Innate lymphoid cells (ILC) in immunity. Marco Colonna Washington University in St Louis
|
|
|
- Millicent Shavonne Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Innate lymphoid cells (ILC) in immunity Marco Colonna Washington University in St Louis
2 Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILC) before 2009: Natural killer cell (NK) Inhibitory Receptor CD43 CD27 CD11b CD11c lo Activating Receptor NK1.1 + NKp46 CD94/NKG2x Ly49 Lymphoid tissue inducer cell (LTi) IFN-γ TNF-α GM-CSF CCL4 Perforin Granyzmes CD127 Id2 Rorγt CD4 α4β7 c-kit RET LTα 1 β 2 CXCL13 CCL21 CCL19 VCAM1 ICAM1 MADCAM1 IL-7 Cytotoxicity Lymphoid organogenesis
3 Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILC) after 2009 IL-15 IL-12 IL-18 NK ILC1 IFN-γ Intracellular pathogens autoimmunity IL-23 IL-1β ILC3 LTi IL-22 IL-17 (IFN-γ) Lymphoid organogenesis Extracellular bacteria fungi autoimmunity IL-25 IL-33 TSLP ILC2 IL-5 IL-9 IL-13 Amphiregulin Helminth Allergies Asthma
4 Functional modules of CD4 Th cells Inducing cytokines TF Effector cytokines Functional properties IFNγ + IL-12 T H 1 Tbet/ STAT4 IL-2, IFN-γ Phagocytic Intracellular pathogens Autoimmunity Naïve CD4 T cell IL-4 TGF-β IL-6 IL-1, IL-23 TGF-β T H 2 GATA3/ STAT6 T H 17 RORγT T Reg FOXP3 IL-4, IL-5 IL-13, Amphiregulin IL-17a/f, IL-22, IL-21 IL-10,TGFβ, IL-35 Mucosal Barrier Acute Inflammatory Regulatory Helminths Allergy and asthma Extracellular bacteria, fungi Autoimmunity Immune tolerance Lymphocyte homeostasis Regulation of immune responses
5 Transcription factors and cytokines in ILC development αlp Cytolytic Helper NKp46 + ILC3
6 ILCs are tissue resident cells s Skin +fat ILC1 ILC1 cnk cell cnk cell ILC1 ILC1 ILC2 ILC2 ILC3 ILC3 cnk cell cnk cell CD4+ LTi CD4+ LTi like CD4- LTi CD4- LTi like ex- Rorgt ILC3 ex- Rorgt ILC3 NKp46 ILC3 NKp46 ILC3 ILC3 ILC3 LTi LTi like uterine NK uterine NK ILC2 ILC2 ILC1 ILC1 cnk cell cnk cell ILC3 ILC3 Rare: IEL ILC1 IEL ILC1 Small intestine Colon Salivary Glands Liver Lung trachea bronchi Brain Spleen Bladder urethra Kidney Heart Pancreas SG NK SG NK ILC2 ILC2 Tonsils ILC1 ILC1 cnk cell cnk cell ILC3 ILC3 Heart
7 Similarity of functional modules in innate and adaptive immunity T H 1 CD8/4T RM T H 2 T H 17 NK ILC1 ILC2 ILC3 IFN-γ IFN-γ IL-5 IL-13 IL-22 IL-17
8 NK cells have multiple receptors m157 MCMV Ly49H DNA damage dsdna breaks RAE MULT1 ULBP NKG2D MIC Target ICAM B7H6 NKp46 NKp30 NKp44 CD48 EBV 2B4 CRACC NTB-A DAP12 DAP10 integrins CD3ζ DAP12 SAP EAT-2 NK cell
9 NKp44 is expressed in the human tonsil Tonsil CD3 lymphocytes CD56 NKp44
10 CD56+NKp44+ cells are found in human oral and gastrointestinal mucosae Surface mucosa Lamina propria Crypt mucosa Peyer s patches NKp44 Cytokeratin-5 appendix
11 Similarity between human NKp44+ cells and TH17/TH22 Type IL-17/22 CD4 T cells IL-23R CCR6 TCR IL-1R NKp44+ cells Innate lymphoid cells type 3 (ILC3) IL-23R NKp44 CCR6 IL-1R STAT3 activation TH17 TH22 RORγt NF-κB adjuvant effect STAT3 activation NKp44 + RORγt NF-κB adjuvant effect IL-17 and/or IL-22 IL-22 Cella, Fuchs et al. Nature. 2009;457:722
12 IL-22 triggers epithelial cell secretion of antimicrobial peptides and chemokines Sonnenberg GF, Nat Immunol 2011 IL-22 protects from bacterial infections but excessive secretion can cause inflammation (psoriasis)
