CURRENTLY IN THE United States, 431,284
|
|
|
- Hester Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Increased Breast Calcifications in Women With ESRD on Dialysis: Implications for Breast Cancer Screening Mario Castellanos, MD, Seema Varma, MD, Kathleen Ahern, PhD, RN, Sue-Jane Grosso, MD, Shalom Buchbinder, MD, Denis D Angelo, MD, Carolyn Raia, MD, Morton Kleiner, MD, and Suzanne Elsayegh, MD Background: Different appearances of breast calcification on mammography can differentiate benign from malignant disease. An increased incidence of breast calcifications in dialysis patients is established, but data for morphological characteristics in renal patients, incidence of benign and malignant calcifications, and clinical consequences are limited. In this study, we compare mammograms and the workup of abnormal calcifications of women on hemodialysis with that of women with normal renal function. Methods: This is a retrospective case-control study; 45 women on hemodialysis had their screening mammograms reviewed. A control group of 86 age-matched women with normal renal function was randomly obtained for comparison. Mammograms were examined and the recommended workup was traced. Breast calcification morphological characteristics, incidence of benign versus malignant calcifications, callback rate, and biopsy recommendation rates were compared to determine whether breast calcifications in renal patients led to excessive workups. Results: Overall, breast calcifications in the renal group were statistically significantly increased compared with controls, mostly because of several benign-appearing morphological characteristics. No statistically significant difference was present between the 2 groups with respect to callback rates. However, incidences of malignancy-associated calcification and hence biopsy recommendation rate were slightly greater for the renal group. Conclusion: Renal patients have an increase in breast calcification, mostly caused by several benign calcifications. The callback rate is no greater than that in the general population. However, there is a slightly greater incidence of malignancy-associated calcifications; hence, once called back, they have a greater probability of being recommended for biopsy. Am J Kidney Dis 48: by the National Kidney Foundation, Inc. INDEX WORDS: Breast calcification; end-stage renal disease (ESRD); chronic kidney disease (CKD); screening mammography. CURRENTLY IN THE United States, 431,284 patients are being treated for end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Females account for about 43%, with the majority older than 45 years. 1,2 According to current recommendations for breast cancer screening, most of these patients are in the age range in which patients are encouraged to undergo screening mammography. Breast calcification is an important finding on screening mammography; the appearance and pattern may be specific, reflecting a benign, malignant, or indeterminate pattern. Patterns of breast calcification in renal dialysis patients are of particular interest because there is an increased incidence of breast calcification in patients with renal disease There were attempts in the past to describe patterns of breast calcifications in renal patients, but these included only 2 old small studies 5,11 and a few scattered case reports, 4,9,12 significantly limited by the poor quality of mammogram resolution of that period. Data for morphological characteristics of breast calcification associated with renal disease, incidence of benign versus malignant calcifications, and their clinical consequences clearly are limited, although thousands of women with ESRD are eligible for mammogram screening. This data is important to aid in management and avoid unnecessary costly erroneous workups and psychological stress for the patient. In this study, we compare mammograms of women with ESRD on long-term dialysis therapy with those of women with normal renal function. We describe morphological characteristics of breast calcifications in each group and compare From the Departments of Medicine and Radiology, Staten Island University Hospital; and Regional Radiology, St Vincent s Medical Center of Richmond, Staten Island, NY. Received October 21, 2005; accepted in revised form May 4, Originally published online as doi: /j.ajkd on June 30, Support: None. Potential conflicts of interest: None. Address reprint requests to Mario Castellanos, MD, Director of Medical Women s Health Division, Associate Director of Research, Department of Medicine, 401 Seaview Ave, Staten Island, NY mario_castellanos@ siuh.edu 2006 by the National Kidney Foundation, Inc /06/ $32.00/0 doi: /j.ajkd American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 48, No 2 (August), 2006: pp
