Three Dimensional Architecture of Collagen Fibrils in the Corpus cavernosum of the Crab-eating Monkey
|
|
|
- Stephanie Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 73(4): , October, 1996 Three Dimensional Architecture of Collagen Fibrils in the Corpus cavernosum of the Crab-eating Monkey By Takashi NAKANO Department of Anatomy, Aichi Medical University, Nagakute, Aichi , Japan -Received for Publication, May 10, Key Words: Penis, Tunica albuginea, Trabecula, Scanning electron microscope, Cell maceration method Summary: The three-dimensional architecture of the collagen fibrils in the corpus cavernosum of the crab-eating monkey was studied by scanning electron microscope, after digestion of cellular and some extracellular elements by NaOH. The tunica was made up of undulating bundles of collagen fibrils which were arranged in inner circular, middle intermingled and outer longitudinal layers. The trabecula appeared as numerous cylindrical tubes which had once accommodated individual smooth muscle fibers. The outer surface of the trabecula was covered with a sheath woven from twisting bundles of collagen fibrils. These architectural features of the collagen fibrils seem to be related to fluctuations in the diameter and shape of the corpus during erection and detumescence. During erection, the corpus cavernosum becomes enormously enlarged, and the intracavernous pressure can greatly exceed systolic blood pressure (Carati et al., 1987; Purohit and Beckett, 1979). Therefore, the tunica albuginea surrounding the corpus requires not only elasticity but also rigidity. Strand-like trabeculae, which penetrate inward to delimit labyrinthine anastomosing cavernous sinuses, have to be slenderized and elongated to cause consequent distension of the sinuses during erection. The tunica as well as the trabeculae consist mainly of the collagen fibers with a few elastic fibers. In order to lead an appropriate hypothesis on the mechanism of penile erection, investigations of the collagen fibrils in the corpus seem important. However, there is still some uncertainty regarding the architecture of the collagen fibers due to their three-dimensional complexity, which stands in contrast to many available publications on the penile vascular system. The NaOH cell-maceration method (Ohtani, 1987) is very effective in removing cellular elements as well as some extracellular elements, making it possible to observe directly the three-dimensional architecture of collagen fibrils. Kurosawa et al. (1993) first induced the method into the human corpus, but could not obtain sufficient findings. Nakano (1995a, b) revealed clearly the three-dimensional architecture of collagen fibrils in the mouse corpus. The investigations on mammals other than the mouse must be of interest, because mechanism of erection seems to be various among different species of mammals (Fujita and Shirai, 1989). The crab-eating monkey was selected in this study, because the corpus of monkey is often used as a suitable model for the study on the mechanism of erection. It is hoped that this study will contribute to a further understanding of the intricate mechanism of penile erection. Materials and Methods Penes of three adult crab-eating monkeys, Macaca irus, bred in the laboratory animal research center in the Aichi Medical University, were used in this study. After removal of the skin, the penes were cut into several sections. For the LM study, the specimens were fixed in Zenker's fluid, dehydrated in a graded ethanol series, and embedded in paraffin. They were cut serially into transverse and longitudinal sections of 311,m and Azan stain was applied. For the SEM study, the specimens were immediately fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer for 2 hours and rinsed in distilled water. Then, the specimens were processed by NaOH cellmaceration method (Ohtani, 1987); they were immersed in a 10% NaOH solution for 4 days at room temperature, and rinsed in distilled water until they became transparent. After immersion in 1% tannic acid for 2-3 hours, they were rinsed in distilled water for several hours, postfixed with 2% osmium tetroxide for 1 hour, dehydrated in a graded ethanol, and dried with t-butyl alcohol freeze-drying method 185
2 186 T. Nakano (Inoue and Osatake, 1988). The specimens were cut longitudinally and transversely to the long axis of the corpus with a blade under a dissecting microscope, coated with gold and observed under a Jeol JSM 6100 scanning electron microscope. Results Light-microscopic findings The tunica albuginea surrounding the corpus cavernosum was made up almost entirely of thick collagen fibers. From the tunica albuginea finger-like trabeculae penetrated inward. In the cross sections, they appeared as rounded or irregularly polygonal profiles around the slit-like cavernous spaces. The trabeculae were predominantly composed of smooth muscle fibers which were partly separated from the cavernous spaces by collagen fibers (Fig: 1). In longitudinal sections of the corpus, the trabeculae appeared as thin strands which were generally arranged along the long axis of the corpus. The trabeculae consisted mainly of bundles of smooth muscle fibers which were oriented along the long axis of the trabeculae. The collagen fibers running along the trabecula showed a winding course (Fig. 2). Scanning electron microscopic findings After NaOH treatment, cellular elements such as smooth muscle fibers as well as some extracellular elements were completely removed without any apparent damage to collagen fibrils. Tunica albuginea Each corpus cavernosum was surrounded by a thick capsule, the tunica albuginea (about 800 1,200 um in thickness) (Fig. 