Inflammatory basis of diabetic retinopathy. Tim Kern, PhD Case Western Reserve University and Stokes VA Hospital, Cleveland, OH
|
|
|
- Morgan Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inflammatory basis of diabetic retinopathy Tim Kern, PhD Case Western Reserve University and Stokes VA Hospital, Cleveland, OH
2 Diabetic retinopathy currently is diagnosed based on vascular abnormalities
3
4 Pericyte ghost Acellular capillary Microaneurysm
5
6
7
8 CURRENT THERAPIES AGAINST DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Laser photocoagulation Anti-VEGF injections (intra-vitreal) Corticosteroids Improved glycemic control Fibrates Blood pressure medications
9 DIABETES ELEVATED BLOOD HEXOSE METABOLIC ABNORMALITIES NONPROLIFERATIVE RETINOPATHY (especially capillary nonperfusion & degeneration) RETINAL ISCHEMIA PROLIFERATIVE RETINOPATHY
10 DIABETES ELEVATED BLOOD HEXOSE METABOLIC INFLAMMATION ABNORMALITIES NONPROLIFERATIVE RETINOPATHY (especially capillary nonperfusion & degeneration)
11 What is the molecular cause of capillary degeneration in diabetic retinopathy? What cell types are involved in the development of diabetic retinopathy, and do those cells offer new ways to inhibit the retinopathy? Leukocytes Photoreceptors
12 Study design Glycemic control Histology 8-10 months diabetes inos, NO and nitrotyrosine 2-3 months diabetes ICAM Leukostasis Superoxide generation by isolated retina NF-κB and C/EBP activation Cell culture studies Induce diabetes Assign to groups 12 wks; biochemical & physiological assays 36 wks; histopathology
13 Leukostasis
14 Examples of glycemia in experimental animals: Effect of PJ-34 therapy Group (n) Duration (month) Body weight (g) Non-fast blood glucose (mg/l) Glycated Hemoglobin(%) Normal (10) ± ± ± 1.0 Diabetes (10) ± ± ± 2.8 D+PJ-34 (7) ± ± ± 1.1 Normal (28) ± ± ± 0.7 Diabetes (19) ± ± ± 1.4 D+PJ-34 (19) ± ± ± 1.0
15 PJ-34 inhibited diabetes-induced capillary cell apoptosis, and formation of acellular capillaries and pericyte ghosts TUNEL+ capillary cells/ retina TUNEL-positive capillary cells Non-diabetes Diabetes Diabetes+PJ-34 9 mos diabetes Acellular capillaries / mm 2 ret Acellular capillaries * * ** ** Ghosts per 1000 capillary cells Pericyte ghosts * * ** ** Zheng, Szabó, and Kern. Diabetes 53:2960, 2004
16 Expression (% of nondiabetic) PJ34 inhibited the diabetes-induced increase in retinal ICAM expression and leukostasis 350% 300% 250% 200% ICAM expression 150% 100% 50% 0% Nondiab normal Diab diabetes D+PJ-34 PARPi 70.0 * Non-diabetes ** Diabetes Adherent leukocytes/retina Diabetes+PJ-34 Leukostasis * * ** ** Arteriolar Venular Microvascular *
17 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
18 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β PARP inhibitors IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
19 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation Salicylates NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
20 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor Aminoguanidine inos -/- mice prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
21 5 lipoxygenase Diabetes RAGE Pro IL-1β? Aldose reductase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - COX inhibitors p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX IL-1β IL-1β receptor TNFα CD40 prostaglandins ICAM Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
22 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM ICAM -/- mice Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
23 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes Lipoxygenase RAGE inhibitors p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
24 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 IL-1β inhibitors Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
25 ? 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation Aldose Antioxidants Mn SOD overexpression reductas inos Cu,Zn SOD overexpression e NO & ONOO - COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
26 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase RAGE p38 MAPK inhibitor p38 Superoxide generation PARP activation NO & ONOO - Diabetes NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
27 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase RAGE inhibitor Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
28 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation AR deletion NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
29 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 CD40 deletion Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
30 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα TNF inhibition CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
31 ? Aldose reductase 5 lipoxygenase Superoxide generation NO & ONOO - Diabetes RAGE p38 PARP activation NF-κB activation inos COX ICAM Pro IL-1β IL-1β IL-1β receptor prostaglandins TNFα CD40 Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
32 What cell types have the biochemical abnormalities that cause capillary degeneration/dysfunction in diabetes? Vascular Neuroglial Blood cells
33 Wildtype C57Bl/6J mouse (Recipient) Genetically modified mouse (inos -/-, PARP -/-, etc) Irradiate (whole body) to kill bone marrow Isolate bone marrow Inject into irradiated recipient Chimeric mouse inos -/- WT only marrow-derived cells lack inos WT inos -/- only marrow-derived cells have inos
