Answer Marks Guidance ( 11.3 ; ; 2 Correct answer = 2 marks even if no working shown. IGNORE - before the number
|
|
|
- Katherine McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) ( 11.3 ; ; 2 Correct answer = 2 marks even if no working shown. IGNORE - before the number If the answer is incorrect, ALLOW 1 mark for seeing ( ) x 100 or 0.31 x If the answer is not given to 1 decimal place, ALLOW 1 mark for A correct but unrounded answer ( , etc) or A correct answer that has been rounded to the wrong number or decimal places or A correct answer seen but has been rounded incorrectly (eg 11.2)
2 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) (i 4 max ACCEPT curve / lung function / amount of exhaled air, as AW for FEV non-smokers FEV higher than smokers ; ora smokers FEV, declines / falls / drops / decreases (over time) ; widening gap (between smokers and non-smokers) / rate of decline is lower in non-smokers / smaller reduction in non-smokers ; non smokers (FEV) increases then decreases / peaks ; non-smokers (curve / FEV / lung function) has peak at 1.5 years and 2.88 dm 3 ; appropriate figures to support mp 1-3 ; 1 DO NOT CREDIT FEV is higher at the start (alone) as this implies it is lower later on 2 IGNORE both decline 3 ACCEPT ora for decline and extent of reduction 6 Figures must include 2 FEVs with units linked to time in years and must support the point being made. 6 ALLOW valid calculated comparison 6 ALLOW comparative dates such as 2 years later
3 Time (years) FEV 1 (dm 3 ) had stopped smoking FEV 1 (dm 3 ) continue to smoke Acceptable range for difference Other useful figures: Increase over 1 ½ years for stopped smoking = 0.06 dm 3 Decrease over 1 ½ years for continue to smoke = dm 3 Decrease over from 1 ½ years to 5 years for stopped smoking = dm 3 Decrease over from 1 ½ years to 5 years for continue to smoke = dm 3 Decrease over 5 years for stopped smoking = dm 3 Decrease over 5 years for continuing smokers = 0.31 dm 3
4 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (b) ( causes 6 max 1 tar ; (cigarette smoke) destroys / damages / paralyses, cilia / ciliated epithelium ; (cigarette smoke stimulates) goblet cells to release more mucus ; mucus ( in airways), builds up / cannot be removed / AW ; more, pathogens / bacteria / viruses / microbes, collect / trapped / accumulate (in mucus) ; idea that cough is an attempt to, increase air flow / remove microbes, by removing mucus ; effects (frequent coughing) damages / inflames, (named) airway / alveoli / elastic fibres ; formation of scar tissue ; airway / bronchi / bronchiole, walls thicken ; lumen of, airway / bronchi / bronchiole, narrows ; flow of air restricted ; (damage to alveoli causes) reduced surface area for, gas exchange / oxygen diffusion ; 2 ALLOW in response to any component of cigarette smoke 2 DO NOT CREDIT kills cilia / cilia die 2 IGNORE cilia stick together 3 ALLOW in response to any component of cigarette smoke 3 Must contain the idea of more mucus than normal 5 IGNORE pathogens alone must have idea of increasing number of pathogens e.g. ACCEPT breeding multiplying /AW 5 ACCEPT higher number of pathogens present 5 ACCEPT infections more likely 6 There must be a reason for removing the mucus 6 ACCEPT to clear the throat by removing mucus 6 ACCEPT to reduce infections by removing mucus 7 IGNORE damage to lungs 7 IGNORE damage as a result of elastase / emphysema 8 CREDIT in any part of lung 9 IGNORE trachea 9 CREDIT smooth muscle (in wall) thickens 10 IGNORE trachea 11 airflow restricted due to extra smooth muscle = 2 marks, mp 9 and 11 QWC One cause of cough and one effect of cough 1 Award if at least 1 mark has been given from each of the mark scheme sections (1-6 and 7-11) for this question.
