Lysosomes, weapons or shield in gentamicin-induced apoptosis.
|
|
|
- Richard Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lysosomes, weapons or shield in gentamicin-induced apoptosis. Hélène Servais Unité de Pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire Promoteur: Prof. M-P Mingeot-Leclercq Co-Promoteur: Prof. P.M. Tulkens
2 1. INTRODUCTION : Aminoglycosides (AG) history. Dr Waksman Kanamycin Amikacin Isepamicin «New aminoglycosides» Streptomycin Dibekacin Neomycin Paromomycin Tobramycin Netilmicin Gentamicin isolated from Micromonospora purpurea Based on the identification of the exact interactions between AG with the bacterial ribosome
3 1. INTRODUCTION : Aminoglycosides structure Mingeot-Leclercq and Tulkens 1999 Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:
4 1. INTRODUCTION: Aminoglycosides mechanism of action «New aminoglycosides» Inducing miscoding during protein synthesis Davies et al., 1965, 1968 Binding to the A-site of the ribosome Moazed et al., 1987 Interaction of amine functions of with phosphate backbone of the RNA François et al., Interactions AG-A-Site similar changes induced that those observed in with corresponding trna-mrna 2000, 2002 Ogle et al., Gentamicin isolated from Micromonospora purpurea Interactions AG-A-Site 30S particle revealed by Crystal structure Moazed et al., 1987 Interactions AG-A- Site oligonucleotide Yoshizawa et al., 1998 Fourmy et al., 1998
5 1. INTRODUCTION: Aminoglycosides insertion inside the 16S rrna A-site Vicens and Westhof 2003 biopolymers 70: 42-57
6 1. INTRODUCTION: Aminoglycosides disturb protein synthesis Wrong AA added His Arg fmet 50S 50S 50S GUG GCG UAC A UG 30S CGC AG mrna Misreading codon for Arg A-site Wimberly et al., 2002 Nature 407: , Ogle et al., 2001 Science 292: , Ogle et al., 2002 Cell 111: Vicens and Westhof., 2003 Biopolymers 70:42-57
7 1. INTRODUCTION: Clinical indications of aminoglycosides Serious, life-threatening gram-negative infection Complicated skin, bone or soft tissue infection Complicated urinary tract infection Septicemia Peritonitis and other severe intra-abdominal infections Severe pelvic inflammatory disease Endocarditis Mycobacterium infection Neonatal sepsis
8 1. INTRODUCTION: Aminoglycosides are interesting drugs but Bactericidal Post-antibiotic effect Synergism with cell wall active antibacterials (penicillin, cephalosporin, monobactam, carbapenem and glycopeptide) But toxicity limits their clinical use - Choclear and vestibular toxicity - Nephrotoxicity: 5-25% (0-50%) * Risk factors nephrotoxicity: * Clinical features: Nonoliguric renal failure Slow rise in creatinine
9 1. INTRODUCTION: Aminoglycosides nephrotoxicity Evidence of and AG nephrotoxicity Falco et al., 1969 Inhibition of phosphatidyl inositol phospholipase C Lipsky et al., 1982 traffics Golgi-endoplasmic reticulum Sandoval et al., 2000 Kidney Lysosomes primary target of AG houghton et al., 1976 Inhibition of PI-PLC houghton et al., Gentamicin isolated from Micromonospora purpurea Lysosomal alterations accumulation phospholipids Kozek et al., 1974 confined proximal tubules mainly in lysosomes Silverblatt et al., 1979 Lysosomal phospholipidosis Aubert-Tulkens et al., 1979 Renal basolateral membrane binding Walker et al., 1987 AG-induced apoptosis In vivo and in vitro with clinicalrelevant low doses El Mouedden et al., 2000a,b Increase cellular calcium content Holohan et al., 1988 Inhibition of lysosomal sphingomyelinase and phospholipase A1 Laurent et al., 1982
