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis C Virus Infection and HCV-Related Chronic Disease: Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, October 16, Volume 47, No. RR Definitions: a. Hepatitis--An inflammation of the liver, usually from a viral infection. This Operating Procedure supersedes: Operating Procedure , dated March 11, 2008 Office of Primary Responsibility: Quality Assessment and Planning/Infection Control Distribution: Florida State Hospital Computer Network Users
2 Operating Procedure July 8, 2009 b. Hepatitis B Carrier--An individual who carries the Hepatitis B Virus in the bloodstream and may be asymptomatic, but is capable of transmitting the infection to other susceptible individuals. c. HBsAG (Hepatitis B Surface Antigen)--An Australian antigen (HAA) which, when present in the bloodstream, is considered the marker for the presence of the Hepatitis B virus. d. H.B.I.G. (Hepatitis B Immune Globulin)--A sterile solution of human immunoglobulin used in providing passive immunization to individuals following exposure to Hepatitis B. e. Hepatitis B Vaccine (recombinant)--the recombinant vaccines are derived from HBsAg produced in yeast cells and are free of association with human blood or blood products. f. Anti-HBs (Antibody to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen)--The presence of anti-hbs in the serum indicates the person has had the Hepatitis B virus or has received the Hepatitis B Immune Globulin (HBIG) or the Hepatitis B Vaccine. g. Isolation Precautions--The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have developed new guidelines for isolation precautions in hospitals. The revised guidelines contain two tiers of precautions a) Standard and b) Transmission based. (1) Standard Precautions: Blends the major features of universal precautions, (blood and body fluid precautions) and body substance isolation into a single set of precautions to be used for the care of all persons in hospitals. The new Standard Precautions apply to blood, all body fluids, secretions, and excretions, except sweat, whether or not they contain visible blood; non intact skin; and mucous membranes. These precautions are designed to reduce the risk of transmission of both recognized and unrecognized sources of infection in hospitals. This new terminology, Standard Precautions, will be used in place of Universal Blood and Body Fluid Precautions. (2) Transmission-Based Precautions: Reduces the disease-specific precautions into three sets of precautions based on routes of transmission. These categories are designed for documented or suspected to be infected or colonized with highly transmissible or epidemiological important pathogens for which additional precautions beyond Standard Precautions are needed to interrupt transmission to others. The three (3) types of Transmission-Based Precautions include: (a) Airborne precautions reduce the risk of airborne transmission of infectious agents such as tuberculosis and varicella viruses. (b) Droplet precautions reduce the risk of transmission of agents such as meningitis, and rubella. (c) Contact precautions are used for persons known to have serious illnesses easily transmitted by direct contact such as herpes simplex, wound or skin infections. All three (3) types of Transmission Based Precautions may be used at one time when the multiple routes of transmission are suspected in a person. Transmission Based Precautions are always used in conjunction with Standard Precautions (Florida State Hospital Operating Procedure 153-8, Medical Isolation Precautions). 2
3 Operating Procedure July 8, 2009 h. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) or Barrier Equipment--Protective equipment is to be worn by employees as barriers to prevent possible exposure to blood/body fluids, secretions, excretions (except sweat), non-intact skin, and mucous membranes. 6. General Information: a. The number of hepatitis diseases caused by different virus continues to increase as research and testing methods improve. The three (3) major types of hepatitis are A, B, and C with D and E also being diagnosed (see Attachment 1). Appropriate laboratory studies are needed for an accurate diagnoses of hepatitis. b. An individual may be exposed when blood or body fluid from an infected person (either someone who presently has hepatitis or a carrier) comes in contact with blood, body fluid, or mucous membrane of an uninfected person. The six (6) principle modes of transmission are: (1) direct percutaneous exposure, such as needlesticks; (2) percutaneous exposure, such as bites, cuts, and abrasions; (3) exposure of broken skin or mucous membranes of the mouth or eye to blood or body fluids which contains the Hepatitis virus; (4) direct exposure of mucous membranes to infective saliva or semen, such as through sexual contact; and (5) indirect transfer of infective serum or plasma through environmental surfaces; (6) perinatal exposure. c. Individuals must be aware of the modes of transmission and the appropriate precautions to be taken to prevent transmission. The Centers for Disease Control s disease specific guidelines are followed at Florida State Hospital (refer to Florida State Hospital Operating Procedure 153-8, Medical Isolation Precautions). The guideline for hepatitis is Standard Precautions. Proper handwashing and having minimal contact with blood and blood contaminated secretions/excretions by using the appropriate barrier (PPE) is of utmost importance. 