5 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (b) (i 2 max Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is correct and an additional answer is given that is incorrect or contradicts the correct answer then = 0 marks ACCEPT phonetic spellings emphysema ; IGNORE emphysemia chronic bronchitis ; asthma ; (iii) elastin is substrate ; (elastin / substrate) binds to / fits into, active site ; active site / enzyme / elastase / substrate / elastin, shape changes ; idea of closer fit (between active site and substrate) ; more bonds form (between substrate and active site) ; forms enzyme-substrate-complex / ESC ; idea that (change in shape of active site) destabilises / weakens, bonds (in substrate) / substrate ; activation energy reduced ; idea of further shape change of, active site / enzyme, after products form ; 5 max 1 Must be a clear statement 2 IGNORE complementary 2 ACCEPT goes in to 3/4 CREDIT mould around once for either mp 3 or mp 4 but award the alternate marking point if seen 4 ACCEPT eg tighter / more precisely / in a better position 5 ACCEPT interactions 7 ACCEPT e.g. puts, pressure / strains, on 9 IGNORE the enzyme is unchanged Total 20
6 Question Answer Mark Guidance 2 (a) ( alveoli ; to provide large(r), surface area / SA ; ACCEPT alveolus / alvioli, alviolis ACCEPT large(r) surface area to volume ratio OR SA:VOL 2 (ii) squamous / pavement ; Look for the name 1 ACCEPT squamas, squamos, squarmous DO NOT CREDIT ref to ciliated (iii) to prevent bursting ; recoil ; to return air sac to original, size / shape ; IGNORE stretch / contract DO NOT CREDIT in context of inhaling IGNORE ref to role returning airways back to size IGNORE ref to fibres returning to original size (b) ( 1 to help expel air ; 2 increases, partial pressure / concentration, of oxygen (in the air sac) ; so concentration of oxygen (in the air sac) is higher than that in the blood ; 2 max DO NOT CREDIT carbon dioxide / waste gas, expelled ACCEPT (provides) high concentration of oxygen (in air sac) IGNORE maintains throughout 3 4 decreases, partial pressure / concentration, of carbon dioxide (in air sac) ; so concentration of CO 2 (in the air sac) is lower than (ii) EITHER D1 (continuous) blood flow (in the capillaries) ; that in the blood ; 2 E1 to, bring in (more) carbon dioxide / take away (more) oxygen ; idea of blood flow ACCEPT good / copious / continuous, blood supply IGNORE highly vascular / many capillaries present IGNORE short diffusion path / capillaries very close to alveoli OR D2 oxygen combines with haemoglobin ; E2 to keep concentration in, blood / plasma, low ; 2 Total 9
7 Question Expected Answer Mark Additional Guidance 3 (a) (i) Mark the first answer. If the first answer is correct and an additional answer is given that is incorrect or contradicts the correct answer then = 0 marks production of vesicles / packaging proteins ; modification of / processing of / adding carbohydrate to, proteins ; ACCEPT lipids IGNORE ref to transport / secretion / exocytosis / substances / materials DO NOT CREDIT stores proteins ACCEPT makes glycoproteins production of lysosomes ; max 1 3 (a) (ii) allow movement (of substances) in or out of nucleus ; correctly named substance (entering or leaving nucleus) ; IGNORE messages / information / communication IGNORE name of substance for MP 1 IGNORE ref to mechanism of movement e.g. RNA / (m)rna / (r)rna (t)rna / polymerase nucleotides / ribosomes / helicase / proteins / (steroid) hormones IGNORE ref nutrients DO NOT CREDIT if incorrect direction of movement described (e.g. RNA into nucleus or RNA in and out of nucleus) DO NOT CREDIT DNA as named substance ref to correct destination of substance ; max 2 Note allows mrna out of nucleus = two marks e.g. RNA to ribosomes or RER helicase to DNA polymerase to, DNA / gene nucleotides to DNA (steroid) hormones to, DNA / gene / chromosome
8 Question Expected Answer Mark Additional Guidance 3 (a) (iii) contain / release, lysins / lytic enzymes / hydrolytic enzymes / digestive enzymes ; DO NOT CREDIT engulf DO NOT CREDIT lysosomes are digestive enzymes digest / break down, organelles / foreign objects / toxins / cells / pathogens ; ACCEPT destroy ACCEPT ref to digestion of contents of phagocytic vesicle IGNORE ref to (unwanted) substances / materials / food IGNORE ref to acrosomes apoptosis / autolysis / described ; max 1 3 (b) idea of more than one (type of) tissue ; working together / performing a function(s) ; 2 ACCEPT named examples of tissues ACCEPT job or task
