Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest)
|
|
|
- Godwin Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest) Carsten Herskind Dept. of Radiation Oncology. Universitätsmedizin Mannheim Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg University Workshop Biological basis of RT, Stockholm
2 Outline Split-dose recovery and radiosensitivity in cell cycle Cell-cycle checkpoints: G1/S, intra-s, G2/M Efficiency and resolution of checkpoint arrest Potential for manipulation; Influence of fraction size (novel fractionation schemes)
3 Radiosensitivity changes with time interval between split-dose fractions CHO cells 18h interval SLD repair Reassortment: partly synchronous progression of cell-cycle Elkind & Sutton, Nature 4695 (1959) Complete recovery: curve shape repeated. asynchr. cohort?
4 Synchronized cells: radioresistant in late S radiosensitive in G2/M and early S SF HeLa Sinclair & Morton, Radiat Res 29 (1966) Sinclair, Radiat Res 33 (1968) in Denekamp, Int J Radiat Biol 49 (1986) Time after synchronization (h)
5 Steep increase of radioresistance through M to G1 Fucci staining: G1: red S-G2-M: green Enrichment of Fr.1 after mitotic shake-off G1 l-m e-m late M early M Fr.1: M G1 fraction G1 l-m e-m Nakayama et al, Radiat Res 176 (2011)
6 Aims of the DNA damage response (DDR) Immediate : survive next cell division block replication of damaged DNA preserve integrity of DNA; repair damage prevent cell division with broken chromosomes Longer-term: maintain genomic stability
7 Regulation of cell-cycle progression Cyclins (CCN) and cyclindependent kinases (Cdk) Hall, Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist. 7th ed. (2012)
8 Textbook view of cell-cycle checkpoints DSB ATM Hall, Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist. 7th ed. (2012) G1/S S S G2/M Cdk2 G1/S: p53 p21 S: Chk2 Cdc25A MRN SMC G2/M: Chk1 Cdc25C
9 Role of ATR in S-phase slow-down DSB ATM Single-stranded DNA Stalled replication forks ATR DSB MRN complex CHK2 CHK1 SMC? CDC25A Degradation Wee1 CDK2 CCNA Degradation Falck et al., Nature 410 (2001), Nat Genet 30 (2002) Replication Initiation S-phase
10 Cell-cycle analysis: block G2 M G1 Cell-cycle distribution (DNA content) arrest progression in all phases: no change block and progression: accumulation (slow) S G2-marker CENP M-Marker HistH3 Inhibitor of mitosis G2 M G1 BrdU-pos in G2 G2 M G1 S BrdUlabeling of S S BrdU-neg in S
11 G2/M: two distinct checkpoints early Lymphoblastoid cell lines Dose: 6 Gy late Xu et al., Mol Cell Biol 22 (2002)
12 G2/M checkpoint characteristics Early G2/M checkpoint: Blocks entry into M (~1h) of cells irradiated in G2 - is observed early after irrad. when cells stop entering M Late G2/M checkpoint: Accumulation in G2 (12-24h) of cells irradiated in S (6 Gy) - is observed late after irrad. when cells progress to G2 ATM dependent Dose independent (>0.4 Gy) ATM independent Duration is dose dependent Xu et al., Mol Cell Biol 22 (2002)
