Brief Report. n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Decrease Anxiety Feelings in a Population of Substance Abusers
|
|
|
- Mariah York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brief Report n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Decrease Anxiety Feelings in a Population of Substance Abusers Laure Buydens-Branchey, MD and Marc Branchey, MD Abstract: There is mounting evidence that low levels of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play a role in the pathophysiology of a number of psychiatric disorders. Preclinical studies have shown that n-3 PUFAs decrease anxietylike behaviors, but there is a paucity of information about their effects on anxiety in humans. In light of our observation that substance abusers have poor dietary habits and the strong association between anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, the possibility that the administration of supplements of n-3 PUFAs would decrease the anxiety level of a group of substance abusers was explored. Thirteen patients were given on a daily basis capsules containing 3 g of n-3 PUFAS (eicosapentaenoic acid + docosahexaenoic acid). Eleven patients received similarly looking placebo capsules containing vegetable oil. The trial was double-blind, randomized, and lasted 3 months. A scale assessing anxiety feelings was administered at baseline and on a monthly basis thereafter. Six PUFA group patients and 8 placebo group patients were followed for an additional 3 months after treatment discontinuation and administered the same questionnaire monthly. Patients who received n-3 PUFAs for 3 months showed a progressive decline in anxiety scores. This was not the case for patients who received placebos. A comparison of the 2 groups was significant (P = 0.010). Anxiety scores remained significantly decreased in the PUFA group for 3 months after treatment discontinuation. A comparison of the 2 groups followed for 6 months was also significant (P = 0.042). In conclusion, these preliminary data indicate that n-3 PUFA supplementation could be beneficial in the treatment of some patients with anxiety disorders. (J Clin Psychopharmacol 2006;26: ) Preclinical studies have indicated that the administration of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) decreases anxietylike behaviors in rodents. Interleukin 1b, the most potent proinflammatory cytokine, was found to induce an inflammatory sickness response, stress and anxietylike behaviors, and a stimulation of corticosterone secretion in rats. These changes were significantly reversed by the New York Harbor Healthcare System, Brooklyn Campus, Brooklyn, NY. Received May 8, 2006; accepted after revision September 18, This work was supported by grant R01-DA15360 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Laure Buydens-Branchey, MD, New York Harbor Healthcare System, Brooklyn Campus, 151/BK, 800 Poly Place, Brooklyn, NY lbuydens@worldnet.att.net. Copyright n 2006 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ISSN: /06/ DOI: /01.jcp f1 administration of the long-chain n-3 PUFA, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3). 1,2 Although human studies have shown that n-3 supplementation was beneficial in a variety of psychiatric disorders, including depression, aggression, attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), borderline personality disorder, and dementia, 3,4 there is a limited amount of information about their effects in anxiety disorders. Yehuda et al who investigated the effects of the administration of a mixture of n-3 and n-6 PUFAs on test anxiety in college students observed an improvement in variables associated with this type of anxiety (ie, appetite, mood, concentration, fatigue, academic organization, and sleep). They also observed a decrease in elevated cortisol level. 5 Fux et al, 6 on the other hand found EPA to be ineffective in a preliminary study of 11 patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. In light of the reported effectiveness of EPA in decreasing anxietylike behaviors in preclinical studies and of the scarcity of human data, a double-blind, placebocontrolled trial of n-3 PUFAs on anxiety symptoms in humans seemed warranted. It could be hypothesized that individuals whose n-3 PUFAs intake is deficient would more readily respond to n-3 supplementation than those whose intake is closer to recommended amounts. Depressive disorders and homicides, believed to be associated with n-3 PUFA deficiencies, are high in countries where the consumption of foods rich in these nutrients, such as fish, is low. 7,8 We had observed that the diets of substance abusers are less than optimal. Moreover, the study of patterns of comorbidity between psychiatric conditions indicates that there is a strong association between anxiety disorders and substance use disorders. 9 For these reasons, the subjects selected as participants in this study were substance abusers. They were treated for 3 months with a combination of EPA and another long-chain n-3 PUFA, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3), because the bulk of the literature so far points to the efficacy of such a combination in improving psychiatric symptoms, whereas DHA alone appears to be less effective. It was hypothesized that patients consumption of n-3 PUFA containing foods before the start of the study would be below recommended amounts and that the administration of long-chain n-3 PUFA supplements would decrease their anxiety level. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients Twenty-four men attending the New York Harbor Healthcare System (Brooklyn site) substance abuse clinics Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Volume 26, Number 6, December
2 Buydens-Branchey and Branchey Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Volume 26, Number 6, December 2006 were selected for participation in this study. They were included if it was determined that they did not present any major physical illness on the basis of a physical examination and after the administration of a battery of laboratory tests. Patients were interviewed by a psychiatrist and administered the Addiction Severity Index questionnaire. 10 The Addiction Severity Index explores the following areas: alcohol and drug use, psychiatric status, family history of alcohol, drug, and psychiatric problems, family and social relationships, medical status, legal status, and employment/support status. Patients were included if they did not present or did not have a history of schizophrenia, major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, mental retardation, or dementia. If subjects were judged to be appropriate for enrollment, written informed consent was obtained after a description of the study. The trial was double blind, and assignment to the active substance group or to the placebo group was random. Initial Assessment The following assessments covering the year and the month preceding the study entry were obtained: nature of the substances used, amount of each substance used, and frequency of use. A diet questionnaire covering the month preceding the study entry was obtained. This questionnaire was an adaptation of the National Institutes of Health Diet History Questionnaire. 11 Based on the results of this questionnaire, each patient s energy (kilocalories) and n-6 and n-3 PUFA intake were calculated, using the US Department of Agriculture National Nutrient Database Reference. 12 A modified version of the Profiles of Mood States (POMS) 13 was administered. The POMS is a selfreport questionnaire that requires subjects to rate the intensity of 65 mood items on a 5-point scale. Ratings are combined into 6 scores assessing vigor, depression, tension, anger, confusion, and fatigue. It was modified for use in this study because we had observed that when patients attending our clinics were asked to make 325 choices when given the complete POMS, they quickly lost interest in the task and gave unreliable answers. The modified POMS version was limited to the 36 items comprising the anger, tension, and depression subscales, with the following 2 choices for each item: present or absent. This reduced the total number of choices to 72, making the questionnaire more readily acceptable. Changes in tension scores only are the topic of the present report. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid and Placebo Treatment Patients were treated for 3 months. They received either capsules containing n-3 PUFAs or placebo capsules. Both types of capsules were purchased from Nordic Naturals (Watsonville, Calif). The PUFA capsules contained 450 mg of EPA, 100 mg of DHA, and 50 mg of other n-3 PUFAs (triglycerides). The placebo capsules contained vegetable oil (soybean). Both types of capsules contained small amounts of lemon oil to mask their taste. Patients were advised to take 5 capsules each day. Those taking the active substances were thus given a daily amount of 3 g of long-chain n-3 PUFAs. Follow-up Assessments Thirteen patients assigned to the PUFA group and 11 patients assigned to the placebo group were available for follow-up during the 3-month treatment period. One, 2, and 3 months after the start of the study, dietary questionnaire and modified POMS covering the 1-month period that elapsed between the 2 interviews were administered to all patients. A subset of 6 patients in the PUFA group and 8 patients in the placebo group was followed for an additional period of 3 months after treatment had been discontinued and administered the questionnaires on a monthly basis. This last group of 14 patients was thus followed for a total of 6 months. To ensure compliance, patients were asked to bring back their empty capsule containers at the time of their monthly interviews before receiving a new batch of capsules. They were asked whether they had experienced any side effect after the ingestion of the capsules. Statistical Analysis Comparisons of the 2 patient groups demographic and baseline dietary data were made with 2-tailed Student t tests, x 2 tests with Yates continuity correction or Fisher exact tests, as appropriate. Comparisons of the 2 patient groups tension scale baseline values were done with Student t tests. Comparisons of the changes over time in the tension scale of the patient groups were done with repeated measures analyses of covariance (ANCOVAs) with baseline values as covariates. Because of the small number of study participants and the resulting low statistical power of the analyses, effect sizes ( f ) for the differences between the 2 groups were also calculated. Small, medium, and large effect sizes correspond to f values of 0.10, 0.25, and 0.50, respectively. 