GENES OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA INVOLVED IN WAX METABOLISM ROXANA-IULIANA TEODOR *, AL. YEPHREMOV *
|
|
|
- Jonah Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Analele ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Al. I. Cuza Iaşi Tomul LIV, fasc. 2, s.ii a. Biologie vegetală, 2008 GENES OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA INVOLVED IN WAX METABOLISM ROXANA-IULIANA TEODOR *, AL. YEPHREMOV * Abstract: The aerial surfaces of land plants are covered with cuticle that acts as a barrier providing protection against water loss, pathogen invasion and other environmental aggressions. Besides physical and chemical barriers, such as a waxy cuticle, plant defense mechanisms also involve a coordinated activation of cellular responses to limit damage. The eceriferum (cer) mutants of Arabidopsis define multiple genes required for various steps in cuticular wax biosynthesis, transport and regulation of lipid-related pathways. Although the basic biochemistry of wax production has been elucidated, very little is known about its regulation and its contribution to the natural immunity. This review presents recently cloned wax biosynthetic genes and discusses regulatory aspects of wax biosynthesis. Key words: wax, Arabidopsis mutants Role of cuticle for plants A distinctive characteristic of all epidermal cell types is the presence of cuticle covering their outer surface as a continuous lipophilic layer, which forms a barrier over the aerial organs of land plants during their primary stages of development [7; 14]. Plant cuticle is formed mainly of cutin, a polyester of hydroxy and hydroxy-epoxy fatty acid derivatives generated from cellular fatty acids [11], embedded in and covered with a complex mixture of highly hydrophobic soluble materials (aliphatic compounds comprised mainly of C24-C34 alkanes, alcohols and ketones) called cuticular waxes, as well as other minor compounds, of an extremely diverse nature [30]. As they are physically very closely associated, it is difficult to distinguish between the relative contribution of the cutin matrix and that of cuticular waxes to the physical properties and the biological roles of the cuticle. However, in biochemical experiments, the cutin and cuticular waxes are usually considered and analyzed separately, due to the soluble properties of the waxes versus the cutin polymer, which remains insoluble. Such a structure gives the cuticle a set of highly protective features and these were studied initially as to limiting nonstomatal water loss and gaseous exchanges, controlling the absorption of lipophilic compounds, and providing mechanical strength and viscoelastic properties [2; 25]. Additionally, the cuticle also functions in normal plant developmental processes, including the prevention of postgenital organ fusion and pollen pistil interactions [17; 28], as well as protecting the plant from biotic and non-biotic environmental stress factors [27]. Pruitt et al. [24] and Sieber et al. [28] have suggested that cuticle permeability also influences cell-to-cell communication by enhancing or attenuating the passage of signal molecules. For example, such signals could be required for organ adhesion, when they * Molecular Plant Genetics, Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research, Carl-von-Linne Weg 10, Cologne, Germany 109
2 would be moving across the cuticle, or for mediating signaling between trichomes and stomata, when moving within the developing epidermis [18; 13]. Arabidopsis mutants offer information on the regulation of cuticle development Mutants with deficient or altered wax coatings have been identified due to their nonglaucous or glossy phenotype. Thus, there are no reports of mutants that lack wax completely, indicating the vital function that waxes play for the normal development of plants. On the other hand, changes in a minor wax component are less likely to lead to a clearly discernable phenotype and therefor have not been reported. Similarly, plants that overproduce waxes are not easily detected by visual screenings. In Arabidopsis, as well as in other species, the mutants that have been identified to be defective in wax and/or cutin formation facilitated the identification of enzymes associated with the cutin and wax pathways. Some of the enzymes catalyzing various steps in the wax pathway have been characterized or their function has been proposed based on the phenotype of the corresponding mutants. The identification of eceriferum (cer) mutant lines described mainly by Koornneef et al. [12] and by McNevin et al. [20] has led to the isolation and characterization of various genes associated with cuticular wax metabolism in Arabidopsis. CER1 intended to encode an aldehyde decarbonylase [1]. Several genes playing a role in the fatty acid elongation pathway that generates very long chain fatty acid (VLCFA) wax precursors have also been characterized. They include the FATTY ACID ELONGATION1 homologs (FAE1) [9], FIDDLEHEAD (FDH) [38; 24], 3-KETOACYL-CoA SYNTHASE [33], CUT1/CER6, and CER60 [21; 5]. CER6 has been suggested to be the key condensing enzyme for wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, due to its expression throughout all stages of stem and leaf development, as well as in the inflorescence [8]. CER2 encodes a CoA-dependent acyltransferase, a component of the fatty acid elongase complex, apparently located in the nucleus [37; 14]. The cer2 mutant shows reduced levels of the decarbonylation pathway products and it accumulates C26 and C28 acyl groups, primary alcohols, and wax esters but the precise function of the gene is still unknown. Furthermore, its nuclear localization is very intriguing for a protein of the fatty acid elongase complex. Many of the cer mutants remain still to be characterized and the isolation of their corresponding genes might bring valuable information on the mechanisms of wax metabolism. Several reports have also provided insights into the biosynthesis of cutin monomers in plants. Chen et al. [3] reported the isolation of the WAX2 gene and showed that the protein it encodes for has 32% similarity to CER1 and contains certain regions with homology to sterol desaturases and short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases. It was suggested therefore that WAX2 plays a metabolic role in both wax and cutin synthesis, thus pointing to a link between wax and cutin metabolism. ADHESION OF CALYX EDGES/HOTHEAD (ACE/HTH) is proposed to be an oxidase catalyzing the formation of dioic acids from ω-hydroxy acyl-coas [13; 16]. The Arabidopsis LACERATE (LCR) gene [36] encodes a cytochrome P450; enzyme activity assays using the recombinant LCR protein showed that it could efficiently catalyze the formation of ω-hydroxy fatty acids (ranging from C12 to C18:1). Expression of LCR gene is predominant in inflorescence and 110
