Videoendoscopy of Colonic Early Cancer
|
|
|
- Hannah Cannon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 1, pp Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in Malaysia Videoendoscopy of Colonic Early Cancer YOSHIHIRO SAKAI Division ofdigestive Endoscopy, Toho University Ohashi Hospital, hashi, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153, Japan (Received November 1, 1993; in finalform, January 22, 1994) Since January 1982, 275 early colonic carcinomas undergoing total endoscopic resection were studied. Of this series, 234 lesions showed some adenoma components, whereas the remaining 41 lesions lacked adenoma components. Minute carcinomas measuring < 5 mm (21 lesions) were most commonly the hemispheric protruding type lesions (IIs, 9 lesions), followed by superficial protruding type lesions with a height of < 3 mm (IIa, 6 lesions). There also were 2 superficial depressed-type lesions that were slightly concave. Eight of these minute carcinomas may have developed by de novo carcinogenesis, and 2 had already invaded the submucosa. Therefore every effort should be made not to overlook lesions measuring < 5 mm in diameter. That none of these lesions were located in the rectum indicates the acute necessity for improved examination procedures. With regard to lla lesions measuring > 5 mm, 92.3% were discovered by videoendoscopy. This high detection rate was attributed to the growing use of videoendoscope systems and reflects heightened interest on the part of endoscopists in superficial type lesions. KEY WORDS: colonic early cancer, minute carcinoma INTRODUCTION The approximately 10-year period since videoendoscopes have become commercially available has witnessed significant improvements in endoscopic instrumentation, resulting in enhanced diagnostic capability, maneuverability, and image recording quality. Despite product enhancement, videoendoscopes still do not possess clear-cut advantages over fiberscopes, because the functions of fiberscopes have been transferred to videoendoscopes and, conversely, technologic improvements obtained during the development of videoendoscopes have been incorporated into fiberscopes. It must be conceded that videoendoscopes relieve the endoscopist ofhaving to having to stare at bright images with a single eye and do not require continual adjustment of the endoscopist s visual acuity. Videoendoscopes also do not require the user to maintain a bent-over posture and are lighter than fiberscopes, because they do not have an eye lens, thereby increasing maneuverability and reducing operator fatigue Address for correspondence: Yoshihiro Sakai, M.D., Division of Digestive Endoscopy, Toho University Ohashi Hospital, hashi, Meguro-ku Tokyo 153. (1). By connecting the system to a TV monitor, multiple images can be displayed simultaneously to ensure accurate diagnosis and reduce the risk of overlooking clinically significant lesions. Although comparable capabilities can be obtained by connecting a fiberscope to an endoscopic TV System, performance is compromised. Videoendoscopes excel in image-filing capability and reproducibility of VTR recordings. They also offer excellent image processing by permitting outline enhancement and hue adjustment. By overcoming the critical flaw of conventional endoscopes with poor outline enhancement capability (i.e., image flattening caused by the close proximity of the illumination lens and the objective lens), videoendoscopes provide sharp image definition and hue contrast in cases with slight depressions or elevations, thereby facilitating the detection and differential diagnosis of abnormalities. CLASSIFICATION OF EARLY CANCER Early cancer of the colon and cofined to mucosa and is not associated with any lymph node metastases confined to the mucosa. The General Rules for Clinical and 125
2 126 Y. SAKAI Pathologic Studies on Carcinoma of the Colon (2) therefore classify lesions with invasion confined to the submucosa and without as early colonic cancer. Based on these criteria, the author studied 275 lesions that were totally resected endoscopically and histologically diagnosed to be colonic cancer during the period from January 1982 to August All of these carcinomas were confined to the mucosa or to the submucosa (Table 1). In this series, 234 lesions showed some adenoma tous components, whereas the remaining 41 lesions consisted of only cancer tissue. The longest dimension of the lesion was < 5 mm, > 5 to < 10 mm, and > 10 mm in 21 lesions, 78 lesions, and 176 lesions, respectively. Although the majority of lesions (64%) were > 10 mm, the remaining 36% measured < 10 mm, and 7.6% of the total were < 5 mm. Histologically, although the possibility cannot be ruled out that cancer cells may have replaced adenoma cells during the development of the 33 lesions without adenomatous components that measured > 5 mm, the remaining 8 lesions without adenomatous components that were < 5 mm in diameter most likely resulted from de novo carcinogenesis. It should also be noted that these 8 lesions accounted for 19.5% ofthe 41 lesions without adenomatous components. This figure is far higher than the 5.5% (13/234) of the lesions measuring < 5 mm with adenomatous components. Detection of carcinomas without adenoma components that measure < 5 mm is therefore of the utmost importance clinically. DIAGNOSIS OF MINUTE CARCINOMAS The 21 lesions measuring < 5 mm, defined as minute carcinomas (3,4) were classified by location and macroscopic type to delineate their characteristics (Table 2). Location was expressed according to the anatomic divisions of the colon. Lesions situated in the sigmoid colon (S) and descending colon (D) were classified together, as were those located in the ascending colon (A) and cecum (C). None of the lesions were found in the rectum (R). Although 11 lesions were situated in the sigmoid or descending colon, 8 were located in the transverse colon (T), Table 1 Size and histologic characteristics of endoscopically resected early carcinomas <= 5 5 < <= mm< Total Ca E ad Ca E ad Note.Ca ad, indicates with adenoma; Ca ad, without adenoma. Table 2 Location and macroscopic type of microcarcinomas < 5 mm in diameter Ip, Isp Is H a (+ H c) H c Total R S, D 3 (2) 4 (2) 3 (1) 11 (5) T 3 3 (1) (1) 8 (2) A,C 2(1) 2(1) 4 (2) 9 (3) 6 (1) 2 (2) 21 (8) Note.