14 RESULTS Patient Characteristics The PUFA and placebo groups did not differ significantly in age (52.0 ± 7.0 vs 50.3 ± 7.0 years). There were no significant differences either in marital status, educational level, employment status, or types of drugs used for a period of 1 year before the start of the study. Drugs used were alcohol, cocaine, and heroin, taken either alone or in various combinations. Nine patients (5 in the PUFA group and 4 in the placebo group) were maintained on doses of methadone ranging from 70 to 120 mg. These doses remained stable throughout the study. Five patients in each group were treated with antidepressants. Doses of antidepressants remained stable throughout the study. Side Effects None of the study participants reported side effects except for 3 patients who stated having loose stools. Dietary Data Dietary data are shown in Table 1. The mean daily fish intake of the 24 study participants was 35.7 ± 18.6 g. Their mean daily n-6 PUFA intake was 16.0 ± 8.8 mg, and their 662 n 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
3 Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Volume 26, Number 6, December 2006 n-3 PUFAs and Anxiety TABLE 1. Baseline Daily Calories, Fish, and PUFA Intakes All Patients (n = 24) n-3 PUFAs (n = 13) Placebo (n = 11) P Energy (kcal) 2286 ± ± ± 1401 NS Fish (g) 35.7 ± ± ± 16.4 NS Total PUFAs (g) ± ± ± 9.38 NS n-6 PUFAs (g) Total ± ± ± 8.70 NS Short chain (C18) ± ± ± 8.56 NS Long chain (C20, C22) 0.24 ± ± ± 0.28 NS n-3 PUFAs (g) Total 1.45 ± ± ± 0.78 NS Short chain (C18) 1.30 ± ± ± 0.71 NS Long chain (C20, C22) 0.15 ± ± ± 0.08 NS Daily intake of long-chain n-3 PUFAs as percentage of ISSFAL recommended intake 30 ± ± ± 16 NS Values are means ± SD. Comparisons between the PUFA and placebo groups were made with 2-tailed Student t tests. mean daily n-3 PUFA intake was 1.45 ± 0.86 mg. Patients consumed thus 11 times more n-6 than n-3 PUFAs. There were no significant differences between the PUFA and control groups in mean daily energy (kilocalories), mean daily amounts of fish, mean daily amounts of total, shortchain, or long-chain n-6 PUFAs, and total, short-chain, or long-chain n-3 PUFAs consumed during the month preceding the start of the study. The fish most frequently consumed were catfish, whiting, flounder, or canned tuna. Calculations of differences between the daily intake of 500 mg of longchain n-3 PUFAs, recommended by the International Society of the Study of Fatty Acids and Lipids (ISSFAL), 15 and patients actual daily intake did not reveal differences between the groups but showed that both groups fell short of the recommended intake. The PUFA group patients consumed on average 27% and the placebo group 33% of this recommended intake. Effects of n-3 PUFAs and Placebo on Tension Scale Scores Figure 1 illustrates baseline and changes in the tension scale scores during the 3-month administration of n-3 PUFAs or placebo capsules. The difference between baseline values assessed by t test was not significant. The figure shows a decline in tension scores in the PUFA group but not in the placebo group. A comparison of the 2 groups by repeated measures ANCOVA (with baseline values as covariates) revealed a significant difference (F 1,21 = 8.070, P = 0.010) and a large effect size ( f = 0.62). Figure 2 illustrates baseline and changes in the tension scale scores of the patients who were followed for 6 months. The difference between baseline values assessed by t test was not significant. Scores remained decreased in patients assigned to the PUFA group from month 4 through month 6 after treatment discontinuation. A comparison of the 2 patient groups who were followed for 6 months by repeated measures ANCOVA (with baseline values as covariates) revealed a significant difference (F 1,11 = 5.269, P = 0.042) and a large effect size ( f = 0.69). DISCUSSION In this study, the daily administration of 3 g of longchain n-3 PUFAs (EPA + DHA) for a period of 3 months significantly decreased scores on a tension scale in a group of substance abusers. These scores did not return to pretreatment levels after treatment discontinuation. Reasons for the persistence of the antianxiety effects after discontinuation of n-3 supplementation are not known. One possibility FIGURE 1. Tension scale scores (mean and SEM) of substance abusers during a 3-month administration of n-3 PUFAs or placebo. A comparison of the scores of the 2 patient groups by a repeated measures ANCOVA (with baseline values as covariates) revealed a significant difference (P = 0.010). The effect size was large (f = 0.62). n 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 663
4 Buydens-Branchey and Branchey Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Volume 26, Number 6, December 2006 FIGURE 2. Tension scale scores (mean and SEM) of substance abusers during a 3-month administration of n-3 PUFAs or placebo and a follow-up period of 3 months (months 4 6), during which no capsules were administered. A comparison of the scores of the 2 patient groups by a repeated measures ANCOVA (with baseline values as covariates) revealed a significant difference (P = 0.042). The effect size was large (f = 0.69). is that, in the course of the present study, patients intake of long-chain n-3 PUFAs that were approximately 20 times larger than those provided by their usual diet induced CNS changes that were not reversed immediately after the interruption of treatment. It is also possible that some of the fatty acids surplus was stored in fatty tissues and continued to leach out of these stores for a few months. On the basis of epidemiological and cross-sectional studies, there is little argument that n-3 deficiencies are associated with astonishingly diverse psychiatric disorders that include, but are not limited to, depression, aggression, ADHD, borderline personality disorder, schizophrenia, autism, dementia, and substance abuse. 3,4,16,17 Interventional studies on the whole support conclusions derived from epidemiological and cross-sectional studies. Supplements of EPA, a combination of EPA and DHA, and, in some studies, DHA alone were found to improve the psychiatric symptoms of patients with mood disorders, ADHD, and schizophrenia. 3,4 The present results should be considered as preliminary. If confirmed by other studies, anxiety disorders could be added to the list of disorders affected by n-3 PUFAs. The apparent multitude of PUFA effects could be understood in light of their extraordinary diversity of actions. They are divided into 2 major families, the n-3 and the n-6 families. EPA and DHA are the main long-chain derivatives of the precursor ALA (a-linolenic acid, 18:3n-3). Arachidonic acid (AA, 20:4n-6) is the main long-chain derivative of the n-6 series precursor linoleic acid (18:2 n-6). Some PUFAs, mostly AA and DHA, and, to a lesser extent, EPA are components of neuronal membranes phospholipids and modulate membranes dynamic properties. Changes in the composition of these phospholipids can affect neurotransmitter release, neurotransmitter receptor function, ion channel function, and enzyme activity. Upon stimulation, both n-6 and n-3 PUFAs are cleaved from membrane phospholipids under the influence of phospholipases and are converted via different pathways to mediators that have opposing effects. Arachidonic acid derived mediators are vasoconstrictive, proaggregant, and proinflammatory, whereas EPA-derived mediators have vasodilating, antiaggregating, and anti-inflammatory actions. Finally, PUFAs and their metabolites regulate gene transcriptions. One could wonder why EPA, which is not abundant in neuronal membranes, appears more effective than DHA alone. It has been suggested that EPA could play a role in brain function by counteracting the AA-mediated signaling. It could, for example, competitively attenuate the formation of the n-6 derived eicosanoids that mediate immune-inflammatory responses that have been linked to the pathophysiology of depressive disorders, bipolar disorders, and schizophrenia. 18,19 EPA could also counteract the vasoconstrictive effects of AA, 3 thereby increasing blood flow in the brain. Recommendations for the intake of n-3 PUFAs necessary to cover human requirements are still in the process of being determined and will have to await the completion of additional trials. These recommendations vary from country to country and depend in part on the amounts of n-6 PUFAs present in different diets. Based on a review of major epidemiological studies conducted in the United States, the daily intake of EPA and DHA recommended by ISSFAL 15 for cardiovascular health is 500 mg. Participants in the present study consumed only, on average, 149 mg of long-chain n-3 PUFAs daily or 30% of the ISSFAL recommendation. Their intake of EPA and DHA was most likely even lower because in our calculations of long-chain n-3 PUFAs, docopentaenoic acid (22:5n-3) was included. This intake, albeit low, lies however within the range of mean long-chain n-3 PUFAs intake found in other population samples in this country, 20,21 indicating that large segments of the US population probably do not consume adequate amounts of n-3 PUFAs. Our interpretation of the data should be taken in the context of our study s possible limitations. The number of participants was small, and some of them received medications. It should be pointed out that medication doses remained stable during the study and that a number of other studies of the efficacy of n-3 PUFAs supplementation in mood disorders involved individuals on standard medication who experienced further improvements that were attributed to the PUFA supplements. In conclusion, in this preliminary study, the daily administration of 3 g of long-chain n-3 PUFAs for a period of 3 months significantly decreased anxiety feelings in comparison with the administration of a placebo. This decrease persisted for 3 months after treatment discontinuation. Data on the efficacy of n-3 PUFAs in anxiety disorders are almost nonexistent. The present data need to be replicated and could lead to the use of treatments or treatment adjuncts in some individuals presenting anxiety symptoms and whose n-3 PUFA intakes are deficient. 664 n 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
