MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: , 2015
|
|
|
- Calvin Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: , 2015 Total alkaloids of Rubus alceifolius Poir inhibit tumor angiogenesis through suppression of the Notch signaling pathway in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma JINYAN ZHAO 1,2, WEI LIN 1,2, ZHIYUN CAO 1, QUNCHUAN ZHUANG 1,2, LIANGPU ZHENG 1,2, JUN PENG 1,2 and ZHENFENG HONG 1,2 1 Academy of Integrative Medicine; 2 Fujian Key Laboratory of Integrative Medicine on Geriatrics, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou, Fujian , P.R. China Received October 21, 2013; Accepted May 2, 2014 DOI: /mmr Abstract. Angiogenesis, which has a critical role in human tumor growth and development, is tightly regulated by the Notch signaling pathway. Total alkaloids are active components of the plant Rubus alceifolius Poir, which is used for the treatment of various types of cancer. A previous study by our group showed that the total alkaloids of Rubus alceifolius Poir (TARAP) induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell apoptosis through the activation of the mitochondria dependent pathway in vitro and in vivo, as well as inhibited angiogenesis in a chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane model. In the present study, to further analyze the specific mechanisms underlying the antitumor activity of TARAP, a HCC xenograft mouse model was used to assess the effect of TARAP on angiogenesis in vivo. TARAP was found to suppress the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) A and VEGF receptor 2 in tumor tissues, which resulted in the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. In addition, TARAP treatment was observed to inhibit the expression of Notch1, delta like ligand 4 and jagged 1, which are key mediators of the Notch signaling pathway. The present study identified that the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis through the suppression of the Notch signaling pathway may be one of the mechanisms through which TARAP may be effective in the treatment of cancer. Correspondence to: Professor Zhenfeng Hong or Dr Jun Peng, Academy of Integrative Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1 Huatuo Road, Fuzhou, Fujian , P.R. China E mail: zfhong1953@163.com pjunlab@hotmail.com Key words: total alkaloids of Rubus alceifolius Poir, hepatocellular carcinoma, tumor angiogenesis, Notch signaling pathway Introduction Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third most common cause of cancer associated mortality worldwide. The HCC incidence rate is increasing more rapidly than most other types of cancers due to the increasing prevalence of hepatitis B and C viral infections (1,2). Therapies for HCC include surgery, radiofrequency ablation and chemotherapy. At present, no drugs are available to prevent or reduce tumor spread and/or recurrence, which severely affects prognosis and survival. HCC is the only type of cancer in which conventional chemotherapeutics must be avoided, due to the underlying liver damage. Thus, a novel drug for the treatment of HCC is urgently required. Tumor angiogenesis is a complex process in which new blood vessels are formed in response to interactions between tumor cells and endothelial cells (ECs) (3,4). Angiogenesis has an important role in cancer growth and metastasis, with tumors able to grow autonomously to a size of 2±3 mm 3, but incapable of growing beyond this size without a blood supply (5 9). Tumor cells continuously stimulate the formation of new blood vessels to grow. New blood vessels that surround tumor tissues provide a gateway for the tumor cells to enter the vascular system and metastasize to distant organs. Thus, the inhibition of angiogenesis has been proposed to suppress tumor growth and metastasis (10). An increasing number of studies have revealed that tumor cells secrete angiogenic growth factors to stimulate EC proliferation and to induce angiogenesis (6). Among them, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the most potent angiogenic factors and it is overexpressed in numerous types of human cancer (11). Genetic studies have shown that Notch signaling has a critical role in vascular formation during early embryonic development (12 14). Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved pathway, which regulates cell fate decisions during the embryonic development of vertebrates and invertebrates (15). There are four mammalian Notch genes, Notch1 4, and five ligands, jagged 1, jagged 2, delta like ligand (DLL) 1, DLL3 and DLL4 (12,16,17). Notch signaling has been reported to have a crucial role in tumor angiogenesis
