Inflammatory Skins. Dr W. Merchant St. James Hospital Leeds
|
|
|
- Nathan Elijah Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inflammatory Skins Dr W. Merchant St. James Hospital Leeds
2 Case1 51 M long standing plaque on back
3 Main Features Low power; Not obvious Rather square edged biopsy. Increased thickness to dermal collagen Minimal inflammation Collagen of deeper dermis appears swollen lacking normal inter-fibre spaces. Eccrine coils; look high up with no surrounding fat
4 Morphoea On histology cannot distinguish from Systemic sclerosis Clinical setting all important. Single plaque ;morphoea. Several variants; Guttate, Linear, Generalised, s/c [profundus].
5 Differential & distinguishing features Systemic Sclerosis; Clinical setting GVHD; late stage; Clinical setting and epidermal changes. DXT, atypical nuclei. Can get morphoea developing post DXT. C.T.Naevus; Different setting, can have ^ elastin Scleroedema of Buschke and lichen myxoedematosus. Distinct clinical and increase in mucin as well as collagen. Lichen Sclerosus, papillary dermal changes can be identical. Lacks deeper dermal changes and has basement membrane changes.
6 Case 2 40F Papular lesions on hands
7 Microscopic features Multiple nodular lesions in dermis Nodules composed of inflammatory cells, mainly histiocytes, with central area of altered collagen. Collagen altered, loss of dermal fibroblasts = Necrobiosis. Few neutrophils in centre Perivascular lymphocytes
8 Granuloma Annulare Few clinical variants; Localised, Generalised and Deep [pseudorheumatoid nodule esp. in kids] Watch out for Epithelioid sarcoma- some mild atypia, more solid proliferation. C.K. pos.
9 Case 3 60F, Lesions on lower legs
10 Microscopy Entire dermis abnormal Collagen shows degenerative changes; Necrobiosis Collections of giant cells, plasma cells Perivascular Lymphocytes
11 Necrobiosis lipoidica Association with diabetes Usually lower legs Microscopic variant ; sarcoidal. Differs from GA: Sarcoidal granuloma s, entire dermis involved, plasma cells.
12 Case 4 40 Male, lump on elbow
13 Microscopy Amorphous material deposits Needle like pattern to deposits on higher power. Foreign-body reaction
14 Gouty Tophus Typical clinical Sodium urate crystals are water soluble, therefore best sent in alcohol and inform lab so processing and sectioning skips aqueous stages. If not done, not all lost, can section and use alcohol not water bath to float sections.
15 Case 5 70M, widespread rash with pustules.
16 Microscopy Mild epidermal acanthosis Collections of neutrophils [neuts] in corneum and sub-corneal. Foci of vacuolar degeneration of superficial epidermis associated with Neutrophils, spongiform pustule of Kogoj Perivascular lymphocytes and neutrophils.
17 Pustular Psoriasis Localised; chronic disease of palms and soles Generalised; serious illness. May or may not have history of psoriasis. May have precipitating factor eg illness, drugs. Withdraw of steroids well known.
18 Differential diagnosis Reiter Syndrome; Classic triad of Arthritis,urethritis, conjuctivitis. Acute generalised exanthamatous pustulosis [AGEP]. Type of drug eruption, acute with no parakeratosis, less marked spongiform pustules, has eosinophils, occ. Dyskeratotic cells.
19 Neut s in the horn Can you name any conditions?
20 Neut s in the horn Infections Fungi, candida,dermatophytes Bacterial impetigo Psoriasis, esp. pustular Reiter s disease Sub-corneal pustular dermatosis IgA pemphigus Syphilis Miliaria Crystallina Acute generalised Exanthamatous pustulosis Seborrheic dermatitis
21 Case 6 30M Sudden onset of widespread blistering eruption also involving mouth.
22
23 Microscopic features Epidermal death. Areas full thickness. Other areas scattered apoptotic cells through epidermis. Minimal Inflammatory cell inflammatory cell infiltrate. Blister due to epidermal death. Corneal layer normal.
24 Differential diagnosis?
25 Toxic epidermal Necrolysis Serious condition. Treat like a burn. Serious form of Erythema Multiforme. Associations; Infections, Drugs, Malignancy, Connective tissue diseases.
