Bone Loss Diseases & Imaging Considerations ( )
|
|
|
- Vivien Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jeana Fleitz, M.Ed., RT(R)(M) The X-Ray Lady 6511 Glenridge Park Place, Suite 6 Louisville, KY Telephone (502) Fax address xrayladyce@gmail.com website Bone Loss Diseases & Imaging Considerations ( ) 1. According to the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF), more than million Americans have osteoporosis. a. 15 b. 24 c. 30 d The World Health Organization (WHO) study group defined osteoporosis as a systemic skeletal disease characterized by all of the following, except: a. low bone mass b. increased bone fragility c. microarchitectual deterioration d. decrease in fracture susceptibility 3. It is estimated that in 2020 one in two Americans over the age of will have or be at risk of developing osteoporosis. a. 15 b. 21 c. 30 d The major organic component of bone is: a. calcium salts b. phosphorus c. sodium d. collagen 5. The skeleton contains % of the total calcium. a. 60 b. 75 c. 87 d The collagen protein content in bones is crucial for maintaining: a. flexibility b. porosity c. hardness d. growth
2 7. Nutrients from ingested foods are absorbed through the walls of the: a. esophagus b. stomach c. liver d. small intestines 8. The excrete excess calcium that is not absorbed. a. small intestines b. kidneys c. lungs d. liver 9. Osteoclasts are sensitive to blood levels and respond by increasing or decreasing activity levels. a. phosphorus b. magnesium c. calcium d. sodium 10. All of the following are true regarding cortical bone, except: a. is found in locations where bone compresses in a limited number of directions b. is more metabolically active than trabecular bone c. consists of dense tightly packed and aligned lamellar osteons d. is found in the skull and shaft of the femur 11. Trabecular bone is found in all of the following, except: a. the head of the femur b. vertebral spine c. calcaneus d. skull 12. Peripheral skeletal sites include all of the following, except: a. calcaneus b. forearm c. tibia d. vertebral spine 13. Peak bone mass is achieved between to years of age. a b c d
3 14. Peak bone mass is approximately % higher in men than in women. a. 45 b. 30 c. 25 d In bone remodeling, the process of destruction is known as: a. reversal b. resorption c. reduction d. restriction 16. The stage starts when osteoclasts become active on the surface of bone and create small cavities. a. activation b. resorption c. reversal d. quiescence 17. The stage occurs when bone-building osteoblasts fill cavities with new bone. a. activation b. resorption c. reversal d. formation 18. After the formation stage, the bone returns to, or a resting state. a. quiescence b. reversal c. resportion d. activation 19. About % of bone surfaces are normally at rest. a. 90 b. 80 c. 70 d All of the following are steps in normal regeneration of bone, except: a. osteoclasts attach to bone surface b. osteoclasts resorb more bone tissue and leave a deeper resorption cavity c. osteoblasts enter a cavity and build new bone d. the amount of bone formed is equal to bone resorbed 21. The most important action of calcitriol is to: a. increase intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus b. maintain blood calcium levels c. decrease excess testosterone and estrogen levels d. control the release of cortisol
4 22. The best bone design to withstand bending loads is referred to as the: a. center of axis rebound b. area moment of inertia c. dimensional apex of the shaft d. none of the above 23. The quantity and quality of the bone matrix content relates directly to and of bone. a. length and width b. age and length c. stiffness and strength d. fragility and resistance 24. Transient osteoporosis has been typically documented in: a. newborns b. adolescents c. young men d. women in the 3 rd trimester of pregnancy 25. Secondary osteoporosis occurs particularly in the decade of life. a. fourth b. fifth c. sixth d. seventh 26. According to the WHO and NOF, a bone mineral density (BMD) T-score of minus or below that of a young normal adult indicates osteoporosis. a. 0.5 b. 1.5 c. 2.0 d Researchers estimate that at least million men are considered to have low bone mass and osteoporosis. a. 2 b. 4 c. 8 d Doses as small as that equivalent to - milligram(s) (mg) of prednisone per day have been associated with fracture increase. a b c d
