5-Fluorouracil Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Oxaliplatin on Colo320 Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Cells
|
|
|
- Sharlene Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5-Fluorouracil Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Oxaliplatin on Colo320 Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Cells Ioana Berindan-Neagoe 1,2,3, Cornelia Braicu 1,3*, Valentina Pileczki 3,4, Roxana Cojocneanu Petric 3,5, Nicolae Miron 2,6, Ovidiu Balacescu 1, Dana Iancu 7, Tudor Ciuleanu 7 1) Department of Functional Genomics and Experimental Pathology, Oncological Institute Ion Chiricuta 2) Department of Immunology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu 3) Research Center for Functional Genomics, Biomedicine and Translational Medicine Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy 4) Faculty of Pharmacy, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy 5) Faculty of Biology and Geology, Babeş-Bolyai University 6) Clinical Laboratory, IRGH Prof. dr. O. Fodor 7) Department of Medical Oncology, Oncological Institute Ion Chiricuta Cluj, Romania Address for correspondence: Cornelia Braicu Functional Genomics and Experimental Pathology Department, Oncological Institute Ion Chiricuta Republicii Str., Cluj-Napoca, Romania. braicucornelia@yahoo.com Received: Accepted: ABSTRACT Background & Aims. The present study was designed to examine the combined effects of Oxaliplatin (OXA) and 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) in the Colo320 cell line. Methods. The antiproliferative effects were evaluated using the MTT assay, apoptosis by flow cytometry, and RT-PCR-array technology was used to determine the major effects of the two chemotherapeutic drugs upon the most important genes involved in apoptosis. Results. The antiproliferative effects of the therapeutic agents, as individual therapy or combined, proved to be dose and time-dependent, with increased efficiency for the combined treatment. Flow cytometry data revealed increased apoptotic processes in the case of the combined treatment at 24 hours after administration. The RT-PCR-array data indicated that at 24 hours after OXA treatment, 49 genes were differentially expressed, of which 45 were up-regulated and 4 down-regulated. In the case of the 5-FU treatment, 35 genes were down regulated and 2 up regulated. In the combined treatment of 5-FU and OXA, 19 genes were up-regulated and 15 down-regulated. Conclusions. This study proved that drug resistance could be counteracted by combining OXA with 5-FU to form a tandem that is capable of reducing cell proliferation and to stimulate extrinsic apoptosis pathway by targeting death receptors on the cell surface. Key words: colorectal cancer Colo320 Oxaliplatin 5-Fluorouracil apoptosis. Abbreviations: APAF1 - apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1; BAK 1 - BCL2-antagonist/killer 1; BID - BH3 interacting domain death agonist; CRC Colorectal cancer; DMSO Dimethyl sulfoxide; FBS Fetal Bovine Serum; FITC - Fluorescein isothiocyanate; 5-FU 5 Fluoro-uracil; IC50 half maximal Inhibitory Concentration; KT1 - v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1; LTA - lymphotoxin alpha (TNF superfamily, member 1); LTBR - lymphotoxin beta receptor (TNFR superfamily, member 3); MTT - Dimethyl thiazolyl diphenyl tetrazolium salt; NAIP - NLR family, apoptosis inhibitory protein; OXA Oxaliplatin; PBS Phosphate Buffered Saline; PI - Propidium Iodide; RIN - RNA integrity number; RT-PCR Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction; TNF Tumor Necrosis Factor; TRAF2 - TNF receptor-associated factor 2; TRAF3 - TNF receptor-associated factor 3; TRAF5 - TNF receptor-associated factor 5; TRAIL - tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 10; TWEAK - tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 12 INTRODUCTION Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a widespread malignant disease, mostly prevailing in industrialized countries. In its early stages, colorectal cancer is a curable disease, but in all advanced cases, without proper treatment regimen, patients have a poor prognosis [1]. The introduction of platinum derivative drugs, like oxaliplatin (OXA), shows good therapeutic results by increasing survival rates [2, 3]. The molecular mechanism of OXA in tumor cells is not yet clear but the drug presents powerful cytotoxic properties and its function is based on the ability to covalently bind DNA, forming platinum-dna adducts which lead to apoptosis [4]. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) exerts its anticancer effects by repressing the thymidylate synthase and incorporating its metabolites into RNA and DNA, and has been extensively used in the treatment of solid tumors [5, 6]. Recent experimental data suggest that this drug combination activates the apoptotic pathways [7, 8]. This study was designed to examine the efficiency of each cytostatic drug in comparison with the combined effects of both OXA and 5-FU in Colo320 cells. The antiproliferative effects, either as individual therapy or combined, were evaluated using the MTT assay, apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry,
2 38 Berindan-Neagoe et al and RT-PCR-array was used to assess apoptotic genes, for a dose equivalent to the IC 50 (the dose that produces halfmaximal inhibition). 5-FU may further enhance cytotoxicity by sensitizing cancer cells to OXA-induced apoptosis [2]. Our current results from in vitro studies on colorectal cancer cells have demonstrated that the combined therapy works together to inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis, but not in a synergistic manner. MATERIAL AND METHODS Cell cultures. Colo320 cell line (human colon adenocarcinoma established, ATCC catalogue: CCL 220) is maintained in culture in RPMI-1460 medium, 10% FBS (Sigma-Aldrich), 100 U/ml penicillin and 2mM glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich). Cell treatment. For the MTT test, we treated cells with different concentrations of OXA, 5-FU and OXA+5-FU, ranging between µm, and determined the IC 50. For the apoptosis and RT-PCR-array evaluations we used a single dose of 10 µm for OXA and 5 µm for 5-FU, either independently or in tandem. Evaluations were made 24 and 48 hours after treatment for cell proliferation, and 24 hours after treatment for RT-PCR-array analysis. Cell