5 Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Volume 26, Number 6, December 2006 n-3 PUFAs and Anxiety REFERENCES 1. Song C, Li X, Leonard BE, et al. Effects of dietary n-3 or n-6 fatty acids on interleukin-1beta induced anxiety, stress, and inflammatory response in rats. J Lipid Res. 2003;44: Song C, Leonard BE, Horrobin DF. Dietary ethyl-eicosapentaenoic acid but not soybean oil reverses central interleukin-1 induced changes in behavior, corticosterone and immune response in rats. Stress. 2004;7: Alessandri JM, Guesnet P, Vancassel S, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the central nervous system: evolution of concepts and nutritional implications throughout life. Reprod Nutr Dev. 2004;44: Young GS, Conquer J. Omega-3 fatty acids and neuropsychiatric disorders. Reprod Nutr Dev. 2005;45: Yehuda S, Rabinovitz S, Mostofsky DI. Mixture of essential fatty acids lowers test anxiety. Nutr Neurosci. 2005;8: Fux M, Benjamin J, Nemets B. A placebo-controlled cross-over trial of adjunctive EPA in OCD. J Psychiatr Res. 2004;38: Hibbeln JR. Fish consumption and major depression. Lancet. 1998; 351: Hibbeln JR, Salem N Jr. Omega-3 fatty acids and psychiatric disorders. Current status of the field. In: Mostofosky D, Yehuda S, Salem N Jr, eds. Fatty Acids: Physiological and Behavioral Functions. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2001: Merikangas KR, Metha RL, Molnar BE, et al. Comorbidity of substance use disorder with mood and anxiety disorders: results of the International Consortium in Psychiatric Epidemiology. Addict Behav. 1998; 23: McLellan AT, Kushner H, Metzger D, et al. The fifth edition of the Addiction Severity Index. J Subst Abuse Treat. 1992;9: National Cancer Institute, US National Institutes of Health. Diet History Questionnaire. Available at: Accessed US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 18. [Nutrient Data Laboratory Home Page]. Available at: usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp. Accessed McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. Manual for the Profile of Mood States. San Diego, CA: Educational Testing Service; Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids and Lipids. Recommendations for Dietary Intake of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Healthy Adults. Brighton, UK: International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids and Lipids; Buydens-Branchey L, Branchey M, McMakin DL, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid status and aggression in cocaine addicts. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2003;71: Buydens-Branchey L, Branchey M, McMakin DL, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid status and relapse vulnerability in cocaine addicts. Psychiatry Res. 2003;120: Maes M, Stevens WJ, Declerck LS, et al. Significantly increased expression of T-cell activation markers (interleukin-2 and HLA-DR) in depression: further evidence for an inflammatory process during that illness. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1993;17: Maes M, Bosmans E, Calabrese J, et al. Interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 in schizophrenia and mania: effects of neuroleptics and mood stabilizers. J Psychiatr Res. 1995;29: Ma J, Folsom AR, Shshar E, et al. Plasma fatty acid composition as an indicator of habitual dietary fat intake in middle-aged adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995;62: Irribaren C, Markovitz JH, Jabobs DR Jr, et al. Dietary intake of n-3, n-6 fatty acids and fish: relationship with hostility in young adults the CARDIA study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2004;58: n 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 665
Omega-3 fatty acids. Epidemiologic data suggest that people who consume diets rich. FOR psychiatric illness
 Omega-3 fatty acids FOR psychiatric illness Evidence suggests they may play a role in treating mood disorders HELEN D SOUZA FOR CURRENT PSYCHIATRY Mary Morreale, MD Assistant Professor Department of Psychiatry
Omega-3 fatty acids FOR psychiatric illness Evidence suggests they may play a role in treating mood disorders HELEN D SOUZA FOR CURRENT PSYCHIATRY Mary Morreale, MD Assistant Professor Department of Psychiatry
Pro-health effects of active substances of Omee3 med bars for proper growth and development of children.
 Pro-health effects of active substances of Omee3 med bars for proper growth and development of children. Presently, there is no doubt that essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)* omega-3 and omega-6
Pro-health effects of active substances of Omee3 med bars for proper growth and development of children. Presently, there is no doubt that essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)* omega-3 and omega-6
n Promotes a healthy mood 1 n Supports attention and learning 2 n Supports normal memory as we age 3
 n Promotes a healthy mood 1 n Supports attention and learning 2 n Supports normal memory as we age 3 n Protects nerve and brain cells from oxidative damage 4 Only with adequate intake of essential fatty
n Promotes a healthy mood 1 n Supports attention and learning 2 n Supports normal memory as we age 3 n Protects nerve and brain cells from oxidative damage 4 Only with adequate intake of essential fatty
The role of omega-3 fatty acids as a treatment for bipolar disorder
 The role of omega-3 fatty acids as a treatment for bipolar disorder Research into omega-3 fatty acids as a possible treatment for mood disorders is a new and interesting area of research Although research
The role of omega-3 fatty acids as a treatment for bipolar disorder Research into omega-3 fatty acids as a possible treatment for mood disorders is a new and interesting area of research Although research
There are three major types of omega-3 fatty acids that are ingested in foods and used by the body:
 Long-chain fatty acids (LC-PUFAs: ARA, DHA and EPA) AT A GLANCE Introduction LC-PUFAs or long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids are mainly found in the form of two families of conditionally essential fatty
Long-chain fatty acids (LC-PUFAs: ARA, DHA and EPA) AT A GLANCE Introduction LC-PUFAs or long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids are mainly found in the form of two families of conditionally essential fatty
: Overview of EFA metabolism
 Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition July, 2004;80:204 16
 1 Dietary intake of n 3 and n 6 fatty acids and the risk of prostate Cancer American Journal of Clinical Nutrition July, 2004;80:204 16 Michael F Leitzmann, Meir J Stampfer, Dominique S Michaud, Katarina
1 Dietary intake of n 3 and n 6 fatty acids and the risk of prostate Cancer American Journal of Clinical Nutrition July, 2004;80:204 16 Michael F Leitzmann, Meir J Stampfer, Dominique S Michaud, Katarina
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Athletics. Current Sports Medicine Reports July 2007, 6:
 Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Athletics 1 Current Sports Medicine Reports July 2007, 6:230 236 Artemis P. Simopoulos, MD The Center for Genetics, Nutrition and Health, Washington, DC, USA EIB exercise-induced
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Athletics 1 Current Sports Medicine Reports July 2007, 6:230 236 Artemis P. Simopoulos, MD The Center for Genetics, Nutrition and Health, Washington, DC, USA EIB exercise-induced
Omega-3 supplementation promotes key anti-inflammatory pathways that naturally support back, neck, and joint health and mobility
 n Promotes key anti-inflammatory pathways n Promotes joint mobility and flexibility n Is a natural adjunct to conventional therapies n Is safe for long-term use Omega-3 supplementation promotes key anti-inflammatory
n Promotes key anti-inflammatory pathways n Promotes joint mobility and flexibility n Is a natural adjunct to conventional therapies n Is safe for long-term use Omega-3 supplementation promotes key anti-inflammatory
Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE
 Page 1 of 6 Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE By Yousry Naguib, PhD Essential fatty acids (EFAs) must be obtained through the diet and cannot be synthesized by the human body. EFAs are
Page 1 of 6 Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE By Yousry Naguib, PhD Essential fatty acids (EFAs) must be obtained through the diet and cannot be synthesized by the human body. EFAs are
THE PROBLEM OMEGA 3. pure
 p2 THE PROBLEM Essential fatty acids (EFAs) are polyunsaturated fats that our bodies need but cannot produce. Therefore, they must be consumed through food or supplements. Omega 3 and Omega 6 are EFAs.
p2 THE PROBLEM Essential fatty acids (EFAs) are polyunsaturated fats that our bodies need but cannot produce. Therefore, they must be consumed through food or supplements. Omega 3 and Omega 6 are EFAs.