5 29. Methotrexate osteopathy in children often manifests as: a. osteopenia b. pathologic fracture c. dense provisional zones of calcification d. all of the above 30. According to the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, in the United States, nearly % of the population experience some problem that is associated with their consumption of alcohol. a. 2 b. 7 c. 11 d Linkage analysis is a gene-hunting technique that traces patterns of disease in high-risk families in an attempt to locate a disease-causing gene by identifying genetic markers. a. True b. False 32. Cystic fibrosis is more common among, and occurs at a rate of 1 in 3,300 births. a. Asians b. Hispanics c. Caucasians d. African-Americans 33. The overall prevalence of all types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome may be about 1 in births worldwide. a. 5 b. 50 c. 500 d. 5, Gaucher s disease is considered to be a/an disorder characterized by the accumulation of glucocerebrosides. a. infectious b. inherited metabolic c. inflammatory autoimmune d. circulatory and respiratory 35. Hypophosphatasia is characterized by: a. excessive urinary excretion b. skeletal anomalies c. poor bone mineralization d. all of the above
6 36. Osteogenesis imperfecta is caused by a genetic defect that impacts the body s production of: a. cortisol b. type 1 collagen c. insulin d. estrogen 37. Cystic fibrosis is a disease resulting from an autosomal recessive genetic defect causing a malfunction of the glands(s). a. exocrine b. pituitary c. adrenal d. thyroid 38. Both Klinefelter and Turner syndromes are associated with: a. hypotension b. hypervascularity c. depression and anxiety d. hypogonadism and delayed maturation 39. Turner s syndrome occurs in 1 out of every female births. a. 500 b. 1,500 c. 2,500 d. 5, Celiac disease or sprue is an inherited intestinal disorder in which intolerance to alters the body s ability to absorb certain nutrients. a. protein b. fats c. gluten d. fruits 41. Sickle cell disease is a group of genetic disorder affecting the: a. red blood cells b. white blood cells c. platelets d. bone marrow blastocytes 42. Individuals with sickle cell disease are resistant to: a. tuberculosis b. cat-scratch fever c. tularemia d. malaria
7 43. A fish vertebra deformity is characteristic of: a. torticollis b. acromegaly c. sickle cell disease d. Hurler s syndrome 44. All of the following are true regarding fibrous dysplasia, except: a. causes expansion of one or more bones b. results from abnormal development of the connective tissue in bone c. the most common site of involvement is the vertebrae d. the disease process does not spread from one bone to another 45. The combination of fibrous dysplasia, hormonal disturbances, and skin pigmentation is called disease. a. McCune-Albright b. McBurney c. Adkinson d. Parkinson 46. When both parents have an abnormal gene for osteopetrosis and pass it on to their offspring, the offspring will have osteopetrosis. a. early adulthood b. malignant infantile c. intermediate d. adult onset 47. The gland is often referred to as the master gland because it produces and secrets many hormones that travel throughout the body. a. pituitary b. thyroid c. pineal d. adrenal 48. Both Addison s disease and Cushing s syndrome are related to the gland. a. pituitary b. thyroid c. pineal d. adrenal 49. The function of cortisol is to help the body s response to stress by: a. maintaining blood pressure and cardiovascular function b. slowing the immune system s inflammatory response c. regulating the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats d. all of the above
8 50. Acromegaly is a chronic metabolic disorder caused by an excess of growth hormone usually resulting from a benign tumor on the gland: a. thyroid b. pituitary c. adrenal d. pineal 51. Growth hormone deficiency is believed to interfere with: a. acquisition and maintenance of bone mass b. a decrease in calcium absorption in the bowel c. an alteration in secretion of thyroid hormone d. increase in phosphorus uptake by bone 52. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is considered to be a/an type disease. a. infectious b. tropical c. hereditary d. inflammatory 53. Myeloma of bone primarily occurs in the: a. vertebral spine b. ribs and pelvis c. skull d. all of the above 54. According to the results of the Women s Health Initiative Observational Study, women with breast cancer have a % greater risk of fracture than the general population. a. 2 b. 5 c. 15 d According to a survey conducted by the WHO, up to % of all tuberculosis (TB) cases, worldwide is resistant to more than one anti-tuberculosis drug. a. 1 b. 4 c. 8 d The average age of onset of idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis (IJO) is years. a. 7 b. 15 c. 17 d. 19
