Cranial Pachymeningeal Involvement in POEMS Syndrome: Evaluation by Pre- and Post-contrast FLAIR and T 1. -weighted Imaging MAJOR PAPER.
|
|
|
- Pearl McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; doi: /mrms.mp Published Online: December 22, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Cranial Pachymeningeal Involvement in POEMS Syndrome: Evaluation by Pre- and Post-contrast FLAIR and -weighted Imaging Fumiaki Ueda 1*, Miho Okuda 2, Hiroyuki Aburano 2, Yuichi Yoshie 2, Osamu Matsui 1, and Toshifumi Gabata 2 Purpose: To evaluate the cranial pachymeningeal involvement of polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, skin changes (POEMS) syndrome using pre- and post-contrast fluidattenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) and -weighted imaging ( WI). Methods: The appearance of pachymeningeal involvement in nine cases of POEMS syndrome was evaluated using pre- and post-contrast FLAIR and The degree of pachymeningeal thickening was graded as normal or abnormal using pre-contrast FLAIR. The degrees of contrast enhancement effect were evaluated based on pre- and post-contrast images, and recorded in each of three separate anatomical areas, i.e., the falx cerebri, cerebral convexity, and tentorium cerebelli. The degrees of contrast enhancement of pachymeninges were graded as not detected (ND), positive, or prominent on post-contrast FLAIR, and normal range (NR), positive, and prominent on post-contrast Results: Pre-contrast FLAIR demonstrated 41% of pachymeningeal anatomical regions as areas of thickening. Post-contrast FLAIR did not detect any contrast enhancement on 26% of the regions but showed positive enhancement on 30% and prominent enhancement on 44%. Post-contrast WI showed normal range enhancement on 48%, positive enhancement on 11%, and prominent enhancement on 41% of the regions. Post-contrast FLAIR showed the highest percentage for detection of pachymeningeal abnormalities (74%). Conclusion: Post-contrast FLAIR may contribute to objective judgment in the evaluation of pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome. Keywords: POEMS syndrome, magnetic resonance imaging, pachymeninges, contrast enhancement, FLAIR Introduction Polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, skin changes (POEMS) syndrome is a rare systemic disease associated with underlying plasma cell dyscrasia. Although its pathogenesis is not yet fully understood, its clinical manifestations have been attributed to increased concentrations of serum or plasma vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). 1 Although a diagnosis of POEMS syndrome can be suspected based on the clinical course, the infrequency of this disease has often resulted in diagnostic and therapeutic delay. 2 No single 1 Department of Advanced Medical Imaging, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kanazawa University, 13-1 Takaramachi, Kanazawa, Ishikawa , Japan 2 Department of Radiology, Kanazawa University Hospital, Ishikawa, Japan *Corresponding author, Phone: , Fax: , fumiaki@staff.kanazawa-u.ac.jp 2016 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives International License. Received: February 3, 2015 Accepted: October 24, 2016 test is sufficient to establish a diagnosis of POEMS syndrome. In addition, even with the previously established diagnostic criteria, 1 there have been reports of patients not satisfying the criteria but for whom a therapeutic strategy also taking into consideration the possibility of POEMS syndrome is needed. 2 In contrast, other cases have been described that despite satisfying these criteria continue to show a clinically benign course inconsistent with POEMS syndrome. 3 The existence of such cases suggests that the recent criteria may be inappropriate in some situations but too strict in others to identify patients that require specific treatment for POEMS syndrome. Therefore, there is a need for an examination that is easy to perform and that can reveal abnormalities specific to POEMS syndrome. The clinical manifestations of POEMS syndrome are thought to be associated with microangiopathy, neovascularization, and accelerated vasopermeability. Tissue vascular permeability is considered to increase in parallel with serum VEGF level. Therefore, VEGF released from plasma cells and/or platelets may induce edema and microangiopathy/macroangiopathy, potentially resulting in the various clinical features of POEMS syndrome. POEMS syndrome Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences Vol. 16, No
