Angiogenesis in urothelial tumors of the upper urinary tract
|
|
|
- Theresa Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(4): Angiogenesis in urothelial tumors of the upper urinary tract FLAVIA BADERCA 1), RODICA LIGHEZAN 1), ALIS DEMA 2), AURORA ALEXA 1), M. RAICA 1) 1) Department of Histology, Victor Babeş University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timişoara 2) Department of Pathology, Victor Babeş University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timişoara Abstract Angiogenesis is an essential process in the progression of malignant tumors. Tumors of the ureter and renal pelvis account for 5% of all urinary tract neoplasms. Little is known about angiogenesis in upper urinary tract urothelial tumors. We tried to demonstrate angiogenesis by using three endothelial markers CD31, CD34, von Willebrand factor and one pericytes marker (α-smooth muscle actin) in 26 cases. The pattern of CD31 immunolabelling was more complex and extensive than the vessel pattern shown by CD34 or factor VIII staining. In non-invasive tumors we observed that angiogenesis process is limited to connective tissue of tumor stroma. In the tumor area, the blood vessels stained with anti-cd31 had large lumen, thin walls and numerous branches, some of them being very thin. Pericyte covered vessels were branching of frequently into smaller, pericyte negative vessels. Keywords: angiogenesis, endothelial cells, urothelial tumors, blood vessels, immunohistochemistry. Introduction Angiogenesis involves extracellular matrix remodeling, associated with proliferation and migration of endothelial cells [1]. During vasculogenesis, the precursor cells differentiate into endothelial cells, which assemble into first vascular networks [2]. During embryonic and fetal development, angiogenesis and vasculogenesis occur concomitantly. In 1971, Folkman popularized the concept of tumor angiogenesis [3], and demonstrated that angiogenesis was essential for the progression of the malignant tumors. Solid tumors could not grow beyond two mm in diameter without a generation of new vessels [4]. Tumors of the ureter and renal pelvis account for 5% of all urinary tract neoplasms and of these greater of 90% are urothelial carcinomas [4]. The incidence of these tumors has increased slightly in the last thirty years being more common in older patients. Because of the reduced incidence of patients with such tumors, relatively few data are available about their natural evolution and behavior. The morphological and immunohistochemical profile overlaps only in part with those reported for similar tumors developed in the urinary bladder, which, in their turn, are well known nowadays. In our region, the incidence of ureter and renal pelvis tumors is higher, reaching more than 9%. Therefore the main objective of the present study was to determine the light microscopic and immunohistochemical characteristics of the angiogenesis in urothelial tumors. Material and methods Specimens We retrospectively investigated 26 patients with urothelial tumors of the upper urinary tract, aged between 47 and 68 years, admitted in the Clinical Hospital of Timişoara. The surgical technique performed in all patients was nephroureterectomy, so in each case specimens were taken from the tumor, kidney and ureter. Specimens were fixed in 4% buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin, and step sections were stained with routine Haematoxylin Eosin method. Immunohistochemistry Additional slides were immunohistochemically stained, using the three steps labeled streptavidin-biotinimmunoperoxidase technique (LSAB2, DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark). After endogenous peroxidase inhibition, antigen retrieval, the sections were incubated with the first step antibodies: anti-factor VIII (von Willebrand, monoclonal, clone F8/86), anti-cd31 (monoclonal, clone JC70A) and anti-cd34 (monoclonal, clone QBEnd10). The pericytes were identified with anti-α-smooth muscle actin antibody (monoclonal, clone 1A4). Thereafter, the slides were washed in PBS and consecutively reacted with a labeled streptavidin-biotin system. The reaction product was visualized in brown with DAB as chromogen. The nuclei were counterstained with Mayer s Haematoxylin. The von Willebrand factor is a large glycoprotein with the multimeric structure confined to endothelial