13 Hypothesis: ILC3 protect the intestinal mucosa from bacterial infections Antimicrobial peptides CXCL1 CXCL1 Antimicrobial peptides Antimicrobial peptides CXCL1 CXCL1 IL-22 IL-22 IL-22 IL-22 IL-22 CCR6 CCR6 IL-26 APC JAML NKp44 CCR6 CD96 GPA33 IL-23/IL-1 NKp44+ cells (ILC3) Cella, Fuchs et al. Nature. 2009;457:722
14 Cooperation between ILC3 and T cells Antimicrobial peptides IL-22 IL-22 IL-17 IL-22 ILC3 Rorγt Ahr Th17 Rorγt Ahr Ahr T-bet Th22 IL-23/IL-1 TGF-β IL-23 IL-6 Th0 IL-6 MΦ DC infection DC d0 Innate immune response d7 Adaptive immune response
15 Mouse models for understanding the function of ILC3 Genetic models: Rag-/- x γc-/- Antibody depletion in RAG-/- mice anti-nk1.1 in Rag-/- mice anti-cd90 (anti-thy1) in Rag-/- mice Use of antibodies in Rag-/- mice or Rag-/- x γc-/- will deplete the cell population in question but will also eliminate other populations as well Need of lineage-specific deletion mutants
16 Which transcription factors are required for ILC3 development? Jacob Lee
17 NKp44+ cells express the transcription factor AHR Retinoic acid-related Orphan Receptors Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
18 Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR): a sensor of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
19 AHR ligands include nutritional components Acidic ph
20 Endogenous AHR ligands Tryptophan metabolism
21 Can we target AHR to block the development of ILC3? Analysis of conditional Ahr-/- mice Chris Bradfield
22 ILC3 subsets in mouse small intestine Human IL-23 IL-1β NKp44+ RORγT NKp46 + Rorγt+ Mouse IL-22 IL-22 Extracellular bacteria fungi autoimmunity Lti-like Rorγt+ Lymphoid organogenesis
23 ILC3 subsets in mouse small intestine Human IL-23 IL-1β NKp44+ RORγT NKp46 + Rorγt+ Mouse IL-22 IL-22 Extracellular bacteria fungi autoimmunity Lti-like Rorγt+ Lymphoid organogenesis
24 Conditional Ahr-deficient mice Ahr fl/fl x Roγt-cre
25 AHR is required for ILC3 development αlp Notch NKp46 + ILC3 Ahr
26 ILC3-deficient mice Mice AHR f/f x RORγt-Cre AHR f/f x RORγt-Cre x TCRβδ-/- Affected cells ILC3 ILC3, T cells RORγt f/f x NKp46-Cre NKp46 + ILC3 RORγt f/f x NKp46-cre x TCRβδ-/- NKp46 + ILC3, T cells RORγt f/f x NKp46-cre x Rag1-/- NKp46 + ILC3, T cells, B cells
27 Are ILC3 important for intestinal homeostasis?
28 Intestinal lymphoid tissues Peyer s Patches Develop pre-natally Eberl, Nat Rev Immunol 2005 CD3 B220
29 Intestinal lymphoid tissues ILF Develop post-natally CP Eberl, Nat Rev Immunol 2005 cryptopatches CD90+(Thy1+) c-kit+ Lti-ILC Isolated lymphoid follicles B220+/CD11c+
30 ILC3-deficient mice lack cryptopatches and isolated lymphoid follicles WT ILC3-deficient CD90+ (Thy1+) clusters identifying CP are absent in Ahr-deficient mice Prenatal lymphoid tissues (Peyer s Patches) are conserved CD90+ (Thy1+) c-kit+ clusters identifying CP are absent in Ahr-deficient mice CD11c+B220+ clusters identifying ILFs are absent in Ahr-deficient mice Rodney Newberry Keely McDonald
31 Are ILC3 important in host response to pathogenic bacteria? Christina Song
32 Citrobacter rodentium infection C. rodentium is a natural mouse pathogen related to enteropathogenic E. coli The infection is restricted to the lumen of the intestine In B6 mice, C. rodentium infection initiates on the surface of caecal patches, peaks at d7-14 pi and is cleared by d21-28 pi. Mundy R et al. Cell Microbiol. 2005;7:1697