10 1. INTRODUCTION: Gentamicin accumulation in renal cortex Accumulated in the renal cortex in proximal tubular epithelial cells 3 H-gentamicin collection of tissue 24hour after injection 40 µm 40 µm 20 µm 20 µm Schmitz et al., 2002 J Biol Chem 277:
11 . INTRODUCTION: Gentamicin uptake by kidney cells accumulation in lysosomes Gentamicin = 95% excreted glomerumar filtration Apical membrane Θ Θ Θ Θ Lumen- urine Endocytic Route G E N Proximal tubular epithelial cell Mitochondria Lysosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Nucleus 0.5 µm 0.5 µm Basolateral membrane Blood Schmitz et al., 2002 J Biol Chem 277:
12 1. INTRODUCTION: Lysosomal perturbations induced by gentamicin Proximal tubular cell - rat treated with 10 mg/kg.day gentamicin for 7 days Kosek et al 1974 Lab. Invest 30: Proximal tubular cell - rat treated with 4 mg/kg of gentamicin for 4 days Pictures from P.M. Tulkens & M.B. Carlier, adaptated from Tulkens 1986 Am J Med 80 Suppl 6B: Magnifications: X 75,000 (& 200,000, insert)
13 1. INTRODUCTION: Inhibition of lysosomal phospholipase and sphingomyelinase Cortex of rat treated with gentamicin 4 or 10 mg/kg.day Day of treatment Carlier et al 1982 Arch Toxicol Suppl. 5:
14 1. INTRODUCTION: Inhibition of lysosomal phospholipase and sphingomyelinase Adaptated from Mingeot-leclercd et al 1991 Biochem (Life Sci Adv). 10:
15 1. INTRODUCTION: Cellular alterations induced by Lipsky et al., 1982 Cronin et al., 1982 Schwertz et al., 1984 Levi et al., 1990 Apical membrane Lumen- urine Kozek et al., 1974 Houghton et al., 1976 Watanabe et al., 1978 Silverblatt et al., 1979 Hostetler et al., 1982 Endocytic Route Laurent et al., 1982 Viotte et al., 1982 Fillastre et al., 1983 Golgi Lysosomes Powell et al., 1983 Williams et al., 1985 Chatterjee et al., 1987 Mingeot-Leclercq et al., 1988 Vera-Roman et al., 1975 Mingeot-Leclercq et al., 1990a,b Bennett et al., 1988 Okuda et al., 1992 Sandoval et al., 1998 Endoplasmic reticulum Mingeot-Leclercq et al.,1991 Sundin et al., 2001 Mitochondria Vera-Roman et al., 1975 Walker et al., 1987 Rustenbeck et al., 1998 Nucleus Basolateral membrane Blood
16 1. INTRODUCTION: Gentamicin induces apoptosis in vivo 20 µm 20 µm Rat kidney cortical specimens of controls (A) and animal treated for 10 days with 10mg/kg of gentamicin. In vivo El Mouedden et al., 2000 Antimicrobial Agents and Chemother 44: Rat treated for 10 days with saline (control), 10mg/kg of gentamicin and netilmicin; and 40mg/kg isepamicin and amikacin. Apoptosis Nephrotoxicity
17 1. INTRODUCTION: Gentamicin induces apoptosis in vitro 4 days Closed symbols: 2 mm Open symbols: Control LLC-PK1 treated 4 days with 2 mm of In vitro El Moudden et al., 2000 Toxicological Sciences 56:
18 1. INTRODUCTION: Apoptotis or programmed cell death A. Apoptosis: Apoptosis: Programmed cell death (PCD) Role: Important in *Tissue Homeostasis *embryogenesis Diseases Toxicological involvement Neurodegenerative disorders Cancer Autoimmune disorders AIDS Excess of apoptotic process Liver CNS Kidney Decrease of apoptotic process
19 1. INTRODUCTION: Apoptotis and necrosis Cell death induced by a toxic Apoptosis Necrosis Cell suicide Cell murder Degree of insult by a toxic
20 1. INTRODUCTION: Morphological appearance of apoptotic cell Morphological changes in apoptotic cells - Cytoplasm shrink - Nuclear condensation margination fragmentation - Formation of apoptotic bodies - Results from the activation of special enzyme: CASPASE
21 1. INTRODUCTION: Apoptotic Pathways Fas Extrinsic pathway TNF-α caspase 8 Intrinsic pathway Mitochondria Lysosome Proteasome Golgi Endoplasmic Reticulum caspase 3 (6-7) Bax caspase 9 Apoptosome Cytochrome c D nucleus