2 264 Flavia Baderca et al. cells and megacaryocytes and mediate platelet adhesion and thrombus formation at the sites of vascular injury. CD31 (PECAM) is a glycoprotein found on various hematopoietic cells such as bone marrow stem cells, CD8+ cells, monocytes, neutrophils, platelets and endothelial cells. This molecule is involved in cell adhesion and mediates the transmigration of leucocytes from blood vessel lumen into the extravascular space. CD34 is a transmembrane glycoprotein present on hematopoietic stem cells and endothelial cells. Actin is a protein, which presents at least six different isotypes. Ultrastructurally, actin forms diffusely distributed cytoplasmic 6 nm microfilaments. The distribution of α-smooth muscle actin is restricted to pericytes, vascular media, smooth muscle of viscera and myoepithelial cells of salivary gland and breast. Anti-vimentin (clone V9) antibody was used as a marker of the optimal fixation and embedding procedures. The external positive control was represented by slides from a capillary haemangioma. As intern positive control, we used immunolabelling of endothelial glomerular cells. As negative control, it was used a nonspecific immunoglobulin, provided by the manufacturer (DAKO, Denmark), performed on slides from the same cases. All reagents for the immunohistochemical technique were supplied from DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark. Results We examined blood vessels in urothelial tumors of upper urinary tract. The site of primary tumor is shown in Table 1. Table 1 The site of primary tumor Tumor location No. of cases % Calyces 4 15 Renal pelvis 5 19 Calyces + Renal pelvis 7 27 Ureter 8 31 Renal pelvis + Ureter 2 8 We studied the morphological aspects of angiogenesis in urothelial tumors of upper urinary tract. There were a lot of differences between cases with the same stage and grade. The sprouting of new vessels from preexisting one could be observed with morphological staining such as Hematoxylin Eosin (Figure 1). Even if some blood vessels could be evaluated on Hematoxylin Eosin stained slides, morphological methods underestimated the number of blood vessels with at least 30%. Moreover, morphological methods could not highlight the presence of single endothelial cells, without lumen, which preceded the canalization phase of new blood vessels formed during angiogenesis (Figure 2). That s why we evaluated the genesis of new blood vessels using the immunohistochemical methods. The first intention was to establish the sensitivity and specificity of the immunohistochemical methods in the urothelial carcinoma. The examination of thin (5 µm) tumor sections stained with anti-von Willebrand factor revealed that the tumor vessels varied greatly in size. The small caliber vessels were predominating. At the smallest end of some vessels there were isolated cells positive for anti-factor VIII related antigen, lacking a visible lumen. These cells stained also for other endothelial cells markers as CD31 and CD34. The pattern of CD31 immunolabelling was more complex and extensive than the vessel pattern shown by CD34 staining. Therefore, the vessels localization and morphology were based on results obtained with these two antibodies. We found that factor VIII related antigen is not enough sensitive for proper counting, because usually it underestimates the mean value of blood vessels. On CD31 immunolabelled slides we observed the largest number of endothelial cells positive for this antibody. In one case, there were observed thin sproutlike filaments without a lumen CD31 positive, which radiated from the vessel wall into the perivascular space of tumor (Figure 3). The tumor vessels were characterized with respect to pericyte coverage, by staining with anti-α smooth muscle actin antibody (SMA). Pericyte positive vessels were defined as CD34 positive structures associated with at least one SMA positive cell (Figure 4). In non-invasive tumors (stage Ta or carcinoma in situ) the blood vessels were sparsely distributed in tumor area. In the connective tissue of tumor, the blood vessels number has been increased in cases associated with presence of inflammatory cells. In most cases, the blood vessels of the tumor area had a large lumen, thin walls and numerous branches, some of them being very thin. The larger blood vessels consisting of endothelial cells and pericytes were branching into smaller, pericyte negative vessels, formed only by endothelial cells. These aspects cannot be observed in the connective tissue from normal urothelial mucosa. On one slide, in the tumor area there were observed small clusters of endothelial cells surrounded by single endothelial cells, a characteristic aspect for the first stage of angiogenesis. The presence of single endothelial cells suggested the progression of tumor angiogenesis. The presence of intravascular embolus could be demonstrated in some vessels using these immunohistochemical methods (Figure 5). We observed few vessels in cases with extensive necrosis. A very important issue for tumor progression was represented by the proliferation of newborn blood vessels. The vascular sprouts arose from blood vessels present in the connective tissue. First we observed the proliferation of single endothelial cells followed by tube formation. While the blood vessels expanded, they invaded the connective tissue of tumor stroma until they reached the stroma-epithelium interface (Figures 6 and 7). Then the blood vessels invaded the tumor parenchyma (Figure 8).