---( indicates Ca gad. making this the most common single segment for the development of minute carcinomas. The macroscopic type was classified, according to the General Rules for Clinical and Pathologic Studies on Carcinoma of the Colon, into the protruding type (I) or superficial type (II) (Fig. 1). Protruding type lesions were further subdivided into pendunculated lesions (Ip) and nonpendunculated (sessile) lesions (Is). Semipendunculated lesions (Isp) were included in Ip. Superficial type lesions were divided into superficial elevated type _< 3 mm in height (IIa) and superficial depressed type (IIc). IIa lesions with a depressed center (IIa +IIc) were included in IIa. No superficial fiat type lesions (IIb) were present in this series. Is lesions were most commonly encountered (9 lesions, 42.9%), followed by IIa (+llc) and Ip/Isp. IIc lesions were the most rare. No particular correlation was noted between location and macroscopic type. The histologic features of these microcarcinomas also were studied by macroscopic type. Only 1 lesion, found in the sigmoid colon, of the 4 Ip/Isp lesions was distinctly pendunculated, whereas the other 3 lesions, presenting with narrowing at their bases, were classified as Isp. Two of these latter 3 lesions did not show any adenomatous components, and 1 had already invaded into the submucosa, although the degree of invasion was slight. Three of the 9 Is lesions lacked adenomatous components. One of the 6 IIa lesions and both ofthe IIc lesions similarly lacked adenoma components; 1 of these latter lesions showed slight invasion of the submucosa. protruded type superficial type superficial protruded type superficial flat type superficial depressed type Figure 1 lp Isp Is /---x_ Ila F-----, IIb llc._/"---, -x.._ lla + llc Schema of macroscopic types of early colonic cancer.
3 VIDEOENDOSCOPY OF COLONIC EARLY CANCER 127 Because routine examinations do not permit lesions with adenomatous components to be distinguished from those without such components in cases of minute carcinomas measuring < 5 mm, a magnifying endoscope should be employed to determine the presence or absence of marginal adenoma tissue. DIAGNOSIS OF lla LESIONS OF > 5 MM No or minimal differences between the hue of low lesions and that of surrounding normal mucosa make endoscopic detection a challenging task. By defining superficial elevated lesions (IIa) as carcinomas measuring <3 mm in height with a border that is distinctly elevated from the surrounding mucosa on dye examination, 26 such lesions with maximum diameters of >5 mm were included in this series (Table 3). These lesions most commonly were located in the sigmoid colon and descending colon (8 lesions), followed by the ascending colon and cecum (7 lesions). The transverse colon was the most common single portion of the colon for lesions of this type. However, 5 of these lesions were found in the rectum. Lesion dimension was categorized in 5-mm intervals. Lesions measuring > 5 to < 10 mm were most frequently encountered (11 lesions). There were 5, 4 and 6 lesion with diameters of > 10 to < 15 mm, > 15 to < 20 and > 20 mm, respectively. There was no correlation between lesion location and size. Only 2 of these 26 lesions were discovered by fiberscopes, and all other 24 remaining lesions were found by videoendoscopes. DISCUSSION Since the introduction of a videoendoscope system in October 1986, about 8,000 endoscopic examinations have been performed as of August Videoendoscope systems have been used in approximately half of these examinations. Recent trends indicate that videoscopes currently are used in about 80% of patients who undergo endoscopy. Initially, the videoendoscope was restricted by Table 3 Location and size of IIa lesions >5 mm in diameter 5< =<10 10< =<15 15mm< Total R 3 5 S,D T 2 (1) 3 6 (1) A,C 2(1) 2 3 7(1) ll (1) 5(1) l0 26(2) Note.---( indicates found by fiberscope. the limited availability of examination rooms able to accommodate the bulky ancillary equipment. More recently, videoendoscope use has been steadily increasing owing to the more widespread availability of videoscope systems and because of its popularity as a result of the reduced fatigue for the endoscopist. Increased use of videoendoscopes also has been promoted by the belief that the "modified two-man technique" (5) using a videoendoscope is an effective training exercise for introductory programs in colonoscopy. In the modified two-man technique, colonoscopy is performed by two physicians: a highly experienced endoscopist and an endoscopist in training. The less experienced endoscopist usually serves as assistant in the initial phase of training. The roles are then reversed, and the experienced endoscopist acts as assistant and instructs the younger endoscopist in the direction of tip flexion and teaches the effects ofinsufflation and aspiration. The senior endoscopist is responsible for rotating the scope, guiding it to the cecum, and removing it, while ensuring minimal discomfort to the patient. To accomplish this procedure successfully it is far more advantageous to use a large TV monitor than a fiberscope combined with a lecturescope or teaching instrument. Moreover, after the operator becomes accustomed to the equipment, tip angulation can be controlled with the left hand alone, leaving the fight hand unencumbered to carry out the tasks of the assistant. The entire procedure therefore can be performed by a single endoscopist. This is referred to as the "one-man technique." The modified two-man technique allows an endoscopist to develop and make a smooth transition to the one-man technique. Another reason that videoendoscope systems are preferred is the reduced time required for endoscopic therapeutic procedures that results when an assistant is able to manipulate forceps or snares while viewing the same image as the operator. Videoendoscopes are also equipped with a freeze function that permits target images to be selected as often as desired. This function eliminates image distortion caused by bubbles on the lens or rapid movement of moving images. Younger endoscopists therefore tend to use videoendoscope systems because of the low risk of failure in image viewing and recording. Consequently, fiberscopes increasingly tend to be used only for screening or as a last resort if a videoendoscope is not available. Massive lesions protruding into the lumen of the colon can be diagnosed easily with either a fiberscope or a videoendoscope. This also applies to small lesions that protrude into the lumen or lesions with a color distinct from the surrounding mucosa. Even low lesions that are large or are different in color from the mucosa most likely