22 2. AIM of the study: HOW INDUCES APOPTOSIS? CH3 Extrinsic pathway Fas TNF-α Intrinsic pathway Mitochondria caspase 8 Lysosome O H 2N R 1 O HO OH R O O 2 H 2N NH 2 Proteasome caspase 3 (6-7) OH H 3C HN Bax caspase 9 Apoptosome Cytochrome c Golgi Endoplasmic Reticulum D nucleus
23 3. RESULTS CH3 Part I: Are lysosomes involved in -induced apoptosis? Lysosome OH H 3C HN O H 2N R 1 O HO OH R 2 O O H 2N NH 2 Apoptosis
24 PI.1. Destabilization of lysosomal membrane by gentamicin: LLC-PK1cells: renal proximal tubular cells from pig Gm 1 mm Gm 3 mm Gm 2 mm MSDH 25 µm AO (530 nm/620 nm) % of control Time (hours) Lysosomal destabilization 2h 0h 6h 12h 18h 24h
25 Apoptotic signalling: CH3 Extrinsic pathway Fas TNF-α Intrinsic pathway Mitochondria caspase 8 Lysosome O H 2N R 1 O HO OH R O O 2 H 2N NH 2 Proteasome caspase 3 (6-7) OH H 3C HN Bax caspase 9 Apoptosome Cytochrome c Golgi Endoplasmic Reticulum D nucleus
26 PI.2. Disruption of mitochondrial membrane by Gm 2mM Gm 3mM Gm 1mM mcccp 20 µm JC-1 610/530 nm intensity ratio (% of control) Lysosomal destabilization Time (hours) Disruption Mitochondrial Ψ 24 0h 2h 10 h 6h 12h 18h 24h
27 PI.3. Release of cytochrome c : 2 mm 12h Ψ m PTP Cytochrome c Lysosomal destabilization Disruption mitochond rial Ψ Release of cyt.c 12 h 0h 2h 10 h 6h 12h 18h 24h
28 Apoptotic signalling: CH3 Extrinsic pathway Fas TNF-α Intrinsic pathway Mitochondria caspase 8 Lysosome O H 2N R 1 O HO OH R O O 2 H 2N NH 2 Proteasome caspase 3 (6-7) OH H 3C HN Bax caspase 9 Apoptosome Cytochrome c Golgi Endoplasmic Reticulum D nucleus
29 PI.4. Time-sequence of the development of apoptosis and caspase-3 activity: 1 mm 2 mm control 2 mm 3 mm 1 mm 3 mm Caspase-3 activity (% of control) Lysosomal destabilization * * * * * Time (hours) Disruption Mitochondrial Ψ Release of cyt.c 12 h % of apoptotic cells (DAPI) Caspase-3 activation 24h * * * Time (hours) Nuclear fragmentation 0h 2h 10 h 6h 12h 18h 24h
30 3. RESULTS : PART II Is able to destabilize membrane? Mather and Rottenberg 2001 Biochem Biophys Acta 1503: Van Bambeke et al., 1993 Eur J Pharmacol 247:
31 PII. Mimicking lysosomes and mitochondria : CHO PC SM PI CL SUV: Small Unilamellar vesicles Diameter: nm LYSO 5.4 Mimic the lysosomal membrane OUTER MITO 7.4 Mimic the outer mitochondrial membrane INNER MITO 7.4 Mimic the inner mitochondrial membrane 33.3 % 24.2 % 24.2 % 18.3 % % 24.2 % 24.2 % 18.3 % % 24.2 % 24.2 % % CHO: Cholesterol; PC: Phosphatidylcholine; SM: Sphingomyelin; PI: Phosphatidylinositol; CL: Cardiolipin
32 PII. Ability of gentamicin to destabilize liposomes : Lysosome Outer Mitoch Inner Mitoch % of calcein released mM PI (Lysosomes) ph 5.4 > PI (outer mitochondria) ph 7.4 > Cardiolipin (inner mitochondria) ph Time (hours)
33 3. RESULTS : PART III Is able to initiate apoptotic signalling if localized in the cytoplasm? Lysosome Apoptosis
34 Delivery of inside cellular cytosol Definition of Electroporation (EP): designates the use of SHORT HIGH VOLTAGE PULSE to OVERCOME the BARRIER of the CELL MEMBRANE This rupture is TRANSIENT and REVERSIBLE Lysosome?? Mitochondria Apoptotic cell death
35 PIII.1. EP cells showed apoptosis with lower concentration of Incubated cells Electroporated cells Incubation tme : 24 hours c 20 Apoptotic cells (%) b b f * * * f d a a d d a e e e e e e e mm mg/l gentamicin extracellular concentration