2 F. Ueda et al. can be associated with cerebral infarction as a result of cerebral vasculopathy. 4,5 Although contrast-enhanced cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of POEMS syndrome has revealed a high frequency of pachymeningeal enhancement, 6,7 to our knowledge, there have been no previous studies using preand post-contrast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) in the evaluation of pachymeningeal involvement of POEMS syndrome. This suggested that contrast-enhanced cranial MRI using both FLAIR and -weighted images ( WI) may contribute to accurate and more specific evaluation of pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome. In this study, we evaluated the distribution and imaging manifestations of cranial pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome using both pre- and post-contrast FLAIR and Materials and Methods This study was approved by the local institutional review board, and informed consent was obtained from each patient for MRI examination using contrast medium. We encountered nine cases of POEMS syndrome diagnosed according to the clinical criteria of Dispenzieri. 8 We performed cranial MRI to evaluate ischemic brain damage in POEMS syndrome. In addition, we also performed contrast-enhanced MRI using both pre- and post-contrast FLAIR and WI to evaluate pachymeningeal involvement. Clinical and laboratory data of the nine cases of POEMS syndrome are listed in Table 1. Most clinical and laboratory examinations were performed before the MRI examination, but cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination was performed after cranial MRI. In our institution, the normal serum VEGF level is < 38 pg/ml, the normal CSF protein concentration range is mg/dl, and the normal CSF pressure range is mmh 2 O. MRI was performed using a 1.5T imager in seven cases and 3.0T imager in two cases (both Signa; GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI). FLAIR imaging was performed using a fast FLAIR sequence with a repetition time/effective echo time/ inversion time of 10000/175/2200 ms on 1.5T MRI and 9000/150/2400 ms on 3.0T MRI. WI was performed using the 2-dimensional spin echo (SE) method (TR, TE: 500, 8) in both 1.5T and 3.0T MRI examinations. We did not use a fat suppression technique. All of the imaging sequences were acquired with a slice thickness/interslice gap = 5/1 mm. In our institution, the routine MRI protocol for meningeal diseases includes both axial and coronal pre- and post- contrast FLAIR and WI, including diffusion-weighted, sagittal WI, and axial T 2 -weighted images. We adopted this protocol to evaluate the pachymeningeal involvement of POEMS syndrome. Postcontrast images were obtained after slow intravenous administration (manual injection) of 0.1 mmol/kg body weight gadopentetate dimeglumine (Gd-DTPA; Magnevist, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceutical, Berlin, Germany, or Gd-DTPA- bismethylamide (Gd [DTPA-BMA]); Omniscan Daiichi-Seiyaku, Tokyo, Japan). Post-contrast FLAIR imaging was performed before post-contrast WI in all MRI examinations. Three neuroradiologists (O.M., H.A., and Y.Y.) each with > 10 years of experience who were unaware of the diagnosis of POEMS syndrome reviewed all of the pre- and post- contrast MR images. The pachymeningeal thickness was evaluated using pre-contrast FLAIR and classified as normal or abnormal. Assessments of the degree and extent of the contrast enhancement effect using a pair of pre- and post-contrast FLAIR and WI were performed. Pre- and post-contrast images were compared side by side to determine the degree of enhancement effect. The degree of contrast enhancement effect in all cases was evaluated by all of the reviewers and recorded independently in each of three separate anatomical regions, i.e., falx cerebri, cerebral convexity, and tentorium cerebelli. After independent review, a consensus was reached regarding the results. On post-contrast FLAIR, the normal dural sinus is occasionally enhanced, 9 but the normal pachymeninges and cortical vessels are usually not enhanced; therefore, we determined Table 1. Patients characteristics and laboratory studies of 9 cases of POEMS syndrome Polyneuropathy Organomegaly Endocrinopathy M protein Systemic edema Bone lesions VEGF (pg/ml) CSF protein (mg/dl) CSF pressure (mmh 2 O) 1 64/M IgAλ + Sclerotic /F IgGλ + Sclerotic /M IgGλ + Sclerotic /M IgAλ + Lytic /F IgAλ + Sclerotic /F IgAλ + Sclerotic /M IgAλ + Sclerotic /F IgAλ + Sclerotic /F IgAλ + Sclerotic CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; POEMS, polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, skin changes; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. 232 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
3 Pachymeningeal Involvement of POEMS the degree of enhancement as not detected, positive (i.e., detectable), or prominent. In addition, the degrees of contrast enhancement of the pachymeninges were graded as normal, positive, or prominent on post-contrast As normal pachymeninges show segmental enhancement on post-contrast WI, 10,11 we determined the degree of contrast enhancement based on accumulated past experience of normal range enhancement of post-contrast WI in our institution. Positive enhancement was determined as more conspicuous or continuous enhancement on WI evaluated by viewing several adjacent slices images and determined based on the consensus of all three reviewers. Prominent enhancement was determined as definitely continuous thick pachymeningeal enhancement on each postcontrast-flair or Results The results of the consensus regarding the range of pachymeningeal thickness of pre-contrast FLAIR and degree of postcontrast enhancement of FLAIR and WI of the pachy me ninges by the three reviewers are shown in Tables 2 4. The detectability of abnormalities in each examination of different anatomical parts and summary data are shown in Table 5. Pre-contrast FLAIR showed 41% (11/27) abnormal regions. Although post-contrast WI showed enhancement in all examinations in all