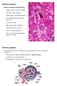
3 Angiogenesis in urothelial tumors of upper urinary tract 265 Figure 1 Small blood vessel of capillary type with sprouting toward malignant cells Figure 2 Blood vessels with large lumen, thin wall and many branches in the tumor stroma Figure 3 CD31 positive sprouts made visible by LSAB-DAB immunohistochemistry extend from the vessel surface into the tumor Figure 4 Pericyte positive vessels stained with anti-sma antibody
4 266 Flavia Baderca et al. Figure 5 Unstained tumor cells observed within a blood vessel lumen lined by endothelial cells, stained for CD31 Figure 6 Newborn blood vessels in connective tissue of urothelial carcinoma Figure 7 The blood vessels at stroma epithelium interface Figure 8 Small blood vessels and single endothelial cells invading the tumor parenchyma
5 On the same slide, depending of site, there could be revealed different aspects of angiogenesis regarding the number and the distribution of newborn blood vessels. The blood vessels are sparse and have bigger lumen in connective tissue of sites with urothelial dysplasia near by tumor carcinoma. In the connective tissue of carcinoma, the blood vessels are frequents and have thin lumen. Discussions Angiogenesis occur mainly during embryonic development and in postnatal tissue growth and differentiation. In adults, angiogenesis takes place mainly in the female reproductive system during the menstrual cycle and in pregnancy. Angiogenesis begins from preexistent vasculature, being either the primitive vascular plexuses formed by vasculogenesis in the embryo or the postcapillary venous compartment of the mature vascular systems. The endpoint is an elaborate vascular network that meets the nutritional and functional demands of the respective organ [5]. Pathologic angiogenesis takes place in numerous diseases such as cancer, diabetic retinopathy, agerelated macula degeneration, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel diseases, endometriosis and many more. The neovascularization is regarded to be causative for the detrimental effects of some diseases and to take part in progression of others. Common characteristics of pathological neovascularization include abnormal vascular permeability and defective vascular remodeling and maturation, which promote leakage, hemorrhaging and inflammation [5]. At least two different types of angiogenesis are known: sprouting of capillaries from preexisting vessels and non-sprouting angiogenesis or intussusceptions [6, 7]. The early phase of angiogenesis consisted in increase of capillary permeability. The normally highly differentiated, flattened endothelial cells and adjacent pericytes become activated, displaying hypertrophy and an increased number of organelles [8]. Then, sprouting angiogenesis implies proteolytic degradation of basement membrane and proliferation and migration of endothelial cells through the extracellular matrix. Both pericytes and endothelial cells contribute to protease degradation of basement membrane in the angiogenic process. After formation of vascular sprouts, the next phase of angiogenesis involves tube formation with final connection of the blind ending sprout to another blood vessel. In contrast to sprouting angiogenesis, which is a well established mode of blood vessel formation, intussusceptive angiogenesis is a relatively rare concept in vascular biology. It was first discovered in the lung as a means capillary network growth [9]. Intussusception causes growth of the capillaries by insertion of columns of cells or interstitial tissue inside the vessel lumen followed by the vessels splitting into multiple vessels. Angiogenesis in urothelial tumors of upper urinary tract 267 In our study, on slides from patients with non-invasive tumors we observed that angiogenesis process is limited to connective tissue of tumor stroma. On our slides, using immunolabelling we were able to demonstrate different phases of angiogenesis in invasive tumors. The immunolabelling of endothelial cells with anti-cd31 antibody was cytoplasmic. Comparing the results obtained for each case, on slides stained with methods mentioned above, we may conclude that the highest sensibility is provided by CD34 and the highest specificity by CD31. Immunohistochemical stains using endothelial markers labeled the vessels sprouts from the early phase of angiogenesis. There have been described some majors differences between normal blood vessels and intratumoral vessels. Tumor blood vessels have multiple structural and functional abnormalities. Their unusual leakiness, potential for rapid growth and remodeling, and expression of distinctive surface molecules are not only responsible for mediating hematogenous spread of tumor cells and maintaining the unusual microenvironment of tumors but also are key to the efficacy of targeted tumor therapy [10, 11]. There have been described three different types of tumor vessels: least mature, intermediate and mature [12]. The least mature vessels were nonperfused endothelial cells sprouts emanating from