Key words: Gastric carcinogenesis - NaC1 - N-Methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine - Rat stomach
|
|
|
- Amelia Hopkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 [Gann, 75, ; June, 1984] EFFECTS OF SODIUM CHLORIDE, SACCHARIN, PHENOBARBITAL AND ASPIRIN ON GASTRIC CARCINOGENESIS IN RATS AFTER INITIATION WITH N-METHYL-N'-NI TRO-N-NI TROSOGUAN I DINE Michihito TAKAHASHI, Takeshi KOKUBO, Fumio FURUKAWA, Yuji KUROKAWA and Yuzo HAYASHI Department of Pathology, National Institute of Hygienic Sciences, Kamiyoga , Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 158 Sodium chloride, saccharin sodium, phenobarbital sodium and aspirin were tested for tumor-promoting activity in the glandular stomach of rats after initiation with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) coupled with administration of a high salt diet. Male outbred Wistar rats were given MNNG in the drinking water (100 mg/liter) for 8 weeks, and during this period they were fed on diet supplemented with 10% sodium chloride. Thereafter, they were divided into 5 groups and fed on the basal diet or one of various diets supplemented with 10% sodium chloride, 5% saccharin, 0.05% phenobarbital or 1% aspirin until the end of the experiment. All animals were killed at the 40th experimental week for necropsy and histological examination. The incidence of adenocarcinoma was increased in the group given sodium chloride following initiation by MNNG and sodium chloride as compared with the group given MNNG and sodium chloride initiation only, but not significantly. However, the incidence of preneoplastic hyperplasia was significantly increased in this group. Saccharin also enhanced the development of adenocarcinomas of the glandular stomach. The results indicated that dietary administration of sodium chloride or saccharin after MNNG tends to promote tumor development. Phenobarbital or aspirin did not enhance tumor development, aspirin in fact rather showing a tendency to decrease the tumor incidence. Key words: Gastric carcinogenesis - NaC1 - N-Methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine - Rat stomach Epidemiologic data show that gastric cancer incidence is high in Japan" and eastern Europe, while its incidence has dramatically decreased in the United States." An epidemiological survey carried out on immigrants from Japan to the United States suggested that changes in their life style, especially in the diet, were responsible for the decrease in the incidence of stomach cancer observed in the second generation." These data suggest that dietary habit is a major environmental factor in gastric carcinogenesis.e' Furthermore, Doll and Peto" and Wynder and Gori28' have indicated, after epidemiological surveys of cancer in the United States, that, among the tumor sites associated with certain diets, gastrointestinal carcinomas have an especial claim to being an example where food-borne factors play an important role. Epidemiologic studies have repeatedly let to the conclusion that an increased sodium chloride content in the diet results in an increased incidence of gastric tumors.10' Sato et al.11, 20' and Hirayama8" 9' have found a close association of excess intake of salted foods with stomach 494 Gun
2 TUMOR PROMOTION IN GASTRIC CARCINOGENESIS cancer. Sodium chloride is thought to play a promoting role in the etiology of gastric cancer. Although attempts to induce gastric cancer in animals by feeding salted foods alone were unsuccessful,"' evidence was obtained suggesting a possible role for sodium chloride in experimental gastric carcinogenesis. We demonstrated experimentally in rats that an excess intake of sodium chloride increased tumor incidences in the forestomach induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4-NQO) and in the glandular stomach induced by N - methyl - N' - nitro - N - nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) when given to rats concomitantly with the carcinogen.25, 271 However, those results failed to establish a role for sodium chloride in the promotion of gastric carcinogenesis. Other previous work 21, 251 also failed to demonstrate promoter action of sodium chloride in the two-stage process of gastric carcinogenesis initiated by MNNG, probably because of inappropriate experimental designs. Therefore, utilizing a two-stage carcinogenesis model with MNNG plus sodium chloride treatment as the initiator, we examined the promoting effects of sodium chloride in gastric carcinogenesis and compared the results with the actions of saccharin sodium, a known bladder promoter '21 phenobarbital, a hepatic promoter,"" and aspirin, a mucosal damaging agent.") MATERIALS AND METHODS Seven-week-old male Wistar rats (Shizuoka Laboratory Center, Shizuoka) were housed in plastic cages, 5 rats/cage and maintained under constant conditions (23±2 temperature, 55±5% relative humidity and a 12-hr-light-12-hr-dark cycle). Two hundred and twenty rats were divided into 10 groups (40 rats in group 1 as a control given the initiation procedure alone and 20 rats in each of the other groups). The animals in groups 1 to 5 were given MNNG (Aldrich Chemicals, Inc., U.S.A.) continuously in their drinking water at a concentration of 100 mg/liter and were simultaneously administered the sodium chloride diet, a stock diet (Oriental MF, Oriental Yeast Co., Ltd., Tokyo) supplemented with 10% sodium chloride (Wako Pure Chemical Ind. Ltd., Tokyo), for the first 8 weeks. After this 8-week treatment period, the carcinogen solution was replaced by tap water. Groups 6 to 10 received neither MNNG nor sodium chloride diet in the first 