2 302 callback rates, incidences of benign and malignant calcifications, diagnostic workups for suspicious calcifications, and biopsy recommendation rates for each group. METHODS Study Population We performed a retrospective case-control study in After institutional review board approval, medical records from 3 dialysis units from a university-affiliated medical center were reviewed. All women who were on hemodialysis therapy were considered. From this cohort, patients who had a previous mammogram performed at the medical center were assigned to the study group. Women attending the institution s medical clinics who had normal renal function were randomly selected to form the control group. Patients with normal renal function were obtained by randomly selecting patients with normal creatinine clearance and serum calcium levels. Patients were screened to ensure that each had a mammogram at the institution. Patients in the control group were age matched to the renal group to create a similar age distribution to the study group because the incidence of breast calcification is influenced by age. 5 Figure 1 shows the age distribution of renal patients. Mammography Mammograms of patients from both the renal and control groups were reviewed. Mammograms were obtained by using a standard 4-view examination with Lorad MIII mammography units (Trex Medical, Danbury, CT). Three experienced mammographers reviewed the films (S.-J.G., D.D., and C.R.). They were blinded to patient renal function and reexamined the mammograms independently (Fig 2). Calcifications were described, categorized, and reported according to the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging Reporting and Data Systems (BIRADS) 13 (Table 1). A component of the BIRADS is that it gives standard terminology for describing findings seen on mammography that are used to provide consistency among radiologists. Using this CASTELLANOS ET AL system, breast calcifications can be grouped as being associated with benign (9 calcification patterns), malignant (3 calcification patterns), and indeterminate breast pathological states (2 calcification patterns). The final diagnosis of mammograms was reported by using the BIRADS final assessment categories. Negative/ normal studies are placed into category 1; benign lesions, category 2; probably benign lesions, category 3; suspicious lesions, category 4; and highly suspicious lesions, category 5. Incomplete screening that requires additional workup is placed in category 0. BIRADS 1, 2, and 3 were regarded as negative studies and BIRADS 4 and 5 were regarded as positive studies for malignancy. Follow-Up Patients were called back for abnormal findings on initial screening mammogram, such as a mass, asymmetric densities, and suspicious breast calcifications. The callback rate, a standard mammography measure, was examined in both groups. The callback rate is the number of cases called back after initial screening mammography of the total number of patients screened. Additional workup included magnification views of the breast with or without breast ultrasound, as needed. Patients who had a final BIRADS description after the additional workup consistent with suspicious calcifications for malignancy were recommended to undergo a biopsy. Biopsy recommendation rates were calculated as total number of patients recommended for biopsy in each group against the total number of patients screened. Statistical Analyses Nonparametric statistics were used. Chi-square and Fisher exact tests were performed as appropriate, with Fisher exact used in all instances in which cell sizes were less than 5. RESULTS Forty-five renal patients from the 3 dialysis units had mammograms at the medical center. Controls consisted of 86 age-matched patients. Fig 1. Age distribution of renal patients.
3 BREAST CALCIFICATIONS IN RENAL DISEASE 303 Fig 2. Mammogram showing vascular calcifications. From the renal group, 38 of 45 patients (84.4%) had calcifications on their mammograms. Conversely, 51 of 86 controls (59.3%) had calcifications on their mammograms. The incidence of Table 1. Abbreviations of Breast Calcification Categories Pattern Malignant association Interrupted, fine, linear, or branching Pleomorphic heterogeneous Amorphous Benign association Skin Vascular Large rod-like Eggshell Spherical or lucent center Suture Dystrophic Punctate ( 0.5 mm) Milk of calcium Indeterminate Coarse Round (0.5-1 mm) Abbreviation IC HC AC SC VC LG EC OC SC1 DC PC MC CC RC calcifications in the renal group versus the control group was statistically significant (P 0.003; Table 2). The frequency of each category is listed in Table 3. Most of the increase in incidence of calcifications in the renal group appears to be caused by several benign calcification patterns (Fig 3; Table 3). Comparing categories of benign calcifications, vascular calcification was the most common pattern seen in both groups, with no statistical difference between groups (P 0.46). The benign pattern that differed between groups was parenchymal spherical or lucent calcification pattern. Renal patients were significantly more likely to have this calcification pattern than controls (P ; Table 3). Comparing only incidence of calcifications commonly considered to be associated with malignancy (BIRADS 4 and 5), amorphous, pleomorphic heterogeneous, and interrupted, fine, linear, or branching, no statistically significant difference was identified between the renal and control groups for the incidence of each indi-
