Assembly. Lecture 11 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring Anatomy is des.ny. - - SIGMUND FREUD
|
|
|
- Trevor Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assembly Lecture 11 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2013 Anatomy is des.ny. - - SIGMUND FREUD 1
2 All virions complete a common set of assembly reac3ons * common to all viruses common to many viruses 2
3 The structure of a virus par3cle determines How it is formed How it enters a new cell How it replicates 3
4 A tale of two picornaviruses Poliovirus virions survive passage through the stomach to replicate in the gut: acid resistant capsid Rhinovirus virions are inacovated in the gut and only replicate in the respiratory tract: acid sensi3ve capsid 4
5 Despite varia3ons in structure and biological proper3es, all infec3ous virions must be METASTABLE Stable enough to survive in the wild Unstable enough to come apart during infecoon The assembly pathway is irreversible in the cell that makes the virions, but reversible in the uninfected cell receiving the virion 5
6 Produc3on of virus par3cles depends on host cell machinery Cellular proteins catalyze or assist the folding of individual protein molecules Transport systems move viral proteins and nucleic acids to and from sites of assembly Secretory pathway processes and moves viral membrane proteins Nuclear import and export machinery moves viral nuclear proteins and nucleic acid in and out of the nucleus 6
7 Concentra3ng components for assembly: Nothing happens fast in dilute solu1ons Viral components owen are concentrated so much that they are visible in the microscope (so- called factories or inclusions Non- enveloped viruses owen use internal membranes to concentrate proteins (poliovirus) Negri bodies (rabies virus) 7
8 Viral proteins achieve high concentra3ons by several methods Viral replicaoon and translaoon occur in a compartment ( factory or localized site) Localized producoon of viral proteins and protein- protein interacoons enable formaoon of independent sub- assemblies Local concentraoons of viral structural components can be boosted by lateral interac.ons between membrane- associated proteins (e.g. membrane patches ) 8
9 GeFng things to the right place 9
10 Viral proteins have addresses built into their structure Membrane proteins go to the appropriate membranes - Signal sequences, fa]y acid modificaoons Membrane proteins stay in the appropriate membranes - RetenOon signals Nuclear proteins go to the nucleus - Nuclear localizaoon sequences (NLS) Viral mrna or ribonucleoprotein complexes move into the cytoplasm - Nuclear export signals Capsids and protein complexes exhibit directed mooon, not diffusion - Microtubules and intermediate filaments are the tracks; dyneins, kinesins, myosins are the motors 10
11 Localiza3on of viral proteins to the nucleus Plasma membrane Golgi apparatus Ribosome Rough endoplasmic reticulum Py(VP1) 5 + VP2/3 Ad hexon kda Nucleus Nuclear envelope: Outer nuclear membrane Inner nuclear membrane Nuclear pore complex Mitochondrion Influenza virus NP Cytoskeleton: Intermediate filament Microtubule Actin filament bundle Extracellular matrix 11
12 Localiza3on of viral proteins to plasma membrane Other viral proteins Viral RNA Nascent viral protein Cell surface viral protein Golgi Transport vesicle Fusion Nucleus Microtubule Mitochondrion ER Cytoskeleton Extracellular matrix 12
13 Movement of VSV nucleocapsids in cytoplasm requires microtubules uclei are in blue. Courtesy of Asit Pattnaik, University of Nebra A B Box
14 Three strategies for making sub- assemblies 14
15 viral chaperone 15
16 Sequen3al capsid assembly: Poliovirus 16
17 Assembly intermediates and the assembly- line concept Assembly- line mechanisms ensure orderly formaoon of viral parocles and virion subunits FormaOon of discrete intermediate structures Can t proceed unless previous structure is formed: quality control 17
18 {sequenoal} Viral scaffolding proteins establish transient intermediate structures viral proteases packaged in these intermediate structures become acovated to finalize structure 18
19 Sequen3al Assembly Adenovirus genome packaged into a preformed shell in the nucleus 19
20 Self- assembly versus assisted assembly reac3ons Self- assembly - HIV capsid proteins can form empty shells - Influenza HA glycoprotein can bud and form virus- like parocles - HBV surface anogen can assemble into virus- like parocles Assisted assembly - Can t assemble on their own - Proteins and nucleic acid genomes are required as scaffolds or chaperones to form structure 20
21 Concerted Assembly Influenza virus parocles form by budding 21
22 22
23 23
24 Concerted Assembly Retrovirus parocles form by budding Mature release 24
25 A Extracellular domain Signal Signal sequence peptidase Fusion Transmembrane Cytoplasmic domain ALV Signal peptidase HIV Variable regions B B S S TM SU Fusion peptide Viral membrane 25
26 AddiOon of lipid to viral proteins allows targeong to membranes independent of signal sequence Viral proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasm, and modified with lipids post- translaoonally Also added - geranylgeranol (C20) or palmitate 26
27 Changes at the myristoylaoon sequence prevent interacoon of Gag with the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane Virus assembly and budding are inhibited 27
28 Genome packaging Viral genomes must be disonguished from cellular DNA or RNA molecules where assembly takes place Requires discriminaoon among similar nucleic acid molecules Example: retrovirus genomes <1% cytoplasmic RNA, yet is the RNA packaged in majority of retrovirus parocles DiscriminaOon is the result of packaging signals in the viral genome - sequences necessary for incorporaoon of nucleic acid into virions; geneocally defined 28
