To: Network of European Neuroscience Schools (NENS) Final report. Daniela Busti
|
|
|
- Lesley Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 To: Network of European Neuroscience Schools (NENS) Final report Daniela Busti address: Contact information of home institution: Prof. Francesco Ferraguti, Innsbruck Medical University, Pharmacological Department, Peter Myer Strasse 1a, 6020 Innsbruck, Austria Contact information of host institution: Dr. Marco Capogna, MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit, Mansfield Road, Oxford, UK Period of training stay: 18 August-30 September
2 Introduction Many recent studies have supported the idea that the amygdala is one of the brain structures involved in fear memory acquisition and storage (Davis 2000, LeDoux 2000, Maren 2001). The amygdala consists of several anatomically and functionally distinct nuclei including the lateral (LA) and basal (BA) nuclei, together referred as basolateral amygdala (BLA), and the central nucleus (CE), further divided in the centrolateral (CeL), centromedial (CeM) and central capsular (CeC, McDonald 1982). The intercalated cell masses (ITCs) of the amygdala are small clusters of GABA-ergic cells surrounding the BLA (Millhouse, 1986) and they have been reported to play a crucial role in gating the information flow from the BLA to the Ce (Royer, 1999) and mediating the expression of fear extinction (Likhtik, 2008). However, many functional aspects of this process remain still unclear. We believe that a better elucidation of the neuronal features of the BLA interneurons and of the ITC neurons will likely provide a better insight of the synaptic network underlying fear and extinction memories. My PhD project, that I carry out at the Department of Pharmacology of Innsbruck, focuses on the identification and characterization of the different neuronal subtypes present in the ITCs of the amygdala. However, so far, I could characterize distinct subclasses of ITC neurons only on the basis of bidimensional reconstructions of biocytin-filled cells obtained by drawing the neuronal elements by camera lucida. During the training stay that I carried out at the MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit in Oxford, I had the possibility to follow in vivo electrophysiological recordings of BLA interneurons in anaesthetized rats. During these experiments, single recorded neurons were also filled with neurobiotin, using the juxtacellular technique. The aim of my stay was to learn: (1) how to visualize the recorded neurons by immuno-fluorescence and (2) how to evaluate some neuronal aspects using both conventional epiflorescence and confocal microscopy. (3) This experience gave me the opportunity to improve my technical skills in tracing the cytoarchitectonic structure of ITC neurons and also to learn how to use Neurolucida. In fact, this is an advanced application that is becoming the gold standard for 3D reconstructions of neuron and quantitative characterization of neuronal morphological features. 2
3 Material and Methods Visualization of in vivo recorded cells. Coronal sections of 60 µm thickness were cut by a vibratome from previously fixed male Sprague Dawley rat brains and the recording neurons were visualized by immunofluorescence. Briefly, free-floating sections containing processes of the recorded cell were washed 3 times with PBS (Phosphate Buffer Saline) and incubated with Cy3 (1:400, Vector Laboratories), AMCA (1:1000, Vector Laboratories) or Alexa 488-coupled streptavidin (1:1000, Molecolar Probes) diluited in PBS, 0.15% Triton X 100 (TX) and 1% Normal Horse Serum (NHS, Vector Laboratories ) for ~24h (4 C). Then, the sections were mounted on slides in Vectashield medium and covered with a coverslip. Micrographs of the recorded neurons were acquired on a Leica Leitz DM RB conventional epiflorescence microscope, equipped with a Hamamatsu (ORCA-ER) CCD camera using the Openlab software (Improvision, version 5.5.0). Investigation of in vivo recorded putative basket cells. Putative basket cells were investigated for their expression of parvalbumin (PV). Specifically, after blocking for 1h at room temperature (RT) with a solution made of PBS, 0.15% TX and 20% NHS, the free-floating sections were incubated with the primary antibody PV (1:1000, goat, Swanson) diluted in PBS and 1% NHS for 48h (4 C), washed in PBS and reacted with the secondary antibody anti-goat Cy3 prepared in a solution containing PBS, 0.15% TX and 2% NHS. After abundant washing, the sections were mounted on slides and analyzed at the conventional epifluorescence microscope. Investigation of in vivo recorded putative axo-axonic cells. Possible axo-axonic interneurons were tested for their postsynaptic immunopositivity to Ankyrin G. Briefly, free-floating sections were blocked with a solution, containing PBS, 0.15% TX and 20% NHS, for 1h at RT and reacted with the primary antibody Ankyrin G (1:4000, mouse, UC Devis) diluted in PBS and 1% NHS for 48h (4 C). After washing in PBS the sections were incubated with anti-mouse Alexa 488 prepared in a solution containing PBS, 0.15% TX and 2% NHS. Afterwards they were washed in PBS and mounted on slides and the immunofluorescence was studied using a laserscanning confocal fluorescence microscope (LSM 510, Karl Zeiss) using a 100x immersion-oil objective. Anatomical analysis of recorded neurons by Neurolucida. Two ITC neurons, previously recorded in vitro in acute slices, filled with biocytin and converted for light microscopy using the avidin biotynilated horseradish method, were reconstructed using the Neurolucida software 3
