Scanning electron microscopy of the trabecular meshwork in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Roberto Sampaolesi and Carlos Argento
|
|
|
- Joleen Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scanning electron microscopy of the trabecular meshwork in normal and glaucomatous eyes Roberto Sampaolesi and Carlos Argento The ultrastructure of traheculectomy specimens obtained from enucleated eyes was compared to that of 23 similar specimens extracted from glaucomatous eyes. It was thus possible to study the trabecular meshwork from Schwalbe's line to the iris root, the comeal endothelium, the canal of Schlemm, its inner and outer walls, and the collectors. In the glaucomatous specimens it was possible to verify, for the first time, two aspects which show clinical correlation. The first aspect is pseudoexfoliation: we find in the trabecular meshwork two types of deposits in great quantity. One is formed by a dense irregular fibrillar net, with a diameter oscillating between 600 and 830 A, surrounding the trabeculae; the others are pigment granules. Both fill the intertrabecular spaces. The first type is also observed on the comeal endothelium lining Schwalbe's ring, stressing the visibility of the intercellular spaces. The second aspect is the pectinate ligament (mesodermic remnant) in late-onset congenital glaucoma. Its pattern is characteristically different from that of the comeoscleral meshwork. Key words: trabecular mesh work, scanning electron microscopy, uveal meshwork, comeoscleral meshwork, canal of Schlemm, external collector of the canal of Schlemm, pseudoexfoliation, late congenital glaucoma, pectinate ligament (mesodermal tissue). I n previous papers we presented the light microscopic study of trabecular specimens obtained from glaucomatous eyes by trabeculectomy. We continued this research, studying the meshwork with scanning electron microscopy. At present, each specimen of trabecular meshwork is divided into three equal parts: one for light micros- This work was done in the scanning electron microscopy laboratory of the Institute of Neurobiology, Buenos Aires. The Director is J. H. Tramezzani, to whom we are very thankful. Reprint requests: Dr. Roberto Sampaolesi, University of Salvador, Department of Ophthalmology, Parana ler. Piso, San Salvador, El Salvador. 302 copy, a second for scanning electron microscopy, and a third for transmission electron microscopy. Material and methods Twenty-three trabecular meshwork specimens obtained by trabeculectomy from glaucomatous eyes were examined. We consider that meticulous surgical technique and careful manipulation of the piece of trabecular meshwork during its excision are very important. Transillumination, as described by Minsky, is essential to place the incision at the level of the corneal endothelium immediately beyond Schwalbe's ring. This technique allows us to section the cornea in the area of light, at 1 mm. from the limit of light and darkness. After dissection of a limbusbased scleral flap, Minsky's maneuver allows us to place the first incision parallel to the limbus. We section only half the thickness of the cornea.
2 Volume 16 Number 4 SEM of trabecular meshwork 303 Fig. 1. Fibers of the trabecular meshwork. A, a, Scleral septum; b, scleral spur; c, Schlemm's canal; 1, scleral trabecular meshwork; 2, scleral trabecular meshwork coming from Briicke's muscle; 3, uveal meshwork. B, A panoramic view of the chamber angle, Schlemm's canal, and trabecular meshwork taken from an eye which had been enucleated because of a malignant melanoma. C, Schematic drawing of Fig. 1, B. a, Scleral septum; b, scleral spur; c, Schlemm's canal; d, lamina iridociliaris; e, circular circulary muscle (Miiller); /, major arterial circle of the iris; 1, scleral trabecular meshwork; 2, fibers of the longitudinal muscle (Briicke); 3, uveal meshwork. Before opening the anterior chamber we mark the lateral incisions, also sectioning half the thickness of the scleral wall. After opening the anterior chamber we complete the first incision with an angled Vannas' scissors (Storz). With the same instrument we complete the lateral incisions perpendicular to the limbus. The trabeculectomy piece is gently grasped with fine-toothed microsurgical forceps (Grieshaber) by the external half of its thickness in order to avoid damaging the delicate structure of the meshwork. In this moment, the chamber angle is exposed to the surgeon's eye, and the final incision is performed with Vannas' scissors between the scleral spur and the ciliary band. The trabeculectomy specimen is immediately fixed by immersion in 2.5 percent glutaraldehyde in 0.1M Millonig's phosphate buffer with glucose, ph 7.4, for about 24 hours. After being rinsed in isotonic buffer for 15 minutes, the specimen is postfixed in 1 percent osmium tetroxide in Millonig's phosphate buffer with glucose, ph 7.4, for 2 hours. Thereafter the sample is dehydrated in graded acetone solutions and dried by the critical-point method in fluid CO 2 with a Sorvall Critical-Point Drying System. This method allows the substitution of acetone by carbon dioxide in a high-pressure chamber. Once dried, the trabeculectomy piece is mounted on a specimen holder, with the trabecular mesh-
3 304 Sampaolesi and Argento Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. April 1977 Fig. 2. A to C, The trabecular meshwork: 1, corneal endothelium; 2, trabecular meshwork; 3, scleral spur; 4, uveal meshwork; 5, pore; 6, intertrabecular spaces of the scleral meshwork; 7, trabeculae; S, Schwalbe's ring. work facing upward, and coated with a thin layer of carbon and gold palladium in a Jeol vacuum-coating unit. The piece is examined in a Jeo JSM-U3 scanning electron microscope. Results Fibers of the trabecular meshwork. Fig. 1, A, shows the three different parts of the trabecular meshwork. Arrow 1 (scleral trabeculae) represents the fibers which go from sclera to sclera, from the scleral spur to the scleral septum near its end in Schwalbe's line. They form an arched bundle enclosing the canal of Schlemm and they are separated from the canal by the porous tissue. Arrow 2 represents the fibers which form the insertion tendon of the ciliary muscle passing over the scleral spur as a bridge