36 PIII.2. Apoptosis versus necrosis: a question of concentration in both cases (EP versus Inc) Electroporated cells Incubated cells Apoptotic cells Necrotic cells Apoptotic cells Necrotic cells 20 Incubation time : 24 hours Incubation time : 24 hours 80 Apoptotic cells (%) mm 1 mm LDH release (%) Apoptotic cells (%) mM 4mM LDH release (%) mm mm mg/l mg/l gentamicin extracellular concentration gentamicin extracellular concentration
37 How cytosolic induces apoptotic signalling? Electroporation of Low amount of cytosolic Intrinsic pathway about times than those needed in incubated cells (10-15 mg/l) Cytosolic apoptotic target? Bax Ψ m Cytochrome c Mitochondria Bax PTP Cytochrome c Apoptosome Nucleus D caspase 3 (6-7) caspase 9
38 PIII.3 Increase in Bax content after incubation or after electroporation of in LLC-PK1 cells Electroporated cells Incubated cells Bax 21kDa OD (% of control OD) mm mg/l Incubation time : 8 hours
39 Increase in Bax cellular content Bax Ubiquitinated Bax 3. Decrease degradation Increase transcription 1. Inhibitors proteasome Proteasomal degradation Increase traduction 2. Bax
40 PIII.4. Increase of ubiquitinated Bax content after incubation or after electroporation of in LLC-PK1 cells IP: Bax IB: Ubiquitinated-protein Electroporated cells Incubated cells Ubiquitinated Bax OD (% of control OD) OD (% of control OD) gentamicin extracellular concentration 0 2 mm mg/l Incubation tme : 8 hours
41 4.ERAL CONCLUSION AND PERSPECTIVES (1) Apical membrane Lumen- urine Endocytic Route Golgi 8h Bax Lysosomal destabilization Mitochondria 2h 10h Endoplasmic reticulum Cyt c 12h 24h Nuclear fragmentation Proteasome Nucleus Caspase-3 24h Basolateral membrane Blood
42 4. ERAL CONCLUSION AND PERSPECTIVES (2) Lipsky et al., 1982 Cronin et al., 1982 Schwertz et al., 1984 Levi et al., 1990 Apical membrane Lumen- urine Kozek et al., 1974 Houghton et al., 1976 Watanabe et al., 1978 Silverblatt et al., 1979 Hostetler et al., 1982 Endocytic Route Laurent et al., 1982 Viotte et al., 1982 Fillastre et al., 1983 Golgi Lysosomes Powell et al., 1983 Williams et al., 1985 Chatterjee et al., 1987 Mingeot-Leclercq et al., 1988 Vera-Roman et al., 1975 Mingeot-Leclercq et al., 1990a,b Bennett et al., 1988 Okuda et al., 1992 Sandoval et al., 1998 Endoplasmic reticulum Mingeot-Leclercq et al.,1991 Sundin et al., 2001 Vera-Roman et al., 1975 Mitochondria Walker et al., 1987 Rustenbeck et al., 1998 Nucleus Proteasome Basolateral membrane Blood
43 4.1 Short term perspectives Lysosomal destabilization Cytosolic Mitochondria permeabilization Ability of to destabilize directly mitochondria Mather and Rottenberg, 2001 Proteasome What about interaction with proteasomal precursor protein PSB-9 Horibe et al., 2004 Endoplasmic reticulum What about their ribosomal target? Ryu et al., 2001 Ryu and Rando, 2002 Apoptotis
44 4.2. Long term perspectives Streptomycin Kanamycin Amikacin isepamicin «New aminoglycosides» Netilmicin Neomycin Tobramycin Gentamicin isolated from Micromonospora purpurea Based on the identification of the exact interactions between AG with the bacterial ribosome New LESS TOXIC aminoglycosides
45 And finally Lysosomes. Shield? Weapons?.in gentamicin-induced apoptosis?
46 Acknowledgment - Pr M-P Mingeot-Leclercq, Pr P-M Tulkens and Dr F. Van Bambeke - Pr Devuyst, Pr Feron, Pr Hermans and Pr Renaud -PrOrtiz andprde Broe - Dr P. Van der Smissen and Pr Courtoy - Dr P. Jacquemin -Dr C. Dax - Dr Y. Jossin and Pr Goffinet - E. Delbecq, N. Duarte, G. Thirion, G Van der Essen. - N. Aguilera, M-C. Cambier, F. Renoird, M. Vergauwen - N. Mesaros and Dr N. Caceres - all the new and old «FACMists» -
Aminoglycosides: What have we learned about toxicity?
