Supplementary Table I. List of mutations presented by the Portuguese pediatric cohort with FH
|
|
|
- Luke Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Table I. List of mutations presented by the Portuguese pediatric cohort with FH Index patients (n=89) FH children Cascade screening (n=82) cdna Mutation Protein 3 0 c.10580g>a p.arg3527gln APOB exon 26 Gene Location Allele classification Functional studies & product activity 32% of protein activity (Innerarity TL et al Proc Natl Acad Sci 84(19): ) Amino acid Segregation analysis conservation Normolipidemic panel (C/A;C/NA) Reported in other populations Moderately conserved 21/21;0/10 (9 families) Innerarity TL et al Proc Natl Acad Sci 84(19): ; Miserez et al J Lipid Res. 34: ; Myant et al Genomics 45: 78-87; Rabés et al Hum Mutat. 10: ; Wenham et al Atherosclerosis. 129(2):185-92; Borén et al J Biol Chem. 276(12): c.10679a>g p.tyr3560cys APOB exon 26 Moderately conserved 4/4;0/0 Liyanage et al Ann Clin Biochem 45(Pt 2): c.-135c>g LDLR Promotor 5-15% LDLR activity in homozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mutat 1(6):445-66); RT-PCR show no transcription from this allele (Bourbon et al J Med Genet 46(5):352-7) 25/26;0/8 (10 families) Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6):445-66; Koivisto et al PNAS 91 : ; Jensen et al Hum Mutat. 7(1):82-4; Mozas et al 2004 Hum Mutat c.[-30-?_190+?del;1061-?_1845+?del] LDLR Promotor FH Siracusa (deletion promotor to exon 2): 45% LDLR activity in heterozygous fibroblasts (Garuti et al Atherosclerosis 121(1):105-17) 39/39;0/14 (13 families) Garuti et al Atherosclerosis 121(1): (20kb deletion of promotor to exon 2 reported as FH Siracusa); Chaves et al Eur J Clin Invest 31(4): (18kb deletion of promoter to exon 2 reported as FH Valencia-1) 1 1 c.1a>c p.met1leu LDLR exon 1 Note: luciferase assays showed that an alteration in the same amoniacid position but for a different nucleotide change (c.1a>t; p.met1leu) produces no detectable protein (Langenhoven et al Atherosclerosis. 125(1):111-9) Moderately conserved 5/5;0/0 Chaves et al J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(10): ; Fouchier et al Hum Mutat 26(6):550-6; Tosi et al Atherosclerosis 194(1): c.58g>a p.gly20arg LDLR exon 1 Moderately conserved 1/2;0/0 Amsellem et al Hum Genet 111(6):501-10; Widhalm et al J Inherit Metab Dis 30(2):239-47; Chmara et al J Appl Genet 51(1): c.68-?_313+?del LDLR exon 2 40% of LDLR activity in homozygote with FH Tomani-2 (Mabuchi et al Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 598: ) 5/5;0/0 Hobbs et al Hum Mutat 1(6): (10kb deletion of exons 2 to 3 reported as FH Tonami-2); Ma et al Clin Genet 36(4): (5kb deletion of exons 2 to 3 reported as FH French Canadian-5); Yamakawa et al Hum Genet 82(4): (5kb deletion of exons 2 to 3 reported as FH Tsukuba-1) 0 1 c.190+4instg LDLR intron 2 Retention of 2 nt of intron 2 generating premature stop codon at aa 206 (Medeiros et al Atherosclerosis 212(2):553-8) 1 1 c.235inst p.val79cysfs*51 LDLR exon 3 4/5;0/1 4/4;0/2 0 1 c.241c>t p.arg81cys LDLR exon 3 Highly conserved 1/1;1/3 Nissen et al Clin Genet 53(6):433-9; Loubser et al Clin Genet 55(5):340-5; Fouchier et al Hum Genet 109(6): c.325t>c p.cys109arg LDLR exon % LDLR activity in heterozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6): ) Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6):445-66; Robles-Osorio et al Arch Med Res. 37(1):102-8; Fouchier et al Hum Mutat. 