3). The tunica was composed of thick bundles of collagen fibrils which took an undulating course. In the inner layer the bundles were arranged circularly, while in the outer layer then ran longitudinally along the long axis of the corpus (Fig. 4). In the region between the inner and outer layers, the circular bundles intei mingled with the longitudinal ones (Fig. 4, 5). That is, the collagen bundles were arranged in three layers (inner circular, middle intermingled and outer longitudinal). In the median plane, the grouped collagen bundles extended inward from the inner circular layer of the tunica to form the median septum (Fig. 3). Each bundle was composed of densely packed collagen fibrils running in parallel. Further, small bundled as well as single collagen fibrils ran in various directions to form the fine networks enmeshing the bundles (Fig. 5). The bundles showed a wide range of widths (about 5-25 pm) and thicknesses (about gm). Trabecula The trabecula, after NaOH treatment, extended inward from the inner circular layer of the tunica (Fig. 3). At higher magnifications, the trabecula displayed a honeycomb appearance on crosscut surface across its long axis (Fig. 6, 7). Each hole in the appearance is surrounded by a wall consisting of collagen fibrils (Fig. 7). On longitudinally cut sections, the trabeculae were arranged along the long axis of the corpus, and were frequently bifurcated and connected with adjacent trabecula to form a complex network (Fig. 8). At higher magnifications, they exhibited numerous cylindrical tubes, occupied by individual muscle fibers prior to the NaOH treatment (Fig. 9). The wall of the tube consisted of single and small-bundled collagen fibrils. The small-bundled fibrils themselves took a twisting course and gave off much thinner bundles and even single fibrils, both of which formed a finer meshwork. These fibrils of one wall frequently extended to and formed part of the neighboring wall. Such collagenous walls varied in density; the meshwork was dense and complicated at some sites but sparse in others (Fig. 9). The outer surface of the trabeculae was covered with a collagenous sheath composed mainly of thick bundles of collagen fibrils, running generally in longitudinal or oblique direction to the long axis of the trabecula. The bundles took a wavy course, often giving off thinner branches and interwound in complex fashion (Figs. 10, 11). The bundles were enmeshed by a delicate lacework knitted together by smallbundled as well as single collagen fibrils. Between the bundles were delicate networks of entangled collagen fibrils, which derived from the lacework around the bundles (Fig. 11). On the basis of the findings described above, a schematic illustration of the architecture of the collagen fibrils and the smooth muscle fibers in the corpus is presented in figure 12a. Discussion Tunica albuginea In the corpus cavernosum, it has been reported that in man the intracavernous pressure during erection can greatly exceed systolic blood pressure to become the corpus rigid (Kano et al., 1986; Carati et al., 1987; Purohit and Beckett, 1979). Therefore, the tunica albuginea surrounding the corpus has to resist possible rupture of the corpus during erection and intercourse. The tunica is made up almost entirely of thick bundles of collagen fibrils. According to widely read textbooks on human histology (Fawcett, 1986; Geneser, 1986; Ito, 1987; Fujita and Fujita, 1992), the collagen bundles are arranged in inner
3 Collagen Fibrilar Architecture in the Corpus cavernosum 187 circular and outer longitudinal layers. However, it is difficult to determine the precise arrangement of the collagen fibrils from thin sections, and threedimensional observation by SEM is indispensable. Nakano (1995a, b) examined three-dimensionally the mouse tunica treated with the NaOH cellmaceration method, and revealed that the bundles in the tunica were arranged in inner circular and outer longitudinal layers. In the present study, the bundles in the tunica of the crab-eating monkey were arranged in three layers. In the inner layer they ran circularly, while in the outer one they were longitudinal. In the middle layer, the circular bundles and the longitudinal ones intermingled. The inner circular layer serves to resist the considerable increase in diameter of the corpus during erection, while the outer longitudinal one resists lengthening. The middle layer may function to coordinate the movement of the inner circular and outer longitudinal layers during erection and detumescence. In this study, it was clear that the collagen bundles took a wavy course in the flaccid state. Such bundles seem to have stretchability until they become straight, with the enlargement of the cavernous sinuses during erection. The change in arrangement of the collagen bundles during erection is speculated on in figure 12b. During erection the tunica appears to be stretched so as to become increasingly thinner and stiffer than in its flaccid state. Trabecula During erection, the trabeculae are slenderized with consequent engorgement of the cavernous spaces. Which component of the trabeculae does relate to their slenderizing? At light microscopic level, the trabeculae in the mouse were mainly constituted of collagen bundles with a few smooth muscle fibers (Nakano, 1995a). After the NaOH cellmaceration method, the mouse trabeculae consisted of grouped collagen bundles which ran along their meshwork taking a winding course. Considered from these findings, Nakano (1995a) suggested in the mouse that the collagen bundles mainly related to changes in the diameter of the trabeculae during erection; i.e., when the tunica is extended, the