9 57. Perthe s disease affects the in children. a. vertebral spine b. hip joints c. skull d. ribs 58. Bones affected by Paget s disease have a characteristic radiographic appearance that is sometimes described as: a. eggshell calcifications b. dense circular areas c. streaks of light d. cotton wool 59. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the leading cause of death in America. a. 2 nd b. 4 th c. 5 th d. 6 th 60. Fracture incidence in the United States is usually highest for : a. Caucasians b. African-Americans c. Asians d. Hispanics 61. FRAX algorithms give a year probability of a major fracture from osteoporosis. a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d A/An fracture occurs when a normal stress breaks a bone that is abnormal and deficient of elasticity. a. burst b. greenstick c. insufficiency d. fatigue 63. A symptomatic or asymptomatic vertebral fracture increases the risk of subsequent hip fracture by -fold. a. 1 b. 1.6 c. 2.3 d. 3.5
10 64. The greatest number of osteoporotic fractures in America are expected to occur in the: a. hip b. spine c. forearm d. proximal humerus 65. Scoliosis is defined as a persistent lateral curvature of the spine of more than degrees in the upright or standing position. a. 2 b. 4 c. 6 d The body of the 2 nd cervical fuses with the odontoid process by year(s) of age. a. 9 months to 1 b. 3 to 6 c. 8 to 12 d. 18 to The most prominent point of the thoracic spine corresponds to the spinous process of the thoracic vertebrae. a. 2 nd b. 7 th c. 9 th d. 12 th 68. The intervertebral foramina in the cervical spine region are best demonstrated by a/an: a. anterior-posterior (AP) projection b. posterior-anterior (PA) projection c. lateral position d. oblique position 69. Among the congenital vertebral anomalies, the most likely to cause neurological problems is: a. coronal cleft b. hemivertebrae c. butterfly vertebrae d. block vertebrae 70. A vertebra is usually caused by vascular insufficiency during fetal development and may affect one or more vertebrae. a. coronal cleft b. butterfly c. hypoplastic d. block
11 71. A limbus vertebra is a distinct type of: a. syndesmophyte b. disc herniation c. bone spur d. fracture 72. Bilateral symmetrical syndesmophytes in the vertebral spine may radiographically appear as: a. bamboo b. corduroy c. Napoleon s hat d. zones of sclerosis 73. The thyroid cartilage corresponds to cervical. a. 1 b. 3 c. 5 d The frequency of elementary acetabular fractures is greatest at the: a. anterior wall b. posterior wall c. posterior column d. transverse anterior column 75. The most sensitive imaging modality for the detection of occult pelvic insufficiency fracture is: a. conventional radiography b. computed tomography (CT) c. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) d. bone scintigraphy 76. Fractures of the bone account for 50-80% of all carpal bone fractures. a. lunate b. scaphoid c. capitate d. hamate 77. The least commonly fractured carpal bone is the: a. trapezium b. trapezoid c. scaphoid d. lunate
12 78. The medical record: a. documents the diagnosis b. is maintained for business purposes c. is a legal document d. all of the above 79. All of the following are true regarding scatter radiation, except: a. occurs during attenuation of the x-ray beam by the object being examined b. increases the radiation exposure of both the patient and the staff c. contributes to the diagnostic value of the radiographic image d. can be minimized by limiting the primary x-ray beam field size to the size of the film, thus reducing the amount of tissue with which the x-rays interact 80. A phenomenon called results in greater radiation intensity being emitted from the cathode side of the x-ray tube. a. reciprocity law b. anode heel effect c. line focus principle d. attenuation factor 81. The exposure factors of milliamperage and time are responsible for the radiographic: a. density b. contrast c. resolution d. detail 82. The controlling factor of radiographic contrast is: a. milliamperage b. kilovoltage c. exposure time d. source to image distance 83. Elongation and foreshortening can be minimized by proper: a. central ray alignment b. central ray entry and exit points c. alignment of the x-ray tube to the part and image receptor d. all of the above 84. The greatest advantage of digital imaging is that the steps of image recording, displaying, and archiving are decoupled, providing the technologist and radiologist the opportunity to optimize each task independently. a. True b. False