26(6): c.326g>t p.cys109phe LDLR exon 4 4/4;0/1 1 0 c.369_370deltc p.arg124alafs*5 LDLR exon c.369_393del p.arg124glyfs*74 LDLR exon 4 1/1;0/0 2/2;0/2 1 1 c.427t>c p.cys143arg LDLR exon 4 Nauck et al Hum Mutat 18(2):165-6; Rukavina et al Clin Chem Lab Med 39(6): c.502g>c p.asp168his LDLR exon 4 <2% LDLR activity in homozygote (Leitersdorf et al Hum Genet 91(2):141-7) 2/2;0/5 Leitersdorf et al Hum Genet Hum Genet. 91(2):141-7; Fouchier et al Hum Mutat. 26(6): c.530c>t p.ser177leu LDLR exon 4 <2% LDLR activity in homozygote (Hobbs et al J Clin Invest 84(2): ) 31/33;0/8 (9 families) Hobbs et al J Clin Invest. 84(2):656-64; Schuster et al Clin Investig. 71(2):172-5; Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6):445-66; Cenarro et al Clin Genet. 49(4):180-5; Gorski et al Hum Genet. 102(5):562-5; Chmara et al J Appl Genet. 51(1):95-106
2 2 0 c.551g>a p.cys184tyr LDLR exon 4 8/10;0/0 Lee et al J Med Genet 35(7):573-8; Graham et al Atherosclerosis 147(2):309-16; Wang et al Hum Mutat 18(4):359; Fouchier et al Hum Genet 109(6): c.590g>t p.cys197phe LDLR exon 4 <2% LDLR activity in heterozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6):445-66) 3/3;0/2 Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6): c.618_638del p.gly207_ser213del LDLR exon 4 14/15;0/7 (5 families) 0 1 c.[631c>g;1816g>t] p.[his211asp;ala606ser] LDLR exon 4 & exon 12 Both amino acids 4/4;1/0 1 1 c.661g>t p.asp221tyr LDLR exon 4 5/5;0/2 Koivisto et al Am J Hum Genet 57(4):789-97; Giesel et al Hum Genet 96(3):301-4; Kotze et al Clin Genet 51(6):394-8; Cenarro et al Hum Mutat 11(5): c.662a>g p.asp221gly LDLR exon % LDLR activity in heterozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6):445-66) Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6):445-66; Ekstrom et al Eur J Clin Invest. 28(9):740-7; Kotze et al S Afr Med J. 76(8): ; Fouchier et al Hum Genet. 109(6):602-15; Chmara et al J Appl Genet. 51(1): c.670g>a p.asp224asn LDLR exon 4 <2% LDLR activity in homozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6): ) 41/44;0/12 (14 families) Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6):445-66; Wang et al J Lipid Res. 46(2): c.682g>a p.glu228lys LDLR exon 4 <2% LDLR activity in homozygote (Leitersdorf et al J Clin Invest.85(4): ) Leitersdorf et al J Clin Invest. 85(4): ; Hobbs et al Annu Rev Genet. 24:133-70; Pimstone et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 17(5):826-33; Pimstone et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 18(2):309-15; Bertolini et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20(9):E41-52; Huijgen et al Hum Mutat. 31(6): c.818-2a>g LDLR intron 5 Retention of 10 nt of intron 5 generating a premature stop codon at aa 303 (Medeiros et al Atherosclerosis 212(2):553-8) 9/9;0/5 1 0 c.862g>a p.glu288lys LDLR exon 6 Varret et al Nucleic Acids Res 1;26(1):248-52; Fouchier et al Hum Genet 109(6):602-15; Bunn et al Hum Mutat 19(3): c.1016_1017insg p.cys340valfs*18 LDLR exon 7 4/4;0/0 1 0 c.1027g>a p.gly343ser LDLR exon % LDLR activity in heterozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6):445-66) 2/2;0/5 Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6):445-66; Reshef et al.1996 Hum Genet. 