proliferation assay evaluation using MTT test. 1x10 4 Colo320 cells were plated in 96-well plates and treated with the doses previously mentioned for 24 and 48 hours. After the incubation period, the culture medium was removed, and the cells were washed with PBS (Phosphate buffered saline, Sigma-Aldrich), incubated for 2 hours with 455 µg/ml MTT in Hanks salt, then was removed and replaced by 200 µl of DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide, Merck) to solubilize the resulted formazan. The absorbance at 490 nm and the IC50 values were determined using GraphPad Prism free trial software. Apoptosis-Flow Cytometry. Each of the triplicate samples from the 4 groups of cells (control and OXA, 5-FU, OXA+5-FU) were resuspended in 100 μl of binding buffer with 2 μl of Annexin V-FITC and 1 μg PI, then incubated 10 minutes at room temperature, in the dark. After washing, each sample was diluted using 250 µl binding buffer and evaluated using a FACSCantoII flow cytometer equipped with BD-FACSDiva software for cell acquisition and data analysis. The RNA extraction and quality control. From each of the 4 groups we extracted the total RNA using TriReagent (Sigma-Aldrich), in accordance with the producer s protocol. DNA contamination was eliminated using DNAse (Qiagen) and the RNA was purified using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). RNA concentrations were evaluated using NanoDrop-1100, and its quality was appraised with Agilent Bioanalyzer The RIN values for all the measured samples were above 8. RT 2 Profiler TM PCR Array technology. The experiment was performed using the Human Apoptosis RT²Profiler PCR Array 96-well plate from SABiosciences. For this we used the RT 2 First Strand Kit (SABiosciences) to reverse transcribe 400ng of RNA. The cdna was pipetted onto the PCR Array plate, after being combined with the RT 2 SYBRGreen qpcr Master Mix (SABiosciences). The plate was run on a LightCycler 480 (Roche), using the following steps: 10 min at 95 C in order to activate the enzyme, then 40 cycles of 15 seconds at 95 C, and in the end, 1 min at 60 C. PCR Array Data Analysis. The data obtained after RT-PCRarray analysis were entered in web-based data analysis software from SABiosciences ( com/pcr/arrayanalysis.php), which uses the ΔΔCt method (p-values 0.05, and fold change ±1.25) RESULTS The combined treatment of OXA and 5-FU induces inhibition of cell proliferation Preliminary studies were done in order to evaluate the antiproliferative effect of OXA, 5-FU and OXA+5-FU on the Colo320 cells. The MTT values 24 and 48h post-treatment were represented as log of concentration (μm), plotted against % of control (Fig. 1). The IC 50 values for OXA, 5-FU, and OXA+5-FU are presented in Table I. The effects are time and dose-dependent, with an increased efficiency for the combined treatment. The results for OXA+5-FU indicate that the combined therapy is more efficient than each compound administered alone. Apoptosis/necrosis evaluation as a response to single or combined treatment with OXA and 5-FU in Colo320 cells Annexin V-FITC/PI staining is presented in Fig. 2, and allows the differentiation between apoptotic and necrotic cells. Fig. 1. The antiproliferative effect measured using MTT assay after 24 and 48 hours post treatment with concentrations between 0 and 100 μm of OXA, 5-FU, alone or combined, on Colo320 cell line; log (conc, μm) = log[concentration drug, μm] (mean ± SD, n = 6).
3 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin effect on Colo320 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells 39 Table I. Overview of IC 50 values for Colo-320 for OXA and 5-FU, alone or combined Time Compound IC 50 Slope R2 OXA FU OXA+5-FU OXA FU OXA+5-FU cell death signaling. After treatment with OXA, 49 genes showed statistically significant values, 45 overexpressed and 4 downregulated (online supplementary Table SI), most genes being inducers of apoptosis. In the case of 5-FU we obtained statistically significant results for 37 genes, of which 35 were downregulated and only 2 were overexpressed. For the combined treatment of 5-FU and OXA, 34 genes were statistically significant, of which 19 were overexpressed and 15 downregulated (Table S1). Most of the genes that were overexpressed encode for caspase induced apoptosis and inhibition of the genes that modulate cell proliferation pathways. In the case of the OXA treatment, we have observed an activation of the p53 gene, while 5-FU causes the reduction of intracellular apoptotic molecules. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis allows us to present the major functional networks modulated by the different treatment variants (Fig 3, Table II). The combined treatment may reduce intrinsic and/or acquired resistance to the individual therapeutic agents, leading to the modulation of death receptors, Myc mediated apoptosis and TWEAK Signaling. Hierarchical cluster analysis showed that the OXA treatment leads to the up-regulation of genes involved in apoptosis pathways, as presented in the supplementary Fig. S1. This study demonstrated that each treatment has a specific modulator effect on each group of genes. TNF receptor and ligand family and death effectors domain family are generally activated by OXA treatment, while 5-FU inhibits these groups of genes. Several genes with anti-apoptotic role are activated by OXA, potentially leading to treatment resistance. The apoptotic genes are down-regulated by 5FU, while for the combined treatment 5 of the genes remain activate and 9 are down-regulated (Table S1). This finding is an additional argument that the combined treatment of OXA and 5-FU is a more effective therapeutic design in colorectal cancer, since the main signal transduction pathway that controls apoptosis and cell death appears more intensely activated. Fig. 2. Effect of OXA, 5-FU, OXA+5-FU on Colo320 apoptosis in vitro measured by Annexin V-FITC and PI binding. Colo320 cells (1 106 cells) were incubated in the absence (control cell samples) or presence of 10 μm of OXA, 5 μm of 5-FU, and respectively 10 μm of OXA and 5 μm of 5-FU at 24 and 48 hours post treatment. In the case of the combined treatment, the yield of necrotic cells is the same or lower than the individual treatment at 24 hours post-treatment. The results are expressed as % of apoptotic cells; an increase of these values was observed, particularly 48 h post treatment. OXA treatment revealed that 24.4% and 33.2% of cells undergo apoptosis at 24 and 48 h, respectively. 