26 Differential Diagnosis GVHD, acute L.E.- Sub-acute Drugs eruption- Fixed, lichenoid Pityriasis Lichenoides Eruption of lymphocyte recovery
27 Case 7 40 M, Previous BM transplant. Now widespread rash
28 Microscopy Upper dermal infiltrate, perivascular and interface. Vacuolar change to basal keratinocytes. Satellite cell necrosis No eosinophils
29 Differential diagnosis See under TEN Main problem is with drugs. No eosinophils. Usually not possible to distinguish between them.
30 Case 8 70 M, itchy rash with on legs
31 Main features Sub-epidermal blister Inflammatory with eosinophils ++
32 Differential diagnosis Bullous Pemphigoid [BP] Herpes gestationis Insect bites
33 Bullous pemphigoid Immunofluorescence very helpful.
34 75 F, urticarial rash Case 9
35 Case 9, main features Epidermal spongiosis Intra-epidermal vesicle? Small sub-epidermal split Infiltrate with many eosinophils
36 Differential diagnosis Eosinophilic spongiosis Pemphigus BP Allergic contact dermatitis Insect bite Incontinentia pigmenti [infants]
37 IMF again useful Bullous pemphigoid
38 BP, Immunofluorescence IgG Basement membrane
39 Case Male, pigmented papular rash
40 Case 10 Low power, very little to see. Closer examination, marked dermal melanin pigmentation. Even closer examination, small pink deposit in Papillary dermis.
41 Differential Diagnosis Post inflammatory hyper pigmentation. Papular/macular amyloid
42 Macular Amyloid Easy to miss the small amyloid deposits. Almost invisible on standard H+E. There is marked dermal melanin pigmentation. Small globular eosinophilic deposits in the papillary dermis. If rack down condenser, easier to see, cracked deposits. Stain with Congo red, Thioflavin T and broad spectrum cytokeratins.
43 Macular Amyloid Clinically; very itchy eruption. Innumerable small papules, often on the trunk. Pigmentation, which can have a ripple appearance. Derived from epidermal keratin.? pruritis plays a role. Amyloid K
44 BIOPSIES WITH VERY LITTLE TO SEE DO NOT DISPAIR REMEMBER INVISIBLE DERMATOSES
45 Invisible dermatoses Subtle changes to epidermis Ichthyosis Granular parakeratosis Mild change in melanin pigment, e.g. Vitiligo Subtle Dermal changes Interstitial GA, anetoderma, PXE, atrophoderma Infections Fungi [Tinea incognito, erythrasma]
46 Invisible dermatoses Deposition disease Amyloid Iron Argyria Mucin Mast cell disease. Urticaria pigmentosa, Telangiectasia macularis perstans [TMEP].
47 Case 11 70M Post-op.?drug rash.
48 Microcopy Papule Acantholysis. Occasional dyskeratotic cell Minimal inflammation Small amount of scale.
49 Supra basal blister with acantholysis Pemphigus Vulgaris Hailey-hailey disease Dariers Disease Grovers Disease Solar keratoses
50 Diagnosis; Grovers Disease Clinical picture; multiple itchy papules on trunk. Negative immunofluorescence [IMF]. Often mixed picture on histology; spongiotic, acantholysis, dykeratotic.
51 Case 12 73M, Nodular lesions on lower legs.
52 Microscopy Squamo-proliferative lesion Inflammation, mainly lymphocytes but a few eosinophils. Scattered colloid bodies At edge, pointed rete ridges.
53 Hypertrophic Lichen Planus Clinical setting important; both lower legs. Often known LP. No cytological atypia Lichenoid infiltrate not as marked. Can be limited to lower rete. Eosins can be present. Increased risk of SCC s. Cytological atypia, deep infiltration.
54 Case13 23F, widespread papular rash.
55 Microscopy Focal process Lichenoid infiltrate Mixture of lymphocytes and histiocytes. Occasional multinucleate cell.
56 Lichen Nitidus Distinct clinical; pinpoint papules in young Afro-Caribbean, trunk and limbs.
57 Lichenoid; Dense band like infiltrate of lymphocytes in papillary dermis which obscures D-E junction. LP Lichen Nitidus Lichen Striatus Lichenoid Drug Lichenoid reaction to tumours; AK, halo naevus Pityriasis Lichenoides Lichen Aureus MF GVHD
58 45F, nodule on leg Case 14
59 Microscopy Nodular infiltrate in dermis Composed of an admixture of large cells with copious eosinophilic cytoplasm, scattered eosinophils, neutrophils and lymphocytes.
