Division of Studies in English (2/6MD winter semester, 2017/2018) MICROBIOLOGY OUTLINE
|
|
|
- Bernice Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C1. General microbiology bacteriological media, methods of the microbiological inoculation and cultivation, preparation of pure cultures, the structure of the bacterial cell, staining methods of the bacterial slides. - the microbiological media (liquid, semi-solid and solid, simple and enriched, selective, diagnostic and selectivediagnostic), - the techniques of the microbiological inoculation, and the methods used to get pure cultures; - how to describe the bacterial growth in the liquid medium (surface growth, turbidity, and sediment) and in the solid medium (bacterial colony characteristics), the growth of bacteria producing pigments; - the shape and the structure of the bacterial cell (the basic and additional components); - the staining methods of bacteria (simple and complex, positive and negative, positive-negative); - the types of microscopes used in bacteriology and their application; - the role of the microscopic slides in the microbiological diagnostics; - methods of the bacterial identification on the basis of the biochemical features and antigenic structure of the bacterium. Practice 1. Regulations and Laboratory Rules 2. Study and describe the types of laboratory equipment and culture media needed do develop and maintain pure cultures in diagnostic process. 3. Describe bacterial growth in solid media describe a single colony appearance in solids media including size, shape, edge, consistency, cross-section, surface, relation to the medium, transparency, release of pigment, suspension, medium changes around colony. 4. Describe release of pigment on solid media. 5. Draw the slide presenting rods negative staining. 6. Draw the slide presenting cocci negative staining. 7. Draw the slide presenting capsule positive-negative staining. 8. Draw the slide presenting flagella. 9. Draw the slide presenting spores stained with a) Gram method b) Schaeffer-Fulton method/(wirtz method). 10. Inoculate the given bacteria from liquid media (broth) or solid medium into solid media using streak-plate technique (looping-out technique): a. Loosen the cap of the bottle containing the inoculum. b. Hold an inoculation loop in your right hand and flame the loop; then allow it to cool. c. Lift the test tube containing the inoculum with your left hand. Remove the cap/ cotton wool plug of the test tube with the little finger of your right hand. d. Flame the neck of the test tube. e. Insert the loop into the culture broth and withdraw. At all times hold the loop as still as possible. f. Flame the neck of the test tube again. g. Replace the cap/ cotton wool plug of the test tube using the little finger of your right hand. Place the test tube in a rack. For a liquid culture, dip the loop into the broth, or for solid media, lightly touch a colony with the loop. h. Partially lift the lid of the Petri dish containing the solid medium. i. Place a loopful of the culture on the agar surface on the area 1. Flame the loop and cool it for 5 seconds by touching an unused part of the agar surface close to the periphery of the plate, and then drag it rapidly several times across the surface of area1. j. Remove the loop and close the Petri dish. k. Reflame and cool the loop, and turn the petri dish 90 C then touch the loop to a corner of the culture in area1 and drag it several times across the agar in area 2, hitting the original streak a few times. The loop should never enter area 1 again. l. Remove the loop and close the Petri dish. m. Reflame and cool the loop and again turn the dish 90 C anticlockwise. streak area 3 in the same manner as area 2, hitting last area several times. Remove the loop and close the Petri dish. n. Flame the loop, again turn the dish 90 C and then drag the culture from a corner of a area3 across area 4, contacting area 3 several times and drag out the culture. Do not let the loop touch any of the previously streaked areas. The flaming 1
2 of the loop at the points indicated is to effect the dilution of the culture so that fewer organisms are streaked in each area, resulting in the final desired separation. o. Remove the loop and close the Petri dish. p. Tape the plate closed and incubates the plate in an inverted position in an incubator for hours. q. Flame the loop before putting it aside. 11. Using pure or mixed cultures, prepare the bacterial smears obeying the following rules: make your slide free of fats by passing it through the flame a) liquid medium - place a few loops of the cell suspension on the slide b) solid medium - take one drop of water on the loop and place it on the centre of the slide; transfer a small amount of the bacterial inoculum from the solid medium into water, and spread both into a thin area - allow the smear to air-dry next to the burner - make a fixation of your preparation: while holding the slide at one end, quickly pass the smear over the Bunsen burner two to three times. Allow the smear to cool down for 10 seconds. GRAM STAINING PROCEDURE - Stain with crystal violet for 1 minute - Gently wash of the stain with tap water - Gently apply Gram s iodine for 1 minute - Gently wash of the stain with tap water - Add the alcohol (decolorizer) for 1 minute - Counterstain with safranin (or fuchsin) for 1 minute - Gently wash of the stain with tap water - Dry with bibulous paper Examine all stained slides under the light microscope (use an immersion objective, 100x), using immersion (cedar oil). Gram-positive bacteria stain deep blue while Gram-negative are red/pink. Draw what you see. 12. Learning assessment questions. C2: General microbiology. Physiology of bacteria. The influence of the physical and chemical factors on bacteria. Knowledge: The student knows: - role of the commensal microbiota in normal and pathogenic host immune responses; - the bacterial physiology, the optimal conditions for their growth in vitro; - the phases of the bacterial growth, - nutritional requirements (chemical components of the bacterial cell, various requirements of nutrients); - temperature (psychrophilic bacteria, mesophiles, and thermophiles); - gaseous requirements (strictly aerobic bacteria, facultatively anaerobic bacteria, strictly anaerobic bacteria, microaerophilic bacteria, capnophiles), ph and the osmotic pressure; - the influence of physical and chemical factors on bacteria; - the methods of the bacteriological control (sanitization, antisepsis, asepsis, disinfection, sterilization); - the tests used to control the process of autoclaving. The student is able to talk over the diagnostic process of bacteria; He/she knows methods which can be used to identify and differentiate microorganisms. 1. Read the results of previous growing bacteria from liquid media (streak-plate method). 2. Analyze the growth curve of microorganisms. 3. Describe bacterial growth in liquid media (broth). Take the growth types in consideration (sediment, turbidity, growth on the surface) according to gaseous requirements. 4. Study the types of hemolysis on a blood dish. 5. Describe the result of catalase test. 6. Describe the growth of E. coli and P. mirabilis - on liquid media a) with tryptophan (Ehrlich/Kovac s reagent!), b) Christensen medium, - in solid media a) Triple Sugar Iron slant, b) soft agar. Notice the changes between sterile and inoculated diagnostic media. 2