34 5 lipoxygenase Diabetes RAGE Pro Il-1β? p38 Superoxide generation PARP activation NF-κB activation inos NO & ONOO - COX-2 IL-1β IL-1β receptor TNFα prostaglandins ICAM Vasoocclusion? Capillary cell death Capillary degeneration
35 Wildtype C57Bl/6J mouse (Recipient) Genetically modified mouse (inos -/-, PARP -/-, etc) Irradiate (whole body) to kill bone marrow Isolate bone marrow Inject into irradiated recipient Chimeric mouse inos -/- WT only marrow-derived cells lack inos WT inos -/- only marrow-derived cells have inos
36 Wildtype C57Bl/6J mouse (Recipient) Genetically modified mouse (inos -/-, PARP -/-, etc) Irradiate (whole body) to kill bone marrow Isolate bone marrow Inject into irradiated recipient Chimeric mouse inos -/- WT only marrow-derived cells lack inos WT inos -/- only marrow-derived cells have inos
37 Degenerate capillaries (per mm 2 retina) Degenerate capillaries per mm2 retina Irradiation does not inhibit the process leading to diabetic retinopathy Nondiab Diabetic Leukostasis (% of nondiab) abetes-induced inflammation (mrna; fold above nondiab) Nondiabetic Diabetic * N D wt wt inos -/- PARP -/- Control wt wt * inos -/- WT PARP -/- WT * inos TNFα COX-2 inos TNFα COX2 Diabetes 2012;61:
38 Degenerate capillaries (per mm 2 retina) Degenerate capillaries per mm2 retina Deletion of inos from marrow-derived cells only inhibits DR but deletion of inos from retinal cells only does not Leukostasis (% of nondiab) abetes-induced inflammation (mrna; fold above nondiab) Nondiabetic Diabetic * N D wt wt inos -/- PARP -/- Control wt wt * inos -/- WT PARP -/- WT * inos TNFα COX-2 inos TNFα COX2 Diabetes 2012;61:
39 Degenerate capillaries (per mm 2 retina) Degenerate capillaries per mm2 retina Deletion of inos from marrow-derived cells only inhibits DR but deletion of inos from retinal cells only does not Leukostasis (% of nondiab) abetes-induced inflammation (mrna; fold above nondiab) Nondiabetic Diabetic * N D wt wt inos -/- PARP -/- Control wt wt * inos -/- WT PARP -/- WT * inos TNFα COX-2 inos TNFα COX2 Diabetes 2012;61:
40 Degenerate capillaries (per mm 2 retina) Degenerate capillaries per mm2 retina Deletion of inos from marrow-derived cells only inhibits DR but deletion of inos from retinal cells only does not Leukostasis (% of nondiab) Deletion of inos or PARP only from leukocytes also inhibited: abetes-induced inflammation (mrna; fold above nondiab) 5 Oxidative stress in the retina in the retina Nondiabetic Diabetic * N D wt wt inos -/- PARP -/- Control wt wt * inos -/- WT PARP -/- WT * Production of inflammatory proteins Leukostasis in the retina inos TNFα COX-2 inos TNFα COX2 Diabetes 2012;61: Diabetes 2012;61:
41 Co-culture of marrow-derived cells or leukocytes with retinal endothelial cells to measure leukocyte-mediated killing of endothelial cells Leukocytes from diabetic or nondiabetic mice Transformed retinal endothelial cells 5 mm glucose 30 mm glucose 1:5 ratio of leukocytes Ratio of WBC to endothelial cells 24 hr co-culture Count endothelial cells that are dead (stained with trypan blue) relative to number of healthy (unstained) endothelial cells Diabetes 2012;61:
42 Leukocytes from diabetic mice kill more retinal endothelial cells in high glucose in vitro, and this is inhibited in leukocytes from inos-deficient mice Retinal endothelial cells killed by overnight incubation with WBC Leukocyte mediated endothelial death (% of total endothelial count) all p< Endothelial cells incubated in: 5mM glucose 30 mm glucose Donor phenotype N N D D SD SD SD SD SD Donor genotype WT WT WT WT WT WT inos -/- inos -/- inos -/- In vitro treatment Lipoic anti- - Lipoic antiacid FasL acid FasL Diabetes 2012;61:
43 Leukocytes from diabetic mice kill more retinal endothelial cells in high glucose in vitro, and this is inhibited in leukocytes from inos-deficient mice Retinal endothelial cells killed by overnight incubation with WBC Leukocyte mediated endothelial death (% of total endothelial count) all p< Endothelial cells incubated in: 5mM glucose 30 mm glucose Endothelial cells Donor phenotype N N D D SD SD SD SD SD Leukocytes Donor genotype WT WT WT WT WT WT inos -/- inos -/- inos -/- In vitro treatment Lipoic anti- - Lipoic antiacid FasL acid FasL Diabetes 2012;61:
44 Leukocytes from diabetic mice kill retinal endothelial cells in high glucose in vitro Retinal endothelial cells killed by overnight incubation with WBC Leukocytes from nondiabetic mice Endothelial cells incubated in: 5mM glucose 30 mm glucose Donor phenotype ND ND SD SD SD SD SD SD SD Donor genotype WT WT WT WT WT WT inos -/- inos -/- inos -/- In vitro treatment Lipoic anti- - Lipoic antiacid FasL acid FasL Diabetes 2012;61:
45 Leukocytes from diabetic mice kill more retinal endothelial cells in high glucose in vitro, and this is inhibited in leukocytes from inos-deficient mice Retinal endothelial cells killed by overnight incubation with WBC Leukocytes from nondiabetic mice Leukocytes from diabetic mice Endothelial cells incubated in: 5mM glucose 30 mm glucose Donor phenotype N N D D SD SD SD SD SD Donor genotype WT WT WT WT WT WT inos -/- inos -/- inos -/- In vitro treatment Lipoic anti- - Lipoic antiacid FasL acid FasL Diabetes 2012;61:
46 The animal studies indicate that capillary degeneration that occurs in diabetic retinopathy and possibly neuropathy are caused by leukocytes. The same leukocyte-mediated killing of endothelial cells occurs in diabetic patients.