60 Reticulohistiocytoma One form of non-langerhan s cell histiocytosis. Has distinct appearance to histiocytes ground glass cytoplasm. If mutiple, can involve joints and and cause arthritis, usually fingers.
61 Non-Langerhans Histiocytoses Xanthogranuloma s; Juvenile Xanthogranuloma archetypal lesion Can be xanthomatous, spindle cell, ground glass histiocytes.
62 Case 15 50M, persistent boil on leg.
63 Microscopy Dense diffuse dermal infiltrate. Infiltrate composed by of histiocytes with abundant pale cytoplasm. Background of mixed inflammatory cells. Within histiocytes; small dots.
64 Leishmaniasis Various forms. Classical persistent sore ;Baghdad boil. Protozoal infection transmitted by sandfly. Main differential; Histoplasmosis. Rare in skin. PAS or Grocott will help.
65 25F? SCC on foot. Case 16
66 Microscopy Squamous proliferation. Dense infiltrate in dermis. Collections of Neutrophils. Surrounding histiocytes.
67 Differential diagnosis Suppurative granulomas; Fungal Atypical mycobacteria Pyoderma gangrenosum, superficial granulomatous variant.
68 ?SCC, Grocott
69 Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia Infections, esp Fungus Chronic friction Lymphomas, esp. CD30 related diseases Tumours, granular cell tumour Connective tissue diseases, Lupus Hypertrophic lichen planus
70 Case 16 Fungal infection with pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia.
71 Types of Granuloma Sarcoidal Tuberculoid Necrobiotic Foreign body Suppurative Xanthogranuloma Vasculitis associated
72 Case m, crusted lesion on forehead.
73 Microscopy Intra-epidermal vesicle. Necrosis of keratinocytes Ballooning degeneration, multinucleate cells. Intranuclear inclusions
74 Herpes infection Herpes varicella-zoster, and simplex 1&2 all produce similar changes. Can involve hair follicles Can be widespread if immunosuppressed.
75 Case 18 40M, recurrent oval lesion on arm.
76 Microscopic features Scattered epidermal cell death Corneal layer normal Mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Exocytosis of lymphocytes with satellite cell necrosis.
77 Fixed drug eruption Inflammatory patch which recurs at same site each time drug taken. Differential; see under TEN.
78 Case Male with orange plaque on leg
79 Case 19 Superficial perivascular inflammation. Lymphocytes and occassional eosinophil. Epidermis shows mild acanthosis and hyperkeratosis. Scattered macrophages in interstitium shows iron deposition.
80 Pigmented purpuric dermatosis Several variants; usually middle aged men, producing purpuric to orange/brown lesions on lower legs. Capilleritis but no true leukocytoclastic vasculitis seen.
81 Differential diagnosis Non-specific inflammation. MF
82 Invisible Dermatoses If stuck, remember above list and do some basic histochemical stains eg Congo red, Toludine blue, perls, elastic stain, Mucin stain, Fungal stain.
83 50F,? cellulitis Case 20
84 Microscopy Superficial and deep inflammation Many eosinophils. Flame figures
85 Well s syndrome [eosinophilic cellulitis] Clinically resembles cellulitis, but no infection found. Differential; Insect bite Parasite infection BP Allergic eczema Drug eruption Churg- Strauss Disease
86 CASE F, numerous small macules with scale.
87 Microscopy Lymphocytic vasculitis; perivascular lymphocytes and red cell extravasation. No fibrin or nuclear debris. Vacuolar interface with exocytosis of lymphocytes and RBC s. Epidermal degenerative changes with vacuolar change and cytoid bodies. Overlying scale crust
88 Pityriasis Lichenoides Acute and chronic forms. Differential diagnosis; Lymphomatoid papulosis, similar clinical and pathology but has clusters of atypical CD30 positive T-cells.
89 CASE 22 50F large patches on trunk.
90 Microscopy Band-like infiltrate in upper dermis Exocytosis. Cells in small clusters and pairs. Cells in epidermis of moderate size, irregular nuclear margin. Mild epidermal acanthosis, minimal spongiosis Papillary dermal fibrosis
91 Differential diagnosis Lichenoid drug eruption Chronic superficial dermatitis Mycosis Fungoides
92 Diagnosis; MF Need correct clinical setting. Large plaques on trunk with slight scale [cigarette paper-like appearance]. Immuno; CD4/CD8 ratio; reactive usually predominantly CD8, MF CD4:CD8 2:1. Antigen aberrance; CD2,CD4, CD5, CD7. Clonality; T cell gene rearrangement.