5-FU treatment caused 22.9% and 25.5% of cells to undergo apoptosis at 24 and 48 h, respectively. The impact of the combined therapy was greater after 48 hours of treatment, as 29.9% and 40.9% of cells underwent apoptosis at 24 and 48h, respectively. Apoptotic and cell death signals evaluation at 24 hours post treatment using RT-PCR-array RT-PCR-array technology simultaneously evaluates the level of expression of 84 genes involved in apoptosis and Table II. The main Canonical Pathways modulated by the selected treatment variants in Colo320 cell line Drug Name p-value Ratio Apoptosis Signaling 2.46E-31 19/96 (0.198) TWEAK Signaling 2.65E-30 15/39 (0.385) OXA Death Receptor 5.42E-26 15/65 (0.231) Signaling Molecular Mechanisms 3.93E-21 20/378 (0.053) of Cancer Death Receptor 4.95E-33 17/65 (0.262) Signaling 5-FU TWEAK Signaling 1.58E-24 12/39 (0.308) Apoptosis Signaling 4.85E-23 14/96 (0.146) TNFR1 Signaling 3.91E-20 11/53 (0.208) Apoptosis Signaling 2.42E-19 12/96 (0.125) Death Receptor 3.01E-17 10/65 (0.154) OXA+5-FU Signaling Myc Mediated Apoptosis 4.06E-13 8/61 (0.131) Signaling TWEAK Signaling 5.95E-13 7/39 (0.179)
4 40 Berindan-Neagoe et al As we can see in Fig. 3A and Table S1, caspases are the principal genes leading to treatment response to OXA, and our results indicate that caspase inhibitor activation is correlated with the modulation of NAIP, BAK1 and LTA genes, which are known to be involved in the response to therapy [9]. For 5-FU, the central molecule is FADD, related to TNSFR10 and TRAF2, which are markers involved in the response to therapy. In the case of the combined treatment (Fig. 3C), the central molecule Fig. 3 (continued on page 41)
5 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin effect on Colo320 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells 41 Fig. 3. (continued) The canonical network related with the genes implicated in apoptosis mediated by (A) OXA, (B) 5-FU, (C) OXA+ 5-FU. is TRAF2, linked to BAK1 and LTA, playing important roles in increased treatment efficiency. Apoptosis is promoted by TRAF3 and TRAF5 via LTBR. DISCUSSION Surgery is the generally applied course of treatment for early stage CRC, while chemotherapy is the first therapeutic option for advanced CRC, when tumor lesions are usually not completely resectable [10]. Controlling cell proliferation using chemotherapy is mainly based on apoptosis but resistance to therapy is observed in all cytostatic drug treatments, and OXA and/or 5-FU do not make an exception [11-13]. The treatment with 5-FU did not show a clear synergistic effect with OXA in Colo320 cells, while in a similar study a synergic effect was observed [14]. OXA and 5-FU together displayed a more reduced number of genes involved in the resistance to treatment than each drug administered individually (Table SI). Restoration of the signaling pathways that are involved in apoptosis induction, based on targeted multitherapy, may result in improved response to treatment, which translates into decreased resistance to cancer therapy [15-17], by stimulation of the intrinsic pathway that enhance TRAIL receptor targeted therapies [18]. The overexpression of the caspases responsible for apoptosis execution (CASP3, CASP4 CASP6, CASP9) and cell death is confirmed by flow cytometry data (Fig. 2). This is supported by a similar study for CASP3 mrna expression leading to the promotion of apoptosis by OXA [18]. Studies revealed that p53 induced tumor cell resistance to OXA, so TP53 can be used as a therapeutic target in modulating the response to therapy [19]. Our previous data showed that p53 and NFκB were upregulated after treatment with OXA [20]. Other recent studies on OXA using p53 wild-type HCT116 colon cancer cells have demonstrated that p53 and Bax genes play an important role in cell apoptosis [21], data confirmed by the present study. The molecular basis of resistance to OXAinduced cytotoxicity is complex and multifactorial. Previous studies have shown that OXA enhances 5-FU cytotoxicity [22] by activating TRAIL induced apoptosis in several models [23-25, 36]. Renewing the susceptibility of adenocarcinoma cells to TRAIL is beneficial to patients with this neoplasia [26, 35]. The present study reveals that the upregulation of CARD6 may inhibit the activation of NFκB pathway [27, 28]. 5-Fluorouracil induces the inhibition of death receptors, whose alterations are involved in cancer development [29, 30]. Also, by modulating the expression of the Bcl-2 family of genes, 5-FU displays a certain degree of pro-apoptotic activity [31]. As shown in Fig 3, the main molecules involved in apoptosis belong to the NFκB complex for 5-FU [14]; death receptors are also blocked by 5-FU, leading to the inhibition of the cell survival pathway controlled by NFκB [32]. The fact that 48 hours after 5-FU treatment the IC 50 is higher that at 24 h can be explained by the overexpression of apoptosis inhibitory gene NAIP [33]. In previous in vitro and in vivo studies it was observed that NAIP is an important
6 42 Berindan-Neagoe et al member of the IAPs that are involved in the resistance to different chemotherapeutics agents [34]. For this reason, the choice for postoperative treatment of colon cancer is often the combination therapy consisting of 5-FU and OXA [35], drugs which are effective in preventing TRAIL drug-resistance, as was demonstrated in a similar study on HT-29 and RKO cells [36], or by their effects on decreasing the expression of IAPs genes, in particular XIAP [36]. Oxaliplalin seems to modulate the activation of TNF-α in a rapid and transient manner through the TWEAK canonical pathway, less active in the case of OXA+5-FU. Like other TNF family members, TWEAK pathway is capable of enhancing proliferation, cell migration, expression and secretion of proinflammatory molecules [37], and displays proangiogenic activity [38-40]. TWEAK pathway is modulated by AKT1 and by the recruitment of TRAF protein family members. In addition, the inhibition of AKT1 expression stimulates apoptosis and intensifies the sensitiveness of gastric cancer to chemotherapy in many mammalian cells [41]. The activation of these pathways leads to the inhibition of the proapoptotic genes BID and APAF1, thus being a connection point between NFκB activation through TWEAK pathways that induce apoptosis signaling as a response to treatment by mediating apoptosis and inflammasome activation [14, 42]. CONCLUSIONS Our study proved that the drug resistance in Colo320 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells could be counteracted by combining OXA with 5-FU to form a tandem that is capable of reducing cell proliferation and stimulate apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of death receptors. The reduction of cell proliferation and the activation of apoptosis are important indicators for the response to therapy in colorectal cancer; the precise molecular mechanism can be described by identifying the genes that are involved in resistance to therapy. This study highlights the importance of in vitro assays in developing novel therapeutic strategies that bring benefit to the patient. Conflicts of interest: The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest to declare. Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the PN-II-ID-PCE UEFISCDI grant. REFERENCES 1. Alberts SR, Wagman LD. Chemotherapy for colorectal cancer liver metastases. Oncologist 2008; 13: Board RE, Valle JW. Metastatic colorectal cancer: current systemic treatment options. Drugs 2007; 67: Wang X, Li M, Wanga J, et al. The BH3-only protein, PUMA, is involved in oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2006; 71: Hato SV, de Vries IJ, Lesterhuis WJ. STATing the importance of immune modulation by platinum chemotherapeutics. Oncoimmunology 2012; 1: Kadoyama K, Miki I, Tamura T, Brown JB, Sakaeda T, Okuno Y. Adverse event profiles of 5-fluorouracil and capecitabine: data mining of the public version of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System, AERS, and reproducibility of clinical observations. Int J Med Sci 2012; 9: Caraglia M, Marra M, Budillon A, et al. Chemotherapy regimen GOLF induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells through multi-chaperone complex inactivation and increased Raf-1 ubiquitin-dependent degradation. Cancer Biol Ther 2005; 4: Raymond E, Faivre S, Coudray AM, Louvet C, Gespach C. Preclinical studies of oxaliplatin in combination chemotherapy. Bull Cancer 2001; 88: S Mani S, Manalo J, Bregman D. Novel combinations with oxaliplatin. Oncology 2000; 14: Qiao L, Wong B. Colon Cancer Experimental Therapy. In: Schwab M. (Ed.) Encyclopedia of Cancer: SpringerReference (www. springerreference.com). Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Chibaudel B, Tournigand C, André T, de Gramont A. Therapeutic strategy in unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol 2012; 4: Reed JC. Apoptosis-targeted therapies for cancer. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: Stevenson L, Allen WL, Turkington R, et al. Identification of galanin and its receptor GalR1 as novel determinants of resistance to chemotherapy and potential biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: Margiotta N, Marzano C, Gandin V, et al. Revisiting [PtCl(2)(cis-1,4- DACH)]: an underestimated antitumor drug with potential application to the treatment of oxaliplatin-refractory colorectal cancer. J Med Chem 2012; 55: Mori R, Yoshida K, Tanahashi T, et al. Decreased FANCJ caused by 5FU contributes to the increased sensitivity to oxaliplatin in gastric cancer cells. Gastric Cancer 2012 Sep 12. [Epub ahead of print]. 15. Amm HM, Oliver PG, Lee CH, Li Y, Buchsbaum DJ.Combined modality therapy with TRAIL or agonistic death receptor antibodies. Cancer Biol Ther 2011; 11: Rodriquez-Nieto S, Zhivotovsky B. Role of alterations in the apoptotic machinery in sensitivity of cancer cells to treatment. Curr Pharm Des 2006; 12: Gao J, Tian Y, Zhang J. Overexpression of interferon regulatory factor 1 enhances chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in gastric cancer cells. J Cancer Res Ther 2012; 8: Lin WL, Li DG, Chen Q, Lu HM. Clinical and experimental study of oxaliplatin in treating human gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10: Harradine KA, Kassner M, Chow D, et al. Functional genomics reveals diverse cellular processes that modulate tumor cell response to oxaliplatin. Mol Cancer Res 2011; 9: Gherman C, Pileczki V, Cojocneanu Petric R, Rapuntean S2, Gherman S, Berindan Neagoe I. Molecular mechanisms of action and prediction of response to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells. Annals of RSCB 2012; 17: Fujie Y, Yamamoto H, Ngan CY, et al. Oxaliplatin, a potent inhibitor of survivin, enhances paclitaxel-induced apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe in colon cancer cells. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2005; 35: Toscano F, Fajoui ZE, Gay F, et al. P53-mediated upregulation of DcR1 impairs oxaliplatin/trail-induced synergistic anti-tumour potential in colon cancer cells. Oncogene 2008; 27: Arnould S, Hennebelle I, Canal P, Bugat R, Guichard S. Cellular determinants of oxaliplatin sensitivity in colon cancer cell lines. Eur J Cancer 2003; 39:
7 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin effect on Colo320 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells Marchetti P, Galla DA, Russo FP, et al. Apoptosis induced by oxaliplatin in human colon cancer HCT15 cell line. Anticancer Res 2004; 24: Ravaioli A, Marangolo M, Pasquini E, et al. Bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin with oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: Zhang, L, Fang B. Mechanisms of resistance to trail-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: Peng H, Wen J, Li H, Chang J, Zhou X. Drug inhibition profile prediction for NFκB pathway in multiple myeloma. PLoS One 2011; 6: e Braicu C, Gherman C. Epigallocatechin gallate induce cell death and apoptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells Hs578T. J Drug Target 2012 Nov 19. [Epub ahead of print]. 