Lipids and biomembranes
|
|
|
- Shona Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lipids and biomembranes Tomáš Kučera Department of Medical hemistry and linical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, harles University in Prague and Motol University Hospital MMXVIII
2 Lipids Definition non-polar (hydrophobic) compounds of biological origin, soluble in organic solvents (in water limitedly or not at all) Major roles structural components of biological membranes energy storage (triacylglycerols) thermal (and electric) insulators protective layers against infection, clashes and dessication vitamins and hormones and their precursors bile acids lipid solubilization
3 Fatty acids FA important components of most other lipids a hydrocarbon chain (4 36 ) with a carboxyl at one end amphipathic non-polar end polar end a 16- fatty acid: 3 ( 2 ) 14 saturated or unsaturated free rotation around bonds no rotation around bonds esterified or free salts with alkali metals soaps
4 Fatty acids of various length SFA (< 6 ) MFA (6 12 ) LFA (12 22 ) (14 20) VLFA (> 22 ) lower (< 10 ) higher (> 12 )
5 Fatty acids Example: octadeca-9,12-dienoic acid γ 4 β 3 α 2 1 H 18- FA with two cis double bonds in positions 9 and 12 linoleic acid (9,12-octadecadienoic) n ω 18:2 Δ 9,12 = 18:2 ω6 = 18:2 n 6 = = cis,cis-18:2 Δ 9,12 = cis,cis-18:2 ω6 = cis,cis-18:2 n 6 = = all-cis-18:2 Δ 9,12 = all-cis-18:2 ω6 = all-cis-18:2 n 6 = = cis,cis-18:2(9,12) = all-cis-18:2(9,12) = 18:2(9c,12c)
6 Fatty acids usually linear hydrocarbon chain an even number of carbon atoms double bonds in cis configuration a rigid kink at each bond H stearic acid acid 18:1(11c) oleic acid linoleic acid FA melting points decrease with shorter chains unsaturation vicinity of the first to the carboxyl
7 Some common fatty acids ommon name Symbol Systematic name m.p. ( ) Formula Saturated lauric 12:0 dodecanoic 44.2 myristic 14:0 tetradecanoic 52.0 palmitic 16:0 hexadecanoic 63.1 stearic 18:0 octadecanoic 69.6 arach(id)ic 20:0 eicosanoic 75.4 behenic 22:0 docosanoic 81.0 lignoceric 24:0 tetracosanoic 84.2 With one double bond (MUFA) palmitoleic 16:1 ω7 hexadec-9-enoic 0.5 oleic 18:1 ω9 oktadec-9-enoic 13.4 erucic 22:1 ω9 docosa-13-enoic nervonic 24:1 ω9 tetracosa-15-enoic 39.0 With two double bonds linoleic 18:2 ω6 octadeca-9,12-dienoic 9.0 With three double bonds ( PUFA ) α-linolenic 18:3 ω3 octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic 17.0 γ-linolenic 18:3 ω6 octadeca-6,9,12-trienoic With four double bonds arachidonic 20:4 ω6 eicosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic 49.5 With five double bonds timnodonic (EPA) 20:5 ω3 eicosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoic 54.0 clupanodonic (DPA) 22:5 ω3 docosa-7,10,13,16,19-pentaenoic With six double bonds cervonic (DHA) 22:6 ω3 docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic essential: linoleic and α-linolenic
8 Some less common fatty acids ommon name Symbol Systematic name ω Formula With odd-numbered chain 13:0 tridecanoic 15:0 pentadecanoic 17:0 heptadecanoic 17:1(9c) cis-heptadec-9-enoic 8 Branched (MUFA) iso-tridecanoic iso-13:0 11-methyldodecanoic 7 iso-tetradecanoic iso-14:0 12-methyltridecanoic iso-pentadecanoic iso-15:0 13-methyltetradecanoic iso-hexadecanoic iso-16:0 14-methylpentadecanoic iso-heptadecanoic iso-17:0 15-methylhexadecanoic anteiso-tridecanoic anteiso-13:0 10-methyldodecanoic anteiso-pentadecanoic anteiso-15:0 12-methyltetradecanoic anteiso-heptadecanoic anteiso-17:0 14-methylhexadecanoic phytanic 3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadecanoic pristanic 2,6,10,14-tetramethylpentadecanoic onjugated linoleic acid (LA) 18:2(9c,11t) 9-cis,11-trans-octadeca-9,11-dienoic 8 18:2(10t,12c) 10-trans,12-cis-octadeca-10,12-dienoic 7 With a triple bond tariric 18:1(6a) octadec-6-ynoic