Contents. Page 2 Page 3 Page 3 Page 4 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 8
 Perfect Contents Introduction... How much fish Oil... Baseline Recommendations for Health... Official Recommendations by Scientific Organizations... Conclusion of Meta-Analysis Scientific Review Papers...
Perfect Contents Introduction... How much fish Oil... Baseline Recommendations for Health... Official Recommendations by Scientific Organizations... Conclusion of Meta-Analysis Scientific Review Papers...
Fatty Acids: The Basics
 Fatty Acids: The Basics Fatty Acids 101 Fatty acids are necessary nutrients found in our food. The problem is how much we eat of each: The historical ratio of omega-6s to omega- 3s may have been 1-to-1.
Fatty Acids: The Basics Fatty Acids 101 Fatty acids are necessary nutrients found in our food. The problem is how much we eat of each: The historical ratio of omega-6s to omega- 3s may have been 1-to-1.
*This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any
 *This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Healthy Fats. Essential for Health. Exceptional Quality. In a nutshell, these are the benefits of Solgar s extensive selection
*This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Healthy Fats. Essential for Health. Exceptional Quality. In a nutshell, these are the benefits of Solgar s extensive selection
Research shows that the most reliable source of omega-3s is a high-quality fish oil supplement
 n Helps the body naturally address occasional eye irritation n Promotes healthy eye moisture for occasional dry eyes n Promotes normal eye function as we age n Contains the fatty acid DHA, found in greatest
n Helps the body naturally address occasional eye irritation n Promotes healthy eye moisture for occasional dry eyes n Promotes normal eye function as we age n Contains the fatty acid DHA, found in greatest
essential fatty acids for a healthy body / healthy mind / healthy mood
 essential fatty acids for a healthy body / healthy mind / healthy mood What are Essential Fatty Acids? Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) are considered essential because they are required for optimal health
essential fatty acids for a healthy body / healthy mind / healthy mood What are Essential Fatty Acids? Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) are considered essential because they are required for optimal health
Nutritional Considerations and Mood Disorders. Dr. Ron Grabowski
 Nutritional Considerations and Mood Disorders Dr. Ron Grabowski Statistics Depression is a common mental disorder with a complex etiology. Depressive disorders affect 121 million people worldwide and are
Nutritional Considerations and Mood Disorders Dr. Ron Grabowski Statistics Depression is a common mental disorder with a complex etiology. Depressive disorders affect 121 million people worldwide and are
Fabio Akira Ito. Technical Services South America Pharma Ingredients & Services. Internal
 Fabio Akira Ito Technical Services South America Pharma Ingredients & Services 1 Omega-3s and Health Benefits 2 Production of Omega-3 products 3 Argentinian Market 2 Definition of Major Omega-3 Polyunsaturated
Fabio Akira Ito Technical Services South America Pharma Ingredients & Services 1 Omega-3s and Health Benefits 2 Production of Omega-3 products 3 Argentinian Market 2 Definition of Major Omega-3 Polyunsaturated
OPINION. of the French Food Safety Agency on the update of French population reference intakes (ANCs) for fatty acids. Maisons-Alfort, 1 March 2010
 Maisons-Alfort, 1 March 2010 OPINION THE DIRECTOR GENERAL of the French Food Safety Agency on the update of French population reference intakes (ANCs) for fatty s 1. REVIEW OF THE REQUEST The French Food
Maisons-Alfort, 1 March 2010 OPINION THE DIRECTOR GENERAL of the French Food Safety Agency on the update of French population reference intakes (ANCs) for fatty s 1. REVIEW OF THE REQUEST The French Food
There is more scientific evidence behind the cardiovascular benefits of fish oil than nearly any other nutritional supplement
 n Provides optimal support for heart health n Reduces triglyceride levels n Reduces cardiovascular risk factors 7, 8 n Complements statin drug therapy n Optimizes circulation and blood vessel function
n Provides optimal support for heart health n Reduces triglyceride levels n Reduces cardiovascular risk factors 7, 8 n Complements statin drug therapy n Optimizes circulation and blood vessel function
FROM ABSTRACT Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) improve on a vegetarian diet or supplementation with fish oil.
 Anti-inflammatory effects of a low arachidonic acid diet and fish oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatol Int (2003) 23: 27 36 Olaf Adam, Corinna Beringer, Thomas Kless, Christa Lemmen, Alexander
Anti-inflammatory effects of a low arachidonic acid diet and fish oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatol Int (2003) 23: 27 36 Olaf Adam, Corinna Beringer, Thomas Kless, Christa Lemmen, Alexander
Section Editor Steven T DeKosky, MD, FAAN Kenneth E Schmader, MD
 Prevention of dementia Author Daniel Press, MD Michael Alexander, MD Section Editor Steven T DeKosky, MD, FAAN Kenneth E Schmader, MD Deputy Editor Janet L Wilterdink, MD Last literature review version
Prevention of dementia Author Daniel Press, MD Michael Alexander, MD Section Editor Steven T DeKosky, MD, FAAN Kenneth E Schmader, MD Deputy Editor Janet L Wilterdink, MD Last literature review version
The Potential Effects of Flaxseed and its Related Products on the Reproductive Performances of Sows
 The Potential Effects of Flaxseed and its Related Products on the Reproductive Performances of Sows L. Eastwood and P. Leterme Department of Animal and Poultry Science, University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon,
The Potential Effects of Flaxseed and its Related Products on the Reproductive Performances of Sows L. Eastwood and P. Leterme Department of Animal and Poultry Science, University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon,
SCIENTIFIC OPINION. Eye q and concentration
 The EFSA Journal (2008) 904, 1-10 SCIENTIFIC OPINION Eye q and concentration Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to Eye q and concentration pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No
The EFSA Journal (2008) 904, 1-10 SCIENTIFIC OPINION Eye q and concentration Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to Eye q and concentration pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No
N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and allergic disease
 N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and allergic disease Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care Volume 7(2) March 2004 pp 123-129 Susan Prescott and Philip Calder Abbreviations DHA: EPA:
N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and allergic disease Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care Volume 7(2) March 2004 pp 123-129 Susan Prescott and Philip Calder Abbreviations DHA: EPA:
Omega-3 requirements - length matters!