98(5):581-6; Thiart et al Mol Cell Probes. 14(5): ; Fouchier et al Hum Genet. 109(6):602-15; Mozas et al Hum Mutat. 24(2): c.1033c>t p.gln345* LDLR exon 7 3/3;0/2 0 3 c g>a LDLR exon 7 Skipping of exon 7 generating a premature stop codon at aa 779 (Medeiros et al Atherosclerosis 212(2):553-8) 7/9;0/2 1 0 c.1061-?_1845+?del LDLR exon 8 Note: 2.1 kb deletion of exons 8 12 reported in Bourbon et al Atherosclerosis 196(2): /6;0/1 1 0 c.1085dela p.asp362alafs*8 LDLR exon c.1216c>t p.arg406trp LDLR exon 9 2/2;0/1 27/29;5/7 (13 families) Reshef et al Hum Genet 98(5):581-6; Chiou et al Am J Cardiol 105(12): c.1222g>a p.glu408lys LDLR exon 9 <2% LDLR activity in homozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6):445-66)); 5-10% LDLR activity in homozygote (very low or virtually undetectable LDLreceptor activity) (Webb et al J Lipid Res 37(2):368-81; Amsellem et al Hum Genet 111(6):501-10) 8 9 c.1291g>a p.ala431thr LDLR exon 9 20% LDLR activity in COS-7 cells (Chang et al J Lipid Res 44(10):1850-8) 103/112;0/23 (33 families) Hobbs et al Annu Rev Genet. 24:133-70; Hattori et al Hum Mutat. 14(1):87; Fouchier et al Hum Genet. 109(6):602-15; Chang et al J Lipid Res. 44(10):1850-8; Dedoussis et al Eur J Clin Invest. 34(6):402-9; Chmara et al J Appl Genet. 51(1):95-106; Chiou KR, Charng MJ Am J Cardiol. 105(12):1752-8
3 2 0 c.1322t>c p.ile441thr LDLR exon 9 9/10;0/2 (4 families) Fouchier et al Hum Genet 109(6):602-15; Chiu et al Metabolism 54(8):1082-6; Chiou et al Am J Cardiol 105(12): c c>g LDLR intron 9 Retention of intron 9 (Bourbon et al J Med Genet 46(5):352-7) 4/5;2/2 1 1 c.1432g>a p.gly478arg LDLR exon % LDLR activity in heterozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6): ) 6/6;0/4 Hobbs et al Hum Mutat. 1(6):445-66; Koivisto et el Am J Hum Genet. 57(4): ; Mak et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 18(10):1600-5; Fouchier et al Hum Genet. 109(6):602-15; Ward et al Hum Mutat. 6(3): c.1455c>g p.his485gln LDLR exon 10 1/1;2/3 1 1 c.1468t>c p.trp490arg LDLR exon 10 5% LDLR activity in COS-7 cells (Silva S. et al Atherosclerosis. 225(1):128-34) 4/4;0/2 1 0 c.1587-?_1845+?del LDLR exon 11 4kb deletion of exons 11 to 12 reported as FH Genoa-1 produces a sequence of 48 novel amino acids preceding a stop codon (Bertolini et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 15(1):81-8) 1/1;0/1 1 0 c.1599g>a p.trp533* LDLR exon c.1618_1620delgcc p.ala540del LDLR exon c.1633g>t p.gly545trp LDLR exon c.1756delt p.ser586glnfs*79 LDLR exon 12 2/3;0/0 23/24;1/9 (7 families) 3 1 c.1775g>a p.gly592glu LDLR exon % LDLR activity when compound heterozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6): ) 17/18;0/3 (7 families) Hobbs et al Hum Mut 1(6): ; Gorski et al Hum Genet. 102(5):562-5; Zakharova et al Bioorg Khim. 27(5):393-6; Bochmann et al Hum Mutat. 17(1):76-7; Mozas et al Hum Mutat. 24(2):187; Chmara et al J Appl Genet. 