4 Volume 16 Number 4 SEM of trabecular meshwork 305 Fig. 3. Outer (A and B) and inner fc and D) walls of Schlemm's canal. A, Opened external collector, diameter 50 p (x 1,000); B, two endothelial cells with nuclei corresponding to the inset of Fig. 6, A (x3,000); C, long endothelial cells, length 90 ft width 7 n (xl,000); D, nuclei of the endothelial cells of Fig. 6, A (x3,000). to insert in Schwalbe's line. They constitute the tendinous continuation of the muscular fibers of the ciliary muscle. Arrow 3 (uveal trabeculae) represents the fibers which originate at different levels between Schwalbe's line and the scleral spur and end at the iris at different levels from the insertion of the iris root up to the iris crests. They form the uveal trabecular meshwork and are, in fact, remainders of the pectinate ligament (also known as mesoderm remnants or iris processes ). Fig. 1, B, is a scanning electron micrograph of a trabeculectomy specimen excised from an eye before enucleation necessitated by a malignant melanoma. In this case, unlike the usual trabeculectomies, the posterior section passes through the iris root. Fig. 1, C, is a schematic representation of Fig. 1, B. In each of these figures, the lefthand third shows a section of the chamber angle and the right-hand two thirds show the chamber angle as it is evidenced by gonioscopy. The sclera emits two prongs:
5 306 Sampaolesi and Argento Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. April 1977 Fig. 4. A to C, Opened Schlemm's canal after trabeculotomy: 1, outer wall of the canal of Schlemm exposed by trabeculotomy; 2, prominent scleral spur; 3, internal wall of the canal of Schlemm and trabecular meshwork rolled over itself; 4, anterior surface of the iris; 5, ciliary processes. Inset: two external collectors subdivided by septa. the scleral septum (a), of which the apex corresponds to Schwalbe's ring, and the scleral spur (b). These two prongs form a furrow in which Schlemm's canal is lodged; d marks the lamina iridociliaris of Rohen (the ciliary band of the gonioscopic image); / is the major arterial circle of the iris and (e) the internal surface of the ciliary muscle (circular or Miiller portion of the ciliary muscle); 1 marks the scleral trabecular meshwork, 2 the insertion tendon of the ciliary muscle, and 3 the uveal trabecular meshwork. Trabecular meshwork. The trabecula is a meshwork which extends from the end of the corneal endothelium to the iris root. Its most superficial layer is formed by the uveal trabecular meshwork, in the shape of roughly cylindrical branches, extending from Schwalbe's ring to the iris root perpendicular to these structures. These trabeculae are anastomosed by similar ele-
6 Volume 16 Number 4 SEM of trabecular meshwork 307 Fig. 5. A, Light microscopy of the persistence of pectinate ligament in late-onset congenital glaucoma. The ciliary muscle goes as far as the spur. B, Light microscopy of high insertion of the iris. The ciliary muscle goes as far as the middle of Schlemm's canal. merits placed horizontally, leaving large intertrabecular spaces between them (Fig. 2, A, B, andc). The uveal trabecular meshwork is easily identified since in normal eyes it is sparser than the corneoscleral trabecula over which it lies. The uveal meshwork passes over the scleral spur to end at the level of the iris root. These trabeculae are thicker and show more relief than the scleral trabecula. They are seen in gonioscopy as the iris processes described by Busacca, known as the pectinate ligament. Both terms describe mesodermic remnants in the chamber angle. The uveal meshwork is enveloped by an endothelium in which pores can be seen, continuous with the corneal endothelium. While the outlines of the corneal endothelial cells and of its nuclei can be barely identified, the size and shape of the trabeculae endothelial cells cannot be appreciated. No pores were identified in the corneal endothelial cells. The scleral (or corneoscleral) meshwork can be seen through the spaces of the trabecular meshwork and at a deeper level than the uveal meshwork, through the uveal trabecular spaces. Its trabeculae are parallel to Schwelbe's ring, i.e., perpendicular to the uveal meshwork. These trabeculae are also cylindrical but they are more slender and have smooth outlines, in contrast with the uveal trabeculae, which resemble gnarled tree trunks due to their irregular and wavy outlines. This disposition determines the shape of the intertrabecular spaces of the scleral trabeculum, which are over holes parallel to Schwalbe's
7 308 Sampaolesi and Argento Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. April 1977 Fig. 6. A to E, Mesodermal tissue: pectinate ligament, late congenital glaucoma. A, The trabecular region shows a dense tissue: uveal meshwork extending from Schwalbe's line (1) to scleral spur (2). These trabeculae are thicker, like gnarled tree trunks. B shows the upper insert of A: between two trabeculae there is a membrane and no intertrabecular space, leaving only small holes. Erythrocytes are retained by this dense meshwork. C shows the lower insert of A unusual trabeculae. D is taken from the same specimen and shows how the blood cells are retained by this meshwork, compared to E, taken from a normal scleral meshwork where it is possible to see the blood cells going through the intertrabecular spaces freely.
8 Volume 16 Number 4 SEM of trabecular meshwork 309 Fig. 6. D and E, For legend see facing page. ring, with very smooth outlines. These structures are quite different from the intertrabecular spaces of the uveal meshwork, which are larger and quadrangular. Through each of these a number of scleral trabecular spaces can be seen because of their smaller size. Pores can also be identified in the endothelium of the scleral trabeculae. Between the two levels of uveal and scleral meshwork some slender fibers perpendicular to Schwalbe's ring can be seen. These are trabeculae that pass as a bridge over the scleral spur toward Schwalbe's ring, forming the insertion tendon of the longitudinal portion of the ciliary muscle (Briickes' muscle), as has been demonstrated by Dvorak Theobald. This fascicle can be seen in some trabeculectomies as a compact layer that reaches the scleral spur and after veering, gives rise to trabeculae. Adjacent to the corneal endothelium and above Schwalbe's ring the scleral trabecular endothelium shows a smooth area. The intertrabecular spaces of the uveal meshwork measure 20 to 30 p.; those of the scleral meshwork are smaller and, since they are oval, show a greater axis 10 /J. long and a lesser axis, 5 fi long. Near Schwalbe's ring the greater axis does not change, but the lesser axis is reduced to only 1 or 2 /A, SO that the mesh becomes tighter. Schlemm's canal. We have studied Schlemm's canal in two eyes enucleated from 2-year-old children because of a retinoblastoma. The opening of Schlemm's canal was made in triangular blocks with the apex in the center of the cornea including cornea, sclera, and iris. Schlemm's canal was intubated with the inferior blade of Vannas' angled scissors and the section was made holding this blade fixed while sectioning the trabecular meshwork in its upper end, closer to Schwalbe's line, with the other blade. In this way, avoiding pressure on the inside of Schlemm's canal, its integrity can be preserved. This section must be made at the moment when the dehydration with acetone solutions in different concentrations is under way. Figs. 3 and 4 show our findings. Schlemm's canal has a greater diameter that ranges between 180 and 250 ju,m. Both this canal and the collectors and aqueous veins are often subdivided by septa, as if there were physiological barriers to the exit of the aqueous humor. The internal wall of Schlemm's canal shows elongated cells, 75 ^m long and 4
