Cell Biology Monographs
|
|
|
- Rachel Walton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Cell Biology Monographs Edited by M. Alfert, Berkeley, Calif. w. Beermann, Tilbingen L. Goldstein, Lexington, Ky. K. R. Porter, Boulder, Colo. Advisory Board J. Brachet, Bruxelles D. Branton, Cambridge, Mass. H. G. Callan, St. Andrews E. C. Cocking, Nottingham W. W. Franke, Heidelberg N. Kamiya, Okazaki G. Rudkin, Philadelphia, Pa. G. F. Springer, Evanston, Ill. L. Stockinger, Wien B. F. Trump, Baltimore, Md. Volume 13 Springer-Verlag Wien New York
3 The Cytoskeleton An Introductory Survey M. Schliwa Springer-Verlag Wien New York
4 Prof. Dr. MANFRED SCHLIWA Department of Zoology University of California Berkeley, California, U.S.A. This work is subject to copyright. All rights are reserved, whether the whole or part of the material is concerned, specifically those of translation, reprinting, re-use of illustrations, broadcasting, reproduction by photocopying machine or similar means, and storage in data banks by Springer-VerlaglWien Softcover reprint oflhe hardcover 1st edition 1986 With 88 Figures ISSN ISBN-13: e-isbn-13: DOl: /
5 Fur Usch
6 Preface The term cytoskeleton has become firmly established in today's scientific vocabulary. Indeed, it is difficult to believe that only ten years ago, it was virtually non-existent. Since then, the modern field of research on the structural organization of the cytoplasm has turned into one of the most productive and rapidly expanding research areas in Cell Biology today. Considerable progress has been made towards the identification of the various structural components of the cytoskeleton and their interactions with one another and with membranes. The first attempts to understand, in molecular terms, complex cellular processes such as shape changes, locomotion, division, and organelle movements have been made. And it is now apparent that the cytoskeleton has impact on other biological processes such as the control of gene expression, protein synthesis, cell cycle regulation, and development. This monograph outlines the basic properties of the major components of the polymeric filament networks and their interactions and associations. Wherever possible, emphasis is placed on more recent references. Any attempt to cover a research field this complex in an introductory monograph is, by necessity, fragmentary, and oversights or omissions are inevitable. I wish to apologize in advance to all those colleagues who feel that their work is not adequately represented. This book would not have possible without the help of Ursula Euteneuer and Susan Spath, whose numerous thoughtful suggestions and comments on the final draft essentially made the text readable. To them I am deeply indebted. I also thank Paul Licht, Mona Radice, and Paul Tibbetts for their help in the struggle with the idiosyncrasies ofthe bibliography program, and the Department of Zoology at Berkeley for providing access to the departmental computer to prepare the list of references. I am grateful to the members of my laboratory for their moral support and indulgence during the months of my preoccupation with this undertaking, and hope that their patience is partly rewarded by the final result. Finally, I wish to thank the many colleagues who kindly supplied illustrative material. They are individually acknowledged in the figure legends. Berkeley, October 1985 MANFRED SCHLIWA
7 Prologue.... Contents Part A. Components I. Cytoplasmic Contractile Proteins II Historical Aspects Actin Structure Actin Assembly in vitro Inhibitors Cytochalasins Phalloidin Proteins Associated with Cytoplasmic Actin Depolymerizing and Polymerization-Inhibiting Proteins Cross-Linking Proteins End-Binding Proteins Some General Considerations on Actin Networks 104. Myosin Structure Myosin Filament Formation 1.5. Actin-Myosin Interaction Regulation of Actin-Myosin Interaction Tropomyosin, Troponin, and Alpha-Actinin in Smooth and Nonmuscle Cells Myosin and Its Interaction with Actin: Outlook Aspects of Contractile Protein Distribution and Function Microtubules II.3. II.4. Historical Aspects.. Microtubule Structure Tubulin Interactions with Other Molecules IIA.1. Ions IIA.2. Nucleotides.... IIA.3. Microtubule-Associated Proteins IIAA. Drugs I Colchicine and Its Analogues 1I Vinblastine and Vincristine II Nocodazole Taxo!... II Other Microtubule Poisons