13 G2/M checkpoint pathways Late (after irrad.) Early (after irrad.) Single-stranded DNA Stalled replication forks Resected DSB DSB ATR ATM CHK1 Plk1 CHK2 Plk1 CDC25A CDC25A/C CDK1 CCNB CDK1 CCNB Centrosome maturation S progression into G2-phase mitosis
14 A third G2/M checkpoint mechanism Early arrest: ATM late arrest: CHK RehTP53+ U698 TP53- ATM inhibitor: KU CHK1 inhibitor: caffeine Intermediate arrest (2-10h after 4 Gy) depends on p53 (TP53) (Reh) (Reh shrna p53-knockdown) 4Gy Caffeine + KU Gy Caffeine 0Gy control 4Gy 4Gy KU Landsverk et al., Cell Cycle 10 (2011)
15 G2/M checkpoint pathways Late (after irrad.) ssdna Intermediate Qi, Martinez, Rad Res 160 (2003) Early (after irrad.) DSB ATR p53 ATM CHK1 Gadd45 CHK2 Sequestration out of nucleus CDC25A Degradation CDC25A/C CDK1 CCNB CDK1 CCNB S progression into G2-phase
16 Low-dose hyper-radiosensitivity (HRS): Induced radioresistance (IRR) is associated with induction of early G2 checkpoint Very early G2 arrest 0.5h after 0.2 Gy (i.e. <0.4Gy): Marples et al., Radiat Res 161 (2004) Martin et al., Cancer Lett 349 (2014) absent in HRS pos T98G present in HRS neg U373 T98G (HRS pos ) U373 (HRS neg ) Very early, low-dose G2 arrest is independent of ATM (not shown) Fernet et al., DNA Repair 9 (2010)
17 G2/M checkpoint adaptation? Late mitotic entry with unrepaired DSB Mitotic cells with foci U2OS cells Syljuåsen et al., Cancer Res 66 (2006)
18 Renewed expression of Plk1 can mediate mitotic entry Syljuåsen et al., Cancer Res 66 (2006) Syljuåsen, Oncogene 26 (2007)
19 Threshold model: DSB appears to be required: insensitive G2 checkpoint induction and release? Lines: mitotic cells Bars: γh2ax foci per cell Time of release depends on number of residual DSB Deckbar et al. J Cell Biol 176 (2007)
20 Cell-cycle progression of BrdU-labelled cells after irradiation in S-phase Artemis and AT cells both have a DSB repair defect but only AT cells have a checkpoint defect. Similar kinetics of release from G2 DSB threshold Pulse-label, detect BrdU+ cells in G2 Foci per BrdU+ cells in G2 1Gy in S AT Artemis wt Krempler et al., Cell Cycle 6 (2007)
21 G2/M adaptation or threshold? Activation of the G2/M checkpoint by Gy Gy corresponds to less than DSB Number of mitotic cells relative to 0 Gy Foci per mitotic cell γh2ax foci in mitotic cells escaped from G2/M arrest at 75 min (<10-15 in 90%) Tkacz-Stachowska et al., Radiother Oncol 101 (2011)
22 G2 adaptation or threshold? Mitotic entry at 30h with <10-15 DSB 75% of cells contain <5-8 DSB (mean ~2 DSB/mitotic cell) A rigid threshold of DSB unlikely? But: counting γh2ax foci is critical Tkacz-Stachowska et al., Radiother Oncol 101 (2011)
23 Summary: G2/M checkpoint arrest 3 (perhaps 4?) different checkpoints / pathways Very early (?): ATM indep. (0.2 Gy), absent in HRS pos cells Early: ATM dep., arrests cells irradiated in G2 ( 0.4 Gy) Intermediate: p53 dep., ATM indep. Late (dose-dep. accum. in G2): ATR/CHK1 dep.; ATM indep. Induction and release Insensitive (threshold of DSB) Release with unrepaired DSB Adaptation (premature release) or Threshold?