4 Y. SAKAI 128 will be detected by either type of scope. However, there is a high risk of overlooking small, low lesions that are the same color as surrounding mucosa (6). Likewise, lesions that are situated on the oral side of taut mucosal folds or lesions that can be viewed directly but have been overdistended by excessive insufflation may be overlooked. This also applies in the event of inadequate pretreatment. It is impractical to analyze factors leading to the discovery of lesions. Although the percentage of IIa lesions discovered with videoendoscopes is high, the aforementioned continual evolution of scopes and techniques for their use precludes unconditional recommendations for one type of endoscope or the other. In cases where endoscopy is used to evaluate lesions already detected by barium enema, a videoendoscope generally is selected because it facilitates the execution of therapeutic procedures. However, that only 2 of the 26 IIa lesions >5 mm were detected by fiberscopy, whereas the other 24 lesions where Figure l C specimen. Microscopic findings of the endoscopically resected discovered by videoendoscopy, indicates that lesions of this type are easier to detect with a videoendoscope. Apart from protruding type lesions (I), superficial type lesions (II) were characterized by minimal differences in color tone from the surrounding mucosa (Fig. 1A), slight semilunar fold deformity, or, in rare instances, an abnormal pattern of illuminated reflection points on the mucosa. Other abnormalities include interrupted course of blood vessels or an unnatural luster of the mucosal surface (Fig. 2A). These changes can be overlooked easily but on close inspection, they can be identified as signs of abnormalities (Fig. 1B). Definition of the extent of some lesions may require dye spray (Fig. 2B). Spraying 10 to 20 ml of 0.05% methylene blue solution through the biopsy channel can help demarcate the borders of lesions. Figure IA A microcarcinoma appears as a reddish spot. Figure 1B Close-up view of the same lesion after dye injection. The dye was retained in the center of the lesion, demonstrating the reddish region to be depressed. Cancer was present in only the depressed region (2mm). Figure 2A A superficial elevated type carcinoma, appearing as indistinctly pigmented patches by conventional observation.
5 VIDEOENDOSCOPY OF COLONIC EARLY CANCER 129 By aspirating off the excess dye and washing the mucosa, Figure 2B The same lesion directly after dyeing. The outline of the lesion became distinct. the outline of the lesion often can be examined in detail. Scopes with zoom-type magnification capability can be used to observe the shape and arrangement of small ducts (Figure 2C). Despite the fact that no microcarcinomas were detected in the rectum, they were frequently noted in the transverse colon. This significant difference in the distribution of lesions from that generally found for carcinomas treated surgically probably indicates a problem in examination methods. Because it is necessary to prevent excess air insufflatio when inserting the scope, observation of the proximal colon was not adequate. Because examination of the colon generally is initiated after arriving at the rectum and observing the terminal ileum, the surface of the mucosa is examined by inflating and deflating as the colon scope is being withdrawn. The rectum is therefore examined last when it is in the most distended state and thus potentially increases the risk of overlooking minute carcinomas in the colon. The relatively high number of minute carcinomas discovered in the transverse colon is apparently caused by this being a region that can be examined easily while either inserting or withdrawing the scope. For regions such as the rectum or sigmoid colon, which are associated with a high risk of cancer, dye spray should be used, even in the apparent absence of anomalies, to increase the possibility of detecting minute lesions. Because lesions > 6 mm in diameter, including difficult-to-detect lesions such as IIa carcinomas, can be diagnosed in these regions as in other segments of the colon, particular caution must be exercised with regard to minute carcinomas. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Figure 2C A portion of the same lesion magnified 30x. Part of this paper was presented at the International Symposium, "The Latest Frontiers of Endoscopy," on March 31, 1993 at the 79th General Meeting of The Japan Society of Gastroenterology. The authors are grateful to Professor J. Patrick Barron of the International Medical Communications Center of Tokyo Medical College for his review of the manuscript. REFERENCES Figure 2C Sakai Y, Fujinuma, S, & Ibe A. Electronic colonoscopy; Past and present, Endoscopia Digestiva 1989; 1: (Japanese) Japan Research Society for Cancer of Colon and Rectum. General rules for clinical and pathological studies on cancer of colon, rectum and anus, 4th ed. Kanahara-Shuppan, Tokyo, (Japanese) Kudo S, Miura K, Takano Y, et al. Detection of colorectal minute cancer, Stomach and Intestine 1990;25: (Japanese)
6 130 Y. SAKAI 4. Okamoto H, & Sasaki T. Detection and importance of colonic diminutive lesions (5mm or less in diameter), Stomach and Intestine 1990;25: (Japanese) 5. Vatanabe S, Ohashi S, Akiya M, et al. the educational utility of the modified two men method, Therapeutic Research 8 (suppl 1) 1988; (Japanese) 6. Katakura S, Satake Y, Aksoz K, et al. Endoscopic and histopathological study about 25 cases of minute superficial depressed neoplastic lesions in the large intestine, Digestive Endoscopy 1993;5:3-12
Clinicopathological Characteristics of Superficial Type
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
The Paris classification of colonic lesions
 The Paris classification of colonic lesions Training to improve the interobserver agreement among international experts Sascha van Doorn, MD, PhD-student in CRC-reserach group of Evelien Dekker Introduction
The Paris classification of colonic lesions Training to improve the interobserver agreement among international experts Sascha van Doorn, MD, PhD-student in CRC-reserach group of Evelien Dekker Introduction
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행
 Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Endoscopic Characteristics of the Healing Process of Ulcerative Colitis
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 37-48 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 37-48 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics
 Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Incidence and Management of Hemorrhage after Endoscopic Removal of Colorectal Lesions
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 12(3), 253-258, September 2000 Original Incidence and Management of Hemorrhage after Endoscopic Removal of Colorectal Lesions Masaaki MATSUKAWA, Mototsugu FUJIMORI, Takahiko KOUDA,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 12(3), 253-258, September 2000 Original Incidence and Management of Hemorrhage after Endoscopic Removal of Colorectal Lesions Masaaki MATSUKAWA, Mototsugu FUJIMORI, Takahiko KOUDA,
Adenoma to Carcinoma Pathway
 It is widely accepted that more than 95% of colorectal cancers arise from adenomatous polyps, which are generally defined as benign lesions with dysplastic epithelium that have variable potential for malignancy.
