CNS GENERAL REACTIONS TO INJURY. Reid Hefner, M.D. Department of Pathology and Anatomical Sciences Tuesday, November 7, 2017
|
|
|
- Tyler Hart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CNS GENERAL REACTIONS TO INJURY Reid Hefner, M.D. Department of Pathology and Anatomical Sciences Tuesday, November 7, 2017
2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Review normal gross CNS anatomy Be familiar with normal cells in CNS Know special stains used in neuropathology Understand basic CNS reactons to injury Know in what conditons a reacton occurs Know defnitons discussed in lecture
3 REFERENCES Robbins Basic Pathology. Kumar et al. Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th Editon. Saunders, Philadelphia, Chapter 28. Robbins 9th editon, 2013, Chapter 22 Or Robbins 10th editon, 2017, Chapter 23
4 MACROSCOPIC EXAM The enlarged brain Difuse=edema Hydrocephalus-early* Mass lesion(s) May create increased intracranial pressure The small brain Atrophic processes Hydrocephalus-late* Destructve processes The focal lesion Infarcts
5 BRAIN EDEMA normal edema Compare the ventricles for size Compare the sulci for width
6 Brain edema-ct scan Ventricles are slit-like
7 BRAIN EDEMA Widened gyri Narrow sulci
8 BRAIN EDEMA-CAUSES Trauma Tumor Stroke Metabolic Infecton
9 BRAIN EDEMA-MECHANISMS Cytotoxic-intracellular Vasogenic-extracellular Membrane permeability is increased Leaky hose= vascular permeability Transependymal-extracellular Increased ventricular pressure
10 CYTOTOXIC EDEMA Cells appear vacuolated Intracellular fluid
11 VASOGENIC EDEMA The leaky pipe principle
12 VASOGENIC EDEMA Most common type Located mainly in white mater Cytotoxic in gray mater Causes Tumor Stroke Abscess Trauma
13 What is wrong?
14 HYDROCEPHALUS Acute or chronic High pressure Block in ventricular fow Block in meningeal circulaton Block in reabsorpton Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Ex vacuo About 500 ml CSF produced each day
15
16
17 Ventral brain
18 Brain-lateral view
19 CSF drainage system
20 HYDROCEPHALUS CLINICAL PROBLEM OF DILATED VENTRICLES Hydrocephalus vs atrophy
21 TRANSEPENDYMAL EDEMA Rapid elevaton of ventricular pressure Fluid crosses ependymal barrier Concentrated around ventricles Brain is large
22 MASS LESIONS The brain is enlarged Cerebral Hemorrhage
23 BRAIN EDEMA/HYDROCEPHALUS/MASS LESIONCONSEQUENCES Raised intracranial pressure (RIP) Diminished cerebral blood fow ischemia Herniatons Shifs within the cranial cavity Compression of third nerve and cerebellar tonsils Blood vessel damage in pons Pressure rises exponentally once all the extra-axial spaces are flled
24 HERNIATIONS Complicatons of edema and/or mass
25 Uncal herniaton
26 Increased intracranial pressure Pressure on third cranial nerve Fixed dilated pupil Parasympathetic fibers compromised
