Unknown Cases. Financial Disclosures & Disclaimers. Unknown Cases Case #2. Unknown Cases Case #1. Differentials in Pediatric Brain Imaging
|
|
|
- April Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Financial Disclosures & Disclaimers Differentials in Pediatric Brain Imaging William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O. Program Director, Diagnostic Radiology Residency, DGMC Associate Clinical Professor of Radiology University of California, Davis School of Medicine Sacramento, CA Receive royalties from Thieme Medical Publishers Top 3 Differentials in Radiology: A Case Review, 2010 Top 3 Differentials in Neuroradiology: A Case Review, 2015 The views expressed in this material are those of the author and do not reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Government, Department of Defense, or U.S. Air Force 2 Differentials in Pediatric Brain Imaging Learning Objectives Recognize and describe pertinent imaging findings from unknown pediatric brain cases Review differential diagnoses for common & important abnormalities within the pediatric brain Understand imaging features of various gamuts in pediatric brain imaging Unknown Cases 3 4 Unknown Cases Case #1 Unknown Cases Case #2 Adolescent 5 6 1
2 Unknown Cases Case #3 Unknown Cases Case #4 7 8 Unknown Cases Case #5 Unknown Cases Case # Case Review Case #
3 Adolescent Confluent white matter disease in a child - Multiple sclerosis (MS) - Acute disseminating encephalomyelitis (ADEM) - Dysmyelinating disease (leukodystrophy) Additional Diagnostic Considerations: - Toxic leukoencephalopathy (chemo/radiation) - Atypical infection (PML, HIV) Diagnosis: Dysmyelinating disease (ALD) Confluent white matter disease in a child Multiple sclerosis (MS) Occurs predominantly in young to middle-aged women May also affect children Schilder variant affects children Marburg variant is fulminant & progressive Relapsing & remitting course most common MR reveals: Ovoid lesions in characteristic locations, may be confluent Active demyelination may enhance and/or restrict diffusion Enhancement nodular or open ring Confluent white matter disease in a child Multiple sclerosis (MS) Young girl with advanced MS Numerous white matter lesions; active lesions demonstrate peripheral nodular and ring-enhancement along leading edge Confluent white matter disease in a child Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis ADEM is a monophasic autoimmune demyelinating dz Occurs in children following a viral infection or vaccination Varies from self-limiting to fulminant encephalitis MRI reveals bilateral T2 bright white matter lesions Often similar distribution & morphology to MS Periventricular Corpus callosum Posterior fossa / brainstem / cord More likely to be confluent and extensive compared to MS Active lesions may enhance or show diffusion restriction Confluent white matter disease in a child Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Young boy with acute onset neurological deficits FLAIR image shows bilateral, confluent regions of abnormal WM hyperintensity Abnormal signal extends into corpus callosum
4 Confluent white matter disease in a child Dysmyelinating Disease Leukodystrophies result in dysmelination Enzyme deficiencies cause accumulation of toxic metabolites Affects myelin formation & repair Patients present with visual or behavioral disturbances MR shows symmetric, confluent WM signal abnormality Metachromatic leukodystrophy is most common ALD commonly affects boys (x-linked) & adrenal glands Alexander dz has frontal lobe predominance & macrocephaly Canavan dz has increased NAA on MRS & macrocephaly Confluent white matter disease in a child Dysmyelinating Disease 12-yo boy with metachromatic leukodystrophy Axial CT shows symmetric confluent regions of WM hypoattenuation FLAIR image better depicts diffuse WM hyperintensity Confluent white matter lesions in a child Toxic Encephalopathy Confluent white matter lesions in a child Toxic Encephalopathy Chemotherapy may result in: Relatively symmetric WM signal abnormality May involve cerebrum (incl corpus callosum), cerebellum, & brainstem Radiation therapy related WM signal abnormalities correlate to treatment field Radiation necrosis may mimic neoplasm recurrence 19-yr-old boy pre and post treatment for germinoma Pre-treatment FLAIR image is normal Post-treatment FLAIR image shows symmetric confluent WM hyperintensity including the CC Pre-treatment Post-treatment Confluent white matter lesions in a child Atypical Infection HIV encephalopathy/dementia may present: Volume loss disproportionate for age (most common) Symmetric periventricular WM signal abnormality PML is an atypical infection (JC virus) in immunosuppressed patients (typically AIDS) Affects oligodendrocytes Results in confluent increased T2 WM signal abnormality May be bilateral but typically asymmetric Enhancement is unusual Confluent white matter lesions in a child Atypical Infection Young adult man with AIDS dementia complex FLAIR image shows symmetric confluent WM hyperintensity with frontal lobe predominance and involvement of CC