33 Host defense against C. rodentium infection depends on IL-22 Zheng Y, et al. Nat Med. 2008;14:282.
34 C. rodentium infection in the absence of ILC3 and T cells AHR f/f x RORγt-cre x TCRβ/δ ko (no ILC3, no T cells) vs AHR f/f x TCRβ/δ-/- (no T cells) no T cells no ILC3, no T cells
35 C. rodentium infection in mice lacking ILC3 only AHR f/f x RORγt-cre (no ILC3) vs AHR f/f ILC3 protect the gastrointestinal tract from bacterial infections Partial redundancy with T cells ctr no ILC3
36 Do ILC3 contribute to IBD? IL-23R STAT3
37 ILC3 worsen anti-cd40-induced colitis α-cd40 0 AHR f/f x RORγt-cre x TCRβ/δ ko (no ILC3, no T cells) vs AHR f/f x TCRβ/δ-/- (no T cells) Body weight after anti-cd40 5-7d
38 Colon length 7 days after anti-cd40 Naive Anti-CD40 (d7) T cell Ctrl (Ahrf/f x TCRbd-/-) T cell ILC3 RORγt-cre x Ahrf/f x TCRbd-/- T cell T cell T cell T cell ILC3 NKp46 + ILC3 RORγt-cre x Ahrf/f x TCRbd-/- RORγtf/f x NKp46-cre x TCRbd-/- Ctrl (Ahrf/f x TCRbd-/-) Cre Ctrl (RORγt-cre+ x TCRbd-/-)
39 ILC3: two-edged sword Induce the development of ILF but have no obvious role in containment of commensal microbiota Protect from C. rodentium infections together with T cells Promote inflammation in a model of IBD
40 Similarity of functional modules in innate and adaptive immunity T H 1 CD8T RM T H 2 T H 17 NK ILC1 ILC2 ILC3 IFN-γ IFN-γ IL-5 IL-13 IL-22 IL-17
41 Human tonsils harbor 2 major subsets of NKp44 + ILCs Produce IL-22 upon stimulation with IL-23 NKp44 + ILC3 FL2-H: NKp44.PE NKp Localized within tonsil surface and crypt epithelium Secrete IFN-γupon stimulation with IL-12 + IL-15 Limited cytolytic capacity FL1-H: CD103.FITC CD103 Gated on CD56+ Anja Fuchs
42 Intraepithelial CD103 + ILC1 are present in human gastrointestinal tract Gated on CD45+CD3- lymphocytes Human appendix
43 Increased CD103 + ILC1 frequencies in the ileum of individuals with Crohn s disease NKp44 + CD103 + in IEL Gated on CD45+CD3- lymphocytes Ratio NKp44+CD103+ / CD3+ within IEL CD * NC Human appendix
44 NK cells or distinct ILC subset? FL2-H: NKp44.PE NKp CD103 FL1-H: CD103.FITC
45 Unique integrin pattern (VLA1+, CD103/Beta7+) NKp44+CD103+ ILC3 NKp44-(conventional NK)
46 Unique features: TGF-beta imprinting CD103 NKp44+CD103+ ILC3 NKp44-(conventional NK)
47 Similarity with Tissue Resident Memory CD8 T cells (T RM ) Memory RECIRCULATE T EM Home to peripheral tissue Pathogen Naive Intraepithelial Effector NKp44+CD103+ are tissue-resident ILC1 T CM Home to secondary lymphoid organs T RM Retained in peripheral tissues
48 Salivary gland NK cells are very similar to intestinal intraepithelial ILC1 Victor Cortez
49 NK cells vs ILC1 Recirculating Tissue resident NK IEL ILC1 uterus Liver ILC1 BM, spleen, LN, silp Intestinal epithelium also SG also silp and skin VLA2 positive negative positive* negative VLA1 negative positive positive positive TRAIL negative positive positive positive CD127 negative dim negative positive* IL-15 Dependent Partially independent Dependent Dependent Tbet Dependent Dependent Dependent Dependent Eomes Dependent Independent Independent Independent Nfil3 Partially independent Dependent Independent Dependent
50 Heterogeneity of ILC αlp iel ILC1 lp ILC1 liver ILC1 spleen ILC1 ILCs are complex! CD4+ CD4- Ahr Notch Ahr NKp46 + ILC3 ILC1 (ex-rorgt)
51 Understanding ILC diversity Unique and shared transcriptional programs of mouse ILCs In collaboration with the Immgen Consortium Michelle Robinette
52 ILC classes and subsets NK ILC2 ILC1 ILC3
53 ILC subsets frequency ILC2 ILC1 ILC1 NK NK ILC3 ILC1 NK
54 Principal component analysis of NK cell and ILC diversity
55 ILC1 and NK cells are intermixed Hierarchical clustering of the top 10% differentially expressed genes
56 Heatmap of ILC2 unique transcripts ILC2 IL4 IL5 IL13 IL9 IL9R IL33R M2-like polarization Arginase 1 PPARγ Dgat2 Lpcat2
57 Heatmap of ILC3 (Lti-like) unique transcripts ILC3 Lti Neuropilin 1
58 NKp46+ILC3 share transcripts with Lti ILC3 but also ILC1 ILC2 Lti ILC3 ILC1 ILC3 Nkp46+
59 Signature Transcription Factors Broad: Id2, GATA3, Nfil3 Small intestine lamina propria ILC and NK share an intestinal gene signature Class-specific: Eomes, Tbet, GATA3, Rorgt signature for silp: Rora, Atf3, Nr4a1
