Long-term consumption of Carnosine contributes to improving effector functions of NK cells
|
|
|
- Brett Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: Long-term consumption of arnosine contributes to improving effector functions of NK cells bstract Guangao Liu ollege of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou51632, hina. arnosine can promote energy metabolism of cells as a kind of extremely natural antioxidant dipeptide, it has a very important role in maintaining body homeostasis. t present, the study of arnosine in the immune system is still at a blank stage. Our study mainly explored the effect started to drinking arnosine-containing water at the early age,we observed an increase in the ability of NK cells to degranulate and secrete IFN-γ in adult mice. Moreover, it helps NK cells to conjugate with tumor cells for better killing function. These results further clarify the importance of arnosine in the development and function of NK cells, providing theoretical and experimental basis for the basic research and clinical application of NK cell development and function. Keywords arnosine; Natural killer cells(nk cells); Function;ytokine; ytotoxicity. 1. Introduction arnosine is a natural dipeptide with strong antioxidant activity. It consists of β-alanine and L- histidine and is a natural antioxidant that is widely distributed in various tissues and organs of the human body[1]. Recent studies have found that arnosine has a variety of biological functions, including antioxidants, anti-aging, anti-glycosylation, etc[2]. arnosine has good water-solubility and easy absorption characteristics. aily doses of arnosine have a very important role in prolonging the lifespan of mice[3]. There were also reported in the related literature that arnosine helps to inhibit the proliferation of cells induced by G and relieve diabetes. t the same time, arnosine also played an important role in anti-cancer[4, 5]. However, the effect of arnosine on the immune system is rarely reported. s an important part of the innate immune system, NK cells can effectively help fight the infection of viruses and tumor cells and have an indispensable role in maintaining the steady state of the body[6]. We fed mice with arnosine-containing drinking water from childhood until the mice matured to analyze NK cells in immune tissues. The results showed that long-term consumption of arnosine helps NK cells become younger and the killing ability of NK cells is further enhanced, which effectively prevents the infection of viruses and tumor cells. 2. Long-term consumption of arnosine can not affect the NK cells differentiation and development To investigate the effect of arnosine on the occurrence and development of NK cells in mice, we started feeding mice with drinking water containing 2g/L of arnosine, after 1 weeks, we analyzed NK cells in the spleen and bone marrow to study whether arnosine affects the proportion and absolute number of NK cells in spleen and bone marrow. Experimental data showed that the effect of arnosine was not significant during the differentiation of NK cells and there was no significant difference in the number of NK cells between the experimental and control groups (Fig. 1., ). Next, we analyzed whether the long-term consumption of arnosine affects the development of NK cells. The experimental results showed that the development of NK cells in the arnosine-treated 252
2 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: experimental group had changed, the b + double positive cells showed an upward trend, which further demonstrating that arnosine can make NK cells younger (Fig. 1., ). M NK (1 5 ) 8 4 NS M NK (1 3 ) 7 5 NS M Percentage (%) 5 N 2 7 S P P=.632 P 1 1 b S P Percentage (%) 5 N 2 7 S P P=.767 P 1 1 b S P M 11b Figure 1. Long-term consumption of arnosine can not affect the NK cell differentiation and development (). Representative flow cytometric profiles of NK cells (3 + ) in the spleens, bone marrow (M) of and experimental groups. () The absolute number of NK cells in the indicated tissues and organs from the and experimental groups. Each symbol represents an individual mouse. Small horizontal lines indicate the average. () 27 vs 11b expression on 3 + NK cells were detected by flow cytometry. The numbers indicate the percentages of cells in each quadrant. () Percentages of four-stage development: N (27 11b ), 27 SP ( b ), P ( b + ), and 11b SP (27 11b + ), in gated 3 + NK cells in the spleen and M of and experimental groups. 3. arnosine can increase the ability of NK cells to secrete cytokines Previous results showed that the treatment of arnosine can increase the population of b + double positive cells in NK cells. Indirectly, arnosine may affect the function of NK cells, such as the secretion of cytokines. NK cells secrete IFN-γ in response to two types of stimuli: target cell ligands or specific antibodies engaging activating receptors, and cytokines, including IL- 12 and IL-18 secreted by and macrophages. First, we stimulated NK cells with hematopoietic RM-S and Y-1 cell lines in vitro. onjugation of NK cells with tumor cells induced IFN-γ production. The results showed that the ability of NK cells to secrete IFN-γ can be effectively increased after treatment with arnosine(fig. 2., ). NK cells possess multiple activating receptors, including, Ly49 and NKp46. To test whether metabolic signaling is required for their effector function, NK cells were stimulated using plate-coated antibodies against ITM-containing receptors, or Ly49. onsistent with the data obtained from tumor cell stimulation, it was demonstrated that arnosine also enhances the ability of specific antibody stimuli to secrete IFN-γ of NK cells (Fig. 2., ). In conclusion, long-term consumption of drinking water containing arnosine helps NK cells secrete IFN-γ, thereby enhancing their immunity. 253