8 x Contents Mechanism of Microtubule Polymerization Microtubule Polarity Nucleation Sites and Organizing Centers Structure Demonstration of Nucleating Activity Biochemistry of MTOCs Microtubule Machineries: Cilia and Flagella Structure Function Ciliary and Cytoplasmic Dyneins Distribution and Function of Microtubules in Cells: A Summary. 81 III. Intermediate Filaments Historical Aspects Classification of Intermediate Filaments: Molecular Composition and Tissue Distribution Vimentin Desmin 87 III.2.3. Cytokeratins Neurofilaments Glial Filaments Cells Without Intermediate Filaments? Intermediate Filaments as Markers For Tumor Characterization Structural, Physical, and Chemical Similarities Between Intermediate Filament Proteins Co-Existence and Co-Assembly of Different Intermediate Filament Subunits III.5. Intermediate Filament-Associated Proteins Phosphorylation of Intermediate Filament Proteins Regulation of Intermediate Filament Assembly in the Cell Aspects of the Cellular Distribution and Function of Intermediate Filaments IV. Dynamic Aspects of Filament Assembly 115 V. Other Filament Types V.1. Spasmin-Like Filaments... V.2. Connectin/Titin-Like Filaments V.3. 3 nm Linkers Part B. Interactions VI. Some General Aspects of the Three-Dimensional Organization of Cytoskeletal Components VII. Interactions Between the Major Filamentous Components of the Cytoskeleton. 145 VII.1. Some Methods for the Detection of Filament Interactions. 146 VII.2. Self-Associations of the Major Cytoskeletal Filament Types. 148 VII.2.1. Actin Filaments
9 Contents VII.2.2. Microtubules.. VII Intermediate Filaments.. VII.3. Interactions Among Different Filament Components VII.3.I. Actin Filaments and Microtubules... VII.3.2. Actin Filaments and Intermediate Filaments VII.3.3. Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments VII.4. Filament Interactions: A Perspective. VIII. The Cytoskeleton and the Cytoplasmic Matrix XI IX. Membrane-Cytoskeleton Interactions IX.I. Introduction IX.2. Paradigm Erythrocyte. 180 IX.2.I. Spectrin 180 IX.2.2. Ankyrin 182 IX.2.3. Band IX.2.4. Actin. 184 IX.2.5. Band IX.2.6. Construction of the Subplasmalemmal Network. 185 IX.3. Proteins Related to the Erythrocyte Skeleton in Other Cell Types. 188 IX.4. Association of Membrane Proteins with the Cytoskeleton 196 IX.5. Association of Cytoskeletal Fibers with the Membranes 203 IX.6. Some Aspects of Organelle-Cytoskeleton Relationships 208 IX.7. Specialized Filament-Membrane Assemblies IX.7.I. Adherens Junctions and Adhesion Plaques IX.7.2. Desmosomes IX.7.3. The Brush Border of Intestinal Epithelial Cells 227 IX.7.3.I. Morphology and Ultrastructure IX Biochemical Anatomy IX A Note on Brush Border "Motility" 234 IX.8. Transmembrane Interactions of the Cytoskeleton with the Extracellular Matrix. 236 References.. Subject Index
The cytoskeleton and cell movement. (Actin microfilaments)
 The cytoskeleton and cell movement (Actin microfilaments) What is the cytoskeleton? A dynamic network of protein filaments extending throughout the cytoplasm Three types: microfilaments (actin), microtubules
The cytoskeleton and cell movement (Actin microfilaments) What is the cytoskeleton? A dynamic network of protein filaments extending throughout the cytoplasm Three types: microfilaments (actin), microtubules
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Orthopaedic Diagnosis
 Hubert A. Sis sons. Ronald O. Murray H.B.S. Kemp Orthopaedic Diagnosis Clinical, Radiological and Pathological Coordinates With 534 Figures, Many in Colour Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Hubert A. Sis sons. Ronald O. Murray H.B.S. Kemp Orthopaedic Diagnosis Clinical, Radiological and Pathological Coordinates With 534 Figures, Many in Colour Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
The Motile Machinery and Cytoskeleton of the Cell
 The Motile Machinery and Cytoskeleton of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy, University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: Distinguish
The Motile Machinery and Cytoskeleton of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy, University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: Distinguish
(Please activate your clickers)
 Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s
 Current Topics in Membranes, Volume 43 Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s Edited by W. James Nelson Contributors xii i Preface xvii Previous Volumes in Series xix CHAPTER 1 Getting There Is