60 ILC1 transcriptional profile is intermediate between NK cells and ILCs slsilpilc1 Core ILC signature
61 ILC core signature: CXCR6 CXCR6 deficiency has no impact on ILC frequencies but influences cytokine responses
62 Conclusions ILC2 express transcripts indicative of M2 polarization Neuropilin1 is defining marker of Lti ILC3 NKp46+ ILC3 may have functional plasticity and convert into ILC1 Intestinal ILC and NK share an intestinal gene signature probably reflecting environmental exposure There is a major functional overlap between ILC1 and NK cells A core signature for ILC distinct from NK: CXCR6, IL-7R, GLT of TCRγ, TMEM176a/b
63 Lab 2014 Aaron Rapaport Alex Barrow Michelle Robinette Christina Song Luisa Cervantes Barragan Marina Cella Renata Sesti Satoru Yoshita Susan Gilfillan Tom Hannan Yaming Wang Victor Cortez
64 Acknowledgements Jacob Lee (Merck) Rodney Newberry Keely McDonald Thadd Stappenbeck ImmGen Collaborators Katerine Rothamel Christophe Benoist Funding R01DE R21CA16719 University of Brescia William Vermi University Toronto Tak Mak Marseille Luminy Eric Vivier University of Wisconsin Chris Bradfield
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
RORγt and IL-17 Responses`
 Falk Workshop Mechanisms of Intestinal Inflammation October 10, 2007 and IL-17 Responses` Dan Littman HHMI, Skirball Institute New York University School of Medicine New paradigm for T Helper Cell Differentiation
Falk Workshop Mechanisms of Intestinal Inflammation October 10, 2007 and IL-17 Responses` Dan Littman HHMI, Skirball Institute New York University School of Medicine New paradigm for T Helper Cell Differentiation
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Micro 204 Innate Lymphocytes & Natural Killer Cells. Lewis L. Lanier
 Micro 204 Innate Lymphocytes & Natural Killer Cells Lewis L. Lanier lewis.lanier@ucsf.edu inkt cell Innate lymphoid cell Nature Reviews Immunology April 2009 Common Lymphoid Progenitor Ets1 NFil3 Eomes
Micro 204 Innate Lymphocytes & Natural Killer Cells Lewis L. Lanier lewis.lanier@ucsf.edu inkt cell Innate lymphoid cell Nature Reviews Immunology April 2009 Common Lymphoid Progenitor Ets1 NFil3 Eomes
Innate lymphoid cells in the initiation, regulation and resolution of inflammation
 Innate lymphoid cells in the initiation, regulation and resolution of inflammation Gregory F Sonnenberg 1 3 & David Artis 1 3 A previously unappreciated cell type of the innate immune system, termed innate
Innate lymphoid cells in the initiation, regulation and resolution of inflammation Gregory F Sonnenberg 1 3 & David Artis 1 3 A previously unappreciated cell type of the innate immune system, termed innate
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
IFNg. IFNg IL-5 IL-13 IL-17 IL-22. LTi NCR+ ILC3. IL-17 IL-22 IFNg
 Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD. Fiona Powrie
 Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD Fiona Powrie Translational Gastroenterology Unit Experimental Medicine Division Nuffield Dept of Clinical Medicine University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk
Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD Fiona Powrie Translational Gastroenterology Unit Experimental Medicine Division Nuffield Dept of Clinical Medicine University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012
 17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
CD4+ T Helper T Cells, and their Cytokines in Immune Defense and Disease
 CD4+ T Helper T Cells, and their Cytokines in Immune Defense and Disease Andrew Lichtman M.D., Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Intro to T cell mediated immunity
CD4+ T Helper T Cells, and their Cytokines in Immune Defense and Disease Andrew Lichtman M.D., Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Intro to T cell mediated immunity
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
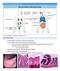 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein)
 Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the T H 17 cell it reg cell balance Rajatava Basu 1,5, Sarah K.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the T H 17 cell it reg cell balance Rajatava Basu 1,5, Sarah K.
