Cell Division. non-mitotic cell. Dividing (mitotic) cell. (This movie has been sped up.) These chromosomes have been marked with RED fluorescence.
|
|
|
- Beverly Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell Division These chromosomes have been marked with RED fluorescence. DNA is found in the cell nucleus Dividing (mitotic) cell non-mitotic cell (This movie has been sped up.)
2 Cell Division and Cancer Our cells divide many times during development, and for some cell types, throughout our lives. Today: how do cells reproduce? Next week: what happens if cells reproduce out of control?
3 What needs to happen for a cell to reproduce (copy itself)? In order for a cell to produce a copy of itself, it must: Replicate its DNA (we ve talked about this!) Condense its DNA (why?) Divide the DNA into two cells (Mitosis!).
4 DNA needs to be condensed before it can be separated into daughter cells
5 DNA gets condensed just prior to cell division
6 In order for a cell to produce a copy of itself, it must: Replicate its DNA Condense its DNA Divide the DNA into two cells (Mitosis!)
7 A cell undergoing Mitosis These chromosomes have been marked with RED fluorescence. Dividing (mitotic) cell DNA is found in the cell nucleus non-mitotic cell
8
9
10 You already know: Natural selection favors variants that reproduce the most. The drawback: cells that are dividing all the time can t do much else. To pass on its genes an organism has to reproduce, but it may also have to perform complex functions.
11 How to reconcile? There can be a division of labor!
12 Evolution of cooperative groups of cells swimmers dividers Volvox carteri
13 Evolution of cooperative groups of cells Somatic cells Cells that do not give rise to gametes (gametes = oocytes,sperm) Germline cells Cells that give rise to gametes swimmers dividers Volvox carteri
14 Division of labor: the bee hive The queen bee is the only reproductive female in the colony.
15 Cells that give rise to gametes Cells that do not give rise to gametes
16 Division vs. Differentiation Our somatic cells divide many times during development. But most of our cells stop dividing at some point, and start doing their jobs. This is called differentiation. (They start doing different jobs)
17 Us! Time (thousands of generations) Evolution Evolution The tendency for our somatic cells to compete with their neighbors is a vestige of our single-celled ancestry. Single-celled ancestor!
18 Breaking Bad Mutiny is a perpetual problem for multicellular organisms. Every day in your tissues there is a cell that breaks rank and sets out on its own. but usually it is stopped. usually.
19 Breaking Bad When regulation fails Unrestricted cell division can lead to Cancer.
20 Multicellular Organisms require teamwork We have a system that keeps most cells from going rogue, and takes out those that do. How does this system normally work? How can it get broken?
21 In a nutshell The system can t get broken with a single mutation- it takes many mutations: Most mutations arise during your lifetime Some mutations can be inherited
22 In a nutshell The system can t get broken with a single mutation- it takes many mutations: Most mutations arise during your lifetime Some mutations can be inherited Inheritance of one of these mutations is a head start towards accumulating enough mutations to get cancer.
23 Cancer: some common questions Is it genetic? Is it environmental? Is it contagious? Is it on the rise? Can my immune system protect me? Is the treatment worse than the disease?
24 The cell cycle A cell may receive a signal to start dividing when needed Genes that promote cell-division are called proto-oncogenes
25 Cell Cycle Control and Mutation Mutations in DNA can: oops. Turn a gene off Turn a gene always on Alter the function of the encoded protein Have little or no effect
26 Cell Cycle Control and Mutation Which type of mutation would cause the most trouble: a mutation that inactivates a proto-oncogene or a mutation that activates it?
27 Cell Cycle Control and Mutation If a proto-oncogene happens to get mutated in a way that it gets stuck on, we call it an Oncogene
28 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Tumor Suppressor genes make proteins that stop cell division. What s more dangerous? A mutation that activates or inactivates a tumor suppressor?
29 Cell Cycle Checkpoints What if your checkpoints fail?? - cells can divide even with widespread errors in DNA replication! more mutations accumulate!
30 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Tumor Suppressor genes make proteins that stop cell division. eg) BRCA1 is a tumor suppressor - Monitors and repairs mistakes in DNA replication - If mistakes are widespread, it instructs cell suicide!