collagen bundles in the trabeculae appear to be stretched until they become straight, causing a slenderizing of the trabeculae. In the crab-eating monkey, the findings were extremely different from those in the mouse. At the light microscopic level, the bulk of the trabeculae was made up of smooth muscle fibers, which were arranged in bundles running along the longer axis of the trabeculae. It is suggested that the relaxation of the smooth muscle fibers contributed to a slenderizing of the trabeculae with consequent distention of the cavernous spaces during erection (Fig. 12b). These findings may provide further support for the description by Cormack (1987) that relaxation of the smooth muscle fibers in the human trabeculae is a factor contributing to distension of the cavernous spaces. Further, contraction of the smooth muscle fibers appear to cause a narrowing of the cavernous spaces with consequent emptying of the spaces during detumescence. After NaOH treatment, the trabeculae of the crab-eating monkey exhibited numerous cylindrical tubes which had once accommodated individual smooth muscle fibers. The wall of the cylindrical tube, which is woven from twisting collagen fibrils, is considered to be highly flexible and to comply with a functional need; i.e., the smooth muscle fibers may be allowed a certain freedom of movement during erection and detumescence. It is noteworthy that collagen fibrils of one wall extended into and formed part of the neighboring wall; i.e., the smooth muscle fibers are tied together by the collagenous wall to form the bundle. This finding suggests that the collagenous wall provides a structure suitable for the coordinated movement of muscle fibers. In the mouse, the outer surface of the trabeculae was covered with a sheath woven from twisting collagen fibrils (Nakano, 1995a, b). It was suggested that the sheath may be highly flexible during erection and detumescense (Nakano, 1995a). In the monkey, however, the outer surface of the trabeculae was covered with a sheath woven from thick collagen bundles, which generally ran along the longer axis of the trabeculae taking a wavy course. Such bundles appear to have an ability to be stretched during erection. The change in arrangement of the collagen bundles during erection is speculated in figure 12b: When the smooth muscle fibers are relaxed to cause a slenderizing of the trabeculae, the stretched collagen bundles contribute to resisting the considerable lengthening of the trabeculae. It further appears that during detumescence, the collagen bundles may regain their twisting course as the smooth muscle fibers may regain their former tonus. References 1) Carati CJ, Creed KE and Keogh EJ. Autonomic control of penile erection in the dog. J Physiol 1987; 384: ) Cormach DH. Ham's Histology. pp (Lippincott, Philadelphia 1987). 3) Fawcett DW. A Textbook of Histology. pp (Saunders, Philadelphia 1986). 4) Fujita H and Fujita T. Textbook of Histology Part 2 (in Japanee). pp (Igaku Shoin, Tokyo 1992). 5) Fujita T and Shirai M. Mechanism of penile erection (in Japanese). J Clin Exp Med 1989; 148: ) Geneser F. Textbook of Histology. pp (Munksgaard, Copenhagen 1986).
4 188 T. Nakano 7) Inoue T and Osatake H. A new drying method of biological specimens for scanning electron microscopy: The t-butyl alcohol freeze-drying method. Arch Histol Cytol 1988; 51 : ) Ito T. Histology (in Japanese). pp (Nanzando, Tokyo 1987). 9) Kano K, Hanyu S and Iwanaga T. Mechanism of erection based on penile vascular organization (in Japanese). Biomed SEM 1986; 15: ) Kurosawa T, Goto Y and Banya Y. Collagen fibers in the tunica albuginea of human penis. Its arrangement and possible function in the mechanism of erection (in Japanese with English abstract). J Iwate Med Ass 1993; 45: ) Nakano T. Three-dimensional architecture of collagen fibrils in the mouse corpus cavernosum penis. Acta Anat 1995a; 152: ) Nakano T. Collagen fibrillar arrangement in corpus cavernosum/corpus spongiosum of mice. Assist Reproduct Technol Androl 1995b; 8: ) Ohtani 0. Three-dimensional organization of the connective tissue fibers of the human pancreas. A scanning electron microscopic study of NaOH treated tissues. Arch Histol Jpn 1987; 50: ) Purohit RC and Beckett SD. Penile pressures and muscle activity associated with erection and ejaculation in the dog. Am J Physiol 1979; 231: Explanation Plate of Figures I Fig. 1. Light micrograph showing the crosscut surface of the corpus cavernosum. The trabeculae (T) consisting mainly of smooth muscle fibers are partly separated from the cavernous spaces by collagen fibers (arrows). Red blood cells are seen in the cavernous spaces (asterisk). Azan stain. x300. Fig. 2. Light micrograph showing the longitudinally cut surface. The trabeculae (T) are made up mainly of smooth muscle fibers which are oriented along the long axis of the trabeculae. The collagen fibers (arrows) run along the trabecula, taking a winding course. Red blood cells are seen in the cavernous spaces (asterisk). Azan stain. x300. Fig. 3. Scanning electron micrograph showing the cross section of the penis. The corpora cavernosum (Cc) are covered with thick tunica albuginea (arrowheads). Arrow = median septum. x 25. Fig. 4. Higher magnification of a cross section of the tunica. It is clear that each collagen bundle takes an undulating course. The collagen bundles are arranged in inner circular (C) and outer longitudinal (L) layers. In the middle layer, the circular bundles (arrows) intermingle with the longitudinal ones (arrowheads). x200. Fig. 5. Higher magnification of the middle intermingled layer of the tunica. Arrow = circular bundle. Arrowheads = longitudinal bundles. x 2,500.
