bad noted the appearance of a few keratotic
|
|
|
- Harry Jonathan Grant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELASTOSIS PET{FORANS SERPIGINOSA A CASE REPOET WITH HISTOCHEMICAL AND ENZYME DIGESTION STUDIES* KEN HASHIMOTO, M.D. AND WILLIAM H. HILL, M.D. In 1952 Lutz (1) described a peculiar serpiginous keratotie eruption that was present on the sides of the neck of a 21-year-old man for 8 years. He named the lesion keratosis follieularis serpiginosa. Histologic studies of the keratotic wall showed that it was composed of a cystic structure containing horny lamellac situated just beneath the epidermis and that it appeared to have arisen from the hair follicles. Under the same title, Beening and limiter (2) in 1954 tiescribed the eruption in a 13-year-old girl who had developed ring-formed and semi-circular lesions on the side and nape of her neck. When first seeo 3 years before, these lesions consisted of a number of closely-set hailstone-sized, hard, reddish papules. The summit of each papule revealed a keratotie plug which when removed revealed a deep depression. The center of the rings appeared depigmented but not atrophic. Three years later most of the lesions had undergone involution. Histologic study of specimens removed by biopsy showed a markedly aeanthotie epidermis which contained horny lamellae. Serial sections demonstrated that the horny masses penetrated into the eutis in some places. Where they remained in contact with connective tissue, inflammatory infiltrate containing small round cells, histioeytes and occasional giant cells were found. The hyperkeratosis appeared to have a direct relationship to the hair follicle and the cyst formations were apparently connected with the sweat glands. Neither of the aforementioned authors elucidated the true nature of the horny lamellae found in the cysts. Mieseher (3) was first to do elastic staining and recognize the presence of elastic fibers in the lesion. He felt that the lesion was caused by the pushing out of the necrotic mass through the * From the Dermatology Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and the Department of Dermatology, Ilarvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts. Received for publication October 22, epidermis which reacted to it with acanthosis, hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis. This suggested an intrapapillary hyperplasia of elastic tissue as the primary disorder. He applied the name of elastoma intrapapillare perforans verruciforme to this disease. Hitch ci al (10) found that the elastic tissue penetrated into the epidermis at the depth of rete ridges and into the sides of follicles. The present paper is a report of histologic and enzyme digestion studies carried out on a recently discovered lesion in an 18-year-old boy. CASE REPORT The patient, an 18-year-old healthy schoolboy, bad noted the appearance of a few keratotic papules on the back and sides of his neck, 17 months prior to his first examination. The lesions had gradually increased in number and become confluent and had formed semi-circular and annular configurations with clear non-atrophic centers. Observation over a period of seven months revealed no essential change in the character of the lesions (Figures 1 & 2). EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES Materials and Methods The material studied consisted of four specimens of skin from the right side of the neck of the patient presented above. They were removed under local procaine anesthesia. The procaine was infiltrated in an area 1 cm. away from the lesion to avoid distortion of the histology. One biopsy specimen measuring 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.3 cm. was fixed in 10% formalin and embedded in paraffin. Sections were cut and examined both unstained and stained with hematoxylin and eosin, Verhoeff elastic tissue stain, Congo red, periodic acid- Schiff, Masson and van Gieson stains. The second piece of skin taken from approximately the same area of the patient measured 1.5 x 0.5 x 0.3 cm. It was frozen, sectioned, and exposed to elastase (prepared by Worthington* within 5 minutes * Worthington Crystalline Elastase is twice crystallized, contains approximately 15 to 20
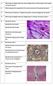