47 Mol Vis : Leukocytes Leukocytes from from diabetic diabetic humans humans likewise kill retinal endothelial cells via direct contact likewise kill retinal endothelial cells human human co-culture Nondiabetic Diabetic L; human retinal endothelial cells incubated in 5mM glucose H; human retinal endothelial cells incubated in 25mM glucose N; leukocytes from nondiabetic patients D; leukocytes from diabetic patients
48 Mol Vis : Leukocytes from from diabetic diabetic humans humans likewise kill retinal endothelial cells via direct contact likewise kill retinal endothelial cells human human co-culture L; human retinal endothelial cells incubated in 5mM glucose H; human retinal endothelial cells incubated in 25mM glucose N; leukocytes from nondiabetic patients D; leukocytes from diabetic patients
49 In vivo inhibition of leukocyte-mediated killing of retinal endothelial cells in diabetic patients 1. Collect blood from diabetic patients, and measure leukocytemediated killing of human retinal endothelial cells (Before). 2. Ask patients to consume the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, berberine, for one month. 3. Recollect blood from the same patients, and re-measure leukocyte-mediated killing of endothelial cells (After). Leukocyte-mediated killing of endo cells (%) Molecular Vision 2013; 19:
50 In vivo inhibition of leukocyte-mediated killing of retinal endothelial cells in diabetic patients 1. Collect blood from diabetic patients, and measure leukocytemediated killing of human retinal endothelial cells (Before). 2. Ask patients to consume the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, berberine, for one month. 3. Recollect blood from the same patients, and re-measure leukocyte-mediated killing of endothelial cells (After). Leukocyte-mediated killing of endo cells (%) Molecular Vision 2013; 19:
51 In vivo inhibition of leukocyte-mediated killing of retinal endothelial cells in diabetic patients 1. Collect blood from diabetic patients, and measure leukocytemediated killing of human retinal endothelial cells (Before). 2. Ask patients to consume the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, berberine, for one month. 3. Recollect blood from the same patients, and re-measure leukocyte-mediated killing of endothelial cells (After). Leukocyte-mediated killing of endo cells (%) Molecular Vision 2013; 19:
52 What is the molecular cause of capillary degeneration in diabetic retinopathy? What cell types are involved in the development of diabetic retinopathy, and do those cells offer new ways to inhibit the retinopathy? Leukocytes Photoreceptors
53 Photoreceptors and diabetic retinopathy Laser photocoagulation has beneficial effects on advanced diabetic retinopathy in patients Patients having retinitis pigmentosa have been reported to have less diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001;85(3): Continuous low intensity light all night inhibits retinal edema. Eye (Lond). 2010;24: and 2011;25: Density of retinal vasculature was preserved in diabetic rhodopsin -/- animals. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47: , 2006
54 PNAS U S A :
55 Photoreceptor cells cause the oxidative stress and secondary inflammatory response in diabetes Photoreceptor degeneration occurs in animals lacking opsin
56 Low-intensity far-red light inhibits early lesions that contribute to diabetic retinopathy: in vivo and in vitro
57 Low intensity far-red light (photobiomodulation): effects on the retina in diabetic rats Light treatment is only 4 minutes per day 670 nm 6 joules cm 2 per session 7days/wk 10wks therapy Diabetes was induced approx 8 days before LED therapy was initiated
58 Light therapy inhibited the diabetesinduced increase in leukostasis in retinal microvessels and induction of ICAM
59 Light therapy inhibits the diabetesinduced increase in retinal production of superoxide and inhibits loss of SOD
60 Light therapy inhibited diabetes-induced apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in vivo TUNEL Ganglion Cell Layer 8 6 TUNEL Cells ND ND +LED SD SD +LED
61 amplitude ( V) Light therapy partially inhibited diabetes-induced loss in retinal function Normal Normal+LED Diabetic+LED Diabetic B Photopic (photopic response) Nondiabetic Nondiabetic +LED Diabetic +LED Diabetic intensities (log cd s m-2)
62 Far-red light also inhibits leukocytemediated degeneration of First day retinal endothelial cells Mice WBCs Co-culture with mrecs Cell Death Ratio 9 p<0.01 p< ND SD SD+LED Light treatment is only 4 minutes per day
63 Optical coherence tomography assessment of macular edema in patients 003
64 Reversal of non-center involved macular edema using 3 min/day of far-red light 7 mos 7 mos 9 mos 2 mos
65 Reversal of non-center involved macular edema using 3 min/day of far-red light 7 mos 7 mos 9 mos 2 mos
66 Conclusions Immune/inflammatory processes play a critical role in the development of at least the vascular lesions of early diabetic retinopathy. The inflammation seems to be derived, or at least initiated by, marrow-derived cells (notably neutrophils). Retinal cells contribute also, but their contribution needs to be studied more. Future investigations on the pathogenesis of diabetic complications need to expand beyond the traditional vascularspecific view of complications, to include also immune cells. We are investigating the possibility that leukocyte studies might be used in the future to predict the likelihood that a particular patient will progress to advanced complications, and to predict their response to particular therapies.
THE ROLE OF POLY(ADP-RIBOSE) POLYMERASE-1 AND NF-κB IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 THE ROLE OF POLY(ADP-RIBOSE) POLYMERASE-1 AND NF-κB IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY by LING ZHENG Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
THE ROLE OF POLY(ADP-RIBOSE) POLYMERASE-1 AND NF-κB IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY by LING ZHENG Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY
 PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction
 Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic Management beyond traditional risk factors and LDL-C control: Can we improve macro and microvascular risks?
 Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Photoreceptor Cells Influence Retinal Vascular Degeneration in Mouse Models of Retinal Degeneration and Diabetes
 Retina Photoreceptor Cells Influence Retinal Vascular Degeneration in Mouse Models of Retinal Degeneration and Diabetes Haitao Liu, 1 Jie Tang, 1 Yunpeng Du, 1 Aicha Saadane, 2 Deoye Tonade, 3 Ivy Samuels,
Retina Photoreceptor Cells Influence Retinal Vascular Degeneration in Mouse Models of Retinal Degeneration and Diabetes Haitao Liu, 1 Jie Tang, 1 Yunpeng Du, 1 Aicha Saadane, 2 Deoye Tonade, 3 Ivy Samuels,
The Human Eye. Cornea Iris. Pupil. Lens. Retina
 The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema
 Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) represents a
 THE MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY: OPPORTUNITIES FOR THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION Lloyd P. Aiello, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Hyperglycemia is the principal underlying cause of diabetic microvascular complications,
THE MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY: OPPORTUNITIES FOR THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION Lloyd P. Aiello, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Hyperglycemia is the principal underlying cause of diabetic microvascular complications,
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy
 Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy Vincent Reppucci, MD Director, Retina Service Mt. Sinai St. Luke s-roosevelt Hospital Attending Physician, Retina Service New York Eye and Ear Infirmary
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy Vincent Reppucci, MD Director, Retina Service Mt. Sinai St. Luke s-roosevelt Hospital Attending Physician, Retina Service New York Eye and Ear Infirmary
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes. Gestational diabetes;
 Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
Diabetic ocular complications are a leading PROCEEDINGS MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Lloyd P.
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Lloyd P. Aiello, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic microvascular complication, affecting approximately 50%
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Lloyd P. Aiello, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic microvascular complication, affecting approximately 50%
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City
 Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Brampton Hurontario Street Brampton, ON L6Y 0P6
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Common Causes of Vision Loss
 Common Causes of Vision Loss Learning Objectives To identify the most common causes of vision loss in the United States To differentiate the most common forms of agerelated macular degeneration and diabetic
Common Causes of Vision Loss Learning Objectives To identify the most common causes of vision loss in the United States To differentiate the most common forms of agerelated macular degeneration and diabetic
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease
 Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
PROCEEDINGS NEW TRENDS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* Paul M. Dodson, MD, FRCP, FRCOphth ABSTRACT
 NEW TRENDS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Paul M. Dodson, MD, FRCP, FRCOphth ABSTRACT Based on a presentation given by Dr Dodson at a symposium held in conjunction with the 12th International
NEW TRENDS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Paul M. Dodson, MD, FRCP, FRCOphth ABSTRACT Based on a presentation given by Dr Dodson at a symposium held in conjunction with the 12th International
Review Article Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Retinopathy
 Experimental Diabetes Research Volume 2007, Article ID 43603, 12 pages doi:10.1155/2007/43603 Review Article Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Retinopathy Renu A. Kowluru and Pooi-See Chan Received 21 December
Experimental Diabetes Research Volume 2007, Article ID 43603, 12 pages doi:10.1155/2007/43603 Review Article Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Retinopathy Renu A. Kowluru and Pooi-See Chan Received 21 December
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
G. LI AND ASSOCIATES
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marrow-Derived Cells Regulate the Development of Early Diabetic Retinopathy and Tactile Allodynia in Mice Guangyuan Li, 1,2 Alexander A. Veenstra, 1 Ramaprasad R. Talahalli, 1 Xiaoqi Wang,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marrow-Derived Cells Regulate the Development of Early Diabetic Retinopathy and Tactile Allodynia in Mice Guangyuan Li, 1,2 Alexander A. Veenstra, 1 Ramaprasad R. Talahalli, 1 Xiaoqi Wang,
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Review Article Diabetic Retinopathy: Vascular and Inflammatory Disease
 Journal of Diabetes Research Volume 2015, Article ID 582060, 16 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/582060 Review Article Diabetic Retinopathy: Vascular and Inflammatory Disease F. Semeraro, 1 A. Cancarini,
Journal of Diabetes Research Volume 2015, Article ID 582060, 16 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/582060 Review Article Diabetic Retinopathy: Vascular and Inflammatory Disease F. Semeraro, 1 A. Cancarini,
Ο ρόλος των τριγλυκεριδίων στην παθογένεια των μικροαγγειοπαθητικών επιπλοκών του σακχαρώδη διαβήτη
 Ο ρόλος των τριγλυκεριδίων στην παθογένεια των μικροαγγειοπαθητικών επιπλοκών του σακχαρώδη διαβήτη Κωνσταντίνος Τζιόμαλος Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Παθολογίας Α Προπαιδευτική Παθολογική Κλινική, Νοσοκομείο
Ο ρόλος των τριγλυκεριδίων στην παθογένεια των μικροαγγειοπαθητικών επιπλοκών του σακχαρώδη διαβήτη Κωνσταντίνος Τζιόμαλος Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Παθολογίας Α Προπαιδευτική Παθολογική Κλινική, Νοσοκομείο
Pathophysiology and management of diabetic retinopathy
 For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Pathophysiology and management of diabetic retinopathy Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 4(6), 627 647 (2009) Ahmed M Abu El-Asrar, Hani S Al-Mezaine
For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Pathophysiology and management of diabetic retinopathy Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 4(6), 627 647 (2009) Ahmed M Abu El-Asrar, Hani S Al-Mezaine
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference
 The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference We will discuss - How exactly does blood sugar control affect retinopathy? - What are other factors that we measure in
The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference We will discuss - How exactly does blood sugar control affect retinopathy? - What are other factors that we measure in
Review Article Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Retinopathy, General Preventive Strategies, and Novel Therapeutic Targets
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 801269, 18 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/801269 Review Article Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Retinopathy, General Preventive Strategies, and Novel Therapeutic