31 Cell suicide is called Apoptosis
32 Tumors Unregulated cell division leads to the production of a tumor- a mass of cells with no function in the body. Not all tumors are a problem. Some are benign- (non-cancerous) why? contact inhibition (cells are polite to their neighbors)
33 Cancer Progression Tumor Benign invasive Malignant = cancer
34 Metastasis when cells leave the original site In order for cells to leave their original place, they must lose their anchorage dependence
35 Cancer Progression Tumor Benign invasive Malignant = cancer traveling Non-metastatic Metastatic
36 Cancer Progression takes many steps
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Cell Death and Cancer. SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou
 Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
9 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell division plays
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell division plays
Notes 7.5: Mitosis Gone Wrong
 Notes 7.5: Mitosis Gone Wrong Central Dogma Review Information to make a protein is stored in a gene Gene: Segment of DNA that codes for a protein Proteins are used for: growth of tissue and organs, energy,
Notes 7.5: Mitosis Gone Wrong Central Dogma Review Information to make a protein is stored in a gene Gene: Segment of DNA that codes for a protein Proteins are used for: growth of tissue and organs, energy,
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of November
 Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November
 Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK. How do normal cells become cancer cells? Workbook Lesson 3.2
 For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. Transformation the process by which a cell acquires characteristics of a tumor cell. LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do normal cells become cancer cells?
For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. Transformation the process by which a cell acquires characteristics of a tumor cell. LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do normal cells become cancer cells?
Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer
 CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
Chapter 9. Cells Grow and Reproduce
 Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Cancer Cells. It would take another 20 years and a revolution in the techniques of biological research to answer these questions.
 Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Mitosis Exploration Pd. Objective: Describe the purpose and process of cellular reproduction. 1. What is a cell?
 Mitosis Exploration Name Pd Objective: Describe the purpose and process of cellular reproduction. Review: 1. What is a cell? 2. Describe the main differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
Mitosis Exploration Name Pd Objective: Describe the purpose and process of cellular reproduction. Review: 1. What is a cell? 2. Describe the main differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
Chapter 12. living /non-living? growth repair renew. Reproduction. Reproduction. living /non-living. fertilized egg (zygote) next chapter
 Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Cell Cycle - Introduction
 Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Functional Limitations
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Cell Growth and Division *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46034 1 Cell Growth and Division * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46034 1 Cell Growth and Division * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 8 DNA Replication, Binary Fission, and Mitosis
 Chapter 8 DNA Replication, Binary Fission, and Mitosis World s tallest man Frederic J. Brown/AFP/Getty Images Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without
Chapter 8 DNA Replication, Binary Fission, and Mitosis World s tallest man Frederic J. Brown/AFP/Getty Images Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections & Steve Thompson:
 SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections 20585 & 20586 Steve Thompson: steven.thompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 We ll start with the exam review. A few people did well,
SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections 20585 & 20586 Steve Thompson: steven.thompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 We ll start with the exam review. A few people did well,
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division
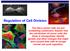 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Let s quickly return to that siliconbased life form, since
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Let s quickly return to that siliconbased life form, since
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
Keywords: Daughter Cells Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Chromosomes Chromatin Homologous Chromosomes Diploid
 Name: CP Biology Unit 5: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 5.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Name: CP Biology Unit 5: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 5.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
2013 Holiday Lectures on Science Medicine in the Genomic Era
 INTRODUCTION You may have read articles that talk about cancer genes. But what exactly are cancer genes and what do they do? Cancer consists of a group of diseases caused by mutations in the DNA of cells.
INTRODUCTION You may have read articles that talk about cancer genes. But what exactly are cancer genes and what do they do? Cancer consists of a group of diseases caused by mutations in the DNA of cells.
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Regulating the Cell Cycle. Lesson Overview THINK ABOUT IT. How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide?
 THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
Cell Cycle Notes chromatin, somatic cells gametes mitosis sister chromatids, centromere cytokinesis binary fission,
 Cell Cycle Notes 1. Importance of Cell Division a. For single celled organisms, cell division increases the number of individuals. b. In a multicellular organism, cell division functions to repair and
Cell Cycle Notes 1. Importance of Cell Division a. For single celled organisms, cell division increases the number of individuals. b. In a multicellular organism, cell division functions to repair and
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 8
 Cellular Reproduction Chapter 8 1. Importance of Cell Division 2. Eukaryotic Cell Cycle 3. Eukaryotic Chromosomes 4. Mitosis 5. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells 6. Sexual Iife cycle 7. Meiosis 8.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 8 1. Importance of Cell Division 2. Eukaryotic Cell Cycle 3. Eukaryotic Chromosomes 4. Mitosis 5. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells 6. Sexual Iife cycle 7. Meiosis 8.