3 7. Study the API E20 test used to biochemical identification of Enterobacteriaceae members. 8. Describe the meaning of biochemical, serological and molecular biology methods in identification of microorganisms. 9. Testing of the presence of bacteria in the air- sedimentation method on blood agar for 30 min. 10. Testing of the presence of bacteria on surfaces with blood agar. 11. Testing of the presence of bacteria on white coat with blood agar. 12. Testing of the presence of bacteria on fingers placing the fingerprints after washing hands with water, soap and disinfectants. 13. Investigation of temperature action inoculation of bacterial suspension (with Bacillus sp., and Staphylococcus sp., before and after boiling). 14. Investigation of UV radiation on bacteria inoculation of bacterial suspension (E. coli) with sterile cotton swab on agar medium. Then put the sterile paper on the culture and leave uncovered plate under bactericidal UV lamp for 10 min. Then take the letter away by using tweezers and cover the plate and incubate for 24h. 15. Study the SPORAL and 3M ATTest used to control the efficacy of autoclaving. 16. Investigation of the microbiota of the oral cavity and skin take a swab from the oral cavity and inoculate TSA agar; take the swab from skin and inoculate TSA agar. 17. Take a swab from nose vestibule to look for Staphylococcus aureus and inoculate Chapman medium. 18. Learning assessment questions. C3: General microbiology Genetics of microorganisms. Vaccines. Knowledge: The student knows: - genetic material of bacteria and viruses (bacterial chromosome, plasmids, transposons, IS); - ways of gene exchange in bacteria (conjugation, transformation, transduction); - structure, function and regulation of the lactose operon; - types of vaccines; - schedules of vaccination; - advantages and disadvantages of vaccination; 1. Read and write down the culture results from class no. 2. Results of sedimentation method: Number of colonies. Number of microorganisms in 1m 3.. Clean standard.. I 70 CFU/1m3 II 300 CFU/1m3 III 700 CFU/1m3 2. Isolate single colony of suspected S. aureus from Chapman agar and inoculate fresh TSA agar (streak plate method). 3. Stain the cultures from skin and oral cavity with Gram method. Streak-plate method is used to... Description of morphology of colonies... The result of staining is.... times magnification was used to observe microorganisms. Which additional elements of bacterial cell do you know?... Shape of bacterial cells:... Arrangement of bacterial cells: Agarose Gel Electrophoresis running the gel and reading the results. 5. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of results. 6. Study vaccination schedules. 7. Plaque test the students dye a dental plaque and then prepare Gram-staining of bacteria from dental plaque. PLEASE BRING TOOTHBRUSHES AND TOOTHPASTES! 3
4 8. Microorganism present in saliva the student prepare the microscopic slide with saliva, stain it and study under the microscope. 9. Learning assessment questions. C4: General microbiology Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics. Knowledge: the student knows the antibacterial drugs: beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycosides, quinolones, tetracyclines, macrolides, lincosamides, glycopeptides, etc.; bacteriostatic versus bactericidal agents, antibacterial spectrum (broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum agents), and the mechanisms of antibacterial action. The side-effects of the antibiotic therapy. Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents - its origin and the ways of transmission (natural and acquired resistance, vertical and horizontal transmission of drug resistance). Standardized techniques determining bacterial susceptibility to antimicrobial agents (antibiogram): qualitative tests (disc-diffusion method), quantitative tests (E-test). The clinical meaning of MIC, MBC and MBQ. 1. Study and draw an example of disc-diffusion method. 2. Study and draw E-test. 3. Analysis of microbial resistance with automated systems BD MAX. 4. Study the examples of susceptibility testing /antibiograms/ samples Prepare the microscopic slide stained with Gram-method, latex test and antibiograms for staphylococci isolated during class no. 2/3. 6. Learning assessment questions. 5a. Identification of bacteria Mention media used to isolate Staphylococcus spp.:... Mention possible ways of identification of staphylococci: Your result of identification:... 5b. Evaluation of the sensitivity of Staphylococcus sp. to antibiotics. 1. Mention possible resistance mechanisms to antibiotics:.. 2. What is cross-resistance? 3. Which antibiotics are used to evaluate resistance mechanisms in staphylococci? Antibiotic Group of antibiotics Mechanism of action Inhibition zone diameter Penicillin Ampicillin Cefoxitin Gentamicin Mupirocin Erythromycin Clindamycin P AMP FOX CN MUP E Da C5: General virology. Colloquium no. 1 (C1-C4 and lecture no. 1) Sensitive/ resistant the basic features of the viruses including their structure, characteristics, and replication phases; diagnostic process of the viral infection (clinical material, the time of sampling, storage, transport to the laboratory, principles of specimen processing for viral investigation, cell cultures, embryonated eggs, laboratory animals, microscopic identification, serologic tests, molecular analysis); The student is able to explain the influence of the viral replication type on the course of the viral infection. 4
5 1. Describe sampling and transport of the material in viral infections. 2. Presentation of virology laboratory. 3. Presentation of uninfected cell lines. 4. Presentation cell lines infected with PIV-3 and RV-1B viruses observe cytopathic effect. 5. Analyze case reports concerning viral hepatitis. 6. Analyze immune response in viral hepatitis. 7. Learning assessment questions. C6: Skin infections. - the etiological factors of skin infections: bacterial (staphylococci - Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci - Streptococcus pyogenes, Clostridium perfringens, Propionibacterium acnes, Bacillus anthracis, Mycobacterium leprae, Nocardia spp., Actinomyces spp.); viral (poxviruses, foot-and-mouth disease virus, measles virus, rubella virus) - postoperative wound infections (S. aureus, Enterococcus spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp., Bacteroides fragilis, Fusobacterium spp., Peptococcus spp., Prevotella spp, Veilonella spp.) - cutaneous tuberculosis - cutaneous infections caused by herpesviruses - the epidemiology, diseases, diagnostics, prevention and treatment for skin infections - the student is able to explain the influence of the virulence factors on the course of infection. 1. Skin infections - describe sampling and transport. 2. Draw slides presenting Staphylococcus aureus and Micrococcus spp. 3. Study and draw Staphylococcus aureus on agar-agar, blood agar and Chapman/Mannitol-Salt Agar. 4. Prepare latex test for S. aureus. 5. Study API20 Staph tests. 6. Analyze difference between strains resistant and sensitive to methicillin. A) growth on medium with an antibiotic B) gel electrophoresis 7. Draw the slide presenting Enterococcus sp. 8. Study and draw Enterococcus faecalis on agar-agar, Coccosel agar and agar with tellurite. 9. Analyze serotyping results Latex Strep Kit. 10. Analyze results of biochemical tests API20 Strep. 11. Resistance in enterococci. Analysis of antibiograms. 12. Prepare simple and Gram stain of Gram-negative rods. 13. Study and draw Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii on: a) agar-agar b) McConkey agar. 14. Study API system for non-fermenting rods. 15. Analyze antibiograms - Pseudomonas sp./acinetobacter sp. 16. Bacteria most commonly isolated from the skin infections use the bacterial liquid cultures and prepare the microscopic slide stained with Gram method. 17. Description of systems used to grow and differentiate anaerobic bacteria. 18. Analyze case reports concerning skin infections. 19. Learning assessment questions. C7: Infections of the respiratory system. - the physiological flora of the respiratory system - the clinical forms of the respiratory system infections - the etiological factors of respiratory tract infections: bacterial (Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and Mycobacterium avium complex, Mycobacterium other than tuberculosis (MOTT), Haemophilus spp., Bordetella spp., Legionella spp., Mycoplasma 5