5 Confluent white matter lesions in a child Atypical Infection Confluent white matter disease in a child Differential Diagnosis Review Young adult man with AIDS and PML FLAIR image reveals asymmetric (L>R) confluent WM hyperintensity in centrum semiovale - Multiple sclerosis (MS) - Acute disseminating encephalomyelitis (ADEM) - Dysmyelinating disease (leukodystrophy) Additional Diagnostic Considerations: - Toxic leukoencephalopathy (chemo/radiation) - Atypical infection (PML, HIV) *Image courtesy of Paul Sherman, M.D Case # Craniopharyngioma - Germ cell tumor (GCT) - Optic pathway/hypothalamic glioma Additional Diagnostic Considerations: - Hypothalamic hamartoma - Rathke cleft cyst Craniopharyngioma Most common suprasellar mass in children Two variants: Adamantinomatous (peak age 5-15) Papillary (age > 50) Pediatric variant presents as multi-cystic mass with calcifications (90%) Cystic contents may be T1 hyperintense (proteinaceous) Calcifications hyperdense on CT & variable on T2 MRI Diagnosis: Optic pathway glioma
6 Craniopharyngioma Craniopharyngioma 9-yr-old boy with cystic and solid suprasellar mass Some cystic components T1 hyperintense Solid components and septations enhance 11-yr-old boy with headaches CT shows a calcified sellar/suprasellar mass Germ Cell Tumor GCTs most common in pediatric population Typically midline Frequently in pineal & suprasellar regions Germinomas are most common subtype Follow gray matter signal intensity Homogeneously enhance May be circumscribed or infiltrative Often seed CSF Teratomas more heterogeneous with macroscopic fat Dermoid cysts may have fat-fluid levels Germ Cell Tumor 14-yr-old boy with suprasellar germinoma T1 post contrast images show a homogeneously enhancing suprasellar mass Germ Cell Tumor Sagittal T1 images in a patient with a germinoma show: Infiltrative sellar/suprasellar mass- isointense to gray matter Homogeneous enhancement Obstructive hydrocephalus Optic pathway/hypothalamic Glioma Low grade neoplasms (WHO Grade 1) Occur between 5-15 years of age May be sporadic or associated with NF-1 Bilateral OPGs pathognomonic of NF-1 Intraorbital OPGs cause enlargement, elongation & buckling of optic nerve Non-NF-1 cases tend to involve optic chiasm & hypothalamus Typically larger and more mass-like than intraorbital OPGs OPGs are T2 hyperintense with variable enhancement
7 Optic pathway/hypothalamic Glioma MR images shows: FLAIR hyperintense suprasellar mass Heterogeneous enhancement along optic chiasm & hypothalamus Hypothalamic Hamartoma Hypothalamic hamartomas are rare, benign lesions Children present with gelastic seizures and/or precocious puberty On MRI, hamartomas are: Isointense to gray matter on T1 Iso- to hyperintense on T2 Hamartomas do not enhance If enhancement is seen, lesion likely a glioma Hypothalamic Hamartoma MRI in a 3-yr-old boy with precocious puberty shows: T2 hyperintense mass centered within hypothalamus Isointense to gray matter on T1 with no enhancement Rathke Cleft Cyst Rathke cleft cysts are non-neoplastic lesions Typically intrasellar lesions Many will have suprasellar extension ~10-15% have curvilinear wall calcifications on CT Lesions with high mucin content are T1 hyperintense Non-enhancing intracystic nodule may be seen Nodule often T2 hypointense Rathke Cleft Cyst Differential Diagnosis Review MR images show an intrasellar cystic lesion: T2 hyperintense cyst with a small hypointense nodule No enhancement on T1 post-contrast image - Craniopharyngioma - Germ cell tumor (GCT) - Optic pathway/hypothalamic glioma Additional Diagnostic Considerations: - Hypothalamic hamartoma - Rathke cleft cyst