9 310 Sampaolesi and Argento st. Ophthalmol. Visual Set. April 1977 Fig. 7. A to D, Mesodermal tissue: pectinate ligament, congenital glaucoma. /j.m wide. The nuclei of these cells are spindle shaped, 16 pxa long and 4.33 jxm wide. Between these cells or on their surface lie minute pores through which the aqueous humor passes. These pores have been carefully described by Bill and Svedberglr 1 (Fig. 3, A, B, C, and D). Fig. 4, A, is a panoramic view of the chamber angle after trabeculectomy. Fig. 4, B and C, are insets showing the areas marked in Fig. 4, A, where the openings of two collectors can be appreciated. These are already subdivided at their origin and their average diameter ranges between 50 and 60 /xm. Congenital glaucoma and late congenital glaucoma. The tissue overlying the normal trabecular meshwork can be referred to by any one of the following synonyms: mesodermal tissue, pectinate ligament, or iridian processes in the trabecular meshwork. This may be either fetal remnants or a developmental anomaly. In a group of cases of congenital glau-
10 SEM of trabecular meshwork 311 Fig. 8. A to C, Endothelial cells in pseudoexfoliation. A, In gray, trabecular meshwork of pseudoexfoliation; in white, pseudoexfoliation material deposited on it (xl,000). B, A trabecula showing pseudoexfoliation material deposited on it (x3,000). C, The same as Fig. 10, B, at higher magnification (xl0,000): a, pseudoexfoliation material like an irregular bundle of fibrils; b, many pigmented granules originated from the posterior surface of the iris, bunched together by pseudoexfoliation material. coma of late onset we observed with the light microscope a dense tissue occluding the sinus, sometimes up to Schlemm's canal and sometimes up to Schwalbe's line, hiding the ciliary band. This is, in fact, an abundant dense uveal meshwork. With Masson's trichrome stain this tissue takes a blue hue. Another group of cases, diagnosed as pigmentary glaucomas, also presents this pectinate ligament; however under light microscopy and with trichrome stain it is colored pink. It is formed by a net of delicate trabeculae, much smaller than those of the corneoscleral meshwork, not covered by nucleated cells. These two groups, histologically distinguishable, cannot be identified by gonios-
11 312 Sampaolesi and Argento Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Set. April 1977 Fig. 9. A, Endothelial cells in a case of pseudoexfoliation. (x3,000.) B, Inset of a; the material of pseudoexfoliation deposits itself as membranes that jut into the anterior chamber. copy as far as the morphology of the pectinate ligament is concerned. With light microscopy we can differentiate two main types of anomalies in children with congenital glaucoma: (1) persistence of the pectinate ligament and (2) aplasia of the pectinate ligament. In the case of persistence, this tissue is formed by dense trabeculae reaching Schwalbe's ring, associated with an anomaly of the position of the ciliary muscle, its internal surface reaching the level of the middle of Schlemm's canal. The same picture may be observed in congenital glaucoma of late onset in adults, but the ciliary muscle is generally in its place, or suffers only slight displacement. The second form, aplasia of the pectinate ligament, corresponds to what American workers call high insertion of the iris, since the iris root ends at the level of the trabecular meshwork. The following preparations present an example of this structure. In Fig. 5, A, we can see with light microscopy the persistence of the pectinate ligament. In Fig. 6, A, B, C, D, and E, scanning microscopy of the same specimen shows a dense tissue with predominance of large trabeculae running perpendicular to Schwalbe's line. This tissue belongs to the uveal meshwork. Among the trabeculae there is a membrane (endothelium?) leaving relatively small perforated spaces which obstructs the flowing of the erythrocytes. Fig. 7, A, B, C, and D, shows the scanning microscopy of a specimen of trabeculectomy with trabeculotomy taken from a case of congenital glaucoma in a child 2 months old. The pattern is the same as that seen in congenital glaucoma of late onset, but light microscopy shows a very different pattern (Fig. 5, B). The ciliary muscle goes as far as the middle of the inner wall of Schlemm's canal. Pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule. In cases of pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule with glaucoma, the trabecular meshwork presents the same aspect as in simple glaucoma but it appears as if it were dirty, with three types of characteristic elements. 1. The first element can also be observed in other preparations but it is never as abundant as in capsular glaucoma. It consists of pigment granules arising in the posterior face of the iris. We have already described this pigmentation, which exceeds Schwalbe's line in the lower part of the chamber angle between 3 and 9 o'clock,
12 Volume 16 Number 4 SEM of trabecular meshwork 313 Fig. 10. Pseudoexfoliation material in the trabecula in the form of irregular meshwork of spiraling fibrils. (xl0,000.) across 6 o'clock, depositing itself in the posterior face of the cornea. These granules are small spheres of an average dimension of 0.8 to 1.2 /t; they are also found inside Schlemm's canal. 2. The second element has not been previously described in the trabecular meshwork: it is a typical pseudoexfoliation material made up of an irregular meshwork of fibrils. Its diameter may be measured with high magnification and it oscillates between 600 and 800 A. 3. The third remarkable finding is the clear identification of the cellular membranes of the corneal endothelium. With high magnification, these limits are formed by a wavy membrane jutting out in the anterior chamber. We do not know whether it is the same fibrillar substance or the pigment which has an affinity with the intercellular space. In Figs. 8 to 10 we can observe these findings. Davanger s> 9 found this same material, of the same size, on the anterior lens surface and in the posterior chamber region. Conclusions A precise microsurgical technique allowed us to identify Schlemm's canal and the trabecular meshwork in 185 out of 190 trabeculectomy specimens. Through correlation of the findings of light and scanning electron microscopy with the clinical study and the gonioscopic image we could confirm or rectify our diagnosis. This method gives new evidence about certain entities whose pathogenesis is still controversial, such as glaucoma associated with pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule, congenital glaucoma and late-onset congenital glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma, and cortisonic glaucoma. REFERENCES 1. Anderson, D. R.: Scanning electron microscopy of primate trabecular meshwork, Am. J. Ophthalmol. 71: 91, Benedikt, O., Aubock, L., Gottinger, W., and Waltinger, H.: Vergleichende rasterelektronenmikroskopische und transmissionselektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an Linsen bei sogenannten Exfoliationssyndrom, Albrecht