regions, 48% (13/27) of MRI examinations were judged to show a normal range in each of the regions (Fig. 1). Post-contrast FLAIR did not detect any contrast enhancement on 26% (7/27) of the regions, but showed positive enhancement on 30% (8/27) and prominent enhancement on 44% (12/27) (Figs. 2 and 3). Post-contrast WI showed prominent enhancement on 41% (11/27) (Fig. 3), and positive enhancement on 11% (3/27) of the regions. Post-contrast WI did not show prominent enhancement on Table 2. Pachymeningeal thickeness of 9 cases of POEMS syndrome: evaluation by pre-contrast FLAIR Magnet Falx cerebri Location and degree of contrast enhancement Cerebral convexity Tentorium cerebelli 1 64/M 1.5T + + NR 2 69/F 1.5T + + NR 3 71/M 1.5T + + NR 4 49/M 3T NR NR NR 5 65/F 1.5T + NR NR 6 73/F 3T /M 1.5T NR NR NR 8 55/F 1.5T NR NR /F 1.5T NR NR NR NR, Normal range; +, Thickening; POEMS, polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, skin changes; FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. Table 3. Degree of pachymeningeal enhancement in 9 cases of POEMS syndrome: evaluation by post-contrast FLAIR Magnet Falx cerebri Location and degree of contrast enhancement Cerebral convexity Tentorium cerebelli 1 64/M 1.5T ND 2 69/F 1.5T ND 3 71/M 1.5T /M 3T + + ND 5 65/F 1.5T /F 3T /M 1.5T + + ND ND 8 55/F 1.5T + + ND /F 1.5T + + ND ND, Not detected; +, Positive enhancement; + +, Prominent enhancement; POEMS, polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, skin changes; FLAIR, fluidattenuated inversion recovery. Table 4. Degree of pachymeningeal enhancement in 9 cases of POEMS syndrome: evaluation by post-contrast WI Magnet Falx cerebri Location and degree of contrast enhancement Cerebral convexity Tentorium cerebelli 1 64/M 1.5T NR 2 69/F 1.5T NR 3 71/M 1.5T NR 4 49/M 3T NR NR NR 5 65/F 1.5T + + NR NR 6 73/F 3T /M 1.5T + + NR NR 8 55/F 1.5T + + NR /F 1.5T NR + NR NR, Normal range enhancement; +, Positive enhancement; + +, Prominent enhancement; POEMS, polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, skin changes. the regions where post-contrast FLAIR did not reveal any enhancement. Detectability of pachymeningeal abnormality was highest in post-contrast FLAIR74% (20/27). Discussion Pachymeningeal involvement is an abnormality associated with POEMS syndrome that has already been discussed from the viewpoints of both imaging and histopathological features, with the former showing prominent enhancement and the latter showing hyperplasia of meningothelial cells, neovascularization, and obstructive vessel remodeling, without inflammation. 6 POEMS syndrome has also been noted to manifest arterial and venous thrombosis that may result in cerebral infarction, and so some reports have attributed the MRI findings of POEMS Vol. 16, No
4 F. Ueda et al. Table 5. Detectablility of pachymeningeal abnormality of POEMS syndrome Image modalitiy location Falx cereberi Crebral convexity Tentorium cerebelli Total Pre-contrast FLAIR 5/9(56%) 4/9(44%) 2/9(22%) 11/27(41%) Gd-FLAIR 9/9(100%) 7/9(78%) 4/9(33%) 20/27(74%) Gd- WI 7/9(78%) 5/9(56%) 13/9(22%) 11/27(48%) POEMS, polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocr monoclonal gammopathy, skin changes; FLAIR, fluidattenuated inversion recovery. A B C D Fig Coronal pre- and post-contrast FLAIR (A, B) and WI (C, D). Pre-contrast FLAIR showed normal range thickness of pachymeninges in both falx and convexity. Post-contrast FLAIR imaging shows positive enhancement of the falx cerebri, where post-contrast WI showed normal range enhancement (arrows). FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. syndrome to the vascular insults of intracranial vessel involvement. 4,12 The performance of contrast-enhanced cranial MRI after routine brain examination can provide additional information in cases of probable POEMS syndrome. We consider there to be two aspects to the clinical impact of pachymeningeal involvement of POEMS syndrome revealed as prominent enhancement, the first being to help improve the diagnostic accuracy and the second to assess the therapeutic results in follow-up, because successful chemotherapy may be reflected by a reduction in the degree of pachymeningeal enhancement corresponding with that in the serum VEGF level, which is an index representing disease severity. 7 With regard to pachymeningeal contrast enhancement on MRI, normal pachymeninges are highly vascularized but do not usually show enhancement on post-contrast FLAIR. However, in practice post-contrast FLAIR images showed more conspicuous linear pachymeningeal enhancement around the operation site than on post-contrast Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