8 Case # Pineal cyst - Germ cell tumor (GCT) - Pineal cell tumor Additional Diagnostic Considerations: - Tectal plate glioma Diagnosis: Germinoma Pineal Cyst Pineal cysts are common & often incidental Cysts typically less than 15 mm in size Large cysts may rarely be symptomatic Simple cysts follow fluid signal & lack enhancement Internal cerebral veins typically displaced laterally Presence of the following should question diagnosis of a cyst and prompt follow-up: Calcification Nodularity Enhancement Pineal Cyst Sagittal T1 & FLAIR MR images show: Sub-centimeter cyst in pineal gland No nodularity, calcification, or enhancement seen Germ Cell Tumor Germinomas are most common pineal gland neoplasms Typically occur in adolescents & young adult men Symptoms related to obstructive hydrocephalus or Parinaud syndrome (paralysis of upward gaze) Hyperdense on CT due to high cellularity May contain calcifications centrally (engulfs pineal calcifications) Intermediate to isointense on T1/T2 MR Lesions avidly enhance Evaluate entire CNS for dissemination
9 Germ Cell Tumor Adolescent boy with disseminated germinoma Sagittal T1 post-contrast image shows: Avidly enhancing pineal region mass Compression of the underlying tectal plate and cerebral aqueduct CNS dissemination with callosal & suprasellar mass Adolescent with a pineal germinoma Axial CT image reveals: Hyperdense pineal mass Central calcifications Germ Cell Tumor Pineal Cell Tumor Pineoblastomas more malignant & occur children Peak incidence in 1 st decade Seeding of CSF is common Pineocytomas have peak incidence in 3 rd -4 th decades Generally less aggressive Both hyperdense on CT due to high cellularity Calcifications occur along periphery in exploded pattern Lesions ae intermediate on T1/T2 & avidly enhance Entire CNS must be imaged for drop metastases Pineal Cell Tumor 10-month-old boy with a pineoblastoma Sagittal CT reveals: Large lobulated mixed cystic and solid pineal mass Peripheral calcification Obstructive hydrocephalus Pineal Cell Tumor MRI shows: Intermediate T2 signal mass with hemorrhagic fluid-fluid level Avid enhancement of solid components Hydrocephalus with transependymal flow of CSF Tectal Plate Glioma Tectal plate gliomas are low-grade neoplasms May cause hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis When large, may simulate a pineal gland mass MR imaging shows: T2 hyperintensity Typically no enhancement Treatment geared towards CSF diversion
10 Tectal Plate Glioma MR images in a girl with tectal plate glioma show: Increased FLAIR signal & mass effect along tectal plate Tectal plate mass with no enhancement Hydrocephalus from aqueductal stenosis Differential Diagnosis Review - Pineal cyst - Germ cell tumor (GCT) - Pineal cell tumor Additional Diagnostic Considerations: - Tectal plate glioma Case # Medulloblastoma - Juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma (JPA) - Ependymoma Additional Diagnostic Consideration: - Brainstem glioma - Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (rare) Diagnosis: Ependymoma Medulloblastoma High grade PNET (WHO grade IV) Most common posterior fossa tumor in children Peak incidence in first decade Typically midline Arises from superior medullary velum (roof of 4 th ventricle) Hyperdense (90%) +/- DWI due to high cellular content Calcification in ~20% of cases T1 hypo- / T2W iso- to hyperintense Heterogeneous enhancement Drop metastases common (1/3 of cases) Image entire neuroaxis prior to surgical intervention
11 Medulloblastoma Medulloblastoma Young child with HA, N/V Axial CT reveals: Hyperdense midline posterior fossa mass Obstructive hydrocephalus O Brien WT. JAOCR 2013: 2(3): MRI in same child shows: T2 hyperintensity Heterogeneous but avid enhancement Restricted diffusion (dark on ADC [not shown]) O Brien WT. JAOCR 2013: 2(3): Medulloblastoma Post-contrast T1 MR images show: CSF metastases along surface of cerebellum, brainstem, & distal cord/conus Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma JPA is a low grade (WHO grade I) astrocytoma Second most common posterior fossa tumor in children Peak incidence 5-15 years of age May occur sporadically or with NF1 Arises from the cerebellar hemisphere (off-midline) Presents as a cystic mass with enhancing mural nodule Enhancement along cyst wall suggests tumor lining cyst O Brien WT. JAOCR 2013: 2(3): Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma Axial MR images reveal: Mixed cystic and solid T2 hyperintense mass Avid enhancement of solid nodule Enhancement along cyst wall Ependymoma Peak age of onset in first decade Slow growing midline tumor Arises from the floor of fourth ventricle Characteristically squeezes thru 4th ventricle foramina Calcification seen in ~50% of cases Cystic change & hemorrhage less common Heterogeneous on T1/hyperintense on T2 Heterogeneous enhancement typically seen O Brien WT. JAOCR 2013: 2(3):