2 8 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY F'o. 1. Note Serpiginous keratotic papular lesions in ring-like formation on the left side of neck. after removal. These sections were kept at 37 C in both elastase and Michaelis buffer control.t The sections were exposed for 1, 1, 1), and 2 hours respectively, in parallel pairs to elastase and control solutions, and then stained with Verhoeff's elastic tissue stain. The third specimen of the lesion was also quickly frozen and subsequently sections were cut and examined unstained, and units per milligram, and is soluble in distilled water. The crystalline preparation has the soluhility characteristics of a euglohulin and has several components of which the principal one (80%) is elastase. A second component representing about 3% is pancreatic insulinase. Immediately before the use, an assay was done using orcein impregnated elastin to test the potency of the enzyme to he used. A unit of activity is such that 1 mg. of elastin is soluhilized in 20 minutes under the conditions of test. Michaelis buffer adjusted to ph 8.8 was used to suspend orcein impregnated elastin with and without elastase. Nothing happened to the tube without elastase, but bluish color of orcein was released in the tube with elastase after 20 minutes incubation in a water bath at 37. t Stock Solution: Sodium acetate , Sodium barbiturate Dissolved in one liter of distilled water. Preparation of ph 8.8 solution: 5 ml. of the above solution, plus 2 ml. of 0.85% NaCI is treated with 0.5 ml. of 0.1 NHC1 and 17.5 ml. of H20. Fiu. 2. Close-up view of Figure 1. Milky white and shiny inclusions are present on the summit of the individual papules. Papules at the lower margin of the ring carry plugs and crusts, and whitish cysts are excavated. after staining with Congo red and Sudan III. The fourth specimen was immediately sectioned into pieces approximately 1 cu. mm. in size and fixed in osmium tetroxide for study under the electron microscope. Histologic Studies Results The epidermis showed spotty areas of hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and keratotie plugging, with a tissue defect extending through the whole thickness of the epidermis due to a perforation by fibrous material invading from beneath (Figure 3). In the vicinity of the perforation, the epidermis showed aeanthosis, especially of the rete ridges. Fibrous material was present in the epidermis, sometimes occupying small, round, cystic spaces one above the other; thus, apparently, forming a spiral (Fig. 5). Although there were similar changes in the hair follicles, as will be described below, none of these spirals could be traced down to hair follicles or sweat ducts. This fibrous material was stained black by Verhoeff, light pink by Congo red, and negative with PAS and Sudan III stains. The Masson and van Gieson stains were negative for collagen.
3 ELASTOSIS PERFORANS SERPIGINOSA 9,*1 FIG. 3. LOW power view of intrapapillary and intradermal increase of Verhoeff positive fibers. On the right there is one perforated lesion. Formalin fixation. Verhoeff's elastic tissue stain. >< 25. Fin. 4. Higher magnification of the intrapapillary lesion shown in the extreme left of Figure 3. Fine and coarse fibers are seen in the papilla. One projection of lesion is close to the surface epidermis, Which is thinned out. Verhoeff's elastic tissue stain. >< 100. The dermis containcd an incrcased amount of short, wavy, fairly thick, curled fibers. In the hematoxylin and eosin prcparations, these varied in color bet ween grcyish blue and pink. The fibers showed the same tinctorial characteristics as those described in the epidermis, i.e. black with Verhoeff's stain, negative with the periodic acid- Sehiff, and pink with the Congo red stains. They ran parallel to the surface epidermis, were sparse in the deep dermis, and dense in the middle and upper portions where they partially lay in clumps (Figure 3). In these foci, there were found lymphocytes. Some of the tips of the rete ridges in the involved areas were invaded by those fibrous
4 FIG. 5. FIG. 6. FIG. 5. Tortuous spiral formation in the epidermis. In the lower field at the left there are several hair follicles which underwent degeneration. Frozen section. Hematoxylin and eosin. X 50. FIG. 6. Invasion of three tips of papillae by coarse reddish fibers from suhpapillary dermis. Hcmatoxylin and cosin. X 100. a ¼. '4 fj C I. FIG. 7. Higher magnification of the perforated area shown to the extreme right in Figure 3. At the right corner of the bottom of the crater, there is a tangled mass of pinkish red coarse fihcrs surrounded by red blood cells. Hcmatoxylin and cosin. 1<
5 ELASTOSIS PERFORANS SERPTGINOSA 11 J!;1&1.L. Fin. 8. FIG. 9. FIG. 8. hour incubation in elastase solution. Minimal digestion of intra-epithelial lesion in centre, plus two almost empty spaces also in the epidermis right to it. Digested epidermis shows fine lattice-work which represents couture of the squamous cells. Shreds of undigested fibers are seen in the papillae as well as in the epidermis. The connective tissues in the dermis appears normal. Frozen section. Verhoeff's elastic tissue stain. X 100. Fio. 9. Control for Figure 9, )4 hour incubation in the plain buffer solution. Intrapapillary as well as intradermal lesions were undigested. At the right, a part of intra-epithelial spiral channel is seen. Frozen section Verhoeff's elastic tissue stain. X 25. elements and, thus, appcarcd chewed off at their