2 358 ZHAO et al: TOTAL ALKALOIDS OF Rubus Aleaefolius Poir INHIBIT TUMOR ANGIOGENESIS and is a novel target for anti angiogenic therapy. Studies have demonstrated that the activation of the Notch signaling pathway inhibits angiogenesis. Activated Notch1 and Notch4 have been reported to decrease the expression of VEGF receptor (VEGFR) 2, resulting in decreased human EC proliferation in response to VEGF (18). Human ECs transduced with DLL4 have been shown to exhibit decreased VEGF induced proliferation and migration, as well as a significant reduction in the expression of VEGFR2 and its coreceptor neuropilin 1, suggesting that DLL4 is an inhibitor of angiogenesis (19). In addition, inhibiting jagged using an antisense oligomer in bovine ECs has been found to induce tube formation and collagen gel invasion in response to fibroblast growth factor, but not VEGF (20). Although Notch signaling has been reported to inhibit sprouting angiogenesis in these studies (18 20), most were performed in vitro. Thus, in vivo tumor angiogenesis assays are required to confirm these findings and to determine their physiological relevance. Rubus alceifolius Poir is a natural product, which is used in Traditional Chinese Medicine in Southern regions of Fujian Province, China, to treat various types of hepatitis. In a previous study, our group identified that total alkaloids of Rubus alceifolius Poir (TARAP) promoted apoptosis in human HCC cells (21). However, the specific mechanism underlying the anticancer effect of TARAP in vivo has yet to be elucidated. In the present study, in order to further investigate the anticancer activity of TARAP, the effect of TARAP on tumor growth and its underlying molecular mechanisms were investigated in a HCC xenograft mouse model. Materials and methods Materials and reagents. Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM), fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin streptomycin, Trypsin EDTA and TRIzol reagent were purchased from Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA, USA). SuperScript II reverse transcriptase was purchased from Promega Corporation (Madison, WI, USA). Antibodies against cluster of differentiation (CD) 31 (human, pab), VEGF A (human, pab), VEGFR2 (human, pab), Notch (human, mab), Dll4 (human, pab) and jagged 1 (human, pab) were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). All antibodies were diluted 1:100. All other chemicals, unless otherwise stated, were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). TARAP preparation. TARAP preparation was performed as described previously (21). The roots of Rubus alceifolius Poir were collected in Anxi (China) and were identified and authenticated at Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Fuzhou, China). The alkaloids were then extracted as follows: The herb powder (1 g) was extracted using 50 ml chloroform:methanol:ammonia solution (15:4:3) for 2 h in an ice bath, sonicated for 30 min, brought to room temperature and filtered. The filtered solution was collected and dessicated. The resultant residue was dissolved in 2 ml of 2% sulfuric acid solution and filtered. The filter paper and residue were re-washed with 2 ml of 2% sulfuric acid solution and buffer solution (ph 3.6). The buffer was then added to make a final volume of 50 ml, and the solution was saved for future use. Acid dye colorimetry was used to measure the total alkaloid content. The total alkaloid content was 0.81 mg alkaloid per gram of initial herb powder. Cell culture and animals. HepG2 human HCC cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA). Cells were grown in DMEM containing 10% (v/v) FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin in a humidified incubator at 37 C with 5% CO 2. Cells were subcultured to 80 90% confluency. Six week old male BALB/c athymic nude mice were purchased from Shanghai Si Lai Ke Experimental Animal Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Mice were housed at five mice per cage in a pathogen free room in an environment with controlled temperature (22 C), humidity and a 12 h light/dark cycle with free access to water and a standard laboratory diet. All animal treatments were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for Animal Experimentation of Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Fuzhou, China). The animal studies were approved by the Fujian Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Animal Ethics Committee (Fuzhou, China). In vivo tumor xenograft study. HepG2 cells were seeded at a density of 4x10 6 cells mixed 1:1 with Matrigel and were subcutaneously injected in the right flank of the mice to initiate tumor growth. Seven days following xenograft implantation, when the tumors reached 3 mm in diameter, the mice were randomly divided into two groups (n=10) and were intragastrically administered 3 g/kg body weight TARAP or saline daily, five days a week for 21 days. At the end of the experiment, the animals were anaesthetized with ether and the mice were sacrificed by cervical vertebra dislocation, and the tumor tissue was removed. A section of the tumor was fixed in buffered formalin and the remaining sections were stored at 80 C for molecular analyses. RNA extraction and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis. Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol Reagent. Oligo(dT) primed RNA (1 µg) was reverse transcribed using SuperScript II reverse transcriptase according to the manufacturer's instructions. The cdna product (1 µl) was added to prepare the PCR reaction mixture containing 200 µm dntps, 1.5 mm MgCl 2 and 1.25 U Platinum Taq polymerase for VEGF-A, VEGFR2, Notch, Dll4 or jagged1 with a Taq DNA polymerase. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Samples were analyzed using gel electrophoresis on a 1.5% agarose gel. DNA bands were analyzed using a Bio Rad Gel Doc 2000 System (Bio Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Immunohistochemistry (IHC). Tumor samples were fixed with 10% formaldehyde for 12 h and processed for the generation of paraffin embedded tumor slides. Slides were subjected to antigen retrieval and endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked using hydrogen peroxide. Sections were then incubated with CD31, VEGF A, VEGFR2, Notch, Dll4 and jagged 1 antibodies diluted 1:100. Subsequent to washing with phosphate buffered saline (PBS), slides were incubated with biotinylated secondary antibodies followed by incubation with conjugated horseradish peroxidase labeled streptavidin (Dako UK Ltd., Ely, UK) and washed with PBS. Slides were then incubated with diaminobenzidine as the chromogen, followed by counterstaining with
3 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: , Figure 1. Effect of TARAP on intratumoral microvessel density in HCC xenograft mice. Tumor tissues were processed for immunohistochemical staining for CD31. Images were captured at a magnification of x400. Immunohistochemical staining was quantified and presented as a percentage of positively stained cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from 10 individual mice in each group. * P<0.05 vs. control group. TARAP, total alkaloids of Rubus alceifolius Poir; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; CD, cluster of differentiation. A B Figure 2. Effect of TARAP on the expression of VEGF A and VEGFR2 in HCC xenograft mice. (A) mrna expression of VEGF A and VEGFR2 was determined using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis. GAPDH was used as the internal control. (B) Tumor tissues were processed for immunohistochemical staining for VEGF A and VEGFR2. Images were captured at a magnification of x400. Immunohistochemical staining was quantified and represented as the percentage of positively stained cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from 10 individual mice in each group. * P<0.05 vs. control group. TARAP, total alkaloids of Rubus alceifolius Poir; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. hematoxylin. Subsequent to staining, five high power fields (magnification, x400) were randomly selected in each slide and the average proportion of positive cells in each field was counted using the true color multi functional cell image analysis management system (Image Pro Plus; Media Cybernetics, Inc., Bethesda, MD, USA). To exclude any non specific staining, PBS was used to replace the primary antibody as a negative control. Statistical analysis. All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. Data were analyzed using the SPSS package for Windows (Version 11.5; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Statistical analysis of the data was performed using the Student's t test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Results and Discussion TARAP inhibits tumor angiogenesis in a xenograft model. Deregulated angiogenesis has a crucial role in the development of various diseases, including cancer (6,22,23). CD31 is a characteristic molecule in vascular ECs which is used as an angiogenesis marker in vivo. In the present study, immunohistochemical staining of CD31 was used to identify the degree of angiogenesis. As shown in Fig. 1A and B, the microvessel