51(1):95-106; Huijgen et al Hum Mutat 31(6): c.1802a>t p.asp601val LDLR exon c.1816g>t p.ala606ser LDLR exon 12 4/5;0/4 1 0 c.1830_1839delcttggccgt p.ala612argfs*50 LDLR exon 12 7/7;0/2 (5 families) 1/1;0/0 Sun et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17(11): ; Dedoussis et al Hum Mutat 23(3): c g>a LDLR intron 12 <2% LDLR activity in homozygote (Hobbs et al Hum Mutat 1(6):445-66); Mutant allele reduced to ~1/3 of the normal allele in heterozygous (Jensen et al Clin Genet 49: 175-9); RT-PCR of exon 10 to 15 revealed 3 transcripts: exon 12 joined to partially deleted exon 13; exon 11 joined to the partially deleted exon 13; exon 12 joined to exon 15 with complete skipping of exons 13 and 14 (Bertolini et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19(2):408-18) 1/1;0/0 0 1 c.1846-?_2311+?dup LDLR exon 13 25% of reduction in LDLR binding/internalization ( Lelli et al Hum Genet. 86(4):359-62) 4/4;0/0 Lelli et al Hum Genet. 86(4): (7kb duplication of exons 13 to 15 reported as FH Bologna-2) 2 0 c.1876g>a p.glu626lys LDLR exon 13 8/8;0/3 Fouchier et al Hum Mutat 26(6): c.1936delc p.leu646tyrfs*19 LDLR exon 13 2/2;0/1 0 1 c.1966c>a p.his656asn LDLR exon 13 2/3;3/6 Mozas et al Hum Mutat 24(2):187; 180(1): c.2054c>t p.pro685leu LDLR exon % LDLR activity in homozygote (Soutar et al Proc Natl Acad Sci 86(11): ) 9/11;0/4 Soutar et al Proc Natl Acad Sci 86(11): ; King-Underwood et al Clin Genet. 40(1):17-28; Maruyama et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 15(10):1713-8; Defesche et al Clin Genet. 42(6):273-80; Mak et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 18(10):1600-5
4 0 1 c.2056c>t p.gln686* LDLR exon 14 4/5;0/1 Thiart et al Mol Cell Probes 11(6):457-8; Gorski et al Hum Genet 102(5):562-5; Chmara et al J Appl Genet 51(1): c.2077_2078delaa p.lys693valfs*23 LDLR exon 14 4/4;0/2 Fouchier et al Hum Mutat 26(6): c.2093g>t p.cys698phe LDLR exon 14 ~50% of reduction in LDL binding/internalization in heterozygote (Alves et al in prep ) 4/5;0/0 Humphries et al J Mol Med (Berl) 84(3): c g>a LDLR intron 14 50% LDLR activity in heterozygote (Takada et al J Hum Genet 47(12):656-64) Takada et al J Hum Genet 47(12):656-64; Mozas et al Hum Mutat. 24(2): c.2389g>a p.val797met LDLR exon 16 Donor site splicing error (Mak et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18(10): ) Weakly conserved 5/5;1/2 Mak et al Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 18(10):1600-5; Fouchier et al Hum Genet. 109(6):602-15; Amsellem et al Hum Genet. 111(6):501-10; Robles-Osorio et al Arch Med Res. 37(1):102-8; Chmara et al J Appl Genet. 51(1): c.2312-?_*220+?del LDLR exon 16 Internalization- phenotype (Lehrman et al Science 227(4683):140-6) Rodningen et al Clin Genet 42(6): (9.6kb deletion of exon 16 to 18 reported as FH Helsinki); Lehrman et al J Biol Chem 262(7): (7.8kb deletion of exons 16 to 18 reported as FH Osaka-1); Lehrman et al Science 227(4683):140-6 (5.5kb deletion of exons 16 to 18 reported as FH Rochester) 0 2 c.2389g>t p.val797leu LDLR exon 16 Skiping of exon 16 (Bourbon et al J Med Genet 46(5):352-7) Weakly conserved Lombardi et al Clin Genet. 