6 pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Nocardia spp.); viral (adenoviruses, Picornaviridae [coxackievirus, echovirus], rhinovirus, parainfluenza viruses 1-4, respiratory syncytial virus, coronavirus, human bocavirus, human metapneumovirus) - necrotizing pneumonia caused by Panton-Valentine leukocidin-releasing S. aureus strains - viral pneumonia as the complication of the primary viral disease (influenza, measles, cytomegalovirus, varicellazoster virus) - influenza virus - epidemiology, diseases, diagnostics, prevention and treatment of respiratory tract infections - the student is able to explain the influence of the virulence factors on the course of infection 1. Respiratory tract infections - describe sampling and transport. 2. Draw the slide presenting Mycobacterium tuberculosis stained with Ziehl-Neelsen method. 3. Draw the slide presenting Mycobacterium tuberculosis cord factor. 4. Study the growth of diverse species of mycobacteria on Loewenstein-Jensen medium. 5. Study the results of tests for mycobacteria Bogen s test, niacin test. 6. Analyze resistance patterns of Mycobacterium spp. 7. Draw the slide presenting Streptococcus pneumoniae stained with Gram method. 8. Study the growth of Streptococcus pneumoniae on blood agar with optochin disc. 9. Draw the slide presenting Streptococcus pyogenes stained with Gram method. 10. Study the growth of Streptococcus pyogenes in broth and on blood agar with bacitracin disc. 11. Describe Lancefield grouping. 12. Draw the slide presenting Haemophilus influenzae stained with Gram method. 13. Study the growth of Haemophilus influenzae on chocolate agar. 14. Description of latex tests for Neisseria spp./haemophilus spp. and API NH strips. 15. Draw the slides presenting Corynebacterium diphtheriae stained with Gram s method, and Neisser staining. 16. Presentation of Löffler's medium. 17. Analyze sputum slides: times magnification was used to observe microorganisms. Which specific elements of Mycobacterium cell do you know? Prepare Gram staining of throat swab...times magnification was used to observe microorganisms. Shape of bacterial cells is... Arrangement of bacterial cells is Analyze of case reports concerning respiratory tract infections. 20. Learning assessment questions. C8: Infections of the digestive tract. Food poisoning. - the physiological flora of the digestive tract; - the clinical forms of the gastrointestinal infections; - the etiological factors: bacteria (Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Escherichia coli pathogenic serotypes, Vibrio cholerae and V. parahaemolyticus, Clostridium difficile and Clostridium perfringens, Bacillus cereus, Campylobacter spp., Helicobacter spp., Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus); viruses (orthoreoviruses and rotaviruses, norovirus, adenovirus, astrovirus, Hepatitis A Virus, Hepatitis E Virus). - Clostridium botulinum bacteria transmitted via the gastrointestinal tracts that severely affect central nervous system; botulinum toxin activity - epidemiology, diseases, diagnostics, prevention and treatment for digestive tract infections - the student is able to explain the influence of the virulence factors on the course of infection 6
7 1. Digestive tract infections - describe sampling and transport. 2. Study and draw Bacillus cereus stained with Gram method. 3. Study and draw the growth of Bacillus cereus on agar-agar medium. 4. Prepare staining of bacilli with Gram method and Schaeffer-Fulton method: Schaeffer-Fulton method for staining endospores I. Air dry and heat fix the organism on a glass slide. II. Pour malachite green stain solution on a smear; the slide should be steamed three times over a container of boiling water. III. Wash the slide with tap water. IV. Counterstain with safranin for 1 min. Wash with tap water; V. Examine the slide under the oil immersion lens (100x). Endospores are bright green and vegetative cells are brownish red to pink. Fill in the protocol:..times magnification was used to observe microorganisms. Which specific elements of Bacillus cell do you know?... Shape of bacterial cells is... Arrangement of bacterial cells is Study and draw enteric rods stained with a) Gram method b) positive-negative staining. 6. Study the growth of Escherichia coli and Salmonella on a) MacConkey agar b) EMB/Lewin s agar c) SS agar d) Kligler s/triple Sugar Iron (TSI) slant 7. Prepare the identification of two species (enteric rods) with API E strips. 8. Analyze biochemical features of enteric rods. Capsule Lactose H2S Citrate Urease VP Indol Methyl Red Adonitol Escherichia coli +/ Klebsiella oxytoca /- -/+ + Enterobacter / Citrobacter /- + - Serratia / /- - Salmonella Shigella /+ + - Proteus /- + +/ Yersinia /
8 9. Prepare the identification of Shigella sp. with agglutination method. 10. Study tests for Clostridium difficile. 11. Stain a sample of yoghurt or kefir with Gram method (diluted and/or non-diluted sample)...times magnification was used to observe microorganisms. Which specific feature of lactic bacteria do you know?... Shape of bacterial cells is... Arrangement of bacterial cells is Analyze case reports concerning digestive tract infections. 13. Learning assessment questions. C9: Urogenital infections. Colloquium no. 2 (C5-C8 and lectures no. 2 and 3) - the physiological flora of the urogenital system; the risk factors of the urogenital infections - clinical forms of the urinary tract infections (UTI) and genital infections - bacteriological analysis of urine the methods of sampling - the purity degrees of the vagina; definition of bacterial vaginosis (Gardnerella vaginalis, Mobilluncus curtisi, Prevotella spp., Peptostreptococcu spp., Veilonella spp., Eubacterium spp., Fusobacterium) - the etiological factors of UTI: bacteria (Enterobacteriaceae members [Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., Proteus spp.], Stahylococcus saprophiticus, Leptospira spp., Corynebacterium urealyticum) - the definitions of intrauterine infections, perinatal infections, TORCH - the etiological factors of vertical infections: bacteria (Streptococcus agalactiae, Listeria monocytogenes, Treponema pallidum, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma spp., Ureaplasma spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae); viruses (parvovirus B19, rubella virus) - Lactobacillus spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. they role in the proper functioning of the human body - epidemiology, diseases, diagnostics, prevention and treatment for urinary tract, intrauterine and perinatal infections - the student is able to explain the influence of the virulence factors on the course of infection 1. Urogenital infections - describe sampling and transport. Prepare the microscopic slide of lactobacilli stained with Gram method. 2. Study and draw Lactobacillus sp. stained with Gram method. 3. Study the growth of Lactobacillus on Rogosa agar. 4. Analyze the role of probiotics. 5. Study and draw slides presenting bacterial vaginosis. 6. Describe bacteriological analysis of urine. 7. Presentation of transport-diagnostic medium Uricult and results interpretation. 8. Inoculate samples of urine on microbiological media. 9. Study Mycoplasma/Ureaplasma test. 10. Analyze of case reports concerning urinary tract infections, perinatal infections, and intrauterine infections. 11. Learning assessment questions. C10: Sexually transmitted diseases. - the etiological factors of sexually transmitted diseases: viral (Human Papilloma Virus, Molluscum contagiosum virus); bacterial (Treponema pallidum, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Haemophilus ducreyi, Klebsiella granulomatis, Mycoplasma spp., Ureaplasma spp.) - sexually transmitted infections caused by herpesviruses - epidemiology, diseases, diagnostics, prevention and treatment for genital tract infections - the student is able to explain the influence of the virulence factors on the course of infection 8
9 1. Sexually transmitted infections - describe sampling and transport. 2. Study and draw Neisseria gonorrhoeae stained with Gram method. 3. Describe API NH kit. 4. Study and draw spirochetes...times magnification was used to observe microorganisms. Which specific features of spirochetes do you know? Analyze diagnostics of syphilis. 6. Analyze detection of sexually transmitted pathogens with molecular biology methods. 7. Culture samples from hospitals. 8. Analyze case reports concerning sexually transmitted diseases. 9. Learning assessment questions. C11: Infections of the nervous system, - the factors predisposing to the central nervous system (CNS) infections, the modes of transmission - etiological factors of meningitis and brain infections - microbiological diagnostics of meningitis (sampling and microbiological analysis of cerebrospinal fluid) - the etiological factors of CNS infections: viral (enteroviruses [coxackie virus A and B, echovirus]; poliovirus, rabies virus, polyomaviruses); bacterial (Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, E. coli K1, Streptococcus agalactiae, Listeria monocytogenes) - activity of neurotoxins released by Clostridium botulinum and C. tetani - CNS complications in bacterial infections (Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Leptospira interrogans, Treponema pallidum, Francisella tularensis, Brucella spp., Ehrlichia spp.) - prions - postvaccinal viral infections of CNS (mumps virus, measles virus, rubella virus, varicella zoster virus) - postinfectious viral infections of CNS (mumps virus, measles virus, rubella virus, HIV, influenza virus, herpesviruses: herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus) - epidemiology, diseases, diagnostics, prevention and treatment for central nervous system infections - the student is able to explain the influence of the virulence factors on the course of infection 1. Nervous system infections - describe sampling and transport. 2. Study and draw bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid. 3. Presentation of Slidex meningite kit 5 latex test. 4. Presentation of an automatic BD Bactec system. 5. Subculture of samples from hospitals. 6. Gram staining of CSF culture. 7. Analysis of case reports concerning nervous system infections. 8. Learning assessment questions. C12: Bloodstream infections. Zoonoses, vector-borne infections. - the difference between bacteremia/fungemia/viremia, sepsis, septic shock, and multi-organ dysfunction syndrome; - etiological factors of bloodstream infections (coagulase-negative staphylococci, toxic shock syndrome caused by S. aureus, streptococci viridans group, Stenotrophomonas spp., Bulkholderia spp.) 9