27
28
29 What s happening here?
30 IIP-DURET HEMORRHAGES Downward movement of pons Stretching of the pontne vessels Secondary brainstem hemorrhages result Coma, death ensue
31 RAISED IP-TONSILLAR HERNATION Herniation through foramen magnum Compression of medulla
32 RAISED IP-TONSILLAR HERNATION Herniation into foramen magnum Compression of medulla
33
34 RIP and EDEMA-TREATMENT Shuntng of CSF from ventricles Acetazolamide Mannitol Reduce CSF producton (temporary) Osmotcally remove fuid from brain Cortcosteroids Works in vasogenic edema Reduces synthesis of prostaglandins Seems to reduce vascular dilaton and permeability
35 ATROPHIC BRAIN Alzheimer s Disease Widened sulci Normal sulci
36 ATROPHIC BRAIN Alzheimer s Disease Hydrocephalus ex vacuo Normal ventricles
37 DESTRUCTIVE LESIONS Old Infarct
38 FOCAL LESIONS Lacunar Infarcts
39 MICROSCOPIC EXAM Neurons Axons Neuropil and myelin Glia Ependyma Meninges
40 CELLULAR REACTIONS Injury or death Regeneraton Proliferaton or hyperplasia Atrophy or cell loss Inclusions Storage Neoplasia
41 SPECIAL STAINS IN NEUROPATHOLOGY Nissl (cresyl violet) Luxol fast blue (LFB) Astrocytc processes stained with metallic tungstc acid Cajal (Nobel Prize)-not used diagnostcally Myelin stains blue PTAH-not used anymore Ribosomes in neurons Gold impregnaton for astrocytes Silver stains (e.g. Bodian) Nerve processes Several types of inclusions, senile plaques
42 Cast of characters Nero the neuron Astrocyte Oligodendroglia Microglia Pac(man) the macrophage Expendable the ependymal cell
43 Cells of the brain
44 Nero the neuron I m pretty special because I m like an emperor All cells pay homage to me-astrocytes dote on me Pear-shaped histologically Too lazy to have offspring-no regeneration
45 Olive the oligodrocyte Myelin Loves myelin Makes and maintains
46 Aster the astrocyte Dotes on Nero Provides support to Nero Has offspring=proliferation during injury
47 Mike the microglia Fights his way between the endothelial cells and the glial cells Battles disease and the Democrats
48 Cast of characters Pac(man) the macrophage Pretty feisty Eats everything in sight
49 Expendable the ependymal cell This boring cell doesn t react much
50 NEURONS Cells do not regenerate or proliferate But axon may regenerate or sprout Necrosis Apoptosis Atrophy Chromatolysis Inclusions Storage
51 NORMAL NEURON Vesicular nucleus Prominent nucleolus Abundant ribosomes Axon Microfilaments/tubules Synapses
52 NORMAL NEURON Pear-shaped Nissl substance Nucleolus
53 Not all neurons are created equal Internal granular layer
54 NISSL SUBSTANCE Rough ER
55 NORMAL NEURON Silver stain (Bodian) shows neuronal processes Neuroflaments and neurotubules
56 ACUTE NEURONAL INJURY normal necrosis apoptosis
57 Mechanisms of Cell Death Frequently inter-related Reduced energy Mitochondrial damage May lead to apoptosis Membrane damage ATP, glucose, oxygen permeability Free radicals
58 INCLUSIONS Accumulatons of virus or proteins Causes Misfolding of normal protein Accumulaton of abnormal protein Autophagic actvity Ofen seen as hyaline or flamentous material within cell Usually eosinophilic in H&E stains Glassy and homogeneous
59 NEURONAL ATROPHY Atrophy in aging
60 INCLUSIONS viral Neurofibrillary tangle tangle
61 AUTOPHAGIC VACUOLES Granulovacuolar change in hippocampus in aging Also seen are neurofibrillary tangle and neuritic plaque
62 Granulovacuolar change
63 AUTOPHAGY Granulovacuolar change Debris in cell Then surrounded by membrane Fuses with lysosome to form autophagic vacuole Debris may be degraded/removed Can trigger cell death by complex
64 NEURONAL STORAGE-LIPID Membranous cytoplasmic bodies Tay-Sachs disease Ganglioside storage due to hexosaminidase A deficiency
65 NEURONAL LOSS Normal cerebellum Loss of granular layer cells and Purkinje cells
66 AXONS AND DENDRITES Wallerian degeneraton Spheroids (swollen axons) Segmental demyelinaton Axonal sproutng