BioMed Research International, Article ID 801269, 18 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/801269 Review Article Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Retinopathy, General Preventive Strategies, and Novel Therapeutic
New Developments in the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
 New Developments in the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy B. Jeroen Klevering University Medical Centre Nijmegen - The Netherlands Topics Management of diabetic retinopathy Interventions a. primary (prevention)
New Developments in the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy B. Jeroen Klevering University Medical Centre Nijmegen - The Netherlands Topics Management of diabetic retinopathy Interventions a. primary (prevention)
The metabolic memory. Antonio Ceriello
 The metabolic memory Antonio Ceriello : DCCT/EDIC - Long-term Microvascular Risk Reduction in Type 1 Diabetes A1C 12% 10% Intensive Retinopathy progression (incidence) Conventional 0.5 0.4 0.3 62% risk
The metabolic memory Antonio Ceriello : DCCT/EDIC - Long-term Microvascular Risk Reduction in Type 1 Diabetes A1C 12% 10% Intensive Retinopathy progression (incidence) Conventional 0.5 0.4 0.3 62% risk
In some people, fluid leaks through the damaged vessels, injuring the retina and causing loss of vision
 Published on: 12 Apr 2013 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) The most common eye disease among people with diabetes High blood sugar levels and high blood pressure (BP) can damage the tiny
Published on: 12 Apr 2013 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) The most common eye disease among people with diabetes High blood sugar levels and high blood pressure (BP) can damage the tiny
Longitudinal Validation Study: Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes as a Model of Diabetic Retinopathy in Brown Norway Rats
 Longitudinal Validation Study: Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes as a Model of Diabetic Retinopathy in Brown Norway Rats Robin Dean, Robert Sukhu, Leslie Nemeth, Qin Zhang, Isaac Hakim, Ali Ebramhimnejad,
Longitudinal Validation Study: Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes as a Model of Diabetic Retinopathy in Brown Norway Rats Robin Dean, Robert Sukhu, Leslie Nemeth, Qin Zhang, Isaac Hakim, Ali Ebramhimnejad,
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic
 Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
Retinab for Diabetic Retinopathy
 Retinab for Diabetic Retinopathy Tarnhelm Therapeutics January 2014 2 2013 Tarnhelm Therapeutics Company Background Virtual company based in Bryn Mawr, PA Developing biologics for diabetic retinopathy
Retinab for Diabetic Retinopathy Tarnhelm Therapeutics January 2014 2 2013 Tarnhelm Therapeutics Company Background Virtual company based in Bryn Mawr, PA Developing biologics for diabetic retinopathy
EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion
 EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina
EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
University of Groningen. Vasoregression in incipient diabetic retinopathy Pfister, Frederick
 University of Groningen Vasoregression in incipient diabetic retinopathy Pfister, Frederick IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Vasoregression in incipient diabetic retinopathy Pfister, Frederick IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Retinylamine benefits early diabetic retinopathy in mice*
 JBC Papers in Press. Published on July 2, 215 as Manuscript M115.655555 The latest version is at http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/1.174/jbc.m115.655555 Retinylamine benefits early diabetic retinopathy in mice*
JBC Papers in Press. Published on July 2, 215 as Manuscript M115.655555 The latest version is at http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/1.174/jbc.m115.655555 Retinylamine benefits early diabetic retinopathy in mice*
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Diabetic Retinopathy: Recent Advances in Treatment and Treatment Approaches
 Diabetic Retinopathy: Recent Advances in Treatment and Treatment Approaches Dr. David Wong Associate Professor Retina Specialist, Department of Ophthalmology & Vision Sciences, University of Toronto, Canada
Diabetic Retinopathy: Recent Advances in Treatment and Treatment Approaches Dr. David Wong Associate Professor Retina Specialist, Department of Ophthalmology & Vision Sciences, University of Toronto, Canada
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient
 Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Use of the Free Electron Laser for the Noninvasive Determination of Retinal Oxyhemoglobin Saturation by Near Infrared Reflectance Spectrophotometry
 Use of the Free Electron Laser for the Noninvasive Determination of Retinal Oxyhemoglobin Saturation by Near Infrared Reflectance Spectrophotometry Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946 Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946
Use of the Free Electron Laser for the Noninvasive Determination of Retinal Oxyhemoglobin Saturation by Near Infrared Reflectance Spectrophotometry Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946 Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946
Diabetic Retinopathy. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
ARVO Annual Meeting, May 1, 2018, Honolulu, Hawaii
 ARVO Annual Meeting, May 1, 2018, Honolulu, Hawaii A novel oral plasma kallikrein (PKal) inhibitor KV123833 blocks VEGF-mediated retinal vascular hyperpermeability in a murine model of retinal edema (#3464)
ARVO Annual Meeting, May 1, 2018, Honolulu, Hawaii A novel oral plasma kallikrein (PKal) inhibitor KV123833 blocks VEGF-mediated retinal vascular hyperpermeability in a murine model of retinal edema (#3464)
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist
 Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
Editorial Inflammation in Retinal Disease
 International Inflammation Volume 2013, Article ID 724648, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/724648 Editorial Inflammation in Retinal Disease Scott M. Whitcup, 1 Robert B. Nussenblatt, 2 Susan L.
International Inflammation Volume 2013, Article ID 724648, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/724648 Editorial Inflammation in Retinal Disease Scott M. Whitcup, 1 Robert B. Nussenblatt, 2 Susan L.
Models of retinal diseases and their applicability in drug discovery
 Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery ISSN: 1746-0441 (Print) 1746-045X (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iedc20 Models of retinal diseases and their applicability in drug discovery
Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery ISSN: 1746-0441 (Print) 1746-045X (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iedc20 Models of retinal diseases and their applicability in drug discovery
Control of Systemic Factors Can Preserve Vision in Diabetic Retinopathy
 dmcjuly05_cme_dr 7/28/05 9:19 AM Page 38 Control of Systemic Factors Can Preserve Vision in Diabetic Retinopathy Jointly sponsored by The Dulaney Foundation and Diabetic Microvascular Complications Today.
dmcjuly05_cme_dr 7/28/05 9:19 AM Page 38 Control of Systemic Factors Can Preserve Vision in Diabetic Retinopathy Jointly sponsored by The Dulaney Foundation and Diabetic Microvascular Complications Today.
Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage. Graham Leese University of Dundee
 Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage Graham Leese University of Dundee Edinburgh July 16 th 2018 NUMBER OF PATIENTS RECEIVING LASER IN TAYSIDE 300 250 200 Number
Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage Graham Leese University of Dundee Edinburgh July 16 th 2018 NUMBER OF PATIENTS RECEIVING LASER IN TAYSIDE 300 250 200 Number
DIABETES AND YOUR EYES. Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler
 DIABETES AND YOUR EYES Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler Tahlequah, OK Forest Grove, OR Brief Review of Diabetes The body s endocrine system is responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and tissue
DIABETES AND YOUR EYES Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler Tahlequah, OK Forest Grove, OR Brief Review of Diabetes The body s endocrine system is responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and tissue
PROGRESSION OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY FOLLOWING CATARACT SURGERY
 PROGRESSION OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY FOLLOWING CATARACT SURGERY Yayan Heryanto, Iwan Sovani, Arief Kartasasmita, Erwin Iskandar, Djonggi Panggabean. Dept. of Ophthalmology Medical Faculty Unpad, Cicendo
PROGRESSION OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY FOLLOWING CATARACT SURGERY Yayan Heryanto, Iwan Sovani, Arief Kartasasmita, Erwin Iskandar, Djonggi Panggabean. Dept. of Ophthalmology Medical Faculty Unpad, Cicendo
RXi Pharmaceuticals. sd-rxrna Demonstrate Robust Efficacy in the Eye. Dr. Geert Cauwenbergh President & CEO OTCQX: RXII. Next Generation in RNAi
 RXi Pharmaceuticals sd-rxrna Demonstrate Robust Efficacy in the Eye Next Generation in RNAi Dr. Geert Cauwenbergh President & CEO OTCQX: RXII 2 Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking
RXi Pharmaceuticals sd-rxrna Demonstrate Robust Efficacy in the Eye Next Generation in RNAi Dr. Geert Cauwenbergh President & CEO OTCQX: RXII 2 Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking
Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) with segmental optic disc edema. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) with segmental optic disc edema Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 75 year old white woman lost vision in the inferior part of her visual
Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) with segmental optic disc edema Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 75 year old white woman lost vision in the inferior part of her visual
INDEX. Genetics. French poodle progressive rod-cone degeneration,
 INDEX Acuity in Stargardt's macular dystrophy, 25-34 ADRP (Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa), see Retinitis pigmentosa and Genetics afgf, 294, 296 Age-related maculopathy, see Macular degeneration
INDEX Acuity in Stargardt's macular dystrophy, 25-34 ADRP (Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa), see Retinitis pigmentosa and Genetics afgf, 294, 296 Age-related maculopathy, see Macular degeneration
A. One to three months of age. Anterior Lens (Mean ± SEM) Posterior Lens (Mean ± SEM) Mid Lens (Mean ± SEM) Cornea (Mean ± SEM) Genotype
 Supplementary Table 1. Location of lens opacification in Aldh1a1(-/-), Aldh3a1(-/-) single and Aldh1a1(-/-)/Aldh3a1(-/-) double knockout mice (DKO) at different ages. A. One to three months of age Genotype
Supplementary Table 1. Location of lens opacification in Aldh1a1(-/-), Aldh3a1(-/-) single and Aldh1a1(-/-)/Aldh3a1(-/-) double knockout mice (DKO) at different ages. A. One to three months of age Genotype
Lesson 5 Penetration & safety. Laserlessons.info
 Lesson 5 Penetration & safety But deep penetration is not always the best. For superficial conditions we want most of the energy to remain superficially and not far away from the target. For instance
Lesson 5 Penetration & safety But deep penetration is not always the best. For superficial conditions we want most of the energy to remain superficially and not far away from the target. For instance
Can VEGF reverse diabetic neuropathy in human subjects?
 Can VEGF reverse diabetic neuropathy in human subjects? Aristidis Veves, George L. King J Clin Invest. 2001;107(10):1215-1218. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci13038. Commentary Peripheral polyneuropathy is
Can VEGF reverse diabetic neuropathy in human subjects? Aristidis Veves, George L. King J Clin Invest. 2001;107(10):1215-1218. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci13038. Commentary Peripheral polyneuropathy is
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Unique peptides for reversing eye aging: Latest inventions in macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy treatment
 Unique peptides for reversing eye aging: Latest inventions in macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy treatment Prof. Svetlana Trofimova,, M.D., Ph.D. Saint Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation
Unique peptides for reversing eye aging: Latest inventions in macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy treatment Prof. Svetlana Trofimova,, M.D., Ph.D. Saint Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation
OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME
 December 2007 Sonia Rani John et al. - IFIS 375 ORIGINAL ARTICLE OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME Dr. Manoj S. DNB FRCS, Dr. Unnikrishnan Nair MS DO FRCS, Dr. Gargi Sathish MS Introduction
December 2007 Sonia Rani John et al. - IFIS 375 ORIGINAL ARTICLE OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME Dr. Manoj S. DNB FRCS, Dr. Unnikrishnan Nair MS DO FRCS, Dr. Gargi Sathish MS Introduction
EFFICACY OF ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR AGENTS IN RETINAL DISORDER FOR BETTER VISUAL ACUITY
 EFFICACY OF ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR AGENTS IN RETINAL DISORDER FOR BETTER VISUAL ACUITY Diwakar chaudhary *1, 2, Hu shuqiong, Long Yuan and Xiong kun 1 Yangtze University, 1 Nanhuan Road
EFFICACY OF ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR AGENTS IN RETINAL DISORDER FOR BETTER VISUAL ACUITY Diwakar chaudhary *1, 2, Hu shuqiong, Long Yuan and Xiong kun 1 Yangtze University, 1 Nanhuan Road
PROCEEDINGS THE IMPORTANCE OF ENDOTHELIAL DAMAGE: DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* Massimo Porta, MD, PhD ABSTRACT
 THE IMPORTANCE OF ENDOTHELIAL DAMAGE: DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* Massimo Porta, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in adults of working age in industrialized countries and
THE IMPORTANCE OF ENDOTHELIAL DAMAGE: DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* Massimo Porta, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in adults of working age in industrialized countries and
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
OCT Angiography The Next Frontier
 Choroid Retina avascular 5/13/2017 OCT Angiography The Next Frontier Pierce Kenworthy OD, FAAO June 9, 2017 OCT Angiography (OCTA) 2016 Non-invasive, motion contrast imaging Represents erythrocyte movement
Choroid Retina avascular 5/13/2017 OCT Angiography The Next Frontier Pierce Kenworthy OD, FAAO June 9, 2017 OCT Angiography (OCTA) 2016 Non-invasive, motion contrast imaging Represents erythrocyte movement
Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT) and NQO1-null (NQO1-/-) mice.
 competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects.
 Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects. a includes one patient who had an aqueous sample taken from the same eye twice b includes one patients who had an aqueous sample taken from the same
Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects. a includes one patient who had an aqueous sample taken from the same eye twice b includes one patients who had an aqueous sample taken from the same
INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
25 Protein Kinase C Inhibitors and
 25 Protein Kinase C Inhibitors and Diabetic Microvascular Disease Arvind Gupta, Rajeev Gupta Abstract: Diabetes is characterized by major changes in the microvascular system. Multiple pathways exist that
25 Protein Kinase C Inhibitors and Diabetic Microvascular Disease Arvind Gupta, Rajeev Gupta Abstract: Diabetes is characterized by major changes in the microvascular system. Multiple pathways exist that
Diabetic Retinopathy: Origin and Complications
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2012, 2 (1):88-94 Diabetic Retinopathy: Origin and Complications Ankur Rohilla *1, Rupesh Kumar 1, Seema Rohilla
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2012, 2 (1):88-94 Diabetic Retinopathy: Origin and Complications Ankur Rohilla *1, Rupesh Kumar 1, Seema Rohilla
Cigarette Smoke Exposure and HIV-Related Neurologic Disease Progression Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Consequences
 Cigarette Smoke Exposure and HIV-Related Neurologic Disease Progression Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Consequences Walter Royal, III, MD Professor of Neurology University of Maryland School of Medicine
Cigarette Smoke Exposure and HIV-Related Neurologic Disease Progression Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Consequences Walter Royal, III, MD Professor of Neurology University of Maryland School of Medicine
Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs
 + Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by CLEARVIEW Training Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman MCOptom FBDO + CET Accreditation C 19106 2 CET Points
+ Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by CLEARVIEW Training Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman MCOptom FBDO + CET Accreditation C 19106 2 CET Points
Oishi A, Miyamoto K, Yoshimura N. Etiology of carotid cavernous fistula in Japanese. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2009;53:40-43.
 Kimura T, Takagi H, Miyamoto K, Kita M, Watanabe D, Yoshimura N. Macular hole with epiretinal membrane after triamcinolone-assisted vitrectomy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Retinal Cases Brief
Kimura T, Takagi H, Miyamoto K, Kita M, Watanabe D, Yoshimura N. Macular hole with epiretinal membrane after triamcinolone-assisted vitrectomy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Retinal Cases Brief
RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PROGRESSION
 2015 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 22(2):159-165 doi: 10.1515/rjdnmd-2015-0020 RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PROGRESSION Mónika
2015 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 22(2):159-165 doi: 10.1515/rjdnmd-2015-0020 RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PROGRESSION Mónika
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
Diabetic Retinopathy and Nephropathy
 27 Diabetic Retinopathy and Nephropathy Ronald Klein, MD, MPH CONTENTS INTRODUCTION NATURAL HISTORY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY RELATIONSHIP OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY TO RETINOPATHY RELATIONSHIP OF DIABETIC
27 Diabetic Retinopathy and Nephropathy Ronald Klein, MD, MPH CONTENTS INTRODUCTION NATURAL HISTORY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY RELATIONSHIP OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY TO RETINOPATHY RELATIONSHIP OF DIABETIC
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
Diabetes, particularly diabetic retinopathy, is
 Chapter 14 Vision Disorders in Diabetes Ronald Klein, MD, MPH, and Barbara E.K. Klein, MD, MPH SUMMARY Diabetes, particularly diabetic retinopathy, is the leading cause of new cases of blindness in people
Chapter 14 Vision Disorders in Diabetes Ronald Klein, MD, MPH, and Barbara E.K. Klein, MD, MPH SUMMARY Diabetes, particularly diabetic retinopathy, is the leading cause of new cases of blindness in people
Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema without Intravitreal injections
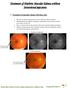 Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema without Intravitreal injections 1. Treatment of macular edema with laser only This 60 year old female presented on 02-01-2007 for retinal evaluation. She had proliferative
Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema without Intravitreal injections 1. Treatment of macular edema with laser only This 60 year old female presented on 02-01-2007 for retinal evaluation. She had proliferative
The Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network. Management of DME in Eyes with PDR
 The Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Management of DME in Eyes with PDR 1 What Has Been Learned? Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Protocol F: Results suggest that clinically meaningful differences
The Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Management of DME in Eyes with PDR 1 What Has Been Learned? Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Protocol F: Results suggest that clinically meaningful differences
OCT Angiography: The Next Step in Retinal Imaging Jonathan Zelenak D.O.