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes
 Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
The Immune Response in Time and Space
 The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription (-) TLR2 PGN MDP. MyD88 IRAK ECSIT TRAF6 NIK. Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IKK.
 D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences
 The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease
 Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Micro 204 Innate Lymphocytes & Natural Killer Cells. Lewis L. Lanier
 Micro 204 Innate Lymphocytes & Natural Killer Cells Lewis L. Lanier lewis.lanier@ucsf.edu inkt cell Innate lymphoid cell Nature Reviews Immunology April 2009 Innate Lymphoid Cells ILC1 Common Lymphoid
Micro 204 Innate Lymphocytes & Natural Killer Cells Lewis L. Lanier lewis.lanier@ucsf.edu inkt cell Innate lymphoid cell Nature Reviews Immunology April 2009 Innate Lymphoid Cells ILC1 Common Lymphoid
Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection
 Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection Moriah J. Castleman, Ph.D. Laboratory of Dr. Cara Wilson University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection Moriah J. Castleman, Ph.D. Laboratory of Dr. Cara Wilson University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
D CD8 T cell number (x10 6 )
 IFNγ Supplemental Figure 1. CD T cell number (x1 6 ) 18 15 1 9 6 3 CD CD T cells CD6L C CD5 CD T cells CD6L D CD8 T cell number (x1 6 ) 1 8 6 E CD CD8 T cells CD6L F Log(1)CFU/g Feces 1 8 6 p
IFNγ Supplemental Figure 1. CD T cell number (x1 6 ) 18 15 1 9 6 3 CD CD T cells CD6L C CD5 CD T cells CD6L D CD8 T cell number (x1 6 ) 1 8 6 E CD CD8 T cells CD6L F Log(1)CFU/g Feces 1 8 6 p
T cell-mediated immunity
 T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
Innate Immunity in the Intestine
 Master s course in biomedical sciences Innate Immunity in the Intestine Dr. Kathy McCoy February 26 th, 2013 1 Host-Microbial Homeostasis: Innate Immunity Pharynx & upper respiratory tract ~1010 - Barriers
Master s course in biomedical sciences Innate Immunity in the Intestine Dr. Kathy McCoy February 26 th, 2013 1 Host-Microbial Homeostasis: Innate Immunity Pharynx & upper respiratory tract ~1010 - Barriers
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION. 1 hour between 8:30 a.m. - 10:00 a.m. McIntyre Medical Rm 504 (Martin Amphitheatre)
 GROUP (Version) 1 Annotated version April 8, 2011, RGEP DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION Course Coordinator: Dr. Roger Palfree Date: Thursday, March
GROUP (Version) 1 Annotated version April 8, 2011, RGEP DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION Course Coordinator: Dr. Roger Palfree Date: Thursday, March
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
CD4 + T-cell subsets in intestinal inflammation
 Matthew Shale Chris Schiering Fiona Powrie CD4 + T-cell subsets in intestinal inflammation Authors addresses Matthew Shale 1, Chris Schiering 1, Fiona Powrie 1,2 1 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology,
Matthew Shale Chris Schiering Fiona Powrie CD4 + T-cell subsets in intestinal inflammation Authors addresses Matthew Shale 1, Chris Schiering 1, Fiona Powrie 1,2 1 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology,
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
SUBDIVISIONS OF THE MUCOSA Distinct features of type I and type II mucosal surfaces
 Alessandra Pernis P&S 9-435 X53763 abp1@columbia.edu CHALLENGES FACED BY THE MUCOSAL SYSTEM SPECIALIZATION OF CELLS INVOLVED IN MUCOSAL IMMUNITY ORGANIZATION OF THE MUCOSAL IMMUNE SYSTEM CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Alessandra Pernis P&S 9-435 X53763 abp1@columbia.edu CHALLENGES FACED BY THE MUCOSAL SYSTEM SPECIALIZATION OF CELLS INVOLVED IN MUCOSAL IMMUNITY ORGANIZATION OF THE MUCOSAL IMMUNE SYSTEM CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Control of intestinal inflammation by regulatory T cells
 Control of intestinal inflammation by regulatory T cells Fiona Powrie Sir William Dunn School of Pathology University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk Regulatory T cells prevent immune pathology in
Control of intestinal inflammation by regulatory T cells Fiona Powrie Sir William Dunn School of Pathology University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk Regulatory T cells prevent immune pathology in
for six pairs of mice. (b) Representative FACS analysis of absolute number of T cells (CD4 + and
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1: Peripheral lymphoid organs of SMAR1 -/- mice have an effector memory phenotype. (a) Lymphocytes collected from MLNs and Peyer s patches (PPs) of WT and SMAR1
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1: Peripheral lymphoid organs of SMAR1 -/- mice have an effector memory phenotype. (a) Lymphocytes collected from MLNs and Peyer s patches (PPs) of WT and SMAR1