10 - zoonotic diseases: viral (Flaviviruses/West Nile virus, St. Louis encephalitis virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, Murray valley virus, Yellow fever virus, Dengue virus/, Togaviruses/Eastern, Western, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis viruses, Chikungunya virus/, Bunyaviruses /La Crosse viru, Rift valley fever virus, California encephalitis Virus, Sandfly fever virus, Congo-Crimean haemorrhagic fever virus, Arenaviridae /Lymphogenic choriomeningitis virus LCM, Lassa virus, Junin virus, Machupo virus, Filoviridae /Marburg virus, Ebola virus); bacterial (Rickettsia spp., Coxiella burnetti, Borrelia spp., Bartonella spp, Brucella spp., Pasteurella spp., Yersinia pestis, Francisella tularensis, Leptospira interrogans, Ehrlichia spp.) - HIV - epidemiology, diseases, diagnostics, prevention and treatment for central nervous system infections - the student is able to explain the influence of the virulence factors on the course of infection. 1. Study the sampling, the storage and transport of blood samples. 2. Presentation of media for blood culture. 3. Study and draw Streptococcus pyogenes on blood agar. 4. Study and grow Staphylococcus epidermidis on the blood agar and Chapman medium. 5. Presentation of slides from positive blood cultures. 6. Presentation of ASO latex test (ASL-SLIDEX). 7. Prepare Gram staining from blood culture...times magnification was used to observe microorganisms. Which specific feature of these bacteria do you know? Identify strains isolated in hospitals with Phoenix system. 9. Analyze case reports concerning blood stream infections and zoonoses. 10. Learning assessment questions. C13. Hospital-acquired infections. Colloquium no. 3 (C9-C12 and lecture no. 4) Knowledge: The student knows: the definition of the nosocomial infection; the etiological factors of the hospitalacquired infections, the methods used to control and prevent from nosocomial infections. 1. Analyze results from Phoenix system. 2. Study and analyze cases of hospital-acquired infections. 3. Revision of microbiological slides and cultures. 4. Learning assessment questions. 10
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year )
 BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 39, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 39, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 49, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 49, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 33, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 33, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 50, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 50, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 38, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 38, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 22, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 22, 2018 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report
 HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 3, 2019 (Notification
HPSC - Weekly Infectious Disease Report Statutory Notifications of Infectious Diseases reported in Ireland via the Computerised Infectious Disease Reporting (CIDR) system for: Week 3, 2019 (Notification
M O L E C U L A R G E N E T I C S
 MOLECULAR GENETICS ADVANTAGES OF MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular genetics is a dynamic and transformative area of diagnostics, leading to insights in research and treatment in many disease states that are
MOLECULAR GENETICS ADVANTAGES OF MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular genetics is a dynamic and transformative area of diagnostics, leading to insights in research and treatment in many disease states that are
II- Streptococci. Practical 3. Objective: Required materials: Classification of Streptococci: Streptococci can be classified according to:
 Practical 3 II- Streptococci Objective: 1. Use of blood agar to differentiate between,, and hemolytic streptococci. 2. To know Gram reaction, shape and arrangement of streptococci. 3. To differentiate
Practical 3 II- Streptococci Objective: 1. Use of blood agar to differentiate between,, and hemolytic streptococci. 2. To know Gram reaction, shape and arrangement of streptococci. 3. To differentiate
Cal OSHA Title 8, Section 5199 Appendix D: Aerosol Transmissible Pathogens Laboratory
 Cal OSHA Title 8, Section 5199 Appendix D: Aerosol Transmissible Pathogens Laboratory This appendix contains a list of agents that, when reasonably anticipated to be present, require a laboratory to comply
Cal OSHA Title 8, Section 5199 Appendix D: Aerosol Transmissible Pathogens Laboratory This appendix contains a list of agents that, when reasonably anticipated to be present, require a laboratory to comply
Fort Detrick Area B11 Removal Action Update
 Area B11 Removal Action Update US Army Corps Restoration Advisory Board Meeting 13 February 2002, 7:30 PM Frederick, Maryland Excavation of overburden material completed and clean soil moved to Area B
Area B11 Removal Action Update US Army Corps Restoration Advisory Board Meeting 13 February 2002, 7:30 PM Frederick, Maryland Excavation of overburden material completed and clean soil moved to Area B
Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations
 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE OUTBREAK MANUAL New Jersey s Public Health Response Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations June 2013 Public Health Emergency Response Capability Requirements as stated
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE OUTBREAK MANUAL New Jersey s Public Health Response Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations June 2013 Public Health Emergency Response Capability Requirements as stated
12/12/2011. Atypical Pneumonia. Objectives. Causative Agents of Acute Pneumonia Bacteria. Causative Agents of Acute Pneumonia Other Agents
 Objectives Atypical Pneumonia K. Sue Kehl, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Associate Professor, Pathology Medical College of Wisconsin Associate Director of Clinical Pathology & Technical Director of Microbiology, Children's
Objectives Atypical Pneumonia K. Sue Kehl, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Associate Professor, Pathology Medical College of Wisconsin Associate Director of Clinical Pathology & Technical Director of Microbiology, Children's
"Wanted Poster" Diseases
 "Wanted Poster" Diseases Part One - Choosing a Disease Listed below are several bacteria and the disease they cause. Pick any one bacteria/disease to research. It is highly recommended that you pick a
"Wanted Poster" Diseases Part One - Choosing a Disease Listed below are several bacteria and the disease they cause. Pick any one bacteria/disease to research. It is highly recommended that you pick a
THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE
 THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DIPLOMA IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES FINAL YEAR EXAMINATION
THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DIPLOMA IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES FINAL YEAR EXAMINATION
KOMAR UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KUST) Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016
 Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