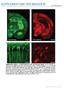
4 (MicroBrightField Neuroscience 8) connected to a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope. Specifically, all the portions of the soma, dendrites and axons present on serial sections were drawn, using a 60X oil-immersion objective, and properly overlapped. In one case some of the anatomical features were quantified by Neurolucida Explorer (MicroBrightField, version ). Results To test whether the in vivo recorded and neurobiotin-filled interneurons of the BLA belong to different subtypes of cell, I investigated specific neuronal markers. To this aim I assessed, at first, the correct location of the single recorded neuron within the BLA by immunofluorescence using conventional epifluorescence microscopy (Fig.1). In order to characterize some morphological features of the recorded interneurons, I used specific neuronal markers such as PV and Ankyrin G. In particular, I tested one recorded cell, showing basket-like axonal arbors, for PV. In fact, PV is a calcium binding protein specifically expressed in the soma and the processes of basket cells. As shown in Figure 2, a recorded interneuron of one of the rat brain that I have processed is positive for PV, corroborating its basket cell nature. In another case, I could investigate a putative axo-axonic neuron by immunohistochemical analysis of the spectrin-binding protein Ankyrin G, a neuronal marker staining the axon initial segment. Regions of the neurobiotin filled axon of the recorded cell were found to make close apposition with Ankyrin G positive axon initial segments of other BLA neurons, as shown by laser-scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 3). During my stay at the MRC, I could also fully reconstruct by Neurolucida two in vitro recorded ITC neurons (s slice 1 and r ), located in the main ITC nucleus of the amygdala. Figure 4 shows the ITC neuron s slice 1, characterized by short dendrites and few axonal branches mainly restricted to the main ITC nucleus and the BA. Figure 5 presents a more complex ITC neuron (r ) whose axonal projections extend in the main ITC nucleus, BLA, in the different subnuclei of the Ce and also in the basal medial amygdala (BMA) and in the medial nucleus (Me). Using Neurolucida Explorer, I could also quantify some anatomical features of this complex neuron, such as the axonal length in each of these regions, that are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. 4
5 Figure 1. An in vivo recorded interneuron located in the BLA. Immunofluorescence picture assessing the location of the in vivo recorded interneuron, filled with neurobiotin and revealed with AMCA-streptavidin, within the BLA complex of the amygdala. LA, lateral amygdala; BA, basal amygdala; ITC, intercalated cells of amygdala; ec, external capsule; Pir, piriform cortex; Ce, central nucleus; AStr, amygdala striatum transition region; CPu, caudate putamen. 5
6 Figure 2. PV positive basket cell interneuron of BLA. Conventional epiflorescence microscopy micrographs of one section, containing dendritic processes of the recorded neuron, reacted (A) with Alexa 488-streptavidin to visualize the neurobiotin and (B) with PV and Cy3-streptavidin. (C) Arrows in the superimposed picture indicate portions of the dendrites positive for PV. 6
7 Figure 3. Investigation of an axo-axonic interneuron of the BLA. Projection of Z-stack images obtained by confocal microscopy of (A) the axonal processes of a recorded BLA interneuron, filled in vivo with neurobiotin, revealed by Cy3-streptavidin and (B) Ankyrin G and Alexa 488-streptavidin immunoreaction. (C) White arrows indicate some neurobiotin filled axon making apposition to Ankirin G positive initial axonal segments. 7
8 Figure 4. ITC neuron s slice 1 reconstructed by Neurolucida. Red, soma; green, dendrites; yellow, axon. 8
9 Figure 5. ITC neuron r reconstructed by Neurolucida. Red, soma; green, dendrites; yellow, axon. *, main ITC nucleus; CeL, lateral nucleus of central amygdala; CeC, paracapsular nucleus of central amygdala; CeM, medial nucleus of the central amygdala; Me, medial amygdala; BMA, basal medial amygdala. Scale bar: 200µm. 9