9 3 Question Expected Answer Mark Additional Guidance (c) allow F marks even if C mark not quite accurate C1 thin / squamous, epithelium ; C2 thin endothelium (of capillary) ; F1 (provides) short diffusion distance / described ; F2 ref to surfactant (from epithelial cells), reducing surface tension / preventing alveoli collapsing ; C3 blood / red blood cells / erythrocytes ; F3 transports (named) gas(es), to / from, exchange surface / alveoli ; C4 diaphragm / intercostals, muscles ; F4 (maintains / creates) diffusion / concentration, gradient ; C5 ciliated epithelium / goblet cells / ciliated cells ; F5 idea of: protection from / removal of, dust / bacteria / pollen / spores ; C1/C2 IGNORE ref to alveolus / alveolar wall / capillary wall, without ref to epithelium / endothelium F1 ACCEPT diffusion barrier, thin / one cell thick IGNORE refs to speed or rate of diffusion IGNORE ref to reduces diffusion distance alone must be in context of short distance DO NOT CREDIT ref to thin, cell walls / membranes F2 IGNORE ref to moisture C3 IGNORE (named) blood vessel ACCEPT blood supply / supply of blood F3 IGNO ref to lungs IGNORE description of gas exchange F4 This can be awarded in context of F3 or C4 F5 AC PT trap, dust / bacteria / pollen / spores IGNORE dirt / germs C6 cartilage ; F6 hold airway open ; C7 smooth muscle ; continued
10 Question Expected Answer Mark Additional Guidance continued F7 constrict / control diameter of, airway / blood vessel ; F7 ACCEPT narrows lumen C8 elastic, fibres / tissue ; F8 for recoil / aiding ventilation ; C9 macrophage / neutrophil ; F9 engulf / destroy pathogens or protect from infection ; max 4 QWC ; 1 Total [11] C8 IGNORE elastin / elasticated F8 ACCEPT prevent alveoli bursting C9 IGNORE ref to white blood cell unqualified Any three with correct spelling and a suitable context from: epithelium / epithelial, endothelium, cartilage, diffuse / diffusion, gradient, goblet, ciliated, concentration, squamous, macrophage, neutrophil, surfactant, muscle, erythrocyte
11 Question Expected Answer Mark Additional Guidance 4 (a) (i) 1 idea of not breathing through nose ; 1 e.g. subject wears nose clip / plug or holds nose 2 subject breathes, evenly / normally / regularly ; 3 idea of (measure) height / amplitude, of waves (from trac e ) ; 2 IGNORE at rest 3 ACC PT (measure) difference between peak and trough ACCEPT annotated diagram / annotations on graph 4 measure at least three waves and calculate mean ; 5 detail of how spirometer works ; max 3 5 e.g. as breathe in lid goes down / as breathe out lid goes up e.g. movement of lid recorded, on trace / by data logger e.g. pen attached to lid moves up/down as breathe DO NOT CREDIT description of water level changing IGNORE ref to using mouthpiece, soda lime, oxygen 4 (a) (ii) 10 further waves drawn with similar heights ; trace falls ; 2 Look for 10 extra peaks and 10 extra troughs Note similar means no wave drawn for vital capacity all waves should be pproximately same height
12 Question Expected Answer Mark Additional Guidance 4 (a) (iii) 1 measure, volume of oxygen used / decrease in volume in chamber ; 1 ACCEPT annotations on graph ACCEPT measure how much the trace has gone down or measure decrease in trace 2 one detail of how to measure volume change ; 3 measure time taken (to use this oxygen) ; 4 divide (volume) by time taken ; 2 e.g. draw line along tips of, peaks / troughs e.g. find difference in height from one, peak / troug h, to another 3 ACCEPT (measure volume of oxygen used) in a given time 4 ACCEPT unit stated to indicate rate has been calculated e.g. dm 3 s -1 / dm 3 min -1 3 NOTE draw line along tips of, peaks / troughs and calculate gradient of line = 3 marks (mark points 1, 3 & 4) 4 (b) Mark the first two factors. 1 check health of volunteer ; 2 oxygen used ; 3 new / sterilised / disinfected, mouthpiece (for each volunteer); 4 idea of: soda lime working ; 5 sufficient oxygen in chamber ; 6 water level not too high / water must not enter tubes ; 7 ensure valves working correctly ; max 2 Total [10] 1 e.g. check medical history of volunteer ask about asthma / TB / pneumonia / flu / bronchitis / emphysema 3 IGNORE clean mouthpiece 4 CREDI need to remove CO 2 / CO 2 accumulates 5 IGNORE enough air in chamber 6 IGNOR general ref to leaks
13 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 5 (a) (b) A = bronchiole ; B = alveolus / alveoli ; 2 Mark the first answer for each letter. If the first answer is correct and an additional answer is given that is incorrect or contradicts the correct answer then = 0 marks. DO NOT CREDIT bronchus ACCEPT phonetic spelling of alveolus and bronchiole e.g. aveoli Mark the first two suggestions only. Read as prose unless candidate has indicated two points by bullets or numbers in this case mark the first comment in each bullet. 1 large, surface area / SA :VOL ; 2 (alveolar) wall / epithelium, one cell thick ; 3 (made of) squamous, cells / epithelium ; 4 ref to surfactant ; ACCEPT large SA / VOL, (alveoli) are small and in large number DO NOT CREDIT large amounts of tiny alveoli ACCEPT thin wall / thin barrier DO NOT CREDIT ref to cell wall / lining IGNORE alveolus one cell thick ACCEPT correct description of squamous cells (e.g. thin flat cell layer) ACCEPT pavement epithelium IGNORE reference to moist DO NOT CREDIT endothelium idea of: 5 (very) close to, capillaries / blood supply OR rich blood supply / many capillaries ; 2 max IGNORE ref to elastic fibres