3 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: Medium RMS Yac-1 P+I IFN-γ %IFN-Y + NK cells 1 5 R M -S Y G2 anti- anti-ly49 IL12/18 IFN-γ %IFN-Y + NK cells Figure 2. arnosine helps NK cells secrete cytokines (). Splenic lymphocytes were prepared from poly I:-treated mice from control and experimental groups were pretreated with the indicated inhibitor and then co-cultured with an equal number of tumor cell lines, RM-S and Y-1, for 4 hours in the presence of a Golgi blocker; MSO alone served as a negative control. Intracellular staining was performed to assess the production of IFN-γ. The numbers are percentages of the IFN-γ positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells. (). The percentage of the IFN-γ positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells under tumor cell stimulation. (). Splenic lymphocytes that were pretreated with the indicated inhibitor were stimulated with plate-coated antibodies for 4 hours in the presence of a Golgi block. Intracellular staining was used for the detection of IFN-γ production. The numbers are percentages of the IFN-γ positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells. (). The percentage of the IFN-γ positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells under antibodies stimulation. 4. arnosine contributes to enhance the ability of NK cell degranulation NK cells contain high concentrations of cytotoxic granules in their cytoplasm as they circulate in the periphery. s degranulation occurs, secretory lysosomes are released, and the lysosome-associated membrane protein-1 (LMP-1, 17a) is transported to the surface of NK cell. Therefore, the upregulated expression of 17a on the surface of NK cells correlates with the lysis of target cell mediated by NK cell. We thus quantified the degranulation pathway by measuring 17a expression in NK cells following multi-stimulations[7]. 17a expression was analyzed by flow cytometry after incubation of NK cells using P-anti-17a. We found enhanced degranulation as demonstrated by the reduced 17a expression after NK cells stimulated with tumor cell lines RM-s and Y-1(Figure3.,). We also analyzed 17a expression when NK cells were stimulated by cross-linking their activating receptors, consistent with the data obtained from tumor cell stimulation(figure3.,). It is further illustrated that arnosine can affect the degranulation ability of NK cells and enhance the effector function of NK cells. 254
4 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: Medium RMS Yac-1 P+I 17a %17a + NK cells 8 4 R M -S Y G2 anti- anti-ly49 17a %17a + NK cells 8 4 R M -S Y -1 Figure 3. arnosine contributes to effect cell degradation of NK cells. (). The mice from control and experimental groups were pre-activated for 16 hours following poly I: stimulation in vivo. Splenic lymphocytes were prepared and co-cultured with an equal number of tumor cell lines, RM-s and Y-1, for 4 hours; medium alone served as a negative control, and PM plus ionomycin served as a positive control. The expression of 17a was analyzed. The numbers are percentages of the 17a positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells. (). The percentage of the 17a positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells was compared between the mice control and experimental groups under tumor cell stimulation. (). Poly I:-activated splenic lymphocytes were seeded on 24-well plates coated with the indicated antibodies or stimulated with cytokines for 4 hours. The expression of 17a was analyzed. The numbers are percentages of the 17a positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells. (). The percentage of the 17a positive cells among the gated 3 NKp46 + cells was compared between WT and PK1 deficient mice under antibodies stimulation. ata represent the mean ± s.d of 3-4 mice and are representative of three independent experiments. *p <.1. min 5 min 1 min RM-S onjugates(%) 3 * m in 5 m in 1 m in * Figure 5. arnosine contributes to regulate NK cells conjugate formation (). NK cell conjugate formation. NK cells from control and experimental mice were purified by MS and expanded for 5 days in the presence of 1 IU IL-2. Equal numbers of -P antibody-stained NK cells and GFP-expressing RM-S cells were mixed and stimulated at 37 for the indicated times. onjugate formation was monitored by FS. ouble-positive GFP + P + 255