13 85. The American College of Radiology (ACR) suggests that CT evaluation of the cervical spine should have effective slice thickness no greater than mm. a. 1.5 b. 3.0 c. 5.5 d MR imaging used to characterize spine infection has a documented sensitivity of %. a. 96 b. 85 c. 75 d In skeletal scintigraphy, the radioactive uptake is greater in the axial skeleton. a. True b. False 88. The FRAX model accepts individuals between the ages of 40 and years. a. 60 b. 70 c. 80 d A family history of fracture is a stronger risk factor than any other bone fracture. a. vertebral spine b. hip c. wrist d. ankle 90. The NOF recommends BMD testing of: a. women age 65 and older b. men age 70 and older, regardless of clinical risk factors c. younger postmenopausal women and men age 50 to 69 years of age based on their clinical risk factors d. all of the above 91. According to the 1997 Bone Measurement Act, the frequency suggestions for BMD testing state that at least months must have passed since the last BMD was performed, except in certain cases of therapeutic monitoring. a. 6 b. 15 c. 23 d. 36
14 92. According to the ACR s Appropriateness Criteria, those procedures considered the most appropriate for a given clinical condition receive a rating of 9 on a scale of 1 to 9. a. True b. False 93. The first documented use of bone densitometry was in the field of: a. aviation b. dentistry c. obstetrics d. surgery 94. Ordinary x-ray techniques cannot detect less than % loss in bone mass. a. 5 b. 15 c. 20 d A quantitative computed tomography (QCT) study of the vertebral spine requires about 30 minutes with a radiation skin dose of - millirems. a b c d Quantitative ultrasonography (QUS) measurements include: a. attenuation b. velocity c. stiffness d. all of the above 97. Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) precision is usually documented to be 1% for the: a. total hip b. bilateral hips c. vertebral spine d. femoral neck 98. A trained technologist should perform DXA quality control procedures at least and always before the first patient measurement on the day performed. a. 3 days a week b. once every 3 weeks c. once a quarter d. every 6 months
15 99. All of the following structural changes or artifacts may detract from either accuracy or precision, or both, of the BMD measurement of the lumbar spine, except: a. facet scoliosis b. ingested calcium c. gas in the bowel d. abdominal aortic calcifications 100. All of the following are true regarding DXA examinations, except: a. certain examination tables may have maximum weight limitations b. the examination should not be performed if there is a possibility of pregnancy c. the patient may take their regular calcium supplements on the day of the examination d. patients who have undergone diagnostic testing with contrast media must wait at least 7 days before having a DXA examination 101. The preferred method for calculation of BMD is to average the BMD for the lumbar 1 to the lumbar area. a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d In a report released March 3, 2009, the National Council on Radiation Protection (NCRP), noted that in 2006, Americans were exposed to more than times as much ionizing radiation exposure as was the case in the early 1980s. a. 10 b. 7 c. 5 d The degree to which a diagnostic study accurately reveals the presence or absence of disease in a patient is diagnostic: a. expediency b. specificity c. efficacy d. sensitivity 104. According to the Executive Director of the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP), self-referral is a primary preventable driver of the dramatic increase in radiation exposure. a. True b. False 105. The concept of ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) encompasses all radiation safety measures, which as a whole minimize radiation dose. a. True b. False
16 106. Once the decision has been made to perform a diagnostic imaging procedure, the physician, radiologist, and the technologist further accept the responsibility for protecting the patient from unnecessary and excessive radiation exposure. a. True b. False 107. One of the most significant recommendations made by the ACR Blue Ribbon Panel concerns: a. providing in-service training for medical physicists b. recording radiation exposure doses for all imaging procedures c. providing oversight for medical residents ordering imaging studies d. adding relative radiation level designations to the imaging procedures listed in the ACR Appropriateness Criteria 108. According to the NCRP Report No. 116, the general public s annual effective radiation dose, exclusive of any exposure received as the result of medical procedures is limited to rem(s). a. 0.1 b. 0.5 c. 1.0 d The annual effective radiation dose limit for occupational radiation personnel is rem(s). a. 0.5 b. 5.0 c. 50 d According to the reference, NOF recommends that repeating BMD examinations generally agree with Medicare guidelines of, but recognizes that testing more frequently may be warranted in certain clinical situations. a. every 6 months b. once a year c. every 18 months d. every 2 years 111. During operation of the DXA scanner, those who should be allowed to remain in the examination room includes the patient and the technologist. a. True b. False 112. Wearing a radiation-monitoring device is voluntary unless the anticipated radiation exposure could be more than of the effective dose limit. a. 1/16 th b. 1/8 th c. 1/4 th d. ½
