Discovering the Dark matters in expression data of mirna based on the mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna networks
|
|
|
- Constance Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Discovering the Dark matters in expression data of mirna based on the mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna networks Cong Pian 1, Guangle Zhang 2, Sanling Wu 3 and Fei Li 1* Abstract Background: Since mirnas can play important roles in different cancer types, how to discover cancer related mirnas is an important issue. In general, the mirnas with differential expression is the focus of attention. However, some important cancer related mirnas are not excavated by differential expression analysis. We take this type of mirnas as dark matters (DM-miRNA). It is our great interests to develop an algorithm to discover DM-miRNAs. Results: An effective method was developed to find DM-miRNAs. This method is mainly for mining potential DMmiRNAs by building basic mirna-mrna network (BMMN) and mirna-lncrna network (BMLN). The results indicate that mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions can be used as novel cancer biomarkers. Conclusions: The BMMN and BMLN can excavate the non-differentially expressed mirnas which play an important role in the cancer. What s more, the edge biomarkers (mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions) contain more information than the node biomarkers. It will contribute to developing novel therapeutic candidates in cancers. Keywords: Dark matters, mirna-mrna network, mirna-lncrna network, Biomarkers Background micrornas (mirnas) are small non-coding RNA with length of 20 ~ 24 nucleotides. In animals, they mainly inhibit target mrnas translation by binding to the 3 untranslated regions (3 UTRs) of mrna. mirnas participate in a variety of physiological processes, such as cell proliferation and differentiation, apoptosis, embryonic development, virus defense, and the hematopoietic process [1, 2]. mirnas have been implicated in many diseases, especially in various types of cancers, such as lung neoplasms [3], breast neoplasms [4], colonic neoplasms [5], etc. Identifying mirnas that have essential roles in tumorigenesis is an important task. A direct method is to find differentially expressed mirnas from expression data. Unfortunately, some non-differentially expressed mirnas may also play important regulatory functions in cancer, whereas some differentially * Correspondence: lifei18@zju.edu.cn Cong Pian and Guangle Zhang contributed equally to this work. 1 Ministry of Agriculture Key Lab of Molecular Biology of Crop Pathogens and Insects, Institute of Insect Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou , Zhejiang, China Full list of author information is available at the end of the article expressed mirnas do not show obvious roles in cancer. Those mirnas that are non-differentially expressed but with important roles in tumorigenesis seems like dark matters in the expression data which is very difficult to be detected. Complex diseases generally result from dysfunctions in regulatory networks rather than from the mutations or malfunctions of a single molecule. We reasoned that mirna-mrna interactions may provide more information for discovering DM-miRNAs. To this end, we intend to develop an algorithm to identify DM-miRNA in the context of mirna-mrna interactions. Long non-coding RNAs (lncrna) account for a large proportion in transcriptome. Some act as a competing endogenous RNA (cerna) which play an important role in the initiation and progression of cancer [6, 7]. So, we also. Generally, prior works of constructing mirna-mrna modules from expression data can be divided into two-step procedures. First, Student t-test is used to obtain differentially expressed mrnas and mirnas. In general, the important step of identification of potential mirna biomarkers is screening differentially expressed mirna. The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 2 of 11 Liao, et al., used five mirnas of 320 differentially expressed mrnas for prognostic signature construction [8]. Li, et al., selected 26 differentially expressed mrnas to construct regulatory pathways in prostate cancer [9]. Second, mirnas-mrna regulatory network is constructed by calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient between the mirnas and mrnas. For example, a regulatory network for colorectal cancer was built using limma algorithms to select differentially expressed mirnas and mrnas [10]. A causality discovery-based method was used to uncover causal regulatory relationship between mirnas and mrnas [11]. However, these methods have two weaknesses: (1) It is difficult to construct a regulatory network when the number of samples is limited. (2) Some important mirnas are not excavated by differential expression analysis. Here, we reasoned that all samples shared a basic mirna-mrna network (BMMN) and a basic mirna-lncrna network (BMLN). The mirnas significantly deviating from BMMN or BMLN are regarded as potential DM-miRNAs. The results indicated that this method is efficient in discovering DM-miRNAs. Moreover, our works showed that mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions could be used as effective cancer biomarkers. Methods Datasets Six different cancer types were selected, including breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA), kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), thyroid carcinoma (THCA), prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD). The expression profiles of 1071 mirnas, 12,727 lncrnas and 20,530 mrnas of six different cancer types were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database ( (Table 1). The 155,044 experimentally validated mirna-mrna interactions were obtained from the mirtarbase database [12]. In addition, we integrated experimentally Table 1 The type and sample number of cancers Cancer abbreviation Full name of cancer Number of cancer tissue sample BRCA Breast invasive carcinoma KIRC Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma THCA Thyroid carcinoma LUAD Lung adenocarcinoma LUSC Lung squamous cell carcinoma PRAD Prostate