24 CHK1 network Scope for manipulation by inhibitors Dai & Grant, Clin Cancer Res 16 (2010)
25 G1 checkpoint and its limitations p53 stabilisation Transcriptional activation (p21) Phosphorylation of CHK2 Phosphorylation of CDC25A inactivation and degradation Arrest in late G1 Deckbar et al., Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 46 (2011) G1 phase
26 Fast G1 checkpoint arrest (1-4h) is sensitive but not immediately effective Microscopy: Cells found in S-phase after irrad. In G1 Fast arrest depends on ATM (no arrest in AT cells) and on CHK2 (sirna knockdown) but not on p53 Double-labelling technique : Entry of unlabelled fibroblasts irradiated in G1 into S-phase Deckbar et al., Cancer Res 70 (2010) Irrad. of synchronized G1 cells 8.5h after release from G 0 (1.5h before S)
27 Slow G1/S checkpoint arrest (~3-10h) Very sensitive (~1 DSB), dose-dependent ( 0.1 Gy) Slow arrest depends on ATM (no arrest in AT cells) and on p53 (sirna knockdown) but not on CHK2 Fibroblasts synchronized by release from density arrest. Irradiation 1.5h before S-entry Deckbar et al., Cancer Res 70 (2010)
28 Leaky late G1/S checkpoint after high doses (irradiation of synchronized cells in G1) Pct. G2-phase cells Cells progress to G2 with DSB after irradiation in G1 Deckbar et al., Cancer Res 70 (2010)
29 Summary of G1/S checkpoint arrest Fast G1/S arrest takes several hours to become fully effective sensitive depends on ATM-CHK2 but not on p53 Slow G1/S arrest requires transcriptional activation and translation very sensitive depends on ATM-p53 but not on CHK2 leaky after moderate-high doses
30 Synthetic lethality of ATM & p53 abrogation Doxorubicin-induced DSB in cancer cells arrest apoptosis HR NHEJ ATM+/+ p53 +/+ (baseline) + (+) + + ATM+/+ p53 --/-- resistant ATM suppr. p53 +/+ resistant ATM suppr. p53 --/-- sensitive - mitotic death - + ATM-CHK2 mediates cell-cycle arrest p53 mediates apoptosis (via ATM-CHK2 or ATR-CHK1) p53 mediates cell-cycle arrest (indep. of ATM-CHK2) Jiang et al., Genes Dev 23 (2009) Genetic background may be important (cf. AT cells)
31 Inhibition of ATM radiosensitizes glioblastoma cells U1242: p53 mut U87 p53 wt p53 mut U87: p53 wt P53 wt ATM inhib p53 mut ATM inhib Biddlestone-Thorpe et al.,clin Cancer Res 19 (2013)
32 ATM Inhibition radiosensitizes p53-mutant tumours Human U87 tumours (nude mice) Radiosensitization only of cells expressing p53 mut p53 mut p53 wt Biddlestone-Thorpe et al., Clin Cancer Res 19 (2013)
33 ATM network Shilo & Ziv, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14 (2013)
34 Summary of cell-cycle checkpoints >10-20 DSB? ATM-CHK2-CDC25 Early (1-2h) Dose-indep. ( 0.4 Gy) p53-gadd45-cdc25 Intermediate (2-10h) G2 M G1 ATM-CHK2-CDC25 Fast (1-4h) (>~1 Gy) ATM-p53-p21 Slow (3-10h) (>~0.1 Gy) Transient or permanent dep. on dose? ATR-CHK1-CDC25 S & late G2/M ( 10h) Dose-dep. duration S MRN-SMC 1 DSB?
35 CONCLUSIONS Different sensitivities, dose dependence, kinetics Heterogeneity of reassortment ATM: independent of dose at low-moderate doses (threshold) ATR, p53: dependent on dose more important at higher doses/fx Checkpoints are imperfect Delayed induction, premature release Escape with unrepaired DSB encounter next checkpoint Different pathways Potential for manipulation (modulates repair, mode of cell death) p53: also apoptosis & permanent G1 arrest (genomic stability; p21) 35
36 Acknowledgements Department of Radiation Oncology, UMM, Medical Faculty Mannheim Cellular and Molecular Radiation Oncology Lab Clinic Heidelberg University Miriam Bierbaum Juliane Bradl Linda Hartman, PhD Anne Kirchner Junqi Liu Xiaolei Liu Patrick Maier, PhD Marlon R. Veldwijk, PhD Frank A. Giordano, MD Frederik Wenz, MD (Director) 36
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition
 Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs. Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica
 Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Factors determining DNA double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase.
 Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology
 Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology Epithelial Ovarian Cancer - Standard Current Treatment: Surgery with De-bulking + Platinum-Taxane based Chemotherapy - No
Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology Epithelial Ovarian Cancer - Standard Current Treatment: Surgery with De-bulking + Platinum-Taxane based Chemotherapy - No
Modelling of Biological Processes
 Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Selective targeting of cancer cells through inhibition of Checkpoint kinase 1
 Selective targeting of cancer cells through inhibition of Checkpoint kinase 1 Grete Hasvold Department of Radiation Biology Institute for Cancer Research The Norwegian Radium Hospital Oslo University Hospital
Selective targeting of cancer cells through inhibition of Checkpoint kinase 1 Grete Hasvold Department of Radiation Biology Institute for Cancer Research The Norwegian Radium Hospital Oslo University Hospital
Cell cycle control (mammalian)
 Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS. Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK
 CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK E-Mail:-snsenapati2007@gmail.com IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY TUMOR CELL DEATH CELL DEATH AFTER IRRADIATION OCCURS MOSTLY
CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK E-Mail:-snsenapati2007@gmail.com IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY TUMOR CELL DEATH CELL DEATH AFTER IRRADIATION OCCURS MOSTLY
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I. Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017
 Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
CHARACTERIZATION OF CHECKPOINT ADAPTATION IN HUMAN FIBROBLASTIC GLIOMA CELLS AND AN ANALYSIS OF PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE INHIBITORS
 CHARACTERIZATION OF CHECKPOINT ADAPTATION IN HUMAN FIBROBLASTIC GLIOMA CELLS AND AN ANALYSIS OF PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE INHIBITORS Brittany Lanser Bachelor of Science Honours, University of Saskatchewan, 2010
CHARACTERIZATION OF CHECKPOINT ADAPTATION IN HUMAN FIBROBLASTIC GLIOMA CELLS AND AN ANALYSIS OF PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE INHIBITORS Brittany Lanser Bachelor of Science Honours, University of Saskatchewan, 2010
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication
 Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication Shilpa Singh, 1 Catherine A. Vaughan, 1 Rebecca A. Frum, 2 Steven R. Grossman, 2 Sumitra Deb, 1 and Swati Palit Deb
Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication Shilpa Singh, 1 Catherine A. Vaughan, 1 Rebecca A. Frum, 2 Steven R. Grossman, 2 Sumitra Deb, 1 and Swati Palit Deb
Targeting the ATR Kinase in Cancer Therapy
 Targeting the ATR Kinase in Cancer Therapy 2017 Chabner Colloquium October 30, 2017 Lee Zou MGH Cancer Center Harvard Medical School Disclosure Consultant/advisory role: Loxo Oncology DNA Damage and Replication
Targeting the ATR Kinase in Cancer Therapy 2017 Chabner Colloquium October 30, 2017 Lee Zou MGH Cancer Center Harvard Medical School Disclosure Consultant/advisory role: Loxo Oncology DNA Damage and Replication
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Computational Systems Biology Modeling of DNA-damage Stress Pathways for Assessing Mutation Rates at Low Doses
 Computational Systems Biology Modeling of DNA-damage Stress Pathways for Assessing Mutation Rates at Low Doses Rebecca Clewell Society of Toxicology March 25, 2015 Exposure & Consumer Use Assessment High-content
Computational Systems Biology Modeling of DNA-damage Stress Pathways for Assessing Mutation Rates at Low Doses Rebecca Clewell Society of Toxicology March 25, 2015 Exposure & Consumer Use Assessment High-content
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
CYCLINS ON THE MOVE: A TIME AND A PLACE FOR CYCLIN A2 AND CYCLIN B1 IN THE HUMAN CELL CYCLE
 From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CYCLINS ON THE MOVE: A TIME AND A PLACE FOR CYCLIN A2 AND CYCLIN B1 IN THE HUMAN CELL CYCLE Helena Silva Cascales
From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CYCLINS ON THE MOVE: A TIME AND A PLACE FOR CYCLIN A2 AND CYCLIN B1 IN THE HUMAN CELL CYCLE Helena Silva Cascales
Self-inflicted DNA double-strand breaks sustain tumorigenicity and stemness of cancer cells
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2017) 27:764-783. www.nature.com/cr Self-inflicted DNA double-strand breaks sustain tumorigenicity and stemness of cancer cells Xinjian Liu 1, Fang Li 1, Qian Huang 2, Zhengxiang