 Omega-3 requirements - length matters! http://www.rejuvenal.info/ images/terminology/omega3.png Professor Peter Howe Nutritional Physiology Research Centre University of South Australia Food Industry Forum
Omega-3 requirements - length matters! http://www.rejuvenal.info/ images/terminology/omega3.png Professor Peter Howe Nutritional Physiology Research Centre University of South Australia Food Industry Forum
Mental Health: Where Nutrition meets Psychiatry By Nicola Walters, Registered Dietitian
 Mental Health: Where Nutrition meets Psychiatry By Nicola Walters, Registered Dietitian Key Focus Areas Overview of Global & SA Statistics Analysis of the Evidence Sugar & Refined Carbohydrates Fat: dietary
Mental Health: Where Nutrition meets Psychiatry By Nicola Walters, Registered Dietitian Key Focus Areas Overview of Global & SA Statistics Analysis of the Evidence Sugar & Refined Carbohydrates Fat: dietary
Seafood consumption, the DHA content of mothers' milk and prevalence rates of postpartum depression: a cross-national, ecological analysis
 Seafood consumption, the DHA content of mothers' milk and prevalence rates of postpartum depression: a cross-national, ecological analysis 1 Journal of Affective Disorders: Volume 69, Issues 1-3, May 2002,
Seafood consumption, the DHA content of mothers' milk and prevalence rates of postpartum depression: a cross-national, ecological analysis 1 Journal of Affective Disorders: Volume 69, Issues 1-3, May 2002,
Fatty acids and cardiovascular health: current evidence and next steps
 Fatty acids and cardiovascular health: current evidence and next steps Emanuele Di Angelantonio, MD, PhD Department of Public Health and Primary Care NICE guidelines on fatty acids Eliminate the use of
Fatty acids and cardiovascular health: current evidence and next steps Emanuele Di Angelantonio, MD, PhD Department of Public Health and Primary Care NICE guidelines on fatty acids Eliminate the use of
FLAXSEED Health Benefits and Functionality. Kelley C. Fitzpatrick Director of Health FLAX COUNCIL OF CANADA
 FLAXSEED Health Benefits and Functionality Kelley C. Fitzpatrick Director of Health FLAX COUNCIL OF CANADA Consumers are interested in Positive Nutrition The trend is no longer just to remove bad ingredients
FLAXSEED Health Benefits and Functionality Kelley C. Fitzpatrick Director of Health FLAX COUNCIL OF CANADA Consumers are interested in Positive Nutrition The trend is no longer just to remove bad ingredients
Pediatric Psychopharmacology
 Pediatric Psychopharmacology General issues to consider. Pharmacokinetic differences Availability of Clinical Data Psychiatric Disorders can be common in childhood. Early intervention may prevent disorders
Pediatric Psychopharmacology General issues to consider. Pharmacokinetic differences Availability of Clinical Data Psychiatric Disorders can be common in childhood. Early intervention may prevent disorders
PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA
 PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Alena Buretić-Tomljanović 1, Jasminka Giacometti 1, Sergej Nadalin 1, Gordana Rubeša 2, Mirjana Vulin 3, Draško
PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Alena Buretić-Tomljanović 1, Jasminka Giacometti 1, Sergej Nadalin 1, Gordana Rubeša 2, Mirjana Vulin 3, Draško
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), 492 ACT. See Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) ADHD. See Attention-deficit/hyperactivity
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), 492 ACT. See Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) ADHD. See Attention-deficit/hyperactivity
A Specially Formulated Medical Food for the Dietary Management of Diabetic Retinopathy
 A Specially Formulated Medical Food for the Dietary Management of Diabetic Retinopathy TM Physician and Patient Focus nuretin is an orally administered Medical Food recommended by physicians for the prevention
A Specially Formulated Medical Food for the Dietary Management of Diabetic Retinopathy TM Physician and Patient Focus nuretin is an orally administered Medical Food recommended by physicians for the prevention
Cetoleic acid makes pelagic fish more healthy
 Cetoleic acid makes pelagic fish more healthy WORKSHOP IN FISHMEAL AND FISH OIL, NOVEMBER 2018 Bente Ruyter Nofima Omega-3 fatty acids and health Eye Brain Cell membrane The marine omega-3 fatty acids
Cetoleic acid makes pelagic fish more healthy WORKSHOP IN FISHMEAL AND FISH OIL, NOVEMBER 2018 Bente Ruyter Nofima Omega-3 fatty acids and health Eye Brain Cell membrane The marine omega-3 fatty acids
Comment from Professor Holub:
 The Medical Officer and associates for Toronto Public Health have just released a major Technical Report entitled 'Fish Consumption: Benefits and Risks for Women in Childbearing Years and Young Children'.
The Medical Officer and associates for Toronto Public Health have just released a major Technical Report entitled 'Fish Consumption: Benefits and Risks for Women in Childbearing Years and Young Children'.
Wise Food & Lifestyle Choices For Better Overall Health THE IMPORTANCE OF OMEGA-3 IN YOUR DIET FOOD FOR THOUGHT
 Wise Food & Lifestyle Choices For Better Overall Health THE IMPORTANCE OF OMEGA-3 IN YOUR DIET FOOD FOR THOUGHT WHY OMEGA-3 FATS MATTER Did you know omega-3 fats are vital for your health? They play important
Wise Food & Lifestyle Choices For Better Overall Health THE IMPORTANCE OF OMEGA-3 IN YOUR DIET FOOD FOR THOUGHT WHY OMEGA-3 FATS MATTER Did you know omega-3 fats are vital for your health? They play important
Study Center(s): The study was conducted at 39 study sites in Japan.
 SYNOPSIS Issue Date: 20 NOVEMBER 2012 Name of Sponsor/Company Janssen Pharmaceutical K. K. Name of Finished Product CONCERTA Name of Active Ingredient(s) Methylphenidate HCl Protocol No.: JNS001-JPN-A01
SYNOPSIS Issue Date: 20 NOVEMBER 2012 Name of Sponsor/Company Janssen Pharmaceutical K. K. Name of Finished Product CONCERTA Name of Active Ingredient(s) Methylphenidate HCl Protocol No.: JNS001-JPN-A01
Soybean Oil Facts: HIGH OLEIC and INCREASED OMEGA-3 SOYBEAN OILS
 Soybean Oil Facts: HIGH OLEIC and INCREASED OMEGA-3 SOYBEAN OILS Soybean Oil Innovations HIGH OLEIC The soybean industry recognizes the need to provide healthful and functional ingredients to the food
Soybean Oil Facts: HIGH OLEIC and INCREASED OMEGA-3 SOYBEAN OILS Soybean Oil Innovations HIGH OLEIC The soybean industry recognizes the need to provide healthful and functional ingredients to the food
QUANTITY VERSUS QUALITY OF FAT IN THE DIET. Marius Smuts
 QUANTITY VERSUS QUALITY OF FAT IN THE DIET Marius Smuts Centre of Excellence in Nutrition marius.smuts@nwu.ac.za CONTENT Background on fatty acids Roles of Essential fats Quantity of fat in the diet Quality
QUANTITY VERSUS QUALITY OF FAT IN THE DIET Marius Smuts Centre of Excellence in Nutrition marius.smuts@nwu.ac.za CONTENT Background on fatty acids Roles of Essential fats Quantity of fat in the diet Quality
A randomized controlled clinical trial of Citalopram versus Fluoxetine in children and adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
 Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (2009) 18:131 135 DOI 10.1007/s00787-007-0634-z ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Javad Alaghband-Rad Mitra Hakimshooshtary A randomized controlled clinical trial of Citalopram versus
Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (2009) 18:131 135 DOI 10.1007/s00787-007-0634-z ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Javad Alaghband-Rad Mitra Hakimshooshtary A randomized controlled clinical trial of Citalopram versus
Depression, omega 3 fatty acid therapy 13
 Subject Index Adhesion molecules fish oil effects 12, 13 omega 3 fatty acid desaturase transfection effects on expression in endothelial cells 31 Alzheimer s disease (AD), omega 6 fatty acid/omega 3 fatty
Subject Index Adhesion molecules fish oil effects 12, 13 omega 3 fatty acid desaturase transfection effects on expression in endothelial cells 31 Alzheimer s disease (AD), omega 6 fatty acid/omega 3 fatty
The use of omega-3 fatty acids in the management of cancer cachexia. Rhys White Principal Oncology Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust
 The use of omega-3 fatty acids in the management of cancer cachexia Rhys White Principal Oncology Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Overview Cancer cachexia Clinical features Pathogenesis
The use of omega-3 fatty acids in the management of cancer cachexia Rhys White Principal Oncology Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Overview Cancer cachexia Clinical features Pathogenesis
The Better Health News2
 February, 2009 Volume 4, Issue 1 The Better Health News2 Special Interest Articles: Curry and Disease Name That Food Nutrition and Disease Diet, Supplmentation and Dementia Elemental Diet and Crohn s Disease