It is widely accepted that more than 95% of colorectal cancers arise from adenomatous polyps, which are generally defined as benign lesions with dysplastic epithelium that have variable potential for malignancy.
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions
 Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
malignant polyp Daily Challenges in Digestive Endoscopy for Endoscopists and Endoscopy Nurses BSGIE Annual Meeting 18/09/2014 Mechelen
 Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Assessment for Ampullary and Bile Duct Malignancy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R
 170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
8. The polyp in the illustration can be described as (circle all that apply) a. Exophytic b. Pedunculated c. Sessile d. Frank
 Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Hidehiko; Kohno, Shigeru. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1997, 42
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Superficial Depressed Type (IIc) Ea Two Cases Iwamoto, Michiko; Makiyama, Kazuya; Yohei; Omagari, Katsuhisa; Yamakawa Shiro; Haraguchi, Masuho; Itsuno,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Superficial Depressed Type (IIc) Ea Two Cases Iwamoto, Michiko; Makiyama, Kazuya; Yohei; Omagari, Katsuhisa; Yamakawa Shiro; Haraguchi, Masuho; Itsuno,
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy
 Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
11/21/13 CEA: 1.7 WNL
 Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
Retroflexion and prevention of right-sided colon cancer following colonoscopy: How I approach it
 Retroflexion and prevention of right-sided colon cancer following colonoscopy: How I approach it Douglas K Rex 1 MD, MACG 1. Indiana University School of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
Retroflexion and prevention of right-sided colon cancer following colonoscopy: How I approach it Douglas K Rex 1 MD, MACG 1. Indiana University School of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
Dysplasia 4/19/2017. How do I practice Chromoendoscopy for Surveillance of Colitis? SCENIC: Polypoid Dysplasia in UC. Background
 SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
Formula One Study. Assessment criteria of pathological parameters. Ver.2. UK Japan Joint Study for Risk Factors of Lymph Node
 APPENDIX 01: Assessment criteria Formula One Study UK Japan Joint Study for Risk Factors of Lymph Node Metastasis in Submucosal Invasive (pt1) Colorectal Cancer Assessment criteria of pathological parameters
APPENDIX 01: Assessment criteria Formula One Study UK Japan Joint Study for Risk Factors of Lymph Node Metastasis in Submucosal Invasive (pt1) Colorectal Cancer Assessment criteria of pathological parameters
Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric carcinoma using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging
 E832 THIEME Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging Authors Masashi Kawamura 1, Hiroshi Naganuma 2, Rie Shibuya 2, Tatsuya Kikuchi 1, Yoshitaka
E832 THIEME Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging Authors Masashi Kawamura 1, Hiroshi Naganuma 2, Rie Shibuya 2, Tatsuya Kikuchi 1, Yoshitaka
Successful Endoscopic Resection of an Early Carcinoma of the Duodenum
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 239-244 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1999 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 239-244 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1999 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
I polyp-cancer sequence' and adenoma-carcinoma
 lat Early Cancers of the Large Intestine HU KUAOO, D, AND AKEHI OOHAA, D rom January 196 to December 19, 3 early colorectal cancers of the flat type were treated. hirtyfour of them (91.9%) were not accompanied
lat Early Cancers of the Large Intestine HU KUAOO, D, AND AKEHI OOHAA, D rom January 196 to December 19, 3 early colorectal cancers of the flat type were treated. hirtyfour of them (91.9%) were not accompanied
A916: rectum: adenocarcinoma
 General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Colon and Rectum. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6th edition
 Colon and Rectum Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, sarcomas, and tumors of the vermiform appendix are excluded. Protocol revision date: January
Colon and Rectum Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, sarcomas, and tumors of the vermiform appendix are excluded. Protocol revision date: January
Page 1. Is the Risk This High? Dysplasia in the IBD Patient. Dysplasia in the Non IBD Patient. Increased Risk of CRC in Ulcerative Colitis
 Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
BENEFIT APPLICATION BLUE CARD/NATIONAL ACCOUNT ISSUES
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.84 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.87 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy 6.01.32 Virtual Colonoscopy/Computed
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.84 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.87 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy 6.01.32 Virtual Colonoscopy/Computed
Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy
 Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy Policy Number: 2.01.84 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy Policy Number: 2.01.84 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
IN THE DEVELOPMENT and progression of colorectal
 Digestive Endoscopy 2014; 26 (Suppl. 2): 73 77 doi: 10.1111/den.12276 Treatment strategy of diminutive colorectal polyp
Digestive Endoscopy 2014; 26 (Suppl. 2): 73 77 doi: 10.1111/den.12276 Treatment strategy of diminutive colorectal polyp
Polyps Adenomas Lipomas
 30 Chapter 2 CT Colonography Chapter 2 Polyps Adenomas Lipomas Case 8 Case 9 Case 10 Case 11 Case 12 Case 13 Case 14 Case 15 Case 16 Case 17 Case 18 Pseudopolyp Polyp after intravenous administration of
30 Chapter 2 CT Colonography Chapter 2 Polyps Adenomas Lipomas Case 8 Case 9 Case 10 Case 11 Case 12 Case 13 Case 14 Case 15 Case 16 Case 17 Case 18 Pseudopolyp Polyp after intravenous administration of
Local recurrence after endoscopic resection of colorectal tumors
 Int J Colorectal Dis (2009) 24:225 230 DOI 10.1007/s00384-008-0596-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Local recurrence after endoscopic resection of colorectal tumors Kinichi Hotta & Takahiro Fujii & Yutaka Saito & Takahisa