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2017) 27:764-783. www.nature.com/cr Self-inflicted DNA double-strand breaks sustain tumorigenicity and stemness of cancer cells Xinjian Liu 1, Fang Li 1, Qian Huang 2, Zhengxiang
Cancer Drug Discovery and Development. Philip J. Tofilon Kevin Camphausen Editors. Increasing the Therapeutic Ratio of Radiotherapy
 Cancer Drug Discovery and Development Philip J. Tofilon Kevin Camphausen Editors Increasing the Therapeutic Ratio of Radiotherapy Cancer Drug Discovery and Development Series Editor Beverly A. Teicher
Cancer Drug Discovery and Development Philip J. Tofilon Kevin Camphausen Editors Increasing the Therapeutic Ratio of Radiotherapy Cancer Drug Discovery and Development Series Editor Beverly A. Teicher
Radiation response in human cells
 Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1157 Radiation response in human cells DNA damage formation, repair and signaling ANN-SOFIE GUSTAFSSON ACTA UNIVERSITATIS
Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1157 Radiation response in human cells DNA damage formation, repair and signaling ANN-SOFIE GUSTAFSSON ACTA UNIVERSITATIS
The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
 O[superscript 6]-Methylguanine DNA lesions induce an intra-s-phase arrest from which cells exit into apoptosis governed by early and late multi-pathway signaling The MIT Faculty has made this article openly
O[superscript 6]-Methylguanine DNA lesions induce an intra-s-phase arrest from which cells exit into apoptosis governed by early and late multi-pathway signaling The MIT Faculty has made this article openly
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements
 Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements Kevin M. Prise Centre for Cancer Research & Cell Biology, Queen s University Belfast Outline Definition of bystander
Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements Kevin M. Prise Centre for Cancer Research & Cell Biology, Queen s University Belfast Outline Definition of bystander
Cell Cycle. Trends in Cell Biology
 Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Supplementary Figure 1
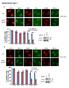 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Chapter 2. Aims & Objectives
 2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
Control of Cell Cycle. Unit 2 Part f III
 Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer.
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0494 TITLE: Tumor Suppression by BRCA-1: A Critical Role at DNA Replication Forks PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jean Gautier, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0494 TITLE: Tumor Suppression by BRCA-1: A Critical Role at DNA Replication Forks PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jean Gautier, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
Genomic instability. Amin Mahpour
 Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Biology of high single doses of IORT: RBE, 5 R s, and other biological aspects
 Herskind et al. Radiation Oncology (2017) 12:24 DOI 10.1186/s13014-016-0750-3 REVIEW Biology of high single doses of IORT: RBE, 5 R s, and other biological aspects Open Access Carsten Herskind 1*, Lin
Herskind et al. Radiation Oncology (2017) 12:24 DOI 10.1186/s13014-016-0750-3 REVIEW Biology of high single doses of IORT: RBE, 5 R s, and other biological aspects Open Access Carsten Herskind 1*, Lin
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity
 International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity Simon Bouffler December 2009 Indicators of radiosenitivity In Patients
International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity Simon Bouffler December 2009 Indicators of radiosenitivity In Patients
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy
 Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy Radiology and Physical Medicine María Trinidad Rueda Cáceres Radiotherapy Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy One of the standard treatment options for various malignant
Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy Radiology and Physical Medicine María Trinidad Rueda Cáceres Radiotherapy Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy One of the standard treatment options for various malignant
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer. Dan Fisher. Friday 27th October Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6.