13 314 Sampaolesi and Argento Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. April von Graefes Arch. Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 187: 249, Bill, A.: Scanning electron microscopic studies of the canal of Schlemm, Exp. Eye Res. 10: 214, Bill, A., and Svedbergh, B.: Scanning electron microscopic studies of the trabecular meshwork and the canal of Schlemm: an attempt to localize the main resistance to outflow of aqueous humor in man, Acta Ophthalmol. 50: 295, Blumcke, S., and Morgenroth, K.: The stereo ultrastructure of the external and internal surface of the cornea, J. Ultrastruct. Res. 18: 502, Boyde, A., and Wood, C.: Preparation of animal tissues for surface scanning electron microscopy, J. Microsc. 90: 221, Cleveland, P. H., and Schneider, C. W.: A simple method of preserving ocular tissue for scanning electron microscopy, Vision Res. 9: 1401, Davanger, M.: The pseudoexfoliation syndrome. A scanning electron microscopic study. I. The anterior lens surface, Acta Ophthalmol. 53: 809, Davanger, M.: The pseudoexfoliation syndrome. A scanning electron microscopic study. II. The posterior chamber region, Acta Ophthalmol. 53: 821, Hager, H., Hoffmann, F., and Dumiterscu, L.: Rasterelectronmikroskopie in der Augenheilkunde, Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 159: 170, Hansson, H. A., and Jerndal, T.: Scanning electron microscopic studies on the development of the iridocorneal angle in the human eye, INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 10: 252, Hervouet, F., and Ertus, M.: Les structures oculaires au microscope a balayage, Paris, 1973, Masson et Cie. 13. Hervouet, F., George, Y., Tusques, J., and Ertus, M.: Observations de diverses structures oculaires humaines au microscope electronique a balayage, Bull. Assoc. Anat. 151: 356, Hervouet, F., George, Y., and Ertus, M.: Premieres explorations de structures pculaires au microscope a balayage, Soc. Ophthalmol. de l'ouest, April, Hervouet, F.: Le trabeculum et le canal de Schlemm au microscope a balayage, Soc. Fr. d'ophthalmol, May, Hoffmann, F., and Dumitrescu, L.: Schlemm's canal under the scanning electron microscope, Ophthalmol. Res. 2: 37, Renard, G., and Galle, P.: Etude en microscopie a balayage du trabeculum humain., Ann. Ocul. 206: 835, Renard, G., and Galle, P.: fitude en microscopie a balayage du trabeculum humain. Les. effets de la trabeculotomie, Ann. Ocul. 206: 835, Segawa, K.: Pore structures of the endothelial cells of the aqueous outflow pathway: scanning electron microscopy, Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 17: 133, Spencer, H. W., Alvarado, J., and Hayes, T. L.: Scanning electron microscopy of human ocular tissues: trabecular meshwork, INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 7: 650, Svedbergh, B., and Bill, A.: Scanning electron microscopy of the comeal endqthelium. The trabecular meshwork and the canal of Schlemm in man, Exp. Eye Res. 12: 373, 1971.
Scanning electron microscopic studies on the development of the iridocorneal angle in human eyes
 Scanning electron microscopic studies on the development of the iridocorneal angle in human eyes Hans-Arne Hansson and Tord Jerndal The structural changes occurring in the iridocorneal angle of human eyes
Scanning electron microscopic studies on the development of the iridocorneal angle in human eyes Hans-Arne Hansson and Tord Jerndal The structural changes occurring in the iridocorneal angle of human eyes
3/16/2018. Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim. Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University
 Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
_ Assessment of the anterior chamber. Review of anatomy of the angle
 Assessment of the anterior chamber Dr Simon Barnard PhD BSc FCOptom FAAO DCLP Department of Optometry & Visual Science City University London, UK Review of anatomy of the angle Figure 1. Anatomical section
Assessment of the anterior chamber Dr Simon Barnard PhD BSc FCOptom FAAO DCLP Department of Optometry & Visual Science City University London, UK Review of anatomy of the angle Figure 1. Anatomical section
Histopathological Study of a Case with Glaucoma Due to Sturge-Weber Syndrome
 Histopathological Study of a Case with Glaucoma Due to Sturge-Weber Syndrome Noriko Akabane* and Teruhiko Hamanaka *Second Department of Ophthalmology, Toho University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan;
Histopathological Study of a Case with Glaucoma Due to Sturge-Weber Syndrome Noriko Akabane* and Teruhiko Hamanaka *Second Department of Ophthalmology, Toho University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan;
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
TRABECULECTOMY-GUIDED DEEP SCLERECTOMY. A NOVEL TECHNIQUE. AHMED MOSTAFA ABDELRAHMAN, M.D., F.R.C.S. (Edin.) Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology
 TRABECULECTOMY-GUIDED DEEP SCLERECTOMY. A NOVEL TECHNIQUE. AHMED MOSTAFA ABDELRAHMAN, M.D., F.R.C.S. (Edin.) Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology Department of Ophthalmology, Cairo University. Purpose:
TRABECULECTOMY-GUIDED DEEP SCLERECTOMY. A NOVEL TECHNIQUE. AHMED MOSTAFA ABDELRAHMAN, M.D., F.R.C.S. (Edin.) Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology Department of Ophthalmology, Cairo University. Purpose:
XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University
 SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
Sinus trabeculectomy. Preliminary results of IOO operations
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 833 Sinus trabeculectomy Preliminary results of IOO operations A. P. NESTEROV, N. V. FEDEROVA, AND Y. E. BATMANOV Department of Ophthalmology, Kazan Medical Institute, Kazan,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 833 Sinus trabeculectomy Preliminary results of IOO operations A. P. NESTEROV, N. V. FEDEROVA, AND Y. E. BATMANOV Department of Ophthalmology, Kazan Medical Institute, Kazan,
Systems for Anterior Chamber Angle Evaluation 長庚紀念醫院青光眼科吳秀琛
 Systems for Anterior Chamber Angle Evaluation 長庚紀念醫院青光眼科吳秀琛 Clinical Techniques for Assessing Angle Width A light from the side showing physiological iris bombe Slit lamp-grading of peripheral AC depth