7. Procedures: a. Hepatitis Screening: Resident admissions will be tested for Hepatitis A, B, and C for baseline status, need for Hepatitis B vaccination and follow up medical evaluation. b. Suspected Hepatitis: (1) Residents with signs or symptoms of hepatitis are on Standard Precautions as are all residents. Appropriate laboratory testing will be conducted for an accurate diagnosis. 3
4 Operating Procedure July 8, 2009 (2) Unit medical physicians will evaluate the need for further restriction and/or medical isolation based on resident s condition and laboratory test results. (3) Residents requiring medical isolation for hepatitis and/or further diagnostic studies may be transferred to Unit 31. (4) Employees with suspected hepatitis will follow guidelines in Florida State Hospital Operating Procedure 153-9, Employee Health Services Program. c. Hepatitis A: (1) Residents with signs or symptoms of acute infection of Hepatitis A will be admitted to Unit 31. (2) Place resident in isolation using Transmission Based Precautions during the first two (2) weeks and until at least one (1) week after onset of jaundice. d. Hepatitis B/Hepatitis B Carrier: (1) Residents with signs or symptoms of acute infection of Hepatitis B will be referred to Unit 31 for evaluation. (2) Place resident on Transmission Based Precaution-Contact Transmission until resident has at least two (2) negative HBsAG (HAA) reports done at six (6) month intervals. (3) Residents who remain positive for HBsAG after clinical improvement will be considered carriers. Appropriate tests for liver function and hepatitis disease status will be done at six (6) month intervals or more frequently to determine whether antigenemia continues to persist. Residents are to be instructed regarding the disease process and modes of transmission with emphasis on eliminating further transmission. e. Preventive Treatment following possible exposure to Hepatitis: (1) Employee: Any employee who in the performance of job duties sustains a possible exposure to Hepatitis will report to the supervisor for immediate referral to the current Hospital Workers Compensation Provider. Unit Personnel will initiate the Resident/Employee Possible Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Report (Attachment 2). (2) Resident: Any resident who sustains a possible exposure to Hepatitis will be reported to the attending physician immediately. (a) Unit personnel will initiate the Resident/Employee Possible Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Report (Attachment 2). The physician will review the status of the resident exposed and take the appropriate action. The action taken will be based on the hepatitis status of the resident causing exposure and the resident exposed (Attachments 3, 4, and 5). (b) If the resident is to receive preventive treatment, it will be ordered by the attending physician and administered by the assigned nurse in the Unit. 4
5 Operating Procedure July 8, 2009 (c) Unit personnel will be responsible for the scheduling and administration of Hepatitis B vaccination injections for residents. (3) All Resident/Employee Possible Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Reports (Form 180) for residents and employees are to be completed and forwarded to the Office of Quality Assessment and Planning/Infection Control and Office Of Risk Managment within 48 hours following completion. (4) The Hospital Infection Control Nurse will review each exposure report form, assess action(s) taken and complete Section III. 8. Reporting Requirements: a. The occurrence or suspected occurrence of Hepatitis is considered dangerous to public health and is a Reportable Disease governed by Chapter 64D-3 of the Florida Statutes. b. Unit personnel will be responsible to report all cases or suspected cases of residents or employees clinically ill with Hepatitis immediately by telephone to the Hospital Infection Control Nurse. c. All resident confirmed positive HBsAg(HAA) reports received by the Laboratory will be telephoned upon receipt to the Hospital Infection Control Nurse and the resident s unit nurse/doctor. Written copies from the lab will follow in the mail. d. The Hospital Infection Control Nurse will be responsible to report any cases or suspected cases of residents or employees clinically ill with Hepatitis to the Hospital Health Care Medical Service Director, Hospital Clinical Director, and the Senior Human Service Program Administrator in the Office of Quality Assessment and Planning. e. The Hospital Infection Control Nurse shall be responsible to report all cases or suspected cases within 48 hours to the Gadsden County Health Officer. 