4 304 CASTELLANOS ET AL Table 2. Results of Mammogram Review Renal Patients Controls P No. of patients No. of cases with calcifications 38 (84.4) 51 (59.3) Callback rate for suspicious calcifications 4/45 (8.8) 3/86 (3.48) 0.23 Final BIRADS description consistent with malignancy-associated calcification and cases sent for biopsy 4/45 (8.8) 1/86 (1.16) 0.047* NOTE. Values expressed as number (percent). *As a group, malignancy-associated calcifications were significantly greater in the renal group (8.8%) versus controls (1.16%), and biopsy recommendation rates were significantly different (P 0.047). vidual calcification (Table 3). However, as a group, the final diagnosis of malignancy-associated calcifications provoking a biopsy recommendation was significantly greater in the renal group (4 of 45 patients) versus controls (1 of 86 patients; P 0.047; Tables 2 and 4). On initial screening mammography, there were 4 cases with suspicious calcifications in the renal group of 45 patients screened and 3 cases with suspicious calcifications in the control group of 86 patients screened (Table 2). Therefore, callback rates for abnormal calcifications were 8.8% for the renal group versus 3.48% for controls. This was not statistically significant (P 0.23). Upon further workup of patients called back for suspicious calcifications, all 4 cases in the renal group, but only 1 case of the 3 callback cases in the control group, had a final BIRADS description consistent with a malignancy-associated calcification pattern, and biopsy was recommended. Therefore, the incidence of final radiological diagnosis of malignant-associated calcifications, reflecting the biopsy recommendation rate, was calculated as the total number of patients recommended for biopsy of the total number of patients screened in each group. In the renal group, this was 8.8%, and in controls, 1.16% (P 0.047, which is statistically significant; Tables 2 and 4). Table 3. Frequencies of Morphological Characteristics of Calcifications on Mammograms of the Renal and Control Groups Morphological Characteristics of Calcification Abbreviation Frequency of Calcification Pattern in the Renal Group (%) Frequency of Calcification Pattern in the Control Group (%) P Malignant Interrupted, fine, linear, or branching IC Pleomorphic heterogeneous HC Amorphous AC Benign Skin SC Vascular VC Large rod-like LG Eggshell EC Spherical or lucent center OC * Suture SC Dystrophic DC Punctate ( 0.5 mm) PC Milk of calcium MC Benign or malignant Coarse CC Round (0.5-1 mm) RC NOTE. As a group, malignancy-associated calcifications were significantly greater in the renal group (4 of 45 patients) versus controls (1 of 86 patients; P 0.047). Vascular calcification was the most common pattern seen in both groups, with no statistical difference between groups. *Categories are statistically significant.
5 BREAST CALCIFICATIONS IN RENAL DISEASE 305 Fig 3. Frequencies of benign and malignant calcifications on mammograms of the renal and control groups. The frequency of spherical or lucent (OC) calcification pattern was more common in the renal group, P DISCUSSION Thousands of patients with ESRD are eligible for breast cancer screening with mammography. However, there is a concern that mammographic interpretation in this population may be difficult because of the increased incidence of breast tissue calcification. Metastatic soft-tissue calcification as a result of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic renal disease is well described. 5,7,8,10 In 1987, Sommer et al 5 described breast calcifications in 68% of patients undergoing dialysis. Since then, there have been several reports describing breast calcifications in patients with renal disease. 3,4,6,9 There is concern that the increased incidence of breast calcifications in patients on dialysis therapy may pose a diagnostic dilemma. Despite this possibility, only 2 old studies 5,11 attempted to describe and categorize morphological characteristics of breast calcifications in dialysis patients. These studies were small and significantly limited by the unavailability of current highresolution mammography techniques. Furthermore, investigators of these studies 5,11 and previous case reports 4,9,12 did not have uniform terminology available for categorizing and reporting breast calcifications because they were done before institution of the American College of Radiology BIRADS. Sommer et al 5 compared mammograms of 15 patients with compensated renal insufficiency, 22 on hemodialysis therapy and 14 who had renal transplants, with a control group of 100 who had normal kidney function. Frequency, size, structure, and location of calcific lesions were assessed. Patients with renal disease had significantly more calcifications than those with normal kidney function. Parenchymal calcifications (61% versus 27%) were the most frequent, followed by vascular (45% versus 8%) and ductal (29% versus 9%). Parenchymal calcifications were categorized as small, round, or oval; scattered; and not associated with a mass. This appears to correspond to punctate and round calcifications in the BIRADS groups. Ductal calcifications, large rod-like in current terms, usually were found behind the areola and also could be seen in other areas of the breast in the typical orientation toward the nipple. No calcification looked like malignant calcification of the breast, according to the investigators. Evans et al 11 studied mammograms of 16 women on renal dialysis therapy and compared them with a control group of 32 women attending for routine mammographic screening. They categorized calcifications as vascular, parenchymal, and ductal. Parenchymal calcifications were grouped as punctate, teacup, or pearl shaped. Using the current BIRADS lexicon, these terms probably would represent dystrophic, milk of calcium, and round, respectively. They categorized ductal calcifica-