8 weeks of the experiment and served as negative controls maintained on stock diet alone. The animals in groups 1 and 6 were control groups which received the stock diet without any supplementation during the promotion stage. Animals in groups 2 and 7 were fed the 10% sodium chloride diet during the promotion stage (week 8 to week 40). Animals in groups 3 and 8 were maintained on diet supplemented with 5% saccharin (Oriental Pharmaceutical & Synthetic Chemical Co., Ltd., Osaka), while groups 4 and 9 received 0.05% phenobarbital (Iwaki Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tokyo) diet, and groups 5 and 10 received the 1% aspirin (Tokyo Kasei Kogyo Co., Ltd., Tokyo) diet during the promotion stage. All animals had free access to food and water. The experimental animals were examined and weighed weekly. Necropsies were performed on all animals which died or which were killed after becoming moribund, except for a few animals in each group which died in the early stages of the experiment. At the end of the 40th experimental week, all surviving animals were sacrificed and autopsied. Animals which survived for more than 30 weeks were included in the effective numbers of rats. The stomach and other organs were subjected to careful macroscopic examination and then fixed in 10% buffered formalin, prepared for histology by routine methods, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H-E). The tumor incidences were analyzed by Fisher's exact probability test and/or the chi-squared test. RESULTS During the initiation period the growth of animals was significantly affected by the presence of MNNG in the drinking water and simultaneous administration of the sodium chloride-supplemented diet. Animals receiving MNNG (groups 1 to 5) showed a marked repression of weight gain (Fig. 1) when compared to MNNG-untreated animals (groups 6 to 10). After cessation of MNNG administration (at 8 weeks), these weight-deficient animals showed a com- 75(6)
3 M. TAKAHASHI, ET AL. Fig. 1. Mean body weight gain of rats fed various diets beginning after the 8th experimental week Animals in groups I to 5 were treated with both MNNG and sodium chloride whereas groups 6 to 10 were maintained on control diet as negative controls. Fig. 2. Preneoplastic hyperplasia showing irregularly arranged glands. H-E. X Gam
4 TUMOR PROMOTION IN GASTRIC CARCINOGENESIS pensatory increase in growth rate although their weights at the termination of the experiment were still lower than those in MNNG-untreated groups. Body weight gains of rats in the different MNNG-treated groups were similar to each other and to the control (group 1) during the promotion period with the exception that in rats receiving the aspirin - supplemented diet (group 5) a marked retardation of growth as compared to the other groups (groups I to 4) was observed. A similar response was observed in group 10 when compared with groups 6 to 9. Gastric tumors were predominantly located in the pyloric region and were grossly observed as plaque-like or nodular lesions with ulceration. MNNG-induced histological lesions in the glandular stomach have been classified simply into 2 categories (Table I) : preneoplastic hyperplasias and adenocarcinomas. Preneoplastic hyperplasias were defined as proliferative, noninvasive mucosal lesions which were located predominantly in the pyloric region. These lesions have previously been known as adenomatous hyperplasia or adenoma 211 but, since they are considered to be the earliest manifestation of carcinogen-induced growth abnormalities in the stomach, the term preneoplastic seems appropriate (Fig. 2). Adenocarcinomas showed irregular glandular structures lined by moderately atypical, darkly stained, or mucin-producing columnar epithelium with enlarged nuclei. Most were relatively well-differentiated and composed of a typical glandular structure with a tubular pattern and cellular or structural atypism. The degree of invasiveness of adenocarcinomas varied from submucosal penetration to involvement of the deeper layers of the stomach wall. No metastasis was found. Pyloric metaplasias are focal abnormalities of the fundic mucosa and represent a type of regenerative lesion after carcinogeninduced damage to the fundic mucosa. Pyloric metaplasias were present in the stomach of many MNNG-treated rats and were apparently unrelated to cancers or sodium chloride; therefore, their incidence is not reported in the table. No lesions were apparent in the fundic region. Table I summarizes the occurrence of gastroduodenal tumors in the various experimental groups (data for groups 6 to 10 are omitted). The incidence of gastric adenocarcinoma tended to increase in sodium chloride-treated rats (group 2) and saccharin-treated rats (group 3) compared to basal diet rats (group 1). In addition, these groups showed higher incidences of preneo- Table I. Promotion Effects of Various Chemicals on Gastroduodenal Carcinogenesis Initiated by MNNG and NaCI Treatment in Male Wistar Rats *P<0.05. a) I fibrosarcoma and 1 hemangiosarcoma. b) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Data for groups 6-10 are ommitted. 75(6)