adenocarcinoma Number of paired normal tissue sample validated and predicted mirna-lncrna interactions from starbase v2.0 [13], mircode [14]andNPInterv3.0[15]. After removing redundant associations, 155,653 mirna-lncrna interactions were obtained. The experimentally verified mirna-disease associations were downloaded from HMDD v2.0 [16], which included experimentally-verified human mirna and disease associations. The construction of BMMN and BMLN The process of constructing BMMN in a cancer can be divided into the following three steps: (1) The reference network is built using the paired normal tissue samples. (2) To quantify the importance of mirna-mrna association, we constructed an individual specific mirna-mrna network (ISMMN) and individual specific mirna-lncrna network (ISMLN) for a cancer sample. Then the frequency of significant change in each mirna-mrna interaction was calculated in all cancer samples. (3) The BMMN and BMLN of this cancer can be constructed using above high frequency mirna-mrna interactions. The processes for constructing ISMMN and ISMLN were given in Fig. 1. For each mirna-mrna pair, g 1 ¼ðg 1 1 ; g2 1 ; ; gn 1 Þ; m 1 ¼ðm 1 1 ; m2 1 ; ; mn 1Þ represent the expression of mrna and mirna in n normal samples (S 1, S 2,, S n ) We calculated Pearson correlation coefficients for each pair of mirna-mrna using g 1 and m 1 ( PCC m1 ;g 1 ) based on 155,044 experimentally verified human mirna-mrna interactions from the mirtarbase database. Finally, 155,044 Pearson correlation coefficients (PCC) were obtained, and a reference mirna-mrna regulatory network (RMMN) was generated (Fig. 1a). The reference network was generally stable with the increase of sample number. To build the ISMMN of the (n+1)th sample S n+1, we measured the disturbance degree of the reference mirna-mrna regulatory network by adding sample S n+1 to the set (S 1, S 2,, S n ).We then constructed the perturbed mirna-mrna regulatory network (PMMN) by calculating the PCC between g 0 1 ¼ðg1 1 ; g2 1 ; ; gn 1 ; gnþ1 1 Þ and m 0 1 ) (Fig. 1b). Finally, we ¼ðm 1 1 ; m2 1 ; ; mn 1 ; mnþ1 1 Þ (PCC m 0 1 ;g0 1 calculated the differential mirna-mrna regulatory network between the reference regulatory network and perturbed regulatory network ΔPCC= ðpcc m 1 1 ;g 0 1 PCC m1 ;g 1 Þ. If the expression of the added sample were similar to that of reference samples, the fluctuation range of perturbed regulatory network would be insignificant. Finally, we select mirna-mrna interactions with high ΔPCC value as the elements of ISMMN based on the statistical theory of Li et al. [17]. The procedures for constructing ISMLN was similar as that for ISMMN except lncrnas were considered in instead of mrna. The distributions of ΔPCC of BRCA samples and paired normal samples were given in Fig. 2. TheX-axisandY-axis
3 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 3 of 11 Fig. 1 Flowchart for constructing an individual specific mirna-mrna network (ISMMN) and an individual specific mirna-lncrna network (ISMLN) for a single cancer sample. a The n normal samples are selected as the reference samples, and a reference mirna-mrna network (RMMN) and a reference mirna-lncrna network (RMLN) are constructed using Pearson Correlation Coefficients (PCC) based on the 155,044 mirna-mrna and 155,653 interactions. b The sample S n+1 is added to the above reference samples, and a perturbed mirna-mrna network (PMMN) and a perturbed mirna-mrna network (PMLN) are built by recalculating the PPC. Finally, we define the difference (PMMN-RMMN) and (PMLN-RMLN) as the ISMMN and ISMLNof sample S n+1 represent the ΔPCC value and corresponding frequency. There is a significant difference between the two distributions. The interval of X-axis are 0.5 and 0.1 in Fig. 2a and b. We can see that the ΔPCC values of BRCA samples are mainly concentrated on [ 0.5,0.5], while the region of ΔPCC of normal samples is [ 0.1,0.1]. The P-value of student T-test is * The results indicated that there were obviously changes in mirna-mrna interactions between cancer samples and normal samples, suggesting that cancer driving mirna-mrna interactions would cause significant changes in PCC. Therefore, we use all mirnamrna interactions with significant changes to construct BMMN. The theory of previous study indicates that the significance level of ΔPCC can be evaluated by the statistical hypothesis test Z-test (or U-test) [17]. Assuming that there arenreferencesamples.thenweaddthen+1sample,and the PCC n and PCC n+1 represent the edge of RMMN and PMMN. The ΔPCC of edge between RMMN and PMMN is Fig. 2 a and b represent the ΔPCC distributions of BRCA samples and paired normal samples. The X-axis represents the ΔPCC values in the BRCA samples and paired normal samples, respectively. The Y-axis represents the number of corresponding ΔPCC values. Most of ΔPCCs in normal samples tend to be 0 compared with it in BRCA samples. This result shows that there are obvious difference in mirna-mrna interactions between the cancer samples and normal samples
4 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 4 of 11 ΔPCC n =PCC n+1 -PCC n. The significance of ΔPCC n can be evaluate by the following equation: Z ¼ ΔPCC n 1 PCC n 2 n 1 ISMLN was built using the abovementioned method based on 155,653 mirna-lncrna interactions. BMMN and BMLN were constructed based on ISMMN and ISMLN. We used BRCA as the example (Fig. 3). First, we built ISMMN and ISMLN for 755 breast cancer samples. Second, we counted the number of mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions that appeared in 755 ISMMNs and ISMLNs. Then we ranked them in descending order. For example, the interaction of mir-145-ndrg2 changed significantly in 630 of 755 breast cancer samples. We set (630/755) as the BRCA score of mir- 145-NDRG2 interaction. The BRCA score of every mirna-mrna interaction were calculated. Finally, the BMMN and BMLN of BRCA were constructed by selecting mirna-mrna interactions with high BRCA scores. The construction of BMLN was similar to the process of BMMN. We set BRCA score = 0.4 as the threshold in the BMMN and BMLN. The calculation of mirna activity scores in BMMN and BMLN The formula of mirna activity score in BMMN and BMLN are as follows: Activity Score BMMN ðmirna 1 Þ ¼ Xc 1 k¼1 BRCA Score BMMN ðmirna; mirna k Þ ðc 1 =c 2 Þ Activity Score BMLN ðmirna 1 Þ ¼ Xd 1 BRCA Score BMLN mirna; mirna p p¼1 ðd 1 =d 2 Þ c 1 indicates that the frequency of mirna 1 appears in the significantly changed mirna-mrna interactions. c 2 indicates that the frequency of mirna 1 appears in all Fig. 3 Construction of the BMMN in BRCA. The BRCA is used as the example. We built ISMMNs and ISMLN for the 755 breast cancer samples, counted the number of mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions that appeared in 755 breast ISMMNs and ISMLN, and ranked them in descending order. The BRCA score of every mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interaction can be calculated. Finally, the BMMN and BMLN of BRCA was constructed by selecting the mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions with high BRCA scores