29. Chaudhry P, Srinivasan R, Patel FD. Differential expression of Fas family members and Bcl-2 family members in benign versus malignant epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) in North Indian population. Mol Cell Biochem 2012;368: Hamed EA, Zakhary MM, Maximous DW. Apoptosis, angiogenesis, inflammation, and oxidative stress: basic interactions in patients with early and metastatic breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2012; 138: Rigas A, Dervenis C, Giannakou N, Kozoni V, Shiff SJ, Rigas B. Selective induction of colon cancer cell apoptosis by 5-fluorouracil in humans. Cancer Invest 2002; 20: Uetsuka H, Haisa M, Kimura M, et al. Inhibition of inducible NF-kappaB activity reduces chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil in human stomach cancer cell line. Exp Cell Res 2003; 289: Romanish MT, Nakamura H, Lai CB, Wang Y, Mager DL. A novel protein isoform of the multicopy human NAIP gene derives from intragenic Alu SINE promoters. PLoS ONE 2009; 4: e Wang Q, Wang X, Evers BM. Induction of ciap-2 in human colon cancer cells through PKC delta/nf-kappa B. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: Chau I, Cunningham D. Treatment in advanced colorectal cancer: what, when and how? Br J Cancer 2009; 100: Stolfi C, Pallone F, Monteleone G. Molecular Targets of TRAIL- Sensitizing Agents in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2012;13: Dohi T, Burkly LC. The TWEAK/Fn14 pathway as an aggravating and perpetuating factor in inflammatory diseases: focus on inflammatory bowel diseases. J Leukoc Biol 2012; 92: Jakubowski A, Browning B, Lukashev M, et al. Dual role for TWEAK in angiogenic regulation. J Cell Sci 2002; 115: Kumar M, Makonchuk DY, Li H, Mittal A, Kumar A. TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) activates proinflammatory signaling pathways and gene expression through the activation of TGF-beta activated kinase 1. J Immunol 2009; 182: Bhattacharjee M, Raju R, Radhakrishnan A, et al. A Bioinformatics Resource for TWEAK-Fn14 Signaling Pathway. J Signal Transduct 2012; 2012: Liu J, Fu XQ, Zhou W, Yu HG, Yu JP, Luo HS. LY potentiates the anti-cancer effect of oxaliplatin for gastric cancer via death receptor pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17:
8 Table S1. Genes differentially expressed in the case of OXA, 5-FU and OXA+5-FU treatment versus control cells at 24 h posttreatment Gene name Unigene Gene symbol Fold change OXA 5-FU OXA+5-FU V-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 Hs AKT Apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 Hs APAF BCL2-associated agonist of cell death Hs BAD BCL2-associated athanogene 3 Hs BAG BCL2-associated athanogene 4 Hs BAG BCL2-antagonist/killer 1 Hs BAK BCL2-associated X protein Hs BAX B-cell CLL/lymphoma 10 Hs BCL B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 Hs BCL BCL2-related protein A1 Hs BCL2A BCL2-like 10 (apoptosis facilitator) Hs BCL2L BCL2-like 11 (apoptosis facilitator) Hs BCL2L BCL2-like 2 Hs BCL2L BCL2-associated transcription factor 1 Hs BCLAF Bifunctional apoptosis regulator Hs BFAR BH3 interacting domain death agonist Hs BID BCL2-interacting killer (apoptosis-inducing) Hs BIK NLR family, apoptosis inhibitory protein Hs NAIP Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 2 Hs BIRC Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 3 Hs BIRC X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis Hs XIAP Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 6 Hs BIRC Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 8 Hs BIRC BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa interacting protein 1 Hs BNIP BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa interacting protein 3 Hs BNIP BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa interacting protein 3-like Hs BNIP3L V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 Hs BRAF Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 Hs NOD Caspase recruitment domain family, member 6 Hs CARD Caspase recruitment domain family, member 8 Hs CARD Caspase 10, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs.5353 CASP Caspase 14, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP Caspase 2, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP Caspase 3, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP Caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP Caspase 5, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP Caspase 6, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP Caspase 7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs.9216 CASP Caspase 8, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP Caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Hs CASP CD40 molecule, TNF receptor superfamily member 5 Hs CD CD40 ligand Hs CD40LG CASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator Hs CFLAR Cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector a Hs CIDEA Cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector b Hs CIDEB CASP2 and RIPK1 domain containing adaptor with death domain Hs CRADD DNA fragmentation factor, 45kDa, alpha polypeptide Hs DFFA Fas (TNFRSF6)-associated via death domain Hs FADD
9 2 Berindan-Neagoe et al Fas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6) Hs FAS Fas ligand (TNF superfamily, member 6) Hs.2007 FASLG Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, alpha Hs GADD45A Harakiri, BCL2 interacting protein (contains only BH3 domain) Hs HRK Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor Hs IGF1R Lymphotoxin alpha (TNF superfamily, member 1) Hs.36 LTA Lymphotoxin beta receptor (TNFR superfamily, member 3) Hs.1116 LTBR Myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (BCL2-related) Hs MCL Nucleolar protein 3 (apoptosis repressor with CARD domain) Hs NOL PYD and CARD domain containing Hs PYCARD Receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 2 Hs RIPK Tumor necrosis factor Hs TNF Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b Hs TNFRSF10B Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1A Hs TNFRSF1A Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 21 Hs TNFRSF Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 25 Hs TNFRSF CD27 molecule Hs CD Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 9 Hs TNFRSF CD70 molecule Hs CD Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 8 Hs TNFSF Tumor protein p53 Hs TP Tumor protein p53 binding protein, 2 Hs TP53BP Tumor protein p73 Hs TP TNF receptor-associated factor 2 Hs TRAF TNF receptor-associated factor 3 Hs TRAF TNF receptor-associated factor 4 Hs.8375 TRAF
10 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin effect on Colo320 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells 3 Fig.. S1. The clustergram for OXA, 5-FU, OXA+ 5-FU treated samples versus control samples. P <0.05, genes with 1.25 or 1.25 fold change are shown.
Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells.
 Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences ijbms.mums.ac.ir Opium induces apoptosis in Jurkat cells via promotion of proapoptotic and inhibition of anti-apoptotic molecules Mohammad Kazemi Arababadi 1,
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences ijbms.mums.ac.ir Opium induces apoptosis in Jurkat cells via promotion of proapoptotic and inhibition of anti-apoptotic molecules Mohammad Kazemi Arababadi 1,
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Epigonal Conditioned Media from Bonnethead Shark, Sphyrna tiburo, Induces Apoptosis in a T-Cell Leukemia Cell Line, Jurkat E6-1
 Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3224-3257; doi:10.3390/md11093224 Article OPEN ACCESS marine drugs ISSN 1660-3397 www.mdpi.com/journal/marinedrugs Epigonal Conditioned Media from Bonnethead Shark, Sphyrna tiburo,
Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3224-3257; doi:10.3390/md11093224 Article OPEN ACCESS marine drugs ISSN 1660-3397 www.mdpi.com/journal/marinedrugs Epigonal Conditioned Media from Bonnethead Shark, Sphyrna tiburo,
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2
 p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line
 Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein. pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is
 ' ^Summary C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is of greater importance because of its various
' ^Summary C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is of greater importance because of its various
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis aubl
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 169-176 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 169-176 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Characterizing the Sphingomyelinase Pathway Triggered by PRIMA-1 Derivatives in Lung Cancer Cells with Differing p53 Status
 Characterizing the Sphingomyelinase Pathway Triggered by PRIMA-1 Derivatives in Lung Cancer Cells with Differing p53 Status EROICA SOANS 1, SUSAN C. EVANS 2, CYNTHIA CIPOLLA 3* and ELROY FERNANDES 4**
Characterizing the Sphingomyelinase Pathway Triggered by PRIMA-1 Derivatives in Lung Cancer Cells with Differing p53 Status EROICA SOANS 1, SUSAN C. EVANS 2, CYNTHIA CIPOLLA 3* and ELROY FERNANDES 4**
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
 The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
Direct Intracellular Regulators of Apoptosis Array 1
 Supplement Table A Direct Intracellular Regulators of Apoptosis 2 Mean Name Description.5 2.2.9 ATM ataxia telangiectasia mutated homolog.9.8.9 Bcl2aa B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 related protein Aa.6 2..9
Supplement Table A Direct Intracellular Regulators of Apoptosis 2 Mean Name Description.5 2.2.9 ATM ataxia telangiectasia mutated homolog.9.8.9 Bcl2aa B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 related protein Aa.6 2..9
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
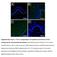 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Mechanisms of Cell Death
 Mechanisms of Cell Death CELL DEATH AND FORMATION OF THE SEMICIRCULAR CANALS Carol M. Troy August 25, 2008 FROM: Fekete et al., Development 124: 2451 (1997) PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH I. DEVELOPMENT A.
Mechanisms of Cell Death CELL DEATH AND FORMATION OF THE SEMICIRCULAR CANALS Carol M. Troy August 25, 2008 FROM: Fekete et al., Development 124: 2451 (1997) PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH I. DEVELOPMENT A.
Apoptotic Pathways in Mammals Dr. Douglas R. Green
 Apoptotic Pathways in Mammals Douglas R. Green 1 Apoptosis A form of cell death that is defined morphologically, and features a number of biochemical events Programmed cell death Cell death that occurs
Apoptotic Pathways in Mammals Douglas R. Green 1 Apoptosis A form of cell death that is defined morphologically, and features a number of biochemical events Programmed cell death Cell death that occurs
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Apoptosome dysfunction in human cancer
 Apoptosis 2004; 9: 691 704 C 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers Apoptosome dysfunction in human cancer K. M. Hajra and J. R. Liu Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan Medical School,
Apoptosis 2004; 9: 691 704 C 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers Apoptosome dysfunction in human cancer K. M. Hajra and J. R. Liu Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan Medical School,
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
The death receptors: signaling and modulation
 The death receptors: signaling and modulation 1 1 The extrinsic cell death pathway 2 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Dec;7(12):1001-12. 2 Death receptors Belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene
The death receptors: signaling and modulation 1 1 The extrinsic cell death pathway 2 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Dec;7(12):1001-12. 2 Death receptors Belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene
CURRICULUM VITAE. Mahafarin Maralani. Educational Background: Date of Birth:
 CURRICULUM VITAE Mahafarin Maralani Date of Birth: Address: Department of Medical Oncology, Azienda hospital polyclinic of Paolo Giaccone, University of Degli studi di palermo, del Vespro street, 129,
CURRICULUM VITAE Mahafarin Maralani Date of Birth: Address: Department of Medical Oncology, Azienda hospital polyclinic of Paolo Giaccone, University of Degli studi di palermo, del Vespro street, 129,
Signaling Apoptosis. Scott André Oakes, M.D. Dept. of Pathology Univ. of Calif-San Francisco. Cyt c Release BAX/BAK. Apoptosome Formation
 Signaling Apoptosis Cyt c Release BAX/BAK Apoptosome Formation Caspase Activation Scott André Oakes, M.D. Dept. of Pathology Univ. of Calif-San Francisco Why do we need cell death? Sculpt Organs Control
Signaling Apoptosis Cyt c Release BAX/BAK Apoptosome Formation Caspase Activation Scott André Oakes, M.D. Dept. of Pathology Univ. of Calif-San Francisco Why do we need cell death? Sculpt Organs Control
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES. Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr.
 BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
Research Article Differential Effects of Alpha-Particle Radiation and X-Irradiation on Genes Associated with Apoptosis
 Radiology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 679806, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2011/679806 Research Article Differential Effects of Alpha-Particle Radiation and X-Irradiation on Genes Associated with
Radiology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 679806, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2011/679806 Research Article Differential Effects of Alpha-Particle Radiation and X-Irradiation on Genes Associated with
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Supplementary Information
 Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
http / / cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology COX-2 NTera-2 NTera-2 RT-PCR FasL caspase-8 caspase-3 PARP.