ID of Most Common Bacterial Pathogens. CLS 417- Clinical Practice in Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 ID of Most Common Bacterial Pathogens CLS 417- Clinical Practice in Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani BACTERIA Gram Positive Gram Negative Cocci Bacilli Bacilli Cocci Coccobacilli - Staph - Strept - Clostridium
ID of Most Common Bacterial Pathogens CLS 417- Clinical Practice in Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani BACTERIA Gram Positive Gram Negative Cocci Bacilli Bacilli Cocci Coccobacilli - Staph - Strept - Clostridium
Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use
 Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use 2 Abstract We will introduce bright-field microscope use, practice Gram staining with foodborne pathogens, and practice endospore staining with Bacillus
Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use 2 Abstract We will introduce bright-field microscope use, practice Gram staining with foodborne pathogens, and practice endospore staining with Bacillus
Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: June 18, 2001 Approved by: Laboratory Director RESIDENT OBJECTIVES AT MSH
 Policy # MI/EDU/08/04/v01 Page1 of 13 Section: Subject Title: Resident Objectives at MSH Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: June 18, 2001 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: SPECIMENS
Policy # MI/EDU/08/04/v01 Page1 of 13 Section: Subject Title: Resident Objectives at MSH Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: June 18, 2001 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: SPECIMENS
Medical Microbiology
 Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview
 MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
INFECTIOUS DISEASE. Page 2
 Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio
 Labquality EQAS Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio Clinically relevant external quality assessment program for microbiology Bacterial serology Bacteriology Mycology Parasitology Preanalytics Virology Labquality
Labquality EQAS Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio Clinically relevant external quality assessment program for microbiology Bacterial serology Bacteriology Mycology Parasitology Preanalytics Virology Labquality
Streptococci facultative anaerobe
 THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
 Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Unofficial translation No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Unofficial translation No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
Potential Reimbursement CPT Codes
 BioFire FilmArray Blood Culture Identification (BCID) Panel Medicare All targets (n) 87150 n x * *BioFire BCID Panel is comprised of 27 total targets. The number of targets allowed for reimbursement may
BioFire FilmArray Blood Culture Identification (BCID) Panel Medicare All targets (n) 87150 n x * *BioFire BCID Panel is comprised of 27 total targets. The number of targets allowed for reimbursement may
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Blood Culture What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected into bottles with culture
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Blood Culture What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected into bottles with culture
Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland N.B. Unofficial translation. Legally valid only in Finnish and Swedish
 Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland N.B. Unofficial translation. Legally valid only in Finnish and Swedish No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 was repealed
Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland N.B. Unofficial translation. Legally valid only in Finnish and Swedish No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 was repealed
Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1
 Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1 Blood Culture 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 2 What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected
Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1 Blood Culture 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 2 What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Normal Human Flora. (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine
 Normal Human Flora (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine 2014-2015 Objectives Describe important human normal flora. Demonstrate the epidemiology of human normal flora. Determine
Normal Human Flora (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine 2014-2015 Objectives Describe important human normal flora. Demonstrate the epidemiology of human normal flora. Determine
SOUTH EASTERN KENYA UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION 2015/2016 FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF PUBLIC HEALTH
 SOUTH EASTERN KENYA UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION 2015/2016 FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF PUBLIC HEALTH HPH 102: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY DATE: 7/12/2015 TIME:10:30-12:30PM INSTRUCTIONS
SOUTH EASTERN KENYA UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION 2015/2016 FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF PUBLIC HEALTH HPH 102: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY DATE: 7/12/2015 TIME:10:30-12:30PM INSTRUCTIONS
Department of Microbiology, IMS, BHU Teaching schedule B.D.S. 4 th Semester 2 nd Year (2017 Batch) Session
 Department of Microbiology, IMS, BHU Teaching schedule B.D.S. 4 th Semester 2 nd Year (2017 Batch) 2018-19 Session Date Topic Name of Faculty members/ Senior Resident* 02.01.2019 Viridans group of Streptococci
Department of Microbiology, IMS, BHU Teaching schedule B.D.S. 4 th Semester 2 nd Year (2017 Batch) 2018-19 Session Date Topic Name of Faculty members/ Senior Resident* 02.01.2019 Viridans group of Streptococci
PATHOGEN DETECTION WITH THE FILMARRAY
 PATHOGEN DETECTION WITH THE FILMARRAY The System Sample-to-Answer in an Hour Single sample Multiple samples The FilmArray integrates sample preparation, amplification, detection, and analysis all into
PATHOGEN DETECTION WITH THE FILMARRAY The System Sample-to-Answer in an Hour Single sample Multiple samples The FilmArray integrates sample preparation, amplification, detection, and analysis all into
SCHEDULE 5 PATHOGENS AND TOXINS VIRUSES
 10/2012 SCHEDULE 5 PATHOGENS AND TOXINS VIRUSES Chikungunya virus Congo- crimean haemorrhagic fever virus Dengue fever virus Dobrava/Belgrade virus Eastern equine encephalitis virus Ebola virus Everglades
10/2012 SCHEDULE 5 PATHOGENS AND TOXINS VIRUSES Chikungunya virus Congo- crimean haemorrhagic fever virus Dengue fever virus Dobrava/Belgrade virus Eastern equine encephalitis virus Ebola virus Everglades
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
 The Microbial Size The Viruses Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Electron Micrograph Images of Viruses Influenza virus (RNA virus) Rotavirus (RNA virus) Adenovirus, showing
The Microbial Size The Viruses Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Electron Micrograph Images of Viruses Influenza virus (RNA virus) Rotavirus (RNA virus) Adenovirus, showing
KENNEL KARE SC DISINFECTANT / CLEANER / DEODORIZER Efficacy Data EPA Reg. #
 Inc. Efficacy: Hospital Disinfection (at ½ ounce per gallon) Kennel Kare SC is bactericidal according to the AOAC Use Dilution Test method on hard inanimate surfaces modified in the presence of 5% organic
Inc. Efficacy: Hospital Disinfection (at ½ ounce per gallon) Kennel Kare SC is bactericidal according to the AOAC Use Dilution Test method on hard inanimate surfaces modified in the presence of 5% organic
Chain of Infection Agent Mode of transmission Contact (direct, indirect, droplet spread) Airborne Common-vehicle spread Host
 Goals Microbiology of Healthcare-associated Infections William A. Rutala, Ph.D., M.P.H. Director, Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology and Research Professor of Medicine, University
Goals Microbiology of Healthcare-associated Infections William A. Rutala, Ph.D., M.P.H. Director, Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology and Research Professor of Medicine, University
Storage conditions. roomtemperature or incubator at 36 C. Other: 2-8 C Blood: roomtemperature or incubator at. A.s.a.p. max 24h. A.s.a.p.