10 Total Length n of spines Mean spine (µm) length (µm) n of nodes Axon Dendrite Table 1. Quantification of some of the main anatomical features of r axon length (µm) ITC nucleus Interm. capsule CeC CeL CeM Me BLA BMA Total % of axon Table 2. Quantification of the axonal length of r in the different subnuclei of the amygdala. Conclusions During the time that I spent at the MRC of Oxford, thanks to the stipend received from the Network of European Neuroscience Schools (NENS), I had the possibility to improve a lot my technical skills on how to analyse in vivo recorded neurons by immuhistochemistry. Thus, I was trained by expert people in the laboratory on how operate confocal microscopes and also the Neurolucida. I firmly believe that this experience was very helpful and constructive and I am sure that my future work will significantly benefit from it. 10
11 References - Davis M. (2000). The role of the amygdala in conditioned and unconditioned fear and anxiety. J.P. Aggleton, Editor, The Amygdala, Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, pp LeDoux J.E. (2000). Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23: Likhtik E., Popa D., Apergis-Schoute J., Fidacaro G.A., Pare D. (2008). Amygdala intercalated neurons are required for expression of fear extinction. Nature 54(7204): Maren S. (2001). Neurobiology of Pavlovian fear conditioning. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24: McDonald A.J. (1982). Cytoarchitecture of the central amygdaloid nucleus of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 208: Millhouse O.E. (1986). The intercalated cells of the amygdala. J. Comp. Neurol. 247: Pinault D. (1996). A novel single-cell staining procedure performed in vivo under electrophysiological control: morpho-functional features of juxtacellularly labeled thalamic cells and other central neurons with biocytin or Neurobiotin. J Neurosci Methods 65: Royer S., Martina M., Parè D. (1999). An inhibitory interface gates impulse traffic between the input and output station of the amygdala. J.Neurosci. 19:
12 Acknowledgments I would like to thank: the NENS for giving me the chance to come to the Medical Research Council Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit, Oxford University, and learn fundamental and interesting techniques. Prof. Francesco Ferraguti for encouraging me to perform this experience and Dr. Marco Capogna for hosting me in his lab. Thomas Bienvenu and Miroslawa Manko for introducing me to electrophysiology, for their excellent and friendly supervision during the experiments and all the interesting discussions. Linda Katona, Dr. Pablo Henny, Dr. Nicolas Mallet for their excellent technical help, in particular with the Neurolucida and the confocal microscope. 12
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of. parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala
 Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Different Fear States Engage Distinct Networks within the Intercalated Cell Clusters of the Amygdala
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 30, 2011 31(13):5131 5144 5131 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Different Fear States Engage Distinct Networks within the Intercalated Cell Clusters of the Amygdala Daniela
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 30, 2011 31(13):5131 5144 5131 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Different Fear States Engage Distinct Networks within the Intercalated Cell Clusters of the Amygdala Daniela
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon Limbic System II. David P. Wolfer MD
 ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon 05.05.2014 Limbic System II David P. Wolfer MD Institute of Anatomy, University of Zurich Institute for Human Movement Sciences and Sport, ETH Zurich http://www.dpwolfer.ch
ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon 05.05.2014 Limbic System II David P. Wolfer MD Institute of Anatomy, University of Zurich Institute for Human Movement Sciences and Sport, ETH Zurich http://www.dpwolfer.ch
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Article begins on next page
 Amygdala intercalated neurons are required for expression of fear extinction Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/29483/story/]
Amygdala intercalated neurons are required for expression of fear extinction Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/29483/story/]
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature21682 Supplementary Table 1 Summary of statistical results from analyses. Mean quantity ± s.e.m. Test Days P-value Deg. Error deg. Total deg. χ 2 152 ± 14 active cells per day per mouse
doi:10.1038/nature21682 Supplementary Table 1 Summary of statistical results from analyses. Mean quantity ± s.e.m. Test Days P-value Deg. Error deg. Total deg. χ 2 152 ± 14 active cells per day per mouse
CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 CELLULAR COMPOSITION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX THE CEREBRAL CORTEX CONSISTS OF THE ARCHICORTEX (HIPPOCAMPAL FORMA- TION), PALEOCORTEX
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 CELLULAR COMPOSITION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX THE CEREBRAL CORTEX CONSISTS OF THE ARCHICORTEX (HIPPOCAMPAL FORMA- TION), PALEOCORTEX
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12107 Supplementary Figure 1. CLARITY preserves GFP and TdTomato signals. (a) 3D rendering of a 1mm-thick Thy1-EGFP M line mouse brain block processed by CLARITY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12107 Supplementary Figure 1. CLARITY preserves GFP and TdTomato signals. (a) 3D rendering of a 1mm-thick Thy1-EGFP M line mouse brain block processed by CLARITY
Physiological identification and infralimbic responsiveness of rat intercalated amygdala neurons
 J Neurophysiol 105: 3054 3066, 2011. First published April 6, 2011; doi:10.1152/jn.00136.2011. Physiological identification and infralimbic responsiveness of rat intercalated amygdala neurons Alon Amir,
J Neurophysiol 105: 3054 3066, 2011. First published April 6, 2011; doi:10.1152/jn.00136.2011. Physiological identification and infralimbic responsiveness of rat intercalated amygdala neurons Alon Amir,
Supplemental Information. Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila. Supplemental Inventory
 1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Background & Rationale Great apes share many behavioral, cognitive, and neuroanatomical similarities with humans. Yet, there are also significant
 Background & Rationale Great apes share many behavioral, cognitive, and neuroanatomical similarities with humans. Yet, there are also significant differences that distinguish humans from apes in terms
Background & Rationale Great apes share many behavioral, cognitive, and neuroanatomical similarities with humans. Yet, there are also significant differences that distinguish humans from apes in terms
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Cell-Type-Specific Recruitment of Amygdala Interneurons to Hippocampal Theta Rhythm and Noxious Stimuli In Vivo
 Article Cell-Type-Specific Recruitment of Amygdala Interneurons to Hippocampal Theta Rhythm and Noxious Stimuli In Vivo Thomas C.M. Bienvenu, 1,3, * Daniela Busti, 2 Peter J. Magill, 1 Francesco Ferraguti,
Article Cell-Type-Specific Recruitment of Amygdala Interneurons to Hippocampal Theta Rhythm and Noxious Stimuli In Vivo Thomas C.M. Bienvenu, 1,3, * Daniela Busti, 2 Peter J. Magill, 1 Francesco Ferraguti,
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease
 Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
CCK mouse 1:5000 *Dr. G. Ohning, CURE, UCLA, USA, Code 9303 (Ohning et al., 1996)
 Supplemental Table 1 antibody to host dilution source CB rabbit 1:5000 Swant, Bellinzona, Switzerland, code no 38 reference of characterization and specificity labelling patterns as published with other
Supplemental Table 1 antibody to host dilution source CB rabbit 1:5000 Swant, Bellinzona, Switzerland, code no 38 reference of characterization and specificity labelling patterns as published with other
MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN STORAGE OF FEAR IN LATERAL AMYGDALA A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY
 MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN STORAGE OF FEAR IN LATERAL AMYGDALA A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY A Thesis presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri Columbia In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement
MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN STORAGE OF FEAR IN LATERAL AMYGDALA A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY A Thesis presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri Columbia In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 October 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2010 April ; 13(4): 489 494. doi:10.1038/nn.2499. SYNAPTIC CORRELATES OF FEAR EXTINCTION IN THE AMYGDALA Taiju Amano
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2010 April ; 13(4): 489 494. doi:10.1038/nn.2499. SYNAPTIC CORRELATES OF FEAR EXTINCTION IN THE AMYGDALA Taiju Amano
Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C. N. Petrok, J.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo
 Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse
 Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Rescue of Impaired Fear Extinction and Normalization of Cortico-Amygdala Circuit Dysfunction in a Genetic Mouse Model by Dietary Zinc Restriction
 13586 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 13, 2010 30(41):13586 13596 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Rescue of Impaired Fear Extinction and Normalization of Cortico-Amygdala Circuit Dysfunction in a Genetic