9. Mandatory Employee Compliance: a. Any employee with signs or symptoms of being clinically ill with Hepatitis is required to comply with the work restriction requirements as outlined in established Florida State Hospital Operating Procedure 153-9, Employee Health Services Program. b. Any employee with a diagnosis of being clinically ill with Hepatitis must have evidence that he/she is no longer infectious before returning to work. c. A copy of approval for the employee to return to work is to be furnished to the Office of Quality Assessment and Planning/Infection Control, upon receipt in the employee s Unit/Department. (Signed original on file in Central Health Information Services) DIANE R. JAMES Hospital Administrator 6 Attachments 1. The ABC s of Hepatitis 2. Resident/Employee Possible Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Report (Form 180) 5
6 Operating Procedure July 8, Hepatitis B Preventative Treatment Algorithm 4. Post-Exposure Prophylaxis of HBsAg- Positive Exposures in Recipients of Hepatitis B. Vaccine 5. Hepatitis C Guidelines for Testing and Post Exposure Recommendations 6. Employee Consent for Treatment (Form 179) SUMMARY OF REVISED, ADDED, OR DELETED MATERIAL This operating procedure was revised with the following changes: deleted all references to Employee Health Clinic and inserted references to current Hospital Workers Compensation Provider; deleted employee Hepatitis B and C baseline testing in paragraph 7a(1); deleted High risk resident in paragraph 7a(2). deleted all reference to post exposure follow up by Employee Health Clinic in paragraph 7e(1)(b)-(f); deleted sentence stating Written copies from lab will follow. in paragraph 8c; added Form 180 and Office of Risk Management in paragraph 7e(3); updated attachments. 6
7 The ABC s of Hepatitis What is it? Incubation Period How is it Spread? Symptoms Treatment of Chronic Disease Vaccine Who is at Risk? Prevention Hepatitis A (HAV) HAV is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. It does not lead to chronic disease. 15 to 50 days. Average 30 days Transmitted by fecal/oral route, through close person to person contact or ingestion of contaminated food and water. May have no symptoms. Adults may have light stools, dark urine, fatigue, fever and jaundice. Not applicable. Two doses of vaccine to anyone over the age of two. Household or sex contact with an infected person or living in an area with HAV outbreak. Travelers to developing countries, homosexual men, and IV drug users. Immune Globulin or vaccination. Wash hands after going to the toilet. Clean surfaces contaminated with feces, such as changing tables. Hepatitis B (HBV) HBV is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. The virus can cause liver cell damage, leading to cirrhosis and cancer. 4 to 25 weeks. Average 8 to 12 weeks. Contact with infected blood, seminal fluid, and vaginal secretions. Sex contact, contaminated needles, tattoo/body piercing and other sharp instruments. Infected mother to newborn. Human bite. May have no symptoms. Some persons have mild flulike symptoms, dark urine, light stools, jaundice, and fever. Interferon is effective in up to 35-45% of those treated. Three doses may be given to persons of any age. Infant born to infected mother, having sex with infected persons or multiple partners, IV drug users, emergency responders and healthcare workers, homosexual men, and hemodialysis patients. Vaccination and safe sex. Clean up any infected blood with bleach/disinfectant and wear protected gloves. Do not share razors or toothbrushes. Hepatitis C (HCV) HCV is virus that causes inflammation of the liver. This infection can lead to cirrhosis and cancer. 2 to 25 weeks. Average 7 to 9 weeks. Contact with infected blood, contaminated IV needles, razors, tattoo/body piercing and other sharp instruments. Infected mother to newborn. It is not easily transmitted through sex. Hepatitis D (HDV) HDV is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. It only infects those persons with HBV. Hepatitis E (HEV) HEV is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. It is rare in the U.S. There is no chronic state. 4 to 26 weeks. 2 to 9 weeks. Average 40 days. Contact with infected blood, contaminated needles. Sexual contact with HDV infected person. Transmitted through fecal/oral route. Outbreaks associated with contaminated water supply in other countries. Same as HBV Same as HBV Same HBV Interferon is effective in 10-20% of those treated. Interferon with varying success. None None None Anyone who had a blood transfusion before 1990; healthcare workers, IV drug users, hemodialysis patients, infants born to infected mother, and multiple sex partners. Safe sex. Clean up spilled blood with bleach/disinfectant Wear gloves when touching blood. Do not share razors or toothbrushes IV drug users, homosexual men, and those having sex with a HDV infected person. Hepatitis B vaccine to prevent HBV infection. Safe sex. Not Applicable. Travelers to developing countries. Avoid drinking or using potentially contaminated water. Attachment 1 Operating Procedure