5 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 5 of 11 mirna-mrna interactions. d 1 indicates that the frequency of mirna 1 appears in the significantly changed mirna-lncrna interactions. d 2 indicates that the frequency of mirna 1 appears in all mirna-lncrna interactions. Results Breast cancer For breast cancer, we set BRCA score = 0.4 as the threshold in the BMMN. The 1078 significantly changed mirna-mrna interactions (Additional file 1) are selected. There are 124 mirnas and 725 mrnas in Fig. 4a. The blue and purple nodes represented mirna and mrnas, respectively. The higher the degree of the node is, the bigger the size will be. The thickness of the line reflects the BRCA score of the mirna-mrna interaction. The top 20 mirna activity scores in BMMN of BRCA are shown in Fig. 4b (The activity scores of 124 above mirnas are show in Additional file 2). We can find that these 20 mirnas are all related to breast cancer by searching the database HMDD. The dotted line represents the mirnas differentially expressed. The solid line represents the mirnas normally expressed. The first and second color mean mir-10 family and the same clustered mirna respectively, and the third color represents signal mirna. Many studies show that the same family and cluster of mirnas play similar regulatory functions. The above results were in accordance with the conclusion. Moreover, the results showed many non-differentially expressed mirnas had an important role in breast cancer. In addition, DAVID is employed for enrichment analyses of the above 725 mrnas. The enrichment analyses results were shown in Fig. 4c. The known cancer mechanism-related pathways are significantly enriched, such as pathways in cancer, Prostate cancer, mirnas in cancer, Pancreatic cancer, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Melanoma, the p53 signaling pathway, small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, acute myeloid leukemia, Transcriptional misregulation in cancer, Glioma and Non-small cell lung cancer. These results indicate that the 725 genes were very important in cancers. The BMLN of BRCA was also built using the abovementioned method. We set BRCA score = 0.4 as the threshold in BMLN. The 2031 significantly changed mirna-lncrna interactions (Additional file 3) are selected. There are 120 mirnas and 725 lncrnas in the above 2031 interactions. The activity scores of 120 mir- NAs are show in Additional file 4). Surprisingly, all top 20 mirna activity scores were non-differential expressed (Fig. 5). The first and third color mean the mir-200 family and mir-196 family, respectively. A previous work verified that mir-200 family is associated with breast cancer by directly targeting ADAM12-L [18]. mirna-196 family was also reported as potent metastasis suppressors and revealed that the ratio of mir-196 family to HOXC8 mrna is an indicator of the metastatic capability of breast tumors [19]. The second color represented the same clustered mirna, and the fourth color represented signal mirna. The result also showed many DM-miRNAs (non-differentially expressed mirnas) have important role in cancers. The mirna activity score in BMMN of BRCA were arranged in descending order (Fig. 6a). The 14 of all 124 mirnas (mir-1468, mir-891a, mir-3677, mir-3662, mir-337, mir-4326, mir-566, mir-589, mir-432, mir-377, mir-2114, mir-3614, mir-3681, mir-92b) marked with red rectangle were not reported to be associated with BRCA, whereas other mirnas have already been documented in BRCA. The mirna activity score in BMLN of BRCA were arranged in descending order (Fig. 6b). The 9 of all 120 mirnas remarked with red rectangle is not confirmed to be associated with BRCA. Figure 6c is the differential expression analysis of above 244 mirnas. The result indicated that most of these mirnas are non-differentially expressed. Therefore, DM-miRNAs can be discovered by calculating the activity score in BMMN and BMLN. Fig. 6d shows the coincidence degree of the above two mirna sets (124 mirnas in BMMN and 120 mirnas in BMLN). The proportion of overlapping mirna is only 27.7%. The result indicates DM-miRNAs regulating mrna can be discovered through BMMN, and DM-miRNAs associated with lncrna can be found through BMLN. The selection of machine learning algorithm We use three types of machine learning algorithms to identify the BRCA samples and paired normal samples based on the top five changed mirna-mrna associations in BMMN. In general, the performance of the machine learning algorithms depends on the content of the study. Every algorithm has its own advantage. Therefore, we constructed three different classifiers using three algorithms based on the same training data set. The results show that the RF (Random Forest) algorithm outperforms the other two algorithms for classifying cancer samples and normal samples. The Area Under the Curve (AUC) measures the performance of an algorithm under different thresholds. On average, the AUC of the RF algorithm is approximately Compared with the AUC of the SVM (0.9909) and ANN (V-ELM) (0.9924), the RF model is robust. The sensitivity and specificity of the RF, SVM and ANN are % ± 0.26 and % ± 0.29, 96.9 % ± 0.18 and % ± 0.31, % ± 0.22, and % ± 0.24 based on the 10-fold cross validation.