Systems for Anterior Chamber Angle Evaluation 長庚紀念醫院青光眼科吳秀琛 Clinical Techniques for Assessing Angle Width A light from the side showing physiological iris bombe Slit lamp-grading of peripheral AC depth
A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 597. A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF THE IRIS WITH PIGMENTATION OF THE SCLERA AND PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA* BY V. CAVKA Beograd, Yugoslavia THE significance of pigmentation
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 597. A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF THE IRIS WITH PIGMENTATION OF THE SCLERA AND PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA* BY V. CAVKA Beograd, Yugoslavia THE significance of pigmentation
non-perforating injury
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
Relationship between limbal incisions. angle. and the structures of the anterior chamber
 Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs. Richard R Dubielzig
 The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs Richard R Dubielzig Overview of Glaucoma Intraocular Pressure too High to Support a Healthy Optic Nerve Terminology used in the classification of
The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs Richard R Dubielzig Overview of Glaucoma Intraocular Pressure too High to Support a Healthy Optic Nerve Terminology used in the classification of
Introduction. Donor tissue preparation for Descemet Membrane Endothelial ASCRS Aim of dissection. DMEK graft preparation
 Introduction Donor tissue preparation for Descemet Membrane Endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) ASCRS - 2015 Endothelial Keratoplasty DSAEK / DSEK DMEK Donor lamellae stroma + DM + endothelium DM + endothelium
Introduction Donor tissue preparation for Descemet Membrane Endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) ASCRS - 2015 Endothelial Keratoplasty DSAEK / DSEK DMEK Donor lamellae stroma + DM + endothelium DM + endothelium
Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature of
 1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE
 SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Are traditional assessments a waste of time? NZAO 2015
 Are traditional assessments a waste of time? NZAO 2015 Disclosures No financial interests other than Optometry Practice owner Full time optometrist Not a glaucoma prescriber ODOB Board Chair Previously
Are traditional assessments a waste of time? NZAO 2015 Disclosures No financial interests other than Optometry Practice owner Full time optometrist Not a glaucoma prescriber ODOB Board Chair Previously
THE EYE: RETINA AND GLOBE
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Composed of stratified squamous epith. n 5% of total corneal thickness (50-90micro m thick)
 Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
Determination of the Distribution of Cilia on the Surface of the Mantle of Cypraea caputserpentis utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy
 Determination of the Distribution of Cilia on the Surface of the Mantle of Cypraea caputserpentis utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy DURATION September 10, 1990- May 7, 1991 Tracie A. Yokoi Advisor
Determination of the Distribution of Cilia on the Surface of the Mantle of Cypraea caputserpentis utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy DURATION September 10, 1990- May 7, 1991 Tracie A. Yokoi Advisor
Secondary open-angle glaucoma
 Secondary open-angle glaucoma Kathy Hondeghem ZNA Middelheim MaNaMa 12/10/13 Definition Open anterior chamber angle (at least 270 ) Trabecular meshwork (and thus aqueous humor outflow) is occluded by a
Secondary open-angle glaucoma Kathy Hondeghem ZNA Middelheim MaNaMa 12/10/13 Definition Open anterior chamber angle (at least 270 ) Trabecular meshwork (and thus aqueous humor outflow) is occluded by a
HISTOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF TRABECULECTOMY SURGERY
 HISTOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF TRABECULECTOMY SURGERY BY Anthony C. Castelbuono MD* AND W. Richard Green MD ABSTRACT Purpose: Trabeculectomy surgery is the most common operative procedure for the treatment
HISTOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF TRABECULECTOMY SURGERY BY Anthony C. Castelbuono MD* AND W. Richard Green MD ABSTRACT Purpose: Trabeculectomy surgery is the most common operative procedure for the treatment
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME
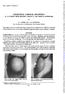 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
Ultrastructural Changes in the Aqueous Outflow Apparatus of Beagles with Inherited Glaucoma
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 30, No. 3, March 1989 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Ultrastructural Changes in the Aqueous Outflow Apparatus of Beagles
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 30, No. 3, March 1989 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Ultrastructural Changes in the Aqueous Outflow Apparatus of Beagles
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Meet Libby. Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies Definitions. Dr. Victor Malinovsky
 Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
5/18/2014. Fundamentals of Gonioscopy Workshop Aaron McNulty, OD, FAAO Walt Whitley, OD, MBA, FAAO
 1 Fundamentals of Gonioscopy Workshop Aaron McNulty, OD, FAAO Walt Whitley, OD, MBA, FAAO 2 3 4 5 6 Optometry s Meeting 2014 The Most Valuable Glaucoma Tool Glaucoma Diagnosis Gonioscopy Central corneal
1 Fundamentals of Gonioscopy Workshop Aaron McNulty, OD, FAAO Walt Whitley, OD, MBA, FAAO 2 3 4 5 6 Optometry s Meeting 2014 The Most Valuable Glaucoma Tool Glaucoma Diagnosis Gonioscopy Central corneal
Written by Administrator Wednesday, 13 January :27 - Last Updated Thursday, 21 January :34
 angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Gonioscopy and Slit Lamp Exam for the Glaucoma Suspect. Disclosure GONIOSCOPY: Gonioscopy Why?? What should I look for? GONIOSCOPY
 Gonioscopy and Slit Lamp Exam for the Glaucoma Suspect Disclosure Michael Chaglasian has the following disclosures:» 1. Advisory Board: Alcon, Allergan, Bausch+Lomb, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Merck, Sucampo»
Gonioscopy and Slit Lamp Exam for the Glaucoma Suspect Disclosure Michael Chaglasian has the following disclosures:» 1. Advisory Board: Alcon, Allergan, Bausch+Lomb, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Merck, Sucampo»
Medical School Histology Basics. VIBS 289 lab. Eye
 Medical School Histology Basics VIBS 289 lab Eye Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Aqueous humor OUTLINE OVERVIEW CELLULAR STRUCTURES THROUGH WHICH LIGHT PASSES A. CORNEA B. LENS C. RETINA STRUCTURES
