DaMocles SoSe Anandamide. Introduction Function Biosynthesis Potential Usage Sources Glossary
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Gregory
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DaMocles SoSe 2011 Anandamide Introduction Function Biosynthesis Potential Usage Sources Glossary
2 Introduction Our organism reacts to various chemicals found in nature but not synthesized by our body. But for what reason? The answer is simple. Our body uses singnal or regulation molecules being quite similar to these naturalsubstances. Just like the molecule this text is about. Between 1988 and 1990 Devane, Howlett and Johnson discovered the two cannabinoid receptors CB1/CB2 at the Saint Louis University of Missouri. The cannabis substance THC binds to these recepors, so the search for the body's own substances started shortly after. In 1992 the Czech chemist Lumír Ondřej Hanuš and the American molecularpharmacologist William Anthony Devane discovered arachidonylethanolamide, which is commonly known as anandamide. Over the years, the two other anandamides homo-gamma-linolenylethanolamide and docosatetraenylethanolamide were found. Thus there are currently three known Anadamide derivates. But Anandamid cannot only be found in the human body but also in cacao beans therefor in chocolate as well. In several studies, researchers have found that are formed upon activation of pain impulses from the brain Anadamide showing an analgesic effect. Because of this effect, the endogenous cannabinoids will certainly play a significant role in the pharmaceutical treatment of pain. Basic informations molecular formular: C22H37NO2 density: 0,92 g/cm³ molar mass: 347,53 g/mol endogenous cannabinoid found in chocolate and cacao beans Ethanolamide derivate of the arachindonic acid IUPAC-name: (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenamid
3 Function Our endocannabinoid system is not made for recognition of THC but for inhibition of neuronal signals using our own cannabinoids (called endocannabinoids). Anandamide (short AEA) is one of them, binding to our cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 but prefering CB1. The receptors are spreaded widely over the human organism but very concentrated in the CNS and in the brain, sitting on top of our neurons. If an action potential arrives at the presynapse the voltage dependend Ca++ channels open up so Ca++ ions diffuse into the stroma of the respective presynapse, leading to the release of transmitter molecules, the essence of signaltransduction from neuron to neuron. These transmitters are about to cross the synaptic gap and bind to ligand depending ion channels at the postsynapse. This causes a depolarisation and leads to a second opening of voltage depending Ca++ ion channels you can find in the membran of a postsynapse causing an Ca++ influx. Unlike the presynaptic influx of Ca++ the postsynaptic influx activates the biosynthesis of endocannabinoids such as AEA or 2-AG using precursors sitting in the neuronal membran. The endocannabinoides are secreted by an endocannabinoid carrier system. They are not stored in vesicles such as transmitters but produced on demand. After secretion, as an agonist, AEA binds to CB1 sitting on the presynapsis. CB1 is a g-protein linked receptor whose activation causes a blocking of Ca++ Channels, decreasing ion influx and eventually leading to a reduced release of transmitter molecules. AEAs function can be compared to a negativ feed back diluting neuronal signals. Schusdziarra V, Azad SC, Erdmann J, et al. AEA binds to potassium channels and rectifies them inwardly. In addition there are so called vanilliod receptors (TRVP1) functioning as pain modulators being activated by a couple of endogenous chemicals, one of them is Anandamide. This interaction could be used for an analgesic therapy.