3 siliques, as well as in roots and young seedling tissue and it is the first cytochrome P450 ω- hydroxylase for which a mutant has been isolated. Results of microarray analysis conducted in our group (Yephremov et al., unpublished data) on three independent cuticular mutants has revealed that a palmytoil protein thyoesterase (PPT) is almost ten fold up-regulated in three mutants, as compared to wild type. In humans, PPT is a lysosomal long-chain fatty acyl hydrolase that removes fatty acyl groups from modified cysteine residues in proteins, and the defective enzyme causes infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, a recessive hereditary neuro-degenerative disorder [34]. In plants, acyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) thioesterases play an essential role in chain termination during de novo fatty acid synthesis and in the channeling of carbon flux between the lipid biosynthesis pathways [10]. Epidermal differentiation and implicitly cuticle formation is essential for the general development of the whole plant, starting from the very early embryo stage. This fact is supported by the characterization of the abnormal leaf shape 1 (ale1) mutant of Arabidopsis, which shows impaired cuticle formation, adhesion of endosperm and embryo, as well as fusion of cotyledons and leaves. The corresponding ALE1 gene encodes a member of the subtilisin-like serine protease family and it is preferentially expressed during seed development, showing a weak transcript expression in young embryo and a strong one within the endosperm cells closely surrounding the developing embryo [32]. Three aminoacid residues (aspartic acid, histidine and serine) are consistently conserved in the catalytic regions of subtilisin-like serin proteases. In animals, such proteases activate precursors of hormones, growth factors, or receptors involved in the control of various developmental processes, including embryonic patterning and proper epidermal differentiation. Although many members of this family of proteases were reported in plants [29; 26], little is known, with few exceptions, about their precise role. In addition to the developmental factors controling the synthesis of cuticular lipids, environmental signals such as light intensity, photoperiod [19; 35], humidity [31], chilling [22; 23] and seasonal variation [6; 4] have also been shown to ifluence wax biosynthesis. In 1984, Sutter [31] described the dramatic response of wax production to environmental cues, during tissue culture, observing that when the relative humidity is high, wax production is low. When tissue-culture-grown plants are transfered to an environment with less humidity (growth chabinet or greenhouse), production of wax is stimulated and within a rather short period of time of a few days only, the plant synthesizes a complete protective layer of wax. Conclusion The fact that cuticular wax is ubiquitously present is testimony to its essential role in the adaptation of plants to the aerial environment, with all its implications. On the other hand, the fact that environmental cues have an influence upon wax composition and quantity is evidence that wax production is an actively regulated process. An active regulatory netword is indicated also by the high diversity of proteins that have been shown, through the Arabidopsis mutants, to be involved in the process of wax biosynthesis. Although the biosynthesis of plant cuticular components has been studied for over four decades, we still know little about the factors regulating the partitioning of fatty 111
4 acid precursors and the synthesis of waxes with the synthesis of cutin and with other cuticular compounds. However, the cloning of wax biosynthetic genes and the further characterization of the respective proteins promises to bring valuable insights into the very deep regulatory mechanisms of wax and cuticle development. REFERENCES 1. AARTS, M.G.M., KEIJZER, C.J., STIEKEMA, W.J., and PEREIRA, A., Molecular Characterization of the CER1 Gene of Arabidopsis Involved in Epicuticular Wax Biosynthesis and Pollen Fertility. The Plant Cell Online, 7: BAKER, C.J., MCCORMICK, S.L., and BATEMAN, D.F., Effects of Purified Cutin Esterase Upon the Permeability and Mechanical Strength of Cutin Membranes. Phytopathology,72: CHEN, X., GOODWIN, S.M., BOROFF, V.L., LIU, X., and JENKS, M.A., Cloning and Characterization of the WAX2 Gene of Arabidopsis Involved in Cuticle Membrane and Wax Production Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at www. plantcell. org/cgi/doi/ /tpc The Plant Cell Online, 15: FAINI, F., LABBÉ, C., AND COLL, J., Seasonal changes in chemical composition of epicuticular waxes from the leaves of Baccharis linearis. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 27: FIEBIG, A., MAYFIELD, J.A., MILEY, N.L., CHAU, S., FISCHER, R.L., AND PREUSS, D., Alterations in CER6, a Gene Identical to CUT1, Differentially Affect Long-Chain Lipid Content on the Surface of Pollen and Stems. The Plant Cell Online, 12: GÜLZ, P.G., AND MÜLLER, E., Seasonal variation in the composition of epicuticular waxes of Quercus robur leaves. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung. C. A journal of biosciences, 47: HOLLOWAY, P.J. (1982). Structure and histochemistry of plant cuticular membranes: an overview. 8. HOOKER, T.S., MILLAR, A.A., AND KUNST, L., Significance of the Expression of the CER6 Condensing Enzyme for Cuticular Wax Production in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 129: JAMES, D.W.J., LIM, E., KELLER, J., PLOOY, I., RALSTON, E., AND DOONER, H.K., Directed Tagging of the Arabidopsis FATTY ACID ELONGATION1 (FAE1) Gene with the Maize Transposon Activator. The Plant Cell Online 7, JONES, A., DAVIES, H.M., AND VOELKER, T.A., Palmitoyl-Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP) Thioesterase and the Evolutionary Origin of Plant Acyl-ACP Thioesterases. The Plant Cell Online, 7: KOLATTUKUDY, P.E., Polyesters in higher plants. Advances in biochemical engineering, biotechnology, 71, KOORNNEEF, M., HANHART, C.J., AND THIEL, F., A Genetic and Phenotypic Description of Eceriferum (cer) Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Heredity, 80: KROLIKOWSKI, K.A., VICTOR, J.L., WAGLER, T.N., LOLLE, S.J., AND PRUITT, R.E., Isolation and characterization of the Arabidopsis organ fusion gene HOTHEAD. The Plant Journal, 35: KUNST, L., and SAMUELS, A.L., Biosynthesis and secretion of plant cuticular wax. Prog. Lipid Res, 42: KUNST, L., SAMUELS, A.L., AND JETTER, R., The plant cuticle: formation and structure of epidermal surfaces. (Oxford,UK: Blackwell). 16. KURDYUKOV, S., FAUST, A., TRENKAMP, S., BÄR, S., FRANKE, R., EFREMOVA, N., TIETJEN, K., SCHREIBER, L., SAEDLER, H., AND YEPHREMOV, A., Genetic and biochemical evidence for involvement of HOTHEAD in the biosynthesis of long-chain α-,ω-dicarboxylic fatty acids and formation of extracellular matrix. Planta, 224: LOLLE, S.J., HSU, W., AND PRUITT, R.E., Genetic Analysis of Organ Fusion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics, 149: LOLLE, S.J., BERLYN, G.P., ENGSTROM, E.M., KROLIKOWSKI, K.A., REITER, W.D., AND PRUITT, R.E., Developmental regulation of cell interactions in the Arabidopsis fiddlehead-1 mutant: a role for the epidermal cell wall and cuticle. Dev. Biol, 189:
5 19. MACEY, M.J.K., The effect of light on wax synthesis in leaves of Brassica oleracea. Phytochemistry 9: MCNEVIN, J.P., WOODWARD, W., HANNOUFA, A., FELDMANN, K.A., AND LEMIEUX, B., Isolation and characterization of eceriferum (cer) mutants induced by T-DNA insertions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome, 36: MILLAR, A.A., CLEMENS, S., ZACHGO, S., GIBLIN, E.M., TAYLOR, D.C., AND KUNST, L., CUT1, an Arabidopsis Gene Required for Cuticular Wax Biosynthesis and Pollen Fertility, Encodes a Very- Long-Chain Fatty Acid Condensing Enzyme. The Plant Cell Online, 11: NORDBY, H.E., AND MCDONALD, R.E., Relationship of epicuticular wax composition of grapefruit to chilling injury. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 39: NORDBY, H.E., AND MCDONALD, R.E., Variations in Chilling Injury and Epicuticular Wax Composition of White Grapefruit with Canopy Position and Fruit Development during the Season. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 43: PRUITT, R.E., VIELLE-CALZADA, J.P., PLOENSE, S.E., GROSSNIKLAUS, U., AND LOLLE, S.J., FIDDLEHEAD, a gene required to suppress epidermal cell interactions in Arabidopsis, encodes a putative lipid biosynthetic enzyme, 97: RIEDERER, M., and SCHREIBER, L., Protecting against water loss: analysis of the barrier properties of plant cuticles. Journal of Experimental Botany, 52: SCHALLER, A., A cut above the rest: the regulatory function of plant proteases. Planta 220, SCHWEIZER, P., FELIX, G., BUCHALA, A., MÜLLER, C., AND MÉTRAUX, J.P. (1996). Perception of free cutin monomers by plant cells. The Plant Journal, 10: SIEBER, P., SCHORDERETA, M., RYSERA, U., BUCHALAA, A., KOLATTUKUDYB, P., MÉTRAUXA, J.-P., AND NAWRATH, C., Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants Expressing a Fungal Cutinase Show Alterations in the Structure and Properties of the Cuticle and Postgenital Organ Fusions. Plant Cell, 12: SIEZEN, R.J., Subtilases: The superfamily of subtilisin-like serine proteases. Protein Science, 6: SUH, M.C., SAMUELS, A.L., JETTER, R., KUNST, L., POLLARD, M., OHLROGGE, J., AND BEISSON, F., Cuticular Lipid Composition, Surface Structure, and Gene Expression in Arabidopsis Stem Epidermis 1 [W]. Plant Physiology, 139: SUTTER, E., Chemical composition of epicuticular wax in cabbage plants grown in vitro. Canadian Journal of Botany, 62: TANAKA, H., ONOUCHI, H., KONDO, M., HARA-NISHIMURA, I., NISHIMURA, M., MACHIDA, C., AND MACHIDA, Y., A subtilisin-like serine protease is required for epidermal surface formation in Arabidopsis embryos and juvenile plants. Development, 128: TODD, J., POST-BEITTENMILLER, D., AND JAWORSKI, J.G., KCS1encodes a fatty acid elongase 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase affecting wax biosynthesis inarabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 17: VESA, J., HELLSTEN, E., VERKRUYSE, L.A., CAMP, L.A., RAPOLA, J., SANTAVUORI, P., HOFMANN, S.L., AND PELTONEN, L., Mutations in the palmitoyl protein thioesterase gene causing infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Nature, 376: VON WETTSTEIN-KNOWLES, P., AVATO, P., AND MIKKELSEN, J.D., Light promotes synthesis of the very long chain fatty acyl chains in maize wax. Biogenesis and Function of Plant Lipids. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, New York: WELLESEN, K., DURST, F., PINOT, F., BENVENISTE, I., NETTESHEIM, K., WISMAN, E., STEINER- LANGE, S., SAEDLER, H., AND YEPHREMOV, A., Functional analysis of the LACERATA gene of Arabidopsis provides evidence for different roles of fatty acid omega-hydroxylation in development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 98: XIA, Y., NIKOLAU, B.J., AND SCHNABLE, P.S., Cloning and Characterization of CER2, an Arabidopsis Gene That Affects Cuticular Wax Accumulation. The Plant Cell Online, 8: YEPHREMOV, A., WISMAN, E., HUIJSER, P., HUIJSER, C., WELLESEN, K., AND SAEDLER, H., Characterization of the FIDDLEHEAD Gene of Arabidopsis Reveals a Link between Adhesion Response and Cell Differentiation in the Epidermis. The Plant Cell Online, 11:
The Role of Lipids in Flowering Development of Arabidopsis Enhanced pah1pah2 Plants. Toshiro Ito 1 & Lee Lishi 2
 The Role of Lipids in Flowering Development of Arabidopsis Enhanced pah1pah2 Plants Toshiro Ito 1 & Lee Lishi 2 Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore,
The Role of Lipids in Flowering Development of Arabidopsis Enhanced pah1pah2 Plants Toshiro Ito 1 & Lee Lishi 2 Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore,
The Acyl-CoA Synthetase Encoded by LACS2 Is Essential for Normal Cuticle Development in Arabidopsis
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 16, 629 642, March 2004, www.plantcell.org ª 2004 American Society of Plant Biologists The Acyl-CoA Synthetase Encoded by LACS2 Is Essential for Normal Cuticle Development in Arabidopsis
The Plant Cell, Vol. 16, 629 642, March 2004, www.plantcell.org ª 2004 American Society of Plant Biologists The Acyl-CoA Synthetase Encoded by LACS2 Is Essential for Normal Cuticle Development in Arabidopsis
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
 Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Biosynthesis and secretion of plant cuticular wax
 Progress in Lipid Research 42 (2003) 51 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/plipres Review Biosynthesis and secretion of plant cuticular wax L. Kunst, A.L. Samuels* Department of Botany, UBC, 6270 University Boulevard,
Progress in Lipid Research 42 (2003) 51 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/plipres Review Biosynthesis and secretion of plant cuticular wax L. Kunst, A.L. Samuels* Department of Botany, UBC, 6270 University Boulevard,
Biosynthesis and functions of free and combined fatty alcohols associated with suberin
 Laboratoire Biosynthesis and functions of free and combined fatty alcohols associated with suberin Collaborating Laboratories: Dr. Owen Rowland Sollapura Vishwanath PhD Candidate Department of Biology
Laboratoire Biosynthesis and functions of free and combined fatty alcohols associated with suberin Collaborating Laboratories: Dr. Owen Rowland Sollapura Vishwanath PhD Candidate Department of Biology
Sealing Plant Surfaces: Cuticular Wax Formation by Epidermal Cells
 Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008. 59:683 707 The Annual Review of Plant Biology is online at plant.annualreviews.org This article s doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.103006.093219 Copyright c 2008 by Annual Reviews.
Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008. 59:683 707 The Annual Review of Plant Biology is online at plant.annualreviews.org This article s doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.103006.093219 Copyright c 2008 by Annual Reviews.
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
 Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
 Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
GLOSSY MUTANTS OF MAIZE
 Heredity (1979), 42 (3), 391-395 GLOSSY MUTATS OF MAIZE IX. CHEMISTRY OF GLOSSY 4, GLOSSY 8, GLOSSY 15 AD GLOSSY 18 SURFACE WAXES* G. BtACHI, P. AVATO and F. SALAMII Istituto di Ch,mica organica, Viale
Heredity (1979), 42 (3), 391-395 GLOSSY MUTATS OF MAIZE IX. CHEMISTRY OF GLOSSY 4, GLOSSY 8, GLOSSY 15 AD GLOSSY 18 SURFACE WAXES* G. BtACHI, P. AVATO and F. SALAMII Istituto di Ch,mica organica, Viale
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
 Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Disruption of the FATB Gene in Arabidopsis Demonstrates an Essential Role of Saturated Fatty Acids in Plant Growth
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 15, 1020 1033, April 2003, www.plantcell.org 2003 American Society of Plant Biologists Disruption of the FATB Gene in Arabidopsis Demonstrates an Essential Role of Saturated Fatty
The Plant Cell, Vol. 15, 1020 1033, April 2003, www.plantcell.org 2003 American Society of Plant Biologists Disruption of the FATB Gene in Arabidopsis Demonstrates an Essential Role of Saturated Fatty
Composition of secondary alcohols, ketones, alkanediols, and ketols in Arabidopsis thaliana cuticular waxes
 Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 60, No. 6, pp. 1811 1821, 2009 doi:10.1093/jxb/erp061 Advance Access publication 3 April, 2009 This paper is available online free of all access charges (see http://jxb.oxfordjournals.org/open_access.html
Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 60, No. 6, pp. 1811 1821, 2009 doi:10.1093/jxb/erp061 Advance Access publication 3 April, 2009 This paper is available online free of all access charges (see http://jxb.oxfordjournals.org/open_access.html
Research and Reviews: Journal of Agriculture and Allied sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Agriculture and Allied sciences Role of Plant Fatty acid Elongase (3 keto acyl-coa Synthase) gene in Cuticular Wax Biosynthesis. Uppala Lokesh, Kurnool Kiranmai, Merum
Research and Reviews: Journal of Agriculture and Allied sciences Role of Plant Fatty acid Elongase (3 keto acyl-coa Synthase) gene in Cuticular Wax Biosynthesis. Uppala Lokesh, Kurnool Kiranmai, Merum
Wax-deficient anther1 Is Involved in Cuticle and Wax Production in Rice Anther Walls and Is Required for Pollen Development W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 18, 3015 3032, November 2006, www.plantcell.org ª 2006 American Society of Plant Biologists Wax-deficient anther1 Is Involved in Cuticle and Wax Production in Rice Anther Walls and
The Plant Cell, Vol. 18, 3015 3032, November 2006, www.plantcell.org ª 2006 American Society of Plant Biologists Wax-deficient anther1 Is Involved in Cuticle and Wax Production in Rice Anther Walls and
The natural genetic variation of the fatty-acyl composition of seed oils in di erent ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana
 Phytochemistry 52 (1999) 1029±1033 The natural genetic variation of the fatty-acyl composition of seed oils in di erent ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana Anthony A. Millar, Ljerka Kunst* Department of Botany,
Phytochemistry 52 (1999) 1029±1033 The natural genetic variation of the fatty-acyl composition of seed oils in di erent ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana Anthony A. Millar, Ljerka Kunst* Department of Botany,
cholesterol structure Cholesterol FAQs Cholesterol promotes the liquid-ordered phase of membranes Friday, October 15, 2010
 cholesterol structure most plasma cholesterol is in the esterified form (not found in cells or membranes) cholesterol functions in all membranes (drives formation of lipid microdomains) cholesterol is
cholesterol structure most plasma cholesterol is in the esterified form (not found in cells or membranes) cholesterol functions in all membranes (drives formation of lipid microdomains) cholesterol is
A Condensing Enzyme from the Seeds of Lesquerella fendleri That Specifically Elongates Hydroxy Fatty Acids 1
 A Condensing Enzyme from the Seeds of Lesquerella fendleri That Specifically Elongates Hydroxy Fatty Acids 1 Hangsik Moon 2, Mark A. Smith, and Ljerka Kunst* Department of Botany, University of British
A Condensing Enzyme from the Seeds of Lesquerella fendleri That Specifically Elongates Hydroxy Fatty Acids 1 Hangsik Moon 2, Mark A. Smith, and Ljerka Kunst* Department of Botany, University of British
Supplemental data. Uppalapati et al. (2012) Plant Cell /tpc
 PAL Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 OPR Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 CHS PR3 CHR PR5 CHI PR10 IFS IFR Supplemental Figure 1. Expression profiles for selected genes in phenylpropanoid pathway
PAL Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 OPR Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 CHS PR3 CHR PR5 CHI PR10 IFS IFR Supplemental Figure 1. Expression profiles for selected genes in phenylpropanoid pathway
Introduction. Lucas Busta 1 Daniela Hegebarth
 Planta (17) 5:97 311 DOI.7/s5-1-3- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changes in cuticular wax coverage and composition on developing Arabidopsis leaves are influenced by wax biosynthesis gene expression levels and trichome
Planta (17) 5:97 311 DOI.7/s5-1-3- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changes in cuticular wax coverage and composition on developing Arabidopsis leaves are influenced by wax biosynthesis gene expression levels and trichome
Dissertation zur Erlangung des naturwissenschaftlichen Doktorgrades der Bayerischen Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg
 The Plasticity of Barley (Hordeum vulgare) Leaf Wax Characteristics and their Effects on Early Events in the Powdery Mildew Fungus (Blumeria graminis f.sp. hordei): Interactive Adaptations at the Physiological
The Plasticity of Barley (Hordeum vulgare) Leaf Wax Characteristics and their Effects on Early Events in the Powdery Mildew Fungus (Blumeria graminis f.sp. hordei): Interactive Adaptations at the Physiological
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids. By Dr.QUTAIBA A. QASIM
 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids By Dr.QUTAIBA A. QASIM Fatty Acids Definition Fatty acids are comprised of hydrocarbon chains terminating with carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids and their associated derivatives
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids By Dr.QUTAIBA A. QASIM Fatty Acids Definition Fatty acids are comprised of hydrocarbon chains terminating with carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids and their associated derivatives
The Lipid Underground: Dissecting the Alkyl Hydroxycinnamate Pathway
 The Lipid Underground: Dissecting the Hydroxycinnamate Pathway Dylan K Kosma, Adam Rice, Isabel Molina, Owen Rowland, Frédéric Domergue, John Ohlrogge, Mike Pollard Department of Plant Biology, Michigan
The Lipid Underground: Dissecting the Hydroxycinnamate Pathway Dylan K Kosma, Adam Rice, Isabel Molina, Owen Rowland, Frédéric Domergue, John Ohlrogge, Mike Pollard Department of Plant Biology, Michigan
Lipids are broadly classified in to simple, complex and derived, which are further subdivided into different groups.