6 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 6 of 11 Fig. 4 a The BMMN of BRCA. b The top 20 mirna activity score in BMMN of BRCA. The first and second color mean the mir-10 family and the same clustered mirna, and the third color represents signal mirna. c The enrichment analyses of the 725 mrnas in Fig. 4a The acquiescent parameters C and g of the support vector machine (SVM) are 2 and 1 respectively. To improve the accuracy, the optimal parameters of SVM are and per the method of the particle swarm optimization (PSO). In addition, we used an artificial neural network algorithm, called the voting based
7 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 7 of 11 extreme learning machine (V-ELM) for comparison. ELM is a kind of quick training algorithm for generalized SLFNs [20, 21]. We selected N = 40 as the number of hidden layer nodes in the V-ELM model. The Random Forest (RF) method is an ensemble learning method that operates by constructing a multitude of decision trees. We chose N = 400 for the decision trees in RF model. Fig. 5 The top 20 mirna activity scores in BMLN of BRCA. The first and third color mean the mir-200 family and mir-196 family. The second color represents the same clustered mirna, and the fourth color represents signal mirna Identification of cancer using the features of mirnas,mrnas, lncrnas,mirna-mrna and mirnalncrna interactions Figure 7 shows the analysis results of RF classifier based on the top 1 5 differentially expressed mrnas, mirnas, lncrnas mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions for BRCA. The results indicate that the information of mirna-mrna interactions is more effective. In addition, we select the bottom five differential mrnas, mirnas mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions for BRCA (BRCA Score > 0.4) as the features of classifier. Figure 7a is the classification performance based on one dimensional feature (top one differential mirna, mrna, lncrna, mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna Fig. 6 The DM-miRNAs in BMMN and BMLN. a The mirna activity score in BMMN of BRCA. b The mirna activity score in BMLN of BRCA. c The differential expression analysis of 244 mirnas in Figure (a and Figure b). d The coincidence degree of two mirna sets in Figure (a) andfigure(b)
8 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 8 of 11 Fig. 7 The classification performance of node biomarkers and edge biomarkers in BRCA. a The ROC curve based on one dimensional feature (top one differential mirna, mrna, lncrna, mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions). b-e is the classification performance based on top twofive features (mirna, mrna, lncrna, mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions). f The classification using the bottom five differential node biomarkers and edge biomarkers interactions). The result indicated that the distinguishing ability of mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions is more effective. With the increasing of feature dimension, the performance of classification (Fig. 7b-e) based on the three node features (mirna, mrna, lncrna) and two edge features (mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna). Figure 7f is the classification result using the bottom differential node and edge features. The classification ability of edges is significantly better than that of nodes. This shows that edges contain more biological information. Therefore, the mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions can be astheeffectivebiomarkers. The effectiveness of top mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions If the difference of mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions between normal and breast cancer is more significant, the classification effect is more effective. Here, we drew scatter plots of the top 5 mirnas with the highest BRCA score in normal and breast tumor samples. Figure 8 is the top 5 mirna-mrna interactions in BMMN of BRCA (mir-145-ndrg2, mir-96-hoxa5, mir-96-synm, mir HOXA5 and mir-21-nfib). The X axis and Y axis represent the expression level of mrna and mirna. The four interactions (mir-96-hoxa5, mir-96-synm, mir- 183-HOXA5 and mir-21-nfib) in orange ellipses indicate the increase of mirna expression results in the decrease of mrna expression level. The interaction (mir-145-ndrg2) in green ellipses may belong to singular interaction. What s more, it can be seen from the scatter plot that any one of these 5 mirnamrna interactions relations interactions can distinguish the normal and breast cancer samples. Figure 9 are scatter plots of the top 6 mirna-lncrna interactions in BMLN of BRCA (mir-141-lnc-trmt61b-1, Fig. 8 The scatter plots of the top five mirna-mrna interactions in BMMN of BRCA. The X axis and Y axis represent the expression level of mrna and mirna. The orange ellipses indicate the increase of mirna expression results in the decrease of mrna expression level. The mirna-mrna interaction in green ellipses is difficult to explain
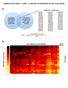
9 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 9 of 11 Fig. 9 The scatter plots of the top 6 mirna-lncrna interactions in BMLN of BRCA. a-f represents the top one-six respectively. The X axis and Y axis represent the expression level of lncrna and mirna mir-200a-lnc- TRMT61B-1, mir-141-lnc-pcsk9 4, mir- 200c-lnc- ARL6IP5 1, mir-429-lnc-trmt61b-1 and mir- 141-GASIRR). The X axis and Y axis represent the expression level of lncrna and mirna. The six interactions in Fig. 9a-f indicate the increase of mirna expression results in the decrease of mrna expression level. Besides, any one of these 5 mirna-lncrna interactions relations interactions can distinguish the normal and breast cancer samples. The specificity of different types of cancer We drew the heat map by using the top 200 mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna associations in six different type of cancers. Figure 10 is the clustering result. Six independent mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interaction clusters can represent six different cancers. For the two different subtypes of lung cancer (LUAD and LUSC), the difference of mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions of LUAD and LUSC is very significant. The results also indicate that the BMMN and BMLN of every kind of cancer is distinctive. The results of the other five cancers (1) KIRC: The Table 2 is the result of activity score of BMMN and BMLN. The 1 in the third and seventh Fig. 10 a and b represent the heat maps of the top 200 mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions in six different type of cancers
10 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 10 of 11 Table 2 The top 12 activity score of BMMN and BMLN mirna Activity in BMMN KIRC FC mirna Activity in BMLN KIRC FC mir mir mir-200c mir mir mir mir mir mir-199b mir mir mir mir mir-216a mir-200a mir mir-106b mir mir Unknown 1.35 mir-216b mir mir Unknown 1.01 mir-15a mir column means that mirnas are related to kidney cancer. The unknow is just the opposite. Fold change (FC) is used to measure differentially expressed level. We can see that most mirnas of the Table 2 have no differential expression but are related to kidney cancer. Only two of the 24 mirnas have not been confirmed to be associated with kidney cancer. Besides, mir-141, mir-200c and mir-200a in the first column belong to the same mirna family. mir-192 and mir-215 in the third column belong to the same mirna family. This result shows that the same mirna family may play similar functions in the cancer. (2) The other four cancer: The top 10 mirnas in BMMN and BMLN of LUSC, LUAD, THCA and PRAD are recorded in Additional file 5. We can find that 0, 2, 4 and 2 mirnas discovered by our method are not confirmed to be associated with the above four cancers respectively. Summery, the results indicate that many DM-miRNAs can be discovered based on the BMMN and BMLN. What s more, most high activity score mirnas in BMMN and BMLN are non-overlapping. Discussion mirna may as the novel potential therapeutic target of cancers. However, most of mirnas without differential expression can participate in regulation mechanism. In order to discover these DM-miRNAs, we use a novel method to discover DM-miRNAs by building a basic mirna-mrna network (BMMN) and mirna-lncrna network (BMLN). The advantage of the method is as follows. (1) The BMMN and BMLN can mining the nondifferentially expressed mirnas which play an important role in the cancer. Since most of gene is non-differentially expressed, how to find functional genes from the above genes is pivotal. The BMMN and BMLN can discover the non-differentially expressed mirnas which play an important role in the cancer. (2) The significant difference of the BMMN and BLNM in different types of cancers. Through the clustering analysis of the top 200 mirna-mrna and mirna-lncrna interactions in six different types of cancer, we can find that the BMMNs and BMLN of six cancers are significantly different. The result indicates that the BMMN and BMLN of each cancer are very specific. It can help us distinguish the type and subtype of each cancer. (3) The edge biomarkers contain more information than the node biomarkers. The classification ability of edge biomarkers is significantly better than that of node biomarkers in BMMN and BMLN. The result shows that edges biomarkers contain more biological information. However, our study has some limits. The mirbase database includes 2588 mirnas, while the TCGA database only contains expression data for 1046 mirnas. Some important mirnas may be ignored. Conclusion In brief, we proposed a new method to effectively discover DM-miRNAs by constructing BMMN and BMLN. This global mirna-mrna and mirnalncrna interaction network will contribute to developing novel therapeutic candidates in cancers. Besides, the BMMN and BLNM may help us distinguish tumor subtypes.