 How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective
 DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective Kavanagh, J. N., Redmond, K. M., Schettino, G., & Prise, K. M. (2013). DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective. Antioxidants & Redox
DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective Kavanagh, J. N., Redmond, K. M., Schettino, G., & Prise, K. M. (2013). DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective. Antioxidants & Redox
Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage
 1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
Early cell death (FGF) B No RunX transcription factor produced Yes No differentiation
 Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
DNA repair and synthetic lethality
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2011 DNA repair and synthetic lethality Gong-she Guo Shandong University Feng-mei Zhang Shandong University Rui-jie
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2011 DNA repair and synthetic lethality Gong-she Guo Shandong University Feng-mei Zhang Shandong University Rui-jie
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
I TESSUTI: Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli Studi di Genova
 I TESSUTI: 1. Repair, Radiosensitivity, Recruitment, Repopulation, Reoxygenation 2. Acute and chronic hypoxia 3. Tissue microenvironment and tissue organization Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli
I TESSUTI: 1. Repair, Radiosensitivity, Recruitment, Repopulation, Reoxygenation 2. Acute and chronic hypoxia 3. Tissue microenvironment and tissue organization Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli
MK-8776, a novel chk1 kinase inhibitor, radiosensitizes p53- defective human tumor cells
 /, Vol. 7, No. 44 MK-8776, a novel chk1 kinase inhibitor, radiosensitizes p53- defective human tumor cells Kathleen A. Bridges 1, Xingxing Chen 1,4, Huifeng Liu 1, Crosby Rock 1, Thomas A. Buchholz 2,
/, Vol. 7, No. 44 MK-8776, a novel chk1 kinase inhibitor, radiosensitizes p53- defective human tumor cells Kathleen A. Bridges 1, Xingxing Chen 1,4, Huifeng Liu 1, Crosby Rock 1, Thomas A. Buchholz 2,
DNA double-strand break repair of parental chromatin in ooplasm and origin of de novo mutations. Peter de Boer
 DNA double-strand break repair of parental chromatin in ooplasm and origin of de novo mutations Peter de Boer Department of Obst.& Gynaecology, Div. Reproductive Medicine Radboud University Nijmegen Medical
DNA double-strand break repair of parental chromatin in ooplasm and origin of de novo mutations Peter de Boer Department of Obst.& Gynaecology, Div. Reproductive Medicine Radboud University Nijmegen Medical
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, et al. Inhibition of poly(adp-ribose)
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, et al. Inhibition of poly(adp-ribose)
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Breast Cancer Susceptibility and HLA Complex: Source of Missing Heritability?
 Breast Cancer Susceptibility and HLA Complex: Source of Missing Heritability? M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info
Breast Cancer Susceptibility and HLA Complex: Source of Missing Heritability? M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info
Cell Cycle Alteration, Apoptosis and Response of Leukemic Cell Lines to Gamma Radiation with High- and Low-Dose Rate
 Physiol. Res. 53: 335-342, 2004 Cell Cycle Alteration, Apoptosis and Response of Leukemic Cell Lines to Gamma Radiation with High- and Low-Dose Rate J. VÁVROVÁ 1, M. ŘEZÁČOVÁ 2, D. VOKURKOVÁ 3, J. PSUTKA
Physiol. Res. 53: 335-342, 2004 Cell Cycle Alteration, Apoptosis and Response of Leukemic Cell Lines to Gamma Radiation with High- and Low-Dose Rate J. VÁVROVÁ 1, M. ŘEZÁČOVÁ 2, D. VOKURKOVÁ 3, J. PSUTKA
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
The Radiobiological Four "R"s of Hypofractionation. Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health Systems
 The Radiobiological Four "R"s of Hypofractionation Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health Systems Overview of the presentation Definition of hypofractionation Radiobiology 4 R s Standard fraction dosing Linear
The Radiobiological Four "R"s of Hypofractionation Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health Systems Overview of the presentation Definition of hypofractionation Radiobiology 4 R s Standard fraction dosing Linear
ATM/Wip1 activities at chromatin control Plk1 re-activation to determine G2 checkpoint duration
