Biochemistry. Classification of Lipids METABOLISM OF LIPIDS. Principal Investigator
|
|
|
- Vincent Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Paper : 05 Metabolism of Lipids Module: 04 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Content Reviewer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Suaib Luqman, Scientist (CSIR-CIMAP) & Assistant Professor (AcSIR) CSIR-CIMAP, Lucknow Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj Prof. Prashant Mishra, Professor, Department of Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology, IIT-Delhi 1
2 DESCRIPTION OF MODULE Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title 05 Metabolism of Lipids 04 Lipids-Classification 2
3 1. Objectives To understand the classification of lipids How many classes of lipids are present What are the significance of each class 2. Concept Map Natural Lipids Phospho Lipids Conn & Stumpf (1966) Glyco Lipids Terpenoids 3
4 3. Description Lipids can be broadly classified into following major classes: (a) Saponifiable lipids and (b) Non-saponifiable lipids. This classification is based on the basics of their reaction with sodium or potassium hydroxide. 4
5 a. The saponifiable lipid has one or more ester groups allocating it to endure hydrolysis in the charisma of an acid, base or enzyme. b. The non-saponifiable lipid includes phospholipids, prostaglandins, sphingolipids, steroids, terpenes, triglycerides and waxes which cannot be wrecked up into smaller molecules by hydrolysis. 5
6 6
7 On the basis of polarity, lipids are divided into two classes: (1) Polar and (2) Non-Polar 1. Polar (Glycerophospholipids & Sphingolipids): Some of the characteristic of polar lipids are as under. a. It forms bilayer impulsively in water. Phosphatidyl choline (PC, a purified polar lipid from membranes) restrain up to 30 combinations of fatty acids on its chains. b. The bilayers of lipid have four states: Crystal, Gel, Liquid and Liquid crystal. It exhibits a sharp Tm defined from the gel to liquid crystal transition. The Tm is very soaring for saturated chains and very short for polyunsaturated chains. c. In the liquid crystal state, biological membranes are always just over the Tm. Examples are fish 7
8 and alcoholics. d. There are three sub-classes of polar lipids: anionic, uncharged and zwitter-ionic. No cationic lipids are reported in nature. Anionic Lipids Examples of the anionic lipids are Cardiolipin (CL), Phosphotidyl glycerol (PG), Phosphotidyl inositol (PI), Phosphotidyl serine (PS) and many others. i. Agreement of X-ray structures of crystals with NMR conformations. ii. Vile interactions improved by screening of cations from solution and H-bonds. iii. ph at the surface lower that of water (2-3 units if not in salt) and the ph difference wanes off at high ionic strength. iv. The anionic lipids constantly involved in fusion and the surface can bind calcium and hydrogen which eases fusion. v. Cardiolipin acts as an acid-anion provokes hydrogen ion to operate as an attractant. Fusion arises because of acid-anion formation and negative charges become striking by trapping protons. vi. The entire membranes have a net negative charge on their exterior that attracts cations (H + & Na ++ ). vii. Similarly, all biological membranes have a proton gradient sustained by a proton pump (except presence of sodium gradient in animal plasma membrane). 8
9 Uncharged Lipids Examples of the uncharged lipids are Cerebrosides, Gangliosides and Glycolipids. The surface of gangliosides & sphingolipids are anionic but have H-bond lateral interactions. Glycolipids have H-bonds amid neighbours with each lipid has three neighbours. Zwitter-Ionic Lipids Examples of the zwitter-ionic lipids are Phosphotidyl choline (PC), Phosphatidyl ethanolamine (PE), Sphingomyelin (SM). i. Position wise phosphate is on top of the glycerol and glycerol is upright to the membrane. ii. Primary ester is underneath the glycerol and secondary ester is parallel to the membrane before (at C2) the chain plunges. iii. Choline/Ethanolamine (base) gyrates at an angle of ~15º to the plane. iv. Each headgroup of zwitter ionic lipids interact with three neighbours ionically (+,-) 2. Non-polar (Triglycerides) A lot of lipids, on the other hand, are non-polar, implicating that the charge allocation is uniformly distributed. Infact, non-polar molecules do not dissolve well in water. Polar and non-polar molecules tend to deter each other in the similar way as the oil and water do not mix and will split from each other even if they are shaken robustly in an endeavor to mix them. This peculiarity between non-polar and polar molecules has imperative effect for living things, which are poised of both molecules. 9
10 10