8
9 RESIDENT/EMPLOYEE POSSIBLE BLOOD/BODY FLUID EXPOSURE REPORT SECTION I: (COMPLETED BY UNIT/DEPARTMENT) DATE: TIME: UNIT/DEPARTMENT: WARD/POD: TYPE OF EXPOSURE: Bite Needle Stick Open Wound Mucous membrane/mouth Mucous membrane/eyes Sexual contact Other (specify) DESCRIPTION OF EXPOSURE: PREVIOUS HEPATITIS/HIV STATUS OF PERSON RECEIVING EXPOSURE: Name and Hospital Number: History of Hepatitis: Yes No History of HIV: Yes No Tested for Hepatitis: Yes No Tested for HIV: Yes No If Yes, Date/Results: If Yes, Date/Results: Rec d HBIG: Yes No Rec d HB Vaccine: Yes No Date Hep B vaccine Completed: Tested for Antibodies: Yes No Date/Results: PREVIOUS HEPATITIS/HIV STATUS OF PERSON CAUSING EXPOSURE: Name and Hospital Number: History of Hepatitis: Yes No History of HIV: Yes No Tested for Hepatitis: Yes No Tested for HIV: Yes No If Yes, Date/Results: If Yes, Date/Results: Rec d HBIG: Yes No Rec d HB Vaccine: Yes No Date Hep B vaccine Completed: Tested for Antibodies: Yes No Date/Results: SIGNATURE/PERSON COMPLETING SECTION I DATE ******************************************************************************************************************* SECTION II: (COMPLETED BY UNIT/DEPARTMENT FOR RESIDENT EXPOSURE; SUPERVISOR FOR EMPLOYEE EXPOSURES) TYPE TESTING/TREATMENT ORDERED SIGNATURE/PERSON COMPLETING SECTION II DATE ******************************************************************************************************************* SECTION III: (COMPLETED BY HOSPITAL INFECTION CONTROL NURSE) REPORT OF HOSPITAL INFECTION CONTROL NURSE SIGNATURE/PERSON COMPLETING SECTION III DATE INSTRUCTIONS: SECTION I: Completed by Unit/Department. If employee exposure, the employee should personally write the Description of Exposure, if resident exposure, the nurse or supervisor should complete the Description of Exposure. SECTION II: Completed by Unit Department if resident exposure; Supervisor if employee exposure. SECTION III: Completed by the Hospital Infection Control Nurse. GENERAL: Sections I and II are to be completed as soon as possible after exposure occurs. All completed forms are to be forwarded to the Office of Quality Assessment and Planning/Hospital Infection Control and Office of Risk Management within forty-eight (48) hours. Form 180, (Revised) Apr 09 Attachment 2 Office of Primary Responsibility: Quality Assessment & Planning/Infection Control Operating Procedure
10
11 HEPATITIS B EXPOSURE PREVENTIVE TREATMENT ALGORITHM EXPOSER AND EXPOSED KNOWN HEPATITIS STATUS EXPOSER AND/OR EXPOSED UNKNOWN HEPATITIS STATUS HAA NOT INDICATED STAT HAA NEEDED DETERMINE INDICATOR FOR TREATMENT EXPOSER POS. EXPOSED NEG. EXPOSER NEG. EXPOSED POS. EXPOSER NEG. EXPOSED NEG. EXPOSER POS. EXPOSED POS. TREAT EXPOSED TREAT EXPOSER NO TREATMENT NO TREATMENT PREVENTIVE TREATMENT REGIMEN FOR EXPOSURE HBIG (WITHIN 24 HRS. FOLLOWING EXPOSURE IF POSSIBLE AND NO LONGER THAN 7 DAYS PAST EXPOSURE) HEPATITUS B VACCINE - 3 DOSES 1st DOSE WITHIN 7 DAYS FOLLOWING HBIG 2nd DOSE ONE MONTH FOLLOWING 1st DOSE 3rd DOSE SIX MONTHS FOLLOWING 1st DOSE
12
13 POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS OF HBsAg-POSITIVE EXPOSURES IN RECIPIENTS OF HEPATITIS B VACCINE 3 Vaccine Doses Complete Vaccine Series Test for Anti-HBS Never Tested Known Responder Known Non- Responder Within Test for 1 year HBIGx1 Positive Negative Anti-HBs 1 year vaccine booster dose x1 No Treatment Complete HBIGx1 Test for vaccine Complete Anti-HBS series vaccine Positive Negative series Positive Negative No Treatment *Adequate anti-hbs-10 SRU by RIA or positive by EIA HBIGx1 vaccine booster dose x1 No Treatment Vaccine booster dose x1 1. Partially vaccinated persons (<3 doses): Test for anti-hbs; if adequate antibody levels are present, no HBIG is necessary and the vaccine series should be completed as scheduled. If anti-hbs is low or absent, the exposed person should be given a single dose of HBIG and complete the vaccine series as scheduled. 2. Fully vaccinated persons never tested for anti-hbs; if adequate antibody levels are present, no treatment is necessary. If anti-hbs is low or absent, give one dose of HBIG immediately and one booster dose of HB vaccine. 3. Fully vaccinated persons known to have developed adequate antibody: Retest for anti-hbs only if previous testing occurred more than one year ago; if adequate antibody levels are present, no treatment is necessary. If anti- HBs is found to be low or absent, give one booster dose of HB vaccine. 4. Fully vaccinated persons known to be non-respondent: If the exposed person has been fully vaccinated, but is know to have had low or absent anti-hbs on post-vaccination testing, give one dose of HBIG immediately and one booster dose of HB vaccine. Attachment 4 Operating Procedure
14