5 M. TAKAHASHI, ET AL. plastic hyperplasias, the difference being significant (P<0.05) in the case of the sodium chloride-treated group. However, the numbers of adenocarcinomas and preneoplastic hyperplasias were not increased in the rats fed phenobarbital or aspirin as compared with the controls. The incidence of duodenal adenocarcinoma did not differ among the treated and control groups although there seemed to be a slight increase in the sodium chloride-treated group. As compared to normal gastric mucosa, diffuse deep gastric pits with a clearly increased number of mucous neck cells in the fundic mucosa were the major finding in the sodium chloride-treated rats (groups 2 and 7). Diffuse alterations in the fundic mucosa were also observed in saccharin-treated rats (groups 3 and 8) where the thickness of the zone of proliferating cells was clearly increased. Histological examination of the mucosa of aspirin-treated animals (groups 5 and 10) revealed the presence of focal erosions or even ulcers, penetrating to a depth of up to the base of the glandular mucosa, flanked by apparently normal tissue. In the phenobarbital-treated rats (groups 4 and 9), the glandular stomach mucosa were intact. Adenocarcinomas of the duodenum were found mostly within 10 cm of the pyloroduodenal junction as localized swellings. The lumenal surface of the tumors was papillary, nodular, or ulcerative. All duodenal adenocarcinomas were well differentiated and of tubular structure. Although malignant tumors outside of the gastroduodenal tract were rare, one hepatocellular carcinoma was found in the initiation plus phenobarbital-treated group (group 4). DISCUSSION Tumor promotion has been widely investigated in several organs such as the skin, liver, kidney, urinary bladder, mammary gland, and thyroid. In the stomach, although croton oil has been experimentally shown to be a promoter in rats by Matsukura et a1.,15' other studies, including our previous experiment, failed to demonstrate tumor. promoting activity of chemicals in twostage rat glandular stomach tumorigenesiṣ22. 25) In the mouse skin model, a single administration of a very small amount of carcinogen such as 7,12 - dimethylbenz [a] anthracene is sufficient for initiation. In contrast, with the glandular epithelium of the stomach, a relatively long period of administration of a carcinogen is required for initiation. The rat MNNG model for gastric carcinogenesis has provided a suitable system for evaluation of the modifying effects of chemicals on gastric carcinogenesis. Even in this model, however, treatment with MNNG alone for over 12 weeks is necessary for induction of a basal level of preneoplastic lesions. "I On the other hand, when combined with administration of a high concentration of sodium chloride, an 8-week treatment with MNNG results in a low incidence of gastric tumors in rats. Our previous experiment demonstrated a significant modifying effect of sodium chloride on the initiation stage of MNNG-carcinogenesis in rats"' and sodium chloride might act as co-initiator. The present investigation has confirmed our previous observation. It was also demonstrated that subsequent administration of sodium chloride or saccharin increased the incidence of neoplastic and preneoplastic lesions of the glandular stomach in rats. This result suggests a possible promoting effect of sodium chloride or saccharin on MNNG-induced gastric tumors in rats. However, the difference is only significant with respect to preneoplastic hyperplasias in the group receiving sodium chloride. One possible reason is the short duration of the experiment, limiting the potential of the compounds to promote the development of adenocarcinomas. Further confirmation is required regarding the 498 Gano
6 TUMOR PROMOTION IN GASTRIC CARCINOGENESIS promoting effect of saccharin on gastric carcinogenesis. The histological classification of the MNNG-induced lesions in Table I was similar to that in previous studies.25, 26) Although the tumor types occurring in each group appeared to be unrelated to the subsequent treatment with chemicals, the incidence of each lesion was higher in group 2 than group 1; 4 adenocarcinomas (20%) and 8 preneoplastic hyperplasias (40%) were found in the pyloric area in group 2 compared with only 7.7% of adenocarcinomas and 12.8% incidences of preneoplastic hyperplasias in group 1. Since the progression of MNNG-induced lesions from preneoplastic hyperplasias to adenocarcinomas has been well characterized,", 12) the results provide strong evidence for a promoting action of sodium chloride in gastric carcinogenesis. In our experiment, as in several previous experiments using MNNG, tumors of the duodenum also occurred, treatment with MNNG in combination with sodium chloride serving as with gastric carcinogenesis to in creasethe yield of carcinomas. The mechanisms underlying the effect of sodium chloride on gastric carcinogenesis remain unclear. One possibility is that initiation is indirectly enhanced by gastric irritation and damage to the mucous membrane. The gastric mucosa contains several kinds of acid mucopolysaccharides, including hyaluronic acid, the viscosity of which is known to decrease markedly in the presence of sodium chloride. It has earlier been proposed that the mucosal barrier in the glandular stomach is important in preventing the induction of stomach carcinomas in rats27 and sodium chloride might reduce its protective action by allowing easier access of the carcinogen and therefore increased damage to the gastric mucosa to occur. Although the mechanism of action of various organospecific promoters is unclear, one common observation during the promoting stage is the induction of hyperplasia or of increased DNA synthesis in target sites." 