4 Biosynthesis Anandamide is a very lipophilic molecule, which is not like other neurotransmitters stored in vesicles and released then into the synaptic gap, but first synthesized out of precursors sitting in the membrane, and then secreted into the synaptic gap. This "on demand" mechanism is triggered by the influx of Ca ++ and activates the AEA-synthesizing enzymes. Initial of the synthesis is the depolarization of the post-synapse, resulting in a Ca ++ influx occurs and the enzyme N- acyltransferase(nat) is enabled. This enzyme transfers of phosphatidylcholine (PC), which is linked at the C1 atom of arachidonic acid to the amino group of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). The result is N-arachidonyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE). The last step is done by the enzyme N-arachidonyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD), a phospholipase, which forms the anandamide. Inactivation of anandamide, it is a hydrolytic cleavage of Ananamidin ethanolamide and arachidonic acid. This step is catalyzed by the intracellular fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). H
5 Potential Usage As an endogenous cannabinoid transmitter Anandamid has several physiological functions in our organism. The pharmalogical effect of Andamide is the basis for a variety of research approaches during the last twenty years.. One studie shows that Endocannabinoids have an emotional influence on the human organism. By blocking the hydrological degradation of Anandamide anxiety can be reduced. This result opens up an approach for studies on the medication of anxiety state or even depression. Researches have shown that psychotic and paranoid illnesses could be leveled off and even controlled by Anandamide. These diagnostic findings could open the door for a therapy of schizophrenia. Just like read before Anandamide affects the central nervous system or the periphery. It affects the cannabaniod receptors CB1 and CB2, whereof the last one is located in the periphery and the immune system. The location of the neurotransmitters shows a connection to its particular function, which I am going to outline in these examples. The immune system in the brain stands under the control of endocannabaniods. This fact has been scientifically proven in a rating of the Anandamide concentration, while the brain suffered damage. This release of Anandamide attracts Microglia cells, which generally negate the harm. The Endocannabanoide controls the Microglia cells in a way that the immune system cannot overreact. The research shows also, that through the influence on the endocannabinoid system, nerve cells could be protected from harmful inflammation. Therefore Anandamide is a regulation substance, which plays an important role in the controlling of Microgliacells and the determination of inflammation in nerve tissues. Regulation of the Anandamide concentration could be a potential treatment for multiple sclerosis. Many of these CB Receptors are located in brain areas being involved in the process of cognition and thinking. Mices, which were injected with Anandamide, showed a significant behavioral difference. Their pain sensation was reduced to 80%. another study shows that Anandamide inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation. Another interesting fact outlines, that Anandamide regulates the feeding behavior and the neural generation of motivation.
6 Sources Yong-Xin SUN*, Kazuhito TSUBOI, Yasuo OKAMOTO*, Takeharu TONAI, Makoto MURAKAMI Ichiro KUDOand Natsuo UEDA - Biosynthesis of anandamide and N -palmitoylethanolamine by sequential actions of phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipase D (2004) Jie Liu, Lei Wang, Judith Harvey-White, Douglas Osei-Hyiaman, Raj Razdan, Qian Gong, Andrew C. Chang,Zhifeng Zhou, Bill X. Huang, Hee-Yong Kim, George Kunos - A biosynthetic pathway for anandamide (2006) Felix Johannes Franz Bonke - Signalwege und Metabolismus des Endocannabinoids Anandamid im Gehirn des Menschen: Expression des Cannabinoid-1-Rezeptors sowie der Enzyme NAPE-PLD und FAAH (2007) Anne-Christin Lehmann - Einfluss des Fettgehalts der Nahrung auf die Aktivität des Endocannabinoid-Systems gesunder schlanker und adipöser Menschen (2010) William,Devane, Julius Axelrod - Enzymatic synthesis of anandamide, an endogenous ligand for thecannabinoid receptor, by brain membranes (1994) Vincenzo Di Marzo - Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain: biosynthetic mechanisms in the limelight (2011) Links 705/
7 Glossary Action potential When a Neuron gets stimulated, this stimulatuion gets transfered via a creepage along the neurons membran. If the stimulation gets bigger than a certain trigger pointg at the axon hillockthe neuron gets depolarized.that means the opening of voltage dependend sodium cahnnels, which increases the sodium influx rapidly, leading agian to an enhanced opening of more voltage depended channels.. The membrane potential gets turned around into positive till a certain limit is reached.at this point many ion channels close again and stay inactive. Almost at the same time potassium channels are opening up causing a huge stream out of potassium ions due to the high cation concentration in the neurons stroma so the decrasing sodium influx gets compensated. Right now the stream of potassium ions directed outside is bigger than the influx of sodium ions resulting into a negative membrane potential (repolarisation). More and more potassium channels are closing or getting blocked but the continuing streaming out results into an even more negativ potential than the resting potential (hyperpolarisation). The resting potential gets rebuilt by the sodium-potassium-pump. The durrance of an actionpotential is around 1 ms. Cannabinoid receptors agonists are substances binding to receptors land eading to their activation there are endgenous (body's own) und exogenous (no from our body) agonists. e.g. THC is an exogenous but Anandamide an endogenous agonist binding both to our cannabinoid receptors. Thats why they are called cannabinoids. Function of a G-Protein linked to CB1 Gi/0: inhibitory G-Protein, camp: cyclic Adenosinmonophosphate, PKA: Protein Kinase A, PKB/AKT: Protein Kinase B, PI3-K: Phosphoinositol-3-Kinase, Raf-1: Raf-1-Kinase, ERK: extracellular regulated Kinase, IEG: immediate early gene, c-fos, c-jun, zif268: transcription factors, BDNF: brain derived neurotrophic factor.