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Copyright 2012 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
 Composition and Physiological Function of the Wax Layers Coating Arabidopsis Leaves: b-amyrin Negatively Affects the Intracuticular Water Barrier 1[W][OA] Christopher Buschhaus and Reinhard Jetter* Department
Composition and Physiological Function of the Wax Layers Coating Arabidopsis Leaves: b-amyrin Negatively Affects the Intracuticular Water Barrier 1[W][OA] Christopher Buschhaus and Reinhard Jetter* Department
MPS Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course. Fall Semester Lecture 11. Lipids III
 MPS 587 - Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course Fall Semester 2011 Lecture 11 Lipids III 9. Triacylglycerol synthesis 10. Engineering triacylglycerol fatty acid composition Today s topics on the Arabidopsis
MPS 587 - Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course Fall Semester 2011 Lecture 11 Lipids III 9. Triacylglycerol synthesis 10. Engineering triacylglycerol fatty acid composition Today s topics on the Arabidopsis
Department of Biological Chemistry, Rothamsted Research, Harpenden, Herts AL5 2JQ, United Kingdom c
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 1252 1272, April 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists Misexpression of FATTY ACID ELONGATION1 in the Arabidopsis Epidermis Induces Cell Death and
The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 1252 1272, April 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists Misexpression of FATTY ACID ELONGATION1 in the Arabidopsis Epidermis Induces Cell Death and
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids
 Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (expert in lipid metabolism) Remarks to the Author:
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (expert in lipid metabolism) Remarks to the Author: In the manuscript by Ohno et al, the authors set out to identify the enzyme responsible for the ester bond formation
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (expert in lipid metabolism) Remarks to the Author: In the manuscript by Ohno et al, the authors set out to identify the enzyme responsible for the ester bond formation
Chemistry and Morphology of Epicuticular Waxes from Various Organs of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis [Link] Schneider)
![Chemistry and Morphology of Epicuticular Waxes from Various Organs of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis [Link] Schneider) Chemistry and Morphology of Epicuticular Waxes from Various Organs of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis [Link] Schneider)](/thumbs/90/102644258.jpg) Chemistry and Morphology of Epicuticular Waxes from Various Organs of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis [Link] Schneider) Paul-Gerhard Gülz Botanisches Institut der Universität zu Köln, Gyrhofstr. 15, D -5000
Chemistry and Morphology of Epicuticular Waxes from Various Organs of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis [Link] Schneider) Paul-Gerhard Gülz Botanisches Institut der Universität zu Köln, Gyrhofstr. 15, D -5000
Why discuss the topic of: lipid Biosynthesis? Lipids as: - Biofuels. Dehesh UC Davis
 Why discuss the topic of: lipid Biosynthesis? Lipids as: - Biofuels Dehesh UC Davis Fossil fuel is believed to be derived from ancient lipid rich organic material such as spores and planktonic algae! Rudolf
Why discuss the topic of: lipid Biosynthesis? Lipids as: - Biofuels Dehesh UC Davis Fossil fuel is believed to be derived from ancient lipid rich organic material such as spores and planktonic algae! Rudolf
(Lai et al., 2007). The ester content in plant cuticular waxes varies greatly among species and, to some extent, even within
 Identification of the Wax Ester Synthase/Acyl-Coenzyme A:Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase WSD1 Required for Stem Wax Ester Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis 1,2[W][OA] Fengling Li, Xuemin Wu, Patricia Lam, David
Identification of the Wax Ester Synthase/Acyl-Coenzyme A:Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase WSD1 Required for Stem Wax Ester Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis 1,2[W][OA] Fengling Li, Xuemin Wu, Patricia Lam, David
Effect of Surfactants and Adjuvants on Postemergence Herbicide Efficacy
 Effect of Surfactants and Adjuvants on Postemergence Herbicide Efficacy Dr. William B. McCloskey Cooperative Extension Weed Specialist Department of Plant Sciences University of Arizona Herbicide Uptake
Effect of Surfactants and Adjuvants on Postemergence Herbicide Efficacy Dr. William B. McCloskey Cooperative Extension Weed Specialist Department of Plant Sciences University of Arizona Herbicide Uptake
Ahmad Ulnar. Faisal Nimri ... Dr.Faisal
 24 Ahmad Ulnar Faisal Nimri... Dr.Faisal Fatty Acid Synthesis - Occurs mainly in the Liver (to store excess carbohydrates as triacylglycerols(fat)) and in lactating mammary glands (for the production of
24 Ahmad Ulnar Faisal Nimri... Dr.Faisal Fatty Acid Synthesis - Occurs mainly in the Liver (to store excess carbohydrates as triacylglycerols(fat)) and in lactating mammary glands (for the production of
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
Huanquan Zheng, Owen Rowland, and Ljerka Kunst 1. Department of Botany, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z4, Canada
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 17, 1467 1481, May 2005, www.plantcell.org ª 2005 American Society of Plant Biologists Disruptions of the Arabidopsis Enoyl-CoA Reductase Gene Reveal an Essential Role for Very-Long-Chain
The Plant Cell, Vol. 17, 1467 1481, May 2005, www.plantcell.org ª 2005 American Society of Plant Biologists Disruptions of the Arabidopsis Enoyl-CoA Reductase Gene Reveal an Essential Role for Very-Long-Chain
Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning
 Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning John L Bowman, University of California, Davis, California, USA The development of flowers and floral organs is directed by genetic programmes likely to be
Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning John L Bowman, University of California, Davis, California, USA The development of flowers and floral organs is directed by genetic programmes likely to be
Fatty Acid Desaturation
 Fatty Acid Desaturation Objectives: 1. Isolation of desaturase mutants 2. Substrates for fatty acid desaturation 3. ellular localization of desaturases References: Buchanan et al. 2000. Biochemistry and