9 Some really exotic fatty acids e.g. haliclonyne (47 FA): 14-oxo-4,5,6,28,33,37,42,45- octahydroxy-trans-26,trans-43-dien-2,31,34,46-tetraynheptatetracontanoic acid H H H H ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) 10 ( 2 ) 4 H H H H H cyclopropane to cyclohexane ring epoxy-, cyclic peroxides, SH, disulfides fatty alcohols similar diversity H H H
10 verview of lipids Simple lipids esters of FA with alcohols fats & oils (acylglycerols, glycerides): alcohol = glycerol waxes: alcohol = long-chain (mono)alcohol omplex lipids esters FA+alcohols + other items phospholipids FA + glycerol + phosphate + something glycolipids contain sugars glycoacylglycerols FA + glycerol + sugar glycosphingolipids FA + sphingosine + sugar (+ sialic acid) sphingolipids contain ceramide (amide FA+sphingosine) sphingomyelins ceramide + phosphocholine glycosphingolipids see above Derived lipids other biological hydrophobic substances, e.g. steroids, eicosanoids, docosanoids, carotenoids and other terpenoids, lipophilic vitamins
11 Simple lipids Esters of fatty acids with alcohols Waxes (cerides) the alcohol is long, monovalent fatty the most fatty of the lipids in animals final metabolites usually a protective function plant cuticule lanolin beeswax beeswax main component 15 H H 61 myricyl palmitate triacontyl hexadecanoate carnauba wax main component 25 H H 61 myricyl cerotate triacontyl hexacosanoate
12 Simple lipids H 2 H H 2 H H H glycerol H R FA H 2 R 1 H R 2 H 2 R 3 triacylglycerol Triacylglycerols (triglycerides, neutral fats and oils) the most abundant dietary lipids energy storage reduced compact (dehydrated) protective layers glycerol backbone + 3 esterified FA most are mixed
13 omplex lipids sphingolipids, glycerolipids phospholipids glycerophospholipids (PE, PS, P, PG, DPG, PI; plasmalogens) sphingomyelins glycolipids glycoacylglycerols glycosphingolipids cerebrosides gangliosides all complex lipids include non-polar FA chains ( tails ) include polar region (glycerol, FA carbonyls, usually P i, the polar head group they are amphipathic
14 Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides) common constituents of biological membranes glycerol backbone hydroxyls at 1 & 2 esterified with fatty acids 3 esterified with P i Phosphatidic acids R 2 H 2 H 2 P R 1 the simplest phospholipids only small amounts in the membranes only intermediates in the synthesis of triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids
15 Glycerophospholipids H 2 R 1 R 2 H 2 P X polar head usually, P i is further esterified to H of a polar head group (signed X in the figure) e.g. serine, choline, ethanolamine, glycerol, or inositol The 2 fatty acids tend to be non-identical. amphipathic (complex polar region)
16 Glycerophospholipids Phosphatidylinositols (PI) membrane lipids R 2 H 2 H 2 P R 1 cellular signaling molecules H H H H H Phosphatidylcholines (lecithins, P) R 2 H 2 H 2 P R N common membrane lipids
17 Glycerophospholipids Plasmalogens H 2 R 1 R 2 H 2 P X glycerol enol-ether phospholipids in mammals R 1 (the fatty alcohol) usually 16:0, 18:0, or 18:1 R 2 usually PUFA X=usually ethanolamine or choline (or serine) brain and muscles PAF (platelet activating factor) platelet aggregation R 1 = 16:0, R 2 = acetyl, X= cholin R 2 acetyl higher solubility
18 Sphingolipids derivatives of the amino alcohol sphingosine H H H H H 2 H H 2 H N H 2 NH H H ( 2 ) 12 (10 14) R ( 2 ) 12 3 sphingosine 3 ceramide amides of sphingosine with FA = ceramides other sphingolipids include a polar head group, esterified to the terminal H of the sphingosine.