11 Pian et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2018) 19:379 Page 11 of 11 Additional files Additional file 1: The 1078 significantly changed mirna-mrna interactions. (XLSX 29 kb) Additional file 2: The activity scores of 124 above mirnas in BMMN are shown in Additional file 2. (XLSX 13 kb) Additional file 3: The 2031 significantly changed mirna-lncrna interactions. (XLSX 65 kb) Additional file 4: The activity scores of 120 mirnas in BMLN are shown in Additional file 4. (XLSX 13 kb) Additional file 5: The top 10 mirnas in BMMN and BMLN of LUSC, LUAD, THCA and PRAD are shown in Additional file 5. (ZIP 32 kb) Abbreviations 3 UTRs: 3 untranslated regions; AUC: Area Under the Curve; BMLN: BasicmiRNA-lncRNA network; BMMN: Basic mirna-mrna network; BRCA: Breast invasive carcinoma; CeRNA: Competing endogenous RNA; FC: Fold change; ISMLN: Individual specific mirna-lncrna network; ISMMN: Individual specific mirna-mrna network; KIRC: Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; LUAD: Lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC: Lung squamous cell carcinoma; PCC: Pearson correlation coefficients; PMLN: Perturbed mirnamrna network; PMMN: Perturbed mirna-mrna regulatory network; PSO: Particle swarm optimization.; RF: Random Forest (RF); RMLN: Reference mirna-lncrna network; RMMN: Reference mirna-mrna regulatory network; SVM: Support vector machine; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; THCA: Thyroid carcinoma; V-ELM: Voting based extreme learning machine Acknowledgements The authors gratefully acknowledge the TCGA database for providing mirna expression profiles and mrna expression profiles of cancers, mirtarbase database for providing experimentally validated mirna-mrna interactions, and HMDD database for providing validated associations between mirnas and diseases. Cong Pian gratefully thank the support received during his visit at the department of statistics at the Chinese University of Hong Kong. Funding This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program [2016YFC ], and The Science and Technology Research Project of the Ministry of Education [V201308]. Availability of data and materials The expression profiles of six different cancer types were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database ( The 155,044 experimentally validated mirna-mrna interactions were from the mirtarbase database(10). The mirna-lncrna interactions were from starbase v2.0 (11), mircode (12) and NPInter v3.0 (13). The experimentally verified mirna-disease associations were from HMDD v2.0 (14). Authors contributions PC and GLZ:Conceived and designed the experiments; SLW: Performed the experiments; PC and GLZ:Analyzed the data; GLZ and PC: Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; PC: Wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable. Consent for publication Not applicable. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Author details 1 Ministry of Agriculture Key Lab of Molecular Biology of Crop Pathogens and Insects, Institute of Insect Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou , Zhejiang, China. 2 Department of Mathematics, College of Science, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing , Jiangsu, China. 3 Analysis Center of Agrobiology and Environmental Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou , Zhejiang, China. Received: 7 May 2018 Accepted: 5 October 2018 References 1. Ambros V. The functions of animal microrna. Nature. 2004;431(2004): Cui Q, Yu Z, Purisima EQ, Wang E. Principles of microrna regulation of a human cellular signaling network. Mol Syst Biol. 2006;2(1): Hirota T, Date Y, Nishibatake Y, Takane H, Fukuoka Y, Taniguchi Y, Burioka N, Shimizu E, Nakamura H, Otsubo K, Ieiri I. Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase(dpd) expression is negatively regulated by certain micrornas in human lung tissues. Lung Cancer. 2012;77(1): Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, Padua D, Wang Q, Bos PD, Gerald WL, Massagué J. Endogenous human micrornas that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2008;451(7175): Akao Y, Nakagawa T, Naoe T. Let-7 microrna functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006;29(5): Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP. A cerna hypothesis: the rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language. Cell. 2010;146(3): Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Leqnini L, Santini O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A, Bozzoni L. A long noncoding RNA controls musclke differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous. Cell. 2011;147(2): Liao X, Zhu G, Huang R, Yang C, Wang X, Huang K. Identification of potential prognostic microrna biomarkers for predicting survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10: Li DY, Hao XY, Song YS. Identification of the key MicroRNAs and the mirnamrna regulatory pathways in prostate Cancer by bioinformatics methods. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018: Zhou X, Xu X, Wang J, Lin J, Chen W. Identifying microrna/mrna negative regulation pairs in colorectal Cancer. Sci Rep. 2015;13(5): Le TD, Liu L, Tsykin A, Goodall GJ, Liu B, Sun BY, Li J. Inferring MicroRNA- MRNA causal regulatory relationships from expression data. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(6): Chou CH, Chang NW, Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Lin YL, Lee WH, Yang CD, Hong HC, Wei TY, Tu SJ, et al. mirtarbase 2016: updates to the experimentally validated mirna-target interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016; 44(Database issue):d Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH. starbase v2.0: decoding mirna-cerna, mirna-ncrna and protein RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP- Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):d Jeqqari A, Marks DS, Larsson E. mircode: a map of putative microrna target sites in the long non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(15): Hao Y, Wu W, Li H, Yuan J, Luo J, Zhao Y, Chen R. NPInter v3.0: an upgraded database of noncoding RNA-associated interactions. Database. 2016;2016: baw Li Y, Qiu C, Tu J, Geng B, Yang J, Jiang T, Cui Q. HMDD v2.0: a database for experimentally supported human microrna and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue): Li XP, Wang YT, Ji HB, Aihara K, Chen LN. Personalized characterization of diseases using sample-specific networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(22):e Sara DM, Anna Z. ADAM12-L is a direct target of the mir-29 and mir-200 families in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2015;15(1): Li Y, Zhang MX, Chen HJ, Dong Z, Ganapathy V, Thangaraju M, Huang SA. Ratio of mir-196s to HOXC8 messenger RNA correlates with breast Cancer cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2010;70(20): Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK. Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. Proc Int Joint Conf Neural Netw. 2005;2: Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK. Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing. 2006;70(1):