tips (Figure 6). Occasionally papillary bodies bulgcd out because of an accumulation of fibrous material (Fig. 4). The fihers stained most distinctly and strongly with cach stain in the upper dermis and in thc involved papillac whcrc they showed partial clumping (Fig. 4). The external hair sheath of some folliclcs appeared to undergo a degenerative process, with vacuolization of squamous cells to form cystic spaces containing granular cytoplasmie debris (Fig. 5). However, there were no fibrous constituents in those cysts. Shrinkage of the involved follicles caused slits, to form between the follicles and surrounding perifollicular connective tissue (Fig. 5). Eccrinc sweat glands and ducts, ns well as blood vessels, appeared normal. At the site of perforation of the epidermis, slight subcpidermal extravasation of red cells was noted (Fig. 7). Collagen, as seen in Masson and Van Gieson stains, did not appear to be altered. Enzyme Digestion Studies j hour incubation in elastase, followed by Verhoeff stain: A eonsiderahln amount of Verhoeff positive material was found dissolved out in comparison to the control sections incubated in Michaelis buffer without elastase. The remaining material showed swelling, segmentation, clumping, and uneven staining. It appeared largely amorphous and structureless. However, some swollen remnants of fibrous structures could be seen (Fig. 8). interestingly enough, the epidermis was simultaneously digested, leaving only faint
6 12 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY V '4. -I "4 e. FIG ) hour iocubation in elastase solution. The epidermis is largely digested. Projecting dermal papillae are devoid of Yerhoeff positive material except for one small area in subpapillary dermis (see arrow). Frozen section. Verhoeff's elastic tissue stain. X 40. fine contours of squamous cells (Fig. 8). Collagen was not obviously altered by this procedure. 1 hour incubation in elastase, followed by Verhocff stain: The dissolution of Verhoeff positive material was more pronounced. Smudgy black material seemed to diffuse from the foci in the dermis and epidermis. Some foci appeared free from the material, while others still had coarse granular pigment. It became more difficult to identify individual fibrous elements in the foci. Collagen in the dermis did not show any change. 1 3 hours incubation, followed by Verhoeff stain: It became very hard to find any fibrous structures. Granulated beads of black materials were found in the foci (Fig. 10). Collagen tissue was still intact. The control sections incubated in plain Michaclis buffer for the same period of time did not show any effect of digestion. 2 hours incubation, followed by Verhoeff stain: The Vcrhoeff positive material was almost completely dissolved out. Only one area had several swollen shreds of black material in a lesion in the epidermis which had simultaneously been digested (Fig. 11). The control sections still contained intact intrapapillary lesions (Fig. 12). Collagen in the digested sections still looked normal. DISCUSSION Since Lutz in 1952 reported the first case of what in retrospect was clastosis pcrforans scrpiginosa, more than ten case reports have appeared (2 13). Clinically this disorder is characterized by the onset in late childhood or early adulthood, affecting an otherwise healthy individual. The outer configuration of the lesion frequently changes, and spontaneous remission may occur. No subjective symptoms or systemic manifestations have been observed. The clinical picture resembles tinea, vcrruca vulgaris, or porokcratosis. There is no evidence of pseudoxanthoma elasticum or senile skin changes in any one of the previously reported cases. Although the etiology is unknown, the basic lesion appears to involve the elastic fibers. The positive Verhoeff, and Congo red stains, the negative Mnsson and Van Gicson stains, and the selective digestion of the fibers with elastasc seem to confirm this. The changes in the elastic tissue arc present in the subpapillary region of the dermis, and this process is seen in the papillary bodies and epidermis. The tinctorial reaction of these elastic fibers is strongest in the subpapillary layer and weakest in the cystic spaces in the upper epidermis. Intrapapillary increase in elastic tissue varied
7 ELASTOSTS PERFORANS SERPIGINOSA 13 p.,j "3) t FIG hour incubation in elastase solution. Advanced degree of dissolution of the Verhoeff positive fibers in the lesion in the epidermis and two completely empty spaces. Partially digested epidermis is left with a number of shreds of Verhoeff positive fibers which appear broken and smudgy. Frozen section elastic tissue stain. X 100. FIG. 12. Control 2 hour incubation in plain huffer solution. Two intrapapillary lesions contain distinctly fibrous, Verhoeff positive components in them. Frozen section Verhoeff's elastic tissue stain. >< 100.