5 Pachymeningeal Involvement of POEMS A B C D Fig Axial pre- and post-contrast FLAIR (A, B) and WI (C, D). Pre-contrast FLAIR showed normal range thickness of pachymeninges in both falx and convexity. Both post-contrast FLAIR and WI showed prominent enhancement of the falx cerebri (arrows). Post-contrast WI showed normal range enhancement of the convexity, whereas post-contrast FLAIR showed negative enhancement (small arrows). FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. Proliferation of meningothelial cells, narrowing or occlusion of arterioles, thickening of the media and endothelial hyperplasia, and neovascularization with prominent capillary endothelial cells within loose extracellular matrix were reported as characteristics of cranial pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome. 6 Another ultrastructural study indicated opening of endothelial cell tight junctions in POEMS syndrome patients and suggested that alteration of microvascular hyperpermeability may be induced by VEGF. 13 Gd distribution remodeling occurring with opening of endothelial cell tight junctions in the involved pachymeninges may reveal stronger pachymeningeal enhancement on both post-contrast FLAIR and However, it is difficult to discuss the signal intensity in dural tissue correlated with Gd concentration. Delayed enhancement of the dura has been reported in even spin-density- and T 2 -weighted images, 14 meaning that when we evaluate the contrast enhancement superiority or inferiority between post-contrast FLAIR and post-contrast WI, it is important to consider image acquisition timing from intravenous injection. We performed post-contrast FLAIR first followed by post-contrast WI, and so the delayed enhancement effect was not more conspicuous in post-contrast FLAIR than post-contrast Although post-contrast WI usually shows enhancement of the pachymeninges because of the rich vascularity of the dura mater, discrimination between normal and abnormal enhancement is not easy. One reason is that the extent of normal pachymeningeal enhancement has a vague range even on standard post-contrast spin echo (SE) 10,11,14 Another reason is that the imaging appearance of postcontrast WI depends on the pulse sequence and parameters selected and the magnetic field strength of the machine. 15,16 With regard to the contrast enhancement effect when using the same amount of contrast medium, MRI at 3.0T showed greater contrast effects than that using a 1.5T machine. 16 Moreover, on comparison of contrast enhancement patterns Vol. 16, No
6 F. Ueda et al. A B C D Fig Axial pre- and post-contrast FLAIR (A, B) and WI (C, D). Pre-contrast FLAIR revealed thickened pachymeninges (arrows). Both pre-contrast FLAIR and WI showed prominent enhancement of the pachymeninges of both the falx cerebri and cerebral convexity (arrows). FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. on 3D gradient-echo and SE images, long segment enhancement of the normal pachymeninges is routinely observed on contrast-enhanced 3D gradient-echo images. 11 The elevated VEGF level is thought to be one major causative factor of POEMS syndrome. Neovascular formation may induce prominent thick enhancement of the pachymeninges. Although we do not feel that prominent pachymeningeal enhancement is specific to POEMS syndrome, the thick pachymeningeal enhancement in POEMS syndrome may be related to the opening of tight junction microvasculature induced by VEGF. Therefore, in patients with POEMS syndrome-like symptoms not satisfying the current criteria, determination of a pachymeningeal abnormal enhancement by post-contrast FLAIR may contribute to decision-making on starting appropriate therapy for POEMS syndrome. Our study had several limitations. First, evaluation of pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome was performed without pathological confirmation, and therefore the actual correlation between pathology and contrast enhancement effect was not determined. This study was retrospective in nature, and was therefore subject to bias. The sample size allowed descriptive analysis, but was too small for statistical analysis. We did not perform fat- suppressed MRI in WI, which is considered to be superior to FLAIR for depicting intracranial meningeal diseases, 17 and so the pachymeninges on post-contrast WI may have been more conspicuous if fat suppression had been used. In addition, 3D imaging methods, such as 3D T 2 -FLAIR and 3D gradient-echo WI, are commonly used in the clinical MRI acquisition. 3D T 2 -FLAIR has high sensitivity to flow, 17 and 3D gradient-echo WI shows normal dural enhancement more prominently than that revealed by SE 11 A correlation study of these two pulse sequences may further develop the discussion. Conclusions Pachymeningeal enhancement can be seen on both post-contrast FLAIR and WI in POEMS syndrome. Although the detectability of contrast enhancement is superior in postcontrast WI, post-contrast FLAIR may contribute to 236 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
7 Pachymeningeal Involvement of POEMS objective judgment in the evaluation of pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome. References 1. Dispenzieri A. POEMS syndrome: 2011 update on diag nosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 2011; 86: Morizane R, Sasamura H, Minakuchi H, et al. A case of atypical POEMS syndrome without polyneuropathy. Eur J Haematol 2008; 80: Yishay O, Eran E. POEMS syndrome: failure of newly suggested diagnostic criteria to anticipate the develop ment of the syndrome. Am J Hematol 2005; 79: Kang K, Chu K, Kim DE, Jeong SW, Lee JW, Roh JK. POEMS syndrome associated with ischemic stroke. Arch Neurol 2003; 60: Dupont SA, Dispenzieri A, Mauermann ML, Rabinstein AA, Brown RD. Cerebral infarction in POEMS syndrome: incidence, risk factors, and imaging characteristics. Neurology 2009; 73: Briani C, Fedridgo M, Manara R, et al. Pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome: MRI and histopathological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2012; 83: Briani C, Manara R, Lessi F, Citton V, Zambello R, Adami F. Pachymeningeal involvement in POEMS syndrome: dramatic cerebral MR improvement after lenalidomide therapy. Am J Hematol 2012; 87: Dispenzieri A. POEMS syndrome. Blood Rev 2007;21: Goo HW, Choi CG. Post-contrast FLAIR MR imaging of the brain in children: normal and abnormal intracranial enhancement. Pediatr Radiol 2003; 33: Sze G, Soletsky S, Bronen R, Krol G. MR imaging of the cranial meninges with emphasis on contrast enhancement and meningeal carcinomatosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1989; 10: Farn JW, Mirowitz SA. MR imaging of the normal meninges: comparison of contrast-enhancement patterns on 3D gradient-echo and spin-echo images. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994; 162: Garcia T, Dafer R, Hocker S, Schneck M, Barton K, Biller J. Recurrent strokes in two patients with POEMS syndrome and Castleman s disease. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2007; 16: Scarlato M, Previtali SC, Carpo M, et al. Polyneuropathy in POEMS syndrome: role of angiogenic factors in the pathogenesis. Brain 2005; 128: Wessbecher FW, Maravilla KR, Dalley RW. Optimizing brain MR imaging protocols with gadopentetate dimeglumine: enhancement of intracranial lesions on spindensity- and T 2 -weighted images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1991; 12: Meltzer CC, Fukui MB, Kanal E, Smirniotopoulos JG. MR imaging of the meninges part 1. normal anatomic features and nonneoplastic disease. Radiology 1996; 201: Krautmacher C, Willinek WA, Tschampa HJ, et al. Brain tumors: full- and half-dose contrast-enhanced MR imaging at 3.0T compared with 1.5T Initial experience. Radiology 2005; 237: Galassi W, Phuttharak W, Hesselink JR, Healy JF, Dietrich RB, Imbesi SG. Intracranial meningeal disease: comparison of contrast-enhanced MR imaging with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery and fat-suppressed -weighted sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005; 26: Vol. 16, No
Frequent central nervous system, pachymeningeal and plexus MRI changes in POEMS syndrome
 Journal of Neurology (2019) 266:1067 1072 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09233-z ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Frequent central nervous system, pachymeningeal and plexus MRI changes in POEMS syndrome Oliver
Journal of Neurology (2019) 266:1067 1072 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09233-z ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Frequent central nervous system, pachymeningeal and plexus MRI changes in POEMS syndrome Oliver
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features
 Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
MRI imaging in meningeal diseases
 Original article MRI imaging in meningeal diseases 1Dr. Narendrakumar M Shah, 2 Dr Vaishali D M 1Associate professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, SDM Medical college, Dharwad 2Consultant radiologist,
Original article MRI imaging in meningeal diseases 1Dr. Narendrakumar M Shah, 2 Dr Vaishali D M 1Associate professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, SDM Medical college, Dharwad 2Consultant radiologist,
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Supratentorial multiple little meningiomas with transitory stroke symptoms like. MRI case presentation
 114 Romanian Neurosurgery (2010) XVII 1: 114-121 Supratentorial multiple little meningiomas with transitory stroke symptoms like. MRI case presentation E. Moldovanu 1,2, Adriana Moldovanu 1,2, Carmen Gherman
114 Romanian Neurosurgery (2010) XVII 1: 114-121 Supratentorial multiple little meningiomas with transitory stroke symptoms like. MRI case presentation E. Moldovanu 1,2, Adriana Moldovanu 1,2, Carmen Gherman
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition
 637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
Waneerat Galassi, Warinthorn Phuttharak, John R. Hesselink, John F. Healy, Rosalind B. Dietrich, and Steven G. Imbesi
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:553 559, March 2005 Intracranial Meningeal Disease: Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging with Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery and Fat-Suppressed T1-Weighted Sequences
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:553 559, March 2005 Intracranial Meningeal Disease: Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging with Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery and Fat-Suppressed T1-Weighted Sequences
Neuroradiology Original Research
 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with Brain MR Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies
 Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hssine, N. Mallat, M. Limeme, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, H. Amara, D. Bakir,
Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hssine, N. Mallat, M. Limeme, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, H. Amara, D. Bakir,
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report
 NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas: is differential diagnosis possible?