5 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: conjugate cells are presented as the percent of NK cells. The numbers are percentages of double positive cells among the gated cells. (). The percentage of the double positive cells was compared between control and experimental mice in the indicated time. 5. arnosine contributes to regulate NK cells conjugate formation NK cell killing function highly relies on integrin-mediated signaling, which helps NK cells to form stable synaptic interfaces with target cells[8]. To determine whether arnosine-treated NK cells could stably contact tumor target cells, NK cell conjugation with target cells was tested. ompared with the control, arnosine-treated NK cells formed fewer conjugates with RM-S cells at the 5 and 1 min time points (Figure 4., ). These results indicated that arnosine-treated NK cells fail to form stable conjugates with targets tumor cells. 6. onclusion The results of this study strongly demonstrate that arnosine helps to increase the function of NK cells in the body's innate immune system. The long-term consumption of arnosine observed that arnosine can promote the NK cells younger, we further confirmed that arnosine can increase NK cell cytokine secretion and degranulation ability in the case of tumor stimulation and specific antibody stimulation. Finally, we further established that arnosine can help NK cells bind to tumor cells, thereby exerting more effective effector functions. This study clarified the regulation of arnosine on the development and function of NK cells. It can provide the theoretical guidance for practical treatment of clinical disease treatment and has a certain social value. References [1] Pegova,., H. be, and. oldyrev, Hydrolysis of carnosine and related compounds by mammalian carnosinases. omp iochem Physiol iochem Mol iol, (4): p [2] Purchas, R.W. and J.R. usboom, The effect of production system and age on levels of iron, taurine, carnosine, coenzyme Q(1), and creatine in beef muscles and liver. Meat Sci, 25. 7(4): p [3] Gallant, S., M. Semyonova, and M. Yuneva, arnosine as a potential anti-senescence drug. iochemistry-moscow, 2. 65(7): p [4] Horii, Y., et al., Effects of L-carnosine on splenic sympathetic nerve activity and tumor proliferation. Neuroscience Letters, (1): p [5] Rybakova, Y.S. and.. oldyrev, Effect of carnosine and related compounds on proliferation of cultured rat pheochromocytoma P-12 cells. ull Exp iol Med, (1): p [6] Goh, W. and N.. Huntington, Regulation of Murine Natural Killer ell evelopment. Front Immunol, : p. 13. [7] Liu, J.X., J.W. Wang, and X.Y. ui, [The significance of peripheral blood natural killer cell surface 17a, NKG2 and serum smi in patients with extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi, (11): p [8] Orange, J.S., Formation and function of the lytic NK-cell immunological synapse. Nat Rev Immunol, 28. 8(9): p
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK
 08 April, 2018 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 90.41 KB 0 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Natural killer T cells (NK T cells) are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell. Natural killer
08 April, 2018 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 90.41 KB 0 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Natural killer T cells (NK T cells) are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell. Natural killer
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies
 NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NK cell flow cytometric assay In vivo DC viability and migration assay
 NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, and Applications to Human Disease Dr. Michael A. Caligiuri
 Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
 Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
C. Incorrect! MHC class I molecules are not involved in the process of bridging in ADCC.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
Acid sphingomyelinase is a critical regulator of cytotoxic granule secretion by
 Supplementary Data Acid sphingomyelinase is a critical regulator of cytotoxic granule secretion by primary T lymphocytes Jasmin Herz, Julian Pardo, Hamid Kashkar, Michael Schramm, Elza Kuzmenkina, Erik
Supplementary Data Acid sphingomyelinase is a critical regulator of cytotoxic granule secretion by primary T lymphocytes Jasmin Herz, Julian Pardo, Hamid Kashkar, Michael Schramm, Elza Kuzmenkina, Erik
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
effect on the upregulation of these cell surface markers. The mean peak fluorescence intensity
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS
 SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS Mice MT/ret RetCD3ε KO α-cd25 treated MT/ret Age 1 month 3 mnths 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 2/87 Survival 87/87 incidence of 17/87 1 ary tumor
SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS Mice MT/ret RetCD3ε KO α-cd25 treated MT/ret Age 1 month 3 mnths 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 2/87 Survival 87/87 incidence of 17/87 1 ary tumor
Supplemental Methods. CD107a assay
 Supplemental Methods CD107a assay For each T cell culture that was tested, two tubes were prepared. One tube contained BCMA-K562 cells, and the other tube contained NGFR-K562 cells. Both tubes contained
Supplemental Methods CD107a assay For each T cell culture that was tested, two tubes were prepared. One tube contained BCMA-K562 cells, and the other tube contained NGFR-K562 cells. Both tubes contained
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplemental Materials
 Supplemental Materials Programmed death one homolog maintains the pool size of regulatory T cells by promoting their differentiation and stability Qi Wang 1, Jianwei He 1, Dallas B. Flies 2, Liqun Luo
Supplemental Materials Programmed death one homolog maintains the pool size of regulatory T cells by promoting their differentiation and stability Qi Wang 1, Jianwei He 1, Dallas B. Flies 2, Liqun Luo
Rapamycin reduced inhibition of V 1 T cells towards V 4 T cells through down-regulating IL-4