functional vessels, the intermediate blood vessels were small, perfused but not covered by pericytes. The mature vessels were large, pericytes covered with quiescent endothelial cells and few associated sprouts. The majority of tumor vessels observed on our slides were intermediate or immature. Many of the intratumoral vessels were collapsed. In non-invasive tumor of the upper urinary tract, the angiogenesis was limited to the tumor stroma. The walls of most intratumoral vessels were immature, consisted only of endothelial cells and comparing with normal blood vessels presented morphological differences. In T2 stage urothelial tumors, there were observed microvessels with large lumen, feature important for the metastatic process. Larger tumors tend to have a lower density of newborn blood vessels and a higher number of mature vessels suggesting that the morphology of tumor blood vessels changes as tumors enlarge. The vasculature in many tumors was not covered by pericytes, which reflected functional immaturity of tumor vascular bed. Conclusions Tumor angiogenesis can be detected by immunohistochemical staining of endothelium. Vascular endothelium had a heterogeneous antigenic profile, expressing a number of molecules such as CD31, CD34 and von Willebrand factor, considered endothelial cells markers.
6 268 Each of the three antibodies used to identify endothelial cells gave a different staining when tested on different tumors of the upper urinary tract. Between the labeling methods that we used, the highest sensitivity was shown by CD34 immunolabelling and the highest specificity by CD31 immunolabelling. Therefore we recommend studying the presence of angiogenesis using a panel consisting of all three antibodies (anti-cd31, anti-cd34 and anti-factor VIII related antigen). Our study highlights vessel development in urothelial tumor. We show that tumor vessels develop through identifiable stages, beginning with lines of endothelial cells emanating from blood vessels. The presence of angiogenic sprouts suggests the tumor angiogenic activity. These proliferate endothelial sprouts evolve into small caliber tumor vessel, consisted of perfused endothelial tubes lacking pericytes. In later stages of angiogenesis, perfused endothelial tubes gain pericytes coverage, by contiguous spread. The blood vessels with pericytes coverage had large caliber and reduced sprouting. A tumor response to anti-angiogenic therapy will be primary influenced by the tumor vessels morphology. Because of this, pericyte coverage and protection of tumor vessels may strongly influence tumor therapeutic response. A better understanding of vessel development and maturation in urothelial tumor and of the factors affecting pericyte coverage of their vessels may advance anti-angiogenic therapy of urothelial tumors. Flavia Baderca et al. References [1] GRIFFIOEN A. W., MOLENA G., Angiogenesis: potentials for pharmacologic intervention in the treatment of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic inflammation, Pharmacol Rev, 2000, 52(2): [2] CARMELIET P., JAIN R. K., Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases, Nature, 2000, 407(6801): [3] FOLKMAN J., Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications, N Engl J Med, 1971, 285(21): [4] LYNCH C. F., COHEN M. B., Urinary system, Cancer, 1995, 75: [5] HOLGER G., BETSHOLTZ C. H., Endothelial-pericyte interactions in angiogenesis, Cell Tissue Res, 2003, 314: [6] PATAN S., Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis as mechanisms of vascular network formation, growth and remodeling, J Neurooncol, 2000, 50(1 2):1 15. [7] NOTOYA M., SHINOSAKI T., KOBAYASHI T. et al., Intussusceptive capillary growth is required for glomerular repair in rat thy-1.1 nephritis, Kidney J, 2003, 63: [8] WITMER A. N, VAN BLIJSWIJK B. C, VAN NOORDEN C. J. F. et al., In vivo angiogenic phenotype of endothelial cells and pericytes induced by vascular endothelial growth factor-a, J Histochem Cytochem, 2004, 52(1): [9] BURRI P. H., DJONOV V., Intussusceptive angiogenesis the alternative to capillary sprouting, Mol Aspects Med, 2002, 23(6S):S1 S27. [10] BALUK P., MORIKAWA S., HASKELL A. et al., Abnormalities of basement membrane on blood vessels and endothelial sprouts in tumors, Am J Path, 2003, 163(5): [11] HASHIMUZE H., BALUK P., MORIKAWA S. et al., Openings between defective endothelial cells explain tumor vessel leakiness, Am J Pathol, 2000, 156: [12] GEE M. S., PROCOPIO N. W., MACONNEN S. et al., Tumor vessel development and maturation impose limits of the effectiveness of antivascular therapy, Am J Pathol, 2003, 162: Mailing address Flavia Baderca, Assistant Professor, M. D., Ph. D, Department of Histology, Victor Babeş University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 2 Eftimie Murgu Square, Timişoara, Romania; Phone , flaviabaderca@yahoo.com Received: December 12 th, 2005 Accepted: February 10 th, 2006
Chapter 6. Villous Growth
 Core Curriculum in Perinatal Pathology Chapter 6 Villous Growth Overview of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis Vasculogenesis Extraembryonic Vasculogenesis Angiogenesis Branching angiogenesis Sprouting angiogenesis