 OCT Angiography: The Next Step in Retinal Imaging Jonathan Zelenak D.O. Hillsdale Hospital Michigan State University Overview Evolution of OCT How does OCT angiography work? Clinical examples Potential
OCT Angiography: The Next Step in Retinal Imaging Jonathan Zelenak D.O. Hillsdale Hospital Michigan State University Overview Evolution of OCT How does OCT angiography work? Clinical examples Potential
University of Groningen. Vasoregression in incipient diabetic retinopathy Pfister, Frederick
 University of Groningen Vasoregression in incipient diabetic retinopathy Pfister, Frederick IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Vasoregression in incipient diabetic retinopathy Pfister, Frederick IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
We know diabetes is a common and growing problem as well as the leading cause
 ebook A GAME-CHANGER IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Early diagnosis and management guidance using objective, functional vision testing. by STEVEN M. SILVERSTEIN, MD We know diabetes is a common and growing problem
ebook A GAME-CHANGER IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Early diagnosis and management guidance using objective, functional vision testing. by STEVEN M. SILVERSTEIN, MD We know diabetes is a common and growing problem
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Understanding the mechanisms of asbestos related diseases
 University of Hawai i Cancer Center Understanding the mechanisms of asbestos related diseases Haining Yang, PhD Professor University of Hawai i Cancer Center Marker of exposure: Bilateral pleural plaques
University of Hawai i Cancer Center Understanding the mechanisms of asbestos related diseases Haining Yang, PhD Professor University of Hawai i Cancer Center Marker of exposure: Bilateral pleural plaques
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine. Heather Bladek Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine,
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 In Adult Patients With Diabetic Macular
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 In Adult Patients With Diabetic Macular
Research Article Differentiation between Good and Low-Responders to Intravitreal Ranibizumab for Macular Edema Secondary to Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 9875741, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9875741 Research Article Differentiation between Good and Low-Responders
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 9875741, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9875741 Research Article Differentiation between Good and Low-Responders
EyeGene Inc. Contact Information Korea Health Industry Development Institute
 EG-Mirotin: First-in-Class recombinant polypeptide novel subcutaneous drug containing RGD-motif targeted to suppress edema and vascular leakage for Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) EyeGene
EG-Mirotin: First-in-Class recombinant polypeptide novel subcutaneous drug containing RGD-motif targeted to suppress edema and vascular leakage for Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) EyeGene
Sequential non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Sequential non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 68 year old white woman had a new onset of floaters in her right eye and was found to have
Sequential non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 68 year old white woman had a new onset of floaters in her right eye and was found to have
Ocular Pathology. I. Congenital and/or developmental. A. Trisomy 21. Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea)
 I. Congenital and/or developmental Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6 th Ed. A. Trisomy 21 Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea) Focal hypoplasia of iris Cataracts frequently
I. Congenital and/or developmental Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6 th Ed. A. Trisomy 21 Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea) Focal hypoplasia of iris Cataracts frequently
Dr David Squirrell. Consultant Ophthalmologist Greenlane Hospital Auckland. 8:20-8:35 Diabetic Retinopathy - So What's New?
 Dr David Squirrell Consultant Ophthalmologist Greenlane Hospital Auckland 8:20-8:35 Diabetic Retinopathy - So What's New? Diabetic Retinopathy: so whats new in 2018? Diabetes no longer leading cause of
Dr David Squirrell Consultant Ophthalmologist Greenlane Hospital Auckland 8:20-8:35 Diabetic Retinopathy - So What's New? Diabetic Retinopathy: so whats new in 2018? Diabetes no longer leading cause of
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Diabetic maculopathy 11/ An update on. Miss Vasuki Sivagnanavel
 Miss Vasuki Sivagnanavel Consultant Ophthalmologist An update on Diabetic maculopathy Despite advances in the management of diabetes, diabetic retinopathy is already the commonest cause of blindness among
Miss Vasuki Sivagnanavel Consultant Ophthalmologist An update on Diabetic maculopathy Despite advances in the management of diabetes, diabetic retinopathy is already the commonest cause of blindness among
: Postdoctoral Fellow, LSU Health Sciences Center : Ph.D., Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
 Yongdong Zhou, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Research, Ophthalmology and Neuroscience Degrees 2007 2009: Postdoctoral Fellow, LSU Health Sciences Center 1996 2001: Ph.D., Sichuan University, Chengdu,
Yongdong Zhou, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Research, Ophthalmology and Neuroscience Degrees 2007 2009: Postdoctoral Fellow, LSU Health Sciences Center 1996 2001: Ph.D., Sichuan University, Chengdu,
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) is a nuclear
 Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Is Involved in the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy via Regulation of Nuclear Factor- B Ling Zheng, 1 Csaba Szabó, 2 and Timothy S. Kern 1,3 The current study investigated
Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Is Involved in the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy via Regulation of Nuclear Factor- B Ling Zheng, 1 Csaba Szabó, 2 and Timothy S. Kern 1,3 The current study investigated
Optical Coherence Tomography: Pearls for the Anterior Segment Surgeon Basic Science Michael Stewart, M.D.
 Optical Coherence Tomography: Pearls for the Anterior Segment Surgeon Basic Science Michael Stewart, M.D. Disclosure OCT Optical Coherence Tomography No relevant financial relationships I will refer to
Optical Coherence Tomography: Pearls for the Anterior Segment Surgeon Basic Science Michael Stewart, M.D. Disclosure OCT Optical Coherence Tomography No relevant financial relationships I will refer to
A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Clinical Case Presentation. Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion. Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital
 Clinical Case Presentation on Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital Introduction Case Study Pathogenesis Clinical Features Investigations Treatment Follow-up
Clinical Case Presentation on Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital Introduction Case Study Pathogenesis Clinical Features Investigations Treatment Follow-up