57(2): c.2397_2412del p.val800glyfs*124 LDLR exon c g>a LDLR intron 17 Skipping of exon 17 generating a premature stop codon at aa 805 (Medeiros et al Atherosclerosis 212(2):553-8) 6/6;0/2 Amino acid conservation was analysed considering 11 species; 95 Portuguese normolipidemic individuals; Segregation analysis is presented as mutation carriers/affected individuals; mutation carriers/non-affected individuals (C/A;C/NA), considering all patients recruited to the PFHS Carriers of mutations shaded in grey were not included in ROC curves and in clinical criteria analysis due to non existence of pre-treatment values
5 Supplementary Table II. Comparison of lipid profile in children identified with FH as index patients versus relatives identified in cascade screening FH children Index patients (n=89) Cascade screening (n=82) Age (years) 10.2± ±4.0 Mae gender 53.9% 50.0% Basic lipid profile (mg/dl) a n=89 n=68 TC 311.1±58.8* 273.0±59.0* LDL-C 233.3±59.7* 204.3±52.0* HDL-C 54.0± ±12.0 TG 92.0± ±44.7 non-hdl-c/hdl-c ratio 5.2± ±1.6 Advanced lipid profile (mg/dl) b n=50 n=50 Lp(a) 50.3± ±49.0 apo A ±25.1* 120.7±20.7* apo B 118.6± ±40.3 apo B/apo A1 ratio 0.9± ±0.6 Specific lipid profile (mg/dl) c n=25 n=13 apo A2 27.8±5.5* 23.5±5.5* apo C2 3.2± ±1.8 apo C3 7.6± ±2.0 apo E 3.4± ±0.8 sdldl 40.1±15.7* 28.1±14.4* Data are expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD) unless otherwise noted. FH: familial hypercholesterolemia; TC: total cholesterol; non-hdl-c: non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Lp(a): lipoprotein(a); sdldl: small, dense LDL cholesterol; a: highest values reported without treatment; b: advanced lipid profile performed at INSA recorded only for children without treatment; c: specific lipid profile performed at INSA (only available after 2010) recorded only for children without treatment. *P<0.05 index patients vs. relatives.
6 Supplementary Table III. Lipid profile of children identified with FH according to the type of mutation Null mutation (n=47) LDLR gene Defective mutation (n=105) Splicing mutation (n=14) APOB gene (n=5) Age (years) 10.23± ± ± ±2.78 Male gender 51.0% 54.2% 50.0% 60.0% Basic lipid profile (mg/dl) a n=46 n=92 n=12 n=5 TC 313.7±60.3* 282.6±60.5* 314.2± ±37.4 LDL-C 240.3±63.7* 205.7±52.9* 238.3± ±38.2 HDL-C 53.3± ± ± ±9.6 TG 102.1± ± ± ±23.4 non-hdl-c/hdl-c ratio 5.1± ± ± ±0.4 Advanced lipid profile (mg/dl) b n=30 n=58 n=9 n=3 Lp(a) 51.1± ± ± ±72.4 apo A ± ± ± ±15.8 apo B 125.6± ± ± ±4.9 apo B/apo A1 ratio 0.99± ± ± ±0.1 Specific lipid profile (mg/dl) c n=10 n=25 n=1 n=2 apo A2 27.0± ±6.5 n.d. 24.7±1.0 apo C2 3.6± ±1.5 n.d. 3.8±0.7 apo C3 7.7± ±1.8 n.d. 6.4±0.5 apo E 3.6± ±0.9 n.d. 2.6±0.3 sdldl 42.3± ±17.1 n.d. 32.8±20.5 Data are expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD) unless otherwise noted. n.d. not determined. FH: familial hypercholesterolemia; TC: total cholesterol; non-hdl-c: non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Lp(a): lipoprotein(a); sdldl: small, dense LDL cholesterol; a: highest values reported without treatment; b: advanced lipid profile performed at INSA recorded only for children without treatment; c: specific lipid profile performed at INSA (only available after 2010) recorded only for children without treatment. *P<0.05 mutation vs. mutation.