Fatty Acid Desaturation Objectives: 1. Isolation of desaturase mutants 2. Substrates for fatty acid desaturation 3. ellular localization of desaturases References: Buchanan et al. 2000. Biochemistry and
PMP ) Plant reproduction. d) Formation of gametes e) Mutations in the development of gametophyte f) Pollination, fertilization
 2015 3) Plant reproduction 1 d) Formation of gametes e) Mutations in the development of gametophyte f) Pollination, fertilization 2 d) Formation of gametes Plant life cycle Microsporogenesis Megasporogenesis
2015 3) Plant reproduction 1 d) Formation of gametes e) Mutations in the development of gametophyte f) Pollination, fertilization 2 d) Formation of gametes Plant life cycle Microsporogenesis Megasporogenesis
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 28 Fatty Acid Synthesis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 28 Outline 1. The first stage of fatty acid synthesis is transfer
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 28 Fatty Acid Synthesis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 28 Outline 1. The first stage of fatty acid synthesis is transfer
Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life
 Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life Chapter 3 Outline 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? p. 38 3.2 How Are Organic Molecules Synthesized? p. 38 3.3 What Are Carbohydrates?
Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life Chapter 3 Outline 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? p. 38 3.2 How Are Organic Molecules Synthesized? p. 38 3.3 What Are Carbohydrates?
RESEARCH ARTICLES. Keywords: Cuticular wax, moisture retention capacity, mulberry, silkworm, wax genes.
 Leaf surface wax composition of genetically diverse mulberry (Morus sp.) genotypes and its close association with expression of genes involved in wax metabolism H. M. Mamrutha 1,5, K. N. Nataraja 1, *,
Leaf surface wax composition of genetically diverse mulberry (Morus sp.) genotypes and its close association with expression of genes involved in wax metabolism H. M. Mamrutha 1,5, K. N. Nataraja 1, *,
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Carbon Compounds. Section 2 Molecules of Life. Biochemistry
 Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM. Fatty Acid Elongation and Desaturation
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition. phospholipids. Sphingolipids. Cholesterol. db=books&itool=toolbar
 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
Plant Cell Biology; Identification and manipulation of plant quality traits
 Plant Cell Biology; Identification and manipulation of plant quality traits Phil Morris, Mark Robbins, Joe Gallagher and Ana Winters Mechanisms of protein protection in forages 30 Determining the constraints
Plant Cell Biology; Identification and manipulation of plant quality traits Phil Morris, Mark Robbins, Joe Gallagher and Ana Winters Mechanisms of protein protection in forages 30 Determining the constraints
LIPID METABOLISM
 LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003
 7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
DOMINANT MUTATIONS AT Cer-yy CHANGE BARLEY SPIKE WAX INTO LEAF BLADE WAX
 Carlsberg Res. Commun. Vol. 47, p. 29--43, 1982 DOMINANT MUTATIONS AT Cer-yy CHANGE BARLEY SPIKE WAX INTO LEAF BLADE WAX by UDDA LUNDQVIST I and PENNY VON WETTSTEIN-KNOWLES 2, 3 i Sval6f AB, S-268 00 Sval6v,
Carlsberg Res. Commun. Vol. 47, p. 29--43, 1982 DOMINANT MUTATIONS AT Cer-yy CHANGE BARLEY SPIKE WAX INTO LEAF BLADE WAX by UDDA LUNDQVIST I and PENNY VON WETTSTEIN-KNOWLES 2, 3 i Sval6f AB, S-268 00 Sval6v,
Fatty acids synthesis
 Fatty acids synthesis The synthesis start from Acetyl COA the first step requires ATP + reducing power NADPH! even though the oxidation and synthesis are different pathways but from chemical part of view
Fatty acids synthesis The synthesis start from Acetyl COA the first step requires ATP + reducing power NADPH! even though the oxidation and synthesis are different pathways but from chemical part of view
Fatty acid synthesis. Dr. Nalini Ganesan M.Sc., Ph.D Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry SRMC & RI (DU) Porur, Chennai - 116
 Fatty acid synthesis Dr. Nalini Ganesan M.Sc., Ph.D Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry SRMC & RI (DU) Porur, Chennai 116 Harper s biochemistry 24 th ed, Pg 218 Fatty acid Synthesis Known as
Fatty acid synthesis Dr. Nalini Ganesan M.Sc., Ph.D Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry SRMC & RI (DU) Porur, Chennai 116 Harper s biochemistry 24 th ed, Pg 218 Fatty acid Synthesis Known as
Glycerolipidome responses to freezingand chilling-induced injuries: examples in Arabidopsis and rice
 Zheng et al. BMC Plant Biology (2016) 16:70 DOI 10.1186/s12870-016-0758-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Glycerolipidome responses to freezingand chilling-induced injuries: examples in Arabidopsis and rice
Zheng et al. BMC Plant Biology (2016) 16:70 DOI 10.1186/s12870-016-0758-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Glycerolipidome responses to freezingand chilling-induced injuries: examples in Arabidopsis and rice
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202
 General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
Energy storage in cells
 Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
Reviewer #1, expert in yeast metabolic engineering and biofuels (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, expert in yeast metabolic engineering and biofuels (Remarks to the Author): In the manuscript by Gajewski et al., the authors engineered a yeast FAS to produce short-chain
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, expert in yeast metabolic engineering and biofuels (Remarks to the Author): In the manuscript by Gajewski et al., the authors engineered a yeast FAS to produce short-chain
Lipid Characterization in Vegetative Tissues of High Saturated Fatty Acid Sunflower Mutants
 78 J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 78 82 Lipid Characterization in Vegetative Tissues of High Saturated Fatty Acid Sunflower Mutants Sara Cantisán, Enrique Martínez-Force, Rosario AÄ lvarez-ortega, and
78 J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 78 82 Lipid Characterization in Vegetative Tissues of High Saturated Fatty Acid Sunflower Mutants Sara Cantisán, Enrique Martínez-Force, Rosario AÄ lvarez-ortega, and
Producing Wax Esters in Transgenic Plants by Expression of Genes Derived from Jojoba
 Reprinted from: Perspectives on new crops and new uses. 1999. J. Janick (ed.), ASHS Press, Alexandria, VA. Producing Wax Esters in Transgenic Plants by Expression of Genes Derived from Jojoba Michael W.