6 306 tions as granular, casting, or linear, which, in BIRADS terms, describes large rod-like calcifications. They found a significant increase in parenchymal, followed by vascular, calcifications in women on renal dialysis therapy. Ductal calcifications were no more prevalent in patients on dialysis therapy compared with the control group, and in no case did calcifications simulate malignancy. These 2 studies correctly concluded that there was an increased incidence of breast calcifications on mammograms of renal patients, and most of these calcifications did not simulate malignancy with the available imaging resolution. However, they did not compare the incidence of malignant calcifications as a group, clinical consequences of increased calcifications, or callback and biopsy recommendation rates. In our study, breast calcifications were more common in patients on long-term dialysis therapy (84.4%) compared with age-matched control patients (59%), and the increased incidence was caused mostly by calcifications associated with benign morphological characteristics categorized according to the current standard BIRADS. This is reflected by the similar callback rates and is consistent with results of the 2 previously reported studies and case reports. 5,7,8,10 However, compared with the control group, the incidence of malignancy-associated calcifications as a group was slightly greater in the renal group, as was the biopsy recommendation rate (P 0.047). Therefore, it appears that renal patients, once called back, were more likely to be recommended for biopsy compared with the general population. However, an increase in cancer rates in renal patients remains uncertain at this time because the study is not designed to clarify this question. Bias related to interval length between mammogram screenings may exist, leading to group differences. Therefore, what can be concluded from this study is that the greater frequency of breast calcifications leads to a greater rate of breast calcifications of indeterminate behavior warranting biopsies. The callback rate at our institution for the entire year of 2005 was about 10%. The renal group in the study had a similar rate of 8.8%. The biopsy rate at the institution is 1.5%, similar to that of controls at 1.16%. However, this is much lower than the 8.8% biopsy rate for the renal group in the study. CASTELLANOS ET AL Additional studies with a larger sample size are recommended to confirm this new finding and determine the positive predictive value of indeterminate calcifications and determine cancer rates in the hemodialysis population. Therefore, at this time, every woman on dialysis therapy should be referred for screening mammography, and the physician taking care of these patients should be aware of the slightly increased risk for workup and possibly resultant psychological stress after screening in dialysis patients. Mammography is an important screening tool and should be offered to all dialysis patients according to standard health care guidelines of the general population. REFERENCES 1. US Renal Data System: Excerpts from the USRDS 2004 Annual Data Report. Am J Kidney Dis 45:S1-S280, 2005 (suppl 1) 2. US Renal Data System: Annual Report. Incidence and prevalence of ESRD. Am J Kidney Dis 34:S40-S50, 1999 (suppl 1) 3. Sarah Rovno HD, Feig SA, Hughes JS, Hurford MT, Karasick D, Filippone E: Breast imaging case of the day. Radiographics 18: , Cooper RA, Berman S: Extensive breast calcification in renal failure. J Thorac Imaging 3:81-82, Sommer G, Kopsa H, Zazgornik J, Salomonowitz E: Breast calcifications in renal hyperparathyroidism. AJR Am J Roentgenol 148: , McDougal BA, Lukert BP: Resolution of breast pain and calcification with renal transplantation. Arch Intern Med 137: , Conger JD, Hammond WS, Alfrey AC, Contiguglia SR, Stanford RE, Huffer WE: Pulmonary calcification in chronic dialysis patients: Clinical and pathologic studies. Ann Intern Med 83: , Parfitt AM: Soft tissue calcification in uremia. Arch Intern Med 124: , Han SY, Witten DM: Diffuse calcification of the breast in chronic renal failure. AJR Am J Roentgenol 129: , Massry SG, Coburn JW, Popovtzer MM, Shinaberger JH, Maxwell MH, Kleeman CR: Secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal failure: The clinical spectrum in uremia, during hemodialysis, and after renal transplantation. Arch Intern Med 124: , Evans AJ, Cohen MEL, Cohen GF: Patterns of breast calcification in patients on renal dialysis. Clin Radiol 45: , Evans SE, Whitehouse GH: Extensive calcification in the breast in chronic renal failure. Br J Radiol 64: , American College of Radiology: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data Systems (BIRADS) (ed 4). Reston, VA, American College of Radiology, 2003
Leonard M. Glassman MD Analysis of Breast Calcifications
 Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications. BI-RADS 5 th Edition
 UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Evaluation of Breast Calcifications Leonard M.