7 Supplementary Table IV. Simon Broome criteria and different criteria established for clinical diagnosis of FH. Results obtained for sensitivity, specificity, number of true and false positives, true and false negatives are also presented. Sensitivity Specificity True positives True negatives False positives False negatives A. Index cases*: 50 FH vs. 105 non-fh (n=155) Criteria # 1 (Simon Broome Criteria) 76.0% 68.6% Criteria #2 70.0% 76.2% Criteria #3 88.0% 55.2% Criteria #4 82.9% 66.0% Criteria #5 86.0% 68.6% B. Relatives*: 50 FH vs. 56 non-fh (n=106) Criteria # 1 (Simon Broome Criteria) 36.0% 100.0% Criteria #2 82.0% 75.0% Criteria #3 86.0% 75.0% Criteria #4 28.0% 100.0% Criteria #5 84.0% 75.0% C. Index cases + Relatives*: 100 FH vs. 161 non-fh (n=261) Criteria # 1 (Simon Broome Criteria) 56.0% 79.5% Criteria #2 76.0% 75.8% Criteria #3 87.0% 62.1% Criteria #4 47.0% 88.8% Criteria #5 85.0% 70.8% *Criteria were determined using pretreatment values (n=155). Bold indicates the best criteria representing optimal balance between sensitivity and specificity. Criteria #1 (Simon Broome Criteria): (TC 260 mg/dl OR LDL-C 155 mg/dl) AND (family history of pcvd OR family history of hypercholesterolemia); Criteria #2: apob/apoa1 ratio 0.68; Criteria #3: [(TC 260 mg/dl OR LDL-C 155 mg/dl) AND (family history of pcvd OR family history of hypercholesterolemia)] OR apob/apoa1 ratio 0.68; Criteria #4: (TC 260 mg/dl OR LDL-C 190 mg/dl) AND (family history of pcvd OR family history of hypercholesterolemia); Criteria #5: [(TC 260 mg/dl OR LDL-C 190 mg/dl) AND (family history of pcvd OR family history of hypercholesterolemia)] OR apob/apoa1 ratio (pcvd: premature cardiovascular disease; TC: total cholesterol).
Names for ABO (ISBT 001) Blood Group Alleles
 Names for ABO (ISBT 001) blood group alleles v1.1 1102 Names for ABO (ISBT 001) Blood Group Alleles General description: The ABO system was discovered as in 1900 and is considered the first and clinically
Names for ABO (ISBT 001) blood group alleles v1.1 1102 Names for ABO (ISBT 001) Blood Group Alleles General description: The ABO system was discovered as in 1900 and is considered the first and clinically
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Huijgen, R. (2012). Familial hypercholesterolemia:
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Huijgen, R. (2012). Familial hypercholesterolemia:
Names for H (ISBT 018) Blood Group Alleles
 Names for H (ISBT 018) Blood Group Alleles General description: The H blood group system consists of one antigen, H, that is carried on glycolipids and glycoproteins on the RBC membrane, where it is synthesised
Names for H (ISBT 018) Blood Group Alleles General description: The H blood group system consists of one antigen, H, that is carried on glycolipids and glycoproteins on the RBC membrane, where it is synthesised
Genetic and biochemical characteristics of patients with hyperlipidemia who require LDL apheresis
 Genetic and biochemical characteristics of patients with hyperlipidemia who require LDL apheresis Mato Nagel, Ioan Duma, Constantina Vlad, Mandy Benke, Sylvia Nagorka Zentrum für Nephrologie & Stoffwechsel,
Genetic and biochemical characteristics of patients with hyperlipidemia who require LDL apheresis Mato Nagel, Ioan Duma, Constantina Vlad, Mandy Benke, Sylvia Nagorka Zentrum für Nephrologie & Stoffwechsel,
Supplementary Table e1. Clinical and genetic data on the 37 participants from the WUSM
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Table e1. Clinical and genetic data on the 37 participants from the WUSM cohort. Supplementary Table e2. Specificity, sensitivity and unadjusted ORs for glioma in participants
Supplementary Data Supplementary Table e1. Clinical and genetic data on the 37 participants from the WUSM cohort. Supplementary Table e2. Specificity, sensitivity and unadjusted ORs for glioma in participants
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/content/354/6319/aaf7000/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Genetic identification of familial hypercholesterolemia within a single U.S. health care system Noura S. Abul-Husn, Kandamurugu
www.sciencemag.org/content/354/6319/aaf7000/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Genetic identification of familial hypercholesterolemia within a single U.S. health care system Noura S. Abul-Husn, Kandamurugu
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Intron p Hybrid with p.leu245val p. Gly336Cys. p.leu62phe p. Ala137Val p. Asn152Thr hybrid with p.leu245val p.