4 360 ZHAO et al: TOTAL ALKALOIDS OF Rubus Aleaefolius Poir INHIBIT TUMOR ANGIOGENESIS A Ba Bb Figure 3. Effect of TARAP on the activation of the Notch signaling pathway in HCC xenograft mice. (A) mrna expression of Notch1, jagged 1 and Dll4 was determined using polymerase chain reaction analysis. GAPDH was used as the internal control. (B) Tumor tissues were processed for immunohistochemical staining for (Ba) Notch1 and (Bb) jagged 1 and Dll4. Images were captured at a magnification of x400. Immunohistochemical staining was quantified and presented as the percentage of positively stained cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from 10 individual mice in each group. * P<0.05 vs. control group. TARAP, total alkaloids of Rubus alceifolius Poir; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; Dll, delta like ligand. density of the HCC xenografts in the TARAP treated mice was observed to be reduced compared with that in the control mice, suggesting that TARAP inhibited angiogenesis in vivo. Thus, TARAP may mediate its antitumor activity through blocking angiogenesis. TARAP inhibits the expression of VEGF A and VEGFR2 in HCC xenograft mice. In the process of tumor growth, interaction between tumor cells and vascular ECs causes increases in tumor blood vessels and promotes tumor growth (24,25). VEGF A is commonly expressed in a wide variety of types of human tumor cells, is one of the most effective biological inducers of angiogenesis and is associated with angiogenesis, growth and metastasis (26 29). To analyze the effect of TARAP on tumor angiogensis, VEGF A and VEGFR2 expression were assessed in a xenograft model using PCR analysis and IHC. PCR analysis revealed that TARAP treatment reduced the mrna expression of VEGF A and VEGFR2 in the HCC xenografts (Fig. 2A). Furthermore, IHC showed that the protein expression of VEGF A and VEGFR2 was similar to their respective mrna expression levels. The percentage of VEGF A and VEGFR2 positive cells in the control group was found to be 84±12.34 and 86.67±11.48%, respectively, while that in TARAP treated mice was 23.5±4.31 and 24.83±5.79%, respectively (Fig. 2B). TARAP suppresses the Notch signaling pathway in HCC xenograft mice. Tumor angiogenesis is tightly regulated by the Notch signaling pathway; therefore, in the present study, the effect of TARAP on the expression of key mediators of the Notch signaling pathway was investigated using PCR and IHC analyses. As shown in Fig. 3A, TARAP treatment was observed to significantly reduce the mrna expression of Notch, Dll4 and jagged 1 in tumor tissues. Furthermore,
5 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: , their protein expression was significantly inhibited by TARAP treatment. The percentages of Notch, Dll4 and jagged 1 positive cells in the control group were 80±10.96, 50.17±9.68 and 61±8.42%, respectively, whereas those in TARAP treated mice were 37.33±7.32, 23.17±3.99 and 19.5±3.1%, respectively (Fig. 3B). These findings suggested that the inhibitory effect of TARAP on tumor angiogenesis in vivo may be mediated through the suppression of the Notch signaling pathway. In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, the present study was the first study to show that TARAP inhibits tumor angiogenesis through the suppression of the Notch signaling pathway, which may in part explain its anticancer activity. Acknowledgements The present study was supported by grants from the Nature Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (nos. 2010J01191 and 2010J01194) and the Medical Originality Foundation of Fujian Province of China (no CX 18). References 1. Tsai WL and Chung RT: Viral hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene 29: , Schütte K, Bornschein J and Malfertheiner P: Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiological trends and risk factors. Dig Dis 27: 80 92, Bikfalvi A: Significance of angiogenesis in tumour progression and metastasis. Eur J Cancer 31A: , Folkman J: What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 4 6, Ingber D, Fujita T, Kishimoto S, Sudo K, Kanamaru T, Brem H and Folkman J: Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumour growth. Nature 348: , Folkman J and Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 267: , Pluda JM: Tumor associated angiogenesis: mechanisms, clinical implications, and therapeutic strategies. Semin Oncol 24: , Folkman J: Anti angiogenesis: new concept for therapy of solid tumors. Ann Surg 175: , Brem H and Folkman J: Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis mediated by cartilage. J Exp Med 141: , Voest EE: Inhibitors of angiogenesis in a clinical perspective. Anticancer