Medical School Histology Basics VIBS 289 lab Eye Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Aqueous humor OUTLINE OVERVIEW CELLULAR STRUCTURES THROUGH WHICH LIGHT PASSES A. CORNEA B. LENS C. RETINA STRUCTURES
Three Dimensional Architecture of Collagen Fibrils in the Corpus cavernosum of the Crab-eating Monkey
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 73(4): 185-194, October, 1996 Three Dimensional Architecture of Collagen Fibrils in the Corpus cavernosum of the Crab-eating Monkey By Takashi NAKANO Department of Anatomy, Aichi
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 73(4): 185-194, October, 1996 Three Dimensional Architecture of Collagen Fibrils in the Corpus cavernosum of the Crab-eating Monkey By Takashi NAKANO Department of Anatomy, Aichi
MIGS Rapid Fire Outline 1 st talk: Goniotomy, Lisa Young, OD, FAAO
 Rapid Fire MIGS A Modern Solution to a Complex Problem Course Description: Minimally (or Micro-) Invasive Glaucoma Surgeries, or MIGS, are an increasingly popular treatment modality in the management of
Rapid Fire MIGS A Modern Solution to a Complex Problem Course Description: Minimally (or Micro-) Invasive Glaucoma Surgeries, or MIGS, are an increasingly popular treatment modality in the management of
Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:101-105 Graefe's Archive for CliniCal and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma* J. Reimer Wolter
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:101-105 Graefe's Archive for CliniCal and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma* J. Reimer Wolter
Mesectodermal suprauveal iridociliary leiomyoma: Transscleral excision without postoperative iris defect
 4 Chapter Mesectodermal suprauveal iridociliary leiomyoma: Transscleral excision without postoperative iris defect Lubna Razzaq 1, Ekaterina A Semenova 2, Marina Marinkovic 1, Rob JW de Keizer 1, Sjoerd
4 Chapter Mesectodermal suprauveal iridociliary leiomyoma: Transscleral excision without postoperative iris defect Lubna Razzaq 1, Ekaterina A Semenova 2, Marina Marinkovic 1, Rob JW de Keizer 1, Sjoerd
Diagnosis and Therapy in Ophthalmology Hand-held optical coherence tomography imaging in children with anterior segment dysgenesis
 Diagnosis and Therapy in Ophthalmology Hand-held optical coherence tomography imaging in children with anterior segment dysgenesis Anastasia V. Pilat, 1,2 Viral Sheth, 1,2 Ravi Purohit, 1,2 Frank A. Proudlock,
Diagnosis and Therapy in Ophthalmology Hand-held optical coherence tomography imaging in children with anterior segment dysgenesis Anastasia V. Pilat, 1,2 Viral Sheth, 1,2 Ravi Purohit, 1,2 Frank A. Proudlock,
CLASS-y Laser Treats Glaucoma
 Article # 404 Comments About the Author Released: Author: Category: March 12th, 2014 Issue #0314 Ehud Assia Feature S S S S S CLASS-y Laser Treats Glaucoma Transforming complex, invasive and risky glaucoma
Article # 404 Comments About the Author Released: Author: Category: March 12th, 2014 Issue #0314 Ehud Assia Feature S S S S S CLASS-y Laser Treats Glaucoma Transforming complex, invasive and risky glaucoma
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation
 Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Trabeculectomy - A Short Term Follow-up
 Trabeculectomy - A Short Term Follow-up Pages with reference to book, From 193 To 196 K.S. Hasan, G. Rabbani, S. Hashmani, M.M. Hasan ( Department of Ophthalmology Civil Hospital and Dow Medical College.
Trabeculectomy - A Short Term Follow-up Pages with reference to book, From 193 To 196 K.S. Hasan, G. Rabbani, S. Hashmani, M.M. Hasan ( Department of Ophthalmology Civil Hospital and Dow Medical College.
Localization of Smooth Muscle Myosin-Containing Cells in the Aqueous Outflow Pathway
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 31, No. 2, February 1990 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Localization of Smooth Muscle Myosin-Containing Cells in the Aqueous
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 31, No. 2, February 1990 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Localization of Smooth Muscle Myosin-Containing Cells in the Aqueous
Morphological Study of Corneal Endothelium and Corneal Thickness in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS Morphological Study of Corneal Endothelium and Corneal Thickness in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome Kenji Inoue*,, Kazuko Okugawa*,, Tetsuro Oshika and Shiro Amano *Department of Ophthalmology,
LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS Morphological Study of Corneal Endothelium and Corneal Thickness in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome Kenji Inoue*,, Kazuko Okugawa*,, Tetsuro Oshika and Shiro Amano *Department of Ophthalmology,
flap. A large segment of the iris including the neoplasm was then LEUCO-SARCOMA OF THE IRIS
 158 THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY LEUCO-SARCOMA OF THE IRIS BY W. S. DUKE-ELDER AND H. B. STALLARD LONDON PRIMARY sarcoma of the iris is a relatively rare condition; and.although there may be little
158 THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY LEUCO-SARCOMA OF THE IRIS BY W. S. DUKE-ELDER AND H. B. STALLARD LONDON PRIMARY sarcoma of the iris is a relatively rare condition; and.although there may be little
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball
 Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Humanity s Vision Is Our Focus. The Ahmed Glaucoma Valve
 Humanity s Vision Is Our Focus The Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Dr. A. Mateen Ahmed President - New World Medical New World Medical is a high tech medical device company whose goal is to help humanity lead a better
Humanity s Vision Is Our Focus The Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Dr. A. Mateen Ahmed President - New World Medical New World Medical is a high tech medical device company whose goal is to help humanity lead a better
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
The identification of adrenergic and cholinergic nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork. Tsunetami Nomura and George K. Smelser
 The identification of adrenergic and cholinergic nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork Tsunetami Nomura and George K. Smelser There are nerves and nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork, but their
The identification of adrenergic and cholinergic nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork Tsunetami Nomura and George K. Smelser There are nerves and nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork, but their
of Ciliary body, Iris and Irido-corneal angle in Adult Marwari Goat (Capra hircus) R. K. Barhaiyaa *, Malsawmkima, D. M. Bhayani and Y. L.