Int J Colorectal Dis (2009) 24:225 230 DOI 10.1007/s00384-008-0596-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Local recurrence after endoscopic resection of colorectal tumors Kinichi Hotta & Takahiro Fujii & Yutaka Saito & Takahisa
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
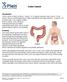 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
The focus of Chapter 9 is on anoscopy, proctosigmoidoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy procedures and all
 9 Anoscopy, 45380 45380 45385 Proctosigmoidoscopy, Flexible Sigmoidoscopy, and Colonoscopy 45378 The focus of Chapter 9 is on anoscopy, proctosigmoidoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy procedures
9 Anoscopy, 45380 45380 45385 Proctosigmoidoscopy, Flexible Sigmoidoscopy, and Colonoscopy 45378 The focus of Chapter 9 is on anoscopy, proctosigmoidoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy procedures
1 Deep Insertion Techniques. Contents 1 Deep Insertion Techniques. Introduction. 1-1 Using Carbon Dioxide Gas 3. Caution. Deep Insertion Techniques
 Introduction With the recent advent of capsule and balloon endoscopy, the way has been opened for endoscopic treatment of the entire small intestine, bringing a new flexibility to the way we approach small
Introduction With the recent advent of capsule and balloon endoscopy, the way has been opened for endoscopic treatment of the entire small intestine, bringing a new flexibility to the way we approach small
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Difficult Polypectomy 2015 Tool of the Trade
 Difficult Polypectomy 2015 Tool of the Trade Jonathan Cohen, MD FACG FASGE Clinical Professor of Medicine NYU Langone School of Medicine Improving Therapeutics in the Colon Improved detection of polyp
Difficult Polypectomy 2015 Tool of the Trade Jonathan Cohen, MD FACG FASGE Clinical Professor of Medicine NYU Langone School of Medicine Improving Therapeutics in the Colon Improved detection of polyp
Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Pharynx and esophagus atlas
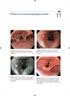 163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
T. Shono, 1 K. Ishikawa, 1 Y. Ochiai, 1 M. Nakao, 1 O. Togawa, 1 M. Nishimura, 1 S. Arai, 1 K. Nonaka, 2 Y. Sasaki, 2 and H. Kita 1. 1.
 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 948293, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/948293 Clinical Study Feasibility of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A New Technique for En Bloc Resection of
International Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 948293, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/948293 Clinical Study Feasibility of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A New Technique for En Bloc Resection of
Billing Guideline. Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/14 Last revision effective 4/16
 Billing Guideline Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/14 Last revision effective 4/16 Florida Hospital Care Advantage plans include full coverage of in-network
Billing Guideline Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/14 Last revision effective 4/16 Florida Hospital Care Advantage plans include full coverage of in-network
Macroscopic Characteristics of Tubular Adenomas in Familial Adenomatosis Coli: The Relationship between Size Gross Configuration and Location
 Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 43, No.2, 63-68, 1995 Macroscopic Characteristics of Tubular Adenomas in Familial Adenomatosis Coli: The Relationship between Size Gross Configuration and Location Yoichi
Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 43, No.2, 63-68, 1995 Macroscopic Characteristics of Tubular Adenomas in Familial Adenomatosis Coli: The Relationship between Size Gross Configuration and Location Yoichi
The addition of high magnifying endoscopy improves rates of high confidence optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps
 E140 The addition of high magnifying endoscopy improves rates of high confidence optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps Authors Mineo Iwatate 1, Yasushi Sano 1, Santa Hattori 1, Wataru Sano 1, Noriaki
E140 The addition of high magnifying endoscopy improves rates of high confidence optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps Authors Mineo Iwatate 1, Yasushi Sano 1, Santa Hattori 1, Wataru Sano 1, Noriaki
Neoplastic Colon Polyps. Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds, October 18, 2012
 Neoplastic Colon Polyps Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds, October 18, 2012 CASE 55M with Hepatitis C, COPD (FEV1=45%), s/p vasectomy, knee surgery Meds: albuterol, flunisolide, mometasone, tiotropium
Neoplastic Colon Polyps Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds, October 18, 2012 CASE 55M with Hepatitis C, COPD (FEV1=45%), s/p vasectomy, knee surgery Meds: albuterol, flunisolide, mometasone, tiotropium
Prevalence and Characteristics of Nonpolypoid Colorectal Neoplasm in an Asymptomatic and Average-Risk Chinese Population
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:463 470 Prevalence and Characteristics of Nonpolypoid Colorectal Neoplasm in an Asymptomatic and Average-Risk Chinese Population HAN MO CHIU,*,, JAW TOWN
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:463 470 Prevalence and Characteristics of Nonpolypoid Colorectal Neoplasm in an Asymptomatic and Average-Risk Chinese Population HAN MO CHIU,*,, JAW TOWN
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Spartan Medical Research Journal
 Spartan Medical Research Journal Research at Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine Volume 2 Number 2 Winter, 2017 Pages 14-21 Title: Endoscopic Combined Snare-Forceps Technique for
Spartan Medical Research Journal Research at Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine Volume 2 Number 2 Winter, 2017 Pages 14-21 Title: Endoscopic Combined Snare-Forceps Technique for
Case presentation. Eran Zittan. MD Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, Canada. Emek Medical Center, Afula, Israel. March, 2016
 Case presentation Eran Zittan. MD Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, Canada. Emek Medical Center, Afula, Israel. March, 2016 60 y/o man with long standing UC+PSC. Last 10 years on clinical and endoscopic remission.