15 Hepatitis C Guidelines for Testing and Post Exposure Recommendations A. Recommendations for testing for Hepatitis C Residents should be tested for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection based on their risk for infection Persons who ever injected illegal drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago and do not consider themselves as drug users. Persons with selected medical conditions, including persons who received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987; persons who were ever on chronic (long-term) hemodialysis; and persons with persistently abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels. Prior recipients of transfusions or organ transplants, including persons who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested for HCV infection; persons who received a transfusion of blood or blood components before July 1992; and persons who received an organ transplant before July Residents/employees who should be tested routinely for HCV-infection based on a recognized exposure Healthcare, emergency medical, and public safety workers after needle sticks, sharps, or mucosal exposures (eye, mouth, nose) to HCV-positive blood. Children born to HCV-positive women. Residents who have exposure to mucosal exposure to HCV-positive blood ie: sexual contact, mucous membranes of eyes, mouth, genitals, assaultative behavior B. Postexposure follow-up of resident/employees for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection For the source, baseline testing for anti-hcv. For the person exposed to an HCV-positive source, baseline and follow-up testing including baseline testing for anti-hcv and ALT activity; and follow up testing for anti-hcv (e.g., at 4-6 months) and ALT activity. (If earlier diagnosis of HCV infection is desired, testing for HCV RNA may be performed at 4-6 weeks.) Confirmation by supplemental anti-hcv testing of all anti-hcv results reported as positive by enzyme immunoassay. Residents who have tested positive will be referred to the Gastroenterology Clinic. Employees will be advised to see their private physicians for evaluation. Immune globulin and antiviral agents are not recommended for postexposure prophylaxis to Hepatitis C. A vaccine is not available for Hepatitis C. Attachment 5 Operating Procedure
16
17 EMPLOYEE CONSENT FOR TREATMENT NAME WORK AREA SOCIAL SECURITY NUMBER WORK PHONE DATE OF BIRTH SEX RACE WEIGHT HOME ADDRESS HOME PHONE ALLERGIES MEDICATION GIVEN \ \ LOT NUMBER EXPIRATION DATE MANUFACTURER POSSIBLE ADVERSE REACTIONS (CHECK AREA THAT APPLIES) HEPATITIS B FEVER MALAISE HEADACHE DIZZINESS NAUSEA/VOMITING MYALGIA PAIN AT INJECTION SITE LOCAL INFLAMMATION H-BIG ANAPHYLAXIS INFLUENZA FEVER MALAISE GULLAIN-BARRE ANAPHYLAXIS ERYTHEMA INDURATION SORENESS TETANUS TOXOID FEVER CHILLS MALAISE FLUSHING ACHES URTICARIA PRURITUS TACHYCARDIA HYPOTENSION ANAPHYLAXIS I HAVE BEEN INFORMED ABOUT THE MEDICATION AND ALL QUESTIONS HAVE BEEN ANSWERED TO MY SATISFACTION. I CONSENT TO RECEIVE THE ABOVE MEDICATION. SIGNATURE OF EMPLOYEE DATE AND TIME WITNESS DATE AND TIME Attachment 6 Form 179, (Revised) Oct 92 Operating Procedure Office of Primary Responsibility: Quality Assessment & Planning/Infection Control
18
Blood Borne Pathogens. Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N.
 Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
Confirmed (Laboratory Tests) Serum positive for IgM anti-hbc or, hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg).
 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Hepatitis STARS Program. Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003
 Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments
 Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Bloodborne Pathogens. Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens. By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc.
 Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview
 Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training
 Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard. An Overview
 The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy. Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011
 HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Training Objectives. Provide a basic understanding of:
 Training Objectives Provide a basic understanding of: 1. Bloodborne pathogens (BBP) 2. Common modes of transmission of BBP 3. Methods to prevent transmission of BBP 4. Information to help school staff
Training Objectives Provide a basic understanding of: 1. Bloodborne pathogens (BBP) 2. Common modes of transmission of BBP 3. Methods to prevent transmission of BBP 4. Information to help school staff
HEPATITIS C, ACUTE CRUDE DATA. Number of Cases 5 Annual Incidence a LA County 0.05 California b 0.10 United States b 0.68 Age at Diagnosis Mean 38
 2016 Annual Morbidity Report HEPATITIS C, ACUTE a Rates calculated based on less than 19 cases or events are considered unreliable b Calculated from: CDC. Notice to Readers: Final 2016 Reports of Nationally
2016 Annual Morbidity Report HEPATITIS C, ACUTE a Rates calculated based on less than 19 cases or events are considered unreliable b Calculated from: CDC. Notice to Readers: Final 2016 Reports of Nationally
What is hepatitis? What is hepatitis A? How is it spread? What are the symptoms? How soon do symptoms appear? How is hepatitis A diagnosed?
 Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
EMPLOYEE HEALTH TABLE OF CONTENTS
 EMPLOYEE HEALTH TABLE OF CONTENTS PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT.2 REPORTING EMPLOYEE INFECTIONS...3 SUMMARY OF IMPORTANT RECOMMENDATIONS AND WORK RESTRICTIONS FOR PERSONNEL WITH INFECTIOUS DISEASES.4 HEPATITIS B
EMPLOYEE HEALTH TABLE OF CONTENTS PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT.2 REPORTING EMPLOYEE INFECTIONS...3 SUMMARY OF IMPORTANT RECOMMENDATIONS AND WORK RESTRICTIONS FOR PERSONNEL WITH INFECTIOUS DISEASES.4 HEPATITIS B
Bloodborne Pathogens
 Bloodborne Pathogens Session Objectives Identify bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) Understand how diseases are transmitted Risk of exposure Protecting yourself from exposure through prevention Responding appropriately
Bloodborne Pathogens Session Objectives Identify bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) Understand how diseases are transmitted Risk of exposure Protecting yourself from exposure through prevention Responding appropriately
Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective
 Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective Infectious A E Enterically transmitted Viral hepatitis NANB Serum B D F, G,? other C Parenterally transmitted Before the discovery of hepatitis A virus (HAV) and
Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective Infectious A E Enterically transmitted Viral hepatitis NANB Serum B D F, G,? other C Parenterally transmitted Before the discovery of hepatitis A virus (HAV) and
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK)
 POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C
 Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff Insert Nurse Name, Credentials Here Insert Organization Here This presentation was adapted from the Ohio Department of Health, School and Adolescent Health
Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff Insert Nurse Name, Credentials Here Insert Organization Here This presentation was adapted from the Ohio Department of Health, School and Adolescent Health
Infection Control in the School Setting. It s In Your Hands
 Infection Control in the School Setting It s In Your Hands What is an Infection? A condition resulting from the presence of, and invasion by, germs (microorganisms) For Infection to Occur an Organism Must:
Infection Control in the School Setting It s In Your Hands What is an Infection? A condition resulting from the presence of, and invasion by, germs (microorganisms) For Infection to Occur an Organism Must:
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BAY-ARENAC BEHAVIORAL HEALTH AUTHORITY POLICIES AND PROCEDURES MANUAL
 Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 5 PURPOSE To provide guidelines on the treatment and care of patients with Hepatitis. POLICY Hepatitis is an injury to hepatic cells and an inflammatory process in the liver. The major causes
PAGE 1 of 5 PURPOSE To provide guidelines on the treatment and care of patients with Hepatitis. POLICY Hepatitis is an injury to hepatic cells and an inflammatory process in the liver. The major causes
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification
 SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
Hepadnaviridae family (DNA) Numerous antigenic components Humans are only known host May retain infectivity for more than 7 days at room temperature
 Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
Hepatitis Case Investigation
 * indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
* indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
Blood Borne Pathogens
 Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
School Nursing and Health. Standard Precautions. (aka Universal Precautions)
 School Nursing and Health Standard Precautions (aka Universal Precautions) August 2016 1 Standard Precautions Occupational Safety and Health Administration Federal Law 29 CFR bloodborne Pathogens 1910.1030(g)(2)(i)
School Nursing and Health Standard Precautions (aka Universal Precautions) August 2016 1 Standard Precautions Occupational Safety and Health Administration Federal Law 29 CFR bloodborne Pathogens 1910.1030(g)(2)(i)
Infectious Disease Control Oi Orientation. Providence Health & Services
 Infectious Disease Control Oi Orientation ti Providence Health & Services Infection Control Who is at risk of infection & why? Exposures and Outcomes What tools do we use to reduce risk? Surveillance Analysis
Infectious Disease Control Oi Orientation ti Providence Health & Services Infection Control Who is at risk of infection & why? Exposures and Outcomes What tools do we use to reduce risk? Surveillance Analysis
Bloodborne Pathogens Training. IEA, Inc.
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing. Origins of Liver Science
 Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training
 Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Viral Hepatitis. Background
 Viral Hepatitis Background Hepatitis or inflammation of the liver can be caused by infectious and noninfectious problems. Infectious etiologies include viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Noninfectious
Viral Hepatitis Background Hepatitis or inflammation of the liver can be caused by infectious and noninfectious problems. Infectious etiologies include viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Noninfectious
COURSE DESCRIPTION. Copyright Information
 COURSE DESCRIPTION This continuing education course will review six types of hepatitis: Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D, Hepatitis E, and Hepatitis G. Information about symptoms, diagnosis,
COURSE DESCRIPTION This continuing education course will review six types of hepatitis: Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D, Hepatitis E, and Hepatitis G. Information about symptoms, diagnosis,
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM
 Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
OSHA INSERVICE. Tuberculosis and Bloodborne Pathogens
 OSHA INSERVICE Tuberculosis and Bloodborne Pathogens Tuberculosis Airborne contagious disease caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis How it is spread: TB Infection TB Disease TB bacteria
OSHA INSERVICE Tuberculosis and Bloodborne Pathogens Tuberculosis Airborne contagious disease caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis How it is spread: TB Infection TB Disease TB bacteria
Safety Tips from the WorkSafe People
 Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools
 Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
Environmental Health and Safety Offices BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 Environmental Health and Safety Offices BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Purpose! Reduce / eliminate exposure potential Comply with Ohio s Public Employment Risk Reduction Act (reference OSHA) 2! Exposure Determination!
Environmental Health and Safety Offices BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Purpose! Reduce / eliminate exposure potential Comply with Ohio s Public Employment Risk Reduction Act (reference OSHA) 2! Exposure Determination!