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer
 Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer Shuqin Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences Fudan University Oct. 4, 2016 Outline Introduction Materials and Methods Results Conclusions Introduction
Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer Shuqin Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences Fudan University Oct. 4, 2016 Outline Introduction Materials and Methods Results Conclusions Introduction
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA LEO TUNKLE *
 CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers
 Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers
 Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association with Pathological Features
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning
 Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
User s Manual Version 1.0
 User s Manual Version 1.0 #639 Longmian Avenue, Jiangning District, Nanjing,211198,P.R.China. http://tcoa.cpu.edu.cn/ Contact us at xiaosheng.wang@cpu.edu.cn for technical issue and questions Catalogue
User s Manual Version 1.0 #639 Longmian Avenue, Jiangning District, Nanjing,211198,P.R.China. http://tcoa.cpu.edu.cn/ Contact us at xiaosheng.wang@cpu.edu.cn for technical issue and questions Catalogue
CURRICULUM VITA OF Xiaowen Chen
 Xiaowen Chen College of Bioinformatics Science and Technology Harbin Medical University Harbin, 150086, P. R. China Mobile Phone:+86 13263501862 E-mail: hrbmucxw@163.com Education Experience 2008-2011
Xiaowen Chen College of Bioinformatics Science and Technology Harbin Medical University Harbin, 150086, P. R. China Mobile Phone:+86 13263501862 E-mail: hrbmucxw@163.com Education Experience 2008-2011
Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes
 Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes Alexandros Manolakos, Idoia Ochoa, Kartik Venkat Supervisor: Olivier Gevaert Abstract Identification of genomic patterns in tumors is an important
Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes Alexandros Manolakos, Idoia Ochoa, Kartik Venkat Supervisor: Olivier Gevaert Abstract Identification of genomic patterns in tumors is an important
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
Solving Problems of Clustering and Classification of Cancer Diseases Based on DNA Methylation Data 1,2
 APPLIED PROBLEMS Solving Problems of Clustering and Classification of Cancer Diseases Based on DNA Methylation Data 1,2 A. N. Polovinkin a, I. B. Krylov a, P. N. Druzhkov a, M. V. Ivanchenko a, I. B. Meyerov
APPLIED PROBLEMS Solving Problems of Clustering and Classification of Cancer Diseases Based on DNA Methylation Data 1,2 A. N. Polovinkin a, I. B. Krylov a, P. N. Druzhkov a, M. V. Ivanchenko a, I. B. Meyerov
Inferring condition-specific mirna activity from matched mirna and mrna expression data
 Inferring condition-specific mirna activity from matched mirna and mrna expression data Junpeng Zhang 1, Thuc Duy Le 2, Lin Liu 2, Bing Liu 3, Jianfeng He 4, Gregory J Goodall 5 and Jiuyong Li 2,* 1 Faculty
Inferring condition-specific mirna activity from matched mirna and mrna expression data Junpeng Zhang 1, Thuc Duy Le 2, Lin Liu 2, Bing Liu 3, Jianfeng He 4, Gregory J Goodall 5 and Jiuyong Li 2,* 1 Faculty
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser
 Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles
 On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
Nature Getetics: doi: /ng.3471
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
38 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'16
 38 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'16 PGAR: ASD Candidate Gene Prioritization System Using Expression Patterns Steven Cogill and Liangjiang Wang Department of Genetics and
38 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'16 PGAR: ASD Candidate Gene Prioritization System Using Expression Patterns Steven Cogill and Liangjiang Wang Department of Genetics and
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity
 Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis
 Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Mature microrna identification via the use of a Naive Bayes classifier
 Mature microrna identification via the use of a Naive Bayes classifier Master Thesis Gkirtzou Katerina Computer Science Department University of Crete 13/03/2009 Gkirtzou K. (CSD UOC) Mature microrna identification
Mature microrna identification via the use of a Naive Bayes classifier Master Thesis Gkirtzou Katerina Computer Science Department University of Crete 13/03/2009 Gkirtzou K. (CSD UOC) Mature microrna identification
Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing. Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven
 Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Research Article A Systematic Evaluation of Feature Selection and Classification Algorithms Using Simulated and Real mirna Sequencing Data
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 5, Article ID 7857, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/5/7857 Research Article A Systematic Evaluation of Feature Selection
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 5, Article ID 7857, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/5/7857 Research Article A Systematic Evaluation of Feature Selection
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression
 omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies
 OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes
 Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Statistics 202: Data Mining. c Jonathan Taylor. Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes.
 Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 5, 2012 1 / 1 Final review Overview Before Midterm General goals of data mining. Datatypes. Preprocessing & dimension
Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 5, 2012 1 / 1 Final review Overview Before Midterm General goals of data mining. Datatypes. Preprocessing & dimension
Measure Specifications Measure Description
 CMS ID/CMS QCDR ID: CAP 15 Title: BRAF Biomarker Testing to Inform Clinical Management and Treatment Decisions in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Specifications Description Denominator
CMS ID/CMS QCDR ID: CAP 15 Title: BRAF Biomarker Testing to Inform Clinical Management and Treatment Decisions in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Specifications Description Denominator
Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD
 Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Review
Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Review
Comparing Multifunctionality and Association Information when Classifying Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes
 000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050
000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050
Predicting microrna-disease associations using bipartite local models and hubness-aware regression
 RNA Biology ISSN: 1547-6286 (Print) 1555-8584 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/krnb20 Predicting microrna-disease associations using bipartite local models and hubness-aware regression
RNA Biology ISSN: 1547-6286 (Print) 1555-8584 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/krnb20 Predicting microrna-disease associations using bipartite local models and hubness-aware regression
Cancer Cell Research 19 (2018)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 LncRNA RP11-597D13.9 expression and clinical significance in serous Ovarian Cancer based on TCGA database Xiaoyan Gu 1, Pengfei Xu 2, Sujuan
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 LncRNA RP11-597D13.9 expression and clinical significance in serous Ovarian Cancer based on TCGA database Xiaoyan Gu 1, Pengfei Xu 2, Sujuan
Prediction of micrornas and their targets
 Prediction of micrornas and their targets Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Computational Methods Mature and precursor mirna prediction mirna target gene prediction Summary micrornas? RNA can
Prediction of micrornas and their targets Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Computational Methods Mature and precursor mirna prediction mirna target gene prediction Summary micrornas? RNA can
Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing SOX4
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
Clustered mutations of oncogenes and tumor suppressors.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Clustered mutations of oncogenes and tumor suppressors. For each oncogene (red dots) and tumor suppressor (blue dots), the number of mutations found in an intramolecular cluster
Supplementary Figure 1 Clustered mutations of oncogenes and tumor suppressors. For each oncogene (red dots) and tumor suppressor (blue dots), the number of mutations found in an intramolecular cluster
The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by upregulating mirna-487a
 Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded
 Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Integrative analysis of survival-associated gene sets in breast cancer
 Varn et al. BMC Medical Genomics (2015) 8:11 DOI 10.1186/s12920-015-0086-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Integrative analysis of survival-associated gene sets in breast cancer Frederick S Varn 1, Matthew
Varn et al. BMC Medical Genomics (2015) 8:11 DOI 10.1186/s12920-015-0086-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Integrative analysis of survival-associated gene sets in breast cancer Frederick S Varn 1, Matthew
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Negative correlation between mir-375 and its predicted target genes, as demonstrated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). 1 The correlation between
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Negative correlation between mir-375 and its predicted target genes, as demonstrated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). 1 The correlation between
Supplemental Information. Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin. Pathway across Cancer Types
 Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin Pathway across Zhongqi Ge, Jake S. Leighton, Yumeng Wang, Xinxin Peng, Zhongyuan Chen, Hu Chen, Yutong Sun,
Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin Pathway across Zhongqi Ge, Jake S. Leighton, Yumeng Wang, Xinxin Peng, Zhongyuan Chen, Hu Chen, Yutong Sun,
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Predicting Breast Cancer Survivability Rates
 Predicting Breast Cancer Survivability Rates For data collected from Saudi Arabia Registries Ghofran Othoum 1 and Wadee Al-Halabi 2 1 Computer Science, Effat University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia 2 Computer
Predicting Breast Cancer Survivability Rates For data collected from Saudi Arabia Registries Ghofran Othoum 1 and Wadee Al-Halabi 2 1 Computer Science, Effat University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia 2 Computer
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Research Article Expression and Clinical Significance of the Novel Long Noncoding RNA ZNF674-AS1 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 3608914, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3608914 Research Article Expression and Clinical Significance of the Novel Long Noncoding RNA ZNF674-AS1
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 3608914, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3608914 Research Article Expression and Clinical Significance of the Novel Long Noncoding RNA ZNF674-AS1
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD. Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China. Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine
 GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
Big Image-Omics Data Analytics for Clinical Outcome Prediction
 Big Image-Omics Data Analytics for Clinical Outcome Prediction Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Associate Professor Dept. Computer Science & Engineering University of Texas at Arlington Dept. CSE, UT Arlington Scalable
Big Image-Omics Data Analytics for Clinical Outcome Prediction Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Associate Professor Dept. Computer Science & Engineering University of Texas at Arlington Dept. CSE, UT Arlington Scalable
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Design of Palm Acupuncture Points Indicator
 Design of Palm Acupuncture Points Indicator Wen-Yuan Chen, Shih-Yen Huang and Jian-Shie Lin Abstract The acupuncture points are given acupuncture or acupressure so to stimulate the meridians on each corresponding
Design of Palm Acupuncture Points Indicator Wen-Yuan Chen, Shih-Yen Huang and Jian-Shie Lin Abstract The acupuncture points are given acupuncture or acupressure so to stimulate the meridians on each corresponding
Predicting Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis by Fully Automated Microscopic Pathology Image Features
 Predicting Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis by Fully Automated Microscopic Pathology Image Features Kun-Hsing Yu, MD, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School
Predicting Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis by Fully Automated Microscopic Pathology Image Features Kun-Hsing Yu, MD, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School
TCGA. The Cancer Genome Atlas
 TCGA The Cancer Genome Atlas TCGA: History and Goal History: Started in 2005 by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) with $110 Million to catalogue