Case presentation Eran Zittan. MD Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, Canada. Emek Medical Center, Afula, Israel. March, 2016 60 y/o man with long standing UC+PSC. Last 10 years on clinical and endoscopic remission.
Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal Neoplasms: A Single Center Clinical Experience in China
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
Supporting Information 2. ESGE QIC Lower GI Delphi voting process: Round 1 Working Group chair: Michal F. Kaminski, Poland
 Supporting Information 2. ESGE QIC Lower GI Delphi voting process: Round 1 Working chair: Michal F. Kaminski, Poland Population Interventions Comparator Outcome Additional evidence 1.1 Rate of adequate
Supporting Information 2. ESGE QIC Lower GI Delphi voting process: Round 1 Working chair: Michal F. Kaminski, Poland Population Interventions Comparator Outcome Additional evidence 1.1 Rate of adequate
Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines
 Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines June 2013 ACRCSP Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines - 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Background... 3 Terms, Definitions
Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines June 2013 ACRCSP Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines - 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Background... 3 Terms, Definitions
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy. Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital
 Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(3):
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 26, 7(3):239 23 ORIGINAL PAPER Predictive parameters for advanced neoplastic adenomas and colorectal cancer in patients with colonic polyps a study in a tertiary
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 26, 7(3):239 23 ORIGINAL PAPER Predictive parameters for advanced neoplastic adenomas and colorectal cancer in patients with colonic polyps a study in a tertiary
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, et al. Quality indicators
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, et al. Quality indicators
Traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection using clip and line: a feasibility study
 E51 Traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection using clip and line: a feasibility study Authors Institution Yasushi Yamasaki, Yoji Takeuchi, Noriya Uedo, Minoru Kato, Kenta Hamada, Kenji
E51 Traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection using clip and line: a feasibility study Authors Institution Yasushi Yamasaki, Yoji Takeuchi, Noriya Uedo, Minoru Kato, Kenta Hamada, Kenji
Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation
 Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts..
 COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts.. Detection: I see an abnormality (usually a polyp) Characterization: Is this abnormality neoplastic? (for example: an adenoma) Treatment: it is neoplastic. Can I treat
COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts.. Detection: I see an abnormality (usually a polyp) Characterization: Is this abnormality neoplastic? (for example: an adenoma) Treatment: it is neoplastic. Can I treat
Management of pt1 polyps. Maria Pellise
 Management of pt1 polyps Maria Pellise Early colorectal cancer Malignant polyp Screening programmes SM Invasive adenocar cinoma Advances in diagnostic & therapeutic endoscopy pt1 polyps 0.75 5.6% of large-bowel
Management of pt1 polyps Maria Pellise Early colorectal cancer Malignant polyp Screening programmes SM Invasive adenocar cinoma Advances in diagnostic & therapeutic endoscopy pt1 polyps 0.75 5.6% of large-bowel
Pathology in Slovenian CRC screening programme:
 Pathology in Slovenian CRC screening programme: Findings, organisation and quality assurance Snježana Frković Grazio University Medical Center Ljubljana, Slovenia Slovenia s population: 2 million Incidence
Pathology in Slovenian CRC screening programme: Findings, organisation and quality assurance Snježana Frković Grazio University Medical Center Ljubljana, Slovenia Slovenia s population: 2 million Incidence
Risk Factors for Incomplete Polyp Resection during Colonoscopic Polypectomy
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 2015, pp. 66-72 ORiginal Article Risk Factors for Incomplete Polyp Resection during Colonoscopic Polypectomy Sang Pyo Lee, In-Kyung Sung, Jeong Hwan Kim, Sun-Young
Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 2015, pp. 66-72 ORiginal Article Risk Factors for Incomplete Polyp Resection during Colonoscopic Polypectomy Sang Pyo Lee, In-Kyung Sung, Jeong Hwan Kim, Sun-Young
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Small Intestine. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition
 Small Intestine Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the small intestine, including those with focal endocrine differentiation. Excludes carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, and stromal tumors (sarcomas).
Small Intestine Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the small intestine, including those with focal endocrine differentiation. Excludes carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, and stromal tumors (sarcomas).
Do any benign polyps require an operation?