 Neuroradiology (1997) 39: 633 638 Springer-Verlag 1997 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY I. Ikushima Y. Korogi J. Kuratsu T. Hirai S. Hamatake M. Takahashi Y. Ushio Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas:
Neuroradiology (1997) 39: 633 638 Springer-Verlag 1997 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY I. Ikushima Y. Korogi J. Kuratsu T. Hirai S. Hamatake M. Takahashi Y. Ushio Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas:
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
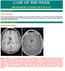 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE 26 years old male patient presented clinically with a grand male fit, confusion, fever, headache, and nausea. Examination showed bilateral papilledema and left sided extensor
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE 26 years old male patient presented clinically with a grand male fit, confusion, fever, headache, and nausea. Examination showed bilateral papilledema and left sided extensor
Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
MR Imaging of the Cranial Meninges with Emphasis on Contrast Enhancement and Meningeal Carcinomatosis
 965 MR Imaging of the Cranial Meninges with Emphasis on Contrast Enhancement and Meningeal Carcinomatosis Gordon Sze 1 2 Susan Soletsky 1 Richard Bronen 2 George Krol 1 MR imaging was used to investigate
965 MR Imaging of the Cranial Meninges with Emphasis on Contrast Enhancement and Meningeal Carcinomatosis Gordon Sze 1 2 Susan Soletsky 1 Richard Bronen 2 George Krol 1 MR imaging was used to investigate
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Imaging of Normal Leptomeningeal Melanin
 Imaging of Normal Leptomeningeal Melanin Stephen S. Gebarski and Mila A. Blaivas PURPOSE: To find the CT and MR characteristics of normal leptomeningeal melanin, which can be macroscopically visible at
Imaging of Normal Leptomeningeal Melanin Stephen S. Gebarski and Mila A. Blaivas PURPOSE: To find the CT and MR characteristics of normal leptomeningeal melanin, which can be macroscopically visible at
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis
 Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis Poster No.: C-3377 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis Poster No.: C-3377 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32: (2010)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32:1117 1123 (2010) Original Research Peripheral Hyperintense Pattern on T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Breast Carcinoma: Correlation With Early Peripheral
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32:1117 1123 (2010) Original Research Peripheral Hyperintense Pattern on T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Breast Carcinoma: Correlation With Early Peripheral
Magnetic resonance imaging (MR!) provides
 0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
The Effect of Contrast Dose, Imaging Time, and Lesion Size in the MR Detection of Intracerebral Metastasis
 The Effect of Contrast Dose, Imaging Time, and Lesion Size in the MR Detection of Intracerebral Metastasis William T. C. Yuh, E. Turgut Tali, Hoang D. Nguyen, Tereasa M. Simonson, Nina A. Mayr, and David
The Effect of Contrast Dose, Imaging Time, and Lesion Size in the MR Detection of Intracerebral Metastasis William T. C. Yuh, E. Turgut Tali, Hoang D. Nguyen, Tereasa M. Simonson, Nina A. Mayr, and David
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum
 Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol. for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS. David K.B.
 Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22: (2005)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
MR Contrast Agents. Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? US Agents. Understanding and Embracing Change
 Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Whole-Body Dynamic Contrast- Enhanced (DCE) MR Imaging in patients with myeloma
 Whole-Body Dynamic Contrast- Enhanced (DCE) MR Imaging in patients with myeloma Alain Rahmouni, Department of Medical Imaging, Mondor Academic Hospital : Centre Hospitalo-Universitaire Henri Mondor-Assistance
Whole-Body Dynamic Contrast- Enhanced (DCE) MR Imaging in patients with myeloma Alain Rahmouni, Department of Medical Imaging, Mondor Academic Hospital : Centre Hospitalo-Universitaire Henri Mondor-Assistance
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note
 High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
Perfusion Physics. ICMRI2018 March 29-31, 2018 Grand Hilton Hotel, Seoul, Korea. Asian Forum Ⅱ: Perfusion MRI SY24-1.
 SY24-1 Perfusion Physics Hiroyuki Kabasawa MR Collaborations and Development, GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan Perfusion is referred as the blood supply to micro capillary in tissue. Perfusion parameter such
SY24-1 Perfusion Physics Hiroyuki Kabasawa MR Collaborations and Development, GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan Perfusion is referred as the blood supply to micro capillary in tissue. Perfusion parameter such
A report of nontraumatic cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent management
 For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com A report of nontraumatic cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent management David Qiyuan Mao*,1, Daniel Addess 1 & Helen Valsamis
For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com A report of nontraumatic cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent management David Qiyuan Mao*,1, Daniel Addess 1 & Helen Valsamis
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department
 298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
Localization and Treatment of Unruptured Paraclinoid Aneurysms: A Proton Density MRI-based Study
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.3.180 Original Article Localization and Treatment of Unruptured Paraclinoid
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.3.180 Original Article Localization and Treatment of Unruptured Paraclinoid
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases
 Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging
 Case Reports Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging Koichi Nomura 1, Masahiro Mishina 1,SeijiOkubo 1, Satoshi Suda
Case Reports Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging Koichi Nomura 1, Masahiro Mishina 1,SeijiOkubo 1, Satoshi Suda
MRIofthe Central Nervous System
 K. Mori (Ed.) MRIofthe Central Nervous System A Pathology Atlas With the Collaboration of M. Kurisaka A. Moriki A. Sawada With 116 Case Studies and 372 Figures Springer-Verlag Tokyo Berlin Heidelberg New
K. Mori (Ed.) MRIofthe Central Nervous System A Pathology Atlas With the Collaboration of M. Kurisaka A. Moriki A. Sawada With 116 Case Studies and 372 Figures Springer-Verlag Tokyo Berlin Heidelberg New
Improving postoperative MR imaging of pituitary macroadenomas: comparison of full and reduced dose of gadopentetate dimeglumine
 Eur. Radiol. 10, 1068±1072 (2000) Ó Springer-Verlag 2000 European Radiology Original article Improving postoperative MR imaging of pituitary macroadenomas: comparison of full and reduced dose of gadopentetate
Eur. Radiol. 10, 1068±1072 (2000) Ó Springer-Verlag 2000 European Radiology Original article Improving postoperative MR imaging of pituitary macroadenomas: comparison of full and reduced dose of gadopentetate
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling chronic demyelinating disease
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
MR imaging of FIGO stage I uterine cervical cancer: The diagnostic impact of 3T-MRI
 MR imaging of FIGO stage I uterine cervical cancer: The diagnostic impact of 3T-MRI Poster No.: C-1191 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: M. Takeuchi, K. Matsuzaki,
MR imaging of FIGO stage I uterine cervical cancer: The diagnostic impact of 3T-MRI Poster No.: C-1191 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: M. Takeuchi, K. Matsuzaki,
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
MR Contrast Enhancement of the Normal Neonatal Brain
 MR Contrast Enhancement of the Normal Neonatal Brain A. James Barkovich, Beatrice Latal-Hajnal, J. Colin Partridge, Augusto Sola, and Donna M. Ferriero PURPOSE: To determine the pattern of enhancement
MR Contrast Enhancement of the Normal Neonatal Brain A. James Barkovich, Beatrice Latal-Hajnal, J. Colin Partridge, Augusto Sola, and Donna M. Ferriero PURPOSE: To determine the pattern of enhancement
Cerebral MR Venography: Normal Anatomy and Potential Diagnostic Pitfalls
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:74 78, January 2000 Cerebral MR Venography: Normal Anatomy and Potential Diagnostic Pitfalls R. H. Ayanzen, C. R. Bird, P. J. Keller, F. J. McCully, M. R. Theobald, and J. E. Heiserman
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:74 78, January 2000 Cerebral MR Venography: Normal Anatomy and Potential Diagnostic Pitfalls R. H. Ayanzen, C. R. Bird, P. J. Keller, F. J. McCully, M. R. Theobald, and J. E. Heiserman
MR of Intraparotid Masses