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera L. Increases Sensitivity of WiDr Colon Cancer Cell Line Towards 5-Fluorouracil
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2010, 1(2):124-128 Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera L. Increases Sensitivity of WiDr Colon Cancer Cell Line Towards 5-Fluorouracil Kholid Alfan Nur, Herwandhani
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2010, 1(2):124-128 Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera L. Increases Sensitivity of WiDr Colon Cancer Cell Line Towards 5-Fluorouracil Kholid Alfan Nur, Herwandhani
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis in chronic hepatitis C
 Apoptosis in chronic hepatitis C Dr med. Anna Parfieniuk-Kowerda Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology Medical University of Bialystok Poland APOPTOSIS Apoptosis - type I programmed cell death
Apoptosis in chronic hepatitis C Dr med. Anna Parfieniuk-Kowerda Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology Medical University of Bialystok Poland APOPTOSIS Apoptosis - type I programmed cell death
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Comparison of Cytotoxic Activity of Anticancer Drugs against Various Human Tumor Cell Lines Using In Vitro Cell-Based Approach
 International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Cytotoxic Activity of Anticancer Drugs against Various Human Tumor Cell Lines Using In Vitro Cell-Based Approach Leila Florento,
International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Cytotoxic Activity of Anticancer Drugs against Various Human Tumor Cell Lines Using In Vitro Cell-Based Approach Leila Florento,
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
In Vitro Studies of the Aurora-Kinase Inhibitor MLN8237 in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines
 In Vitro Studies of the Aurora-Kinase Inhibitor MLN837 in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines Nicole V. Julian Mentor: Ana Aparicio, M.D. Special Thanks to Brittany Kleb Department of Genitourinary Medical Oncology
In Vitro Studies of the Aurora-Kinase Inhibitor MLN837 in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines Nicole V. Julian Mentor: Ana Aparicio, M.D. Special Thanks to Brittany Kleb Department of Genitourinary Medical Oncology
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
AKT apoptosis. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) TNF superfamily. apoptosis TRAIL 2 apoptosis
 Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) TNF superfamily apoptosis TRAIL 2 apoptosis TRAIL (epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR) EGFR EGFR EGFR-TKI) EGFR-TKI EGFR TNFIL-8IL-1IL-1
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) TNF superfamily apoptosis TRAIL 2 apoptosis TRAIL (epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR) EGFR EGFR EGFR-TKI) EGFR-TKI EGFR TNFIL-8IL-1IL-1
ASCO Annual Meeting 2013, May 31 June , Chicago, IL
 Phase I Study of Safety and Pharmacokinetics of GDC-0917, an Antagonist of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors or Lymphoma 1 A Tolcher, 1 K Papadopoulos, 1 A Patnaik,
Phase I Study of Safety and Pharmacokinetics of GDC-0917, an Antagonist of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors or Lymphoma 1 A Tolcher, 1 K Papadopoulos, 1 A Patnaik,
PI3K Background. The SignalRx R & D pipeline is shown below followed by a brief description of each program:
 PI3K Background The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is a key cell signaling node whose dysregulation commonly results in the transformation of normal cells into cancer cells. The role of PI3K
PI3K Background The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is a key cell signaling node whose dysregulation commonly results in the transformation of normal cells into cancer cells. The role of PI3K
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Part I Molecular Cell Biology
 1 Part I Molecular Cell Biology RNA Regulation: Advances in Molecular Biology and Medicine, First Edition. Edited by Robert A. Meyers. 2014 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. Published 2014 by Wiley-VCH
1 Part I Molecular Cell Biology RNA Regulation: Advances in Molecular Biology and Medicine, First Edition. Edited by Robert A. Meyers. 2014 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. Published 2014 by Wiley-VCH
CHK1 Inhibitor. Prexasertib, LY MsOH H 2 O. Drug Discovery Platform: Cancer Cell Signaling
 CHK1 Inhibitor Prexasertib, LY2606368 MsOH H 2 O Derived from Garrett MD and Collins I 1 ; Thompson R and Eastman A. 2 Drug Discovery Platform: Cancer Cell Signaling A Phase 2 Study of LY2606368 in Patients
CHK1 Inhibitor Prexasertib, LY2606368 MsOH H 2 O Derived from Garrett MD and Collins I 1 ; Thompson R and Eastman A. 2 Drug Discovery Platform: Cancer Cell Signaling A Phase 2 Study of LY2606368 in Patients
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS
 CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
Effects of AFP gene silencing on Survivin mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells
 mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors
 Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors Celeste Alverez Topic Seminar October 26, 2013 Celeste Alverez @ Wipf Group 10/26/2013 1 Protein Kinase D (PKD) A novel family of serine/threonine
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors Celeste Alverez Topic Seminar October 26, 2013 Celeste Alverez @ Wipf Group 10/26/2013 1 Protein Kinase D (PKD) A novel family of serine/threonine
Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 #19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Key words: apoptosis, beta-amyrin, cell cycle, liver cancer, tritepenoids
 JBUON 2018; 23(4): 965-970 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Antitumor effects of beta-amyrin in Hep-G2 liver carcinoma cells are
JBUON 2018; 23(4): 965-970 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Antitumor effects of beta-amyrin in Hep-G2 liver carcinoma cells are
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The New Breakout Stars in Cancer Treatment
 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The New Breakout Stars in Cancer Treatment 1 Introductions Peter Langecker, MD, PhD Executive Medical Director, Global Oncology Clinipace Worldwide Mark Shapiro Vice President
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The New Breakout Stars in Cancer Treatment 1 Introductions Peter Langecker, MD, PhD Executive Medical Director, Global Oncology Clinipace Worldwide Mark Shapiro Vice President
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
qpcr-array Analysis Service
 qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
Enhanced Anti-cancer Efficacy in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells by Combined Drugs of Metformin and Sodium Salicylate
 Biomedical Science Letters 2017, 23(3): 290~294 https://doi.org/10.15616/bsl.2017.23.3.290 eissn : 2288-7415 Brief Communication Enhanced Anti-cancer Efficacy in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells by Combined Drugs
Biomedical Science Letters 2017, 23(3): 290~294 https://doi.org/10.15616/bsl.2017.23.3.290 eissn : 2288-7415 Brief Communication Enhanced Anti-cancer Efficacy in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells by Combined Drugs