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Evaluation of Breast Calcifications Leonard M.
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) has standardized the description and management of findings identified on mammograms, thereby f
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BREAST IMAGING Elizabeth S. Burnside, MD, MPH, MS Jennifer E. Ochsner, MD Kathryn J. Fowler, MD Jason P. Fine, PhD Lonie R. Salkowski, MD Daniel L. Rubin, MD, MS Gale A. Sisney, MD Use
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BREAST IMAGING Elizabeth S. Burnside, MD, MPH, MS Jennifer E. Ochsner, MD Kathryn J. Fowler, MD Jason P. Fine, PhD Lonie R. Salkowski, MD Daniel L. Rubin, MD, MS Gale A. Sisney, MD Use
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review
 Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2009; 50(9) :
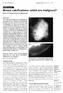 907 Pictorial Essay CME Article Breast calcifications: which are malignant? Muttarak M, Kongmebhol P, Sukhamwang N ABSTRACT Most calcifications depicted on mammograms are benign. However, calcifications
907 Pictorial Essay CME Article Breast calcifications: which are malignant? Muttarak M, Kongmebhol P, Sukhamwang N ABSTRACT Most calcifications depicted on mammograms are benign. However, calcifications
BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases?
 BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases? Poster No.: B-0966 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Etxano Cantera, I. Simon-Yarza, G.
BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases? Poster No.: B-0966 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Etxano Cantera, I. Simon-Yarza, G.
Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography
 Progress in Public Health Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography JMAJ 44(7): 318 324, 2001 Tokiko ENDO Director, Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast cancer has been increasing
Progress in Public Health Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography JMAJ 44(7): 318 324, 2001 Tokiko ENDO Director, Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast cancer has been increasing
BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1
 Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
DESCRIPTION: Percentage of final reports for screening mammograms that are classified as probably benign
 Measure #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F
Measure #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F
DESCRIPTION: Percentage of final reports for screening mammograms that are classified as probably benign
 Quality ID #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL
Quality ID #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL
Hiding in Plain Sight / Site: Archictectural Distortions and Breast Asymmetries
 Hiding in Plain Sight / Site: Archictectural Distortions and Breast Asymmetries Dianne Georgian-Smith MD Associate Professor Harvard Med School Brigham and Women s Hospital Financial Disclosures Book Publication
Hiding in Plain Sight / Site: Archictectural Distortions and Breast Asymmetries Dianne Georgian-Smith MD Associate Professor Harvard Med School Brigham and Women s Hospital Financial Disclosures Book Publication
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Retrospective Analysis on Malignant Calcification Previously Misdiagnosed as Benign on Screening Mammography 스크리닝유방촬영술에서양성으로진단되었던악성석회화에대한후향적분석
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.4.251 Retrospective Analysis on Malignant Calcification Previously Misdiagnosed as Benign on Screening 스크리닝유방촬영술에서양성으로진단되었던악성석회화에대한후향적분석
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.4.251 Retrospective Analysis on Malignant Calcification Previously Misdiagnosed as Benign on Screening 스크리닝유방촬영술에서양성으로진단되었던악성석회화에대한후향적분석
Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography
 Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography Poster No.: C-1957 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H. J. Lim, K. R. Cho, K. W. Hwang, B. K. Seo, O.
Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography Poster No.: C-1957 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H. J. Lim, K. R. Cho, K. W. Hwang, B. K. Seo, O.
Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns
 Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast
Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast
Linear Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Lai et al. Linear reast alcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Kenny. Lai 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Lai K, Slanetz
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Lai et al. Linear reast alcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Kenny. Lai 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Lai K, Slanetz
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Is Probably Benign Really Just Benign? Peter R Eby, MD, FSBI Virginia Mason Medical Center Seattle, WA
 Is Probably Benign Really Just Benign? Peter R Eby, MD, FSBI Virginia Mason Medical Center Seattle, WA Disclosures: CONSULTANT FOR DEVICOR MEDICAL ARS Question 1 Is probably benign really just benign?