 Aminoglycosides: What have we learned about toxicity? Paul M. Tulkens, MD, PhD Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology Unit & Center for Clinical Pharmacy Catholic University of Louvain, Brussels, Belgium
Aminoglycosides: What have we learned about toxicity? Paul M. Tulkens, MD, PhD Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology Unit & Center for Clinical Pharmacy Catholic University of Louvain, Brussels, Belgium
Aminoglycosides. Not orally absorbed. Interact with negatively charged lipopolysaccharide on Gram- cell wall. Aminoglycoside properties
 Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
life-threatening infections
 Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
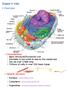 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Cell morphology. Cell organelles structure and function. Chapter 1: UNIT 1. Dr. Charushila Rukadikar
 UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Gentamicin Causes Apoptosis at Low Concentrations in Renal LLC-PK 1 Cells Subjected to Electroporation
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 2006, p. 1213 1221 Vol. 50, No. 4 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.50.4.1213 1221.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 2006, p. 1213 1221 Vol. 50, No. 4 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.50.4.1213 1221.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ZIN EN ONZIN VAN ANTIBIOTICASPIEGELS BIJ NEONATEN
 ZIN EN ONZIN VAN ANTIBIOTICASPIEGELS BIJ NEONATEN Anne Smits Fellow neonatologie UZ Leuven Use of antibiotics in neonates 50 European hospitals 23 non-european hospitals Countries n = 14 n = 9 Pediatric
ZIN EN ONZIN VAN ANTIBIOTICASPIEGELS BIJ NEONATEN Anne Smits Fellow neonatologie UZ Leuven Use of antibiotics in neonates 50 European hospitals 23 non-european hospitals Countries n = 14 n = 9 Pediatric
Endomembrane system 11/1/2018. Endomembrane System. Direct physical continuity. Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles. Outer Nuclear envelope
 Endomembrane system Endomembrane System Outer Nuclear envelope Direct physical continuity Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles Endoplasmic reticulum BUT membranes are not identical in structure and
Endomembrane system Endomembrane System Outer Nuclear envelope Direct physical continuity Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles Endoplasmic reticulum BUT membranes are not identical in structure and
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM. BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled
 Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
AMINOGLYCOSIDES TDM D O N E B Y
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES TDM DONE BY: SARA ALARFAJ 2014 OUTLINE Introduction about Aminoglycosides. Spectrum/uses. TDM Aminoglycosides TDM Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics. Dosing in AG. Sampeling time and Monitoring.
AMINOGLYCOSIDES TDM DONE BY: SARA ALARFAJ 2014 OUTLINE Introduction about Aminoglycosides. Spectrum/uses. TDM Aminoglycosides TDM Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics. Dosing in AG. Sampeling time and Monitoring.
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 #19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
Aminoglycosides John A. Bosso, Pharm.D.