Current Topics in Membranes, Volume 43 Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s Edited by W. James Nelson Contributors xii i Preface xvii Previous Volumes in Series xix CHAPTER 1 Getting There Is
George R. Honig Junius G. Adams III. Human Hemoglobin. Genetics. Springer-Verlag Wien New York
 George R. Honig Junius G. Adams III Human Hemoglobin Genetics Springer-Verlag Wien New York George R. Honig, M.D., Ph.D. Professor and Head Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine University of Illinois
George R. Honig Junius G. Adams III Human Hemoglobin Genetics Springer-Verlag Wien New York George R. Honig, M.D., Ph.D. Professor and Head Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine University of Illinois
Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden
 Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden 1 Molec Biol Cell 5 th ed. Supplemental Videos Actin-dependent ATP hydrolysis by myosin generates motile force The Myosin ATPase activity cycle 2 ATP binding releases
Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden 1 Molec Biol Cell 5 th ed. Supplemental Videos Actin-dependent ATP hydrolysis by myosin generates motile force The Myosin ATPase activity cycle 2 ATP binding releases
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 1)
 Cytoskeleton Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 1) Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 4) 5.3 Eukaryotic Cells Contain Organelles Cytoskeleton: Supports and maintains cell shape Holds organelles in position
Cytoskeleton Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 1) Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 4) 5.3 Eukaryotic Cells Contain Organelles Cytoskeleton: Supports and maintains cell shape Holds organelles in position
cell movement and neuronal migration
 cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Subcellular biochemistry
 Department of Medical Biochemistry Semmelweis University Subcellular biochemistry February-March 2017 Subcellular biochemistry (biochemical aspects of cell biology) Miklós Csala Semmelweis University Dept.
Department of Medical Biochemistry Semmelweis University Subcellular biochemistry February-March 2017 Subcellular biochemistry (biochemical aspects of cell biology) Miklós Csala Semmelweis University Dept.
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
Lumbar Spine Syndromes
 Gunnar B. J. Andersson and Thomas W. McNeill Lumbar Spine Syndromes Evaluation and Treatment Springer-Verlag Wien New York Gunnar B. J. Andersson, M.D., Ph.D. Thomas W. McNeill, M.D. Department of Orthopedic
Gunnar B. J. Andersson and Thomas W. McNeill Lumbar Spine Syndromes Evaluation and Treatment Springer-Verlag Wien New York Gunnar B. J. Andersson, M.D., Ph.D. Thomas W. McNeill, M.D. Department of Orthopedic
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis!
 Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
The Jobs of Cells. Food & water storage. Vacuoles & vesicles. Vacuoles in plants 10/5/2015. plant cells
 Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them make more
Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them make more
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
CMB621: Cytoskeleton. Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved
 CMB621: Cytoskeleton Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved Lecture(s) Overview Lecture 1: What is the cytoskeleton? Membrane interaction
CMB621: Cytoskeleton Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved Lecture(s) Overview Lecture 1: What is the cytoskeleton? Membrane interaction
(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Fig Intermediate Filaments
 Fig 16-20 Intermediate Filaments Overview: Intermediate filaments are easily bent and stretched but highly resistant to breaking. They provide mechanical strength to cells. Unlike actin filaments and microtubules,
Fig 16-20 Intermediate Filaments Overview: Intermediate filaments are easily bent and stretched but highly resistant to breaking. They provide mechanical strength to cells. Unlike actin filaments and microtubules,
Name 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of
 Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center. The Golgi apparatus. Functions of the Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes: Digestive Compartments