OVERVIEW OF PRESENTATION
 OVERVIEW OF PRESENTATION This training is required by the Texas Department of Health Ch. 96, Bloodborne Pathogen Control. Every employee of the district will be required to have some training on bloodborne
OVERVIEW OF PRESENTATION This training is required by the Texas Department of Health Ch. 96, Bloodborne Pathogen Control. Every employee of the district will be required to have some training on bloodborne
patients with blood borne viruses Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled Document Lead:
 CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS
 F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS page 1 Viral Hepatitis Pain in the stomach Skin and whites of the eyes turning yellow, also called jaundice Q: What are the types of viral hepatitis? A: Hepatitis A Q: What
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS page 1 Viral Hepatitis Pain in the stomach Skin and whites of the eyes turning yellow, also called jaundice Q: What are the types of viral hepatitis? A: Hepatitis A Q: What
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of Transmission for School Staff
 CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training.
 You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
2013 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS. Frostburg State University Frostburg, Maryland 21532
 2013 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Frostburg State University Frostburg, Maryland 21532 OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens 29 CFR 1910.1030 Our plan is Reviewed annually, or as necessary to reflect changes in technology,
2013 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Frostburg State University Frostburg, Maryland 21532 OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens 29 CFR 1910.1030 Our plan is Reviewed annually, or as necessary to reflect changes in technology,
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING
 ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard
 Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
Goldenrod Hills Community Action. Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR
 Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
Hepatitis B. What Is Hepatitis? What Are The Two Stages Of Hepatitis? Published on: 5 Oct 2010
 Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Infection Control Handout
 Modes of Transmission Contact Routes Direct Contact Transmission Indirect Contact Transmission Droplet Transmission Indirect contact contamination Clothes Soiled bed linen Personal care products Personal
Modes of Transmission Contact Routes Direct Contact Transmission Indirect Contact Transmission Droplet Transmission Indirect contact contamination Clothes Soiled bed linen Personal care products Personal
Hepatitis B is a virus that attacks the liver. It is highly infectious. Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
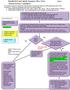 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Diane Lockman, Public Health Nurse. Marilyn Mitchell, Registered Nurse. Sue Mulhall, Public Health Nurse
 Diane Lockman, Public Health Nurse Marilyn Mitchell, Registered Nurse Sue Mulhall, Public Health Nurse Agenda Pre-evaluation Minimizing Your Risk Emergency Service Worker Exposures Scenarios Questions
Diane Lockman, Public Health Nurse Marilyn Mitchell, Registered Nurse Sue Mulhall, Public Health Nurse Agenda Pre-evaluation Minimizing Your Risk Emergency Service Worker Exposures Scenarios Questions
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens
 Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Bloodborne Pathogens. Exposure Control Plan
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Self-Instructional Packet (SIP)
 Self-Instructional Packet (SIP) Advanced Infection Prevention and Control Training Module 1 Intro to Infection Prevention Control February 11, 2013 Page 1 Learning Objectives Module One Introduction to
Self-Instructional Packet (SIP) Advanced Infection Prevention and Control Training Module 1 Intro to Infection Prevention Control February 11, 2013 Page 1 Learning Objectives Module One Introduction to
Bloodborne Pathogens. Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager. ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018
 Bloodborne Pathogens Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018 What s This About? Infectious microorganisms (viruses and diseases) found in blood and bodily
Bloodborne Pathogens Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018 What s This About? Infectious microorganisms (viruses and diseases) found in blood and bodily
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Universal Precautions
 Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees
 Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees Waynesboro Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training and Annual Review Created on May 5, 2010 Reviewed/Revised April 6, 2017 Introduction In an educational
Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees Waynesboro Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training and Annual Review Created on May 5, 2010 Reviewed/Revised April 6, 2017 Introduction In an educational
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update. Primary Causes of Chronic Liver Disease in the U.S. Hepatitis Definition. Hepatitis Viruses.
 Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Infection Prevention and Control - General Orientation
 Infection Prevention and Control - General Orientation Hand Hygiene-CDC Isolation Precautions - CDC Medical Waste - OSHA Environmental Cleaning - CDC Safe Injection Practices - CDC Bloodborne Pathogens
Infection Prevention and Control - General Orientation Hand Hygiene-CDC Isolation Precautions - CDC Medical Waste - OSHA Environmental Cleaning - CDC Safe Injection Practices - CDC Bloodborne Pathogens
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update JHS Annual Mandatory Education
 2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
Preventing Disease Transmission
 Chapter 4 Preventing Disease Transmission KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Describe how the immune system works. 2. Identify four ways in which diseases are transmitted, and give an example of how each can occur.
Chapter 4 Preventing Disease Transmission KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Describe how the immune system works. 2. Identify four ways in which diseases are transmitted, and give an example of how each can occur.
BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of transmission for school staff. for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood
 BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of transmission for school staff for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood MASSACHUSETTS DIVISION OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY Robert Prezioso,
BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of transmission for school staff for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood MASSACHUSETTS DIVISION OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY Robert Prezioso,
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Bloodborne Pathogens Training Lakeville Area Public Schools
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training Lakeville Area Public Schools Questions? Contact the District s Health & Safety Consultant Dan Fitch at IEA, Inc. 763-315-7900 dan.fitch@ieasafety.com OR District s Exposure
Bloodborne Pathogens Training Lakeville Area Public Schools Questions? Contact the District s Health & Safety Consultant Dan Fitch at IEA, Inc. 763-315-7900 dan.fitch@ieasafety.com OR District s Exposure
HEPATITIS HEPATITIS A. The Hepatitis Alphabet HOW DOES ONE GET HEPATITIS A? THE SYMPTOMS of HEPATITIS A
 HEPATITIS Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses, chemicals or drugs. The two most common types of viral hepatitis are Hepatitis A (also called infectious hepatitis ) and
HEPATITIS Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses, chemicals or drugs. The two most common types of viral hepatitis are Hepatitis A (also called infectious hepatitis ) and
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: OR: DO WE REALLY HAVE TO DO THIS AGAIN????
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: OR: DO WE REALLY HAVE TO DO THIS AGAIN???? YES THIS YEAR AND EVERY YEAR HEREAFTER REMEMBER: A REVIEW IS NEVER A BAD IDEA YOUR JOBS PUT YOU AT RISK THE DAY YOU KNOW EVERYTHING AND
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: OR: DO WE REALLY HAVE TO DO THIS AGAIN???? YES THIS YEAR AND EVERY YEAR HEREAFTER REMEMBER: A REVIEW IS NEVER A BAD IDEA YOUR JOBS PUT YOU AT RISK THE DAY YOU KNOW EVERYTHING AND
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1
 PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV. Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya.
 TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya. Nevada Hepatitis C Outbreak Tied to Las Vegas Clinic. Thousands Now At Risk for Hepatitis,
TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya. Nevada Hepatitis C Outbreak Tied to Las Vegas Clinic. Thousands Now At Risk for Hepatitis,
Blood borne Pathogen
 Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
May Safety Subject. Bloodborne Pathogens
 May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Biological Page
 Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.233 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide
Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.233 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide
C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官
 C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官 HCV:Structure and Classification Unclassified virus, Member of the flavivirus family (other members yellow fever and dengue) Enveloped single stranded RNA virus Humans
C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官 HCV:Structure and Classification Unclassified virus, Member of the flavivirus family (other members yellow fever and dengue) Enveloped single stranded RNA virus Humans
Gwynedd Mercy University Bloodborne Pathogen Safety and Awareness Training
 Gwynedd Mercy University Bloodborne Pathogen Safety and Awareness Training Education is the KEY Here are Gwynedd Mercy University, we recognize the importance of providing a safe working environment for
Gwynedd Mercy University Bloodborne Pathogen Safety and Awareness Training Education is the KEY Here are Gwynedd Mercy University, we recognize the importance of providing a safe working environment for
PENTUCKET REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT. Edited July 2014 by Kim Therrien
 PENTUCKET REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT Edited July 2014 by Kim Therrien This program meets the following guidelines: OSHA Standard of Bloodborne pathogens (29 CFR 1910.1030) Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne
PENTUCKET REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT Edited July 2014 by Kim Therrien This program meets the following guidelines: OSHA Standard of Bloodborne pathogens (29 CFR 1910.1030) Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne
Communicable Diseases. Detection and Prevention
 Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
B. Tasks and Procedures where employees, students or contractors can be exposed to bloodborne pathogens:
 Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A
 December 2011 Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Key Points Between 2000 and 2010, 209 cases of hepatitis A were reported in Hennepin County residents. This represents 30% of the cases reported
December 2011 Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Key Points Between 2000 and 2010, 209 cases of hepatitis A were reported in Hennepin County residents. This represents 30% of the cases reported
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Blood borne Diseases Blood borne pathogens are microorganisms carried by human blood and other body fluids. The two most common the hepatitis A, B (HBV), C and the human immunodeficiency
IMPORTANT INFORMATION Blood borne Diseases Blood borne pathogens are microorganisms carried by human blood and other body fluids. The two most common the hepatitis A, B (HBV), C and the human immunodeficiency
9/12/2018. Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatitis B Infection
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Hepatitis B and Hepatitis B Vaccine Adult Track Chapter 10 Photographs and images included in this presentation
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Hepatitis B and Hepatitis B Vaccine Adult Track Chapter 10 Photographs and images included in this presentation
Hepatitis B Control. Table of Contents
 Control Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 2.0 GOALS... 1 3.0 DEFINITIONS... 1 4.0 CASE MANAGEMENT... 3 5.0 HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT... 4 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS...
Control Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 2.0 GOALS... 1 3.0 DEFINITIONS... 1 4.0 CASE MANAGEMENT... 3 5.0 HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT... 4 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS...