8 14 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY from place to place according to the fiber size; from fine mesh-work (of probably young fibers) to a clumping of thicker ones in the bulged papillae. It was ahnost always possible to see a direct communication of the intrapapillary elastic fibers with those sitnated beneath in the upper dermis. The elastic tissue in several areas invaded the lower poles of rete ridges. On the other hand, direct invasion of appendages by the elastic tissue was not seen, although several degenerated hair follicles in the epidermis were observed. The elastase digestion experiment demonstrated progressive disruption and digestion of the fibers in the lesion, while the controls showed essentially no change. Marshall and Lurie (7) showed that the elastic material lost its staining reactions after digestion with elastase, and Dammert and Putkonen (9), demonstrated that trypsin removed the elastic material. Epidermal cells were also digested by the elastase preparation which is known to contain minor protein contaminants. The elastase was prepared from porcine pancreas and presumably a small amount of a proteolytic enzyme that escaped destruction in the repeated crystallization of the elastase digested the epidermal cells. This contaminant enzyme, however, does not affect elastic tissue (14). The present lesion has been variously named by several authors. Originally it was named Keratosis Follicularis Serpiginosa by W. Lutz. Subsequently, the terms Elastoma Intrapapillare Perforans T7erruciforme and Elastosis Perforans,Serpiginosa were suggested by G. Miescher and by Dammert and Putkonen, respectively. As Hitch has pointed out, the elastic tissue increase is not primarily or necessarily "intrapapillar" or "follieular" but in the cutis in general. There is no evidence that it is a tumor, as the suffix "oma" suggests, but a morbid process of abnormal increase in elastic tissue, as the name elastosis might convey. Clinically it takes serpiginous configuration with eruptive individual lesions. Therefore, we feel that the term suggested by Dammert and Putkonen Elastosis Perforans Serpiginosa is more suitable than the others. 5UMMAEY 1. Histoehemical and enzyme digestion studies have been carried out on biopsy material from a patient with elastosis perforans serpiginosa. 2. The nature of the lesion, as representing primarily a proliferation and degeneration of elastic tissue, has been confirmed. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors should like to thank Drs. Maurice M. Tolman and Walter F. Lever of the Department of Dermatology, who have kindly reviewed the manuscript and gave us many valuable suggestions; Drs. Edmund Klein and Laszlo Fekete of the Department of Dermatology and Richard Cohen of the Department of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, for much technical assistance. REFERENCES 1. LUTZ, W. Keratosis follicularis serpiginosa. Dermatologica, 106: 318, BEaNING, C. W.&Nn ROTTER, M. Keratosis follicularis serpiginosa. Dermatologica, 110: 175, MIRsCHEH, C.: Elastoma intrapapillare perforans verruciforme. Dermatologica, 110: , MIEsCHEH, C.: Em unter dem Bilde des Morhus Kyrle verlaufender Fall von elastoma intrapapillare. Dermatologica, 112: , MIEsCHER, C.: tiber einen weiteren Fall von elastoma intrapapillare verruciforme (Keratosis Follicularis Serpiginosa, Lutz). Hautarzt 7: , HElTER, M.: Elastoma intrapapillare perf o- rans (Mieseher). Hautarzt, 7: , MARSHALL, J. AND LURIE, H. I.: Keratosis follicularis serpiginosa (Lutz) Elastoma intrapapillare perforans verruciforme (Miescher). Dermatologica, 113: 13 25, MARSHALL, J. AND Luara, H. I. Keratosis follicularis serpiginosa (Lutz) Elastoma intrapapillare perforans verruciforme (Miescher). Brit. J. Dermat., 69: , DAMMERT, K. AND PUTKONEN, T.: Keratosis follicularis serpiginosa (Lutz). Dermatologiea, 116: HITCH, J. M. AND LUND, H. Z.: Elastosis perforans serpiginosa. Arch. Dermat. & Syph., 79: , Go'rz, H., RöexL, H. AND BANDMANN, H. J.: Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Keratosis Follicularis Serpiginosa Lutz (Elastosis intrapapillare perforans verruciforme Mieseher). Dermatologica, 117: 231, WOERDEMAN, M. J. AND SCOTT, F. P.: Keratosis follicularis serpiginosa (Lutz). Dermatologica, 118: 18, HABER, H.: Mieseher's elastoma (Elastoma intrapapillare perforans verrueiforme.) Brit. J. Dermat., 71: 85, 1959.