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES Therapeutics/PHRMP-73 Aminoglycoside Mechanism of Action Aminoglycosides bind to 30s ribosomal subunit resulting in mistranslation of mrna thus disrupting protein synthesis. They are rapidly
AMINOGLYCOSIDES Therapeutics/PHRMP-73 Aminoglycoside Mechanism of Action Aminoglycosides bind to 30s ribosomal subunit resulting in mistranslation of mrna thus disrupting protein synthesis. They are rapidly
TDM of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
 TDM Lecture 3 5 th Stage TDM of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics The aminoglycoside antibiotics are widely used for the treatment of gram-negative infections, often in combination with a β-lactam antibiotic
TDM Lecture 3 5 th Stage TDM of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics The aminoglycoside antibiotics are widely used for the treatment of gram-negative infections, often in combination with a β-lactam antibiotic
The Biochemistry of apoptosis
 The Biochemistry of apoptosis 1 1 The apoptosis is composed of multiple biochemical events 2 2 Biochemical, cellular, and molecular events in Apoptosis 1. Membrane blebbing; phosphatidyl serine exposure
The Biochemistry of apoptosis 1 1 The apoptosis is composed of multiple biochemical events 2 2 Biochemical, cellular, and molecular events in Apoptosis 1. Membrane blebbing; phosphatidyl serine exposure
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine
 Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
INHIBITION OF POLYPHOSPHOINOSITIDE PHOSPHODIESTERASE BY AMINOGLYCOSIDE ANTIBIOTICS*
 Neurochemical Research, Vol. 10, No. 8, 1985, pp. 1019-1024 INHIBITION OF POLYPHOSPHOINOSITIDE PHOSPHODIESTERASE BY AMINOGLYCOSIDE ANTIBIOTICS* Lvcxo A. A. VAN ROOIJEN 1 AND BERNARD W. AGRANOFF 2 Neuroscience
Neurochemical Research, Vol. 10, No. 8, 1985, pp. 1019-1024 INHIBITION OF POLYPHOSPHOINOSITIDE PHOSPHODIESTERASE BY AMINOGLYCOSIDE ANTIBIOTICS* Lvcxo A. A. VAN ROOIJEN 1 AND BERNARD W. AGRANOFF 2 Neuroscience
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: immunoprecipitation with anti-casr antibody The Casr protein was expressed in transiently transfected HEK cells. Cell lysates from HEK cells were subjected
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: immunoprecipitation with anti-casr antibody The Casr protein was expressed in transiently transfected HEK cells. Cell lysates from HEK cells were subjected
Enzymuria determination in children treated with aminoglycosides drugs
 Human & Experimental Toxicology (2008) 27: 879 882 www.het.sagepub.com treated with aminoglycosides drugs A Mohammadi-Karakani 1,2, S Asgharzadeh-Haghighi 1, M Ghazi-Khansari 2, A Seyed-Ebrahimi 1, A Ghasemi
Human & Experimental Toxicology (2008) 27: 879 882 www.het.sagepub.com treated with aminoglycosides drugs A Mohammadi-Karakani 1,2, S Asgharzadeh-Haghighi 1, M Ghazi-Khansari 2, A Seyed-Ebrahimi 1, A Ghasemi
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics. Question No. 1 of 10. Question. Feedback. Question
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Gentamicin-induced apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells: Involvement of lysosomes and mitochondria
 Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 206 (2005) 321 333 www.elsevier.com/locate/ytaap Gentamicin-induced apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells: Involvement of lysosomes and mitochondria Hélène Servais a, Patrick Van
Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 206 (2005) 321 333 www.elsevier.com/locate/ytaap Gentamicin-induced apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells: Involvement of lysosomes and mitochondria Hélène Servais a, Patrick Van
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7)
 Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Functions of Lysosomes
 Functions of Lysosomes Intro - Degradation of cell components -Cell death -Autophagy 1st - Exocytosis / Secretory pathway - Calcium signalling 2nd O BayDH., (2009) Phosphatidylcholine Intro Phosphatidylcholine
Functions of Lysosomes Intro - Degradation of cell components -Cell death -Autophagy 1st - Exocytosis / Secretory pathway - Calcium signalling 2nd O BayDH., (2009) Phosphatidylcholine Intro Phosphatidylcholine
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes. Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment.
 Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER. Dr. S. P. Pattanayak
 APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
B.4B Cellular Processes
 B.4B Cellular Processes Picture Vocabulary homeostasis The process of maintaining a constant state of balance cell membrane Cell part surrounding the cytoplasm and is also a barrier between the inside
B.4B Cellular Processes Picture Vocabulary homeostasis The process of maintaining a constant state of balance cell membrane Cell part surrounding the cytoplasm and is also a barrier between the inside
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Reduction of Experimental Gentamicin Nephrotoxicity in Rats by Dietary Calcium Loading
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 1982, p. 508-512 0066-4804/82/090508-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 22, No. 3 Reduction of Experimental Gentamicin Nephrotoxicity
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 1982, p. 508-512 0066-4804/82/090508-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 22, No. 3 Reduction of Experimental Gentamicin Nephrotoxicity
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
B. Incorrect! Peginterferon α-2a is used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and may be preferable to interferon- α.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 24: Antibiotics, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs Question No. 1 of 10 1. reduces the replication of influenza A and B viruses by inhibiting viral neuraminidase. Question #01
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 24: Antibiotics, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs Question No. 1 of 10 1. reduces the replication of influenza A and B viruses by inhibiting viral neuraminidase. Question #01
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Na+,K+-ATPase Activities in Renal Tissues of Rats
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 1983, p. 815-818 0066-4804/83/110815-04$02.00/0 Copyright C 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 5 Effect of Gentamicin Treatment on Adenylate
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 1983, p. 815-818 0066-4804/83/110815-04$02.00/0 Copyright C 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 5 Effect of Gentamicin Treatment on Adenylate
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
(A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids. A. Incorrect! Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have cell membranes.