Keywords: Daughter Cells Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Chromosomes Chromatin Homologous Chromosomes Diploid
 Name: CP Biology Unit 6: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 6.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Name: CP Biology Unit 6: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 6.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
An adult human has somewhere around one hundred trillion (10 14 ) cells
 2/22/10 Cancer genetics Inside cancer web site http://www.insidecancer.org/ National Cancer Institute http://www.cancer.gov/cancerinfo/ An adult human has somewhere around one hundred trillion (10 14 )
2/22/10 Cancer genetics Inside cancer web site http://www.insidecancer.org/ National Cancer Institute http://www.cancer.gov/cancerinfo/ An adult human has somewhere around one hundred trillion (10 14 )
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Aberrant cell Growth. Younas Masih New Life College of Nursing Karachi. 3/4/2016 Younas Masih ( NLCON)
 Aberrant cell Growth Younas Masih New Life College of Nursing Karachi 1 Objectives By the end of this session the learners will be able to, Define the characteristics of the normal cell Describe the characteristics
Aberrant cell Growth Younas Masih New Life College of Nursing Karachi 1 Objectives By the end of this session the learners will be able to, Define the characteristics of the normal cell Describe the characteristics
PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Why do cells reproduce?
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Cancer and Cell Differentiation
 Cancer and Cell Differentiation Recall The cell cycle consists of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Recall During S phase of interphase, the DNA is replicated to prepare for mitosis. Each daughter
Cancer and Cell Differentiation Recall The cell cycle consists of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Recall During S phase of interphase, the DNA is replicated to prepare for mitosis. Each daughter
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division. Making new cells. Getting the right stuff. Overview of mitosis 1/5/2015
 Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
Biology: Cell Division and Cancer
 Cancer Cells [Photo by Dr. Cecil Fox via Wikimedia Commons] Biology: Cell Division and Cancer High School 9-12 Corin Malone Auburn Riverside High School, Auburn School District Materials adapted from Not
Cancer Cells [Photo by Dr. Cecil Fox via Wikimedia Commons] Biology: Cell Division and Cancer High School 9-12 Corin Malone Auburn Riverside High School, Auburn School District Materials adapted from Not
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle
 Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5-6 DNA Replication Notes 7-8 DNA replication
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5-6 DNA Replication Notes 7-8 DNA replication
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother
 Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS SECOND EDITION URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell)
 Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
3. Staying Alive What does a living thing need to do to stay alive? Use e Store m Take m from the e Remove w Move s R
 1. What does cell theory say? Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things Every living thing is made of cells all cells come from other cells 2. Cell Organization Prokaryotic Do
1. What does cell theory say? Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things Every living thing is made of cells all cells come from other cells 2. Cell Organization Prokaryotic Do
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Control of Cell Cycle. Unit 2 Part f III
 Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Cancer. October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle
 Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
REGULATING the CELL CYCLE.
 REGULATING the CELL CYCLE http://www.travel-net.com/~andrews/images/animations/traffic.gif CELL DIVISION GENES Some cells divide frequently (some human skin cells divide once/hour) Some cells divide occasionally
REGULATING the CELL CYCLE http://www.travel-net.com/~andrews/images/animations/traffic.gif CELL DIVISION GENES Some cells divide frequently (some human skin cells divide once/hour) Some cells divide occasionally
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Why are cells small? What are some of the difficulties a cell faces as it increases in size? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Why are cells small? What are some of the difficulties a cell faces as it increases in size? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 The cell cycle and mitosis Now that we ve seen how DNA
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 The cell cycle and mitosis Now that we ve seen how DNA
Personalized Genetics
 Personalized Genetics Understanding Your Genetic Test Results Tracey Evans, MD September 29, 2017 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 2 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 3 It s not
Personalized Genetics Understanding Your Genetic Test Results Tracey Evans, MD September 29, 2017 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 2 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 3 It s not
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
THE EUKARYOTIC CELL CYCLE AND CANCER
 THE EUKARYOTIC CELL CYCLE AND CANCER ABOUT THIS WORKSHEET This worksheet complements the Click and Learn The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer developed in conjunction with the 2013 Holiday Lectures on
THE EUKARYOTIC CELL CYCLE AND CANCER ABOUT THIS WORKSHEET This worksheet complements the Click and Learn The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer developed in conjunction with the 2013 Holiday Lectures on
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