19 Sphingolipids Sphingomyelins (phosphosphingolipids) 3 H 3 N P 3 H H 2 H NH H R ( 2 ) 12 3 ceramides with the phosphocholine or phosphoethanolamine head group common constituent of plasma membranes in brain and nerve tissue
20 Glycosphingolipids erebrosides β,d-glc (or β,d-gal) H 2 H NH H R H ( 2 ) 12 3 ceramides with a monosaccharide such as glucose or galactose as polar head group Gangliosides H 3 NH H H 2 H H H H N-acetylneuraminic acid ceramides with a polar head group that is a complex oligosaccharide, containing a sialic acid common in the outer layer of the plasma membrane sugar chains extend outwards
21 Glycolipids glycoacylglycerols R 2 R 2 H 2 H 2 H 2 H 2 R 1 β,d-gal-1,6-α,d-gal H R 1 H mono- and digalactosyl diacyl glycerols sulfoquinovosyl diacyl glycerols 3 S H 2 H important constituents of plant membranes thylakoid membrane
22 Derived lipids Isoprenoids isoprene geranene farnesene geranylgeranene phytene squalene phytoene monoterpenes (menthol, limonene, camphor, pinene, geraniol) sesquiterpenes (humulene, zingiberene) diterpenes (geranylgeraniol, taxadiene, kahweol, cafestol, phytol (chains of chlorophyll, vitamins E and K) triterpenes (steroids) tetraterpenes (carotenoids vitamin A)
23 Steroids cholesterol H 21 H H 3 important constituent of cell membranes a rigid ring system and a short branched hydrocarbon tail hydrophobic amphipathy (weak) conferred by the H precursor of D vitamin bile acids sex hormones adrenocortical hormones
24 Biological membranes lipids in polar environments aggregation to complexes in which polar regions are in contact with water and hydrophobic regions away from water. possible molecular arrangements: various micelle structures spherical micelles stable form of FA a bilayer stable form for amphipathic lipids such as phospholipids zdroj
25 Biological membranes phospholipid bilayer with proteins inserted in it or bound to the surface zdroj Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, Gatto, G. J. Jr., J. L., Stryer, L.: Biochemistry, W. H. Freeman and ompany, 2012 (8th edition) integral proteins embedded in the bilayer trans-membrane peripheral proteins bound to the surface of the membrane many of the proteins and lipids carry oligosaccharide chains
26 Biological membrane fluidity the interior of a lipid bilayer is normally highly fluid. liquid (fluid) state hydrocarbon chains disordered and in constant motion (higher temperatures) crystalline state fatty acid tails are fully extended, packing is highly ordered (lower temperatures) Voet, D., Voet, J. G.: Biochemistry, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011 (4th edition) Stryer, L.: Biochemistry, W. H. Freeman and ompany, 1981 (2nd edition)
27 Biological membrane fluidity FA types see above holesterol inserts into bilayer membranes hydroxyl group oriented out polar environment hydrogen bonds with polar heads of membrane lipids hydrophobic ring system adjacent to FA chains of membrane lipids hydrophobic interactions rather rigid molecule interactions with membrane lipid hydrocarbon chains decreases the membrane fluidity H H zdroj
28 Biological membrane assymmetry Stryer, L.: Biochemistry, W. H. Freeman and ompany, 1981 (2nd edition) lateral mobility of a lipid is high transversal mobility (flip-flop) of lipids is very low of proteins has never been observed Stryer, L.: Biochemistry, W. H. Freeman and ompany, 1981 (2nd edition)
29 Biological membrane assymmetry the two leaflets are different assymmetry in lipid composition protein composition and orientation saccharides of glycoproteins and glycolipides function
30 Membrane microdomains lipid rafts more sphingolipids (by 50 %) cholesterol (3 5 ) saturated FA less phosphatidylcholine ( equal choline) function intercellular signalling, endocytosis, interaction vith viruses