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Felix Yarovinsky. Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii
 Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
T Regulatory Cell and Body Tolerance
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 [5]:23-28 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 [5]:23-28 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
Chapter 13: Cytokines
 Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Gene+c fate mapping. x loxp. Foxp3 3 UTR ROSA26 RFP IRES GFP CRE. STOP loxp. Stable Foxp3 expression. Foxp3 expression in new Treg.
 1 Introduc+on (CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + )are indispensable for immune homeostasis. Muta+ons in Foxp3 gene leads to fatal autoimmune disorder. Condi+onal dele+on of Foxp3 reprograms cells into pathogenic Th
1 Introduc+on (CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + )are indispensable for immune homeostasis. Muta+ons in Foxp3 gene leads to fatal autoimmune disorder. Condi+onal dele+on of Foxp3 reprograms cells into pathogenic Th
Characterization of Il-22-Producing Cells in the Human Thymus and the Mechanism by Which Il-22 Expression Is Modulated by Thymic Epithelial Cells.
 Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Master's Theses Theses and Dissertations 2016 Characterization of Il-22-Producing Cells in the Human Thymus and the Mechanism by Which Il-22 Expression Is Modulated
Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Master's Theses Theses and Dissertations 2016 Characterization of Il-22-Producing Cells in the Human Thymus and the Mechanism by Which Il-22 Expression Is Modulated
Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas. Veronica Langenes
 Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas Veronica Langenes Department of Microbiology and Immunology Institute of Biomedicine The Sahlgrenska academy, University of Gothenburg
Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas Veronica Langenes Department of Microbiology and Immunology Institute of Biomedicine The Sahlgrenska academy, University of Gothenburg
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Relevant Disclosures
 6/18/215 Therapeutic developments for autoimmune demyelinating diseases: Musings from a MD (Mouse Doctor) Michael K. Racke, M.D. May 28, 215 Relevant Disclosures Editorial Boards for Journal of Neuroimmunology,
6/18/215 Therapeutic developments for autoimmune demyelinating diseases: Musings from a MD (Mouse Doctor) Michael K. Racke, M.D. May 28, 215 Relevant Disclosures Editorial Boards for Journal of Neuroimmunology,
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy
 Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Mucosal Immunology. Cathryn Nagler University of Chicago Department of Pathology/Committee on Immunology
 Mucosal Immunology Cathryn Nagler University of Chicago Department of Pathology/Committee on Immunology cnagler@bsd.uchicago.edu Mucosal surfaces are the major portals of entry for antigen Largest area
Mucosal Immunology Cathryn Nagler University of Chicago Department of Pathology/Committee on Immunology cnagler@bsd.uchicago.edu Mucosal surfaces are the major portals of entry for antigen Largest area
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis. Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany
 IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection. Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science
 Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
Gut Microbiota and IBD. Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI
 Gut Microbiota and IBD Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI 1393.3.1 2 GUT MICROBIOTA 100 Trillion Microbes - 10 times more than cells in our body Collective weight of about 1kg in human
Gut Microbiota and IBD Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI 1393.3.1 2 GUT MICROBIOTA 100 Trillion Microbes - 10 times more than cells in our body Collective weight of about 1kg in human
Diseases of Immunity CL Davis General Pathology. Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc
 Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 6 th Ed Veterinary Immunology,
Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 6 th Ed Veterinary Immunology,
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
Innate Immunity II. Integration. Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2
 Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Development of innate lymphoid cells
 I n n at e ly m p h o i d c e l l s Development of innate lymphoid cells Erin C Zook & Barbara L Kee Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are a family of immune effector cells that have important roles in host
I n n at e ly m p h o i d c e l l s Development of innate lymphoid cells Erin C Zook & Barbara L Kee Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are a family of immune effector cells that have important roles in host
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
This is the author s final accepted version.