 Article ATM/Wip activities at chromatin control Plk re-activation to determine G2 checkpoint duration Himjyot Jaiswal,, Jan Benada 2,3,, Erik M ullers,,, Karen Akopyan, Kamila Burdova 2, Tobias Koolmeister
Article ATM/Wip activities at chromatin control Plk re-activation to determine G2 checkpoint duration Himjyot Jaiswal,, Jan Benada 2,3,, Erik M ullers,,, Karen Akopyan, Kamila Burdova 2, Tobias Koolmeister
MARCH 2001 VOLUME 14, NUMBER 3. Copyright 2001 by the American Chemical Society. p53 Signaling and Cell Cycle Checkpoints
 MARCH 2001 VOLUME 14, NUMBER 3 Copyright 2001 by the American Chemical Society Invited Review p53 Signaling and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Zoe A. Stewart and Jennifer A. Pietenpol* Department of Biochemistry,
MARCH 2001 VOLUME 14, NUMBER 3 Copyright 2001 by the American Chemical Society Invited Review p53 Signaling and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Zoe A. Stewart and Jennifer A. Pietenpol* Department of Biochemistry,
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Open Access Book Chapter
 ERC-OAPEN-2015, Deposit cover page Open Access Book Chapter Published version Chapter title Signalling DNA Damage Title in English Author(s) Andres Joaquin Lopez-Contreras and Oscar Fernandez-Capetillo
ERC-OAPEN-2015, Deposit cover page Open Access Book Chapter Published version Chapter title Signalling DNA Damage Title in English Author(s) Andres Joaquin Lopez-Contreras and Oscar Fernandez-Capetillo
DNA repair pathway choice at various conditions immediately post irradiation
 DNA repair pathway choice at various conditions immediately post irradiation Min Liu, Jilin University Hongyan Wang, affiliation Solah Lee, Emory University Bailong Liu, Jilin University Lihua Dong, Jilin
DNA repair pathway choice at various conditions immediately post irradiation Min Liu, Jilin University Hongyan Wang, affiliation Solah Lee, Emory University Bailong Liu, Jilin University Lihua Dong, Jilin
Regulation of Cell Division
 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Sierra Oncology (SRRA)
 Initiating Coverage June 8, 2017 Sierra Oncology (SRRA) Initiation Report LifeSci Investment Abstract Sierra Oncology (NasdaqGM: SRRA) is a biotechnology company focused on developing oncology treatments
Initiating Coverage June 8, 2017 Sierra Oncology (SRRA) Initiation Report LifeSci Investment Abstract Sierra Oncology (NasdaqGM: SRRA) is a biotechnology company focused on developing oncology treatments
CONTENTS. Preface... xii
 CONTENTS Preface... xii 1. Autocrine Transformation: Cytokine Model... 1 James A. McCubrey, Xiao-Yang Wang, Paul A. Algate, William L. Blalock and Linda S. Steelman Abstract... 1 Cytokine Regulation of
CONTENTS Preface... xii 1. Autocrine Transformation: Cytokine Model... 1 James A. McCubrey, Xiao-Yang Wang, Paul A. Algate, William L. Blalock and Linda S. Steelman Abstract... 1 Cytokine Regulation of
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics
 Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics Q1 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking statement
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics Q1 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking statement
Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration between LNS INFN and Vinca Institute of Nuclear Sciences
 ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
Ex vivo functional assays for Homologous Recombination deficiency in breast cancer. Dik C. van Gent
 Ex vivo functional assays for Homologous Recombination deficiency in breast cancer Dik C. van Gent Breast cancer types treatments ER/PR: anti-hormonal therapy HER2: Herceptin Triple negative (TNBC): no
Ex vivo functional assays for Homologous Recombination deficiency in breast cancer Dik C. van Gent Breast cancer types treatments ER/PR: anti-hormonal therapy HER2: Herceptin Triple negative (TNBC): no
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Homeostatic control of polo-like kinase-1 engenders non-genetic heterogeneity in G2 checkpoint fidelity and timing
 Received 27 Sep 213 Accepted 6 May 214 Published 4 Jun 214 DOI: 1.138/ncomms48 Homeostatic control of polo-like kinase-1 engenders non-genetic heterogeneity in G2 checkpoint fidelity and timing OPEN Hongqing
Received 27 Sep 213 Accepted 6 May 214 Published 4 Jun 214 DOI: 1.138/ncomms48 Homeostatic control of polo-like kinase-1 engenders non-genetic heterogeneity in G2 checkpoint fidelity and timing OPEN Hongqing
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting
 BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