The effect of elemene reversing the multidurg resistance of A549/DDP lung cancer cells
 213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Comparative Evaluation of Silibinin Effects on Cell Cycling and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 and T47D Cell Lines
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative Evaluation of Silibinin Effects on Cell Cycling and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 and T47D Cell Lines Zohreh Jahanafrooz 1, Nasrin Motameh 1 *, Behnaz Bakhshandeh
RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative Evaluation of Silibinin Effects on Cell Cycling and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 and T47D Cell Lines Zohreh Jahanafrooz 1, Nasrin Motameh 1 *, Behnaz Bakhshandeh
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 #19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis: The role of apoptosis regulators. Joanne M. Bowen BHSc(Hons)
 Chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis: The role of apoptosis regulators. Joanne M. Bowen BHSc(Hons) Thesis submitted for degree of Doctor of Philosophy Department of Medicine The University of Adelaide
Chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis: The role of apoptosis regulators. Joanne M. Bowen BHSc(Hons) Thesis submitted for degree of Doctor of Philosophy Department of Medicine The University of Adelaide
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Assessment of cell survival (MTT) Assessment of early apoptosis and cell death
 Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 34: , Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Safat 13060, Kuwait
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 34: 513-532, 2014 Valproic acid, an anti-epileptic drug and a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with proteasome inhibitors exerts antiproliferative,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 34: 513-532, 2014 Valproic acid, an anti-epileptic drug and a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with proteasome inhibitors exerts antiproliferative,
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach
 Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk in a Chinese Han population
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology
 Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Johannes F Fahrmann and W Elaine Hardman *
 Fahrmann and Hardman Lipids in Health and Disease 2013, 12:36 RESEARCH Open Access Omega 3 fatty acids increase the chemo-sensitivity of B-CLL-derived cell lines EHEB and and of B-PLL-derived cell line
Fahrmann and Hardman Lipids in Health and Disease 2013, 12:36 RESEARCH Open Access Omega 3 fatty acids increase the chemo-sensitivity of B-CLL-derived cell lines EHEB and and of B-PLL-derived cell line
Supporting Information. FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce. apoptosis
 1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
Table S1. New colony formation 7 days after stimulation with doxo and VCR in JURKAT cells
 Table S1. New colony formation 7 days after stimulation with and in JURKAT cells drug co + number of colonies 7±14 4±7 48±11 JURKAT cells were stimulated and analyzed as in Table 1. Drug concentrations
Table S1. New colony formation 7 days after stimulation with and in JURKAT cells drug co + number of colonies 7±14 4±7 48±11 JURKAT cells were stimulated and analyzed as in Table 1. Drug concentrations
Butyrate induces cell apoptosis through activation of JNK MAP kinase pathway in human colon cancer RKO cells.
 Chem Biol Interact. 2010 May 14;185(3):174-81. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Butyrate induces cell apoptosis through activation of JNK MAP kinase pathway in human colon cancer RKO cells. Zhang Y, Zhou L, Bao YL, Wu
Chem Biol Interact. 2010 May 14;185(3):174-81. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Butyrate induces cell apoptosis through activation of JNK MAP kinase pathway in human colon cancer RKO cells. Zhang Y, Zhou L, Bao YL, Wu
A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor for treating lung cancer
 698358TUB1.1177/11428317698358Tumor BiologyXia et al. research-article217 Original Article A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor for treating lung cancer Tumor Biology April 217: 1 5 The Author(s)
698358TUB1.1177/11428317698358Tumor BiologyXia et al. research-article217 Original Article A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor for treating lung cancer Tumor Biology April 217: 1 5 The Author(s)
Tea polyphenol decreased growth and invasion in human ovarian cancer cells
 674480EJI0010.1177/1721727X16674480European Journal of InflammationHuang et al. research-article2016 Letter to the editor Tea polyphenol decreased growth and invasion in human ovarian cancer cells European
674480EJI0010.1177/1721727X16674480European Journal of InflammationHuang et al. research-article2016 Letter to the editor Tea polyphenol decreased growth and invasion in human ovarian cancer cells European
Types of cell death and apoptosis resistance mechanisms. Institut for Experimental Cancer Research
 Types of cell death and apoptosis resistance mechanisms Prof.Dr.rer. rer. nat.anna Trauzold Institut for Experimental Cancer Research Physiological cell death Embryogenesis Control of the tissue size Renewal
Types of cell death and apoptosis resistance mechanisms Prof.Dr.rer. rer. nat.anna Trauzold Institut for Experimental Cancer Research Physiological cell death Embryogenesis Control of the tissue size Renewal
Immunotherapie: algemene principes
 Immunotherapie: algemene principes Prof. dr. Evelien Smits Tumorimmunologie, UAntwerpen 14 Oktober 2017, IKG evelien.smits@uza.be Concept of immune evasion Finn O. J. Ann Oncol. 2012 Sep; 23(Suppl 8):
Immunotherapie: algemene principes Prof. dr. Evelien Smits Tumorimmunologie, UAntwerpen 14 Oktober 2017, IKG evelien.smits@uza.be Concept of immune evasion Finn O. J. Ann Oncol. 2012 Sep; 23(Suppl 8):
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
GMS 6644: Apoptosis. Introduction
 GMS 6644: Apoptosis Introduction (Feb. 15, 2006) Lei Xiao, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology UF Shands Cancer Center ARB Rm R4-250, 846-1199, lxiao@ufl.edu Outline of the Lecture Different types
GMS 6644: Apoptosis Introduction (Feb. 15, 2006) Lei Xiao, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology UF Shands Cancer Center ARB Rm R4-250, 846-1199, lxiao@ufl.edu Outline of the Lecture Different types
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets PUMA to promote host cell survival
 An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
Apoptotic cell signaling in cancer progression and therapyw
 Integrative Biology Dynamic Article Links Cite this: Integr. Biol., 2011, 3, 279 296 www.rsc.org/ibiology REVIEW ARTICLE Apoptotic cell signaling in cancer progression and therapyw Jessica Plati, a Octavian
Integrative Biology Dynamic Article Links Cite this: Integr. Biol., 2011, 3, 279 296 www.rsc.org/ibiology REVIEW ARTICLE Apoptotic cell signaling in cancer progression and therapyw Jessica Plati, a Octavian
NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals?
 The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis
 Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: Evidence for a regulatory loop between
Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: Evidence for a regulatory loop between