93 Case 23 65F, Renal failure, ulceration on leg
94 Microscopy Superficial ulceration. Epidermis shows thinning and necrosis. Dermal inflammation with many neutrophils. Superficial vessels contain thrombi. S/c vessels show Ca deposition in small vessel walls. Lumen occluded.
95 Diagnosis Calciphylaxis; very serious disease. Often causes death. Usually history of chronic renal disease.
96 60F, Nodule on nose. Case 24
97 Microscopy Dense dermal inflammation. Grenz zone. Adnexal structures spared. Polymorphous infiltrate; Neutrophils, eosinophils, hitiocytes. Neutrophils centred upon small vessels. Focal nuclear dust and small amount of fibrin. Small amount of fibrosis.
98 Granuloma Faciale One type of chronic vasculitis. Erythema Elivatum Diutinum, similar, occurs on limbs over bony prominances.
99 Neuts in the dermis Infections, Cellulitis Vasculitis, and variant's Sweets syndrome Behcet s Blistering disorders; DH, AML, but abnormal primitive forms.
100 Case 25 60F with skin rash and muscle weakness
101 Microscopy Epidermis, thin with basal vacuolar change Dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Dermis, appears pale, collagen fibres widely separated. Due to mucin, [useful for diagnosis].
102 Dermatomyositis. Peri-ocular oedema and erythema Erythema in photosensitive distribution. Myositis; proximal muscle weakness. Can check for creatinine kinase. Gottron s papules on acral skin. In adults 25% associated with underlying visceral cancer.
103 Dermatomyositis Not possible to exclude L.E. on histology. Clinically distinct. IMF; negative.
104 Case 26 LH F Linear lesion on arm.
105 Cornoid Lamella - Columns of parakeratotic scales, loss of granular layer, vacuolated or dyskeratotic cells in spinous layer -? Clonal abnormality - Seen in - Porokeratosis: Mibelli, DSAP, D.S. (Non-A)P, linear, punctate (palmar/plantar) - Other - Seb K, A.K, SCC
106 Linear Porokeratosis CASE 26
107 Blaschko's lines An unexplained phenomenon of human anatomy first presented in 1901 by German dermatologist Alfred Blaschko. Many inherited and acquired diseases of the skin or mucosa manifest themselves according to these patterns, creating the visual appearance of stripes. The cause of the stripes is thought to result from mosaicism; they do not correspond to nervous, muscular, or lymphatic systems. It is theorized that the lines define the natural areas of growth between the original cells of the embryo and the later (copied) cells of mature adults.
108
109
110 Blaschko's lines Genetic disorders Epidermal Naevi [ILVEN] Incontinentia pigmenti Acquired skin disorders Lichen Striatus Linear LP Linear LE Linear Porokeratosis
111 60F Diffuse swelling Case 27
112 Microscopy Not much to see Collagen fibres widely spaced
113 Differential Diagnosis Dermal mucinosis Lymphoedema
114 Pre-tibial myxoedema Occurs in hyperthyroisism [Graves disease]. Use AB with Van Gieson or Hale e colloidal iron to demontrate. Diagnosis needs clinico-pathological correlation.
115 Increase Mucin only Dermal Mucinoses Pre-tibial myxoedema Focal mucinosis Generalised myxoedema [subtle] Increased fibroblasts Papular mucinosis,scleromyxedema Increased collagen Scleredema Inflammation REM, SLE, Dermatomyositis
116 Case 28 68M, Intense deep inflammation lower legs.
117 Microscopy Deep inflammatory process centred upon s/c fat, panniculitis Whole lobule affected. lobular pattern. Ghost cells of fat cells Dense acute and chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate. No vasculitis
118 Pancreatic Panniculitis Fat necrosis due to release of enzymes from pancreas. Can do serum amylase. Legs most affected. Associated with pancreatic disease; benign and malignant. This case had pancreatic carcinoma
119 Case29 3year old male with multiple brown macules on trunk.
120 Microscopy Superficial perivascular infiltrate, Epidermis not inflamed. Prominent basal pigmentation.
121 Urticarial Pigmentosa Number of mast cell very variable. Mast cell can look like lymphocytes so easily missed. Often a few eosinophils present. Can be associated with systemic disease, especially in adults. CD117 and Toludine blue can identify.