 Do any benign polyps require an operation? Kevin Waschke MD.,CM., FRCPC, FASGE McGill University Health Center President Elect Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Colonoscopy Education Day - Tuesday
Do any benign polyps require an operation? Kevin Waschke MD.,CM., FRCPC, FASGE McGill University Health Center President Elect Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Colonoscopy Education Day - Tuesday
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
ALIMENTARY TRACT FIBEROPTIC PANSIGMOIDOSCOPY. An evaluation and comparison with rigid sigmoidoscopy
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 72:644-649, 1977 Copyright 1977 by The American Gastroenterological Association Vol. 72, No.4, Part 1 Printed in U.S.A. ALIMENTARY TRACT FIBEROPTIC PANSIGMOIDOSCOPY An evaluation and comparison
GASTROENTEROLOGY 72:644-649, 1977 Copyright 1977 by The American Gastroenterological Association Vol. 72, No.4, Part 1 Printed in U.S.A. ALIMENTARY TRACT FIBEROPTIC PANSIGMOIDOSCOPY An evaluation and comparison
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Endoscopic and histolological findings in INR and FR study subjects
 Supplemental Digital Content 1. Endoscopic and histolological findings in INR and FR study subjects Patient Group Macroscopic examination Ileum Histology Colon/rectum Histology 1 INR Normal Acute and chronic
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Endoscopic and histolological findings in INR and FR study subjects Patient Group Macroscopic examination Ileum Histology Colon/rectum Histology 1 INR Normal Acute and chronic
Association office, Department of Digestive Surgery, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, Kawaramachi, Kamigyo-ku, Kyoto , Japan
 Gastric Cancer (2001) 4: 1 8 Special article 2001 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma 2nd English Edition Response assessment of chemotherapy
Gastric Cancer (2001) 4: 1 8 Special article 2001 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma 2nd English Edition Response assessment of chemotherapy
Advances in Endoscopic Imaging
 Advances in Endoscopic Imaging SGNA meeting February 20, 2010 Amar R. Deshpande, MD Asst Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Objectives To recognize
Advances in Endoscopic Imaging SGNA meeting February 20, 2010 Amar R. Deshpande, MD Asst Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Objectives To recognize
Enhancing the Scope of Patient Care
 THE COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING INITIATIVE Enhancing the Scope of Patient Care FOCUSONE VIDEOSCOPE SYSTEM: CV-60 VIDEO PROCESSOR & LIGHT SOURCE OSF-V60 FLEXIBLE VIDEO SIGMOIDOSCOPE PRIMARY ENDOSCOPY You
THE COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING INITIATIVE Enhancing the Scope of Patient Care FOCUSONE VIDEOSCOPE SYSTEM: CV-60 VIDEO PROCESSOR & LIGHT SOURCE OSF-V60 FLEXIBLE VIDEO SIGMOIDOSCOPE PRIMARY ENDOSCOPY You
Development of a new contrast endoscopic method With Techno Color blue P
 Bulletin of the Osaka Medical College 53 1 45-55, 2007 45 Original Article Development of a new contrast endoscopic method With Toshihisa TAKEUCHI, Eiji UMEGAKI, Satoshi TOKIOKA, Nozomi TAKEUCHI, Minekazu
Bulletin of the Osaka Medical College 53 1 45-55, 2007 45 Original Article Development of a new contrast endoscopic method With Toshihisa TAKEUCHI, Eiji UMEGAKI, Satoshi TOKIOKA, Nozomi TAKEUCHI, Minekazu
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia
 Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
The Importance of Complete Colonoscopy and Exploration of the Cecal Region
 The Importance of Complete Colonoscopy and Exploration of the Cecal Region Kuangi Fu, Takahiro Fujii, Takahisa Matsuda, and Yutaka Saito 2 2.1 The Importance of a Complete Colonoscopy Ever since case-control
The Importance of Complete Colonoscopy and Exploration of the Cecal Region Kuangi Fu, Takahiro Fujii, Takahisa Matsuda, and Yutaka Saito 2 2.1 The Importance of a Complete Colonoscopy Ever since case-control
High Resolution Colonoscopy With Chromoscopy Versus Standard Colonoscopy for the Detection of Colonic Neoplasia: A Randomized Study
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:349 354 High Resolution Colonoscopy With Chromoscopy Versus Standard Colonoscopy for the Detection of Colonic Neoplasia: A Randomized Study MARC LE RHUN,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:349 354 High Resolution Colonoscopy With Chromoscopy Versus Standard Colonoscopy for the Detection of Colonic Neoplasia: A Randomized Study MARC LE RHUN,*
Department of Surgery, Aizu Central Hospital, Fukushima
 Case Reports Resection of Asynchronous Quadruple Advanced Colonic Carcinomas Followed by Reconstruction with Ileal Interposition between the Transverse Colon and Rectum Sho Mineta 1, Kimiyoshi Shimanuki
Case Reports Resection of Asynchronous Quadruple Advanced Colonic Carcinomas Followed by Reconstruction with Ileal Interposition between the Transverse Colon and Rectum Sho Mineta 1, Kimiyoshi Shimanuki
[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
![[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE] [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]](/thumbs/88/117127924.jpg) 2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD?
 How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
Birthday: 1952/07/31 Date of admission:1999/12/30 Age:48 y/o Past medication:esrd under regular HD for 5+ years; denied DM and HTN
 Birthday: 1952/07/31 Date of admission:1999/12/30 Age:48 y/o Past medication:esrd under regular HD for 5+ years; denied DM and HTN Chief Complaint : 1)intermittent LLQ cramping pain for 2 months 2) LGI
Birthday: 1952/07/31 Date of admission:1999/12/30 Age:48 y/o Past medication:esrd under regular HD for 5+ years; denied DM and HTN Chief Complaint : 1)intermittent LLQ cramping pain for 2 months 2) LGI
Present Status and Perspectives of Colorectal Cancer in Asia: Colorectal Cancer Working Group Report in 30th Asia-Pacific Cancer Conference
 Present Status and Perspectives of Colorectal Cancer in Asia: Colorectal Cancer Working Group Report in 30th Asia-Pacific Cancer Conference Jpn J Clin Oncol 2010;40(Supplement 1)i38 i43 doi:10.1093/jjco/hyq125
Present Status and Perspectives of Colorectal Cancer in Asia: Colorectal Cancer Working Group Report in 30th Asia-Pacific Cancer Conference Jpn J Clin Oncol 2010;40(Supplement 1)i38 i43 doi:10.1093/jjco/hyq125
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels.
 Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Colonic Polyp. Najmeh Aletaha. MD
 Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
THE INS & OUTS OF COLONOSCOPY
 THE INS & OUTS OF COLONOSCOPY INSERTION TIPS & FEATURES OF HIGH-QUALITY WITHDRAWAL C A M E R O N B E L L R O Y A L N O R T H S H O R E H O S P I T A L C H A I R, N E T I N A T I O N A L T C T L E A D WHY
THE INS & OUTS OF COLONOSCOPY INSERTION TIPS & FEATURES OF HIGH-QUALITY WITHDRAWAL C A M E R O N B E L L R O Y A L N O R T H S H O R E H O S P I T A L C H A I R, N E T I N A T I O N A L T C T L E A D WHY
Acta Med. Okayama Vol. 70, No. 2. Iwamuro et al.
 140 Iwamuro et al. cta Med. Okayama Vol. 70, No. 2 emission tomography (PET) scanning showed tracer uptake in the spleen and iliac bone as well as in the swollen lymph nodes. There were no abnormalities
140 Iwamuro et al. cta Med. Okayama Vol. 70, No. 2 emission tomography (PET) scanning showed tracer uptake in the spleen and iliac bone as well as in the swollen lymph nodes. There were no abnormalities
ASGE and AGA Issue Consensus Statement on Surveillance and Management of Dysplasia in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 ASGE and AGA Issue Consensus Statement on Surveillance and Management of Dysplasia in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease DOWNERS GROVE, Ill., (March 5, 2015) The American Society for Gastrointestinal
ASGE and AGA Issue Consensus Statement on Surveillance and Management of Dysplasia in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease DOWNERS GROVE, Ill., (March 5, 2015) The American Society for Gastrointestinal
Cancer emerging from the recurrence of sessile serrated adenoma/polyp resected endoscopically 5 years ago
 Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2016, 46(1) 89 95 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv154 Advance Access Publication Date: 3 November 2015 Case Report Case Report Cancer emerging from the recurrence of sessile
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2016, 46(1) 89 95 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv154 Advance Access Publication Date: 3 November 2015 Case Report Case Report Cancer emerging from the recurrence of sessile
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) & Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) & Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) Minimally Invasive Polyp Removal IE-02700-Understanding EMR and ESD Brochure_R3.indd 1 Occasionally, a polyp that infiltrates
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) & Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) Minimally Invasive Polyp Removal IE-02700-Understanding EMR and ESD Brochure_R3.indd 1 Occasionally, a polyp that infiltrates
Bowel Cancer Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
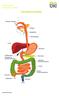 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
ADENOMAS WITH ADENOCARCINOMA: A STUDY EVALUATING THE RISK OF RESIDUAL CANCER AND LYMPH NODE METASTASIS
 253SJS102210.1177/1457496913482253S. E. Steigen, et al.adenomas with adenocarcinomas and risk factors Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 102: 90 95, 2013 ADENOMAS WITH ADENOCARCINOMA: A STUDY EVALUATING THE
253SJS102210.1177/1457496913482253S. E. Steigen, et al.adenomas with adenocarcinomas and risk factors Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 102: 90 95, 2013 ADENOMAS WITH ADENOCARCINOMA: A STUDY EVALUATING THE
Vital staining and Barrett s esophagus
 Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Adequate endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer obtained from the dissecting microscopic features of the resected specimens
 Gastric Cancer (2001) 4: 122 131 Original article 2001 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Adequate endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer obtained from the dissecting
Gastric Cancer (2001) 4: 122 131 Original article 2001 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Adequate endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer obtained from the dissecting
Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
Handling & Grossing of Colo-rectal Specimens for Tumours. for Medical Officers in Pathology
 Handling & Grossing of Colo-rectal Specimens for Tumours for Medical Officers in Pathology Dr Gayana Mahendra Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Your Role in handling colorectal
Handling & Grossing of Colo-rectal Specimens for Tumours for Medical Officers in Pathology Dr Gayana Mahendra Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Your Role in handling colorectal
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
 Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Clinical Study Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Colorectal Neoplasms: Clinical Experience in a Tertiary Medical Center in Taiwan
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 891565, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891565 Clinical Study Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Colorectal Neoplasms: Clinical
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 891565, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891565 Clinical Study Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Colorectal Neoplasms: Clinical
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: chromoendoscopy_as_an_adjunct_to_colonoscopy 7/2012 11/2017
Corporate Medical Policy Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: chromoendoscopy_as_an_adjunct_to_colonoscopy 7/2012 11/2017
colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer hereditary sporadic Familial 1/12/2018
 colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Feasibility of endoscopic mucosa-submucosa clip closure method (with video)
 Feasibility of endoscopic mucosa-submucosa clip closure method (with video) Authors Toshihiro Nishizawa 1, Shigeo Banno 2, Satoshi Kinoshita 1,HidekiMori 2, Yoshihiro Nakazato 3,YuichiroHirai 2,Yoko Kubosawa
Feasibility of endoscopic mucosa-submucosa clip closure method (with video) Authors Toshihiro Nishizawa 1, Shigeo Banno 2, Satoshi Kinoshita 1,HidekiMori 2, Yoshihiro Nakazato 3,YuichiroHirai 2,Yoko Kubosawa
A. Incorrect! The esophagus connects the pharynx and the stomach.
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 19: Digestive Physiology and Nutrition Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. This organ
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 19: Digestive Physiology and Nutrition Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. This organ