11 On the basis of function, lipids can be classified into following: 1. Storage lipids (Fatty acids, Triacylglycerols, Sterols) 2. Structural lipids in membranes (Phospholipids, Saccharolipids) 3. Lipids as signals, cofactors and pigments (Lipoproteins, Proteolipids, Polyketides) In the beginning it was understood that lipids are oily substance utilized for two major reasons: (a) dole out as energy souce and (b) structural blocks of membranes. George & Mildred Burr (1929) on the other hand drive out this allegory and established linoleic acid as an indispensable dietary constituent that play an imperative function in many processes in the body. Bergström et al., (1964) also revealed arachidonate (EFA) as the antecedent of the prostaglandins and explained its effect on inflammation and allied disease giving impetus to lipids that gained new-fangled significance among biochemists. Amphipathic nature of membrane lipids and orientation of their hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions articulate their stuffing into the bilayer. Among structural membrane lipids, three types have been described: (a) Glycerophospholipids (two fatty acids connected to glycerol are present in hydrophobic regions), (b) Sphingolipids (sphingosine: a fatty amine linked to single fatty acid) and (c) sterols (compounds with four fused hydrocarbon rings arranged in an inflexible arrangement). Glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids include charged alcohols at their polar ends and a few in addition contain phosphate moeity. In these amphipathic compounds, the hydrophilic moieties could be more complex or as elementary as a single -OH group at one end of the sterol ring system. Among these membrane lipids classes, colossal miscellany results from various combinations of tails and polar heads of fatty acid. 11
12 The products of hydrolysis have also been considered for classifying the lipids into following category. 1. Simple Lipids: On hydrolysis yield alcohol (monohydric or trihydric) and fatty acids Simple glyceride: Include identical FAs Mixed glyceride: Include dissimilar FAs Oils: Glycerol with UFAs Fats: Glycerol with SFAs Waxes: Mono or dihydric alcohol with FAs 2. Complex Lipids: (Compound lipids): On hydrolysis yield fatty acids, glycerol and phosphoric acid along with serine, sphingosine, ethanolamine and various sugars. Phospholipid: Glycerol + fatty acids + phosphoric acid + nitrogenous base 12
13 e.g. Lecithin: Glycerol + fatty acids + phosphoric acid + choline Cephalin: Glycerol + fatty acids + phosphoric acid + ethanolamine Glycolipids: Glycerol + fatty acid + carbohydrates (on hydrolysis) They are sub-classified as sulpholipids, galactosyl diglyceride and cerebrosides. Sphingophosphoiplds: Sphingosine + fatty acids + phosphoric acid + choline 3. Derived Lipids: Are the hydrolytic commodities of complex and simple lipids. Examples are Alcohols (Sterol and glycerol), fatty acids, terpenoids etc. 4. Summary In this lecture we learnt about: The Different types of classifications of the lipids 13
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Chapter 20 Lipids. Organic and Biochem
 Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature
 GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
Classification of Lipids
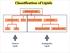 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on C number 3 of a triacylglycerol molecule O O CH 2 O C R CH 2 O P O X OH.
 Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Biochemistry. Catabolism METABOLISM OF LIPIDS. Principal Investigator. Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi
 Paper : 05 Metabolism of Lipids Module: 20 of Lipids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Content Reviewer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr.
Paper : 05 Metabolism of Lipids Module: 20 of Lipids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Content Reviewer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr.
Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example:
 Carboxylic acids LECTURE 3 Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example: Lipids: classification, structure and biological role. By/Arshed Abd
Carboxylic acids LECTURE 3 Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example: Lipids: classification, structure and biological role. By/Arshed Abd
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Functions of Lipids. - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g).
 Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Chapter 11: Lipids. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
3.1.3 Lipids. Source: AQA Spec
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
CH 3. Lipids CHAPTER SUMMARY
 H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids and Biological Membranes
 Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Ahmad O. Olimat. Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh. Dr.Mamoun
 10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
Lipid Chemistry. Presented By. Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair
 Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Membrane transport. Pharmacy Dr. Szilvia Barkó
 Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS:
 LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202
 General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
Lipids. Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids.
 Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Membranes & Membrane Proteins
 School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry. General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4. Lipids
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
II- Compound Lipids. 1- Phospholipids
 II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
Organic molecules highly hydrophobic and water insoluble.
 UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
Lipids. Lipids. Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague
 Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Seminar 6 Theoretical part
 Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
Lipids are used to store and excess energy from extra carbohydrates in animals
 Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
EH1008 Biomolecules. Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Water. Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry.
 EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12
 BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds.
 Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
Lipids. Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals. Storage Lipids: derivatives of fatty acids. 11/21/10
 1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
Inorganic compounds: Usually do not contain carbon H 2 O Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 NaCl Carbon containing molecules not considered organic: CO 2
 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
Biomolecules: lipids
 Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Organism. Organ and organ systems. Tissue. Cells. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids
 hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
Lipids are broadly classified in to simple, complex and derived, which are further subdivided into different groups.
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*)
 NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
2. Simple lipids: Triacylglycerols and waxes are classified as simple lipids. The characteristics of each are described in the sections below.
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Section 8: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons. Outline
 hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
Dr. Mamoun. Loai Azar
 13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
Chapter Sections: 3.1 Carbon s Place in the Living World 3.2 Functional Groups 3.3 Carbohydrates 3.4 Lipids 3.5 Proteins 3.
 Chapter Sections: 3.1 Carbon s Place in the Living World 3.2 Functional Groups 3.3 Carbohydrates 3.4 Lipids 3.5 Proteins 3.6 Nucleic Acids Student Goals: By the end of this lecture series, students should
Chapter Sections: 3.1 Carbon s Place in the Living World 3.2 Functional Groups 3.3 Carbohydrates 3.4 Lipids 3.5 Proteins 3.6 Nucleic Acids Student Goals: By the end of this lecture series, students should
From Atoms to Cells: Fundamental Building Blocks. Models of atoms. A chemical connection
 From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapters 9 and 10 Lipids and Membranes
 Chapters 9 and 10 Lipids and Membranes Lipids- a class of biological molecules defined by low solubility in water and high solubility in nonpolar solvents. Lipids contain or are derived from fatty acids.
Chapters 9 and 10 Lipids and Membranes Lipids- a class of biological molecules defined by low solubility in water and high solubility in nonpolar solvents. Lipids contain or are derived from fatty acids.
Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Chapter 17: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons
 hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY
 BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Carbon Compounds. Section 2 Molecules of Life. Biochemistry
 Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Lipids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8
 Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids. Chapter 11: Outline. Fatty Acids. Lipid Classes. Fatty Acids-2. Fatty Acids-3. General Types eg. A fatty acid
 Chapter 11: utline Lipid Classes Fatty Acids and Derivatives Triacylglycerols Phospholipids Isoprenoids Membranes Membrane Structure Membrane Function Wax Esters Sphingolipids Lipoproteins Lipids General
Chapter 11: utline Lipid Classes Fatty Acids and Derivatives Triacylglycerols Phospholipids Isoprenoids Membranes Membrane Structure Membrane Function Wax Esters Sphingolipids Lipoproteins Lipids General
Topic 3: Molecular Biology
 Topic 3: Molecular Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids Essen=al Understanding: Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are used to supply and store energy. Carbohydrates CARBOHYDRATES CHO sugars Primarily consist
Topic 3: Molecular Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids Essen=al Understanding: Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are used to supply and store energy. Carbohydrates CARBOHYDRATES CHO sugars Primarily consist
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
 LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport. 阮雪芬 May/9/2004
 Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport 阮雪芬 May/9/2004 Outline Introduction Fatty Acids Triacylglycerols Polar lipids Steroids and other lipids Biological membranes Membrane transport Examples
Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport 阮雪芬 May/9/2004 Outline Introduction Fatty Acids Triacylglycerols Polar lipids Steroids and other lipids Biological membranes Membrane transport Examples
Organic Molecules. 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1
 Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Emulsification. An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment. By Noel Ways
 Emulsification An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment By Noel Ways To begin the process of understanding emulsification, let's start with water. First, we note that
Emulsification An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment By Noel Ways To begin the process of understanding emulsification, let's start with water. First, we note that
Biomolecules Lecture Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
 www.aiouinfo.com Biomolecules Lecture Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Monosaccharides 4 Examples: 1. Glucose 2. Fructose 3. Ribose 4. Deoxyribose Glucose Structure Function of
www.aiouinfo.com Biomolecules Lecture Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Monosaccharides 4 Examples: 1. Glucose 2. Fructose 3. Ribose 4. Deoxyribose Glucose Structure Function of
3150:112 SAMPLE TEST 2. Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck!
 SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
CHAPTER 2- BIOCHEMISTRY I. WATER (VERY IMPORTANT TO LIVING ORGANISMS) A. POLAR COMPOUND- 10/4/ H O KENNEDY BIOLOGY 1AB
 CHAPTER 2- BIOCHEMISTRY KENNEDY BIOLOGY 1AB I. WATER (VERY IMPORTANT TO LIVING ORGANISMS) WATER S UNIQUE PROPERTIES MAKE IT ESSENTIAL FOR ALL LIFE FUNCTIONS IT IS POLAR, AND HAS BOTH ADHESIVE AND COHESIVE
CHAPTER 2- BIOCHEMISTRY KENNEDY BIOLOGY 1AB I. WATER (VERY IMPORTANT TO LIVING ORGANISMS) WATER S UNIQUE PROPERTIES MAKE IT ESSENTIAL FOR ALL LIFE FUNCTIONS IT IS POLAR, AND HAS BOTH ADHESIVE AND COHESIVE
the properties of carbon
 Carbon Compounds Learning Objectives Describe the unique qualities of carbon. Describe the structures and functions of each of the four groups of macromolecules. For each macromolecule you will need to
Carbon Compounds Learning Objectives Describe the unique qualities of carbon. Describe the structures and functions of each of the four groups of macromolecules. For each macromolecule you will need to
Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chapter 12 Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide 12.1 a) Identify alkenes, alkynes and aromatics as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Determine the number of hydrogen atoms needed to complete an alkene structure.
Chapter 12 Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide 12.1 a) Identify alkenes, alkynes and aromatics as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Determine the number of hydrogen atoms needed to complete an alkene structure.
Chem Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes
 Chem 452 - Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes 111114 Like carbohydrates, lipids are one of the four major classes of biomolecules, which also include the proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. Lipids
Chem 452 - Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes 111114 Like carbohydrates, lipids are one of the four major classes of biomolecules, which also include the proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. Lipids
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules CARBON BASED MOLECULES
 CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
Lipids. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
Chapter 19 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 19 Lecture utline Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Lipids! Introduction to Lipids! Lipids are biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in
Chapter 19 Lecture utline Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Lipids! Introduction to Lipids! Lipids are biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in
Chapter Three (Biochemistry)
 Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Experiment 12 Lipids. Structures of Common Fatty Acids Name Number of carbons
 Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids
 WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids PART A: Understanding Lipids Lipids are more commonly known as fats and include triglycerides,
WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids PART A: Understanding Lipids Lipids are more commonly known as fats and include triglycerides,
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
Good Afternoon! 11/30/18
 Good Afternoon! 11/30/18 1. The term polar refers to a molecule that. A. Is cold B. Has two of the same charges C. Has two opposing charges D. Contains a hydrogen bond 2. Electrons on a water molecule
Good Afternoon! 11/30/18 1. The term polar refers to a molecule that. A. Is cold B. Has two of the same charges C. Has two opposing charges D. Contains a hydrogen bond 2. Electrons on a water molecule
Week 5 Section. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: AP Biology
 Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes. Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment.
 Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Water Carbon Macromolecules
 Water Carbon Macromolecules I. CHEMISTRY: THE BASIS FOR LIFE Hydrogen bond Hydrogen bonds happen mainly between water molecules. The electrons between hydrogen and the other atoms are shared unequally
Water Carbon Macromolecules I. CHEMISTRY: THE BASIS FOR LIFE Hydrogen bond Hydrogen bonds happen mainly between water molecules. The electrons between hydrogen and the other atoms are shared unequally
Section 1 Lecture 1- Origins of Life Life probably started by Hydrothermal Vents.
 Section 1 Lecture 1- Origins of Life Life probably started by Hydrothermal Vents. Photosynthesis originated around 3GA, as cells figured out how to fix CO2 and release O2. Eukaryotes originates 1.5-2.5
Section 1 Lecture 1- Origins of Life Life probably started by Hydrothermal Vents. Photosynthesis originated around 3GA, as cells figured out how to fix CO2 and release O2. Eukaryotes originates 1.5-2.5