Drugs 7: , Jung YD, Ahmad SA, Liu W, Reinmuth N, Parikh A, Stoeltzing O, Fan F and Ellis LM: The role of the microenvironment and intercellular cross talk in tumor angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 12: , Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, et al: Notch signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes Dev 14: , Krebs LT, Shutter JR, Tanigaki K, Honio T, Stark KL and Gridley T: Haploinsufficient lethality and formation of arteriovenous malformations in Notch pathway mutants. Genes Dev 18: , Xue Y, Gao X, Lindsell CE, et al: Embryonic lethality and vascular defects in mice lacking the Notch ligand Jagged1. Hum Mol Genet 8: , Artavanis Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ: Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284: , Guo S, Liu M and Gonzalez-Perez RR: Role of Notch and its oncogenic signaling crosstalk in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1815: , Li JL and Harris AL: Notch signaling from tumor cells: a new mechanism of angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 8: 1-3, Taylor KL, Henderson AM and Hughes CC: Notch activation during endothelial cell network formation in vitro targets the basic HLH transcription factor HESR 1 and downregulates VEGFR 2/KDR expression. Microvasc Res 64: , Williams CK, Li JL, Murga M, Harris AL and Tosato G: Upregulation of the Notch ligand Delta like 4 inhibits VEGF induced endothelial cell function. Blood 107: , Zimrin AB, Pepper MS, McMahon GA, Nguyen F, Montesano R and Maciag T: An antisense oligonucleotide to the notch ligand jagged enhances fibroblast growth factor induced angiogenesis in vitro. J Biol Chem 271: , Zhao J, Chen X, Lin W, et al: Total alkaloids of Rubus aleaefolius Poir inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma growth in vivo and in vitro via activation of mitochondrial dependent apoptosis. Int J Oncol 42: , Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other diseases. Nat Med 1: 27 31, Folkman J: Angiogenesis. Annu Rev Med 57: 1 18, Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, et al: Vascular specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 407: , Ishiwata I, Sudo T, Kiguchi K and Ishikawa H: Tumor angiogenesis factors produced by cancer cells. Hum Cell 12: 37 46, Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386: , Jain RK: Tumor angiogenesis and accessibility: role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Semin Oncol 29 (6 Suppl 16): 3 9, Ferrara N: Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol 29 (6 Suppl 16): 10 14, Houck KA, Ferrara N, Winer J, et al: The vascular endothelial growth factor family: identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol Endocrinol 5: , 1991.
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
A Phase I Study of RO , a γ-secretase Inhibitor of Notch Signaling, in Patients with Refractory Metastatic or Locally Advanced Solid Tumors
 A Phase I Study of RO4929097, a γ-secretase Inhibitor of Notch Signaling, in Patients with Refractory Metastatic or Locally Advanced Solid Tumors Tolcher, et al Data Supplement 1 ONLINE APPENDIX Appendix
A Phase I Study of RO4929097, a γ-secretase Inhibitor of Notch Signaling, in Patients with Refractory Metastatic or Locally Advanced Solid Tumors Tolcher, et al Data Supplement 1 ONLINE APPENDIX Appendix
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis
 The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
SOMATOSTATIN RECEPTORS IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA. Marie LEQUOY Saint-Antoine Hospital, Department of Hepatology, Paris, France
 SOMATOSTATIN RECEPTORS IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA Marie LEQUOY Saint-Antoine Hospital, Department of Hepatology, Paris, France Somatostatin : SST Somatostatin (SST) protein : 2 active forms (alternative
SOMATOSTATIN RECEPTORS IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA Marie LEQUOY Saint-Antoine Hospital, Department of Hepatology, Paris, France Somatostatin : SST Somatostatin (SST) protein : 2 active forms (alternative
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model
 CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Simultaneous blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 induces synergistic. Short title: Synergistic antitumour effect by dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2
 carticle Simultaneous blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 induces synergistic antitumour effect in vivo 1 Short title: Synergistic antitumour effect by dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 S. Yasuda 1, M. Sho 1, I.