Reprinted from: Perspectives on new crops and new uses. 1999. J. Janick (ed.), ASHS Press, Alexandria, VA. Producing Wax Esters in Transgenic Plants by Expression of Genes Derived from Jojoba Michael W.
Roles of Lipids. principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular
 Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
number Done by Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb
 number 23 Done by A. Rawajbeh Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are used by the peripheral tissues like the skeletal and cardiac muscles, where they are the preferred source
number 23 Done by A. Rawajbeh Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are used by the peripheral tissues like the skeletal and cardiac muscles, where they are the preferred source
Lipids. Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals. Storage Lipids: derivatives of fatty acids. 11/21/10
 1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
23.1 Lipid Metabolism in Animals. Chapter 23. Micelles Lipid Metabolism in. Animals. Overview of Digestion Lipid Metabolism in
 Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
UC Davis The Proceedings of the International Plant Nutrition Colloquium XVI
 UC Davis The Proceedings of the International Plant Nutrition Colloquium XVI Title The content of ß-sitosterol in maize plants growing under different nitrogen nutrition Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/72j7v14x
UC Davis The Proceedings of the International Plant Nutrition Colloquium XVI Title The content of ß-sitosterol in maize plants growing under different nitrogen nutrition Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/72j7v14x
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol
 Fatty Acid Synthesis Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Requires Carbon Source: Reducing Power: NADPH Energy Input: ATP Why Energy? Why Energy? Fatty Acid Fatty Acid + n(atp) ΔG o : -ve Fatty
Fatty Acid Synthesis Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Requires Carbon Source: Reducing Power: NADPH Energy Input: ATP Why Energy? Why Energy? Fatty Acid Fatty Acid + n(atp) ΔG o : -ve Fatty
Objectives. Carbon Bonding. Carbon Bonding, continued. Carbon Bonding
 Biochemistry Table of Contents Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of carbon bonding in biological molecules. Identify functional groups in biological
Biochemistry Table of Contents Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of carbon bonding in biological molecules. Identify functional groups in biological
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe
 number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
Biological molecules
 Biological molecules 04-04-16 Announcements Your lab report 1 is due now Quiz 1 is on Wednesday at the beginning of class, so don t be late Review Macromolecues are large molecules necessary for life made
Biological molecules 04-04-16 Announcements Your lab report 1 is due now Quiz 1 is on Wednesday at the beginning of class, so don t be late Review Macromolecues are large molecules necessary for life made
CHY2026: General Biochemistry. Lipid Metabolism
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry Lipid Metabolism Lipid Digestion Lipid Metabolism Fats (triglycerides) are high metabolic energy molecules Fats yield 9.3 kcal of energy (carbohydrates and proteins 4.1 kcal)
CHY2026: General Biochemistry Lipid Metabolism Lipid Digestion Lipid Metabolism Fats (triglycerides) are high metabolic energy molecules Fats yield 9.3 kcal of energy (carbohydrates and proteins 4.1 kcal)
What are the molecules of life?
 Molecules of Life What are the molecules of life? Organic Compounds Complex Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Organic Compounds Carbon- hydrogen based molecules From Structure to Function Ø Carbon
Molecules of Life What are the molecules of life? Organic Compounds Complex Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Organic Compounds Carbon- hydrogen based molecules From Structure to Function Ø Carbon
Cell wall components:
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure.
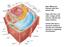 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol
 Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Lippincott s Chapter 16 Fatty Acid Synthesis Mainly in the Liver Requires Carbon Source: Acetyl CoA Reducing Power: NADPH 8 CH 3 COO C 15 H 33 COO Energy Input:
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Lippincott s Chapter 16 Fatty Acid Synthesis Mainly in the Liver Requires Carbon Source: Acetyl CoA Reducing Power: NADPH 8 CH 3 COO C 15 H 33 COO Energy Input:
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids
 Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
Summary of fatty acid synthesis
 Lipid Metabolism, part 2 1 Summary of fatty acid synthesis 8 acetyl CoA + 14 NADPH + 14 H+ + 7 ATP palmitic acid (16:0) + 8 CoA + 14 NADP + + 7 ADP + 7 Pi + 7 H20 1. The major suppliers of NADPH for fatty
Lipid Metabolism, part 2 1 Summary of fatty acid synthesis 8 acetyl CoA + 14 NADPH + 14 H+ + 7 ATP palmitic acid (16:0) + 8 CoA + 14 NADP + + 7 ADP + 7 Pi + 7 H20 1. The major suppliers of NADPH for fatty
International Journal of Environmental & Agriculture Research (IJOEAR) ISSN:[ ] [Vol-2, Issue-3, March- 2016]
![International Journal of Environmental & Agriculture Research (IJOEAR) ISSN:[ ] [Vol-2, Issue-3, March- 2016] International Journal of Environmental & Agriculture Research (IJOEAR) ISSN:[ ] [Vol-2, Issue-3, March- 2016]](/thumbs/75/71824963.jpg) Transcriptional regulation of functional genes involved in cuticular wax biosynthesis by MYB family transcriptional factors in plants U. Lokesh 1, B. Venkatesh 2, K. Kiranmai 3, A. Naresh kumar 4, V. Amarnatha
Transcriptional regulation of functional genes involved in cuticular wax biosynthesis by MYB family transcriptional factors in plants U. Lokesh 1, B. Venkatesh 2, K. Kiranmai 3, A. Naresh kumar 4, V. Amarnatha
Biochemistry Macromolecules and Enzymes. Unit 02
 Biochemistry Macromolecules and Enzymes Unit 02 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. What is Carbon? Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds
Biochemistry Macromolecules and Enzymes Unit 02 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. What is Carbon? Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND GENETICS OF PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 157 161) MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND GENETICS
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 157 161) MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND GENETICS
4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions
 4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University
4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University
Supplemental Figure S1. The number of hydathodes is reduced in the as2-1 rev-1
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. The number of hydathodes is reduced in the as2-1 rev-1 and kan1-11 kan2-5 double mutants. A, The numbers of hydathodes in different leaves of Col-0, as2-1 rev-1,
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. The number of hydathodes is reduced in the as2-1 rev-1 and kan1-11 kan2-5 double mutants. A, The numbers of hydathodes in different leaves of Col-0, as2-1 rev-1,
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
Subtilisin-like proteins and lipid signaling events: the missing links in grapevine resistance to P. viticola
 Subtilisin-like proteins and lipid signaling events: the missing links in grapevine resistance to P. viticola Andreia Figueiredo, Joana Figueiredo, Gonçalo Laureano, Ana Rita Cavaco, Marisa Maia, Ana Rita
Subtilisin-like proteins and lipid signaling events: the missing links in grapevine resistance to P. viticola Andreia Figueiredo, Joana Figueiredo, Gonçalo Laureano, Ana Rita Cavaco, Marisa Maia, Ana Rita
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS
 Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS Fatty acids obtained by hydrolysis of fats undergo different oxidative pathways designated as alpha ( ), beta ( ) and omega ( ) pathways. -oxidation -Oxidation of fatty
Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS Fatty acids obtained by hydrolysis of fats undergo different oxidative pathways designated as alpha ( ), beta ( ) and omega ( ) pathways. -oxidation -Oxidation of fatty
Signaling in the Nitrogen Assimilation Pathway of Arabidopsis Thaliana
 Biochemistry: Signaling in the Nitrogen Assimilation Pathway of Arabidopsis Thaliana 38 CAMERON E. NIENABER ʻ04 Abstract Long recognized as essential plant nutrients and metabolites, inorganic and organic
Biochemistry: Signaling in the Nitrogen Assimilation Pathway of Arabidopsis Thaliana 38 CAMERON E. NIENABER ʻ04 Abstract Long recognized as essential plant nutrients and metabolites, inorganic and organic
THE EFFECT OF DROUGHT STRESS ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION IN SOME ROMANIAN SUNFLOWER HYBRIDS
 THE EFFECT OF DROUGHT STRESS ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION IN SOME ROMANIAN SUNFLOWER HYBRIDS Elena Petcu, Adrian Arsintescu, Danil Stanciu *) ABSTRACT Five Romanian sunflower hybrids were grown under greenhouse
THE EFFECT OF DROUGHT STRESS ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION IN SOME ROMANIAN SUNFLOWER HYBRIDS Elena Petcu, Adrian Arsintescu, Danil Stanciu *) ABSTRACT Five Romanian sunflower hybrids were grown under greenhouse
BIOSYNTHESIS OF FATTY ACIDS. doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc.
 BIOSYNTHESIS OF FATTY ACIDS doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc. The pathway for the of FAs is not the reversal of the oxidation pathway Both pathways are separated within different cellular compartments In
BIOSYNTHESIS OF FATTY ACIDS doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc. The pathway for the of FAs is not the reversal of the oxidation pathway Both pathways are separated within different cellular compartments In
Prentice Hall. Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th Edition (Campbell, et al) High School
 Prentice Hall Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th Edition (Campbell, et al) 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Biology I Students should understand that scientific knowledge is gained from observation
Prentice Hall Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th Edition (Campbell, et al) 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Biology I Students should understand that scientific knowledge is gained from observation
A mutant in Arabidopsis Lacking a Chloroplast Specific Lipid. Lewis Kurschner and Karen Thulasi Masters in Botany
 A mutant in Arabidopsis Lacking a Chloroplast Specific Lipid Lewis Kurschner and Karen Thulasi Masters in Botany Fatty acid nomenclature Fatty acyl composition Chain length Degree of unsaturation and position
A mutant in Arabidopsis Lacking a Chloroplast Specific Lipid Lewis Kurschner and Karen Thulasi Masters in Botany Fatty acid nomenclature Fatty acyl composition Chain length Degree of unsaturation and position
Problem Set #5 4/3/ Spring 02
 Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]
![EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]](/thumbs/87/96059079.jpg) EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
ib Blackwell Publishing
 Plant Lipids Biology, Utilisation and Manipulation Edited by DENIS J. MURPHY Biotechnology Unit School of Applied Sciences University of Glamorgan Cardiff, UK ib Blackwell Publishing CRC Press Contents
Plant Lipids Biology, Utilisation and Manipulation Edited by DENIS J. MURPHY Biotechnology Unit School of Applied Sciences University of Glamorgan Cardiff, UK ib Blackwell Publishing CRC Press Contents
Journal of Visualized Experiments. Video Article Isolation and Compositional Analysis of Plant Cuticle Lipid Polyester Monomers
 Video Article Isolation and Compositional Analysis of Plant Cuticle Lipid Polyester Monomers 1 Seamus Jenkin, Isabel Molina 1 1 Department of Biology, Algoma University Correspondence to: Isabel Molina
Video Article Isolation and Compositional Analysis of Plant Cuticle Lipid Polyester Monomers 1 Seamus Jenkin, Isabel Molina 1 1 Department of Biology, Algoma University Correspondence to: Isabel Molina
Biology. Chapter 3. Molecules of Life. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 3 Molecules of Life 2015 3.1 What Are the Molecules of Life? The molecules of life contain a high proportion of carbon atoms: Complex carbohydrates
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 3 Molecules of Life 2015 3.1 What Are the Molecules of Life? The molecules of life contain a high proportion of carbon atoms: Complex carbohydrates
BRIEF CONTENTS COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL III METABOLIC AND DEVELOPMENTAL INTEGRATION COMPARTMENTS CELL REPRODUCTION PLANT ENVIRONMENT AND AGRICULTURE
 BRIEF CONTENTS I COMPARTMENTS 1 Membrane Structure and Membranous Organelles 2 2 The Cell Wall 45 3 Membrane Transport 111 4 Protein Sorting and Vesicle Traffic 151 5 The Cytoskeleton 191 II CELL REPRODUCTION
BRIEF CONTENTS I COMPARTMENTS 1 Membrane Structure and Membranous Organelles 2 2 The Cell Wall 45 3 Membrane Transport 111 4 Protein Sorting and Vesicle Traffic 151 5 The Cytoskeleton 191 II CELL REPRODUCTION
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