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras
 Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Cannabinoids 101. Matthew Hill, Ph.D. Hotchkiss Brain Institute University of Calgary
 Cannabinoids 101 Matthew Hill, Ph.D. Hotchkiss Brain Institute University of Calgary Disclosures Have received honoraria for Scientific Consultation: Pfizer International GW Pharmaceuticals Receive operating
Cannabinoids 101 Matthew Hill, Ph.D. Hotchkiss Brain Institute University of Calgary Disclosures Have received honoraria for Scientific Consultation: Pfizer International GW Pharmaceuticals Receive operating
Communication within a Neuron
 Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
JNJ : selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor. Central and Peripheral PK/PD
 JNJ-42165279: selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor Central and Peripheral PK/PD The Endocannabinoid System Research initiated by efforts to elucidate the active substance of Cannabis (THC in
JNJ-42165279: selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor Central and Peripheral PK/PD The Endocannabinoid System Research initiated by efforts to elucidate the active substance of Cannabis (THC in
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Branches of the Nervous System
 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
AP Biology Unit 6. The Nervous System
 AP Biology Unit 6 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading
AP Biology Unit 6 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons. Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire
 Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons
 5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
The Endocannabinoid System
 The Endocannabinoid System Think of this system as the wizard behind the curtain. It underlies all the other systems, including the Autonomic Nervous System. Overall it influences well-being and the perception
The Endocannabinoid System Think of this system as the wizard behind the curtain. It underlies all the other systems, including the Autonomic Nervous System. Overall it influences well-being and the perception
3) Most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the A) dendritic region. B) axon hillock. C) axon. D) cell body. E) axon terminals.
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
3.E.2 Continued. This is the essential knowledge statement from the curriculum framework. Detect---process--- response
 Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Ameen Alsaras. Ameen Alsaras. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling. Chapter 48
 Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Endocannabinoid System Cannabinoid Drugs
 Cannabinoid Drugs STCM Conference Bern 22.1.2013 Rudolf Brenneisen University of Bern, DKF 1 www.phytopharm.dkf.unibe.ch rudolf.brenneisen@dkf.unibe.ch Milestones 1988: First cannabinoid receptor (rat
Cannabinoid Drugs STCM Conference Bern 22.1.2013 Rudolf Brenneisen University of Bern, DKF 1 www.phytopharm.dkf.unibe.ch rudolf.brenneisen@dkf.unibe.ch Milestones 1988: First cannabinoid receptor (rat
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?!
 Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems
 CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
Neuropharmacology NOTES
 Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]](/thumbs/86/94924826.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
Cell Membrane and Transport
 Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Fundamentals of Pharmacology
 Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission. BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Action potential. Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon
 Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Cellular Communication
 (a) Communicating cell junctions. by direct cell-cell contact lasma membranes 1. Direct cell contact. Vesicle-mediated 3. Chemical messengers (b) Cell-cell recognition. Gap junctions between animal cells
(a) Communicating cell junctions. by direct cell-cell contact lasma membranes 1. Direct cell contact. Vesicle-mediated 3. Chemical messengers (b) Cell-cell recognition. Gap junctions between animal cells
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS. AP Biology Chapter 48
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
H. An electrical signal travel down the dendrite.
 Nervous System Group Activity Objectives: To be able to describe the nervous system structure and function To understand how neurons communicate using both electrical and chemical signals To know how the
Nervous System Group Activity Objectives: To be able to describe the nervous system structure and function To understand how neurons communicate using both electrical and chemical signals To know how the
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
- Biosignaling: Signal transduction. References: chapter 8 of Lippincots chapter 1 3 of Lehningers
 Basic concepts of Metabolism Metabolism and metabolic pathway Metabolic Map Catabolism Anabolism - Regulation of Metabolism Signals from within the cell (Intracellular) Communication between cells. - Biosignaling:
Basic concepts of Metabolism Metabolism and metabolic pathway Metabolic Map Catabolism Anabolism - Regulation of Metabolism Signals from within the cell (Intracellular) Communication between cells. - Biosignaling:
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3
 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II
 BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
10.1: Introduction. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial cells) Dendrites.
 10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
Notes are online at The Neuron
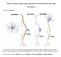 Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Lojayn Salah. Razan Aburumman. Faisal Muhammad
 20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES. Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I.
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Master 2.1
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Elizabeth Biopsychology (PSY 302) The Synapses 08/29/2017. The Synapses
 Elizabeth Biopsychology (PSY 302) The Synapses 08/29/2017 The Synapses Conduction of a Depolarization o In dendrites: passive propagation : There is attenuation of signal transmission -Further away they
Elizabeth Biopsychology (PSY 302) The Synapses 08/29/2017 The Synapses Conduction of a Depolarization o In dendrites: passive propagation : There is attenuation of signal transmission -Further away they
Omar Ismail. Dana Almanzalji. Faisal Mohammad
 11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
I. OVERVIEW DIRECT. Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of
 THE CHOLINERGIC NEURON 1 I. OVERVIEW DIRECT Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of ACTING neuron involved in their mechanism of action.
THE CHOLINERGIC NEURON 1 I. OVERVIEW DIRECT Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of ACTING neuron involved in their mechanism of action.
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nervous System Communication. Nervous System Communication. The First Nerve Cells 1/2/11
 Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
Notes: Synapse. Overview. PSYC Summer Professor Claffey PDF. Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the
 PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
Membrane Potentials. (And Neuromuscular Junctions)
 Membrane Potentials (And Neuromuscular Junctions) Skeletal Muscles Irritability & contractility Motor neurons & motor units Muscle cells have two important and unique properties: They are irritable and
Membrane Potentials (And Neuromuscular Junctions) Skeletal Muscles Irritability & contractility Motor neurons & motor units Muscle cells have two important and unique properties: They are irritable and
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Voltage-Gated Na + Channel. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
PMT. Explain the importance of reflex actions (3) Page 1 of 19
 Q1. When a finger accidentally touches a hot object, a reflex action occurs. The biceps muscle contracts, causing the arm to be flexed and the finger is pulled away. The diagram shows the arrangement of
Q1. When a finger accidentally touches a hot object, a reflex action occurs. The biceps muscle contracts, causing the arm to be flexed and the finger is pulled away. The diagram shows the arrangement of
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Plasma membranes. Plasmodesmata between plant cells. Gap junctions between animal cells Cell junctions. Cell-cell recognition
 Cell Communication Cell Signaling Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Communicate by chemical messengers Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect
Cell Communication Cell Signaling Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Communicate by chemical messengers Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline
 Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
Omar Sami. Muhammad Abid. Muhammad khatatbeh
 10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
 6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis IB Biology SL Part 1 - Nerves Outcomes Part 1 6.5.1State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis IB Biology SL Part 1 - Nerves Outcomes Part 1 6.5.1State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed
Neurons. Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons.
 Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
GPCR. General Principles of Cell Signaling G-protein-Coupled Receptors Enzyme-Coupled Receptors Other Signaling Pathways. G-protein-Coupled Receptors
 G-protein-Coupled Receptors General Principles of Cell Signaling G-protein-Coupled Receptors Enzyme-Coupled Receptors Other Signaling Pathways GPCR G-protein-coupled receptors Figure 15-30 Molecular Biology
G-protein-Coupled Receptors General Principles of Cell Signaling G-protein-Coupled Receptors Enzyme-Coupled Receptors Other Signaling Pathways GPCR G-protein-coupled receptors Figure 15-30 Molecular Biology
Learning Objectives. How do drugs work? Mechanisms of Drug Action. Liam Anderson Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology
 How do drugs work? Mechanisms of Drug Action Liam Anderson Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology Learning Objectives Describe the potential drug targets within a human body. Describe the role of receptors,
How do drugs work? Mechanisms of Drug Action Liam Anderson Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology Learning Objectives Describe the potential drug targets within a human body. Describe the role of receptors,
Applied Neuroscience. Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017
 Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
The Endocannabinoid System: Directing Eating Behavior and Macronutrient Metabolism
 The Endocannabinoid System: Directing Eating Behavior and Macronutrient Metabolism Watkins and Kim 2015 Council of Hypothalamic Metabolites Agenda The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Intro The ECS in the
The Endocannabinoid System: Directing Eating Behavior and Macronutrient Metabolism Watkins and Kim 2015 Council of Hypothalamic Metabolites Agenda The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Intro The ECS in the
Anatomy Review. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (
 Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Neurons communicate with other cells at junctions
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Neurons communicate with other cells at junctions
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 CHAPTER 10 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Summarized by B.-W. Ku, E. S. Lee, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University.
 Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
The Nervous System AP Biology
 The Nervous System 2005-2006 Neuron (nerve cell) signal direction dendrites cell body Structure fits function, it have many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal Nodes of Ranvier axon signal
The Nervous System 2005-2006 Neuron (nerve cell) signal direction dendrites cell body Structure fits function, it have many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal Nodes of Ranvier axon signal
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Examples of smallmolecule. peptide neurotransmitters
 Examples of smallmolecule and peptide neurotransmitters Small- molecule transmitters are transported from the cytosol into vesicles or from the synaptic cleft to the cytosol by TRANSPORTERS Neuromodulatory
Examples of smallmolecule and peptide neurotransmitters Small- molecule transmitters are transported from the cytosol into vesicles or from the synaptic cleft to the cytosol by TRANSPORTERS Neuromodulatory
Nervous System. 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands. 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data
 Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
Nervous System. Nervous system cells. Transmission of a signal 2/27/2015. Neuron
 Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73
 DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
Division Ave. High School AP Biology. cell body. signal direction
 signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
Homeostasis. Endocrine System Nervous System
 Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Cellular Communication
 Cellular Communication But before we get into that What have we learned about so far? Energy and Matter Why do living things need energy? Grow Reproduce Maintain homeostasis Cellular signaling Cells communicate
Cellular Communication But before we get into that What have we learned about so far? Energy and Matter Why do living things need energy? Grow Reproduce Maintain homeostasis Cellular signaling Cells communicate
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology
 Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
BIOL Week 6. Nervous System. Transmission at Synapses
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis. Keith Sharkey
 Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis Keith Sharkey Department of Physiology & Pharmacology University of Calgary Dr. Keith Sharkey Financial Interest
Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis Keith Sharkey Department of Physiology & Pharmacology University of Calgary Dr. Keith Sharkey Financial Interest
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling
 Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
Fig Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
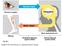 Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Test Bank for Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems 8th Edition by Sherwood
 Test Bank for Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems 8th Edition by Sherwood Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bankfor-human-physiology-from-cells-to-systems-8thedition-by-sherwood
Test Bank for Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems 8th Edition by Sherwood Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bankfor-human-physiology-from-cells-to-systems-8thedition-by-sherwood
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Neurons & Impulses
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