5 Collagen Fibrilar Architecture in the Corpus cavemosum 189 Plate I
6 190 T. Nakano Plate II Fig. 6. Cross section of the trabeculae. The trabeculae (T) form a complex framework around the cavernous spaces (asterisk). x 100. Fig. 7. Higher magnification of a cross section. The trabecula displays a honeycomb appearance. Each hole (arrowheads) in this appearance is surrounded by a collagenous wall (arrows). Asterisk = cavernous space. x 1,000. Fig. 8. A longitudinally cut section of the trabeculae. The trabeculae (T) are arranged longitudinally, and are bifucated and connect with adjacent trabecula. Asterisk = cavernous space. C = inner circular layer of the tunica. x 100. Fig. 9. Higher magnification of a longitudinally cut section. The trabecula exhibits cylindrical tubes (t). The wall (arrows) of the tube is woven from collagen fibrils which take a twisting course. x 1,000. Fig. 10. Scanning electron micrograph showing the outer surface of the trabeculae (T). The surface is covered with collagenous sheath composed of thick bundles, taking a wavy course (arrowheads). The crosscut surface of the trabecula displays a honeycomb appearance (arrows). x250. Fig. 11. Higher magnification of the outer surface of the trabecula. The collagen bundles take a wavy course, and are enmeshed by a lacework knitted by collagen fibrils (arrowheads). x2,500.
7 Collagen Fibrilar Architecture in the Corpus cavernosum 191 Plate II
8 192 T. Nakano Plate III Fig. 12. Schematic illustration on the architecture of collagen fibrils and smooth muscle fibers in a longitudinally cut surface of the corpus cavernosum. a Flaccid: In the tunica, the collagen bundles take an undulating course, and are arranged in inner circular (C), middle intermingled (I) and outer longitudinal (L) layers. The trabecula (T) ran along the long axis of the corpus, and consisted mainly of bundles of smooth muscle fibers (S). The outer surface of the trabecula is covered with a collagenous sheath composed of thick collagen bundles taking a wavy course (arrows). b Erect (speculation): The collagen bundles in the inner circular (C) middle intermingled (I) and outer longitudinal layers of the tunica appear to be stretched, reducing the thickness of the tunica. The collagen bundles (arrows) covering the smooth muscle fibers (S) in the trabecula (T) seem to be stretched, causing a slenderizing of the trabecula. Asterisk = cavernous space.