Is Probably Benign Really Just Benign? Peter R Eby, MD, FSBI Virginia Mason Medical Center Seattle, WA Disclosures: CONSULTANT FOR DEVICOR MEDICAL ARS Question 1 Is probably benign really just benign?
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU?
 MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht. Chair Dutch Expert Centre for Screening Board EUSOBI
 Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht Best practice in Breast Imaging: what s new and what women need to know and Update on the Second Implementation Report of the 2003 Council Recommendation
Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht Best practice in Breast Imaging: what s new and what women need to know and Update on the Second Implementation Report of the 2003 Council Recommendation
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay
 CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report
 Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Mammography Education, Inc.
 Mammography Education, Inc. 2018 3D image of the breast tissue BREAST SEMINAR SERIES Faculty LÁSZLÓ TABÁR, MD, FACR (Hon) Professor emeritus of Radiology Using the Multimodality Approach. A FULLY INTERACTIVE,
Mammography Education, Inc. 2018 3D image of the breast tissue BREAST SEMINAR SERIES Faculty LÁSZLÓ TABÁR, MD, FACR (Hon) Professor emeritus of Radiology Using the Multimodality Approach. A FULLY INTERACTIVE,
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET
 Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions 1. 21 year old female presenting with left breast palpable mass, what is the most appropriate
Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions 1. 21 year old female presenting with left breast palpable mass, what is the most appropriate
Sonographic and Mammographic Features of Phyllodes Tumours of the Breast: Correlation with Histological Grade
 Sonographic and Mammographic Features of Phyllodes Tumours of the Breast: Correlation with Histological Grade Poster No.: C-0046 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit C. Y.
Sonographic and Mammographic Features of Phyllodes Tumours of the Breast: Correlation with Histological Grade Poster No.: C-0046 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit C. Y.
now a part of Electronic Mammography Exchange: Improving Patient Callback Rates
 now a part of Electronic Mammography Exchange: Improving Patient Callback Rates Overview This case study explores the impact of a mammography-specific electronic exchange network on patient callback rates
now a part of Electronic Mammography Exchange: Improving Patient Callback Rates Overview This case study explores the impact of a mammography-specific electronic exchange network on patient callback rates
Segmental Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center
 Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications
 Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Radiology Review Course Hotel del Coronado Coronado, California
 37 th Annual Radiology Review Course Hotel del Coronado Coronado, California Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM TABLE OF CONTENTS Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM SAM Session - Breast Imaging Update 12:45 PM 1:30
37 th Annual Radiology Review Course Hotel del Coronado Coronado, California Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM TABLE OF CONTENTS Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM SAM Session - Breast Imaging Update 12:45 PM 1:30
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
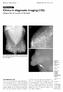 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Breast asymmetries in mammography: Management
 Breast asymmetries in mammography: Management Poster No.: C-1026 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan 1, F. J. Hidalgo Ramos 2, J. L. Ortega Garcia 3, Keywords: DOI:
Breast asymmetries in mammography: Management Poster No.: C-1026 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan 1, F. J. Hidalgo Ramos 2, J. L. Ortega Garcia 3, Keywords: DOI:
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
2017BREAST SEMINAR SERIES
 Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 510 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 510 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Electrical impedance scanning of the breast is considered investigational and is not covered.
 ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): Medical Policy Title: Electrical Impedance Scanning of the Breast Document: ARB0127 Administered by: Public Statement:
ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): Medical Policy Title: Electrical Impedance Scanning of the Breast Document: ARB0127 Administered by: Public Statement:
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
 Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium. Sat Nov 12 th 2016
 Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY
 Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Mammography Education, Inc.
 Mammography Education, Inc. 2018 3D image of the breast tissue Sept 18-21 Hs-on Screening Course combined with Multimodality Diagnosis of Breast Diseases with Emphasis on Breast MRI SIGTUNA Hotel Kristina
Mammography Education, Inc. 2018 3D image of the breast tissue Sept 18-21 Hs-on Screening Course combined with Multimodality Diagnosis of Breast Diseases with Emphasis on Breast MRI SIGTUNA Hotel Kristina
Mammography. What is Mammography? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography, full-field digital mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis
 Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
PLACE LABEL HERE BASELINE / PRE-TREATMENT. ACRIN 6657 Extension MRI Form: Baseline / Pre-Treatment MRI 1. o Unknown
 T1 ACRIN 6657 Extension MRI Form: Baseline / Pre-Treatment MRI 1 If this is a revised or corrected form, please box. ACRIN Study 6657 No. Instructions: In accordance with the protocol, four MRI exams are
T1 ACRIN 6657 Extension MRI Form: Baseline / Pre-Treatment MRI 1 If this is a revised or corrected form, please box. ACRIN Study 6657 No. Instructions: In accordance with the protocol, four MRI exams are
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography
 Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD!
 Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD! ACS Estimated Cancers Statistics 2014! Breast! New Cases in Women! 232,670 (+67,570 in situ)! Deaths in Women! 40,000! Colon! 48,380! 24,040! Cervical! 12,360! 4,020!
Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD! ACS Estimated Cancers Statistics 2014! Breast! New Cases in Women! 232,670 (+67,570 in situ)! Deaths in Women! 40,000! Colon! 48,380! 24,040! Cervical! 12,360! 4,020!
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography
 BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Atypical And Suspicious Categories In Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology Of The Breast
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (October. 216), PP 57-61 www.iosrjournals.org Atypical And Suspicious Categories in
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (October. 216), PP 57-61 www.iosrjournals.org Atypical And Suspicious Categories in
PLACE LABEL HERE. ACRIN 6657 MRI Form: Pre-Treatment (MRI-1)
 M3 ACRIN 6657 MRI Form: Pre-Treatment (MRI-1) If this is a revised or corrected form,indicate by checking box. ACRIN Study 6657 Case # Instructions: In accordance with the protocol, four MRI exams are
M3 ACRIN 6657 MRI Form: Pre-Treatment (MRI-1) If this is a revised or corrected form,indicate by checking box. ACRIN Study 6657 Case # Instructions: In accordance with the protocol, four MRI exams are
Mammography Education, Inc.
 Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 315 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 315 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Disclosures. Breast Cancer. Breast Imaging Modalities. Breast Cancer Screening. Breast Cancer 6/4/2014
 : Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
: Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
 Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Breast Tomosynthesis. What is breast tomosynthesis?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients
 Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Tissue Breast Density
 Tissue Breast Density Reporting breast density within the letter to the patient is now mandated by VA law. Therefore, this website has been established by Peninsula Radiological Associates (PRA), the radiologists
Tissue Breast Density Reporting breast density within the letter to the patient is now mandated by VA law. Therefore, this website has been established by Peninsula Radiological Associates (PRA), the radiologists
May-Lin Wilgus. A. Study Purpose and Rationale
 Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions?
 Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Mammography Education, Inc.
 Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 315 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 315 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Observer Agreement Using the ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)-Ultrasound, First Edition (2003)
 Observer Agreement Using the ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)-Ultrasound, First Edition (2003) Chang Suk Park, MD 1 Jae Hee Lee, MD 2 Hyeon Woo Yim, MD 3 Bong Joo Kang, MD 4 Hyeon
Observer Agreement Using the ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)-Ultrasound, First Edition (2003) Chang Suk Park, MD 1 Jae Hee Lee, MD 2 Hyeon Woo Yim, MD 3 Bong Joo Kang, MD 4 Hyeon
Breast Health and Imaging Glossary
 Contact: Lorna Vaughan HerSpace Breast Imaging & Biopsy Associates 300 State Route 35 South W. Long Branch, NJ 07764 732-571-9100, ext. 104 lorna@breast-imaging.com Breast Health and Imaging Glossary Women
Contact: Lorna Vaughan HerSpace Breast Imaging & Biopsy Associates 300 State Route 35 South W. Long Branch, NJ 07764 732-571-9100, ext. 104 lorna@breast-imaging.com Breast Health and Imaging Glossary Women
Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions A. Zulfiqar, MMed* v. Param, DMRD** F.A. Meah, FRACS* s. Nair, FRCS** M.A. Siti-Aishah, DCP* A. N orizan, DCP** * Departments of Radiology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions A. Zulfiqar, MMed* v. Param, DMRD** F.A. Meah, FRACS* s. Nair, FRCS** M.A. Siti-Aishah, DCP* A. N orizan, DCP** * Departments of Radiology,
Correlation Between BIRADS Classification and Ultrasound -guided Tru-Cut Biopsy Results of Breast Lesions: Retrospective Analysis of 285 Patients
 Correlation Between BIRADS Classification and Ultrasound -guided Tru-Cut Biopsy Results of Breast Lesions: Retrospective Analysis of 285 Patients Poster No.: C-1433 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
Correlation Between BIRADS Classification and Ultrasound -guided Tru-Cut Biopsy Results of Breast Lesions: Retrospective Analysis of 285 Patients Poster No.: C-1433 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Development of a Bayesian Network for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