14 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (c) 1 (histamine), binds / attaches, to, receptor / glycoprotein ; idea of : 2 in / on, plasma / cell surface, membrane (of muscle cell) ; binds to complementary receptor = 2 marks ACCEPT glycolipids IGNORE binding site, ref antigens ACCEPT in / on, cell surface / cell membrane (of muscle cells) ACCEPT membrane bound receptors (on muscle cells) 3 complementary (shape) ; 4 triggers response / causes effect, inside cells ; 2 max CREDIT correct examples of effects / details inside cells e.g. ref to opening sodium channes in cell surface membrane ref to second messenger ref to cyclic AMP ref to activation of enzymes / kinases ref to phosphorylation (d) idea of : 1 more tissue fluid formed / increase in volume of tissue fluid ; 2 increase pressure in tissue ; 3 swelling / inflammation / oedema; 4 (more) white blood cells pass into tissues ; Mark the first two suggestions only. Read as prose unless candidate has indicated two points by bullets or numbers in this case mark the first comment in each bullet. IGNORE refs to the capillaries becoming more leaky IGNORE more water passes out DO NOT CREDIT cells swell ACCEPT (more) white blood cells leave the capillary 5 larger molecules / (named) proteins, pass into tissue fluid ; 2 max IGNORE ref to more, glucose / nutrients / gases, leave blood capillary IGNORE ref to increased rate of diffusion Total 8
Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) (i) peptide (bond / link) ; 1 DO NOT CREDIT dipeptide 1 (a) (ii) hydrolysis ;
 Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) (i) peptide (bond / link) ; 1 DO NOT CREDIT dipeptide 1 (a) (ii) hydrolysis ; IGNORE name of bond 1 (b) 1 water / H O, is, added / used / needed
Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) (i) peptide (bond / link) ; 1 DO NOT CREDIT dipeptide 1 (a) (ii) hydrolysis ; IGNORE name of bond 1 (b) 1 water / H O, is, added / used / needed
PMT GCE. Biology. Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport. Mark Scheme for June Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
sphere A diameter / cm 1 3 (i) The student calculated the surface area: volume ratio of sphere B as 2:1.
 1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
GCE Human Biology. Mark Scheme for June Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange. Advanced Subsidiary GCE
 GCE Human Biology Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2017 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
GCE Human Biology Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2017 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Cell Structure. Mark Scheme 2. Exam Board Foundations in biology. Booklet Mark Scheme 2. Score: / 56. Percentage: /100.
 Cell Structure Mark Scheme Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board OCR Topic Foundations in biology Sub-Topic Cell Structure Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 68 minutes Score: / 56 Percentage: /100 Grade
Cell Structure Mark Scheme Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board OCR Topic Foundations in biology Sub-Topic Cell Structure Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 68 minutes Score: / 56 Percentage: /100 Grade
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) 3 max
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) phospholipid bilayer containing proteins ; head / hydrophilic region, facing outwards OR tail / hydrophobic region, facing inwards ; Marks can
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) phospholipid bilayer containing proteins ; head / hydrophilic region, facing outwards OR tail / hydrophobic region, facing inwards ; Marks can
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) 2 max Mark the first answer on each prompt line. ACCEPT ora throughout nucleus / nuclei ; 1 ACCEPT DNA not free
 Question answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) max Mark the first answer on each prompt line. ACCEPT ora throughout 1 6 7 nucleus / nuclei ; other named organelle / membrane bound organelles ; linear chromosomes
Question answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) max Mark the first answer on each prompt line. ACCEPT ora throughout 1 6 7 nucleus / nuclei ; other named organelle / membrane bound organelles ; linear chromosomes
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Movement of Substances in and out of cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure
![Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure](/thumbs/83/88046543.jpg) Respiratory Structure Nose mouth Function Pharynx epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchi (bronchus) Bronchioles Alveoli [alveolus] Diaphragm Jan 13 1:28 PM 1 NOSE Pharynx LUNGS Larynx/Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles
Respiratory Structure Nose mouth Function Pharynx epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchi (bronchus) Bronchioles Alveoli [alveolus] Diaphragm Jan 13 1:28 PM 1 NOSE Pharynx LUNGS Larynx/Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Q1. (a) Scientists who investigate disease may look at risk factors. What is a risk factor? (1)
 Q. (a) Scientists who investigate disease may look at risk factors. What is a risk factor?...... () Scientists investigated the link between pollution from vehicle exhausts and the number of cases of asthma.