31 The End konec the end Thank you for your attention!
32 Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides) H 2 R 1 R 2 H 2 P
33 Glycerophospholipids H 2 R 1 R 2 H 2 P X
34 Glycerophospholipids R 2 H 2 R 1 mem cellu H 2 P H H H H H
35 Glycerophospholipids H 2 R 1 R 2 3 H 2 P 2 2 N + 3 3
36 cerol enol-ether pho Glycerophospholipids H 2 R 1 R 2 H 2 P X
37 Sphingolipids H H H H 2 H H 2 N H 2 H ( 2 ) 12 (10 14) 3 sphingosine c
38 Sphingolipids H H H 2 H NH R H ( 2 ) 12 3 ceramide
39 Sphingolipids 3 H 3 N P 3 H H 2 H NH R H ( 2 ) 12 3
40 Glycosphingolipids β,d-glc (or β,d-gal) H 2 H NH H R H ( 2 ) 12 3
41 Gangliosides Glycosphingolipids H 3 NH H H 2 H H H H N-acetylneuraminic acid
42 lycoacylglycerols Glycolipids H 2 R 1 R 2 H 2 β,d-gal-1,6-α,d-gal H 2 R 1
43 Glycolipids H 2 R 1 su R 2 H 2 H H H 3 S H 2
44 Derived lipids isoprene 5 geranene 10 farnesene 15 geranylgeranene 20 phytene 20 squalene 30 phytoene 40 monoterpenes (menthol, limonene, camphor geraniol) sesquiterpenes (humulene, zingiberene) diterpenes (geranylgeraniol, taxadiene, kahw
45 Steroids cholesterol important constituent of c H H H
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
Fats and Lipids (Ans570)
 Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature
 GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
Chapter 11: Lipids. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Organic molecules highly hydrophobic and water insoluble.
 UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
Lipids and Biological Membranes
 Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202
 General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry. General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4. Lipids
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Lipids are broadly classified in to simple, complex and derived, which are further subdivided into different groups.
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
Lipids. Lipids. Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague
 Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Experiment 12 Lipids. Structures of Common Fatty Acids Name Number of carbons
 Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
Chapter 20 Lipids. Organic and Biochem
 Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
26.1 Acetyl Coenzyme A
 Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Lipids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8
 Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY
 BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
Lipids. Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals. Storage Lipids: derivatives of fatty acids. 11/21/10
 1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
Lipids. Water vsoil. Water is a Polar Molecule δ + Polarity vs Nonpolarity H O
 Water vsil SCBC203 Lipids Jirundon Yuvaniyama, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science Mahidol University Figure taken from https://www.healthtap.com/user_questions/558342 Figures taken from
Water vsil SCBC203 Lipids Jirundon Yuvaniyama, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science Mahidol University Figure taken from https://www.healthtap.com/user_questions/558342 Figures taken from
Optimising. membranes
 Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Functions of Lipids. - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g).
 Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Microreview. A.-F. Miller, 2008, pg
 Microreview Polysaccharides: a vast diversity based on stereochemistry. Stereochemical differences are associated with secondary and tertiary structural differences: nature s huge and plentiful polymers.
Microreview Polysaccharides: a vast diversity based on stereochemistry. Stereochemical differences are associated with secondary and tertiary structural differences: nature s huge and plentiful polymers.