February, 2009 Volume 4, Issue 1 The Better Health News2 Special Interest Articles: Curry and Disease Name That Food Nutrition and Disease Diet, Supplmentation and Dementia Elemental Diet and Crohn s Disease
Developing your Integrative Self-Care Plan
 Developing your Integrative Self-Care Plan Erin Sweet ND, MPH, FABNO Assistant Research Scientist Bastyr University [PRESENTER PHOTO] Naturopathic Oncology Red Cedar Wellness Center & Orion Center for
Developing your Integrative Self-Care Plan Erin Sweet ND, MPH, FABNO Assistant Research Scientist Bastyr University [PRESENTER PHOTO] Naturopathic Oncology Red Cedar Wellness Center & Orion Center for
Brain Health and Seafood Omega-3 fats
 Brain Health and Seafood Omega-3 fats CAPT Joseph R. Hibbeln, M.D. Acting Chief, Section on Nutritional Neurosciences, NIAAA, NIH, Rockville, MD Seafood Nutrition Partnership 2nd Annual State of the Science
Brain Health and Seafood Omega-3 fats CAPT Joseph R. Hibbeln, M.D. Acting Chief, Section on Nutritional Neurosciences, NIAAA, NIH, Rockville, MD Seafood Nutrition Partnership 2nd Annual State of the Science
The Role of Nutrition in Mental Health: Depression
 The Role of Nutrition in Mental Health: Depression Abstract: Jesse A Solomon, Ziv Zukier, Mazen J Hamadeh School of Kinesiology and Health Science, Faculty of Health, York University 4700 Keele Street,
The Role of Nutrition in Mental Health: Depression Abstract: Jesse A Solomon, Ziv Zukier, Mazen J Hamadeh School of Kinesiology and Health Science, Faculty of Health, York University 4700 Keele Street,
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: The Older People, Omega-3, and Cognitive Health (EPOCH) trial design and methodology: A randomised, double-blind, controlled trial investigating the effect of long-chain
Author's response to reviews Title: The Older People, Omega-3, and Cognitive Health (EPOCH) trial design and methodology: A randomised, double-blind, controlled trial investigating the effect of long-chain
The Impact of Diet on Cognition
 The Impact of Diet on Cognition The Shape of Things to Come The Economist, Dec 11 2003 Dr Alex Richardson Senior Research Fellow, University of Oxford Founder Director, Food and Behaviour Research The
The Impact of Diet on Cognition The Shape of Things to Come The Economist, Dec 11 2003 Dr Alex Richardson Senior Research Fellow, University of Oxford Founder Director, Food and Behaviour Research The
DIETARY LIPIDS, IMMUNE FUNCTION AND PATHOGENESIS OF DISEASE IN FISH
 DIETARY LIPIDS, IMMUNE FUNCTION AND PATHOGENESIS OF DISEASE IN FISH Santosh P. Lall and Joyce E. Milley National Research Council Canada, Institute for Marine Biosciences, 1411 Oxford Street, Halifax,
DIETARY LIPIDS, IMMUNE FUNCTION AND PATHOGENESIS OF DISEASE IN FISH Santosh P. Lall and Joyce E. Milley National Research Council Canada, Institute for Marine Biosciences, 1411 Oxford Street, Halifax,
Guilt Suicidality. Depression Co-Occurs with Medical Illness The rate of major depression among those with medical illness is significant.
 1-800-PSYCH If you are obsessive-compulsive, dial 1 repeatedly If you are paranoid-delusional, dial 2 and wait, your call is being traced If you are schizophrenic, a little voice will tell you what number
1-800-PSYCH If you are obsessive-compulsive, dial 1 repeatedly If you are paranoid-delusional, dial 2 and wait, your call is being traced If you are schizophrenic, a little voice will tell you what number
Brain&Mitochondrial&Metabolism& and&psychiatric&illness&&
 Brain&Mitochondrial&Metabolism& and&psychiatric&illness&& Benjamin&Brown,&ND& :meforwellness.org& N&Engl&J&Med.&2007& Mar&15;356(11): 1140L51& Energy Production OXYGEN DIET Carbohydrates, fats, proteins.
Brain&Mitochondrial&Metabolism& and&psychiatric&illness&& Benjamin&Brown,&ND& :meforwellness.org& N&Engl&J&Med.&2007& Mar&15;356(11): 1140L51& Energy Production OXYGEN DIET Carbohydrates, fats, proteins.
Omega-3 Index Complete We are pleased to bring you a new test for fatty acids that requires no blood draw, at a great price.
 The Great Plains Laboratory, Inc. Omega-3 Index Complete We are pleased to bring you a new test for fatty acids that requires no blood draw, at a great price. Many studies have shown that people with higher
The Great Plains Laboratory, Inc. Omega-3 Index Complete We are pleased to bring you a new test for fatty acids that requires no blood draw, at a great price. Many studies have shown that people with higher
Future directions for nutritional and therapeutic research in omega-3 3 lipids
 Future directions for nutritional and therapeutic research in omega-3 3 lipids Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University of Southampton Aim To review dietary sources and intakes of long
Future directions for nutritional and therapeutic research in omega-3 3 lipids Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University of Southampton Aim To review dietary sources and intakes of long
Differentiating omega-3 fatty acids from SPMs (specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators)
 NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Differentiating omega-3 fatty acids from SPMs (specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators) Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University
NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Differentiating omega-3 fatty acids from SPMs (specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators) Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University
UCLA Nutrition Noteworthy
 UCLA Nutrition Noteworthy Title Effects of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Breast Cancer Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/12g6398b Journal Nutrition Noteworthy, 2(1) ISSN 1556-1895
UCLA Nutrition Noteworthy Title Effects of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Breast Cancer Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/12g6398b Journal Nutrition Noteworthy, 2(1) ISSN 1556-1895
HIGH OLEIC and INCREASED OMEGA-3
 SOYBEAN OIL FACTS HIGH OLEIC and INCREASED OMEGA-3 SOYBEAN OILS Soybean Oil Innovations The soybean industry recognizes the need to provide healthful and functional ingredients to the food industry, and
SOYBEAN OIL FACTS HIGH OLEIC and INCREASED OMEGA-3 SOYBEAN OILS Soybean Oil Innovations The soybean industry recognizes the need to provide healthful and functional ingredients to the food industry, and
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids?
 Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
Other Health Benefits of Flax
 Chapter 7 Other Health Benefits of Flax Previous chapters examined the benefits of flax and its key constituents the lignan secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), dietary fibre and alpha-linolenic acid
Chapter 7 Other Health Benefits of Flax Previous chapters examined the benefits of flax and its key constituents the lignan secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), dietary fibre and alpha-linolenic acid
Roles of Lipids in the body
 Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Name of Policy: Measurement of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Red Blood Cell Membranes as a Cardiac Risk Factor
 Name of Policy: Measurement of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Red Blood Cell Membranes as a Cardiac Risk Factor Policy #: 239 Latest Review Date: July 2010 Category: Laboratory Policy Grade: Active
Name of Policy: Measurement of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Red Blood Cell Membranes as a Cardiac Risk Factor Policy #: 239 Latest Review Date: July 2010 Category: Laboratory Policy Grade: Active
David M. Klurfeld Agricultural Research Service Beltsville, MD
 David M. Klurfeld Agricultural Research Service Beltsville, MD Disclaimers The views presented here are those of the speaker and do not necessarily reflect official positions of the USDA or the Agricultural
David M. Klurfeld Agricultural Research Service Beltsville, MD Disclaimers The views presented here are those of the speaker and do not necessarily reflect official positions of the USDA or the Agricultural
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centers: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Omega-3 fatty acids and neuropsychiatric disorders
 Omega-3 fatty acids and neuropsychiatric disorders Genevieve Young, Julie Conquer To cite this version: Genevieve Young, Julie Conquer. Omega-3 fatty acids and neuropsychiatric disorders. Reproduction
Omega-3 fatty acids and neuropsychiatric disorders Genevieve Young, Julie Conquer To cite this version: Genevieve Young, Julie Conquer. Omega-3 fatty acids and neuropsychiatric disorders. Reproduction
Facts on Fats. Ronald P. Mensink
 Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Nutritional Risk Factors for Peripheral Vascular Disease: Does Diet Play a Role?