67 NEURON AND PROCESSES Disease targets Neuron Axon Wallerian-afer neuron dies Spheroid Wallerian-afer axon is cut Spheroid Myelin Demyelinaton
68 WALLERIAN DEGENERATION Severe axonal injury or afer neuron dies Changes occur distal to injury Axonal atrophy & break-up of myelin Myelin stain
69 WALLERIAN DEGENERATION Axon shrinks (black arrow) Myelin debris with phagocytosis
70 ALS-Tract degeneraton LFB stain Rob. Fig
71 AXONAL SPHEROIDS Axon swollen Causes-sublethal injury Trauma Aging Near an infarct Toxins Vincristne Bodian silver stain
72 AXONAL SPHEROIDS Axonal transport slows/stops Distended axon Myelin may be intact, at least early Axons contain Filaments Other organelles accumulate Debris collects
73 Peripheral Nerve Injury Segmental demyelinaton=primary myelin disease Remyelinaton with onion bulbs Axonal injury May be secondary to myelin loss May be Wallerian with axonal atrophy Myelin ovoids May produce spheroids Ofen induces axonal sproutng This probably also occurs in CNS too
74 Teased nerve fbers Axons stained with osmium
75 PERIPHERAL NERVE-TEASED FIBERS 1 2 Myelin stained with osmium tetroxide (black) Normal (1), demyelinated (2) and remyelinated axons (3)
76 Segmental Demyelinaton Segments of myelin lost Between internodes typically Causes Guillain-Barré syndrome Diabetes
77 REMYELINATION Schwann cells proliferate Encircle demyelinated axon NORMAL NERVE ONION BULBS
78 Onion bulb Spiraling Schwann cells Rob. Fig. 27-5
79 AXONAL INJURY WITH MYELIN OVOIDS Myelin breaks down (ovoids) after axonal injury More diffuse, not segmental
80 Axonal sproutng Axon injury
81 NEUROPIL AND MYELIN Neuropil is the background in the grey mater Neuritc plaques Spongiform change Myelin is abundant in the white mater Primary demyelinaton-multple sclerosis Secondary demyelinaton-infarcton
82 NEUROPIL Senile (neuritc) plaque (Bodian) CJ Disease (spongiform)
83 MYELIN MS plaque NORMAL LFB STAIN
84 ASTROCYTES Proliferate to form a glial scar Cytoplasmic swelling (gemistocytes) Elaboraton of processes Inclusions Increased cellularity (see only nuclei) Rosenthal fbers, Alzheimer II cells Neoplasia
85 NORMAL ASTROCYTE STARS IN SKY CAJAL GOLD STAIN
86 NORMAL GLIA Oligos look like lymphocytes Astrocytes have larger, vesicular (open) nuclei
87 ASTROCYTES Glial fbrillary Acidic protein (GFAP)
88 GLIOSIS CNS s answer to fbrosis Increased astrocytes seen as increased numbers of nuclei
89 GLIOSIS Gemistocytes ([Gr] gemistos) Astrocyte cytoplasm is swollen or hypertrophic Seen in early gliosis but can remain for months
90 Gemeste or Greek stuffed pepper
91 FIBRILLARY GLIOSIS Glial processes form a scar (PTAH)
92 ASTROCYTE INCLUSIONS Rosenthal fbers Seen in long term gliosis, especially in benign childhood astrocytomas Masses of intermediate filaments Contain αβ-crystalline and ubiquitin
93 Alzheimer type II astrocytes Nothing to do with Alzheimer s disease Type of reactive astrocyte seen in hepatic disease Nucleus enlarged and clear
94 ASTROCYTE type II INCLUSIONS Seen in liver disease with serum NH3 Nucleus enlarged, clear, contains glycogen Alzheimer I cell larger, multiple nuclei, visible cytoplasm Alz II cell
95 OLIGODENDROGLIA Make and maintain myelin Limited regeneraton/limited remyelinaton Vacuolizaton Inclusions Damage and loss demyelination Ischemia, MS, PML Neoplasia
96 OLIGODENDROCYTES Major dense line (dark)=inner membrane Intraperiod line=extracellular space
97 OLIGODENDROCYTES LFB stain showing myelinated areas
98 OLIGODENDROCYTES NORMAL BRAIN Satellite oligos Near neurons Rows of oligos in white matter
99 OLIGODENDROCYTES Cytoplasmic vacuoles in (cytotoxic) edema
100 OLIGODENDROCYTES Intranuclear viral inclusions in PML
101 OLIGODENDROCYTE Necrosis Eosinophilic cytoplasm with fuzzy nucleus
102 MICROGLIA Derived mainly from monocytes in blood Begin as rod cells giter cells Proliferate at site of injury Difuse in large lesions Focal lesions Neuronophagia Glial nodules