TCGA The Cancer Genome Atlas TCGA: History and Goal History: Started in 2005 by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) with $110 Million to catalogue
Predicting Kidney Cancer Survival from Genomic Data
 Predicting Kidney Cancer Survival from Genomic Data Christopher Sauer, Rishi Bedi, Duc Nguyen, Benedikt Bünz Abstract Cancers are on par with heart disease as the leading cause for mortality in the United
Predicting Kidney Cancer Survival from Genomic Data Christopher Sauer, Rishi Bedi, Duc Nguyen, Benedikt Bünz Abstract Cancers are on par with heart disease as the leading cause for mortality in the United
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 An example of the gene-term-disease network automatically generated by Phenolyzer web server for 'autism'. The largest word represents the user s input term, Autism. The pink round
Supplementary Figure 1 An example of the gene-term-disease network automatically generated by Phenolyzer web server for 'autism'. The largest word represents the user s input term, Autism. The pink round
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Workflow of CDR3 sequence assembly from RNA-seq data.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow of CDR3 sequence assembly from RNA-seq data. Paired-end short-read RNA-seq data were mapped to human reference genome hg19, and unmapped reads in the TCR regions were extracted
Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow of CDR3 sequence assembly from RNA-seq data. Paired-end short-read RNA-seq data were mapped to human reference genome hg19, and unmapped reads in the TCR regions were extracted
Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Session 4 Rebecca Poulos
 The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis
 Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis M.L. Zhi 1 *, Z.J. Liu 2 *, X.Y. Yi 1, L.J. Zhang 1 and Y.X. Bao 1 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated
Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis M.L. Zhi 1 *, Z.J. Liu 2 *, X.Y. Yi 1, L.J. Zhang 1 and Y.X. Bao 1 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated
Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10413-10418 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058793 Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma Chao-Bing
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10413-10418 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058793 Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma Chao-Bing
Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics
 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'18 85 Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics Bing Liu 1*, Xuan Guo 2, and Jing Zhang 1** 1 Department
Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'18 85 Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics Bing Liu 1*, Xuan Guo 2, and Jing Zhang 1** 1 Department
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
About OMICS Group Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer
 The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
Prediction of potential disease-associated micrornas based on random walk
 Bioinformatics, 3(), 25, 85 85 doi:.93/bioinformatics/btv39 Advance Access Publication Date: 23 January 25 Original Paper Data and text mining Prediction of potential disease-associated micrornas based
Bioinformatics, 3(), 25, 85 85 doi:.93/bioinformatics/btv39 Advance Access Publication Date: 23 January 25 Original Paper Data and text mining Prediction of potential disease-associated micrornas based
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities
 Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success
 micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS
 RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis
 Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Breast cancer. Risk factors you cannot change include: Treatment Plan Selection. Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data
 Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
A Statistical Framework for Classification of Tumor Type from microrna Data
 DEGREE PROJECT IN MATHEMATICS, SECOND CYCLE, 30 CREDITS STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN 2016 A Statistical Framework for Classification of Tumor Type from microrna Data JOSEFINE RÖHSS KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
DEGREE PROJECT IN MATHEMATICS, SECOND CYCLE, 30 CREDITS STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN 2016 A Statistical Framework for Classification of Tumor Type from microrna Data JOSEFINE RÖHSS KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS
 RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Download slides and package http://odin.mdacc.tmc.edu/~rverhaak/package.zip http://odin.mdacc.tmc.edu/~rverhaak/rna-seqlecture.zip Overview Introduction into the topic
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Download slides and package http://odin.mdacc.tmc.edu/~rverhaak/package.zip http://odin.mdacc.tmc.edu/~rverhaak/rna-seqlecture.zip Overview Introduction into the topic
A Panoptic Approach to Studying MicroRNA Expression in Breast. Tumors. Priyanka Bhatt
 A Panoptic Approach to Studying MicroRNA Expression in Breast Tumors By Priyanka Bhatt A Dissertation Submitted to Rutgers University School of Health Related Professions In partial fulfillment of the
A Panoptic Approach to Studying MicroRNA Expression in Breast Tumors By Priyanka Bhatt A Dissertation Submitted to Rutgers University School of Health Related Professions In partial fulfillment of the
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies
 Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies Dr. Maricel G. Kann Assistant Professor Dept of Biological Sciences UMBC 2 The term protein domain
Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies Dr. Maricel G. Kann Assistant Professor Dept of Biological Sciences UMBC 2 The term protein domain
Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6506-6510 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0024531 Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma Zhihong
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6506-6510 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0024531 Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma Zhihong
MicroRNA-mediated incoherent feedforward motifs are robust
 The Second International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 8) Lijiang, China, October 31 November 3, 8 Copyright 8 ORSC & APORC, pp. 62 67 MicroRNA-mediated incoherent feedforward motifs
The Second International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 8) Lijiang, China, October 31 November 3, 8 Copyright 8 ORSC & APORC, pp. 62 67 MicroRNA-mediated incoherent feedforward motifs
Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
LncRNA TUSC7 affects malignant tumor prognosis by regulating protein ubiquitination: a genome-wide analysis from 10,237 pancancer
 Original Article LncRNA TUSC7 affects malignant tumor prognosis by regulating protein ubiquitination: a genome-wide analysis from 10,237 pancancer patients Xiaoshun Shi 1 *, Yusong Chen 2,3 *, Allen M.
Original Article LncRNA TUSC7 affects malignant tumor prognosis by regulating protein ubiquitination: a genome-wide analysis from 10,237 pancancer patients Xiaoshun Shi 1 *, Yusong Chen 2,3 *, Allen M.
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks
 Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Supplementary data for:
 Supplementary data for: Prediction of treatment efficacy for prostate cancer using a mathematical model Huiming Peng 1, Weiling Zhao 1, Hua Tan 1, Zhiwei Ji 1, Jingsong Li 2, King Li 1, Xiaobo Zhou 1,*
Supplementary data for: Prediction of treatment efficacy for prostate cancer using a mathematical model Huiming Peng 1, Weiling Zhao 1, Hua Tan 1, Zhiwei Ji 1, Jingsong Li 2, King Li 1, Xiaobo Zhou 1,*