Core Curriculum in Perinatal Pathology Chapter 6 Villous Growth Overview of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis Vasculogenesis Extraembryonic Vasculogenesis Angiogenesis Branching angiogenesis Sprouting angiogenesis
Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
 Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance
 Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Tissue renewal and Repair. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science
 Tissue renewal and Repair Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Email: nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science Topic Objectives 1. Describe processes of tissue repair, regeneration
Tissue renewal and Repair Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Email: nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science Topic Objectives 1. Describe processes of tissue repair, regeneration
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
CD105/Smooth muscle actin double immunostaining discriminate between immature and mature tumor blood vessels
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(1):41 45 ORIGINAL PAPER CD105/Smooth muscle actin double immunostaining discriminate between immature and mature tumor blood vessels ANCA MARIA CÎMPEAN,
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(1):41 45 ORIGINAL PAPER CD105/Smooth muscle actin double immunostaining discriminate between immature and mature tumor blood vessels ANCA MARIA CÎMPEAN,
1. The metastatic cascade. 3. Pathologic features of metastasis. 4. Therapeutic ramifications. Which malignant cells will metastasize?
 1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer
 Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):361 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma GABRIELA IEREMIA 1), M. RAICA 2), ANCA MARIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):361 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma GABRIELA IEREMIA 1), M. RAICA 2), ANCA MARIA
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2012, 53(3 Suppl):749 753 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ The characterization of PDGFR-alpha and PDGFR-beta expression in malignant
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2012, 53(3 Suppl):749 753 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ The characterization of PDGFR-alpha and PDGFR-beta expression in malignant
Tissue repair. (3&4 of 4)
 Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
6/5/2010. Renal vein invasion & Capsule Penetration (T3a) Adrenal Gland involvement (T4 vs. M1) Beyond Gerota s Fascia? (?T4).
 GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Healing & Repair. Tissue Regeneration
 Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
CD15 and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
 Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma T.J. Zhou 1, X.H. Huang 1, L. Gong 1 and L. Xiang 2 1 Department of Pathology, the Affiliated Hospital
Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma T.J. Zhou 1, X.H. Huang 1, L. Gong 1 and L. Xiang 2 1 Department of Pathology, the Affiliated Hospital
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017
 Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
A classification of epithelial tissues
 A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice
 Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues
 A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization with Colorectal Carcinoma: A Pilot Study
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA
 PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Angiogenesis in Human Development. Vascular Development
 Angiogenesis in Human Development Jan Kitajewski ICRC 217B, ph 851-4688, email: jkk9 BACKGROUND READING: Vascular Development Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan. Science 277:
Angiogenesis in Human Development Jan Kitajewski ICRC 217B, ph 851-4688, email: jkk9 BACKGROUND READING: Vascular Development Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan. Science 277:
Prepared By Student. Dania Abed Al-majeed. Rahma Raad Hanna. Balqees Mohammed Aasim. Dania Hisham. Rasha Rafiee
 Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay Staining in Urothelial Carcinoma Interpretation Guide
 VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay Staining in Urothelial Carcinoma Interpretation Guide 2 VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay in Urothelial Carcinoma Interpretation Guide Table of Contents Introduction 4 Intended Use
VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay Staining in Urothelial Carcinoma Interpretation Guide 2 VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay in Urothelial Carcinoma Interpretation Guide Table of Contents Introduction 4 Intended Use
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A in Invasive Micropapillary Colorectal Carcinoma