29 Packaging signals - DNA genomes Adenovirus Packaging signal near lew inverted repeat and origin Signal is complex: a set of repeated sequences; overlapping with enhancers that somulate late transcripoon Structure is recognized by viral protein IV2a (also a transcripoon acovator) 29
30 Herpesvirus genome replicaoon produces concatemers with head- to- tail copies of viral genome HSV- 1 packaging signals pac1 and pac2 needed for recognioon of viral DNA and cleavage within DR1 30
31 Packaging signals - RNA genomes 350 nt; necessary and sufficient env mrnas not packaged Necessary but not sufficient for HIV- 1 genome packaging 31
32 Packaging signals - RNA genomes NC of Gag mediates selecove encapsidaoon of genomic RNA during assembly Central region binds RNAs with Ψ sequences Structure of HIV- 1 NC bound to Ψ SL3 shows protein contacts with RNA 32
33 Packaging signals - RNA genomes Packaging limits - upper limit on size of viral nucleic acid that can be accommodated in icosahedral capsid or nucleocapsid; ~5-10% larger than viral genome Coupling of encapsidaoon of viral nucleic acid with its synthesis may contribute to specificity, e.g. poliovirus RNA replicaoon on membrane vesicles; no packaging signal idenofied in genome 33
34 Packaging of segmented genomes How to ensure that virions receive one copy of each segment? Random or selec.ve mechanisms for influenza virus (8 segments) cannot be disonguished Random mechanism would yield 1 infecoous parocle per 400 assembled - within the known parocle to pfu raoo If 12 segments are packaged, 10% of parocles would contain complete viral genome New evidence for specific packaging sequence on each RNA segment 34
35 Influenza virus RNA packaging h]p:// of- the- segmented- influenza- rna- genome/ 35
36 Selec3ve packaging Bacteriophage ϕ6-3 dsrna segments S, M, L S segment enters alone; entry of M depends on presence of S; entry of L depends on presence of S + L Serial dependence of packaging ParOcle:pfu raoo ~1 36
37 Acquisi3on of an envelope May follow assembly of internal structures (most enveloped viruses) May be simultaneous with assembly of internal structures (retroviruses) 37
38 Four budding strategies Envelope glycoproteins and capsid are essenoal for budding - alphaviruses Internal matrix or capsid proteins drive budding - retroviruses Envelope proteins drive budding - coronavirus Matrix proteins drive budding, but addioonal components (glycoproteins, RNP) needed for efficiency or accuracy 38
39 Internal structure assembly and budding spaoally & temporally separated 39
40 40
41 When synthesized alone, Gag directs budding of virus- like parocles Internal structure assembly and budding are coincident in space & Ome 41
42 Amino acid change in Gag cause arrest of budding at a late stage (late or L domains) Three different classes of L domains, found in + and - strand enveloped viruses L domains bind cell proteins, involved in vesicle trafficking, needed for virus release 42
43 L domain mo3fs 43
44 Involvement of the ESCRT machinery in three topologically equivalent types of membrane abscission 44
45 45
46 Exocytosis: reverse of endocytosis; used by viruses that assemble within vesicular compartments of the ER or Golgi Pathways of herpesvirus assembly and egress 46
47 The majority of viruses leave an infected cell by one of two general mechanisms Release from the cell by budding or lysis Movement from cell to cell 47
48 HIV- 1 infected T- cell Polarized release Of HIV from Infected T- cell Epithelial cell 48
49 Egress (exit) in vivo is a controlled process, ozen polarized Via apical surface places virus in the outside world (sneezing) Via basal surface of epithelial cells places virus in contact with blood, lymph, nerves (systemic spread, bad news) Can occur at sites of cell contact (lungs, gut, synapses) DirecOon and mode of egress influence pathogenesis 49
50 Polarized spread of infec3on by an alpha herpesvirus: Release from axon terminals and infec3on of epithelial cells in vitro Single Axon Purple: nuclei of epithelial cells Green: GFP expressing virus 50
51 Why do infected cells lyse? InhibiOon of cell macromolecular processes and transport ApoptoOc lysis Specific mechanisms - Adenovirus L3 protease cleaves intermediate filament proteins - Damages structural integrity of cell, facilitates virus release - Adenovirus glycoprotein required for cell lysis, mechanism not known 51
52 439 Intracellular Trafficking B Inhibition of secretion Induction of autophagy Endoplasmic reticulum Model for nonly3c release of poliovirus par3cles Transport vesicle Cytosolic contents Intermediate compartment Protein 3A Endosomal fusion cis Medial trans Golgi Lysosomal fusion 2BC 3A Lc3-pe Poliovirus polymerase Lamp-1/2 llular secretory pathway in poliovirus-infected cells. (A) Electron lls (left) and HeLa cells 5 h after poliovirus infection (right) preserved fected cell-specific vesicles can been seen in the infected cells. G, Golgi virus particles. The bars indicate 1 µm. Adapted from A. Schlegel with permission. Courtesy of Karla Kirkegaard, University of Colorado, 52
53 Extracellular virion matura3on Acidianus convivator virus, from acidic hot spring (ph 1.5, C) 53
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Overview of virus life cycle
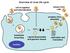 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Virus Entry/Uncoating
 Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued
 Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Molecular Trafficking
 SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis!
 Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
11/15/2011. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Viral Genomes. Structural Features and Characteristics
 Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2. Bacteriophages. 3. Animal Viruses. 4. Viroids & Prions
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
19 Viruses BIOLOGY. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Structural Features and Characteristics
 9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. What exactly is a Virus? 11/7/ Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2.
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
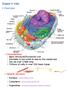 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222
 Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222 Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collec=on of ma>er that can live Cell structure is correlated to cellular
Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222 Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collec=on of ma>er that can live Cell structure is correlated to cellular
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION
 VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Cell Biology. A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division
 The Cell Cell Biology 1 A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division Tight connection with 1. Molecular biology 2. Biochemistry Cell theory 2 1838, 1839 Theodor Schwann
The Cell Cell Biology 1 A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division Tight connection with 1. Molecular biology 2. Biochemistry Cell theory 2 1838, 1839 Theodor Schwann
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, Please print your name: Instructions:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
AP Biology Reading Guide. Concept 19.1 A virus consists of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 19: Viruses Overview Experimental work with viruses has provided important evidence that genes are made of nucleic acids. Viruses were also important in working out
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 19: Viruses Overview Experimental work with viruses has provided important evidence that genes are made of nucleic acids. Viruses were also important in working out
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
Section 6. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section 6 Junaid Malek, M.D. The Golgi and gp160 gp160 transported from ER to the Golgi in coated vesicles These coated vesicles fuse to the cis portion of the Golgi and deposit their cargo in the cisternae
Section 6 Junaid Malek, M.D. The Golgi and gp160 gp160 transported from ER to the Golgi in coated vesicles These coated vesicles fuse to the cis portion of the Golgi and deposit their cargo in the cisternae
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES
 STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Coronaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Coronaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Spherical enveloped particles studded with clubbed spikes Diameter 120-160 nm Coiled helical
Coronaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Spherical enveloped particles studded with clubbed spikes Diameter 120-160 nm Coiled helical
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
2) What is the difference between a non-enveloped virion and an enveloped virion? (4 pts)
 Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses
 Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Viral reproductive cycle
 Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department
 Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222
 Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
BIOL*1090 Introduction To Molecular and Cellular Biology Fall 2014
 Last time... BIOL*1090 Introduction To Molecular and Cellular Biology Fall 2014 Lecture 3 - Sept. 15, 2014 Viruses Biological Membranes Karp 7th ed: Chpt. 4; sections 4-1, 4-3 to 4-7 1 2 VIRUS Non-cellular
Last time... BIOL*1090 Introduction To Molecular and Cellular Biology Fall 2014 Lecture 3 - Sept. 15, 2014 Viruses Biological Membranes Karp 7th ed: Chpt. 4; sections 4-1, 4-3 to 4-7 1 2 VIRUS Non-cellular
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral sizes and structures. Workbook Lesson 1.4
 Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses
 Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses 7:1 Viral Structure and Classification VIRUS: a biological particle composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protein coat CAPSID: protein coat surrounding a
Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses 7:1 Viral Structure and Classification VIRUS: a biological particle composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protein coat CAPSID: protein coat surrounding a
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Picornaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
19/06/2013. Viruses are not organisms (do not belong to any kingdom). Viruses are not made of cells, have no cytoplasm, and no membranes.
 VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Virus Entry. Steps in virus entry. Penetration through cellular membranes. Intracellular transport John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Virus Entry Steps in virus entry Penetration through cellular membranes Intracellular transport Steps in virus entry How do virions get into cells? Viruses of bacteria, archaea, algae and plants use different
Virus Entry Steps in virus entry Penetration through cellular membranes Intracellular transport Steps in virus entry How do virions get into cells? Viruses of bacteria, archaea, algae and plants use different
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
AP Biology. Viral diseases Polio. Chapter 18. Smallpox. Influenza: 1918 epidemic. Emerging viruses. A sense of size
 Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Virology Introduction. Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment.
 DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. PROTEIN SORTING. Lecture 10 BIOL 266/ Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S.
 PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Influenza viruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Influenza viruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped particles, quasi-spherical or filamentous Diameter 80-120 nm Envelope is derived
Influenza viruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped particles, quasi-spherical or filamentous Diameter 80-120 nm Envelope is derived
10/5/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells eye 100 mm (10 cm) Chicken egg aid n 10 mm
 Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Peroxisomes. Endomembrane System. Vacuoles 9/25/15
 Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
