An additional trigeminal system in certain snakes possessing infrared receptors
|
|
|
- Letitia Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 340 Brain Research, 78 (l ;~:) Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam - Printed in The Netherlands An additional trigeminal system in certain snakes possessing infrared receptors GERARD J. MOLENAAR Institute of Veterinary Anatomy, State University Utrecht, Utrecht (The Netherland~,i (Accepted June 14th, 1974) This communication describes a nucleus and tract of the trigeminal system whose existence is not mentioned m any account of brain stem architecture known to the present author. The structures were first recognised in the brain stem of a giant snake (Python reticulatus) and later were also found in rattlesnakes lcrotalus cerastes and C. atrox), but not in the brain of a viper ( Vipera ammodytes). The description is based primarily upon serial sections of python brains. 5 from normal animals and 9 from animals in which the trigeminal nerve roots had been transected (under Fluothane anaesthesia days before sacrifice). The normal series were stained by Luxol fast blue and cresyl fast violet, by cresyt fast violet alone or by gallocyanine and methyl greenl The degeneration series was prepared according to the Fink-Heimer I procedure s. Reference series of rattlesnake and viper brains, stained by Luxol fast blue and cresyl fast violet, were kindly made available by Prof. P. Dullemeyer, Leiden, On entering the medulla oblongata the majority of the trigeminal sensory fibres either terminate in the main sensory nucleus, or turn caudally to form the descending tract, the fibres of which terminate partly in the associated nucleus, and partly continue as the spinal trigeminal tract. Those sensory fibres that ascend to the mesencephalon or cerebellum will not be discussed here. Fig. I. Semi-schematic drawings of sections through the brain stem of the python showing the distribution pattern of sensory trigeminal fibre contingents. A. at the level of the trigeminal roots: B, at the level of the abducens root: C. at the cranial level of the VIIIth root: D, just caudal to the VIIlth root: E, at the level of IXth and Xth roots: F. at the level of the XIIth root: G, at the beginning of the first cervical segment. Key for both figures: 1, sensory root of V" 2, main sensory nucleus of V; 3, lateral descending tract of V (LTTD); 4, descending tract of V (TTD); 5, nucleus of the descending tract: 6. nucleus of the lateral descending tract: 7, spinal tract of V: 8. nucleus of the spinal tract; and a, motor root of V; b, ventrolateral motor nucleus of V: c. dorsomedial motor nucleus of V; d~ colliculus caudalis: e, cerebellum; f, fourth ventricle: g, nucleus of VI: h. fasciculus longitudinalis medialis: i. root of Vt; j, root of VIII: k, fasciculus solitarius: m. area acustica, n. roots of IX and X: o, motor n ucleus of X: p, central canal; q, root of XII.
2 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS 341 A /3 3 C D F ~ G
3 342 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS In the python an additional bundle is present, formed by fibres representing all of the 3 primary divisions of the sensory trigeminus. This bundle follows the peripheral aspect of the descending tract proper (TTD) and is provismnally named the lateral descending tract (LTTD). The two tracts are separated by a layer of coarse. loosely arranged fibres, tentatively assigned to the TTD. The two tracts can also be distinguished by the orientation of their fi bres i n transverse sections o f t he brain stem : the fibres of the TTD are cut obliquely, those of the LTTD transverselw The fibres of the LTTD terminate in a large nucleus placed lateral to the TTD and extending from the level of entrance of the VllIth nerve to the caudal part of the third cervical segment. The nucleus has its greatest cross-sectional area a short distance behind its rostral pole where it forms a conspicuous elevation on the ctorsolateral aspect of the brain stem. It tapers caudally and is reduced to a thin layer of gray matter at the level of exit of the IXth and Xth nerves. The nucleus and the TTD migrate dorsally at the transition between medulla oblongata and cervical cord and the nucleus then comes to lie over the dorsolatera[ aspect of the trigeminal spinal tract where it is not easily recognised without the help of degeneration preparations. The detailed topography is given in Fig. I Neurones are relatively sparse within the neuropil of the nucleus. Most are small, round or oval but some, in the rostral part of the nucleus, are larger and bi- or multipolar. The projection of the TTD fibres to the associated nucleus and the cervical medulla was confirmed in the degeneration preparations: the details of the arrangement are the subject of current work. In these degeneration preparations the fibres of the LTTD were found to be more densely packed than the normal preparattons had suggested. They run directly towards the lateral nucleus which they penetrate over the greater part of its surface: those which enter more caudally form a distinct fibre layer that sharply delineates the nucleus. After penetration, the fibres run in small bundles, mostly in a caudal direction, and abundant terminal degeneration is found throughout the nucleus. In rattlesnake a similar distribution of the descending fibres was found (Fig. 2B). The large cell mass at the termination of the lateral tract forms an even more prominent ridge on the dorsolateral aspect of the medulla in this species. The cranial border of the nucleus is level with the root of the vagus nerve, caudal to the region in which the descending tract shifts dorsomedially to become the spinal tract. The main mass o! the nucleus takes a position over the dorsolateral aspect of the spinal tract and thus the nucleus as a whole occupies a position corresponding to that of the tail of the nucleus in the python. A narrow caudal extension of the nucleus follows the dorsolateral aspect of the spinal tract. In the viper neither a lateral descending tract nor a lateral nucleus could be identified (Fig. 2C). It is remarkable that these large structures should previously have gone unnoticed, for, though relatively little is known of the anatomy of the reptilian brain stem, there is at least one article which deals specifically with the medulla oblongata of the rattlesnake, C. atroxl The author of that study makes no mention of the