ELASTOSIS PERFORANS (PERFORATING ELASTOSIS)
 ELASTOSIS PERFORANS (PERFORATING ELASTOSIS) THE ASS0CTATI0N OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES, SALIENT FACTS IN THE HISTOLOGY, STUDIES OF ENZYME DIGESTION AND A REPOET OF NECROPSY IN A CASE5 HENRY J. WHYTE, MB.,
ELASTOSIS PERFORANS (PERFORATING ELASTOSIS) THE ASS0CTATI0N OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES, SALIENT FACTS IN THE HISTOLOGY, STUDIES OF ENZYME DIGESTION AND A REPOET OF NECROPSY IN A CASE5 HENRY J. WHYTE, MB.,
ELASTIC GLOBES IN HUMAN SKIN* HERMANN PINKUS, MD., AMIR H. MEHREGAN, MD. AND RENATO G. STARICCO, MD.
 THE JOURNAL OF NVESTOATVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1565 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 45, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. ELASTC GLOBES N HUMAN SKN* HERMANN PNKUS, MD., AMR H. MEHREGAN, MD. AND RENATO G. STARCCO,
THE JOURNAL OF NVESTOATVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1565 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 45, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. ELASTC GLOBES N HUMAN SKN* HERMANN PNKUS, MD., AMR H. MEHREGAN, MD. AND RENATO G. STARCCO,
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Preface 1. Fixation and Processing 1
 Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):361 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma GABRIELA IEREMIA 1), M. RAICA 2), ANCA MARIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):361 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma GABRIELA IEREMIA 1), M. RAICA 2), ANCA MARIA
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
in alopeeia areata are not entirely defined. Sabouraud (1) made the fundamental observation
 MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PILOSEBACEOUS UNITS AND ANAGEN HAIRS IN ALOPECIA AREATA* The normal growth of scalp hair is a result of a continuous, rapid proliferation of tissue by the matrix of the hair bulb
MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PILOSEBACEOUS UNITS AND ANAGEN HAIRS IN ALOPECIA AREATA* The normal growth of scalp hair is a result of a continuous, rapid proliferation of tissue by the matrix of the hair bulb
DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS
 J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types. Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed
 External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
SKIN. 3. How is the skin structured around the finger joints to allow for flexible movement of the fingers?
 SKIN Objectives for Exam #1: 1. List various skin structures and describe their functions. 2. Describe skin responses to increases and decreases in body temperature. 3. Provide examples of various skin
SKIN Objectives for Exam #1: 1. List various skin structures and describe their functions. 2. Describe skin responses to increases and decreases in body temperature. 3. Provide examples of various skin
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma
 Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION*
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. during postnatal period and to provide elasticity during prenatal and early
 CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
BI 121 LAB. WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System
 BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
Abrupt Intralesional Color Change on Dermoscopy as a New Indicator of Early Superficial Spreading Melanoma in a Japanese Woman
 Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1
 PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of
 Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Dual Wavelength Phototherapy System
 Dual Wavelength Phototherapy System The AKLARUS Blue and Red Combination System is an effective, drugfree alternative for treating acne & photodamaged skin. The non-invasive Aklarus treatment has been
Dual Wavelength Phototherapy System The AKLARUS Blue and Red Combination System is an effective, drugfree alternative for treating acne & photodamaged skin. The non-invasive Aklarus treatment has been
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
INHIBITION OF INTRACUTANEOUS LEISHMANIN REACTION BY HYDROCORTISONE ACETATE
 INHIBITION OF INTRACUTANEOUS LEISHMANIN REACTION BY HYDROCORTISONE ACETATE COMPARISON WITH CoRTIsoNE, ACTH, AND HYALURONIDASE* A. DOSTROVSKY, M.D. AND H. A. COHEN, M.D. The inhibitory effect of cortisone
INHIBITION OF INTRACUTANEOUS LEISHMANIN REACTION BY HYDROCORTISONE ACETATE COMPARISON WITH CoRTIsoNE, ACTH, AND HYALURONIDASE* A. DOSTROVSKY, M.D. AND H. A. COHEN, M.D. The inhibitory effect of cortisone
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
(From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) Materials and Methods
 HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN XI. THF. DISTRIBUTION OF /~-GLucURONIDASE* BY WILLIAM MONTAGNA, PH.D. (From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) PLATES
HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN XI. THF. DISTRIBUTION OF /~-GLucURONIDASE* BY WILLIAM MONTAGNA, PH.D. (From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) PLATES
the upper part of the stratum mueosum Blum (1) and Laymon and Murphy (6) THE HISTOLOGY OF ICHTHYOSIS*
 Ten JOURNAL OF NVESTGATVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 966 by The williams & wilkins Co. vol. 6, No. & Printed in U.S.A. Descriptions of histological characteristics in ichthyosis differ on the significance of
Ten JOURNAL OF NVESTGATVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 966 by The williams & wilkins Co. vol. 6, No. & Printed in U.S.A. Descriptions of histological characteristics in ichthyosis differ on the significance of
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE
 TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses
 Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 12, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA
 NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems Welcome to Lesson 3 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. I
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems Welcome to Lesson 3 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. I
Canadian Scientific Journal. Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
 Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell
Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell
Disclosure. Objectives. PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016
 PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016 1 Disclosure The speaker has no conflict of interest, financial agreement, or working affiliation with any group or organization.
PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016 1 Disclosure The speaker has no conflict of interest, financial agreement, or working affiliation with any group or organization.
COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS. photocoagulation of the rabbit's retina.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
THE sebaceous glands of the rabbit consist of clusters of about ten cells
 79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance?
 1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh
 Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms
 J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF HUMAN WARTS; SITES OF VIRUS PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF THE INCLUSION
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF HUMAN WARTS; SITES OF VIRUS PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF THE INCLUSION BODIES * JUNE D. ALMEIDA, ALLAN F. HOWATSON, Pn.D. AND MURRAY G. WILLIAMS, M.D. The viral etiology of human
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF HUMAN WARTS; SITES OF VIRUS PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF THE INCLUSION BODIES * JUNE D. ALMEIDA, ALLAN F. HOWATSON, Pn.D. AND MURRAY G. WILLIAMS, M.D. The viral etiology of human
Sheet #9. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
Tissues organs system organism. pg151
 Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Appendix : Dermoscopy
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details APP Appendix : Dermoscopy Dermoscopy, also known as dermatoscopy, epiluminoscopy and epiluminescent microscopy, is an effective non-invasive
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details APP Appendix : Dermoscopy Dermoscopy, also known as dermatoscopy, epiluminoscopy and epiluminescent microscopy, is an effective non-invasive
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Brief Report. Shivanand Gundalli 1, Smita Kadadavar 1, Somil Singhania 1, Rutuja Kolekar 2 INTRODUCTION. Melanocytic Nevus
 Our Dermatology Online Histopathological spectrum of benign melanocytic nevi our experience in a tertiary care centre Shivanand Gundalli 1, Smita Kadadavar 1, Somil Singhania 1, Rutuja Kolekar 2 1 Department
Our Dermatology Online Histopathological spectrum of benign melanocytic nevi our experience in a tertiary care centre Shivanand Gundalli 1, Smita Kadadavar 1, Somil Singhania 1, Rutuja Kolekar 2 1 Department
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Severely itchy skin lesions on extremities
 2 nd EDS Monthly Meeting-Dubai 03 June 2016 Severely itchy skin lesions on extremities Dr.Hani Gamil Montaser Dermatologist Hili Health Center-Al Ain The aim of this presentation is to highlight the fact
2 nd EDS Monthly Meeting-Dubai 03 June 2016 Severely itchy skin lesions on extremities Dr.Hani Gamil Montaser Dermatologist Hili Health Center-Al Ain The aim of this presentation is to highlight the fact
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE
 ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Elastofibroma dorsi. CASE 1 M.J., a white female clerk, age 61, presented. with a mass below the right scapula which she had noticed
 Elastofibroma dorsi J. R. TIGHE, A. E. CLARK, AND D. J. TURVEY J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 463-469 From the Department ofpathology, St. Thomas' Hospital and Medical School, London SYNOPSIS Two cases of
Elastofibroma dorsi J. R. TIGHE, A. E. CLARK, AND D. J. TURVEY J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 463-469 From the Department ofpathology, St. Thomas' Hospital and Medical School, London SYNOPSIS Two cases of
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID
 HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings
 Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Topical Preparations
 Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