 MR of Intraparotid Masses Bruce N. Schlakman and David M. Yousem PURPOSE: To determine which MR techniques are best for identifying intraparotid masses and to assess the utility of MR for predicting specific
MR of Intraparotid Masses Bruce N. Schlakman and David M. Yousem PURPOSE: To determine which MR techniques are best for identifying intraparotid masses and to assess the utility of MR for predicting specific
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
The relationship of multiple sclerosis and cerebral developmental venous anomaly with an advantageous role in the multiple sclerosis diagnosis
 Iranian Journal of Neurology Original Paper Iran J Neurol 2017; 16(4): 168-72 The relationship of multiple sclerosis and cerebral developmental venous anomaly with an advantageous role in the multiple
Iranian Journal of Neurology Original Paper Iran J Neurol 2017; 16(4): 168-72 The relationship of multiple sclerosis and cerebral developmental venous anomaly with an advantageous role in the multiple
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Sulcal Hyperintensity on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images in Patients Without Apparent Cerebrospinal Fluid Abnormality
 Toshiaki Taoka 1,2 William T. C. Yuh 1 Matthew L. White 1 Jerome P. Quets 1 Joan E. Maley 1 Toshihiro Ueda 1 Received pril 25, 2000; accepted after revision ugust 10, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Magnetic
Toshiaki Taoka 1,2 William T. C. Yuh 1 Matthew L. White 1 Jerome P. Quets 1 Joan E. Maley 1 Toshihiro Ueda 1 Received pril 25, 2000; accepted after revision ugust 10, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Magnetic
Combined Fat- and Water-Suppressed MR Imaging of Orbital Tumors
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1963 1969, November/December 1999 Combined Fat- and Water-Suppressed MR Imaging of Orbital Tumors Alan Jackson, Scott Sheppard, Andrew C. Johnson, Deborah Annesley, Roger D. Laitt,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1963 1969, November/December 1999 Combined Fat- and Water-Suppressed MR Imaging of Orbital Tumors Alan Jackson, Scott Sheppard, Andrew C. Johnson, Deborah Annesley, Roger D. Laitt,
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego. MR Angiography. Techniques & Applications. John R. Hesselink, M.D.
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
 Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Corpus Callosal Signal Changes in Patients with Obstructive Hydrocephalus after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:158 162, January 2001 Corpus Callosal Signal Changes in Patients with Hydrocephalus after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting John I. Lane, Patrick H. Luetmer, and John L. Atkinson BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:158 162, January 2001 Corpus Callosal Signal Changes in Patients with Hydrocephalus after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting John I. Lane, Patrick H. Luetmer, and John L. Atkinson BACKGROUND
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving the Laterocavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging has been reported to be a sensitive and specific method in the diagnosis of disease of the sub-
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Seeing is Believing... Look Beneath the Surface
 References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging in Pediatric Bell s Palsy
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:162-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.162 Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:162-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.162 Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis
 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5398-5402 The Role of Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI) in Evaluation of Acute Stroke Maha Abdelhamed El Nouby*, Eman Ahmed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5398-5402 The Role of Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI) in Evaluation of Acute Stroke Maha Abdelhamed El Nouby*, Eman Ahmed
Original Research Article
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY INFARCT AND ITS CORRELATION WITH FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY Neethu Tressa Jose 1, Rajan Padinharoot 2, Vadakooth Raman Rajendran 3, Geetha Panarkandy 4 1Junior
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY INFARCT AND ITS CORRELATION WITH FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY Neethu Tressa Jose 1, Rajan Padinharoot 2, Vadakooth Raman Rajendran 3, Geetha Panarkandy 4 1Junior
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
 Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Case Report Castleman disease variant of POEMS syndrome complicated with multiple cerebral infarction: a rare case report and review of literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(10):13578-13583 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014415 Case Report Castleman disease variant of POEMS syndrome complicated with multiple cerebral infarction: a rare case
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(10):13578-13583 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014415 Case Report Castleman disease variant of POEMS syndrome complicated with multiple cerebral infarction: a rare case
Masayuki Maeda, Tatsuya Yamamoto, Shouichiro Daimon, Hajime Sakuma, and Kan Takeda
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