13586 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 13, 2010 30(41):13586 13596 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Rescue of Impaired Fear Extinction and Normalization of Cortico-Amygdala Circuit Dysfunction in a Genetic
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization. Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience
 Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
PARVALBUMIN IMMUNOREACTIVITY CHANGES DURING THE MATURATION OF THE THALAMIC RETICULAR NUCLEUS OF THE RAT
 Доклади на Българската академия на науките Comptes rendus de l Académie bulgare des Sciences Tome 66, No 7, 2013 MEDECINE Morphologie PARVALBUMIN IMMUNOREACTIVITY CHANGES DURING THE MATURATION OF THE THALAMIC
Доклади на Българската академия на науките Comptes rendus de l Académie bulgare des Sciences Tome 66, No 7, 2013 MEDECINE Morphologie PARVALBUMIN IMMUNOREACTIVITY CHANGES DURING THE MATURATION OF THE THALAMIC
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
basolateral amygdala; dendritic spines; GABA; synaptic currents
 J Neurophysiol 114: 942 957, 2015. First published June 3, 2015; doi:10.1152/jn.00824.2014. Structural and functional characterization of dendritic arbors and GABAergic synaptic inputs on interneurons
J Neurophysiol 114: 942 957, 2015. First published June 3, 2015; doi:10.1152/jn.00824.2014. Structural and functional characterization of dendritic arbors and GABAergic synaptic inputs on interneurons
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits Stephane Ciocchi 1,*, Cyril Herry 1,,*, François Grenier 1, Steffen B.E. Wolff 1, Johannes J. Letzkus 1, Ioannis Vlachos 3, Ingrid Ehrlich
Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits Stephane Ciocchi 1,*, Cyril Herry 1,,*, François Grenier 1, Steffen B.E. Wolff 1, Johannes J. Letzkus 1, Ioannis Vlachos 3, Ingrid Ehrlich
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
The Amygdaloid Complex: Anatomy and Physiology
 Physiol Rev 83: 803 834, 2003; 10.1152/physrev.00002.2003. The Amygdaloid Complex: Anatomy and Physiology P. SAH, E. S. L. FABER, M. LOPEZ DE ARMENTIA, AND J. POWER Division of Neuroscience, John Curtin
Physiol Rev 83: 803 834, 2003; 10.1152/physrev.00002.2003. The Amygdaloid Complex: Anatomy and Physiology P. SAH, E. S. L. FABER, M. LOPEZ DE ARMENTIA, AND J. POWER Division of Neuroscience, John Curtin
Amygdala Mechanisms of Fear Suppression
 Amygdala Mechanisms of Fear Suppression By Alon Amir A Dissertation submitted to the Graduate School-Newark Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
Amygdala Mechanisms of Fear Suppression By Alon Amir A Dissertation submitted to the Graduate School-Newark Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quality control of CD4 + T-cell purification. CD4 + T cells were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the RosetteSep CD4 + T Cell Enrichment
Supplemental Figure 1. Quality control of CD4 + T-cell purification. CD4 + T cells were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the RosetteSep CD4 + T Cell Enrichment
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Neurobiology. Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2010 1 The nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) 2 Enteric nervous system (digestive tract, gall bladder and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2010 1 The nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) 2 Enteric nervous system (digestive tract, gall bladder and
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Sensory Inputs to Intercalated Cells Provide Fear- Learning Modulated Inhibition to the Basolateral Amygdala
 Article Sensory Inputs to Intercalated ells Provide Fear- Learning Modulated Inhibition to the Basolateral Amygdala Highlights d Amygdala medial paracapsular cells (mpis) receive sensory stimulus-related
Article Sensory Inputs to Intercalated ells Provide Fear- Learning Modulated Inhibition to the Basolateral Amygdala Highlights d Amygdala medial paracapsular cells (mpis) receive sensory stimulus-related
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
J. Cell Sci. 129: doi: /jcs : Supplementary information
 Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Systems Neuroscience November 29, Memory
 Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Genetic Analysis of Anxiety Related Behaviors by Gene Chip and In situ Hybridization of the Hippocampus and Amygdala of C57BL/6J and AJ Mice Brains
 Genetic Analysis of Anxiety Related Behaviors by Gene Chip and In situ Hybridization of the Hippocampus and Amygdala of C57BL/6J and AJ Mice Brains INTRODUCTION To study the relationship between an animal's
Genetic Analysis of Anxiety Related Behaviors by Gene Chip and In situ Hybridization of the Hippocampus and Amygdala of C57BL/6J and AJ Mice Brains INTRODUCTION To study the relationship between an animal's
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH).