 Rapamycin reduced inhibition of V 1 T cells towards V 4 T cells through down-regulating IL-4 Wanjun Huang Biomedical Translational Research Institute, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China. Abstract
Rapamycin reduced inhibition of V 1 T cells towards V 4 T cells through down-regulating IL-4 Wanjun Huang Biomedical Translational Research Institute, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China. Abstract
Supplemental Materials for. Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to. FTY720 during neuroinflammation
 Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
T cell-mediated immunity
 T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
Immune Surveillance. Immune Surveillance. Immune Surveillance. Neutrophil granulocytes Macrophages. M-cells
 he immune system is everywhere Some organs have developed strategies towards the immune system to keep it out or to put it under control Immune privileged organs: Brain Eye estis hyroid gland Humoral immunity
he immune system is everywhere Some organs have developed strategies towards the immune system to keep it out or to put it under control Immune privileged organs: Brain Eye estis hyroid gland Humoral immunity
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune
 Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
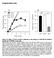 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Chapters 20 & 21
 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Shime et al. 1.173/pnas.11139919 SI Methods Reagents. was purchased from GE Healthcare, which was free from LPS contamination. TNF-α and IFN-β ELISA kit was purchased from eioscience
Supporting Information Shime et al. 1.173/pnas.11139919 SI Methods Reagents. was purchased from GE Healthcare, which was free from LPS contamination. TNF-α and IFN-β ELISA kit was purchased from eioscience
A Slfn2 mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence
 Supplementary Information A Slfn mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence Michael Berger, Philippe Kres, Karine Crozat, Xiaohong Li, Ben A. Croker, Owen
Supplementary Information A Slfn mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence Michael Berger, Philippe Kres, Karine Crozat, Xiaohong Li, Ben A. Croker, Owen
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Supplemental Information. CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + Regulatory T Cells Promote. Th17 Cells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance
 Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway
 Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway Yuan Zhang 1,2, Xing Li 1,2, Bogoljub Ciric 1, Cun-gen Ma 3, Bruno Gran 4, Abdolmohamad
Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway Yuan Zhang 1,2, Xing Li 1,2, Bogoljub Ciric 1, Cun-gen Ma 3, Bruno Gran 4, Abdolmohamad
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
windows of my lab Prof. Allan Wiik, emeritus director Department of Autoimmunology Statens Serum Institute, Copenhagen
 The normal immune system windows of my lab, Prof. Allan Wiik, emeritus director Department of Autoimmunology Statens Serum Institute, Copenhagen The immune defence Theinnateimmune system Cells: Eater cells
The normal immune system windows of my lab, Prof. Allan Wiik, emeritus director Department of Autoimmunology Statens Serum Institute, Copenhagen The immune defence Theinnateimmune system Cells: Eater cells
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Title: NATURAL KILLER CELL FUNCTIONS AND SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 14 Title: NATURAL KILLER CELL FUNCTIONS AND SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the general morphology of the NK-cells. Enumerate the different functions
LECTURE: 14 Title: NATURAL KILLER CELL FUNCTIONS AND SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the general morphology of the NK-cells. Enumerate the different functions
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Acquired Immunity Cells are initially and require before they can work Responds to individual microbes
 1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response
 chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
Acupuncture Immune System Discovery
 Acupuncture Immune System Discovery Published by HealthCMi on November 2017 Researchers conclude that acupuncture benefits the immune system. In a controlled laboratory experiment, Hubei University of
Acupuncture Immune System Discovery Published by HealthCMi on November 2017 Researchers conclude that acupuncture benefits the immune system. In a controlled laboratory experiment, Hubei University of
Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel
 Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection. Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science
 Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Figure S1. Gating strategy used in NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes coculture An example of flow cytometry analysis shows the gating of NK cells and γδ
 Figure S1. Gating strategy used in NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes coculture An example of flow cytometry analysis shows the gating of NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes used in all NK activation and cytotoxicity
Figure S1. Gating strategy used in NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes coculture An example of flow cytometry analysis shows the gating of NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes used in all NK activation and cytotoxicity