 The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center The Golgi apparatus Receives (on the cis-side) many of the transport vesicles produced in the rough ER Consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center The Golgi apparatus Receives (on the cis-side) many of the transport vesicles produced in the rough ER Consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function A. Early observations revealed an unseen world: 1. Galileo saw the facets of an insect's eyes. Animacules and Cells Fill'd with Juices 2. Robert Hooke saw small compartments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function A. Early observations revealed an unseen world: 1. Galileo saw the facets of an insect's eyes. Animacules and Cells Fill'd with Juices 2. Robert Hooke saw small compartments
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
Characterization of Epithelial Cells
 EPITHELIAL BIOLOGY Characterization of Epithelial Cells Gabriela Rodrigues Dept. Animal Biology Faculty of Sciences University of Lisboa Centre for Environmental Biology 2-6 July 2007 Gulbenkian Institute
EPITHELIAL BIOLOGY Characterization of Epithelial Cells Gabriela Rodrigues Dept. Animal Biology Faculty of Sciences University of Lisboa Centre for Environmental Biology 2-6 July 2007 Gulbenkian Institute
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Top 10 Contributions on Biomedical Sciences: 2nd Edition. St Vincent s Hospital, The University of Melbourne, Australia 2
 Chapter 06 Cancer Progression: The Impact of Cytoskeletal Molecules Sam L Francis 1 and Juliana Antonipillai 2 * 1 St Vincent s Hospital, The University of Melbourne, Australia 2 School of Health and Biomedical
Chapter 06 Cancer Progression: The Impact of Cytoskeletal Molecules Sam L Francis 1 and Juliana Antonipillai 2 * 1 St Vincent s Hospital, The University of Melbourne, Australia 2 School of Health and Biomedical
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life
 Slide 1 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Slide 1 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued
 Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments
 02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Plant organelle used for storage. Some store starches and lipids and pigments. Named according to the color or pigment that they contain.
 Animal Cell: Plant Cell: Plastid: Plant organelle used for storage. Some store starches and lipids and pigments. Named according to the color or pigment that they contain. Chloroplasts:contain light absorbing
Animal Cell: Plant Cell: Plastid: Plant organelle used for storage. Some store starches and lipids and pigments. Named according to the color or pigment that they contain. Chloroplasts:contain light absorbing
Microfilaments. myosin. In muscle cells. Microfilaments. Microfilaments. Video: Cytoplasmic Streaming. amoeboid movement. Pseudopodia.
 Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
Cytology. Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges
 Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Schriftenreihe Neurologie
 Schriftenreihe Neurologie 18 Neurology Series Herausgeber H.I Bauer, Gottingen. H. Ganshirt, Heidelberg P. Vogel, Heidelberg Beirat H.Caspers, Munster H.Hager, GieBen M.Mumenthaler, Bern A. Pentschew,
Schriftenreihe Neurologie 18 Neurology Series Herausgeber H.I Bauer, Gottingen. H. Ganshirt, Heidelberg P. Vogel, Heidelberg Beirat H.Caspers, Munster H.Hager, GieBen M.Mumenthaler, Bern A. Pentschew,
Mechanism of Muscular Contraction
 ~ Sorin2:er Jack A. Rail Mechanism of Muscular Contraction Contents 1 Setting the Stage: Myosin, Actin, Actomyosin and ATP... 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Muscle Structure as Observed by Nineteenth Century
~ Sorin2:er Jack A. Rail Mechanism of Muscular Contraction Contents 1 Setting the Stage: Myosin, Actin, Actomyosin and ATP... 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Muscle Structure as Observed by Nineteenth Century
Anaesthesiology and Resuscitation Anaesthesiologie und Wiederbelebung Anesthesiologie et Reanimation
 Anaesthesiology and Resuscitation Anaesthesiologie und Wiederbelebung Anesthesiologie et Reanimation 75 Editors Prof. Dr. R. Frey, Mainz' Dr. F. Kern, St. Gallen Prof. Dr. O. Mayrhofer, Wien Managing Editor:
Anaesthesiology and Resuscitation Anaesthesiologie und Wiederbelebung Anesthesiologie et Reanimation 75 Editors Prof. Dr. R. Frey, Mainz' Dr. F. Kern, St. Gallen Prof. Dr. O. Mayrhofer, Wien Managing Editor:
Chapter 6 Review Page 1
 hapter 6 Review Page 1 1 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is FLS? They both contain ribosomes. They both contain mitochondria. They are both bounded by a plasma