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning
 Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Basal ganglia macrocircuits
 Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Behavioral Neuroscience: Fear thou not. Rony Paz
 Behavioral Neuroscience: Fear thou not Rony Paz Rony.paz@weizmann.ac.il Thoughts What is a reward? Learning is best motivated by threats to survival Threats are much better reinforcers Fear is a prime
Behavioral Neuroscience: Fear thou not Rony Paz Rony.paz@weizmann.ac.il Thoughts What is a reward? Learning is best motivated by threats to survival Threats are much better reinforcers Fear is a prime
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb. by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral
 Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Dako IT S ABOUT TIME. Interpretation Guide. Agilent Pathology Solutions. ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis)
 INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability
 Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
Neocortex. Cortical Structures in the Brain. Neocortex Facts. Laminar Organization. Bark-like (cortical) structures: Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12
 Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
The structure of Pavlovian fear conditioning in the amygdala
 Brain Struct Funct (2013) 218:1569 1589 DOI 10.1007/s00429-012-0478-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The structure of Pavlovian fear conditioning in the amygdala Hadley C. Bergstrom Craig G. McDonald Smita Dey Haying
Brain Struct Funct (2013) 218:1569 1589 DOI 10.1007/s00429-012-0478-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The structure of Pavlovian fear conditioning in the amygdala Hadley C. Bergstrom Craig G. McDonald Smita Dey Haying
The Excitatory Neuronal Network of Rat Layer 4 Barrel Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 15, 2000, 20(20):7579 7586 The Excitatory Neuronal Network of Rat Layer 4 Barrel Cortex Carl C. H. Petersen and Bert Sakmann Department of Cell Physiology, Max-Planck-Institute
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 15, 2000, 20(20):7579 7586 The Excitatory Neuronal Network of Rat Layer 4 Barrel Cortex Carl C. H. Petersen and Bert Sakmann Department of Cell Physiology, Max-Planck-Institute
Morphological and Electrophysiological Properties of Principal Neurons in the Rat Lateral Amygdala In Vitro
 Morphological and Electrophysiological Properties of Principal Neurons in the Rat Lateral Amygdala In Vitro E.S.L. FABER, 1 R. J. CALLISTER, 2 AND P. SAH 1 1 Division of Neuroscience, John Curtin School
Morphological and Electrophysiological Properties of Principal Neurons in the Rat Lateral Amygdala In Vitro E.S.L. FABER, 1 R. J. CALLISTER, 2 AND P. SAH 1 1 Division of Neuroscience, John Curtin School
Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery. against melanoma
 Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
CSE511 Brain and Memory Modeling Lecture 1 Notes Mon 8/30/10
 CSE511 Brain and Memory Modeling Lecture 1 Notes Mon 8/30/10 Displayed syllabus from http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511; discussed course texts, exam, sample projects, and goals (learn brain terminology
CSE511 Brain and Memory Modeling Lecture 1 Notes Mon 8/30/10 Displayed syllabus from http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511; discussed course texts, exam, sample projects, and goals (learn brain terminology
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 590.1 (2012) pp 131 143 131 Heterosynaptic long-term potentiation at interneuron principal neuron synapses in the amygdala requires nitric oxide signalling M. D. Lange 1,2, M. Doengi 1,J.Lesting
J Physiol 590.1 (2012) pp 131 143 131 Heterosynaptic long-term potentiation at interneuron principal neuron synapses in the amygdala requires nitric oxide signalling M. D. Lange 1,2, M. Doengi 1,J.Lesting
doi: /nature09554
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia
 Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
Prof. Anagnostaras, Lecture 7: Fear
 Historical views that thought and emotion were processed separately in the brain Prof. Anagnostaras, Lecture 7: So far, fear is the best understood What is fear? Dictionary: A feeling of agitation and
Historical views that thought and emotion were processed separately in the brain Prof. Anagnostaras, Lecture 7: So far, fear is the best understood What is fear? Dictionary: A feeling of agitation and
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex
 Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review
 The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
Chapter 3. Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons. on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs bind protein factors to
 22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