 Extract Vademecum Department of Medical Microbiology Status: Code: Version: Approval date: Geldig MMB-PR-04/1 1 Juni 2017 Name request Specimen Material needed Transport Bacteriology Bacterial culture
Extract Vademecum Department of Medical Microbiology Status: Code: Version: Approval date: Geldig MMB-PR-04/1 1 Juni 2017 Name request Specimen Material needed Transport Bacteriology Bacterial culture
Interstate Shipment of Etiologic Agents 42 CFR Part 72
 Interstate Shipment of Etiologic Agents 42 CFR Part 72 Federal Register, Vol. 45, No. 141-Monday, July 21, 1980. Part 72-Interstate Shipment of Etiologic Agents 1 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Interstate Shipment of Etiologic Agents 42 CFR Part 72 Federal Register, Vol. 45, No. 141-Monday, July 21, 1980. Part 72-Interstate Shipment of Etiologic Agents 1 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Gram-negative rods. Enterobacteriaceae. Biochemical Reactions. Manal AL khulaifi
 Gram-negative rods Enterobacteriaceae Biochemical Reactions Bacteria Gram positive Gram negative Cocci Bacilli Cocci Rods Characters of Enterobacteriaceae All Enterobacteriaciae Gram-negative rods Reduce
Gram-negative rods Enterobacteriaceae Biochemical Reactions Bacteria Gram positive Gram negative Cocci Bacilli Cocci Rods Characters of Enterobacteriaceae All Enterobacteriaciae Gram-negative rods Reduce
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia
 Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM. ITEMS NECESSARY BUT NOT INCLUDED IN THE KIT A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM Reagent (ref ) Mycoplasma Transport Broth (ref.
 A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM ENGLISH System for detection, count and susceptibility test of pathogenic urogenital microorganisms DESCRIPTION A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM is a 24-well system containing desiccated biochemical
A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM ENGLISH System for detection, count and susceptibility test of pathogenic urogenital microorganisms DESCRIPTION A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM is a 24-well system containing desiccated biochemical
LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY
 LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY 1. General characteristics of piogenic cocci. 2. Staphylococcus, staphylococcus species, differentiation signs of staphylococci. Factor
LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY 1. General characteristics of piogenic cocci. 2. Staphylococcus, staphylococcus species, differentiation signs of staphylococci. Factor
STUDY PLAN II year students 2nd semester 1 Class
 STUDY PLAN II year students 2nd semester 1 Class 1. Pyogenic cocci. Staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus species, differentiation of staphylococci. Pathogenicity factors and toxins. Characteristics of
STUDY PLAN II year students 2nd semester 1 Class 1. Pyogenic cocci. Staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus species, differentiation of staphylococci. Pathogenicity factors and toxins. Characteristics of
Microsan rx Anti-Microbial Healthcare Professional Soap. Organism Positives ATCC #
 : Contact Time: 30 seconds 17,500 ppm. PCMX active Organism Positives ATCC # Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus 0 s Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. woffii 0 s Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia 0
: Contact Time: 30 seconds 17,500 ppm. PCMX active Organism Positives ATCC # Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus 0 s Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. woffii 0 s Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia 0
Infectious Material. hazmat.dot.gov/regs/rules.htm iata.org/dangerousgoods
 Infectious Material Most medical specimens sent to an esoteric laboratory such as Mayo Medical Laboratories are flown on passenger aircraft or are carried by common air carrier such as FedEx. The International
Infectious Material Most medical specimens sent to an esoteric laboratory such as Mayo Medical Laboratories are flown on passenger aircraft or are carried by common air carrier such as FedEx. The International
1430 West McCoy Lane Santa Maria, CA p:
 091217TR HardyCHROM BluEcoli 1 HardyCHROM Candida 2 HardyCHROM ECC 3 HardyCHROM ESBL 4 HardyCHROM Listeria 5 HardyCHROM MRSA 6 HardyCHROM O157 7 HardyCHROM Salmonella 8 HardyCHROM SS NoPRO 9 HardyCHROM
091217TR HardyCHROM BluEcoli 1 HardyCHROM Candida 2 HardyCHROM ECC 3 HardyCHROM ESBL 4 HardyCHROM Listeria 5 HardyCHROM MRSA 6 HardyCHROM O157 7 HardyCHROM Salmonella 8 HardyCHROM SS NoPRO 9 HardyCHROM
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AAP. See American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Acyclovir dosing in infants, 185 187 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) COFN of, 199 204 Amphotericin
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AAP. See American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Acyclovir dosing in infants, 185 187 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) COFN of, 199 204 Amphotericin
Chapter 19. Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria. Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
 Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Microbiology Department Contact: Dr David Ashburn Zone 3 Raigmore Hospital Tel: +44 (0) 1463 704108 Old Perth Road Fax: +44 (0) 1463 705648
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Microbiology Department Contact: Dr David Ashburn Zone 3 Raigmore Hospital Tel: +44 (0) 1463 704108 Old Perth Road Fax: +44 (0) 1463 705648
M E D I C A L L A B O R A T O R Y
 M E D I C A L L A B O R A T O R Y E V A L U A T I O N PARTICIPANT SUMMARY 2 0 1 7 Microbiology 2017 MLE-M1 Total Commitment to Education and Service Provided by ACP, Inc. Evaluation Criteria... 2 Microbiology
M E D I C A L L A B O R A T O R Y E V A L U A T I O N PARTICIPANT SUMMARY 2 0 1 7 Microbiology 2017 MLE-M1 Total Commitment to Education and Service Provided by ACP, Inc. Evaluation Criteria... 2 Microbiology
ZINEX. Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg
 ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
Ch 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
 Ch 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope SLOs Review the metric units of measurement Define total magnification and resolution Explain how electron and light microscopy differ Differentiate
Ch 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope SLOs Review the metric units of measurement Define total magnification and resolution Explain how electron and light microscopy differ Differentiate
Bacterial Metabolism & Growth Characteristics. Stijn van der Veen
 Bacterial Metabolism & Growth Characteristics Stijn van der Veen Differentiating bacterial species Morphology (shape) Composition (cell envelope and other structures) Metabolism & growth characteristics
Bacterial Metabolism & Growth Characteristics Stijn van der Veen Differentiating bacterial species Morphology (shape) Composition (cell envelope and other structures) Metabolism & growth characteristics
Urine bench. John Ferguson Sept 2013
 Urine bench John Ferguson Sept 2013 Overview Specimen collection- separate presentation Urinalysis: protein, blood, white cells, nitrite Microscopy- crystals and casts- separate presentations quantitative
Urine bench John Ferguson Sept 2013 Overview Specimen collection- separate presentation Urinalysis: protein, blood, white cells, nitrite Microscopy- crystals and casts- separate presentations quantitative
IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS YUSRON SUGIARTO
 IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS YUSRON SUGIARTO BACKGROUND One of the most fundamental tasks that someone working with micro-organisms must perform is to identify microorganisms. There are a number of
IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS YUSRON SUGIARTO BACKGROUND One of the most fundamental tasks that someone working with micro-organisms must perform is to identify microorganisms. There are a number of
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology
 NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
Staphylococci. Gram stain: gram positive cocci arranged in clusters.