Cell Mediated Immunity CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY. Basic Elements of Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
 Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Cytotoxicity assays. Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1. Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
 Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
The encephalitogenicity of TH17 cells is dependent on IL-1- and IL-23- induced production of the cytokine GM-CSF
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat.Immunol. 12, 568 575 (2011) The encephalitogenicity of TH17 cells is dependent on IL-1- and IL-23- induced production of the cytokine GM-CSF Mohamed El-Behi, Bogoljub Ciric, Hong
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat.Immunol. 12, 568 575 (2011) The encephalitogenicity of TH17 cells is dependent on IL-1- and IL-23- induced production of the cytokine GM-CSF Mohamed El-Behi, Bogoljub Ciric, Hong
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Dissecting T cell activation and function at the single cell level
 Dissecting T cell activation and function at the single cell level Regulation and outcome of immune cell interactions in vivo Lymph node In vivo imaging of immune responses with two-photon microscopy
Dissecting T cell activation and function at the single cell level Regulation and outcome of immune cell interactions in vivo Lymph node In vivo imaging of immune responses with two-photon microscopy
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Increased IL-12 induced STAT-4 signaling in CD8 T cells. from aged mice
 Increased IL-2 induced STAT-4 signaling in CD8 T cells from aged mice Erin Rottinghaus * Abstract: Aging is associated with poor immune function leading to increased susceptibility to infectious diseases
Increased IL-2 induced STAT-4 signaling in CD8 T cells from aged mice Erin Rottinghaus * Abstract: Aging is associated with poor immune function leading to increased susceptibility to infectious diseases
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis
 Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
CD44
 MR1-5-OP-RU CD24 CD24 CD44 MAIT cells 2.78 11.2 WT RORγt- GFP reporter 1 5 1 4 1 3 2.28 1 5 1 4 1 3 4.8 1.6 8.1 1 5 1 4 1 3 1 5 1 4 1 3 3.7 3.21 8.5 61.7 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 TCRβ 2 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 CD44 1 2 GFP
MR1-5-OP-RU CD24 CD24 CD44 MAIT cells 2.78 11.2 WT RORγt- GFP reporter 1 5 1 4 1 3 2.28 1 5 1 4 1 3 4.8 1.6 8.1 1 5 1 4 1 3 1 5 1 4 1 3 3.7 3.21 8.5 61.7 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 TCRβ 2 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 CD44 1 2 GFP
Quantitative PPARγ expression affects the balance between tolerance and immunity
 Quantitative PPARγ expression affects the balance between tolerance and immunity Ya-Hui Liu 1, Yau-Sheng Tsai 1,2,3, Shih-Chieh Lin 4, Nan-Shih Liao 5, Ming-Shiou Jan 6, Chung-Tiang Liang 7, Shih-Wen Hsu
Quantitative PPARγ expression affects the balance between tolerance and immunity Ya-Hui Liu 1, Yau-Sheng Tsai 1,2,3, Shih-Chieh Lin 4, Nan-Shih Liao 5, Ming-Shiou Jan 6, Chung-Tiang Liang 7, Shih-Wen Hsu
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Direct TLR2 Signaling Is Critical for NK Cell Activation and Function in Response to Vaccinia Viral Infection
 Direct TLR2 Signaling Is Critical for NK Cell Activation and Function in Response to Vaccinia Viral Infection Jennifer Martinez 1, Xiaopei Huang 2, Yiping Yang 1,2 * 1 Department of Immunology, Duke University
Direct TLR2 Signaling Is Critical for NK Cell Activation and Function in Response to Vaccinia Viral Infection Jennifer Martinez 1, Xiaopei Huang 2, Yiping Yang 1,2 * 1 Department of Immunology, Duke University
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do? Monoclonal antibody approach
 How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
A second type of TCR TCR: An αβ heterodimer
 How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1293 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1293 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity
 Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity Dr. Julia Rempel Section of Hepatology 789-3825 jdrempel@cc.umanitoba.ca 804D JBRC Topics: I. Types of Cell-Mediated Immunity II. Migration of Effector T Lymphocytes
Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity Dr. Julia Rempel Section of Hepatology 789-3825 jdrempel@cc.umanitoba.ca 804D JBRC Topics: I. Types of Cell-Mediated Immunity II. Migration of Effector T Lymphocytes
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
PLAN. Réponses B thymodépendantes et thymoindépendantes. B cell development and classification. B cell activation. Thymodependent B(2) cell response
 Réponses B thymodépendantes et thymoindépendantes PLAN B cell development and classification B cell activation Thymodependent B(2) cell response BMC 423 (IF) - 2007 Antonino Nicoletti Thymo-independent
Réponses B thymodépendantes et thymoindépendantes PLAN B cell development and classification B cell activation Thymodependent B(2) cell response BMC 423 (IF) - 2007 Antonino Nicoletti Thymo-independent
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells
 Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
Supplementary Figure 1. ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons
 Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