17 113. Because of the possibility of gastrointestinal disturbance, those taking bisphosphonate drugs should be instructed to stay fully upright for at least after taking the drug. a. 30 minutes b. 1 hour c. 4 hours d. 6 hours 114. A contraindication to both vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty procedures is: a. hypertension b. liver disease c. diabetes d. coagulation disorders 115. A major advantage of kyphoplasty is that the injection is able to: a. eliminate pain b. restore motion c. repair disc herniation d. restore height of the vertebral body 116. The time out required by the Universal Protocol for Preventing Wrong Site, Wrong Procedure, Wrong Surgery involves: a. the entire operative team b. uses active communication c. verification of required information on a checklist d. all of the above 117. The largest influx of calcium into the fetal skeleton occurs during the of pregnancy. a. first 2 weeks b. first month c. second trimester d. last trimester 118. Even when premature infants are fed a formula that provides additional calcium and phosphorus, it can take up to years for their bone mass to catch up with that of full-term newborns. a. 10 b. 7 c. 5 d. 3
18 119. The American Academy of Pediatrics has suggested that all infants who are exclusively breastfed receive international units (IU) of vitamin D daily to lessen the likelihood of developing rickets. a. 200 b. 100 c. 75 d In rickets and osteomalacia, the radiographic appearance of short, lucent lines that are seen at the lateral margin of the scapula and the medial femoral neck are called zones. a. Schatzki s b. Looser s c. Bright s d. Ewald s
Prevalence of Osteoporosis p. 262 Consequences of Osteoporosis p. 263 Risk Factors for Osteoporosis p. 264 Attainment of Peak Bone Density p.
 Dedication Preface Acknowledgments Continuing Education An Introduction to Conventions in Densitometry p. 1 Densitometry as a Quantitative Measurement Technique p. 2 Accuracy and Precision p. 2 The Skeleton
Dedication Preface Acknowledgments Continuing Education An Introduction to Conventions in Densitometry p. 1 Densitometry as a Quantitative Measurement Technique p. 2 Accuracy and Precision p. 2 The Skeleton
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES
 NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS ARRT BOARD APPROVED: JANUARY 2017 IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis
 Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Bone Densitometry. Total 30 Maximum CE 14. DXA Scanning (10) 7
 STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio
 Osteoporosis 1 Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio 1) Objectives: a) To understand bone growth and development
Osteoporosis 1 Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio 1) Objectives: a) To understand bone growth and development
Bone Mass Measurement BONE MASS MEASUREMENT HS-042. Policy Number: HS-042. Original Effective Date: 8/25/2008
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Osteoporosis Update (Reference revised 2012)
 Fleitz Continuing Education Jeana Fleitz, M.E.D., RT(R)(M) The X-Ray Lady 6511 Glenridge Park Place, Suite 6 Louisville, KY 40222 Telephone (502) 425-0651 Fax (502) 327-7921 Website www.x-raylady.com Email
Fleitz Continuing Education Jeana Fleitz, M.E.D., RT(R)(M) The X-Ray Lady 6511 Glenridge Park Place, Suite 6 Louisville, KY 40222 Telephone (502) 425-0651 Fax (502) 327-7921 Website www.x-raylady.com Email
The Bone Densitometry Examination
 The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
Bone Densitometry. What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)? Bone density scanning, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or bone densitometry, is an enhanced form of x-ray technology
Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)? Bone density scanning, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or bone densitometry, is an enhanced form of x-ray technology
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
To understand bone growth and development across the lifespan. To develop a better understanding of osteoporosis.