12 Ependymoma MR images in a boy with an ependymoma show: Enhancing midline mass with extension thru foramen magnum Extension thru foramen of Luschka on left Brainstem Glioma Represents ~10-20% of pediatric brain tumors Commonly presents in 1 st & 2 nd decades Most often a diffuse, infiltrating pontine mass WHO grade II-III Imaging demonstrates: T1 hypo-/t2 hyperintense mass Variable enhancement Higher grade regions show restricted diffusion, increased enhancement, & increased perfusion Exophytic components engulf basilar or project into 4 th ventricle Prognosis is poor Brainstem Glioma MR images in a child with DIPG show: Diffuse infiltrating FLAIR hyperintense mass Exophytic components anteriorly (engulf basilar) and posteriorly Peripheral mass-like enhancement with central necrosis Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor Rare, aggressive embryonal tumor Composed of rhabdoid cells and PNET components Presents in first few years of life (key distinction) Majority located in posterior fossa Remainder supratentorial Imaging appearance identical to medulloblastoma: Hyperdense on CT Regions of restricted diffusion Subarachnoid seeding common at presentation Prognosis dismal (mean survival <6 months) Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor 2-yr-old girl with ATRT Axial CT shows: Hyperdense midline posterior fossa mass Vasogenic edema Obstructive hydrocephalus Differential Diagnosis Review - Medulloblastoma - Juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma (JPA) - Ependymoma Additional Diagnostic Consideration: - Brainstem glioma - Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (rare)
13 Case # Posterior fossa CSF collection - Mega cisterna magna - Arachnoid cyst - Dandy-Walker variant Diagnosis: Arachnoid cyst Posterior fossa CSF collection Mega Cisterna Magna Mega cistern magna is a common normal variant CSF-filled cisterna magna is prominent Posterior fossa otherwise normal in size & morphology Typically no mass effect on subjacent parenchyma May see mild mass effect due to altered CSF flow Vessels & dural reflections seen within cisterna magna Posterior fossa CSF collection Mega Cisterna Magna Posterior fossa CSF collection Arachnoid Cyst Developmental CSF-filled spaces (less often acquired) Majority supratentorial (middle cranial fossa) Common infratentorial locations incl CPA & cistern magna May cause hydrocephalus due to 4 th ventricle obstruction Follow CSF signal on all MR sequences Mass effect evident MR images show: Prominent posterior fossa CSF collection Dural reflections within CSF collection and not displaced
14 Posterior fossa CSF collection Arachnoid Cyst MR images demonstrate: Posterior fossa CSF collection Mass effect on cerebellum & 4 th ventricle Obstructive hydrocephalus Posterior fossa CSF collection Dandy-Walker Variant Developmental abnormality of vermis & 4th ventricle Malformation consists of: Enlarged posterior fossa Vermian agenesis or hypogenesis Posterior CSF collection communicating with dilated 4 th ventricle Malformation demonstrates torcular-lambdoid inversion Associated anomalies include: Corpus callosal agenesis/hypogenesis Neuronal migration abnormalities DW variant less severe Posterior fossa CSF collection Dandy-Walker Malformation Posterior fossa CSF collection Differential Diagnosis Review - Mega cisterna magna - Arachnoid cyst - Dandy-Walker variant MR images in patient with DWM reveal: Inferior vermian hypoplasia Posterior fossa CSF collection in communication with 4 th vent Enlarged posterior fossa with torcular-lambdoid inversion Case #
15 Massive supratentorial CSF collection - Hydrocephalus - Hydranencephaly - Alobar holoprosencephaly Diagnosis: Hydranencephaly Massive supratentorial CSF collection Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus may result from: Obstruction (aqueductal stenosis, mass) Overproduction (choroid plexus papilloma) Decreased resorption (bleed, infxn, villous immaturity) Results in macrocephaly in newborns (open sutures) Displaces & compresses parenchyma peripherally Look for thin mantle of cortex along inner table Falx typically present though may see pressure erosion Communicating hydrocephalus not as severe Massive supratentorial CSF collection Hydrocephalus MR images in 2-wk-old girl with macrocephaly show: Massive hydrocephalus with erosion of falx Peripheral displacement of brain parenchyma Aqueductal stenosis Massive supratentorial CSF collection Hydranencephaly Refers to parenchymal liquefactive necrosis in anterior vascular distribution Results from