103 MICROGLIA The Unglia -Not really glia Monocytes enter brain from blood
104 MICROGLIA Rod cells frst Flaten out to travel between axons and other cell processes
105 Pacman the macrophage Pac Man eats everything in sight
106 PHAGOCYTIC MICROGLIA Gitter cells (macrophages) Cytoplasm resembles a lattice
107 MICROGLIA Neuronophagia Phagocytotosis of neurons in apoptosis Glial nodules Focal clusters of microglia et al
108 EPENDYMAL CELLS The pathologically boring cell that doesn t react much Ependyma keeps CSF within ventricles Limited regeneratve or reactve potental Cell loss Infecton/infammaton Hydrocephalus, infecton Ependymits granularis (actually astrocytc gliosis) From meningits CMV infecton Neoplasia
109 NORMAL EPENDYMA Ciliated epithelium
110 EPENDYMAL CELLS Ependymits granularis Proliferaton of subependymal astrocytes Seen afer hydrocephalus or infammaton of the ventricles
111 CMV infecton of ependyma CMV loves ependyma Intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions
112 MENINGES: DURA AND PIAARACHNOID Blood or infammatory cells may be seen in these spaces Fibrosis of the leptomeninges Tumors Meningiomas
113 MENINGES Focal hyperplasia of arachnoid Derived from neural crest Pia-arachnoid (leptomeninges)
114 MENINGEAL FIBROSIS Causes Aging Meningits Bleeding Consequences Slows CSF circulaton or reabsorpton May result in hydrocephalus
115 MENINGES Meningioma
116 THE END Augustus Waller Franz Nissl Raymond Cajal del Rio Hortega
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
features of CNS pathology
 سالي ابو رمان Characteristic features of CNS pathology Important notes : - In this sheet I arranged slides within what the doctor said plus what is written in the book, hopefully it will be helpful and
سالي ابو رمان Characteristic features of CNS pathology Important notes : - In this sheet I arranged slides within what the doctor said plus what is written in the book, hopefully it will be helpful and
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019. Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 1: an introduction: Nervous system cells and their response to injury.
 CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 1: an introduction: Nervous system cells and their response to injury. CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 1: an introduction: Nervous system cells and their response to injury. CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA
 THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are important for your clinical years and your work as
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are important for your clinical years and your work as
CNS third year med students Summary of midterm material H Awad
 CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Chapter 7. The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Human Histology The Nervous System. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System
 Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Nervous system part 1. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Tumors of the Central Nervous System
 Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
HISTOLOGY د.عبد الجبار فالح الربيعي
 Nervous System The human Nervous system is the most complex system in the human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Anatomically
Nervous System The human Nervous system is the most complex system in the human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Anatomically
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei
 Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more
 Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Nerve Cell Flashcards
 1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
NERVOUS TISSUE. 1. Functional units of the nervous system; receive, process, store and transmit information to other neurons, muscle cells or glands.
 NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
A. Subdivisions of the Nervous System: 1. The two major subdivisions of the nervous system:
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
The Nervous System An overview
 Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 CHAPTER 10 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Overview of the Nervous System A. Subdivisions of the Nervous System: 1. The two major subdivisions of the nervous system:
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Neural Tissue. Chapter 12 Part A
 Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part A Homeostasis Homeostasis refers to maintaining internal environment. How does body maintain homeostasis?? 1. Each cell, tissue or organ maintain their own internal environment
Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part A Homeostasis Homeostasis refers to maintaining internal environment. How does body maintain homeostasis?? 1. Each cell, tissue or organ maintain their own internal environment
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Disease of Myelin. Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 9, 2019
 Disease of Myelin Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 9, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES TO DECLARE. I HAVE NO
Disease of Myelin Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 9, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES TO DECLARE. I HAVE NO
The Neuron. Consists Of: - cell body. - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin. dendrites Axon terminal. Cell body. nucleus. axon.
 The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1 NORMAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY
 1 NORMAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY OF THE CNS Anatomy 1 Histology 4 ANATOMY Knowledge of nervous system anatomy is essential for success in surgical neuropathology. Familiarity with native cellular elements
1 NORMAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY OF THE CNS Anatomy 1 Histology 4 ANATOMY Knowledge of nervous system anatomy is essential for success in surgical neuropathology. Familiarity with native cellular elements
Cerebrovascular diseases-2
 Cerebrovascular diseases-2 Primary angiitis of CNS - Other causes of infarction i. Hypercoagulable states ii. Drug-abuse such as amphetamine, heroin and cocain Note - The venous side of the circulation
Cerebrovascular diseases-2 Primary angiitis of CNS - Other causes of infarction i. Hypercoagulable states ii. Drug-abuse such as amphetamine, heroin and cocain Note - The venous side of the circulation
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
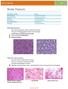 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Nervous System. Basic Divisions of the Nervous System C H A P T E R 12.
 C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
10.1: Introduction. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial cells) Dendrites.
 10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019. Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Nervous system. 1. Neurons :
 Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells!
 Bio 3411 Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells September 2, 2011 Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells Bio 3411 Friday September 2, 2011 T. Woolsey 3802 North Building 362-3601 woolseyt@wusm.wustl.edu
Bio 3411 Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells September 2, 2011 Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells Bio 3411 Friday September 2, 2011 T. Woolsey 3802 North Building 362-3601 woolseyt@wusm.wustl.edu
Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells!
 Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells Bio 3411 Friday T. Woolsey Center for History Of Medicine 6 th Floor Becker Medical Library &/or Department of Neurological Surgery 3802 North Building 362-2725
Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells Bio 3411 Friday T. Woolsey Center for History Of Medicine 6 th Floor Becker Medical Library &/or Department of Neurological Surgery 3802 North Building 362-2725
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
The Nervous System 7PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat
 Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
Functions of the Nervous System. Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue
 Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue Overview Structure cell types & structures Neurophysiology membrane potential Synapse, neurotransmitters & receptors Functions of the Nervous System
Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue Overview Structure cell types & structures Neurophysiology membrane potential Synapse, neurotransmitters & receptors Functions of the Nervous System
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System
 Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves. Chapter 14 Part A
 Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Lecture II. The Nervous System and Its Cells!