carticle Simultaneous blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 induces synergistic antitumour effect in vivo 1 Short title: Synergistic antitumour effect by dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 S. Yasuda 1, M. Sho 1, I.
CD133 induced tumorigenicity mice express TGF-beta receptor type II (TBRII) and embryonic liver fodrin (ELF) along with stem cell markers
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 2296-2301 CD133 induced tumorigenicity mice express TGF-beta receptor type II (TBRII) and embryonic liver fodrin (ELF) along with stem
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 2296-2301 CD133 induced tumorigenicity mice express TGF-beta receptor type II (TBRII) and embryonic liver fodrin (ELF) along with stem
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer
 Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Chorion Allantois Membrane (CAM) Assay
 Chorion Allantois Membrane (CAM) Assay Introduction: The CAM assay was based on Nguyen et al. (1994). It is a simple and commonly used test to assess the angiogenesis inhibiting or stimulating properties
Chorion Allantois Membrane (CAM) Assay Introduction: The CAM assay was based on Nguyen et al. (1994). It is a simple and commonly used test to assess the angiogenesis inhibiting or stimulating properties
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2016, 7(2): 49-53 ISSN: 2088 0197 Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin Laeli
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2016, 7(2): 49-53 ISSN: 2088 0197 Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin Laeli
IMMP8-1. Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells
 IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
MELANOMA CANCER TEST
 MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE
 92 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 11(2): 92 --96, 1999 ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE LI Peiyu z}~r~]~-,1 YUAN Mei 3~'J~,
92 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 11(2): 92 --96, 1999 ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE LI Peiyu z}~r~]~-,1 YUAN Mei 3~'J~,
TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis
 Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT
 Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Bcl-2 and p53 protein expression in all grades of astrocytomas
 Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Senior Research Projects Southern Scholars 11-1994 Bcl-2 and p53 protein expression in all grades of astrocytomas Robyn L. Castleberg Follow this
Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Senior Research Projects Southern Scholars 11-1994 Bcl-2 and p53 protein expression in all grades of astrocytomas Robyn L. Castleberg Follow this
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Human Colon Cancer: Biology and Therapeutic Implications
 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Human Colon Cancer: iology and Therapeutic Implications LEE M. ELLIS, YUTK TKHSHI, WENIO LIU, RYMOND M. SHHEEN University of Texas M.D. nderson Cancer Center, Departments
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Human Colon Cancer: iology and Therapeutic Implications LEE M. ELLIS, YUTK TKHSHI, WENIO LIU, RYMOND M. SHHEEN University of Texas M.D. nderson Cancer Center, Departments
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Catechin s anti-angiogenic effects in epithelial ovarian cancer
 Catechin s anti-angiogenic effects in epithelial ovarian cancer Brian Krug Background Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is a common and lethal malignancy of the female reproductive tract (2). Often detected
Catechin s anti-angiogenic effects in epithelial ovarian cancer Brian Krug Background Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is a common and lethal malignancy of the female reproductive tract (2). Often detected
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Original Article Expression of FOXC2 in renal cell carcinoma and its relationship to clinical pathological features
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13388-13392 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0009294 Original Article Expression of FOXC2 in renal cell carcinoma and its relationship to clinical pathological features Ting-Yi
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13388-13392 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0009294 Original Article Expression of FOXC2 in renal cell carcinoma and its relationship to clinical pathological features Ting-Yi
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
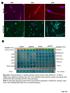 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation
 Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
 Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3726-3731 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0077355 Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma Minhua
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3726-3731 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0077355 Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma Minhua
Value of serum galectin-3 and midkine level determination for assessing tumor severity in patients with thyroid cancer
 148 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2017; 23(3): 148-152 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Value of serum galectin-3 and midkine level determination for assessing tumor