 Nutritional Risk Factors for Peripheral Vascular Disease: Does Diet Play a Role? John S. Lane MD, Cheryl P. Magno MPH, Karen T. Lane MD, Tyler Chan BS, Sheldon Greenfield MD University of California, Irvine
Nutritional Risk Factors for Peripheral Vascular Disease: Does Diet Play a Role? John S. Lane MD, Cheryl P. Magno MPH, Karen T. Lane MD, Tyler Chan BS, Sheldon Greenfield MD University of California, Irvine
Significance of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) for the development and behaviour of children
 Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:149 164 DOI 10.1007/s00431-009-1035-8 REVIEW Significance of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) for the development and behaviour of children Jan Philipp Schuchardt
Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:149 164 DOI 10.1007/s00431-009-1035-8 REVIEW Significance of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) for the development and behaviour of children Jan Philipp Schuchardt
Depression and anxiety increase the risk for preterm birth
 1 Proinflammatory cytokines rise in last trimester Women s highest risk of depression in the last trimester Cytokines remain elevated postpartum Depression and anxiety increase the risk for preterm birth
1 Proinflammatory cytokines rise in last trimester Women s highest risk of depression in the last trimester Cytokines remain elevated postpartum Depression and anxiety increase the risk for preterm birth
Table 1: Dietary Sources of Omega-3 and Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Fatty Acid. Food Sources. (i) Omega-6 Types. LA, linoleic acid (18:2 n-6)
 As for saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, the omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are chemically linked to fat structures known as triglycerides in the various foods and oils
As for saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, the omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are chemically linked to fat structures known as triglycerides in the various foods and oils
FATS The Facts. compiled by the Nestlé Research Center
 FATS The Facts compiled by the Nestlé Research Center Dietary fats are a public health concern Dietary fats are necessary for ensuring optimal health. Recent dietary guidelines focus on fat quality and
FATS The Facts compiled by the Nestlé Research Center Dietary fats are a public health concern Dietary fats are necessary for ensuring optimal health. Recent dietary guidelines focus on fat quality and
NORDIC NATURALS NORDIC PET
 NORDIC NATURALS NORDIC PET Introducing The Nordic Pet Range Exceptional Products for Your Exceptional Pet Nordic Naturals achieves exceptional products by using fish oils that surpass stringent quality
NORDIC NATURALS NORDIC PET Introducing The Nordic Pet Range Exceptional Products for Your Exceptional Pet Nordic Naturals achieves exceptional products by using fish oils that surpass stringent quality
January Issue. Omega-3. Research. help mild to. takes the right. simple as. percent of. American. people with. Enter the
 January 2012 Issue Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Mood Disorderss By Sari Harrar Today s Dietitian Vol. 14 No. 1 P. 22 Research suggests omega-3s can help mild to major depression and even schizophrenia. Long
January 2012 Issue Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Mood Disorderss By Sari Harrar Today s Dietitian Vol. 14 No. 1 P. 22 Research suggests omega-3s can help mild to major depression and even schizophrenia. Long
Omega-3 fatty acids in clinical nutrition
 Omega-3 fatty acids in clinical nutrition Alastair Forbes With thanks to Jon Shaffer, UK and many ESPEN colleagues Omega-3 fatty acids in clinical nutrition Review of lipids in nutrition Why and how lipids
Omega-3 fatty acids in clinical nutrition Alastair Forbes With thanks to Jon Shaffer, UK and many ESPEN colleagues Omega-3 fatty acids in clinical nutrition Review of lipids in nutrition Why and how lipids
Cyclooxygenase, COX-2 polymorphisms in prostate cancer 164, 166, 168
 Subject Index Actinin, ACTN3 alleles and muscle function 146 Aging cognition, see Dementia omega-6/omega-3 balance studies 17 Agribusiness, see Food industry Alzheimer s disease (AD) ApoE4 92 fatty acid
Subject Index Actinin, ACTN3 alleles and muscle function 146 Aging cognition, see Dementia omega-6/omega-3 balance studies 17 Agribusiness, see Food industry Alzheimer s disease (AD) ApoE4 92 fatty acid
Use natural fish oil with 2g daily dose? Yes Use other omega-3? Replicate test? Date of birth
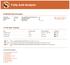 Fatty Acid Analysis NORSAN Fatty Acid Analysis Analyse-ID RL44UA52 Date of analysis 31.03.2017 Country GB Sex Male Use natural fish oil with 2g daily dose? Yes Use other omega-3? No Replicate test? Yes
Fatty Acid Analysis NORSAN Fatty Acid Analysis Analyse-ID RL44UA52 Date of analysis 31.03.2017 Country GB Sex Male Use natural fish oil with 2g daily dose? Yes Use other omega-3? No Replicate test? Yes
FISH. College of Applied Medical Sciences Department of Community Health Sciences Clinical Nutrition Functional Foods CHS 457 Level 9
 College of Applied Medical Sciences Department of Community Health Sciences Clinical Nutrition Functional Foods CHS 457 Level 9 FISH Presented By: Nada Abdullah Al-Akeil Supervised By: Mrs.Madawi Al-Dhwayan
College of Applied Medical Sciences Department of Community Health Sciences Clinical Nutrition Functional Foods CHS 457 Level 9 FISH Presented By: Nada Abdullah Al-Akeil Supervised By: Mrs.Madawi Al-Dhwayan
LIPIDOMIC PROFILE MEMBRANE Assessment of the lipidomic profile of the erthyrocyte membrane
 TEST RESULTS: Cod. ID: 123456 CCV: 2c9 Date: 01/01/2013 Patient: Rossi Mario Rapport de: NatrixLab Via Cavallotti, 16 42122 Reggio Emilia Aut.n. 67 del 26.01.10 Direttore Sanitario Dott. Michele Cataldo
TEST RESULTS: Cod. ID: 123456 CCV: 2c9 Date: 01/01/2013 Patient: Rossi Mario Rapport de: NatrixLab Via Cavallotti, 16 42122 Reggio Emilia Aut.n. 67 del 26.01.10 Direttore Sanitario Dott. Michele Cataldo
SOYBEAN OIL INNOVATIONS:
 INNOVATE COLLABORATE ADVANCE SOYBEAN OIL INNOVATIONS: COMING TO A PLATE NEAR YOU A GUIDE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS SOYBEAN OIL REACHES NEW HEIGHTS CONSUMERS WANT TO EAT HEALTHIER Soybean oil is one of the
INNOVATE COLLABORATE ADVANCE SOYBEAN OIL INNOVATIONS: COMING TO A PLATE NEAR YOU A GUIDE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS SOYBEAN OIL REACHES NEW HEIGHTS CONSUMERS WANT TO EAT HEALTHIER Soybean oil is one of the
NEW SOYBEAN OIL INNOVATIONS:
 INNOVATE COLLABORATE ADVANCE NEW SOYBEAN OIL INNOVATIONS: COMING TO A PLATE NEAR YOU A GUIDE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS SOYBEAN OIL REACHES NEW HEIGHTS Soybean oil is one of the most abundant vegetable oils
INNOVATE COLLABORATE ADVANCE NEW SOYBEAN OIL INNOVATIONS: COMING TO A PLATE NEAR YOU A GUIDE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS SOYBEAN OIL REACHES NEW HEIGHTS Soybean oil is one of the most abundant vegetable oils
Why. Children Need Healthy Fat?