 The coexpression of VEGF-A and CD31 may play a prominent role in the neoangiogenesis of IMPC. This Way to Gas. Photograph courtesy of Craig Damlo. www.soapboxrocket.com. Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial
The coexpression of VEGF-A and CD31 may play a prominent role in the neoangiogenesis of IMPC. This Way to Gas. Photograph courtesy of Craig Damlo. www.soapboxrocket.com. Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
Vascular Basement Membrane Components in Angiogenesis An Act of Balance
 Directions in Science TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2008) 8, 1246 1249 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2008.155 Vascular Basement Membrane Components in Angiogenesis An Act of Balance Lars Jakobsson 1, *
Directions in Science TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2008) 8, 1246 1249 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2008.155 Vascular Basement Membrane Components in Angiogenesis An Act of Balance Lars Jakobsson 1, *
Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(3):229 233 Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma CARMEN ARDELEANU 1, 2), MARIA COMĂNESCU 3), VIOLETA COMĂNESCU 4), F. ANDREI 1) 1)
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(3):229 233 Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma CARMEN ARDELEANU 1, 2), MARIA COMĂNESCU 3), VIOLETA COMĂNESCU 4), F. ANDREI 1) 1)
3D Tissue Models. Simple, Low Cost Fabrication. Simple, Robust Protocols
 3D Tissue Models SynVivo is a physiological, cell-based microfluidic platform that provides a morphologically and physiologically realistic microenvironment allowing real-time study of cellular behavior,
3D Tissue Models SynVivo is a physiological, cell-based microfluidic platform that provides a morphologically and physiologically realistic microenvironment allowing real-time study of cellular behavior,
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
Immunohistochemical Maspin Expression in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 (2):103-109 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 (2):103-109 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Evaluation of Angiogenesis in Canine Mammary Tumors by Quantitative Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Immunohistochemistry
 Vet Pathol 7:297 01 (2000) Evaluation of Angiogenesis in Canine Mammary Tumors by Quantitative Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Immunohistochemistry B. RESTUCCI, G.DE VICO, AND P. MAIOLINO Dipartimento
Vet Pathol 7:297 01 (2000) Evaluation of Angiogenesis in Canine Mammary Tumors by Quantitative Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Immunohistochemistry B. RESTUCCI, G.DE VICO, AND P. MAIOLINO Dipartimento
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice
 Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice Abdullah Alajati, Anna M. Laib, Holger Weber, Anja M. Boos, Arne Bartol, Kristian Ikenberg, Thomas Korff, Hanswalter Zentgraf, Cynthia Obodozie,
Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice Abdullah Alajati, Anna M. Laib, Holger Weber, Anja M. Boos, Arne Bartol, Kristian Ikenberg, Thomas Korff, Hanswalter Zentgraf, Cynthia Obodozie,
Tumor Angiogenesis in Stage II Colorectal Carcinoma Association With Survival
 ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY Original Article Tumor Angiogenesis in Stage II Carcinoma Association With Survival BARBARA F. BANNER, MD, ROB WHITEHOUSE, STEPHEN P. BAKER, MSPH, AND RICHARD S. SWANSON, MD We studied
ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY Original Article Tumor Angiogenesis in Stage II Carcinoma Association With Survival BARBARA F. BANNER, MD, ROB WHITEHOUSE, STEPHEN P. BAKER, MSPH, AND RICHARD S. SWANSON, MD We studied
VEGF/VEGFR2 Axis in Periodontal Disease Progression and Angiogenesis: Basic Approach for a New Therapeutic Strategy
 VEGF/VEGFR2 Axis in Periodontal Disease Progression and Angiogenesis: Basic Approach for a New Therapeutic Strategy MIRCEA VLADAU 1, ANCA MARIA CIMPEAN 2, RALUCA AMALIA BALICA 2, ANDREEA ADRIANA JITARIU
VEGF/VEGFR2 Axis in Periodontal Disease Progression and Angiogenesis: Basic Approach for a New Therapeutic Strategy MIRCEA VLADAU 1, ANCA MARIA CIMPEAN 2, RALUCA AMALIA BALICA 2, ANDREEA ADRIANA JITARIU
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
C.L. Davis Foundation Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course
 C.L. Davis Foundation 2015 Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course IHC Resources IHC Identification Targets Antibodies Antibodies 1 Antibodies Specimens Antigen Retrieval Unmasks antigen epitopes Methods
C.L. Davis Foundation 2015 Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course IHC Resources IHC Identification Targets Antibodies Antibodies 1 Antibodies Specimens Antigen Retrieval Unmasks antigen epitopes Methods
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Urinary system. Urinary system
 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Immunohistochemical expression of VEGF in normal human renal parenchyma