 DHR International Journal Of Biomedical and Life Sciences (DHR-IJBLS) ISSN 2278-8301, Vol.5(3), 2014 Available online http://www.doublehelixresearch.com/dhrijbls Double Helix Research Original Article
DHR International Journal Of Biomedical and Life Sciences (DHR-IJBLS) ISSN 2278-8301, Vol.5(3), 2014 Available online http://www.doublehelixresearch.com/dhrijbls Double Helix Research Original Article
Eye Fluids. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Vascular changes in the iris in chronic
 Vascular changes in the iris in chronic anterior uveitis LEILA LAATIKAINEN From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Helsinki, Finland British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 145-149 SUMMARY
Vascular changes in the iris in chronic anterior uveitis LEILA LAATIKAINEN From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Helsinki, Finland British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 145-149 SUMMARY
ANGLE VESSELS IN NORMAL EYES
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 551. ANGLE VESSELS IN NORMAL EYES A GONIOSCOPIC EVALUATION AND ANATOMIC. CORRELATION*t BY PAUL HENKIND From the Department of Ophthalmology, New York University College of
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 551. ANGLE VESSELS IN NORMAL EYES A GONIOSCOPIC EVALUATION AND ANATOMIC. CORRELATION*t BY PAUL HENKIND From the Department of Ophthalmology, New York University College of
Case Study. Monocular Malignant Melanoma
 Case Study Monocular Malignant Melanoma Case History A 52 year old Caucasian female presented with a number of naevi on the skin and a right ciliary body malignant melanoma twelve years ago and had an
Case Study Monocular Malignant Melanoma Case History A 52 year old Caucasian female presented with a number of naevi on the skin and a right ciliary body malignant melanoma twelve years ago and had an
LEUKAEMIA*t INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC. pattemn * Received for pubiication November io, i967.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
Glaucoma. How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing
 Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma
 www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
STAB INCISION GLAUCOMA SURGERY (SIGS)
 STAB INCISION GLAUCOMA SURGERY (SIGS) Dr. Soosan Jacob, MS, FRCS, DNB Senior Consultant Ophthalmologist, Dr. Agarwal's Eye Hospital, Chennai, India dr_soosanj@hotmail.com Videos available in Youtube channel:
STAB INCISION GLAUCOMA SURGERY (SIGS) Dr. Soosan Jacob, MS, FRCS, DNB Senior Consultant Ophthalmologist, Dr. Agarwal's Eye Hospital, Chennai, India dr_soosanj@hotmail.com Videos available in Youtube channel:
Plate/Valve Specifications: Thickness: 0.9mm Width: 13.00mm Length: 16.00mm Surface Area: mm 2
 Distribué en France par FCI S.A.S. France Chirurgie Instrumentation SAS 20/22 rue Louis Armand 75015 PARIS Tél. 01.53.98.98.98 / Fax. 01.53.98.98.99 fci@fci.fr / www.fci.fr CATALOGUE DE VENTE Features:
Distribué en France par FCI S.A.S. France Chirurgie Instrumentation SAS 20/22 rue Louis Armand 75015 PARIS Tél. 01.53.98.98.98 / Fax. 01.53.98.98.99 fci@fci.fr / www.fci.fr CATALOGUE DE VENTE Features:
Graefe's Archive. Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
relative s privacy, do not identify your relative by full name in any assignment.
 Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
TISSUE* ABERRANT INTRA-OCULAR LACRIMAL GLAND. of the left eye of a full-term infant of 2 weeks; the tumour was globular and
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 619. ABERRANT INTRA-OCULAR LACRIMAL GLAND TISSUE* BY W. S. HUNTERt Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE occurrence of aberrant lacrimal
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 619. ABERRANT INTRA-OCULAR LACRIMAL GLAND TISSUE* BY W. S. HUNTERt Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE occurrence of aberrant lacrimal
Ake Holmberg and Ernst H. Bdrdny
 The effect of pilocarpine on the endothelium forming the inner wall of Schlemm's canal: An electron-microscopic study in the monkey Cercopithecus aethiops Ake Holmberg and Ernst H. Bdrdny Eight Cercopithecus
The effect of pilocarpine on the endothelium forming the inner wall of Schlemm's canal: An electron-microscopic study in the monkey Cercopithecus aethiops Ake Holmberg and Ernst H. Bdrdny Eight Cercopithecus
AET-treated normal red cells (PNH-like cells)
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 677-684 Electron microscope study of PNH red cells and AET-treated normal red cells (PNH-like cells) S. M. LEWIS, G. LAMBERTENGHI, S. FERRONE, AND G. SIRCHIA From the Department
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 677-684 Electron microscope study of PNH red cells and AET-treated normal red cells (PNH-like cells) S. M. LEWIS, G. LAMBERTENGHI, S. FERRONE, AND G. SIRCHIA From the Department
CVS HISTOLOGY. Dr. Nabil Khouri.
 CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
Application manual for the Trabeculas-Laser 532 nm wavelength
 Selective Laser Trabeculoplastic Application manual for the Trabeculas-Laser 532 nm wavelength Bessemerstr. 14 90411 Nürnberg Tel.: +49(0)911.21779-0 Fax: +49(0)911.21779-99 info@arclaser.de www.arclaser.de
Selective Laser Trabeculoplastic Application manual for the Trabeculas-Laser 532 nm wavelength Bessemerstr. 14 90411 Nürnberg Tel.: +49(0)911.21779-0 Fax: +49(0)911.21779-99 info@arclaser.de www.arclaser.de
arthritis "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid (opposite). Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 Peterborough District Hospital
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid arthritis A. J. LYNE Peterborough District Hospital It has been noted that patients suffering from long-standing rheumatoid arthritis
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid arthritis A. J. LYNE Peterborough District Hospital It has been noted that patients suffering from long-standing rheumatoid arthritis
Age-related changes in trabecular meshwork cellularity
 Age-related changes in trabecular meshwork cellularity Jorge Alvarado, Collin urphy, Jon Polansky, and Richard Juster* To investigate whether alterations in the cellular component of the trabecular meshwork
Age-related changes in trabecular meshwork cellularity Jorge Alvarado, Collin urphy, Jon Polansky, and Richard Juster* To investigate whether alterations in the cellular component of the trabecular meshwork
Uveal Melanoma. Protocol applies to malignant melanoma of the uvea.
 Uveal Melanoma Protocol applies to malignant melanoma of the uvea. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying Checklist) Biopsy (No Accompanying
Uveal Melanoma Protocol applies to malignant melanoma of the uvea. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying Checklist) Biopsy (No Accompanying
Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D.
 Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D., FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others
Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D., FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others
Scanning Electron Microscopical Observation on the Penetration Mechanism of Fowl Spermatozoa into the Ovum in the Process of Fertilization
 J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Husb., Hiroshima Univ. (1976), 15: 85-92 Scanning Electron Microscopical Observation on the Penetration Mechanism of Fowl Spermatozoa into the Ovum in the Process of Fertilization Shunsaku
J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Husb., Hiroshima Univ. (1976), 15: 85-92 Scanning Electron Microscopical Observation on the Penetration Mechanism of Fowl Spermatozoa into the Ovum in the Process of Fertilization Shunsaku
Intraoperative Gonioscopy: A Key to Angle Surgery
 Intraoperative Gonioscopy: A Key to Angle Surgery Shakeel Shareef, MD Associate Professor Flaum Eye Institute Univ. of Rochester School of Med. Rochester, NY Phaco vs. MIGS PHACO MIGS Viewing Full corneal
Intraoperative Gonioscopy: A Key to Angle Surgery Shakeel Shareef, MD Associate Professor Flaum Eye Institute Univ. of Rochester School of Med. Rochester, NY Phaco vs. MIGS PHACO MIGS Viewing Full corneal
MESHWORK*t NODULAR DYSTROPHY OF THE TRABECULAR
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 31. NODULAR DYSTROPHY OF THE TRABECULAR MESHWORK*t BY J. S. SPEAKMAN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto THE description of the microscopic structure of individual
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 31. NODULAR DYSTROPHY OF THE TRABECULAR MESHWORK*t BY J. S. SPEAKMAN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto THE description of the microscopic structure of individual
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology. Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta )
 Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Scanning electron microscopy of pulmonary alveolar capillary vessels
 Thorax (1973), 28, 222. Scanning electron microscopy of pulmonary alveolar capillary vessels I. G. S. ALEXANDER', B. C. RITCHIE, and J. E. MALONEY Departments of Anatomy and Medicine, Monash University,
Thorax (1973), 28, 222. Scanning electron microscopy of pulmonary alveolar capillary vessels I. G. S. ALEXANDER', B. C. RITCHIE, and J. E. MALONEY Departments of Anatomy and Medicine, Monash University,
"^mz-cypo cricxj. dissection, we will examine the 3-dimensional structure of the mammalian brain and consider the functions of some of its parts.
 "^mz-cypo cricxj Sidogy083 ^ ^ furore fx^t-^tb ' BRAIN DISSECTION PURPOSE The brain, more than any other organ, is what determines the capabilities of an organism. It affects all aspects of the body from
"^mz-cypo cricxj Sidogy083 ^ ^ furore fx^t-^tb ' BRAIN DISSECTION PURPOSE The brain, more than any other organ, is what determines the capabilities of an organism. It affects all aspects of the body from
2/26/2017. Sameh Galal. M.D, FRCS Glasgow. Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology
 Sameh Galal M.D, FRCS Glasgow Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology No financial interest in the subject presented 1 Managing cataracts in children remains a challenge. Treatment
Sameh Galal M.D, FRCS Glasgow Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology No financial interest in the subject presented 1 Managing cataracts in children remains a challenge. Treatment
Angle recession and secondary glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 6o8 Angle recession and secondary glaucoma D. MOONEY Kent County Ophthalmic and Aural Hospital, Maidstone In a previous article (Mooney, I972), the incidence and extent of
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 6o8 Angle recession and secondary glaucoma D. MOONEY Kent County Ophthalmic and Aural Hospital, Maidstone In a previous article (Mooney, I972), the incidence and extent of
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015
 Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Leiomyoma of the ciliary body
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1970) 54, 383 Leiomyoma of the ciliary body A clinico-pathological case report RONALD F. LOWE AND C. H. GREER Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, East Melbourne, Australia Although
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1970) 54, 383 Leiomyoma of the ciliary body A clinico-pathological case report RONALD F. LOWE AND C. H. GREER Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, East Melbourne, Australia Although
The Orbit. The Orbit OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION 9/25/2014. The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? Openings in the orbit
 The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
2. Obtain the following: eye guards gloves dissection tools: several blunt probes, scissors, a scalpel and forceps dissection pan sheep heart
 Week 04 Lab Heart Anatomy LEARNING OUTCOMES: Describe the gross external and internal anatomy of the heart. Identify and discuss the function of the valves of the heart. Identify the major blood vessels
Week 04 Lab Heart Anatomy LEARNING OUTCOMES: Describe the gross external and internal anatomy of the heart. Identify and discuss the function of the valves of the heart. Identify the major blood vessels
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Aqueous Shunts and Devices for Glaucoma File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: aqueous_shunts_and_devices_for_glaucoma 3/2010 6/2017 6/2018 6/2017
Corporate Medical Policy Aqueous Shunts and Devices for Glaucoma File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: aqueous_shunts_and_devices_for_glaucoma 3/2010 6/2017 6/2018 6/2017
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3%
 The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs
 The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman BSc MCOptom FBDO CET Accreditation C19095 2 CET Points (General)
The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman BSc MCOptom FBDO CET Accreditation C19095 2 CET Points (General)
1 Eyelids. Lacrimal Apparatus. Orbital Region. 3 The Orbit. The Eye
 1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
Posterior corneal folds and endothelial cell damage in human donor eyes
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 121-125 Posterior corneal folds and endothelial cell damage in human donor eyes ISRAEL N NARTEY,' WILLIAM NG,2 EMIL S SHERRARD,2 AND A D McG STEELE' From the
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 121-125 Posterior corneal folds and endothelial cell damage in human donor eyes ISRAEL N NARTEY,' WILLIAM NG,2 EMIL S SHERRARD,2 AND A D McG STEELE' From the
STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 343. STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY* OBSERVATIONS BY MEANS OF THE PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPE BY ANTONIO A. ROSSI From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London (Director of Research,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 343. STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY* OBSERVATIONS BY MEANS OF THE PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPE BY ANTONIO A. ROSSI From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London (Director of Research,
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
The effects of topical pilocarpine on the morphology of the outflow apparatus of the baboon (Papio cynocephalus)
 The effects of topical pilocarpine on the morphology of the outflow apparatus of the baboon (Papio cynocephalus) Ian Grierson, William R. Lee, and Shahida Abraham The morphology of the outflow system of
The effects of topical pilocarpine on the morphology of the outflow apparatus of the baboon (Papio cynocephalus) Ian Grierson, William R. Lee, and Shahida Abraham The morphology of the outflow system of
A LITTLE ANATOMY. three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera. 2. middle - uvea. anterior - iris,ciliary body. posterior - choroid
 GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