9 Collagen Fibrilar Architecture in the Corpus cavernosum 193 Plate III 12a 12b
Biomechanics. and Functional Anatomy. of Human Male Genitalia. For designers and creators of biomimetic androids, dolls and robots
 Biomechanics and Functional Anatomy of Human Male Genitalia For designers and creators of biomimetic androids, dolls and robots The Penis The shaft or body of the penis is formed principally by a fused
Biomechanics and Functional Anatomy of Human Male Genitalia For designers and creators of biomimetic androids, dolls and robots The Penis The shaft or body of the penis is formed principally by a fused
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
Elastic Skeleton of Intracranial Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats
 1722 Elastic Skeleton of Intracranial Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats Naohiro Yamazoe, MD, Nobuo Hashimoto, MD, Haruhiko Kikuchi, MD, and Fumitada Hazama, MD In an attempt to clarify the developmental mechanism
1722 Elastic Skeleton of Intracranial Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats Naohiro Yamazoe, MD, Nobuo Hashimoto, MD, Haruhiko Kikuchi, MD, and Fumitada Hazama, MD In an attempt to clarify the developmental mechanism
Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 78(2-3): 49-54, August. 2001 Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve By Hiromitsu EZURE, Noboru GOTO, Naoko NONAKA, Jun GOTO and Hiroaki TANI Department of Anatomy,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 78(2-3): 49-54, August. 2001 Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve By Hiromitsu EZURE, Noboru GOTO, Naoko NONAKA, Jun GOTO and Hiroaki TANI Department of Anatomy,
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Scanning Electron Microscopic Observation of the Rat Cerebellar Cortex
 Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 42, No.1, 25-29, 1994 Scanning Electron Microscopic Observation of the Rat Cerebellar Cortex Hiromi TAKAHASHI-IWANAGA and Tsuneo FUJITA Department of Anatomy, Niigata University
Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 42, No.1, 25-29, 1994 Scanning Electron Microscopic Observation of the Rat Cerebellar Cortex Hiromi TAKAHASHI-IWANAGA and Tsuneo FUJITA Department of Anatomy, Niigata University
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS
 NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS IOANNIS VARKARAKIS ASOSCIATE PROFESSOR OF UROLOGY 2 ND DEPT OF UROLOGY NATIONAL & KAPODISTRIAN UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS PENILE GROSS ANATOMY 3 ERECTILE COLUMNS TWO CORPORA CAVERNOSA
NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS IOANNIS VARKARAKIS ASOSCIATE PROFESSOR OF UROLOGY 2 ND DEPT OF UROLOGY NATIONAL & KAPODISTRIAN UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS PENILE GROSS ANATOMY 3 ERECTILE COLUMNS TWO CORPORA CAVERNOSA
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA. Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962),
 Title ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA Author(s) OKADA, Yoshio; SAGAWA, Yanosuke; IS DAIDO, Shigeo Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962), Issue Date 1962-03-30 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/51710
Title ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA Author(s) OKADA, Yoshio; SAGAWA, Yanosuke; IS DAIDO, Shigeo Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962), Issue Date 1962-03-30 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/51710
Determination of the Distribution of Cilia on the Surface of the Mantle of Cypraea caputserpentis utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy
 Determination of the Distribution of Cilia on the Surface of the Mantle of Cypraea caputserpentis utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy DURATION September 10, 1990- May 7, 1991 Tracie A. Yokoi Advisor
Determination of the Distribution of Cilia on the Surface of the Mantle of Cypraea caputserpentis utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy DURATION September 10, 1990- May 7, 1991 Tracie A. Yokoi Advisor
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Three-Dimensional Architecture of the Subepithelial Connective Tissue Layer in the Mouse Retromolar Region
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 70(5): 219-230. December, 1993 Three-Dimensional Architecture of the Subepithelial Connective Tissue Layer in the Mouse Retromolar Region By Takashi NAKANO Department of Anatomy,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 70(5): 219-230. December, 1993 Three-Dimensional Architecture of the Subepithelial Connective Tissue Layer in the Mouse Retromolar Region By Takashi NAKANO Department of Anatomy,
Penis and Prostate. Holly White Jennifer Zang September 7, Penis and Prostate. 1) Other Names None
 Penis and Prostate Penis and Prostate Holly White Jennifer Zang September 7, 2006 1) Other Names None 2) Definition/ Location The prostate is a doughnut-like gland that lies inferior to the urinary bladder
Penis and Prostate Penis and Prostate Holly White Jennifer Zang September 7, 2006 1) Other Names None 2) Definition/ Location The prostate is a doughnut-like gland that lies inferior to the urinary bladder
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module. 1) Connective tissue
 D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
Intercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida
 JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development
 Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 47: 433-444, 1971 A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development By Hsi-Kuei Tsai Department of Anatomy, College
Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 47: 433-444, 1971 A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development By Hsi-Kuei Tsai Department of Anatomy, College
Scanning electron microscopy of pulmonary alveolar capillary vessels
 Thorax (1973), 28, 222. Scanning electron microscopy of pulmonary alveolar capillary vessels I. G. S. ALEXANDER', B. C. RITCHIE, and J. E. MALONEY Departments of Anatomy and Medicine, Monash University,
Thorax (1973), 28, 222. Scanning electron microscopy of pulmonary alveolar capillary vessels I. G. S. ALEXANDER', B. C. RITCHIE, and J. E. MALONEY Departments of Anatomy and Medicine, Monash University,