122 Mast cell disease Range from benign end, urticaria pigmentosa, mastocytoma TMEP to borderline systemic mastocytosis to malignant; Malignant mastocytosis, Mast cell leukemia. At lower end; can look just like a lymphocytes. Often a few eosinophils around.
123 Mast cell disease Range from benign end, urticaria pigmentosa, mastocytoma TMEP to borderline systemic mastocytosis to malignant; Malignant mastocytosis, Mast cell leukemia. At lower end; can look just like a lymphocytes. Often a few eosinophils around.
124 Case 30 21F; numerous papules
125 Microscopy Follicles dilated. Increased amount of mucin within follicle. Minimal inflammatory infiltrate. No atypia.
126 Follicular mucinosis 2 main types; Case 30 1] Inflammatory/benign, 2] Lymphoma associated. Range from limited group papules, often scalp [Alopecia mucinosa] to widespread papules. Careful follow up required as may transform from benign to malignant.
127 THE END
Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of
 Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Patterns and mechanisms of inflammatory skin conditions: the pathologist s survival kit SALVADOR J. DIAZ-CANO BAHRAIN, APRIL 2017
 Patterns and mechanisms of inflammatory skin conditions: the pathologist s survival kit SALVADOR J. DIAZ-CANO 0000-0003-1245-2859 BAHRAIN, APRIL 2017 Basic Elements of Lesions Repair Injury Time & Intensity
Patterns and mechanisms of inflammatory skin conditions: the pathologist s survival kit SALVADOR J. DIAZ-CANO 0000-0003-1245-2859 BAHRAIN, APRIL 2017 Basic Elements of Lesions Repair Injury Time & Intensity
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies
 My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 12, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
Update in deposition diseases
 Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 13, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Pathology of the skin. Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE
 Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
4. Pityriasis lichenoides
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details usually more than 5 cm in diameter and accompanied by poikiloderma. Some but not all patients may develop mycosis fungoides (Fig. 22.35).
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details usually more than 5 cm in diameter and accompanied by poikiloderma. Some but not all patients may develop mycosis fungoides (Fig. 22.35).
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123
 BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand
 Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Superficial Perivascular Dermatitis Interface Dermatitis Vacuolar Dermatitis Lichenoid Dermatitis Barnhill Textbook
Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Superficial Perivascular Dermatitis Interface Dermatitis Vacuolar Dermatitis Lichenoid Dermatitis Barnhill Textbook
Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma
 AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology. Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders. Acne. Acne Vulgaris. Pomade Acne. Steroid Acne
 Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Some skin conditions
 Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
الفتوي الاصفر الحبيبوم = Xanthogranuloma_Juvenile JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9
 JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Spongiotic Dermatitis
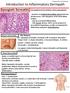 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Inflammatory Dermpath Spongiotic Dermatitis intraepidermal intercellular edema (spongiosis) - presence of widened intercellular spaces between keratinocytes, with
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Inflammatory Dermpath Spongiotic Dermatitis intraepidermal intercellular edema (spongiosis) - presence of widened intercellular spaces between keratinocytes, with
Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition
 National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
Self assesment Case 21
 17-18 MAY 2018 London Dermatopathology Symposium 2018 Self assesment Case 21 MARC HASPESLAGH CASE 21 1802-50585 48 year old lady with eczematous lesions at ear helix and red patch on nose bridge since
17-18 MAY 2018 London Dermatopathology Symposium 2018 Self assesment Case 21 MARC HASPESLAGH CASE 21 1802-50585 48 year old lady with eczematous lesions at ear helix and red patch on nose bridge since
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
THERE IS A GROUP OF PAtients. Defining Urticarial Dermatitis. A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern
 STUDY Defining Urticarial Dermatitis A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern Steven Kossard, FACD; Ian Hamann, FACD; Barbara Wilkinson, BSc Background: Urticarial dermatitis may represent