4 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS 343 Fig. 2. Photomicrographs of transverse sections of brain stems of python (A), rattlesnake (B) and viper (C), at the level of the VIllth root (1) and the motor X nucleus (2). Staining: Luxol fast blue and cresyl fast violet. Magnification: AI and A2 ~ 30; BI ~ 50; B2, CI and C2 60. lateral descending t r a c t a n d nucleus. His omission is perhaps explained by the limitations o f the m a t e r i a l available to him, since the structures are u n d o u b t e d l y more obtrusive in d e g e n e r a t i o n t h a n in n o r m a l p r e p a r a t i o n s. Even so, the rostral pole o f the nucleus a p p e a r s to be present in his Fig. 10. It is p r o b a b l y significant t h a t the species which have been found to possess this a d d i t i o n a l system are distinguished from o t h e r reptiles by the possession o f pit organs,
5 344 SHORT COMMUNICAI'ION~q i.e. infrared sensors 2,3 allowing the animal to recognise and locate warm-blooded prey 4. Since it is known that all 3 primary subdivisions of the trigeminal nerve suppb the pit organs z, the finding that all 3 contribute to the lateral tract is consistent with this conjectured association. By analogy with other trigeminal sensory s~stems, involvement of some part of the trigeminal nuclear complex in mediating the information from the pit organs would be expected. No particular subdivision of the trigeminal complex, however, has yet been identified with the pit-organ sensorium, and it appears that the only relevant physiological finding published is that infrared stimulation of the pit organs activates units in the tectum mesencephali ~ Further degeneration experiments to determine the projectmns of the lateral descending tract in more detail, as well as the connections of the nucleus, are in progress, whilst investigation of the involvement of the lateral nucleus in infrared perception is planned. The author wishes to thank Dr. J. L. Dubbeldam, Prof. P. Dultemeyer and Prof. K. M. Dyce for critical discussions, and Miss A. Oostveen. Mr. H. Otter and Mr. H. Schifferstein for skilled assistance. 1 AUGULIS, V.. AND SEPINWALI_. J.. Use of gallocyanin as a myelin stain for brain and spinal cord. Stain Technol.. 46 (1971) BARRETT. R.. The pit organs of snakes. In C. GANS AND T. S. PARSONS (Eds. ~. Biolog)' ot the Reptilia, VoL 2. Academic Press. London pp BULLOCK. T. U.. AND BARRETT. R.. Radiant heat reception in snakes. Contmm~. Behar. BioL. 1 (1968) DULLEMEYER. P.. Some remarks on the feeding behaviour of rattlesnakes. Proc. kml. ned Akad Wet., 64 (1961) F~NK, R. P.. AND HEMMER, L., Two methods for selective silver impregnation of degenerating axons and their synaptic endings in the central nervous system. Brain Research, 4 (1967} GORIS, R. C.. AND TERASHIMA, S. I.. Central response to infrared stimulation of the pit receptors in a Crotatine snake. Trimeresurus flavoviridis. J. exp. Biol., 58 (1973) WARNER. F, J.. The medulla of Crotalus atrox. J. nerv. ment. Dis',. 81 [1935) ,
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
1/10/2013. What do neurons look like? Topic 14: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves. How do neurons work? The nervous impulse. Specialized Neurons
 Topic 4: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves What do neurons look like? Neurons What do they look like? How do they work? Neuronal and spinal organization What is the difference between neuron & nerve? How
Topic 4: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves What do neurons look like? Neurons What do they look like? How do they work? Neuronal and spinal organization What is the difference between neuron & nerve? How
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi
 Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Cranial Nerve Nuclei MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning materials,
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Cranial Nerve Nuclei MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning materials,
Laboratory Manual for Comparative Anatomy and Physiology Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
 Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord
 Bio101 Laboratory 13 Neuron/Spinal Cord Histology Brain Anatomy Ear & Eye Anatomy 1 Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord Objectives for today s lab Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the brain
Bio101 Laboratory 13 Neuron/Spinal Cord Histology Brain Anatomy Ear & Eye Anatomy 1 Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord Objectives for today s lab Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the brain
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu
 Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
Hypothalamus. To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine secretions NTA Ch 14, pgs Key Figs: 14-3; 14-4,
 Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Nervous System. The Peripheral Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Reflexes Pathways
 Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons
 Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons 1. Overview of the brainstem subdivisions 2. Embryonic development of the brainstem 3. Medulla oblongata external features 4. Internal structure of the medulla oblongata
Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons 1. Overview of the brainstem subdivisions 2. Embryonic development of the brainstem 3. Medulla oblongata external features 4. Internal structure of the medulla oblongata
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Teacher Key. Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body.
 Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body. Introduction to Neurons An individual s survival and reproductive success depends upon
Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body. Introduction to Neurons An individual s survival and reproductive success depends upon
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla
 Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES
 [218] UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES BY S. WOLDRING AND M. N. J. DIRKEN Physiological Institute, Groningen, Netherlands (Received 17 July 1950) (With Plate 2 and one Text-figure) Adrian
[218] UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES BY S. WOLDRING AND M. N. J. DIRKEN Physiological Institute, Groningen, Netherlands (Received 17 July 1950) (With Plate 2 and one Text-figure) Adrian
YASUSHI SEKI ABSTRACT
 ANATOMICAL STUDIES ON THE CELL COLUMN LOCATED CLOSELY MEDIAL TO THE NUCLEUS OF THE SPINAL ROOT OF THE TRIGEMINAL NERVE IN THE SPERM AND THE PYGMY SPERM WHALES YASUSHI SEKI Department qf Anatonry, Kanazawa
ANATOMICAL STUDIES ON THE CELL COLUMN LOCATED CLOSELY MEDIAL TO THE NUCLEUS OF THE SPINAL ROOT OF THE TRIGEMINAL NERVE IN THE SPERM AND THE PYGMY SPERM WHALES YASUSHI SEKI Department qf Anatonry, Kanazawa
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Unit Six The Nervous System
 Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways
 General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Doctor Osama Asa ad Khader. Mohammad Alsalem
 6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
Review or skim Ch 12 on the vascular supply of the brain. Just look at pictures and legends for the clinical part at the end.
 Dental Neuroanatomy January 20 and 27, 10-12, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. Dear Students: Please print these notes and bring them with you. My style is to use a Tablet PC and I draw on either a Word
Dental Neuroanatomy January 20 and 27, 10-12, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. Dear Students: Please print these notes and bring them with you. My style is to use a Tablet PC and I draw on either a Word
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
The Nervous System An overview
 Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
PSY 215 Lecture #5 (01/26/2011) (Anatomy of the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96
 Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
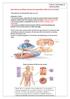 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull. Emphasis on Amniota
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull Emphasis on Amniota Initial introduction to components parts of a vertebrate head. This lecture
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull Emphasis on Amniota Initial introduction to components parts of a vertebrate head. This lecture
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Model 3-50B or 3-88 III VIII. Olfactory Nerve. Optic Nerve. Oculomotor Nerve. Trochlear Nerve. Trigeminal Nerve. Abducens Nerve.
 Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Review of Nervous System Anatomy
 For the real amazement, if you wish to be amazed, is this process. You start out as a single cell derived from the coupling of a sperm and an egg; this divides in two, then four, then eight, and so on,
For the real amazement, if you wish to be amazed, is this process. You start out as a single cell derived from the coupling of a sperm and an egg; this divides in two, then four, then eight, and so on,
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet
 The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
Nervous tissue. Lab. 7
 Nervous tissue Lab. 7 Nervous tissue :- is responsible for transport nervous impulse (motor and sensory impulse), and it is formed by network more than 100 million nerve cell (neurons), nerve fiber and
Nervous tissue Lab. 7 Nervous tissue :- is responsible for transport nervous impulse (motor and sensory impulse), and it is formed by network more than 100 million nerve cell (neurons), nerve fiber and
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day)
 Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE. Academic Year Study Guide
 NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide CNS Objectives At the end of this course, students should recognize the followings: 1. Histological structure of the brain meninges and the supporting
NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide CNS Objectives At the end of this course, students should recognize the followings: 1. Histological structure of the brain meninges and the supporting
Brainstem: Midbrain. 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain:
 Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System. Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D.
 Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D. Third week of Embryogenesis Primitive streak/pit appears on the epiblast (day
Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D. Third week of Embryogenesis Primitive streak/pit appears on the epiblast (day
Student Lab #: Date. Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System)
 Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