 Why Children Need Healthy Fat? Fat has always been associated with being harmful to our health. Too much fat intake is said to cause many diseases such as obesity, heart attack, diabetes and the list goes
Why Children Need Healthy Fat? Fat has always been associated with being harmful to our health. Too much fat intake is said to cause many diseases such as obesity, heart attack, diabetes and the list goes
SCIENTIFIC OPINION. I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and learning ability
 The EFSA Journal (2008) 848, 1-10 SCIENTIFIC OPINION I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and learning ability Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and learning ability
The EFSA Journal (2008) 848, 1-10 SCIENTIFIC OPINION I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and learning ability Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and learning ability
simply the best... Generations of families have known the healthy benefits of Cod Liver Oil. Now, Carlson offers
 Generations of families have known the healthy benefits of Cod Liver Oil. Now, Carlson offers simply the best... pure and fresh from the clean arctic waters, far off the coast of Norway. Available in great
Generations of families have known the healthy benefits of Cod Liver Oil. Now, Carlson offers simply the best... pure and fresh from the clean arctic waters, far off the coast of Norway. Available in great
The Nutritional-Toxicological Conflict related to Seafood Consumption
 The Nutritional-Toxicological Conflict related to Seafood Consumption Isabelle Sioen PhD defence, 4 October 27 Promoters: Prof. dr. S. De Henauw Prof. dr. ir. J. Van Camp Outline 1. Introduction: omega-3
The Nutritional-Toxicological Conflict related to Seafood Consumption Isabelle Sioen PhD defence, 4 October 27 Promoters: Prof. dr. S. De Henauw Prof. dr. ir. J. Van Camp Outline 1. Introduction: omega-3
The Role of LCPUFA in Obesity. M.Tom Clandinin. The Alberta Institute for Human Nutrition The University of Alberta Edmonton, Alberta, Canada
 The Role of LCPUFA in Obesity by M.Tom Clandinin The Alberta Institute for Human Nutrition The University of Alberta Edmonton, Alberta, Canada How big is the Conceptual Problem? Some assumptions: 150lb
The Role of LCPUFA in Obesity by M.Tom Clandinin The Alberta Institute for Human Nutrition The University of Alberta Edmonton, Alberta, Canada How big is the Conceptual Problem? Some assumptions: 150lb
Super Omega-3 EPA/DHA with Sesame Lignans & Olive Extract
 Better Nutrition 2016 Best of Supplements Award Winner http://www.lifeextension.com Super Omega-3 EPA/DHA with Sesame Lignans & Olive Extract Get enough omega-3s 120 softgels Item Catalog Number: 01982
Better Nutrition 2016 Best of Supplements Award Winner http://www.lifeextension.com Super Omega-3 EPA/DHA with Sesame Lignans & Olive Extract Get enough omega-3s 120 softgels Item Catalog Number: 01982
CHILD & ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRY ALERTS, VOLUME XV, 2013 INDEX
 A acceptance and commitment therapy Posttraumatic Stress, 69 ADHD Adjunctive Fatty Acids, 5 Adjunctive Guanfacine Pharmacokinetics, 27 Amantadine, 21 Atomoxetine, 23 Cancer Risk, 31 CBT for Comorbid Anxiety,
A acceptance and commitment therapy Posttraumatic Stress, 69 ADHD Adjunctive Fatty Acids, 5 Adjunctive Guanfacine Pharmacokinetics, 27 Amantadine, 21 Atomoxetine, 23 Cancer Risk, 31 CBT for Comorbid Anxiety,
Essential fatty acids: theoretical aspects and treatment implications for schizophrenia and depression
 EFAs in schizophrenia and Advances in Psychiatric APT (2002), Treatment vol. 8, p. (2002), 223 vol. 8, pp. 223 229 Essential fatty acids: theoretical aspects and treatment implications for schizophrenia
EFAs in schizophrenia and Advances in Psychiatric APT (2002), Treatment vol. 8, p. (2002), 223 vol. 8, pp. 223 229 Essential fatty acids: theoretical aspects and treatment implications for schizophrenia
Overview. Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Risk Factors. Inflammation & Prostate Cancer
 Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Inflammation, and Outcome in Men with and without Prostate Cancer Julie A. Feifers, BA, BS MS Candidate Graduate Programs in Human Nutrition Oregon Health & Science University Overview
Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Inflammation, and Outcome in Men with and without Prostate Cancer Julie A. Feifers, BA, BS MS Candidate Graduate Programs in Human Nutrition Oregon Health & Science University Overview
The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Maternal Depression during Pregnancy: A Double Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
 Original Article The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Maternal Depression during Pregnancy: A Double Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Maasumeh Kaviani 1, MSc; Laleh Saniee 2, MSc;
Original Article The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Maternal Depression during Pregnancy: A Double Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Maasumeh Kaviani 1, MSc; Laleh Saniee 2, MSc;
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different?
 Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
Understanding the Science behind Guiding Stars
 Understanding the Science behind Guiding Stars The Guiding Stars nutrition guidance program is based on national and international dietary recommendations and aligns with the most current 2015 Dietary
Understanding the Science behind Guiding Stars The Guiding Stars nutrition guidance program is based on national and international dietary recommendations and aligns with the most current 2015 Dietary
Erythrocyte Fatty Acid
 Dr ******* **** ** ********** **** **** ******** Reference: :******** Receive date:02/11/2011 Print date:24/09/2013 Les données administratives enregistrées dans notre fichier informatisé sont celles qui
Dr ******* **** ** ********** **** **** ******** Reference: :******** Receive date:02/11/2011 Print date:24/09/2013 Les données administratives enregistrées dans notre fichier informatisé sont celles qui
Nutrition Basics. Chapter McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
 Nutrition Basics Chapter 12 1 The Body s Nutritional Requirements Essential nutrients The Six Essential Nutrients: Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates, Vitamins, Minerals, Water Defined as : Nutrients one must
Nutrition Basics Chapter 12 1 The Body s Nutritional Requirements Essential nutrients The Six Essential Nutrients: Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates, Vitamins, Minerals, Water Defined as : Nutrients one must
SCIENTIFIC OPINION. I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and concentration
 The EFSA Journal (2008) 846, 1-10 SCIENTIFIC OPINION I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and concentration Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and concentration pursuant
The EFSA Journal (2008) 846, 1-10 SCIENTIFIC OPINION I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and concentration Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to I omega kids /Pufan 3 kids and concentration pursuant
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY
 Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Optimize Your Omega-3 Status Personalized Blood Test Reveals a Novel Cardiac Risk Factor
 http://www.lef.org/ Life Extension Magazine May 2010 Optimize Your Omega-3 Status Personalized Blood Test Reveals a Novel Cardiac Risk Factor By Julius Goepp, MD Suppose you could assess with precision
http://www.lef.org/ Life Extension Magazine May 2010 Optimize Your Omega-3 Status Personalized Blood Test Reveals a Novel Cardiac Risk Factor By Julius Goepp, MD Suppose you could assess with precision
Does the Use of Oral Amphetamines Reduce Cocaine Use in Cocaine-Dependent Individuals?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2016 Does the Use of Oral Amphetamines Reduce
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2016 Does the Use of Oral Amphetamines Reduce
Weight Loss NOTES. [Diploma in Weight Loss]
![Weight Loss NOTES. [Diploma in Weight Loss] Weight Loss NOTES. [Diploma in Weight Loss]](/thumbs/82/86567947.jpg) Weight Loss NOTES [Diploma in Weight Loss] Fat s: The good, the bad and the ugly Fat s function in your body 1. Energy stores 2. Muscle fuel 3. Transportation 4. Cell membrane 5. Padding 6. Muscle fuel
Weight Loss NOTES [Diploma in Weight Loss] Fat s: The good, the bad and the ugly Fat s function in your body 1. Energy stores 2. Muscle fuel 3. Transportation 4. Cell membrane 5. Padding 6. Muscle fuel
Pharmacotherapy of ADHD with Non-Stimulants
 Pharmacotherapy of ADHD with Non-Stimulants Timothy E. Wilens, M.D. Chief, Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, (Co)Director of Center for Addiction Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital Massachusetts
Pharmacotherapy of ADHD with Non-Stimulants Timothy E. Wilens, M.D. Chief, Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, (Co)Director of Center for Addiction Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital Massachusetts
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is TRUE about essential fatty acids? 1) A) No vegetables contain
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is TRUE about essential fatty acids? 1) A) No vegetables contain