some form of intrauterine insult Parenchyma supplied by posterior circulation spared Key findings include: Presence of the falx Intact posterior fossa & deep structures Absence of supratentorial cortical mantle Neonates present with macrocrania & neurologic function limited to the brainstem Massive supratentorial CSF collection Hydranencephaly CT images in a 6-month-old boy reveal: Supratentorial CSF collection Intact deep/posterior structures with unfused thalami No cortical mantle Intact falx Massive supratentorial CSF collection Alobar Holoprosencephaly Holoprosencephaly is a spectrum of forebrain malformations Alobar is most severe form: Cerebral parenchyma flattened anteriorly & fused Thalami fused Large dorsal interhemispheric cyst (monoventricle) Anterior falx, corpus callosum, interhemispheric fissure, & Sylvian fissures absent Craniofacial abnormalities include hypotelorism, fused metopic suture, & cleft palate Semilobar & lobar variants are less severe forms
16 Massive supratentorial CSF collection Alobar Holoprosencephaly Massive supratentorial CSF collection Differential Diagnosis Review - Hydrocephalus - Hydranencephaly - Alobar holoprosencephaly MR images demonstrate: Interhemispheric cyst / monoventricle Fused parenchyma anteriorly Fused thalami Absent falx Summary It is important to be able to recognize & describe pertinent imaging findings in the pediatric brain Organized gamut-based differentials are helpful in working through unknown pediatric brain cases Knowledge of key imaging features for each entity within a gamut will aid in reaching a reasonable & useful list of differentials Top 3 Differentials in Neuroradiology: A Case Review. New York: Thieme, Top 3 Differentials in Radiology: A Case Review. New York: Thieme, References Suggested Readings The End! Banwell B, Shroff M, Ness JM, et al. MRI features of pediatric multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2007; 68 (supp 2): S Barkovich AJ, Kjos BO, Norman D, etal. Revised classification of posterior fossa cysts and cyst-like malformations based on the results of multiplanar MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgen 1989; 153: Cheon JE, Kim IO, Hwang YS, et al. Leukodystrophy in children: a pictorial review of MR imaging features. RadioGraphics 2002; 22: Dublin AB, French BN. Diagnostic image evaluation of hydranencephaly and pictorially similar entities, with emphasis on computed tomography. Radiology 1980; 137: Hershey BL. Suprasellar masses: diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 1993; 14(3): Marin SE, Callen DJA. Imaging appearance of monophasic acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neuroimag Clin N Am 2013; 23: O Brien WT. Imaging of posterior fossa brain tumors in children. J Am Osteopath Coll Radiol 2013; 2(3): Oh KY, Kennedy AM, Frias AE, et al. Fetal schizencephaly: pre- and postnatal imaging with a review of the clinical manifestations. RadioGraphics 2005; 25: Poretti A, Meoded A, Huisman TAGM. Neuroimaging of pediatric posterior fossa tumors including review of the literature. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012; 35: Smith AB, Rushing EJ, Smirniotopoulos JG. Lesions of the pineal region: radiologic-pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 2010; 30: Ten Donkelaar HJ, Lammens M. Development of the human cerebellum and its disorders. Clin Perinatol 2009; 36(3):
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity
 Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Metastasis. 57 year old with progressive Headache and Right Sided Visual Loss
 Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
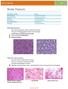 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS. Kim Learned, MD
 PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
Lesions of the Pineal Region: A Practical Approach
 Lesions of the Pineal Region: A Practical Approach Poster No.: C-0937 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Calles Blanco, J. A. Guzman de Villoria ; Madrid/ES, Madrid, Ma/ES Keywords:
Lesions of the Pineal Region: A Practical Approach Poster No.: C-0937 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Calles Blanco, J. A. Guzman de Villoria ; Madrid/ES, Madrid, Ma/ES Keywords:
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD
 Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region. Child thirsty, increased urination. Imaging. Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) No Disclosures
 Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions.
 Differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0215 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. G. Alandete, M. A. Meseguer, E. De la Via, D. Uceda, C. Poyatos; Valencia/ES
Differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0215 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. G. Alandete, M. A. Meseguer, E. De la Via, D. Uceda, C. Poyatos; Valencia/ES
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
Laurie A. Loevner, MD
 Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours. Colin Kennedy March 2015
 Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
S Alandete, M Meseguer, CR Poyatos, D Uceda, E de la Via, J Sales, J Vilar. H.U. Dr Peset, Valencia (Spain)
 S Alandete, M Meseguer, CR Poyatos, D Uceda, E de la Via, J Sales, J Vilar. H.U. Dr Peset, Valencia (Spain) Introduction Cystic lesions are usually a common finding in clinical practice and you can find
S Alandete, M Meseguer, CR Poyatos, D Uceda, E de la Via, J Sales, J Vilar. H.U. Dr Peset, Valencia (Spain) Introduction Cystic lesions are usually a common finding in clinical practice and you can find
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings
 Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings Robert J Sevick, MD, FRCPC, FACR Professor, Radiology and Clinical Neurosciences Cumming School of Medicine University of Calgary Learning objectives:
Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings Robert J Sevick, MD, FRCPC, FACR Professor, Radiology and Clinical Neurosciences Cumming School of Medicine University of Calgary Learning objectives:
Aria Fallah MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Aria Fallah MD, MSc, FRCSC Department of Neurosurgery David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pineal Region Tumors Brain Tumor Symposium August 22, 2015 Disclosures None Pineal Gland Arises from an invagination
Aria Fallah MD, MSc, FRCSC Department of Neurosurgery David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pineal Region Tumors Brain Tumor Symposium August 22, 2015 Disclosures None Pineal Gland Arises from an invagination
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
 EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics. Disclosures. Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor 4/14/2017
 Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN. Scalp, Skull. Anatomically Based Differentials. Skull Normal Variants. Scalp Mass, Child.
 Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Disclosures. Posterior Fossa Masses. I m from the Government. and I here to help! Differential Diagnosis
 Posterior Fossa Masses Differential Diagnosis James G. Smirniotopoulos, M.D. Radiology, Neurology, Biomedical Informatics Uniformed Services University Bethesda, Maryland http://rad.usuhs.edu http://medpix.usuhs.edu
Posterior Fossa Masses Differential Diagnosis James G. Smirniotopoulos, M.D. Radiology, Neurology, Biomedical Informatics Uniformed Services University Bethesda, Maryland http://rad.usuhs.edu http://medpix.usuhs.edu
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Financial Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose. Templar Eye Foundation Oppenheimer Family Foundation
 Financial Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose. Templar Eye Foundation Oppenheimer Family Foundation 2 Case 7 year old girl Initially parents noticed photophobia Then started to complain
Financial Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose. Templar Eye Foundation Oppenheimer Family Foundation 2 Case 7 year old girl Initially parents noticed photophobia Then started to complain
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Peter Canoll MD. PhD.
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI
 Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov Dandy-Walker Malformation
 REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
MRI OF THE THALAMUS. Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI
 1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
Tumors of the Central Nervous System
 Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Posterior fossa malformations
 ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses)
 Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Brain tumors: tumor types
 Brain tumors: tumor types Tumor types There are more than 120 types of brain tumors. Today, most medical institutions use the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system to identify brain tumors.
Brain tumors: tumor types Tumor types There are more than 120 types of brain tumors. Today, most medical institutions use the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system to identify brain tumors.
In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales
 28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management. Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP
 Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS BACKGROUND: Incidence: Third most common pediatric tumor type (leukemia, neuroblastoma,
Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS BACKGROUND: Incidence: Third most common pediatric tumor type (leukemia, neuroblastoma,
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated.
 Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated. Poster No.: C-1092 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Ospina Moreno, I. Montejo
Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated. Poster No.: C-1092 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Ospina Moreno, I. Montejo
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of White Matter Disease
 The Neuroradiology Journal 22 (Suppl. 1): 26-32, 2009 www. centauro. it Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of White Matter Disease J.G. SMIRNIOTOPOULOS 1,2,3,.. SMITH 1,2, E. RUSHING 2,4, F.M. MURPHY 2,
The Neuroradiology Journal 22 (Suppl. 1): 26-32, 2009 www. centauro. it Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of White Matter Disease J.G. SMIRNIOTOPOULOS 1,2,3,.. SMITH 1,2, E. RUSHING 2,4, F.M. MURPHY 2,
Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância. Silvia Tenembaum
 Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância Silvia Tenembaum Acquired CNS inflammatory/demyelinating disorders: Background information More frequent in children than
Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância Silvia Tenembaum Acquired CNS inflammatory/demyelinating disorders: Background information More frequent in children than
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
EEG IN FOCAL ENCEPHALOPATHIES: CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE, NEOPLASMS, AND INFECTIONS
 246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brainstem diffuse gliomas: radiologic findings.
 Brainstem diffuse gliomas: radiologic findings. Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. GARCIA MARTINEZ 1, D. H. Jiménez 1, L. Navarro Vilar 2, C. P. Fernandez Ruiz
Brainstem diffuse gliomas: radiologic findings. Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. GARCIA MARTINEZ 1, D. H. Jiménez 1, L. Navarro Vilar 2, C. P. Fernandez Ruiz
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Central nervous system
 Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Part II - Revising the sellar and parasellar region: differential diagnosis of a sellar region mass
 Part II - Revising the sellar and parasellar region: differential diagnosis of a sellar region mass Poster No.: C-1390 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Candelaria, C. Figueira,
Part II - Revising the sellar and parasellar region: differential diagnosis of a sellar region mass Poster No.: C-1390 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Candelaria, C. Figueira,
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
DISCLOSURES LEARNING OBJECTIVES WE WILL NOT DISCUSS. CSB: Birdseye View MESSAGE NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE
 NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE Christopher P. Hess, M.D., Ph.D. DISCLOSURES Research Support, General Electric SLIDES: http://www.radiology.ucsf.edu/research/meetings/rsna LEARNING OBJECTIVES
NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE Christopher P. Hess, M.D., Ph.D. DISCLOSURES Research Support, General Electric SLIDES: http://www.radiology.ucsf.edu/research/meetings/rsna LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Craniopharyngioma. Michael Gottschalk, MD,PhD University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital
 Craniopharyngioma Michael Gottschalk, MD,PhD University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital Objectives Incidence Clinical Presentation Treatment Options Perioperative concerns Long-term endocrine
Craniopharyngioma Michael Gottschalk, MD,PhD University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital Objectives Incidence Clinical Presentation Treatment Options Perioperative concerns Long-term endocrine
Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
MR Evaluation of Hydrocephalus
 591 MR Evaluation of Hydrocephalus Taher EI Gammal 1 Marshall B. Allen, Jr. 2 Betty Sue Brooks 1 Edward K. Mark2 An analysis of sagittal T1-weighted MR studies was performed in 23 patients with hydrocephalus,
591 MR Evaluation of Hydrocephalus Taher EI Gammal 1 Marshall B. Allen, Jr. 2 Betty Sue Brooks 1 Edward K. Mark2 An analysis of sagittal T1-weighted MR studies was performed in 23 patients with hydrocephalus,
NEUROIMAGING. July 2013, Vol. 2, Issue 3. Official Journal of the American Osteopathic College of Radiology. Editor: William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O.
 ISSN: 2165-3259 JAOCR Official Journal of the American Osteopathic College of Radiology NEUROIMAGING Editor: William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O. July 2013, Vol. 2, Issue 3 JAOCR About the Journal Aims and Scope
ISSN: 2165-3259 JAOCR Official Journal of the American Osteopathic College of Radiology NEUROIMAGING Editor: William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O. July 2013, Vol. 2, Issue 3 JAOCR About the Journal Aims and Scope
Imaging The Turkish Saddle. Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