hapter 6 Review Page 1 1 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is FLS? They both contain ribosomes. They both contain mitochondria. They are both bounded by a plasma
Social Psychology of Self-Referent Behavior
 Social Psychology of Self-Referent Behavior Social Psychology of Self-Referent Behavior Howard B. Kaplan Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Teras Springer Science + Business Media, LLC Library of Congress
Social Psychology of Self-Referent Behavior Social Psychology of Self-Referent Behavior Howard B. Kaplan Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Teras Springer Science + Business Media, LLC Library of Congress
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 4. Most cells are microscopic. Cells vary in size and shape
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
Neuronal plasma membrane
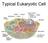 ORGANELLES ORGANELLES Neuronal plasma membrane The neuronal plasma membrane contains several local domains with unique properties Presynaptic terminal Endoplasmic Reticulum In neurons the Nissl bodies
ORGANELLES ORGANELLES Neuronal plasma membrane The neuronal plasma membrane contains several local domains with unique properties Presynaptic terminal Endoplasmic Reticulum In neurons the Nissl bodies
Mitosis vs. microtubule
 Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Chapman and Hall Animal Behaviour Series
 ANIMAL MOTIVATION Chapman and Hall Animal Behaviour Series SERIES EDITORS D.M.Broom Colleen Macleod Professor of Animal Welfare, University of Cambridge, UK P.W. Colgan Professor of Biology and Psychology,
ANIMAL MOTIVATION Chapman and Hall Animal Behaviour Series SERIES EDITORS D.M.Broom Colleen Macleod Professor of Animal Welfare, University of Cambridge, UK P.W. Colgan Professor of Biology and Psychology,
Dr. Ramesh. AP Biology Chapter 6 Quiz A Tour of the Cell
 Dr Ramesh AP Biology Chapter 6 Quiz A Tour of the Cell 1) The smallest cell structure that would most likely be visible with a standard (not super- resolution) research-grade light microscope is a A mitochondrion
Dr Ramesh AP Biology Chapter 6 Quiz A Tour of the Cell 1) The smallest cell structure that would most likely be visible with a standard (not super- resolution) research-grade light microscope is a A mitochondrion
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Neuroethology. Jorg-Peter Ewert. An Introduction to the Neurophysiological Fundamentals of Behavior. Translation: Transemantics, Inc.
 Jorg-Peter Ewert Neuroethology An Introduction to the Neurophysiological Fundamentals of Behavior Translation: Transemantics, Inc. With 171 Figures, Most in Color Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New
Jorg-Peter Ewert Neuroethology An Introduction to the Neurophysiological Fundamentals of Behavior Translation: Transemantics, Inc. With 171 Figures, Most in Color Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
3. Endomembrane System: It s all integrated!
 3. Endomembrane System: It s all integrated! 4. Vacuoles ii. Large Central Vacuole (Plants)! Fills up most of plant cell! Membrane bound (tonoplast)! Helps cell s water balance! Dump site for hazardous
3. Endomembrane System: It s all integrated! 4. Vacuoles ii. Large Central Vacuole (Plants)! Fills up most of plant cell! Membrane bound (tonoplast)! Helps cell s water balance! Dump site for hazardous
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo
 Integration of Cells into Tissues Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital Lahore 1. How
Integration of Cells into Tissues Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital Lahore 1. How
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells. Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari
 Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Neuronal plasma membrane
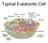 ORGANELLES ORGANELLES Neuronal plasma membrane The neuronal plasma membrane contains several local domains with unique properties Presynaptic terminal Endoplasmic Reticulum In neurons the Nissl bodies
ORGANELLES ORGANELLES Neuronal plasma membrane The neuronal plasma membrane contains several local domains with unique properties Presynaptic terminal Endoplasmic Reticulum In neurons the Nissl bodies
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
Goals. Cells. Cells: The Living Units. By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe.