Ahmad O. Olimat. Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh. Dr.Mamoun
 10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS:
 LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
CH 3. Lipids CHAPTER SUMMARY
 H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Biomolecules: lipids
 Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
Saba Al Fayoumi. Nour Hamdan. Bann Khraisat. Dr. Mamoun Ahram
 9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
Organism. Organ and organ systems. Tissue. Cells. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids
 hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules CARBON BASED MOLECULES
 CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
Recap: A little chemistry helps to understand a lot of biology
 Recap: A little chemistry helps to understand a lot of biology Covalent Bonds Polar and Non-Polar Electronegativity is key! Non-covalent bonds: Intra and inter molecular interactions Hydrogen Bonds Ionic
Recap: A little chemistry helps to understand a lot of biology Covalent Bonds Polar and Non-Polar Electronegativity is key! Non-covalent bonds: Intra and inter molecular interactions Hydrogen Bonds Ionic
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
2. Simple lipids: Triacylglycerols and waxes are classified as simple lipids. The characteristics of each are described in the sections below.
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Lipids. Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids.
 Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example:
 Carboxylic acids LECTURE 3 Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example: Lipids: classification, structure and biological role. By/Arshed Abd
Carboxylic acids LECTURE 3 Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example: Lipids: classification, structure and biological role. By/Arshed Abd
II- Compound Lipids. 1- Phospholipids
 II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12
 BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
 LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
Biomolecules Lecture Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
 www.aiouinfo.com Biomolecules Lecture Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Monosaccharides 4 Examples: 1. Glucose 2. Fructose 3. Ribose 4. Deoxyribose Glucose Structure Function of
www.aiouinfo.com Biomolecules Lecture Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Monosaccharides 4 Examples: 1. Glucose 2. Fructose 3. Ribose 4. Deoxyribose Glucose Structure Function of
Dr. Mamoun. Loai Azar
 13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
Lipids. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Lipids. Chapter 11: Outline. Fatty Acids. Lipid Classes. Fatty Acids-2. Fatty Acids-3. General Types eg. A fatty acid
 Chapter 11: utline Lipid Classes Fatty Acids and Derivatives Triacylglycerols Phospholipids Isoprenoids Membranes Membrane Structure Membrane Function Wax Esters Sphingolipids Lipoproteins Lipids General
Chapter 11: utline Lipid Classes Fatty Acids and Derivatives Triacylglycerols Phospholipids Isoprenoids Membranes Membrane Structure Membrane Function Wax Esters Sphingolipids Lipoproteins Lipids General
Chapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids
 common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES. Lipid Chemistry NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE
 ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic CH 3 (CH 2 ) 2 COOH 6 Caproic Hexanoic CH 3 (CH
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic CH 3 (CH 2 ) 2 COOH 6 Caproic Hexanoic CH 3 (CH
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
Classification of Lipids
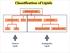 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
The main biological functions of the many varied types of lipids include: energy storage protection insulation regulation of physiological processes
 Big Idea In the biological sciences, a dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction) is typically defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecules. This reaction
Big Idea In the biological sciences, a dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction) is typically defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecules. This reaction
FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS
 FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS Dicarboxylic acids, ketone bodies. Department of General Chemistry Structure and classification of lipids Lipids can be divided into five categories, on the
FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS Dicarboxylic acids, ketone bodies. Department of General Chemistry Structure and classification of lipids Lipids can be divided into five categories, on the
Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition. phospholipids. Sphingolipids. Cholesterol. db=books&itool=toolbar
 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane
 Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
Lipid Chemistry. Presented By. Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair
 Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15
 Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15 Principle: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long (usually > 14) carbon chains which can be saturated (no carbon-carbon double bonds) are unsaturated
Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15 Principle: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long (usually > 14) carbon chains which can be saturated (no carbon-carbon double bonds) are unsaturated
Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver. Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids
 Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids Activation of hormone sensitive lipase This enzyme is activated when phosphorylated (3,5 cyclic AMPdependent
Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids Activation of hormone sensitive lipase This enzyme is activated when phosphorylated (3,5 cyclic AMPdependent
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
General Chemistry. Ch. 10
 General Chemistry Ch. 10 Essentials of Organic Chemistry Most biological important molecules are composed of organic compounds. These are mostly produced by biological systems. Organic molecules contain
General Chemistry Ch. 10 Essentials of Organic Chemistry Most biological important molecules are composed of organic compounds. These are mostly produced by biological systems. Organic molecules contain
Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds.
 Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
CHY2026: General Biochemistry. Unit 3: Lipid Chemistry
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry Unit 3: Lipid Chemistry Lipids The are heterogeneous and are related to fatty acids They include fats, oils and waxes Fatty acids have the general formula R-COOH where R =
CHY2026: General Biochemistry Unit 3: Lipid Chemistry Lipids The are heterogeneous and are related to fatty acids They include fats, oils and waxes Fatty acids have the general formula R-COOH where R =
Lipids & Membranes. Lecture 28 (11/27/17) NEXT. Lipids & Membranes A. Lipids 1. Roles 2. Classes a. Fatty Acids b. Fats c. Waxes d.
 Lecture 28 (11/27/17) Reading: Ch10; 361-368, 370, 372, 376 Ch11; 387-393, 395-401 Problems: Ch10 (text); 1,3,4,8,10,12,14,16 Ch10 (study-guide: applying); 1,3,4 Ch10 (study-guide: facts);1-5,6-8 Ch11
Lecture 28 (11/27/17) Reading: Ch10; 361-368, 370, 372, 376 Ch11; 387-393, 395-401 Problems: Ch10 (text); 1,3,4,8,10,12,14,16 Ch10 (study-guide: applying); 1,3,4 Ch10 (study-guide: facts);1-5,6-8 Ch11
ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS General Chemistry of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerols
 ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS General Chemistry of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerols I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic
ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS General Chemistry of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerols I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic
A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Molecules
 Biological Substances found in Living Tissues Lecture Series 3 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Lipids can form large biological molecules, but these aggregations
Biological Substances found in Living Tissues Lecture Series 3 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Lipids can form large biological molecules, but these aggregations
3.9 Carbohydrates. Provide building materials and energy storage. Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
 3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function
 Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
3.1.3 Lipids. Source: AQA Spec
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
Basic Building Blocks of Cells Course 1 / Lecture 119
 Basic Building Blocks of Cells Course 1 / Lecture 119 vladimira.kvasnicova@lf3.cuni.cz Department of biochemistry the 4 th floor office 411 Biogenic elements = elements essential for structure and function
Basic Building Blocks of Cells Course 1 / Lecture 119 vladimira.kvasnicova@lf3.cuni.cz Department of biochemistry the 4 th floor office 411 Biogenic elements = elements essential for structure and function
Organic Molecules. 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1
 Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Lipids. Types of lipids. Fatty acid structure. Lipid functions. Fatty acid structure
 Lipids Types of lipids lassification of Lipids Fatty Acids Glycerides Nonglycerol Lipids omplex Lipids Structure of Biological Membranes Fatty Acids Saturated Unsaturated omplex Lipids Lipoproteins Glycolipids
Lipids Types of lipids lassification of Lipids Fatty Acids Glycerides Nonglycerol Lipids omplex Lipids Structure of Biological Membranes Fatty Acids Saturated Unsaturated omplex Lipids Lipoproteins Glycolipids
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
Seminar 6 Theoretical part
 Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Chemistry B11 Chapters 15 Lipids
 Chapters 15 ipids ipids: are family of biomolecules that have the common property of being soluble in organic solvents but not in water. Role of lipids: they have three important roles in nature: 1. They
Chapters 15 ipids ipids: are family of biomolecules that have the common property of being soluble in organic solvents but not in water. Role of lipids: they have three important roles in nature: 1. They
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function
 Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Biology. Chapter 3. Molecules of Life. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 3 Molecules of Life 2015 3.1 What Are the Molecules of Life? The molecules of life contain a high proportion of carbon atoms: Complex carbohydrates
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 3 Molecules of Life 2015 3.1 What Are the Molecules of Life? The molecules of life contain a high proportion of carbon atoms: Complex carbohydrates