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):315 322 ORIGINAL PAPER Immunohistochemical expression of VEGF in normal human renal parenchyma FLAVIA BADERCA 1), RODICA LIGHEZAN 1), ALIS DEMA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):315 322 ORIGINAL PAPER Immunohistochemical expression of VEGF in normal human renal parenchyma FLAVIA BADERCA 1), RODICA LIGHEZAN 1), ALIS DEMA
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2015, 56(4):1319 1328 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Correlations between intratumoral interstitial fibrillary network and
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2015, 56(4):1319 1328 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Correlations between intratumoral interstitial fibrillary network and
VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay Guiding immunotherapy
 VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay Guiding immunotherapy Hiker s path: VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay on urothelial carcinoma tissue Location: Point Conception, CA VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay Identify patients most
VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay Guiding immunotherapy Hiker s path: VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay on urothelial carcinoma tissue Location: Point Conception, CA VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay Identify patients most
CYTOMORPHOLOGY MODULE 28.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 28.2 GENERAL GUIDELINES. Notes
 28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
External Quality Assessment of melanocytic marker analyses NordiQC experience
 External Quality Assessment of melanocytic marker analyses NordiQC experience Jan Klos MD, Department of Pathology Stavanger University Hospital Norway 1 Content 18 Runs = 2112 submissions between 2001-2014
External Quality Assessment of melanocytic marker analyses NordiQC experience Jan Klos MD, Department of Pathology Stavanger University Hospital Norway 1 Content 18 Runs = 2112 submissions between 2001-2014
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(3 Suppl):1041 1045 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Conventional examination versus immunohistochemistry in the prediction
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(3 Suppl):1041 1045 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Conventional examination versus immunohistochemistry in the prediction
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2.
 Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Sheet #9. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION
 INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF UROLOGIC PATHOLOGY PATHOLOGIC STAGING OF SELECT UROLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Mahul B. Amin, MD Professor and Chairman Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF UROLOGIC PATHOLOGY PATHOLOGIC STAGING OF SELECT UROLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Mahul B. Amin, MD Professor and Chairman Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Interpretation Manual - Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma. PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmdx is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use
 Interpretation Manual - Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmdx is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use For countries outside of the United States, see the local
Interpretation Manual - Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmdx is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use For countries outside of the United States, see the local
The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced
 Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
S pecific monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) recognising the
 202 ORIGINAL ARTICLE LYVE-1 immunohistochemical assessment of lymphangiogenesis in endometrial and lung cancer M I Koukourakis, A Giatromanolaki, E Sivridis, C Simopoulos, K C Gatter, A L Harris, D G Jackson...
202 ORIGINAL ARTICLE LYVE-1 immunohistochemical assessment of lymphangiogenesis in endometrial and lung cancer M I Koukourakis, A Giatromanolaki, E Sivridis, C Simopoulos, K C Gatter, A L Harris, D G Jackson...
Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
Table of Contents. 1. Overview. 2. Interpretation Guide. 3. Staining Gallery Cases Negative for CINtec PLUS
 Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs
 151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
Jesse K. McKenney, MD
 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Outline Microscopic anatomy of the urinary bladder Diagnosing invasion Subtle patterns (variants) of carcinoma Clinically important variants of carcinoma Microanatomy of Bladder Initial
Jesse K. McKenney, MD Outline Microscopic anatomy of the urinary bladder Diagnosing invasion Subtle patterns (variants) of carcinoma Clinically important variants of carcinoma Microanatomy of Bladder Initial