 C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CELL JUNCTIONS AND TISSUES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
TRACE ELEMENTS ANO IRON IN HUMAN METABOLISM
 TRACE ELEMENTS ANO IRON IN HUMAN METABOLISM TOPICS IN HEMATOLOGV Series Editor: Maxwell M. Wintrobe, M.D. University of Utah, Salt Lake City THE RESPIRATORY FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD Lars Garby, M.D. and Jerry
TRACE ELEMENTS ANO IRON IN HUMAN METABOLISM TOPICS IN HEMATOLOGV Series Editor: Maxwell M. Wintrobe, M.D. University of Utah, Salt Lake City THE RESPIRATORY FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD Lars Garby, M.D. and Jerry
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
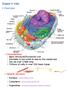 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber
 INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
6 Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cells * 1 Prokaryotes * Bacteria No nucleus No internal membranes Fewer organelles 2 Eukaryotes *
 1 Cell Biology Mark Mayo Cypress College 2 Cell Theory All organisms are made up of cells All substances in organisms are products of cells Cells come from other cells by reproduction 3 Types of Cells
1 Cell Biology Mark Mayo Cypress College 2 Cell Theory All organisms are made up of cells All substances in organisms are products of cells Cells come from other cells by reproduction 3 Types of Cells
Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS. Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles
 Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles Use the info on the following slides to complete pages 4 5 in your
Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles Use the info on the following slides to complete pages 4 5 in your
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
CELL II. SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL CYTOSKELETON
 CELL II. SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Basic requirements: Chapter 4 The working units of life (page: 68-94), parts dealing with cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix Chapter 9 Chromosome, the cell cycle
CELL II. SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Basic requirements: Chapter 4 The working units of life (page: 68-94), parts dealing with cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix Chapter 9 Chromosome, the cell cycle
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 7
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
Guide to the Ultrasound Examination of the Abdomen
 Guide to the Ultrasound Examination of the Abdomen Guide to the Ultrasound Examination of the Abdomen M. Leon Skolnick, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Director,
Guide to the Ultrasound Examination of the Abdomen Guide to the Ultrasound Examination of the Abdomen M. Leon Skolnick, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Director,
2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU HISTOLOGY: w Study of the structure and function of tissues and organs at the microscopic levels. w Tissues
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU HISTOLOGY: w Study of the structure and function of tissues and organs at the microscopic levels. w Tissues
Transesophageal Echocardiography
 N. Kolev, G. Huemer, M. Zimpfer Transesophageal Echocardiography A New Monitoring Technique Springer-Verlag Wien New York Nikolai Kolev, MD, FACC Research Cardiologist Associate in Anesthesia and Consultant
N. Kolev, G. Huemer, M. Zimpfer Transesophageal Echocardiography A New Monitoring Technique Springer-Verlag Wien New York Nikolai Kolev, MD, FACC Research Cardiologist Associate in Anesthesia and Consultant
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
4. Which accurately explains the functions of the organelles lysosomes? They:
 1. Although the basic structure of the cell plasma membrane is formed by a lipid bilayer, most of the specific membrane functions are carried out by: A) Bound and transmembrane proteins B) Complex, long
1. Although the basic structure of the cell plasma membrane is formed by a lipid bilayer, most of the specific membrane functions are carried out by: A) Bound and transmembrane proteins B) Complex, long
The Linear Regression Model Under Test
 Walter Kramer Harald Sonnberger The Linear Regression Model Under Test Physica-Verlag Heidelberg Wien Professor Dr. WALTER KRAMER, Fachbereich Wirtschaftswissenschaften, UniversWit Hannover, Wunstorfer
Walter Kramer Harald Sonnberger The Linear Regression Model Under Test Physica-Verlag Heidelberg Wien Professor Dr. WALTER KRAMER, Fachbereich Wirtschaftswissenschaften, UniversWit Hannover, Wunstorfer
Urolithiasis: Etiology Diagnosis. Hans-Joachim Schneider. M.Peacock W. G. Robertson H.-J. Schneider W. Vahlensieck
 Urolithiasis: Etiology Diagnosis Edited by Hans-Joachim Schneider Contributions by M.Peacock W. G. Robertson H.-J. Schneider W. Vahlensieck With 168 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Urolithiasis: Etiology Diagnosis Edited by Hans-Joachim Schneider Contributions by M.Peacock W. G. Robertson H.-J. Schneider W. Vahlensieck With 168 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell
 Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
The. Vertebral Artery. Pathology and Surgery. Bernard George. Claude Laurian. Springer-Verlag Wi en New York
 The Vertebral Artery Pathology and Surgery Bernard George Claude Laurian Springer-Verlag Wi en New York Bernard George, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, H6pital Lariboisiere, Paris, France Claude Laurian,
The Vertebral Artery Pathology and Surgery Bernard George Claude Laurian Springer-Verlag Wi en New York Bernard George, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, H6pital Lariboisiere, Paris, France Claude Laurian,
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