5.17 In this study it was also shown that the enhancing treatments with sodium chloride and saccharin induced diffuse proliferative changes in the superficial epithelium or generative zone of the glandular stomach, whereas the nonenhancers, phenobarbital and aspirin, showed neither effect, although focal erosive lesions could be seen in the aspirin groups. Such a proliferation-stimulating mechanism found diffusely in the gastric mucosa could be important in enhancing gastric carcinogenesis by sodium chloride and saccharin. However, elucidation of the exact biochemical alterations underlying the effect of sodium chloride or saccharin on glandular stomach tumors will require further investigation. In this study, phenobarbital did not increase tumor incidence, and aspirin appeared to show an inhibitory activity, although because of the relatively low incidence of gastric tumors in the control group in this experiment, no statistical significance of the effect could be established. However, the tendency for a decrease of gastric tumors observed in group 5 might be expected in relation to the pharmacological properties of aspirin, which acts as a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis."' In animal studies, prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors, such as indomethacin and aspirin, have been reported to be effective in reducing the rate of tumor growth in a number of gastrointestinal sites. 16, 16, 24) Further studies are needed to evaluate fully the inhibitory effect of aspirin on gastric carcinogenesis. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Dr. M. A. Moore in the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Cancer Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture (1982, 1983). (Received Feb. 14, 19841Accepted April 26, 1984) 75(6)
7 REFERENCES 1) Baird, W. M., Sedgwick, J. A. and Boutwell, R. K. Effects of phorbol and four diesters of phorbol on the incorporation of tritiated precursors into DNA, RNA and protein in mouse epidermis. Cancer Res., 31, (1971). 2) Cohen, S. M., Arai, M., Jacobs, J. B. and Friedell, G. H. Promoting effect of saccharin and DL-tryptophan in urinary bladder carcinogenesis. Cancer Res., 39, (1979). 3) Devesa, S. S. and Silverman, D. T. Trends in incidence and mortality in the United States. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol., 3, (1981). 4) Doll, R. and Peto, R. The causes of cancer: quantitative estimates of the avoidable risks of cancer in the United States today. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 66, (1981). 5) Fukushima, S and Cohen, S. M. Saccharininduced hyperplasia of the rat urinary bladder. Cancer Res., 40, (1980). 6) Habs, M. and Schmahl, D. Diet and cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol., 96, 1-10 (1980). 7) Haenszel, W., Kurihara, M., Segi, M. and Lee, R. K. C. Stomach cancer among Japanese in Hawaii. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 49, (1972). 8) Hirayama, T. Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Gann Monogr., 11, 3-19 (1971). 9) Hirayama, T. The epidemiology of cancer of the stomach in Japan; with special reference to the role of diet. Gann Monogr., 3, (1968). 10) Joossens, J. V. and Ceboers, J. Nutrition and gastric cancer. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 40, (1981). 11) Kobori, 0. Analytical study of precancerous lesions in rat stomach mucosa induced by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Gann Monogr., 25, (1980). 12) Kuroishi, T., Tominaga, S., Hirose, K. and Segi, M. Cancer mortality in Japan. Gann Monogr., 26, 1-91 (1981). 13) Lynch, N. R., Castes, M., Astoin, M. and Salomon, J. C. Mechanism of inhibition of tumor growth by aspirin and indomethacin. Br. J. Cancer, 38, (1978). 14) Mann, N. S. and Sachdev, A. J. Gastric effects of aspirin vs ketoprofen and ibuprofen. Gastroenterology, 68, 944 (1975). 15) Matsukura, N., Kawachi, T., Sato, T., Sasajima, K. and Sugimura, T. Promoting action of croton oil on gastrocarcinogenesis by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine M. TAKAHASHI, ET AL. in rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol., 93, (1979). 16) Narisawa, T., Sato, M., Tani, M., Takahashi, T. and Goto, A. Inhibition of development of methylnitrosourea - induced rat colon tumors by indomethacin treatment. Cancer Res., 41, (1981). 17) Peraino, C., Fry, R. J. M., Staffeldt, E. and Christopher, J. P. Comparative enhancing effects of phenobarbital, amobarbital, diphenylhydantoin, and dichlorodiphenyl. trichloroethane on 2-acetylaminofluorene. induced hepatic turnorigenesis in the rat. Cancer Res., 35, (1974). 18) Pollard, M. and Luckert, P. H. Indometh. acin treatment of rats with dimethylhydra. zine-induced intestinal tumors. Cancer Treat. Rep., 64, (1980). 19) Sato, T., Fukuyama, T., Suzuki, T., Taka. yanagi, J., Murakami, T., Shiotsuki, N., Tanaka, R. and Tsuji, R. Studies of the causation of gastric cancer. Bull. Inst. Public Health, 8, (1959). 20) Sato, T., Fukuyama, T., Urata, G. and Suzuki, T. Studies of the causation of gastric cancer. 1. Bleeding in the glandular stomach of mice by feeding with highly salted foods, and a comment on salted foods in Japan. Bull. Inst. Public Health, 8, (1959). 21) Shirai, T. Periodical observations of the glandular stomach in rats treated with N - methyl - N'- nitro - N - nitrosoguanidine. Nagoya Med. J., 19, (1974). 22) Shirai, T., Imaida, K., Fukushima, S., Hasegawa, R., Tatematsu, M. and Ito, N. Effects of NaCl, Tween 60 and a low dose of N-ethyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine on gastric carcinogenesis of rat given a single dose of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Carcinogenesis, 3, (1982). 23) Shirai, T., Takahashi, M., Fukushima, S., Tatematsu, M., Hirose, M. and Ito, N. Induction of preneoplastic hyperplasia and carcinoma by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitroh soguanidine from regenerated mucosa of ulcers induced by iodoacetamide in fundus of rat stomach. Gann, 69, (1978)- 24) Smith, B. J., Wills, M. R. and Savory, J Prostaglandins and cancer. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci., 13, (1983). 25) Takahashi, M., Kokubo, T., Furukawa, F., Kurokawa, Y., Tatematsu, M. and Haya14 Y. Effect of high salt diet on rat gastric carcinogenesis induced by N-methyl-N'- nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine. Gann, 74, (1983). 500 Gs