 Joeris, T., Müller-Luda, K., Agace, W.W. and Mowat, A. M. (2017) Diversity and functions of intestinal mononuclear phagocytes.mucosal Immunology, 10(4), pp. 845-864. (doi:10.1038/mi.2017.22) This is the
Joeris, T., Müller-Luda, K., Agace, W.W. and Mowat, A. M. (2017) Diversity and functions of intestinal mononuclear phagocytes.mucosal Immunology, 10(4), pp. 845-864. (doi:10.1038/mi.2017.22) This is the
Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease
 Nature Reviews Immunology AOP, published online 22 April 2014; doi:10.1038/nri3661 REVIEWS Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease Markus F. Neurath Abstract Cytokines have a crucial role in the pathogenesis
Nature Reviews Immunology AOP, published online 22 April 2014; doi:10.1038/nri3661 REVIEWS Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease Markus F. Neurath Abstract Cytokines have a crucial role in the pathogenesis
Innate Lymphoid Cells in Immunity and Disease
 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Immunity and Disease 2 You Yi Hwang and Andrew N.J. McKenzie Abstract The family of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) comprises of natural killer (NK) cells, Ror g t-dependent ILCs
Innate Lymphoid Cells in Immunity and Disease 2 You Yi Hwang and Andrew N.J. McKenzie Abstract The family of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) comprises of natural killer (NK) cells, Ror g t-dependent ILCs
Following T-cell activation and differentiation with HTRF reagents: IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-17
 Following T-cell activation and differentiation with HTRF reagents: IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-17 4 th HTRF Symposium for Drug Discovery Avignon, Sept. 24-26, 28 Introduction: T-cells have effector and helper
Following T-cell activation and differentiation with HTRF reagents: IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-17 4 th HTRF Symposium for Drug Discovery Avignon, Sept. 24-26, 28 Introduction: T-cells have effector and helper
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System
 Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
The role of IL-22 produced by Th17 cells in Type 1 Diabetes
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository September 213 The role of IL-22 produced by Th17 cells in Type 1 Diabetes Stacey M. Bellemore The University of Western
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository September 213 The role of IL-22 produced by Th17 cells in Type 1 Diabetes Stacey M. Bellemore The University of Western
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Prof. Dr. David Voehringer
 Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Department of Infection Biology Institute of Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene Outline of the presentation The concept of type 2 immunity Basophil
Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Department of Infection Biology Institute of Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene Outline of the presentation The concept of type 2 immunity Basophil
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
NASPGHAN Physiology Education Series Immunology in the gastrointestinal tract
 NASPGHAN Physiology Education Series Immunology in the gastrointestinal tract Esi Lamousé-Smith, MD, PhD Morgan Stanley Children s Hospital of New York Columbia University enl2118@columbia.edu Content
NASPGHAN Physiology Education Series Immunology in the gastrointestinal tract Esi Lamousé-Smith, MD, PhD Morgan Stanley Children s Hospital of New York Columbia University enl2118@columbia.edu Content
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline Consensus characteristics/incidence data Immune/inflammatory basis Etiology/Genetic basis Hygiene
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline Consensus characteristics/incidence data Immune/inflammatory basis Etiology/Genetic basis Hygiene
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury
 Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Cytotoxic
Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Cytotoxic
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Nutrition & Gut Immunity
 Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Immune response to pathogens
 Bari, May 26, 2017 Immune response to pathogens Francesco Dieli Department of Biopathology and Medical Biotechnologies Central Laboratory of Advanced Diagnosis and Biomedical Research University of Palermo
Bari, May 26, 2017 Immune response to pathogens Francesco Dieli Department of Biopathology and Medical Biotechnologies Central Laboratory of Advanced Diagnosis and Biomedical Research University of Palermo