STUDY Defining Urticarial Dermatitis A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern Steven Kossard, FACD; Ian Hamann, FACD; Barbara Wilkinson, BSc Background: Urticarial dermatitis may represent
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Diploma examination. Dermatopathology: First paper. Tuesday 21 March Candidates must answer FOUR questions ONLY. Time allowed: Three hours
 Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Diploma Examination. Dermatopathology: First paper. Tuesday 20 March Candidates must answer FOUR questions. Time allowed: 3 hours
 Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 20 March 2018 Candidates must answer FOUR questions Time allowed: 3 hours 1. Give an account of the genetic aberrations encountered in Spitzoid neoplasms and how these
Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 20 March 2018 Candidates must answer FOUR questions Time allowed: 3 hours 1. Give an account of the genetic aberrations encountered in Spitzoid neoplasms and how these
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin
 Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Index. Angiosarcoma diagnosis, 47 lymphedema-related vs. non-lymphedemarelated, 48
 A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Principi ed Aggiornamenti in Dermatologia Roma, 6-7 Aprile Grand rounds. Lorenzo Cerroni, Graz
 Principi ed Aggiornamenti in Dermatologia Roma, 6-7 Aprile 2018 Grand rounds Lorenzo Cerroni, Graz "Computer palms" Described in patient using computer keyboards for long periods; similar features described
Principi ed Aggiornamenti in Dermatologia Roma, 6-7 Aprile 2018 Grand rounds Lorenzo Cerroni, Graz "Computer palms" Described in patient using computer keyboards for long periods; similar features described
Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2
 Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad. Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
 Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Guttate psoriasis =ﻒدﺼﻠا ﻲﻄﻘﻨﻠا
 1 / 69 Psoriasis Psoriasis may be divided into psoriasis vulgaris, generalized pustular psoriasis, and localized pustular ps Psoriasis Vulgaris Clinical Features 2 / 69 Psoriasis vulgaris is a common chronic
1 / 69 Psoriasis Psoriasis may be divided into psoriasis vulgaris, generalized pustular psoriasis, and localized pustular ps Psoriasis Vulgaris Clinical Features 2 / 69 Psoriasis vulgaris is a common chronic
Psoraisis = ﻒدﺼﻠا 1 / 84
 1 / 84 2 / 84 3 / 84 4 / 84 5 / 84 6 / 84 Psoriasis Psoriasis may be divided into psoriasis vulgaris, generalized pustular psoriasis, and localized pustular ps Psoriasis Vulgaris Clinical Features 7 /
1 / 84 2 / 84 3 / 84 4 / 84 5 / 84 6 / 84 Psoriasis Psoriasis may be divided into psoriasis vulgaris, generalized pustular psoriasis, and localized pustular ps Psoriasis Vulgaris Clinical Features 7 /
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Synonyms. Mast cell disease Mast cell proliferative disease
 Mastocytosis Definition Mastocytosis is a proliferation of mast cells and their subsequent accumulation in one or more organ systems. Mast cells are derived from hematopoietic progenitors, thus mastocytosis
Mastocytosis Definition Mastocytosis is a proliferation of mast cells and their subsequent accumulation in one or more organ systems. Mast cells are derived from hematopoietic progenitors, thus mastocytosis
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease:
 Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES. DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE
 DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
Common Benign Lesions and Skin Cancers. 22nd May 2015 Dr Mark Foley
 Common Benign Lesions and Skin Cancers 22nd May 2015 Dr Mark Foley Thank you for downloading this file. This intended to supplement the presentation given at the NZ Wound Care Conference, it is not intended
Common Benign Lesions and Skin Cancers 22nd May 2015 Dr Mark Foley Thank you for downloading this file. This intended to supplement the presentation given at the NZ Wound Care Conference, it is not intended
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Contents. Part I Genodermatoses
 Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Porokeratosis: Introduction
 Porokeratosis: Introduction Benign epidermal proliferation Distinct clinical & histologic features 5 clinical subtypes Erroneously named porokeratosis CLINICAL SUBTYPES 1. Porokeratosis of Mibelli 2. Disseminated
Porokeratosis: Introduction Benign epidermal proliferation Distinct clinical & histologic features 5 clinical subtypes Erroneously named porokeratosis CLINICAL SUBTYPES 1. Porokeratosis of Mibelli 2. Disseminated
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
B. Autoimmune blistering diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
ISPUB.COM. A Case of Actinic Lichen Planus. K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern
 Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges
 Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges Michael B. Morgan EPIDEMIOLOGY: Second most common skin cancer, rare in the dark-skinned races. ETIOLOGY: Ultraviolet light, HPV infection. PATHOGENESIS:
Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges Michael B. Morgan EPIDEMIOLOGY: Second most common skin cancer, rare in the dark-skinned races. ETIOLOGY: Ultraviolet light, HPV infection. PATHOGENESIS:
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants
 Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
Malignant tumors of melanocytes: Part 1. Deba P Sarma, MD., Omaha
 Malignant tumors of melanocytes: Part 1 Deba P Sarma, MD., Omaha The melanocytic tumor is one of the most difficult and confusing areas in Dematopathology. It is true that most (95%) of such lesions are
Malignant tumors of melanocytes: Part 1 Deba P Sarma, MD., Omaha The melanocytic tumor is one of the most difficult and confusing areas in Dematopathology. It is true that most (95%) of such lesions are
BSD SELF-ASSESSMENT CASES 21-24
 BSD SELF-ASSESSMENT CASES 21-24 EDINBURGH, 2 JULY 2018 LASZLO IGALI CASE 21 CLINICAL HISTORY Female, 43 years, nodule on left side of face/jaw angle area. Slow growth over years. MACRO (NOT GIVEN) Skin
BSD SELF-ASSESSMENT CASES 21-24 EDINBURGH, 2 JULY 2018 LASZLO IGALI CASE 21 CLINICAL HISTORY Female, 43 years, nodule on left side of face/jaw angle area. Slow growth over years. MACRO (NOT GIVEN) Skin
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Dermatology GP Referral Guidelines
 Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Viral Infections. Chicken Pox 5/21/2018
 Napa Valley Dermatopathology Meeting 2018 - Select Infections & Infestations Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director
Napa Valley Dermatopathology Meeting 2018 - Select Infections & Infestations Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN
 CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY
 WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
My Algorithm. Questions to ask. Do you or your family have a history of?... Allergic rhinitis, Sensitive skin, Asthma Skin Cancer
 Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Case year female. Routine Pap smear
 Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
CPC. Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand
 CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Invisible Dermatoses. Dermal Diseases. Epidermal Diseases
 Invisible Dermatoses To our knowledge, Martin Brownstein and Asher Rabinowitz first used the term "invisible dermatoses."* Generations of dermatologists, however, have struggled with biopsy 3. specimens
Invisible Dermatoses To our knowledge, Martin Brownstein and Asher Rabinowitz first used the term "invisible dermatoses."* Generations of dermatologists, however, have struggled with biopsy 3. specimens
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. A newborn with a papulonodular rash at birth
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A newborn with a papulonodular rash at birth June 2001 2 Glanzmann R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, UKKB Basel, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas M Berger, Webmaster
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A newborn with a papulonodular rash at birth June 2001 2 Glanzmann R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, UKKB Basel, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas M Berger, Webmaster
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
Common Cutaneous Signs of Medical Illnesses
 Common Cutaneous Signs of Medical Illnesses DR COLIN THENG MBBS, MMED (FAM. MED), MRCP(UK), FAMS SENIOR CONSULTANT DERMATOLOGIST THE SKIN SPECIALISTS & LASER CLINIC MOUNT ALVERNIA MEDICAL CENTRE D, #07-61
Common Cutaneous Signs of Medical Illnesses DR COLIN THENG MBBS, MMED (FAM. MED), MRCP(UK), FAMS SENIOR CONSULTANT DERMATOLOGIST THE SKIN SPECIALISTS & LASER CLINIC MOUNT ALVERNIA MEDICAL CENTRE D, #07-61
Skin Disorders of the Nose in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Skin Disorders of the Nose in Dogs (Canine Nasal Dermatoses) Basics OVERVIEW Conditions
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Skin Disorders of the Nose in Dogs (Canine Nasal Dermatoses) Basics OVERVIEW Conditions
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Ross NA, Chung H-J, Li Q, Andrews JP, Keller MS, Uitto J. Pityriasis rubra pilaris: a case series of patients. Published online March 9, 26. JAMA Dermatol. doi:./jamadermatol.26.9.
Supplementary Online Content Ross NA, Chung H-J, Li Q, Andrews JP, Keller MS, Uitto J. Pityriasis rubra pilaris: a case series of patients. Published online March 9, 26. JAMA Dermatol. doi:./jamadermatol.26.9.
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Introduction. Results. Discussion. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings. Results. conclusions,
 1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