8 TUMOR PROMOTION IN GASTRIC CARCINOGENESIS 26) Takahashi, M., Shirai, T., Fukushima, S., Ito, N., Kokubo, T., Furukawa, F. and Kurata, Y. Ulcer formation and associated tumor production in multiple sites within the stomach and duodenum of rats treated with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 67, (1981). 27) Tatematsu, M., Takahashi, M., Fukushima, S., Hananouchi, M. and Shirai, T. Effects in rats of sodium chloride on experimental gastric cancers induced by N-methyl-N'- nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine or 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 55, (1975). 28) Wynder, E. L. and Gori, G. B. Contribution of the environmental cancer incidence: an epidemiologic exercise. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 58, (1977). 75(6)
NOTE. [GANN, 65, ; August, 1974]
![NOTE. [GANN, 65, ; August, 1974] NOTE. [GANN, 65, ; August, 1974]](/thumbs/83/88553148.jpg) NOTE [GANN, 65, 371-376; August, 1974] COMBINED EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON GASTRIC CARCINO- GENESIS IN RATS TREATED WITH N-METHYL-N'-NITRO-N-NITROSOGUANI- DINE*1 Shoji FUKUSHIMA, Masae TATEMATSU,
NOTE [GANN, 65, 371-376; August, 1974] COMBINED EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON GASTRIC CARCINO- GENESIS IN RATS TREATED WITH N-METHYL-N'-NITRO-N-NITROSOGUANI- DINE*1 Shoji FUKUSHIMA, Masae TATEMATSU,
Go AKAGI, AKIKO AKAGI, Masuo KIMURA, and Hisashi OTSUKA (2nd Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Tokushima University*2) Synopsis
 [GANN, 64, 331-336; August, 1973] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.62] COMPARISON OF BLADDER TUMORS INDUCED IN RATS AND MICE WITH N-BUTYL-N-(4-HYDROXYBUTYL)- NITROSOAMINE*1 (Plates LIII-LV) Go AKAGI, AKIKO AKAGI,
[GANN, 64, 331-336; August, 1973] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.62] COMPARISON OF BLADDER TUMORS INDUCED IN RATS AND MICE WITH N-BUTYL-N-(4-HYDROXYBUTYL)- NITROSOAMINE*1 (Plates LIII-LV) Go AKAGI, AKIKO AKAGI,
ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE. (Plates I-V)
 [GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
[GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study. of Diphenylamine. in F344 Rats
 Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
EFFECT OF VARIOUS FACTORS ON INDUCTION OF URINARY BLADDER TUMORS IN ANIMALS BY N-BUTYL-N-(4-HYDROXYBUTYL) NITROSOAMINE
 [GANN, 64, 151-159; April, 1973] UDC 615.277.4: 616-006-021.6[616.62] EFFECT OF VARIOUS FACTORS ON INDUCTION OF URINARY BLADDER TUMORS IN ANIMALS BY N-BUTYL-N-(4-HYDROXYBUTYL) NITROSOAMINE (Plate XXI)
[GANN, 64, 151-159; April, 1973] UDC 615.277.4: 616-006-021.6[616.62] EFFECT OF VARIOUS FACTORS ON INDUCTION OF URINARY BLADDER TUMORS IN ANIMALS BY N-BUTYL-N-(4-HYDROXYBUTYL) NITROSOAMINE (Plate XXI)
of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice
 Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Tumorigenicity Study of Sodium Erythorbate Administered Orally to Mice
 Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol.38, No.3, 135-139, September, 1989 HJM 38-23 135 Tumorigenicity Study of Sodium Erythorbate Administered Orally to Mice Kouki NA, Hiroshi AKAMZU, Ryozo ETO, Toshihiro NSHDA,
Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol.38, No.3, 135-139, September, 1989 HJM 38-23 135 Tumorigenicity Study of Sodium Erythorbate Administered Orally to Mice Kouki NA, Hiroshi AKAMZU, Ryozo ETO, Toshihiro NSHDA,
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1
 TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study. of Isopropyl Acetate. in F344 Rats
 Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Isopropyl Acetate in F344 Rats March 2009 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Isopropyl Acetate in F344 Rats March 2009 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Masao Hirose 1, Yasuko Takesada, Hikaru Tanaka, Seiko Tamano, Toshio Kato and Tomoyuki Shirai
 Carcinogenesis vol.19 no.1 pp.207 212, 1997 Carcinogenicity of antioxidants BHA, caffeic acid, sesamol, 4-methoxyphenol and catechol at low doses, either alone or in combination, and modulation of their
Carcinogenesis vol.19 no.1 pp.207 212, 1997 Carcinogenicity of antioxidants BHA, caffeic acid, sesamol, 4-methoxyphenol and catechol at low doses, either alone or in combination, and modulation of their
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study. of Tetrachloroethylene. in BDF 1 Mice
 Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Tetrachloroethylene in BDF 1 Mice March 1993 Japan Bioassay Laboratory Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Tetrachloroethylene in BDF 1 Mice March 1993 Japan Bioassay Laboratory Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and
Flow Cytometric Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Chloride on Gastric Cancer Risk in the Rat1
 [CANCER RESEARCH 45, 5608-5616. November 1985] Flow Cytometric Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Chloride on Gastric Cancer Risk in the Rat1 Gail Charnley2 and Steven R. Tannenbaum3 Massachusetts Institute
[CANCER RESEARCH 45, 5608-5616. November 1985] Flow Cytometric Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Chloride on Gastric Cancer Risk in the Rat1 Gail Charnley2 and Steven R. Tannenbaum3 Massachusetts Institute