 Lecture II. The Nervous System Bio 3411! Friday! T. Woolsey! 3802 North Building 362-3601 woolseyt@wusm.wustl.edu! 2! 3! 4! Readings! Movie - vmjr-brain.mov! NEUROSCIENCE:!3 rd ed, pp 1-22! THE BRAIN ATLAS:!3
Lecture II. The Nervous System Bio 3411! Friday! T. Woolsey! 3802 North Building 362-3601 woolseyt@wusm.wustl.edu! 2! 3! 4! Readings! Movie - vmjr-brain.mov! NEUROSCIENCE:!3 rd ed, pp 1-22! THE BRAIN ATLAS:!3
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office # 117 Chapter 7 The Nervous System The Nervous System 1.Organization of the nervous system. 2.Nervous tissue:
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office # 117 Chapter 7 The Nervous System The Nervous System 1.Organization of the nervous system. 2.Nervous tissue:
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Func?ons of the Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System 1/28/ Sensory input. 2. Integra?on
 Func?ons of the Nervous System 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A 1. Sensory input Informa?on gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes 2. Integra?on
Func?ons of the Nervous System 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A 1. Sensory input Informa?on gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes 2. Integra?on
! BIOL 2401! Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College BIOL Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
PRIMARY DISEASES OF MYELIN. By: Shifaa Al Qa qa
 PRIMARY DISEASES OF MYELIN By: Shifaa Al Qa qa Most diseases of myelin are primarily white matter disorders??? Myelinated axons most diseases of CNS myelin do not involve the peripheral nerves to any significant
PRIMARY DISEASES OF MYELIN By: Shifaa Al Qa qa Most diseases of myelin are primarily white matter disorders??? Myelinated axons most diseases of CNS myelin do not involve the peripheral nerves to any significant
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your scantron answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet ID
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your scantron answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet ID
Nervous Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
Unit Three. I. General Functions of the Nervous System. I. General Functions of the Nervous System
 10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body
 Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
sensory input receptors integration Human Anatomy motor output Ch. 7 effectors Structural classification
 Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
Disorders of the Nervous System. Disorders of the Neurological System. General Endpoints of CNS Disease. General Endpoints of CNS Disease
 HD in Nursing-Pathophysiology Disorders of the Nervous System What are some disorders of the nervous system? Disorders of the Neurological System Dr. C.H. Lai The nervous system is vulnerable to various
HD in Nursing-Pathophysiology Disorders of the Nervous System What are some disorders of the nervous system? Disorders of the Neurological System Dr. C.H. Lai The nervous system is vulnerable to various
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology
 BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
IV. Cerebrovascular diseases
 IV. Cerebrovascular diseases - Cerebrovascular disease denotes brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving the blood vessels. - The three main pathogenic mechanisms are: 1. Thrombotic occlusion
IV. Cerebrovascular diseases - Cerebrovascular disease denotes brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving the blood vessels. - The three main pathogenic mechanisms are: 1. Thrombotic occlusion
(3) Chemical synapse ---structure
 (3) Chemical synapse ---structure LM: in silver preparation dark brown color button-liked on the surface of cell body and dendrites called synaptic button LM: synaptic button (3) Chemical synapse ---structure
(3) Chemical synapse ---structure LM: in silver preparation dark brown color button-liked on the surface of cell body and dendrites called synaptic button LM: synaptic button (3) Chemical synapse ---structure
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS
 Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
April 29, Neurophysiology. Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University,
 April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
Symptoms of spinal cord injury:
 Symptoms of spinal cord injury: involuntary muscle spasms loss of voluntary movement sensation, balance control of breathing autonomic functions (blood pressure) bladder, sexual, bowel control All due
Symptoms of spinal cord injury: involuntary muscle spasms loss of voluntary movement sensation, balance control of breathing autonomic functions (blood pressure) bladder, sexual, bowel control All due
Chapter 12 The Nervous System INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Central Nervous System (CNS): STRUCTURE BRAIN SPINAL CORD NERVES
 Chapter 12 The Nervous System PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE BRAIN SPINAL CORD NERVES Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain Spinal
Chapter 12 The Nervous System PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE BRAIN SPINAL CORD NERVES Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain Spinal
The cells of the nervous system
 The cells of the nervous system LESSON N.9 - PSYCHOBIOLOGY because of the location and volume as compared to our body, the brain has always been a matter of conjecture about its fundamental role in the
The cells of the nervous system LESSON N.9 - PSYCHOBIOLOGY because of the location and volume as compared to our body, the brain has always been a matter of conjecture about its fundamental role in the