 Microbiology lab Respiratory system Third medical year Lab contents: Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp), two types of filamentous fungi (Aspergillus and Penicillium spp), and
Microbiology lab Respiratory system Third medical year Lab contents: Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp), two types of filamentous fungi (Aspergillus and Penicillium spp), and
Microbiology Specimen Collection Instructions. Table I Culture and Sensitivities/TB
 Specimen Page 1 of 10 Source / Type of Specimen Culture and Sensitivities () Abscess aspirate, wound aspirate in sterile screw cap or swab in charcoal. Obtain anaerobic swab from lab. Pilonidal and perirectal
Specimen Page 1 of 10 Source / Type of Specimen Culture and Sensitivities () Abscess aspirate, wound aspirate in sterile screw cap or swab in charcoal. Obtain anaerobic swab from lab. Pilonidal and perirectal
Preventing & Controlling the Spread of Infection
 Preventing & Controlling the Spread of Infection Contributors: Alice Pong M.D., Hospital Epidemiologist Chris Abe, R.N., Senior Director Ancillary and Support Services Objectives Review the magnitude of
Preventing & Controlling the Spread of Infection Contributors: Alice Pong M.D., Hospital Epidemiologist Chris Abe, R.N., Senior Director Ancillary and Support Services Objectives Review the magnitude of
References Required document for Laboratory Accreditation by the College of American Pathologists.
 Subject Culture: Lower Respiratory Tract Index Number Lab-3375 Section Laboratory Subsection Microbiology Category Departmental Contact Sarah Stoner Last Revised 9/11/2017 References Required document
Subject Culture: Lower Respiratory Tract Index Number Lab-3375 Section Laboratory Subsection Microbiology Category Departmental Contact Sarah Stoner Last Revised 9/11/2017 References Required document
Viral Diseases. T Bamdad, PhD, Tarbiat Modares University
 Viral Diseases 1 Categorizing viral infections by the organ system most commonly affected (eg, lungs, GI tract, skin, liver, CNS, mucous membranes) can be clinically useful, although certain viral disorders
Viral Diseases 1 Categorizing viral infections by the organ system most commonly affected (eg, lungs, GI tract, skin, liver, CNS, mucous membranes) can be clinically useful, although certain viral disorders
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
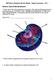 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
KENNEL KARE SC DISINFECTANT / CLEANER / DEODORIZER Efficacy Data EPA Reg. #
 Inc. Efficacy: Disinfection (at ½ ounce per gallon) Kennel Kare SC is bactericidal according to the AOAC Use Dilution Test method on hard inanimate surfaces modified in the presence of 5% organic serum
Inc. Efficacy: Disinfection (at ½ ounce per gallon) Kennel Kare SC is bactericidal according to the AOAC Use Dilution Test method on hard inanimate surfaces modified in the presence of 5% organic serum
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Clinical Microbiology QMC Campus Derby Road Nottingham NG7 2UH Contact: Jil Bowskill Tel: +44 (0) 1905 760192 Ext 30659 E-Mail: jilean.bowskill@nuh.nhs.uk
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Clinical Microbiology QMC Campus Derby Road Nottingham NG7 2UH Contact: Jil Bowskill Tel: +44 (0) 1905 760192 Ext 30659 E-Mail: jilean.bowskill@nuh.nhs.uk
Infection Data: Form Updates
 Infection Data: Form Updates Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Why is infection data important?
Infection Data: Form Updates Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Why is infection data important?
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
Class 15. Infections of the Central Nervous System
 English Division 6 E.D. Class 15 Infections of the Central Nervous System Pathogenesis, etiologic agents, clinical symptoms, and laboratory diagnosis To be performed: - Read carefully attached case studies
English Division 6 E.D. Class 15 Infections of the Central Nervous System Pathogenesis, etiologic agents, clinical symptoms, and laboratory diagnosis To be performed: - Read carefully attached case studies
EXERCISE. Proteins,Amino Acids, and Enzymes VII: Oxidase Test. Suggested Reading in Textbook. Pronunciation Guide. Materials per Student
 EXERCISE 30 Proteins,Amino Acids, SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS Be careful with the Bunsen burner flame. No mouth pipetting. The oxidase reagent is caustic. Avoid contact with eyes and skin. In case of contact,
EXERCISE 30 Proteins,Amino Acids, SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS Be careful with the Bunsen burner flame. No mouth pipetting. The oxidase reagent is caustic. Avoid contact with eyes and skin. In case of contact,
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the
 Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Babak Valizadeh, DCLS
 Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
4. The most common cause of traveller s diarrheoa is a. Rotavirus b. E coli c. Shigella d. Giardia e. Salmonella
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
Introduction. Crowded environments where the air is re-circulated can often be heavily infected with unseen germs and viruses.