Anatomy and Histology of the Lacrimal Fluid Drainage System
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 77(5): 155-160, December. 2000 Anatomy and Histology of the Lacrimal Fluid Drainage System By Rieko KOMINAMI, Satoru YASUTAKA, Yutaka TANIGUCHI and Harumichi SHINOHARA Department
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 77(5): 155-160, December. 2000 Anatomy and Histology of the Lacrimal Fluid Drainage System By Rieko KOMINAMI, Satoru YASUTAKA, Yutaka TANIGUCHI and Harumichi SHINOHARA Department
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
On the presence and function of closed lymphatic stomata in the diaphragm of the golden hamster
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 66 (2-3): 69-80, August, 1989 On the presence and function of closed lymphatic stomata in the diaphragm of the golden hamster By Harumichi SHINOHARA, Yoshifumi FUKUO and Takeshi
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 66 (2-3): 69-80, August, 1989 On the presence and function of closed lymphatic stomata in the diaphragm of the golden hamster By Harumichi SHINOHARA, Yoshifumi FUKUO and Takeshi
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder
 Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 3 Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 5 6 Atlas of the Shoulders
Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 3 Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 5 6 Atlas of the Shoulders
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Soft tissue biomechanics
 Soft tissue biomechanics Caroline Öhman Pula, 22/06-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to soft tissues Tendon and ligaments Introduction Composition Function and structure In vitro testing Stress-strain
Soft tissue biomechanics Caroline Öhman Pula, 22/06-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to soft tissues Tendon and ligaments Introduction Composition Function and structure In vitro testing Stress-strain
O SSIFICATION of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 J Neurosurg 61:131-135, 1984 Ultrastructure of early calcification in cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament TOSHIHIKO KUBOTA, M.D., KAZUHUMI SATO, M.D., HIROKAZU KAWANO, M.D., SHINJIRO
J Neurosurg 61:131-135, 1984 Ultrastructure of early calcification in cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament TOSHIHIKO KUBOTA, M.D., KAZUHUMI SATO, M.D., HIROKAZU KAWANO, M.D., SHINJIRO
Scanning Electron Microscopical Observation on the Penetration Mechanism of Fowl Spermatozoa into the Ovum in the Process of Fertilization
 J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Husb., Hiroshima Univ. (1976), 15: 85-92 Scanning Electron Microscopical Observation on the Penetration Mechanism of Fowl Spermatozoa into the Ovum in the Process of Fertilization Shunsaku
J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Husb., Hiroshima Univ. (1976), 15: 85-92 Scanning Electron Microscopical Observation on the Penetration Mechanism of Fowl Spermatozoa into the Ovum in the Process of Fertilization Shunsaku
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Anatomical and Histological Study of local dog Penis Alaa, H. Saadon 1 1
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alaa, H. Saadon, (2016); 5 (3), 8-14 Mirror of MRVSA/ Research in Open Veterinary Access Sciences DOAJ and Animals Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA) Journal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alaa, H. Saadon, (2016); 5 (3), 8-14 Mirror of MRVSA/ Research in Open Veterinary Access Sciences DOAJ and Animals Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA) Journal
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
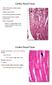 Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Urinary system. Urinary system
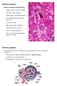 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Histological Features of the Renal Arteries in Indian Goat (Capra hircus)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
The Intermediate Epithelium Lining the Nasopharynx
 Okajima Folia Anat. Jpn., 67 (2-3): 169-174, August, 1990 The Intermediate Epithelium Lining the Nasopharynx of the Suncus murinus By Takashi NAKANO, Yoshie IWAMA, Kaori HASEGAWA and Hiroshi MUTO Department
Okajima Folia Anat. Jpn., 67 (2-3): 169-174, August, 1990 The Intermediate Epithelium Lining the Nasopharynx of the Suncus murinus By Takashi NAKANO, Yoshie IWAMA, Kaori HASEGAWA and Hiroshi MUTO Department
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING
 Acta orthop. scand. 52, 5-10, 1981 ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING A Histological and Scanning Electron Microscopical Study H. ARO*, H. KALLIONIEMI**, A. J. AHO* & P. KELLOKUMPU-LEHTINEN*** *Department
Acta orthop. scand. 52, 5-10, 1981 ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING A Histological and Scanning Electron Microscopical Study H. ARO*, H. KALLIONIEMI**, A. J. AHO* & P. KELLOKUMPU-LEHTINEN*** *Department
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
Muscle Tissue. Xie Fenfen. Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Anhui Medical University
 Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Published Online: 25 November, 1956 Supp Info: on November 16, 2018 jcb.rupress.org Downloaded from
 Published Online: 25 November, 1956 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.2.6.799 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 16, 2018 B~IEF NOrmS 799 Permanganate--A New Fixative for Electron Microscopy.*
Published Online: 25 November, 1956 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.2.6.799 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 16, 2018 B~IEF NOrmS 799 Permanganate--A New Fixative for Electron Microscopy.*
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Information for Patients. Priapism. English
 Information for Patients Priapism English Table of contents What is priapism?... 3 What causes priapism?... 3 Diagnosing priapism... 3 Treating priapism... 4 Conservative, first- and second-line treatments...
Information for Patients Priapism English Table of contents What is priapism?... 3 What causes priapism?... 3 Diagnosing priapism... 3 Treating priapism... 4 Conservative, first- and second-line treatments...