 Development of a Bayesian Network for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Linda M. Roberts, Charles E. Kahn, Jr., Peter Haddawy {roberts,kahn,haddawy}@cs.uwm.edu Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Development of a Bayesian Network for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Linda M. Roberts, Charles E. Kahn, Jr., Peter Haddawy {roberts,kahn,haddawy}@cs.uwm.edu Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
2017BREAST SEMINAR SERIES
 Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 510 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 510 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection
 White Paper Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection WHITE PAPER 2 3 Abstract PowerLook Tomo Detection, a concurrent computer-aided detection (CAD)
White Paper Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection WHITE PAPER 2 3 Abstract PowerLook Tomo Detection, a concurrent computer-aided detection (CAD)
Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique
 Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique Specimen Handling: The breast specimen when received should be measured and grossly inspected for any orientation designated by the
Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique Specimen Handling: The breast specimen when received should be measured and grossly inspected for any orientation designated by the
Dense Breasts, Get Educated
 Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
«àπ π â Õ μ «å «π Áß μâ π π ßæ π ª
 «æ å μ Ù-ı ªï Ë Ûapple Ë Ù μ.. -.. ÚııÙ Reg 4-5 Med J Vol. 30 No. 4 Oct - Dec 2011 π æπ åμâπ Original Article «μ»ÿ º æ.., Cheerawan Tansupaphon M.D., «.«. ß «π Thai Board of Diagnostic Radiology ÿà ß π
«æ å μ Ù-ı ªï Ë Ûapple Ë Ù μ.. -.. ÚııÙ Reg 4-5 Med J Vol. 30 No. 4 Oct - Dec 2011 π æπ åμâπ Original Article «μ»ÿ º æ.., Cheerawan Tansupaphon M.D., «.«. ß «π Thai Board of Diagnostic Radiology ÿà ß π
Advanced Course on Multimodality Detection and Diagnosis of Breast Diseases
 BREAST SEMINAR Advanced Course on Multimodality Detection and 3D image of the breast tissue Invited speaker LÁSZLÓ TABÁR, MD,FACR (Hon) Falun, Sweden Nov 22-23, 2014 ATHENS, Greece Royal Olympic Hotel
BREAST SEMINAR Advanced Course on Multimodality Detection and 3D image of the breast tissue Invited speaker LÁSZLÓ TABÁR, MD,FACR (Hon) Falun, Sweden Nov 22-23, 2014 ATHENS, Greece Royal Olympic Hotel
Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer: Imaging and Clinical Characteristics
 Women s Imaging Original Research Krizmanich-Conniff et al. Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Women s Imaging Original Research Kristin M. Krizmanich-Conniff 1 Chintana Paramagul 2 Stephanie K. Patterson
Women s Imaging Original Research Krizmanich-Conniff et al. Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Women s Imaging Original Research Kristin M. Krizmanich-Conniff 1 Chintana Paramagul 2 Stephanie K. Patterson
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice
 Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
Breast Imaging Donald L. Renfrew, MD
 This free educational material is provided by 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Breast cancer is the most frequent non-skin cancer diagnosis in women, with an
This free educational material is provided by 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Breast cancer is the most frequent non-skin cancer diagnosis in women, with an
11/1/2014. Radiologic incidentalomas Ordering pitfalls Newer technology and applications
 Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- AIDED DETECTION (CAD) POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Investigating the performance of a CAD x scheme for mammography in specific BIRADS categories
 Investigating the performance of a CAD x scheme for mammography in specific BIRADS categories Andreadis I., Nikita K. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University of
Investigating the performance of a CAD x scheme for mammography in specific BIRADS categories Andreadis I., Nikita K. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University of
Name of Policy: Computer-aided Detection (CAD) Mammography
 Name of Policy: Computer-aided Detection (CAD) Mammography Policy #: 112 Latest Review Date: October 2010 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature
Name of Policy: Computer-aided Detection (CAD) Mammography Policy #: 112 Latest Review Date: October 2010 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature
High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography
 Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