 Nutrition Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment t Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, OH. Objectives To understand bone growth and development across the lifespan.
Nutrition Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment t Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, OH. Objectives To understand bone growth and development across the lifespan.
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging
 Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Quantitative CT (QCT) Bone Mineral Densitometry Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Quantitative CT (QCT) Bone Mineral Densitometry Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007
Objectives: What is Osteoporosis 10/8/2015. Bone Health/ Osteoporosis: BASICS OF SCREENING, INTERPRETING, AND TREATING
 Bone Health/ Osteoporosis: BASICS OF SCREENING, INTERPRETING, AND TREATING TIFFANY PAUL, APN, CNP, CCD Objectives: Review the diagnosis of Osteoporosis Describe the basics of a bone density exam Identify
Bone Health/ Osteoporosis: BASICS OF SCREENING, INTERPRETING, AND TREATING TIFFANY PAUL, APN, CNP, CCD Objectives: Review the diagnosis of Osteoporosis Describe the basics of a bone density exam Identify
Bell Work. Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies.
 Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Bone Mineral Density Studies in Adult Populations
 Bone Mineral Density Studies in Adult Populations Last Review Date: July 14, 2017 Number: MG.MM.RA10aC6 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician
Bone Mineral Density Studies in Adult Populations Last Review Date: July 14, 2017 Number: MG.MM.RA10aC6 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative. International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011
 Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011 Slide 1-3 Topics to be covered: What is vertebral fracture assessment? How does VFA compare to standard
Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011 Slide 1-3 Topics to be covered: What is vertebral fracture assessment? How does VFA compare to standard
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
Bone Mineral Densitometry with Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
 Bone Mineral Densitometry with Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry R Gilles, Laurentius Ziekenhuis Roermond 1. Introduction Osteoporosis is characterised by low bone mass, disruption of the micro-architecture
Bone Mineral Densitometry with Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry R Gilles, Laurentius Ziekenhuis Roermond 1. Introduction Osteoporosis is characterised by low bone mass, disruption of the micro-architecture
Osteoporosis. Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease
 Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi
 DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
LUMBAR IS IT IMPORTANT? S. Tantawy,, M.D.
 بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم DEXA LATERAL LUMBAR IS IT IMPORTANT? By S. Tantawy,, M.D. Osteopenia,, bone mineral deficiency in the absence of fracture, is an indicator of the bone structural integrity and compared
بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم DEXA LATERAL LUMBAR IS IT IMPORTANT? By S. Tantawy,, M.D. Osteopenia,, bone mineral deficiency in the absence of fracture, is an indicator of the bone structural integrity and compared
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Bone Densitometry Equipment Operator
 Bone Densitometry Equipment Operator The purpose of the Bone Densitometry Equipment Operator Examination, which is made available to state licensing agencies, is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills
Bone Densitometry Equipment Operator The purpose of the Bone Densitometry Equipment Operator Examination, which is made available to state licensing agencies, is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend
 Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
nogg Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK
 nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of
 Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526)
 RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
Official Positions on FRAX
 196 96 DEPLIANT 3,5x8,5.indd 1 2010 Official Positions on FRAX 21.03.11 11:45 Interpretation and Use of FRAX in Clinical Practice from the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and International
196 96 DEPLIANT 3,5x8,5.indd 1 2010 Official Positions on FRAX 21.03.11 11:45 Interpretation and Use of FRAX in Clinical Practice from the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and International
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal Manifestations
 Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis
 Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
Building Bone Density-Research Issues
 Building Bone Density-Research Issues Helping to Regain Bone Density QUESTION 1 What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? Symptoms Bone Fractures Osteoporosis 1,500,000 fractures a year Kyphosis
Building Bone Density-Research Issues Helping to Regain Bone Density QUESTION 1 What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? Symptoms Bone Fractures Osteoporosis 1,500,000 fractures a year Kyphosis
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Understanding Osteoporosis
 Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Warm-Up Activity. Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram.
 Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Osteoporosis and Lupus. Andrew Ruthberg, MD University Rheumatologists
 Osteoporosis and Lupus Andrew Ruthberg, MD University Rheumatologists 1 Forget the medical terminology (osteoporosis, osteopenia, low bone mass, DEXA, DXA, T score etc) The bottom line is that you don
Osteoporosis and Lupus Andrew Ruthberg, MD University Rheumatologists 1 Forget the medical terminology (osteoporosis, osteopenia, low bone mass, DEXA, DXA, T score etc) The bottom line is that you don
Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource
 Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource Every year In the United States, 2.5 million fractures occur due to osteoporosis. Out of these, 330,000 are hip fractures, and half
Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource Every year In the United States, 2.5 million fractures occur due to osteoporosis. Out of these, 330,000 are hip fractures, and half
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Osteoporosis. When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of.
 Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Section 4. Scans and tests. How do I know if I have osteoporosis? Investigations for spinal fractures. Investigations after you break a bone
 Section 4 Scans and tests How do I know if I have osteoporosis? Investigations for spinal fractures Investigations after you break a bone Investigations if you have risk factors Investigations for children
Section 4 Scans and tests How do I know if I have osteoporosis? Investigations for spinal fractures Investigations after you break a bone Investigations if you have risk factors Investigations for children
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
created by high-voltage devices Examples include medical and dental x-rays, light, microwaves and nuclear energy
 What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
What is Osteoporosis?
 What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Bone Densitometry Pathway
 Bone Densitometry Pathway The goal of the Bone Densitometry pathway is to manage our diagnosed osteopenic and osteoporotic patients, educate and monitor the patient population at risk for bone density
Bone Densitometry Pathway The goal of the Bone Densitometry pathway is to manage our diagnosed osteopenic and osteoporotic patients, educate and monitor the patient population at risk for bone density
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention
 Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
LAB: The Skeletal System System
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name LAB: The Skeletal System System Background: The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are bone with more than 270 bones that
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name LAB: The Skeletal System System Background: The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are bone with more than 270 bones that
Section 1. What is osteoporosis? Your bones. Bones and osteoporosis. Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis
 4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist
 VOLUME 8, ISSUE 3, YEAR 2009 Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist Peter R. McNally, DO, FACP, FACG University Colorado at Denver, School of Medicine, Center for Human Simulation Series Introduction:
VOLUME 8, ISSUE 3, YEAR 2009 Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist Peter R. McNally, DO, FACP, FACG University Colorado at Denver, School of Medicine, Center for Human Simulation Series Introduction:
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie. Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis
 BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
In addition to bone health, emerging science reveals a non-skeletal benefit of vitamin D for several other health outcomes.
 Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
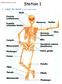 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Contractor Number 03201
 Local Coverage Article for Bone Mass Measurements Coverage - 2012 CPT Updates (A51577) Contractor Information Contractor Name Noridian Administrative Services, LLC opens in new window Contractor Number
Local Coverage Article for Bone Mass Measurements Coverage - 2012 CPT Updates (A51577) Contractor Information Contractor Name Noridian Administrative Services, LLC opens in new window Contractor Number
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It!
 The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Bone density scanning and osteoporosis
 Bone density scanning and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break
Bone density scanning and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break
Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients. Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist
 Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist Important Websites Resources for Clinicians and Patients www.nof.org www.iofbonehealth.org
Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist Important Websites Resources for Clinicians and Patients www.nof.org www.iofbonehealth.org
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
1
 www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Osteoporosis: Risk Factors, Diagnostic Methods And Treatment Options
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Academic Physician Assistants Volume 1 Number 1 Osteoporosis: Risk Factors, Diagnostic Methods And Treatment Options K Ihrke Citation K Ihrke.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Academic Physician Assistants Volume 1 Number 1 Osteoporosis: Risk Factors, Diagnostic Methods And Treatment Options K Ihrke Citation K Ihrke.. The Internet Journal of
Objectives. Discuss bone health and the consequences of osteoporosis on patients medical and disability status.
 Objectives Discuss bone health and the consequences of osteoporosis on patients medical and disability status. Discuss the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and major risk factors. Assess the major diagnostic
Objectives Discuss bone health and the consequences of osteoporosis on patients medical and disability status. Discuss the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and major risk factors. Assess the major diagnostic
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