A Mitotic Phosphorylation Feedback Network Connects Cdk1, Plk1, 53BP1, and Chk2 to Inactivate the G2/M DNA Damage Checkpoint
 A Mitotic Phosphorylation Feedback Network Connects Cdk1, Plk1, 53BP1, and Chk2 to Inactivate the G2/M DNA Damage Checkpoint The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how
A Mitotic Phosphorylation Feedback Network Connects Cdk1, Plk1, 53BP1, and Chk2 to Inactivate the G2/M DNA Damage Checkpoint The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE: A RECORD OF POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 ACTIVITY
 From DEPARTMENT OF CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE: A RECORD OF POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 ACTIVITY Elvira Hukasova Stockholm 2017
From DEPARTMENT OF CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE: A RECORD OF POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 ACTIVITY Elvira Hukasova Stockholm 2017
Revisiting post-translational regulation of cell cycle CDKs
 Revisiting post-translational regulation of cell cycle CDKs Cyclin-CDK complexes during cell cycle Cyclin B-CDK1 G0 E2F prb Cyclin A-CDK1 G2 M Cyclin D-CDK4 CDK6 + prb Cyclin A-CDK2 S R G1 Cyclin E-CDK2
Revisiting post-translational regulation of cell cycle CDKs Cyclin-CDK complexes during cell cycle Cyclin B-CDK1 G0 E2F prb Cyclin A-CDK1 G2 M Cyclin D-CDK4 CDK6 + prb Cyclin A-CDK2 S R G1 Cyclin E-CDK2
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Radiobiological Effects of Alpha-Particles from Astatine-211
 Radiobiological Effects of Alpha-Particles from Astatine-211 From DNA Damage to Cell Death Kristina Claesson Department of Oncology Institute of Clinical Sciences The Sahlgrenska Academy at University
Radiobiological Effects of Alpha-Particles from Astatine-211 From DNA Damage to Cell Death Kristina Claesson Department of Oncology Institute of Clinical Sciences The Sahlgrenska Academy at University
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics
 Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics September 19, 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics September 19, 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts
 Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Accumulation of DNA double strand breaks. in normal tissues after fractionated low dose irradiation
 Aus der Klinik für Strahlentherapie und Radioonkologie Direktor: Prof. Dr. Ch. Rübe UniversitätskliniKum des Saarlandes Accumulation of DNA double strand breaks in normal tissues after fractionated low
Aus der Klinik für Strahlentherapie und Radioonkologie Direktor: Prof. Dr. Ch. Rübe UniversitätskliniKum des Saarlandes Accumulation of DNA double strand breaks in normal tissues after fractionated low
Dynamics of p53 and NF-κB regulation in response to DNA damage and identification of target proteins suitable for therapeutic intervention
 Poltz and Naumann BMC Systems Biology 2012, 6:125 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dynamics of p53 and NF-κB regulation in response to DNA damage and identification of target proteins suitable for therapeutic
Poltz and Naumann BMC Systems Biology 2012, 6:125 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dynamics of p53 and NF-κB regulation in response to DNA damage and identification of target proteins suitable for therapeutic
SV40 Utilizes ATM Kinase Activity to Prevent Non-homologous End Joining of Broken Viral DNA Replication Products
 SV40 Utilizes ATM Kinase Activity to Prevent Non-homologous End Joining of Broken Viral DNA Replication Products Gregory A. Sowd 1 *, Dviti Mody 1, Joshua Eggold 1, David Cortez 2, Katherine L. Friedman
SV40 Utilizes ATM Kinase Activity to Prevent Non-homologous End Joining of Broken Viral DNA Replication Products Gregory A. Sowd 1 *, Dviti Mody 1, Joshua Eggold 1, David Cortez 2, Katherine L. Friedman
APC/C Cdh1 controls CtIP stability during the cell cycle and in response to DNA damage
 Article APC/C Cdh1 controls stability during the cell cycle and in response to DNA damage Lorenzo Lafranchi 1,, Harmen R de Boer 2,, Elisabeth GE de Vries 2, Shao-En Ong 3, Alessandro A Sartori 1,* & Marcel
Article APC/C Cdh1 controls stability during the cell cycle and in response to DNA damage Lorenzo Lafranchi 1,, Harmen R de Boer 2,, Elisabeth GE de Vries 2, Shao-En Ong 3, Alessandro A Sartori 1,* & Marcel
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics
 Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics Q2 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking statement
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics Q2 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking statement