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. during postnatal period and to provide elasticity during prenatal and early
 CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology. Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta )
 Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 56(5) : 309-316, December 1979 Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle By IKUO YOSHIOKA, MICHIKO IIDA and HIROSHI MUTO
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 56(5) : 309-316, December 1979 Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle By IKUO YOSHIOKA, MICHIKO IIDA and HIROSHI MUTO
Light and Scanning Electron Microscopical Studies on the Structure of the Vitelline Membrane of the Hen's Egg
 J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Hush. Hiroshima Univ. (1972), 11: 1 ~13 Light and Scanning Electron Microscopical Studies on the Structure of the Vitelline Membrane of the Hen's Egg Shunsaku FuJII, Tatsudo TAMURA
J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Hush. Hiroshima Univ. (1972), 11: 1 ~13 Light and Scanning Electron Microscopical Studies on the Structure of the Vitelline Membrane of the Hen's Egg Shunsaku FuJII, Tatsudo TAMURA
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
FIGURE 54 represents the urogenital apparatus
 CHAPTER VI THE UROGENITAL ORGANS FIGURE 54 represents the urogenital apparatus of a thirty-inch female specimen of Alligator mississippiensis. Figure 55 shows the corresponding organs of a male A lucius;
CHAPTER VI THE UROGENITAL ORGANS FIGURE 54 represents the urogenital apparatus of a thirty-inch female specimen of Alligator mississippiensis. Figure 55 shows the corresponding organs of a male A lucius;
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS
 FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
If necessary, you should review the proper care and use of the light microscope before beginning this exercise.
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ********************************************************************************************************* HISTOLOGY THE EXAMINATION OF TISSUES **********************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ********************************************************************************************************* HISTOLOGY THE EXAMINATION OF TISSUES **********************************************************************************************************
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
The Fine Structure of the Neck Region of Cat Spermatozoa. Nobuhiro SATO and Chikayoshi OURA
 Okajimas Folia Anal. Jpn., 61(4): 267 286, OLiober 1984 The Fine Structure of the Neck Region of Cat Spermatozoa By Nobuhiro SATO and Chikayoshi OURA Department of Anatomy, Miyazaki Medical College, Miyazaki,
Okajimas Folia Anal. Jpn., 61(4): 267 286, OLiober 1984 The Fine Structure of the Neck Region of Cat Spermatozoa By Nobuhiro SATO and Chikayoshi OURA Department of Anatomy, Miyazaki Medical College, Miyazaki,
Histology of Male Reproductive System
 Histology of Male Reproductive System Lecture Objectives Describe the histological features of the male reproductive system Male Reproductive System The male structures of reproduction include the: testes,
Histology of Male Reproductive System Lecture Objectives Describe the histological features of the male reproductive system Male Reproductive System The male structures of reproduction include the: testes,
Distribution of the Pores of Epithelial Basement Membrane in the Rat Small Intestine
 FULL PAPER Anatomy Distribution of the Pores of Epithelial Basement Membrane in the Rat Small Intestine Takashi TAKEUCHI 1) and Tatsuo GONDA 1) 1) Institute of Experimental Animals, Shimane Medical University,
FULL PAPER Anatomy Distribution of the Pores of Epithelial Basement Membrane in the Rat Small Intestine Takashi TAKEUCHI 1) and Tatsuo GONDA 1) 1) Institute of Experimental Animals, Shimane Medical University,
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Small Intestine of a Normal Unsuckled Calf and a Calf with Enteric Colibacillosis
 Vet. Pathol. 15; 400-406 (1978) Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Small Intestine of a Normal Unsuckled Calf and a Calf with Enteric Colibacillosis G. R. PEARSON. E. F. LOGAN and G. P. BRENNAN Departmcnt
Vet. Pathol. 15; 400-406 (1978) Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Small Intestine of a Normal Unsuckled Calf and a Calf with Enteric Colibacillosis G. R. PEARSON. E. F. LOGAN and G. P. BRENNAN Departmcnt
CVS HISTOLOGY. Dr. Nabil Khouri.
 CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
ELASTIC FIBRE SYSTEM IN THE SHAFT OF ADULT HUMAN PENIS
 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Anatomy Journal of Africa 2015. 4(1): 466 475. ELASTIC FIBRE SYSTEM IN THE SHAFT OF ADULT HUMAN PENIS Peter Gichangi, Sara Mugania, Otieno Beda Correspondence to: Prof. Peter Gichangi,
ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Anatomy Journal of Africa 2015. 4(1): 466 475. ELASTIC FIBRE SYSTEM IN THE SHAFT OF ADULT HUMAN PENIS Peter Gichangi, Sara Mugania, Otieno Beda Correspondence to: Prof. Peter Gichangi,
8 - Muscular System. Introduction Taft College Human Physiology
 8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Scanning Electron Microscopic Studies of Tissue Elastin Components Exposed by a KOH-Collagenase or Simple KOH Digestion Method
 Arch. Histol. Cytol., Vol. 54, No. 4 (1991) p. 427-436 Scanning Electron Microscopic Studies of Tissue Elastin Components Exposed by a KOH-Collagenase or Simple KOH Digestion Method Tatsuo USHIKII and
Arch. Histol. Cytol., Vol. 54, No. 4 (1991) p. 427-436 Scanning Electron Microscopic Studies of Tissue Elastin Components Exposed by a KOH-Collagenase or Simple KOH Digestion Method Tatsuo USHIKII and
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
An anatomical structure which results in puffiness of the upper eyelid and a narrow palpehral fissure in the Mongoloid eye
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2000), 53, 466-472 9 2000 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons DOI: 10.1054/bjps.2000.3387 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical structure which
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2000), 53, 466-472 9 2000 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons DOI: 10.1054/bjps.2000.3387 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical structure which
Gross Anatomy. Landmarks on a typical long bone. Membranes. Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes. Periosteum Endosteum
 BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
Periodontal ligament
 Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Electron Microscopy. dishes in Eagle minimum essential medium with 10% serum to a density that allowed them to grow in a C02
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, p. 1452-1456 0021-9193/78/0133-1452$02.00/0 Copyright 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 133, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Positive Detection of Mycoplasma Contamination
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, p. 1452-1456 0021-9193/78/0133-1452$02.00/0 Copyright 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 133, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Positive Detection of Mycoplasma Contamination
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Connective Tissue. Answer Choices(In CAPITAL BOLD): RETICULAR ELASTIC. IRREGULAR Spongy bone ELASTIC BLOOD
 Connective Tissue Answer Choices(In CAPITAL BOLD): Proper: Specialized: Loose- Cartilage- AREOLAR HYALINE ADIPOSE FIBROCARTILAGE RETICULAR ELASTIC Dense- Bone- REGULAR COMPACT BONE IRREGULAR Spongy bone
Connective Tissue Answer Choices(In CAPITAL BOLD): Proper: Specialized: Loose- Cartilage- AREOLAR HYALINE ADIPOSE FIBROCARTILAGE RETICULAR ELASTIC Dense- Bone- REGULAR COMPACT BONE IRREGULAR Spongy bone
Morphological Studies on the Union of the Frontal Bone: Blood Vessels in the Non-obliterated Frontal Suture
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 57(4) : 201-218, October 1980 Morphological Studies on the Union of the Frontal Bone: Blood Vessels in the Non-obliterated Frontal Suture By HIROSHI MUTO and bum YOSHIOKA Department
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 57(4) : 201-218, October 1980 Morphological Studies on the Union of the Frontal Bone: Blood Vessels in the Non-obliterated Frontal Suture By HIROSHI MUTO and bum YOSHIOKA Department
Mechanical Properties and Active Remodeling of Blood Vessels. Systemic Arterial Tree. Elastic Artery Structure
 Mechanical Properties and Active Remodeling of Blood Vessels Gross anatomy of systemic and pulmonary circulation Microscopic structure Mechanical properties and testing Residual stress Remodeling Systemic
Mechanical Properties and Active Remodeling of Blood Vessels Gross anatomy of systemic and pulmonary circulation Microscopic structure Mechanical properties and testing Residual stress Remodeling Systemic
URINARY SYSTEM. Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3
 URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
Acta Medica Okayama. Electron microscopic demonstration of a new virus isolated from a patient with SMON. Zensuke Ota DECEMBER 1970
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 24, Issue 6 1970 Article 3 DECEMBER 1970 Electron microscopic demonstration of a new virus isolated from a patient with SMON Zensuke Ota Okayama University, Copyright c 1999
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 24, Issue 6 1970 Article 3 DECEMBER 1970 Electron microscopic demonstration of a new virus isolated from a patient with SMON Zensuke Ota Okayama University, Copyright c 1999
Histology of the Cardiac System. Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department
 Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing Low-vacuum scanning electron microscope
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2017 Vol. 9 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2017 Vol. 9 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
SCPA602 Cardiovascular System
 SCPA602 Cardiovascular System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCPA602 Cardiovascular System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Observations of the Fenestrated Membrane of the Human Arterial Wall
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 60(6): 415-426, March 1984 Observations of the Fenestrated Membrane of the Human Arterial Wall By Tadao MITSUI, Joji GARASHI, Hiroshi WATANABE and Tsuyuka KUSHIDA Department
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 60(6): 415-426, March 1984 Observations of the Fenestrated Membrane of the Human Arterial Wall By Tadao MITSUI, Joji GARASHI, Hiroshi WATANABE and Tsuyuka KUSHIDA Department
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