Q. (a) Scientists who investigate disease may look at risk factors. What is a risk factor?...... () Scientists investigated the link between pollution from vehicle exhausts and the number of cases of asthma.
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
10.1 The Pulmonary-Circulatory System
 pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9700 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9700 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9700 BIOLOGY
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
PMT GCE. Biology. Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport. Mark Scheme for June Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
GCE. Human Biology. Mark Scheme for January Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange
 GCE Human Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Mark Scheme for January 0 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
GCE Human Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Mark Scheme for January 0 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
a. dissolved gases b. nutrients c. globulins d. surfactants e. hormones
 Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
PMT. GCE Biology. Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport. Advanced Subsidiary GCE. Mark Scheme for June Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2015 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
GCE Biology Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2015 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
#8 - Respiratory System
 Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
Equipment on table: Pen, ruler, pencil and planner.
 Question 1 Name two flat bones and, using a sporting action of your choice, suggest how these bones provide protection during performance. Question 2 Describe 4 ranges of movement. Question 3 Question
Question 1 Name two flat bones and, using a sporting action of your choice, suggest how these bones provide protection during performance. Question 2 Describe 4 ranges of movement. Question 3 Question
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2 If answer incorrect, allow one mark for appropriate working i.e. 60 divided
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2 If answer incorrect, allow one mark for appropriate working i.e. 60 divided
GCE. Human Biology. Mark Scheme for January Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange
 GCE Human Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Mark Scheme for January 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK
GCE Human Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Mark Scheme for January 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9700 BIOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/21 Paper 2 (AS Structured Questions), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/21 Paper 2 (AS Structured Questions), maximum
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
GCE Biology B (Advancing Biology) Mark Scheme for June Unit H022/01: Foundations of biology. Advanced Subsidiary GCE PMT
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCE Biology B (Advancing Biology) Unit H022/01: Foundations of biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2016 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge
Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCE Biology B (Advancing Biology) Unit H022/01: Foundations of biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2016 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge
GAS EXCHANGE IB TOPIC 6.4 CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM. Terminal bronchiole Nasal cavity. Pharynx Left lung Alveoli.
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9700 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/21
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/21
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
How does COPD really work?
 How does COPD really work? by Alex Goodell View online Where does COPD fit in the mix of respiratory diseases? I ve made a map of the major pathologies outlined in Robbins and First Aid (obviously these
How does COPD really work? by Alex Goodell View online Where does COPD fit in the mix of respiratory diseases? I ve made a map of the major pathologies outlined in Robbins and First Aid (obviously these
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Station A: YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament. Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5.
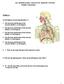 YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
PomPom SHOOTER. Activity Background: Common Obstructive Lung Disorders:
 CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
GCE Human Biology. Mark Scheme for June Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange. Advanced Subsidiary GCE
 GCE Human Biology Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
GCE Human Biology Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
Respiratory Toxicology
 Respiratory Toxicology Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 1 Breathing Oxygen Carbon Dioxide http://www.webmd.com/lung/picture-of-the-lungs Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 2 Breathing Enlarged view of the airways,
Respiratory Toxicology Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 1 Breathing Oxygen Carbon Dioxide http://www.webmd.com/lung/picture-of-the-lungs Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 2 Breathing Enlarged view of the airways,
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Digestion. Key Term. Regional specialisations of the human gut
 Key Term Mucus = a slimy glycoprotein, secreted by gland cells in the mucosa, forming a protective layer. It also lubricates food as it passes through the gut. Before food is digested it must be broken
Key Term Mucus = a slimy glycoprotein, secreted by gland cells in the mucosa, forming a protective layer. It also lubricates food as it passes through the gut. Before food is digested it must be broken
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