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals
 FORMALDEHYDE 171 3.1 Inhalation 3.1.1 Mouse 3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals Groups of 4260 C3H mice [sex and age unspecified] were exposed to concentrations of 0, 50, 100 or 200 mg/m 3 formaldehyde
FORMALDEHYDE 171 3.1 Inhalation 3.1.1 Mouse 3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals Groups of 4260 C3H mice [sex and age unspecified] were exposed to concentrations of 0, 50, 100 or 200 mg/m 3 formaldehyde
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
5/2/2018. Low Grade Dysplasia of GI Tract. High Grade Dysplasia of GI Tract. Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues
 Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues Arief Suriawinata, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Department of Pathology and
Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues Arief Suriawinata, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Department of Pathology and
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin
 Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin Hironori TANAKA, Yoshimi KUWAHARA and Susumu OKABE Department of Applied Pharmacology,
Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin Hironori TANAKA, Yoshimi KUWAHARA and Susumu OKABE Department of Applied Pharmacology,
Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 213-217, 1984 Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats By Gary A. Boorman* and Scot L. Eustis* While the rat pancreas is susceptible
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 213-217, 1984 Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats By Gary A. Boorman* and Scot L. Eustis* While the rat pancreas is susceptible
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer. Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
[GANN, 65, ; August, 1974] ADENOMATOUS POLYPS OF LARGE INTESTINE IN AUTOPSY AND SURGICAL MATERIALS
![[GANN, 65, ; August, 1974] ADENOMATOUS POLYPS OF LARGE INTESTINE IN AUTOPSY AND SURGICAL MATERIALS [GANN, 65, ; August, 1974] ADENOMATOUS POLYPS OF LARGE INTESTINE IN AUTOPSY AND SURGICAL MATERIALS](/thumbs/87/96461832.jpg) [GANN, 65, 295-306; August, 1974] ADENOMATOUS POLYPS OF LARGE INTESTINE IN AUTOPSY AND SURGICAL MATERIAL*1 Eiichi SATO Department of Pathology, Tohoku University School of Medicine*2 A study of the large
[GANN, 65, 295-306; August, 1974] ADENOMATOUS POLYPS OF LARGE INTESTINE IN AUTOPSY AND SURGICAL MATERIAL*1 Eiichi SATO Department of Pathology, Tohoku University School of Medicine*2 A study of the large
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R
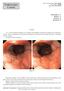 Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Synthesis of N-Butyl-N-nitrosourethan (BNUR) BNUR was synthesized as follows:
 [GANN, 65, 227-236; June, 1974] INDUCTION OF TUMORS OF THE FORESTOMACH, ESOPHAGUS, PHARYNX, AND ORAL CAVITY OF THE DONRYU RAT GIVEN N-BUTYL-N-NITROSOURE- THAN IN THE DRINKING WATER*1 Masaya TAKEUCHI,*2
[GANN, 65, 227-236; June, 1974] INDUCTION OF TUMORS OF THE FORESTOMACH, ESOPHAGUS, PHARYNX, AND ORAL CAVITY OF THE DONRYU RAT GIVEN N-BUTYL-N-NITROSOURE- THAN IN THE DRINKING WATER*1 Masaya TAKEUCHI,*2
The international health care burden of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract and liver
 The international health care burden of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract and liver William R. Brown 1*, Dennis J. Ahnen 2 1 Department of Medicine, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver,
The international health care burden of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract and liver William R. Brown 1*, Dennis J. Ahnen 2 1 Department of Medicine, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver,
A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS
 A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS KANEMATSU SUGIURA AND STANLEY R. BENEDICT (From tha Huntington Fund for Cancer hearch, Memorial Hoepitcrl and the Hamman Raearch Fund, New York) In recent
A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS KANEMATSU SUGIURA AND STANLEY R. BENEDICT (From tha Huntington Fund for Cancer hearch, Memorial Hoepitcrl and the Hamman Raearch Fund, New York) In recent
Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and
 Gut, 1977, 18, 214-218 Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and large intestine I. YOKOYAMA, S. KOZUKA, K. ITO, K. KUBOTA, Y. YOKOYAMA, AND T. KONDO From the Second Department of Surgery and the Second
Gut, 1977, 18, 214-218 Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and large intestine I. YOKOYAMA, S. KOZUKA, K. ITO, K. KUBOTA, Y. YOKOYAMA, AND T. KONDO From the Second Department of Surgery and the Second
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
Increasing Trend in the Incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Japan
 Cancer Increasing Trend in the Incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Japan JMAJ 46(6): 251 256, 2003 Susumu KODAIRA Professor, Department of Surgery, Teikyo University School of Medicine Abstract: Malignant
Cancer Increasing Trend in the Incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Japan JMAJ 46(6): 251 256, 2003 Susumu KODAIRA Professor, Department of Surgery, Teikyo University School of Medicine Abstract: Malignant
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
The surface mucous cells and the cardiac and pyloric glands secrete mucus which protects the stomach from self-digestion.
 PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Hepatocarcinogenesis: chemical models
 Hepatocarcinogenesis: chemical models Introduction Earliest observations that human exposure to certain chemicals is related to an increased incidence of cancer John Hill 1761 Nasal cancer in snuff users
Hepatocarcinogenesis: chemical models Introduction Earliest observations that human exposure to certain chemicals is related to an increased incidence of cancer John Hill 1761 Nasal cancer in snuff users
colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer hereditary sporadic Familial 1/12/2018
 colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
The Incidence and Significance of Villous Change in Adenomatous Polyps
 The Incidence and Significance Villous Change in Adenomatous Polyps CHRISTOPHER H. K. FUNC, M.D., AND HARVEY GOLDMAN, M.D. Department Pathology, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Hospital, Boston,
The Incidence and Significance Villous Change in Adenomatous Polyps CHRISTOPHER H. K. FUNC, M.D., AND HARVEY GOLDMAN, M.D. Department Pathology, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Hospital, Boston,
Threshold-Based Risk Assessment is the Same for Cancer and Non-cancer Endpoints for Non-DNA Reactive Carcinogens
 Threshold-Based Risk Assessment is the Same for Cancer and Non-cancer Endpoints for Non-DNA Reactive Carcinogens Samuel M. Cohen, MD, PhD Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical
Threshold-Based Risk Assessment is the Same for Cancer and Non-cancer Endpoints for Non-DNA Reactive Carcinogens Samuel M. Cohen, MD, PhD Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
 Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
UNIVERSA MEDICINA. Evaluation of the oral toxicity of formaldehyde in rats
 UNIVERSA MEDICINA July-September, 2008 Vol.27 - No.3 Evaluation of the oral toxicity of formaldehyde in rats David *a, and Hanslavina Arkeman * ABSTRACT *Department of Histology, Medical Faculty, Trisakti
UNIVERSA MEDICINA July-September, 2008 Vol.27 - No.3 Evaluation of the oral toxicity of formaldehyde in rats David *a, and Hanslavina Arkeman * ABSTRACT *Department of Histology, Medical Faculty, Trisakti
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA
 A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2
 Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2 Daniel S. Longnecker 3 and Barbara G. Crawford 3.4 SUMMARY-Long-term studies of the carcinogenicity of azaserine in
Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2 Daniel S. Longnecker 3 and Barbara G. Crawford 3.4 SUMMARY-Long-term studies of the carcinogenicity of azaserine in
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 66: 113-117, 1974 Copyright 1974 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 66, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING KARIM
GASTROENTEROLOGY 66: 113-117, 1974 Copyright 1974 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 66, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING KARIM
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 17: 1051-1055, 2007 Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma SUN-YOUNG LEE 1, HYE SEUNG HAN 2, KYUNG YUNG LEE 3, TAE SOOK HWANG 2, JEONG HWAN KIM 1, IN-KYUNG SUNG
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 17: 1051-1055, 2007 Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma SUN-YOUNG LEE 1, HYE SEUNG HAN 2, KYUNG YUNG LEE 3, TAE SOOK HWANG 2, JEONG HWAN KIM 1, IN-KYUNG SUNG
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
Page # 1. Endometrium. Cellular Components. Anatomical Regions. Management of SIL Thomas C. Wright, Jr. Most common diseases:
 Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
 PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
Polyps in general: is a descriptive term of forming a mass that is exophytic & polypoid.
 ميحرلا نمحرلا هللا مسب Gastric Tumors: Benign tumours & tumor-like conditions: -Mucosal: Gastric polyps (they are uncommon) -Mesenchymal tumours: Leiomyoma & Lipoma (can occur anywhere in the body) Malignant:
ميحرلا نمحرلا هللا مسب Gastric Tumors: Benign tumours & tumor-like conditions: -Mucosal: Gastric polyps (they are uncommon) -Mesenchymal tumours: Leiomyoma & Lipoma (can occur anywhere in the body) Malignant:
Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease
 Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease Edited by J.H.STEWART Associate Dean, Western Clinical School University of Sydney, Australia Oxford New York Tokyo Melbourne OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS
Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease Edited by J.H.STEWART Associate Dean, Western Clinical School University of Sydney, Australia Oxford New York Tokyo Melbourne OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS
Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data. March, 2003
 Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data March, 2003 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data March, 2003 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis
 Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
Morphogenesis of Minute Adenomas in Familial Polyposis Co1i 1,2
 Morphogenesis of Minute Adenomas in Familial Polyposis Co1i 1,2 Shin-ichi Nakamura 3 and Isamu Kino 3,4,5 ABSTRACT-The morphogenesis of minute colonic adenomas was investigated by complete serial sectioning
Morphogenesis of Minute Adenomas in Familial Polyposis Co1i 1,2 Shin-ichi Nakamura 3 and Isamu Kino 3,4,5 ABSTRACT-The morphogenesis of minute colonic adenomas was investigated by complete serial sectioning
Case Report Adenocarcinoma In Situ Arising from Brunner s Gland Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
 Hindawi Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 7916976, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7916976 Case Report Adenocarcinoma In Situ Arising from Brunner s Gland Treated by
Hindawi Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 7916976, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7916976 Case Report Adenocarcinoma In Situ Arising from Brunner s Gland Treated by
Clinicopathological Characteristics of Superficial Type
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
Proliferative Lesions of the Glandular Stomach and Liver in F344 Rats Fed Diets Containing Aroclor 1254
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 60, pp. 89-95, 1985 Proliferative Lesions of the Glandular Stomach and Liver in F344 Rats Fed Diets Containing Aroclor 1254 by Jerrold M. Ward* Aroclor 1254 was fed
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 60, pp. 89-95, 1985 Proliferative Lesions of the Glandular Stomach and Liver in F344 Rats Fed Diets Containing Aroclor 1254 by Jerrold M. Ward* Aroclor 1254 was fed
Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3
 Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3 Takaaki Ohmori, 4,5 Kenshi Watanabe, 4,6 and Gary M. Williams 4,7, e, 9 ABSTRACT-Fragments of normal
Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3 Takaaki Ohmori, 4,5 Kenshi Watanabe, 4,6 and Gary M. Williams 4,7, e, 9 ABSTRACT-Fragments of normal
Experimental Induction of Ovarian Sertoli
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 73, pp. 115-123, 1987 Experimental Induction of Ovarian Sertoli Cell Tumors in Rats by N-Nitrosoureas by Akihiko Maekawa,* H. Onodera,* H. Tanigawa,* K. Furuta,*
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 73, pp. 115-123, 1987 Experimental Induction of Ovarian Sertoli Cell Tumors in Rats by N-Nitrosoureas by Akihiko Maekawa,* H. Onodera,* H. Tanigawa,* K. Furuta,*
Acta Med. Okayama Vol. 70, No. 2. Iwamuro et al.