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Name: Per/row: Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology
 Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
Potential biomarkers for chronic kidney disease. Diana Lebherz-Eichinger 3rd of october
 Potential biomarkers for chronic kidney disease Diana Lebherz-Eichinger 3rd of october Background Course of Chronic kidney disease Increased cell death and counterregulation Cytokeratin-18 as biomarker
Potential biomarkers for chronic kidney disease Diana Lebherz-Eichinger 3rd of october Background Course of Chronic kidney disease Increased cell death and counterregulation Cytokeratin-18 as biomarker
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae.
 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Objectives: Prof.Dr. H.D.El-Yassin
 Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Significance of p53 dynamics in regulating apoptosis in response to ionizing radiation, and polypharmacological strategies Bing Liu 1,, Divesh Bhatt 1,, Zoltan N. Oltvai 2, Joel
Supplementary Information Significance of p53 dynamics in regulating apoptosis in response to ionizing radiation, and polypharmacological strategies Bing Liu 1,, Divesh Bhatt 1,, Zoltan N. Oltvai 2, Joel
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death
 Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope.
 1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope. Select your answers from the list below. 10x 40x 100x light microscope... x transmission
1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope. Select your answers from the list below. 10x 40x 100x light microscope... x transmission
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
2) What component of plasma assists in the transport of bilirubin? 2) A) Enzymes B) Calcium C) Hydrogen D) Albumin Answer: D
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which two populations account for the greatest difference in reference intervals? 1) A) Whites
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which two populations account for the greatest difference in reference intervals? 1) A) Whites
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane
 Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
MECHANISM AND MODE OF HORMONE ACTION. Some definitions. Receptor: Properties of receptors. PRESENTED BY MBUNKUR GLORY NKOSI.
 MECHANISM AND MODE OF HORMONE ACTION. PRESENTED BY MBUNKUR GLORY NKOSI. OUTLINE. Introduction Some definitions Hormone secretion, transport, and clearance from the blood. Feedback control of hormone secretion.
MECHANISM AND MODE OF HORMONE ACTION. PRESENTED BY MBUNKUR GLORY NKOSI. OUTLINE. Introduction Some definitions Hormone secretion, transport, and clearance from the blood. Feedback control of hormone secretion.
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Anatomy & Physiology Lab Thurs! Fun again!
 Anatomy & Physiology Lab Thurs! Fun again! BI 121 Lecture 3 I. Announcements AEC Notes? aec.uoregon.edu/peer-notetaking II. Connections Q re: Homeostatic Model for BP? Active work! III.Cell Anatomy, Physiology
Anatomy & Physiology Lab Thurs! Fun again! BI 121 Lecture 3 I. Announcements AEC Notes? aec.uoregon.edu/peer-notetaking II. Connections Q re: Homeostatic Model for BP? Active work! III.Cell Anatomy, Physiology
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids
 Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222
 Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222 Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collec=on of ma>er that can live Cell structure is correlated to cellular
Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222 Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collec=on of ma>er that can live Cell structure is correlated to cellular
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis
 Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Journey to the World of Cells
 Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Renal Pharmacology of Netilmicin
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGZNTS AND CHEMOTHBRAPY, May 1977, p. 821-825 Vol. 11, No. 5 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Renal Pharmacology of Netilmicin PETER J. S. CHIU,* GEORGE
ANTIMICROBIAL AGZNTS AND CHEMOTHBRAPY, May 1977, p. 821-825 Vol. 11, No. 5 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Renal Pharmacology of Netilmicin PETER J. S. CHIU,* GEORGE