 Introduction The continued increase in urbanisation,, population growth and global travel means germs and viruses can spread faster and further than ever before. Air, sea, rail and road travel have never
Introduction The continued increase in urbanisation,, population growth and global travel means germs and viruses can spread faster and further than ever before. Air, sea, rail and road travel have never
PAMET Continuing Education 2016
 PAMET Continuing Education 2016 Agent of gastroenteritis Medium/method] used for routine screening/detection in stool samples Salmonella, Shigella, MacConkey, Hektoen, Bismuth sulfite,etc. Plesiomonas
PAMET Continuing Education 2016 Agent of gastroenteritis Medium/method] used for routine screening/detection in stool samples Salmonella, Shigella, MacConkey, Hektoen, Bismuth sulfite,etc. Plesiomonas
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Luton and Dunstable University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Lewsey Road Luton Bedfordshire LU4 0DZ Contact: Pauline Philip Tel: +44 (0)1582
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Luton and Dunstable University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Lewsey Road Luton Bedfordshire LU4 0DZ Contact: Pauline Philip Tel: +44 (0)1582
Types of infections & Mode of transmission of diseases
 Types of infections & Mode of transmission of diseases Badil dass Karachi King s College of Nursing Types of Infection Community acquired infection: Patient may acquire infection before admission to the
Types of infections & Mode of transmission of diseases Badil dass Karachi King s College of Nursing Types of Infection Community acquired infection: Patient may acquire infection before admission to the
Respiratory Pathogen Panel TEM-PCR Test Code:
 Respiratory Pathogen Panel TEM-PCR Test Code: 220000 Tests in this Panel Enterovirus group Human bocavirus Human coronavirus (4 types) Human metapneumovirus Influenza A - Human influenza Influenza A -
Respiratory Pathogen Panel TEM-PCR Test Code: 220000 Tests in this Panel Enterovirus group Human bocavirus Human coronavirus (4 types) Human metapneumovirus Influenza A - Human influenza Influenza A -
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL (A) Further inclusion criteria and categorisation of ICD-10 diagnostic codes Pneumonia: A310 Pulmonary mycobacterial infection A420 Pulmonary actinomycosis A481 Legionnaires' disease
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL (A) Further inclusion criteria and categorisation of ICD-10 diagnostic codes Pneumonia: A310 Pulmonary mycobacterial infection A420 Pulmonary actinomycosis A481 Legionnaires' disease
ENG MYCO WELL D- ONE REV. 1.UN 29/09/2016 REF. MS01283 REF. MS01321 (COMPLETE KIT)
 ENG MYCO WELL D- ONE MYCO WELL D-ONE System for the presumptive identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test of urogenital mycoplasmas, Gardnerella vaginalis, Trichomonas vaginalis, Candida albicans
ENG MYCO WELL D- ONE MYCO WELL D-ONE System for the presumptive identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test of urogenital mycoplasmas, Gardnerella vaginalis, Trichomonas vaginalis, Candida albicans
Lecture 3. Microbial Physiology
 Micro-Biology For 3 rd Sem. Students of ISM-IUK, Bishkek Lecture 3 Microbial Physiology LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Bacterial Growth 2. Growth Requirements 3. Nutritional types of microorganisms 4. Enzymes,
Micro-Biology For 3 rd Sem. Students of ISM-IUK, Bishkek Lecture 3 Microbial Physiology LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Bacterial Growth 2. Growth Requirements 3. Nutritional types of microorganisms 4. Enzymes,
CHAPTER 515. COMMUNICABLE DISEASE AND INJURY REPORTING EFFECTIVE 9/12/2014
 TITLE 310. CHAPTER 515. COMMUNICABLE DISEASE AND INJURY REPORTING EFFECTIVE 9/12/2014 310:515-1-1. Purpose The rules in this Chapter implement the Communicable Diseases Reporting Regulations, 63 O.S. 1981,
TITLE 310. CHAPTER 515. COMMUNICABLE DISEASE AND INJURY REPORTING EFFECTIVE 9/12/2014 310:515-1-1. Purpose The rules in this Chapter implement the Communicable Diseases Reporting Regulations, 63 O.S. 1981,
CHAPTER IV ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF BACTERIA FROM SEPSIS SAMPLES
 62 CHAPTER IV ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF BACTERIA FROM SEPSIS SAMPLES 4.1 INTRODUCTION Infectious diseases remain major cause of mortality in both child and maternal populations. The mortality rate
62 CHAPTER IV ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF BACTERIA FROM SEPSIS SAMPLES 4.1 INTRODUCTION Infectious diseases remain major cause of mortality in both child and maternal populations. The mortality rate
Perform Gram stain only. Select Survey D5, Gram Stain
 www.cap.org Bacteriology This flowchart is provided as a guide for ordering the appropriate Bacteriology Surveys for your laboratory s testing menu. In order to meet CLIA requirements for the subspecialty
www.cap.org Bacteriology This flowchart is provided as a guide for ordering the appropriate Bacteriology Surveys for your laboratory s testing menu. In order to meet CLIA requirements for the subspecialty
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/Weds. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/Thurs. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Manal AL khulaifi. Enterobacteriaceae
 Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics E.coli Most significant species in the genus Important potential pathogen in humans Common isolate from colon flora Dry, pink (lactose positive) pink colony with area
Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics E.coli Most significant species in the genus Important potential pathogen in humans Common isolate from colon flora Dry, pink (lactose positive) pink colony with area
PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY
 18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
IMMUVIEW S. PNEUMONIAE ANTIGEN TEST. Lateral flow test for qualitative detection of S. pneumoniae in urine and cerebrospinal fluid.
 IMMUVIEW S. PNEUMONIAE ANTIGEN TEST Lateral flow test for qualitative detection of S. pneumoniae in urine and cerebrospinal fluid. 2 IMMUVIEW S. PNEUMONIAE ANTIGEN TEST For in vitro diagnostic use Application
IMMUVIEW S. PNEUMONIAE ANTIGEN TEST Lateral flow test for qualitative detection of S. pneumoniae in urine and cerebrospinal fluid. 2 IMMUVIEW S. PNEUMONIAE ANTIGEN TEST For in vitro diagnostic use Application
Efficacy Data. Disinfectant Cleaner & Odor Counteractant EPA REG. #
 SENTS-ALE Hospital Disinfection (at 2 ounces per gallon)) Scents-Able is bactericidal according to the AOA Use Dilution Test method on hard inanimate surfaces modified in the presence of 5% organic serum
SENTS-ALE Hospital Disinfection (at 2 ounces per gallon)) Scents-Able is bactericidal according to the AOA Use Dilution Test method on hard inanimate surfaces modified in the presence of 5% organic serum
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Infectious Disease Antibodies and Antigens. ...Viro Stat. Supplying Researchers and Manufacturers Since
 Infectious Disease Antibodies and Antigens...Viro Stat Supplying Researchers and Manufacturers Since 1985 Infectious Disease Antibodies and Antigens...Viro Stat Supplying Researchers and Manufacturers
Infectious Disease Antibodies and Antigens...Viro Stat Supplying Researchers and Manufacturers Since 1985 Infectious Disease Antibodies and Antigens...Viro Stat Supplying Researchers and Manufacturers
List of teams: Practice question: Which of the following individuals was among the first to recognize the importance of handwashing?
 List of teams: 1. Group 1 - Room 304 - Dr. Dobkin 2. Group 2 - Room 306 - Dr. Yin 3. Group 3 - Room 308 - Dr. Lowy 4. Group 4 - Room 310 - Dr. Neu 5. Group 5 - Room 316 - Dr. Prince 6. Group 6 - Room 320
List of teams: 1. Group 1 - Room 304 - Dr. Dobkin 2. Group 2 - Room 306 - Dr. Yin 3. Group 3 - Room 308 - Dr. Lowy 4. Group 4 - Room 310 - Dr. Neu 5. Group 5 - Room 316 - Dr. Prince 6. Group 6 - Room 320