 140 Iwamuro et al. cta Med. Okayama Vol. 70, No. 2 emission tomography (PET) scanning showed tracer uptake in the spleen and iliac bone as well as in the swollen lymph nodes. There were no abnormalities
140 Iwamuro et al. cta Med. Okayama Vol. 70, No. 2 emission tomography (PET) scanning showed tracer uptake in the spleen and iliac bone as well as in the swollen lymph nodes. There were no abnormalities
MECHANISM BY WHICH FAT IN THE UPPER SMALL INTESTINE INHIBITS GASTRIC ACID
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.3 Printea in U.S.A. MECHANISM BY WHICH FAT IN THE UPPER SMALL INTESTINE INHIBITS GASTRIC ACID H. T. DEBAS, M.D., B. S. BEDI, M.B.,
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.3 Printea in U.S.A. MECHANISM BY WHICH FAT IN THE UPPER SMALL INTESTINE INHIBITS GASTRIC ACID H. T. DEBAS, M.D., B. S. BEDI, M.B.,
Gastric Carcinoma in Young Adults. Hitoshi Katai, Mitsuru Sasako, Takeshi Sano and Keiichi Maruyama
 Gastric Carcinoma in Adults Hitoshi Katai, Mitsuru Sasako, Takeshi Sano and Keiichi Maruyama Department of Surgical Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo ' Among 4608 patients with gastric carcinoma
Gastric Carcinoma in Adults Hitoshi Katai, Mitsuru Sasako, Takeshi Sano and Keiichi Maruyama Department of Surgical Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo ' Among 4608 patients with gastric carcinoma
chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium
 chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium CHAPTER 1 All squamous cervical cancer (and probably all cervical adenocarcinoma) is associated with oncogenic HPV, and the absence
chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium CHAPTER 1 All squamous cervical cancer (and probably all cervical adenocarcinoma) is associated with oncogenic HPV, and the absence
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Clinicopathological Study of Mass-forming Gallbladder Cancer Focusing on the Grade of Cellular Dysplasia
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 30 1, 35 42, March 2018 Original Clinicopathological Study of Mass-forming Gallbladder Cancer Focusing on the Grade of Cellular Dysplasia Nobukazu SHIMA 1, Nobuyuki OHIKE 2), Reika
Showa Univ J Med Sci 30 1, 35 42, March 2018 Original Clinicopathological Study of Mass-forming Gallbladder Cancer Focusing on the Grade of Cellular Dysplasia Nobukazu SHIMA 1, Nobuyuki OHIKE 2), Reika
ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1. ed by cytotoxicity tests. Cells from leukemia without thymus involvement
 [Gann, 66, 37-42; February, 1975] ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1 Hayase SHISA, Yasue MATSUDAIRA, Hiroshi HIAI, and Yasuaki NISHIZUKA Laboratory of Experimental
[Gann, 66, 37-42; February, 1975] ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1 Hayase SHISA, Yasue MATSUDAIRA, Hiroshi HIAI, and Yasuaki NISHIZUKA Laboratory of Experimental
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications
 594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions.
 Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Clinicopathological Study on Gastri Murata, Ikuo; Oda, Hidetoshi; Muta, Nakamuta, Kohji; Tsuruta, Hideo; Oh Makiyama, Kazuya; Hara, Kohei Citation Acta
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Clinicopathological Study on Gastri Murata, Ikuo; Oda, Hidetoshi; Muta, Nakamuta, Kohji; Tsuruta, Hideo; Oh Makiyama, Kazuya; Hara, Kohei Citation Acta
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy
 Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10
 > Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10 stage iii; Carcinoma of colon, stage iv; Colon cancer metastatic to unspecified site; Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer; Malignant tumor of colon; Metastasis.
> Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10 stage iii; Carcinoma of colon, stage iv; Colon cancer metastatic to unspecified site; Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer; Malignant tumor of colon; Metastasis.
The usual dose is 40 mg daily with amoxycillin 1.5 g (750 mg b.d.) for 2 weeks. Up to 2 g/day of amoxycillin has been used in clinical trials.
 Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Avances en patología gástrica. Novedades de la clasificación WHO (2010)
 XXV Congreso de la Sociedad Española de Anatomía Patológica y División Española de la International Academy of Pathology Avances en patología gástrica. Novedades de la clasificación WHO (2010) Fátima Carneiro
XXV Congreso de la Sociedad Española de Anatomía Patológica y División Española de la International Academy of Pathology Avances en patología gástrica. Novedades de la clasificación WHO (2010) Fátima Carneiro
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues
 A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.5.2765 RESEARCH ARTICLE Correlation between Magnifying Narrow-band Imaging Endoscopy Results and Organoid Differentiation Indicated by Cancer Cell Differentiation
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.5.2765 RESEARCH ARTICLE Correlation between Magnifying Narrow-band Imaging Endoscopy Results and Organoid Differentiation Indicated by Cancer Cell Differentiation
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 288 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure Oral contraceptives have been used since the early 1960s and are now used by about 90 million women worldwide. The pill is given as a combination
288 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure Oral contraceptives have been used since the early 1960s and are now used by about 90 million women worldwide. The pill is given as a combination
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
ABSTRACTS: FISH OILS AND CANCER
 ABSTRACTS: FISH OILS AND CANCER J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 May;74(5):1145-50. Dietary effects of menhaden oil on the growth and membrane lipid composition of rat mammary tumors. Jurkowski JJ, Cave WT Jr.
ABSTRACTS: FISH OILS AND CANCER J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 May;74(5):1145-50. Dietary effects of menhaden oil on the growth and membrane lipid composition of rat mammary tumors. Jurkowski JJ, Cave WT Jr.