148 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2017; 23(3): 148-152 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Value of serum galectin-3 and midkine level determination for assessing tumor
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Endostar Combined with Cisplatin Inhibits Tumor Growth and Lymphatic Metastasis of Lewis Lung Carcinoma Xenografts in Mice
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.5.3079 RESEARCH ARTICLE Endostar Combined with Cisplatin Inhibits Tumor Growth and Lymphatic Metastasis of Lewis Lung Carcinoma Xenografts in Mice Xiao-Peng
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.5.3079 RESEARCH ARTICLE Endostar Combined with Cisplatin Inhibits Tumor Growth and Lymphatic Metastasis of Lewis Lung Carcinoma Xenografts in Mice Xiao-Peng
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT
 CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
Regulation of cell signaling cascades by influenza A virus
 The Second International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 08) Lijiang, China, October 31 November 3, 2008 Copyright 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 389 394 Regulation of cell signaling cascades
The Second International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 08) Lijiang, China, October 31 November 3, 2008 Copyright 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 389 394 Regulation of cell signaling cascades
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells *
 Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 2671-2676, 2015 Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer JIE CHEN *, JUNKAI WANG *, XINGANG CUI, YUSHAN LIU, LEI YIN, YAO LI,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 2671-2676, 2015 Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer JIE CHEN *, JUNKAI WANG *, XINGANG CUI, YUSHAN LIU, LEI YIN, YAO LI,
Tumor Angiogenesis: Determined By VEGF Expression, MAGS Scoring, Doppler Study, As Prognostic Indicator In Carcinoma Breast
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Tumor Angiogenesis: Determined By VEGF Expression, MAGS Scoring, Doppler Study, As Prognostic Indicator In Carcinoma Breast R Shankar, S Tiwary,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Tumor Angiogenesis: Determined By VEGF Expression, MAGS Scoring, Doppler Study, As Prognostic Indicator In Carcinoma Breast R Shankar, S Tiwary,
Expression and clinical significance of Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 in breast cancer
 Expression and clinical significance of Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 in breast cancer L. Zhang*, W.P. Yang*, L.Y. Wu, X. Zhu and C.Y. Wei Department of Breast Surgery, Affiliated Tumor
Expression and clinical significance of Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 in breast cancer L. Zhang*, W.P. Yang*, L.Y. Wu, X. Zhu and C.Y. Wei Department of Breast Surgery, Affiliated Tumor
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS
 CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
PD-L1 Analyte Control DR
 Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant molecular mechanism.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
 Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel
 KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk in a Chinese Han population
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells
 CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Cancer Tumor Therapy Drug Vicrostatin Shows. Promising Inhibition of Glioma Growth and. Angiogenesis in Vivo. Rupan Bose
 Bose p. 1 of 23. Cancer Tumor Therapy Drug Vicrostatin Shows Promising Inhibition of Glioma Growth and Angiogenesis in Vivo Rupan Bose B.A. Neuroscience 2011 Candidate Senior Thesis Dana and David Dornsife
Bose p. 1 of 23. Cancer Tumor Therapy Drug Vicrostatin Shows Promising Inhibition of Glioma Growth and Angiogenesis in Vivo Rupan Bose B.A. Neuroscience 2011 Candidate Senior Thesis Dana and David Dornsife
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Ginsenoside-Rh2 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Side Population Cells
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ginsenoside-Rh2 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Side Population Cells Jun Qian 1& *, Jing Li 1&, Jian-Guang Jia 1, Xin Jin 1, Da-Jun Yu 1,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Ginsenoside-Rh2 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Side Population Cells Jun Qian 1& *, Jing Li 1&, Jian-Guang Jia 1, Xin Jin 1, Da-Jun Yu 1,
Sorafenib inhibits liver cancer growth by decreasing mtor, AKT, and PI3K expression
 JBUON 2015; 20(1): 218-222 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sorafenib inhibits liver cancer growth by decreasing mtor, AKT, and
JBUON 2015; 20(1): 218-222 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sorafenib inhibits liver cancer growth by decreasing mtor, AKT, and
(PDGF), 9 ( -2 (FGF-2), SMO
 Abstract An ethanol extract from shark muscle has been shown to have potent angiogenic activity when mixed together with olive oil in a ratio of 1part extract to 9 parts olive oil. This mixture has been
Abstract An ethanol extract from shark muscle has been shown to have potent angiogenic activity when mixed together with olive oil in a ratio of 1part extract to 9 parts olive oil. This mixture has been
Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p.
 Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the clinical features of HBsAg-positive liver cancer
 JBUON 2017; 22(4): 942-946 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the
JBUON 2017; 22(4): 942-946 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the
Novel Epothilone Methyl Derivatives Inhibit HUVEC Cell Proliferation and Angiogenesis
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 9 28 9 818 ~ 825 * 116024 MTT Transwell MMP2 RT-PCR MMP2 RNA 1 HUVEC Ⅳ 2 Ⅳ Q78 Novel
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 9 28 9 818 ~ 825 * 116024 MTT Transwell MMP2 RT-PCR MMP2 RNA 1 HUVEC Ⅳ 2 Ⅳ Q78 Novel
Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian cancer
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth
 210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 102-108; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells Jun-Na Ge, 1 Dan
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 102-108; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells Jun-Na Ge, 1 Dan
The Effects of Combination of Coix Seed Extract and Cisplatin on TAM and Expression of HIF-1αin vivo in Lewis Lung Carcinoma
 Iran J Public Health, Vol. 47, No.6, Jun 2018, pp.838-843 Original Article The Effects of Combination of Coix Seed Extract and Cisplatin on TAM and Expression of HIF-1αin vivo in Lewis Lung Carcinoma Guo
Iran J Public Health, Vol. 47, No.6, Jun 2018, pp.838-843 Original Article The Effects of Combination of Coix Seed Extract and Cisplatin on TAM and Expression of HIF-1αin vivo in Lewis Lung Carcinoma Guo
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
TABLE OF CONTENTS 6.1. INTRODUCTION 6.2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
 CHAPTER 6 EFFECT OF VERNOLIDE-A ON RADIATION INDUCED HYPOXIA MEDIATED TUMOUR ANGIOGENESIS TABLE OF CONTENTS 6.1. INTRODUCTION 6.2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 6.2.1. Animals 6.2.2. Cell line 6.2.3. Chemicals
CHAPTER 6 EFFECT OF VERNOLIDE-A ON RADIATION INDUCED HYPOXIA MEDIATED TUMOUR ANGIOGENESIS TABLE OF CONTENTS 6.1. INTRODUCTION 6.2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 6.2.1. Animals 6.2.2. Cell line 6.2.3. Chemicals
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Shangqiu Medical College, Shangqiu, China 2. Corresponding author: M.Z. Zhang
 Comparison of the expression of human equilibrative nucleotide transporter 1 (hent1) and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 (RRM1) genes in seven non-hodgkin lymphoma cell lines H.B. Zhao 1,2, X.F. Zhang
Comparison of the expression of human equilibrative nucleotide transporter 1 (hent1) and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 (RRM1) genes in seven non-hodgkin lymphoma cell lines H.B. Zhao 1,2, X.F. Zhang
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Supporting Information Nitric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines
 upporting Information itric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines Priya udhesh a, Kaviyarasan Tamilarasan a, Palaniappan Arumugam a and
upporting Information itric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines Priya udhesh a, Kaviyarasan Tamilarasan a, Palaniappan Arumugam a and
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