 RHD negative, i.e. null Phenotype Allele name Nucleotide change Exon Predicted amino acid change D RHD*01N.01 RHD deletion 1-10 p.0 Allele name detail Comments D RHD*08N.01 RHD*Pseudogene RHD* Ψ 37- bp
RHD negative, i.e. null Phenotype Allele name Nucleotide change Exon Predicted amino acid change D RHD*01N.01 RHD deletion 1-10 p.0 Allele name detail Comments D RHD*08N.01 RHD*Pseudogene RHD* Ψ 37- bp
Assessing the phenotypic effects in the general population of rare variants in genes for a dominant Mendelian form of diabetes
 Assessing the phenotypic effects in the general population of rare variants in genes for a dominant Mendelian form of diabetes Supplementary Information Jason Flannick*, Nicola L Beer*, Alexander G Bick,
Assessing the phenotypic effects in the general population of rare variants in genes for a dominant Mendelian form of diabetes Supplementary Information Jason Flannick*, Nicola L Beer*, Alexander G Bick,
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a metabolic disorder
 Pvu II Polymorphism of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene and Familial Hypercholesterolemia Study of Italians Antonio Daga, Marina Fabbi, Tiziana Mattioni, Stefano Bertolini, and Giorgio Corte Familial
Pvu II Polymorphism of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene and Familial Hypercholesterolemia Study of Italians Antonio Daga, Marina Fabbi, Tiziana Mattioni, Stefano Bertolini, and Giorgio Corte Familial
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL
 Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Genotype to phenotype correlations in cartilage oligomeric matrix protein associated chondrodysplasias
 (2014) 22, 1278 1282 & 2014 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1018-4813/14 www.nature.com/ejhg ARTICLE Genotype to phenotype correlations in cartilage oligomeric matrix protein associated
(2014) 22, 1278 1282 & 2014 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1018-4813/14 www.nature.com/ejhg ARTICLE Genotype to phenotype correlations in cartilage oligomeric matrix protein associated
LMM / emerge III Network Reference Sequences October 2016 LMM / emerge III Network Consensus Actionable Gene List *ACMG56 gene
 LMM / emerge III Network Consensus Actionable Gene List *ACMG56 gene ACTA2* Exon 02-09 NM_001613.2 DSG2* Exon 01-15 NM_001943.3 ACTC1* Exon 01-06 NM_005159.4 DSP* Exon 01-24 NM_004415.2 APC* Exon 01-15
LMM / emerge III Network Consensus Actionable Gene List *ACMG56 gene ACTA2* Exon 02-09 NM_001613.2 DSG2* Exon 01-15 NM_001943.3 ACTC1* Exon 01-06 NM_005159.4 DSP* Exon 01-24 NM_004415.2 APC* Exon 01-15
Geographical Clustering of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene Mutations (C292X; Q363X; D365E & C660X) in Cyprus
 HUMAN MUTATION Mutation in Brief #302 (2000) Online MUTATION IN BRIEF Geographical Clustering of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene Mutations (C292X; Q363X; D365E & C660X) in Cyprus Stavroulla L. Xenophontos
HUMAN MUTATION Mutation in Brief #302 (2000) Online MUTATION IN BRIEF Geographical Clustering of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene Mutations (C292X; Q363X; D365E & C660X) in Cyprus Stavroulla L. Xenophontos
Supplemental material Mutant DNMT3A: A Marker of Poor Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Ana Flávia Tibúrcio Ribeiro, Marta Pratcorona, Claudia
 Supplemental material Mutant DNMT3A: A Marker of Poor Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Ana Flávia Tibúrcio Ribeiro, Marta Pratcorona, Claudia Erpelinck-Verschueren, Veronika Rockova, Mathijs Sanders,
Supplemental material Mutant DNMT3A: A Marker of Poor Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Ana Flávia Tibúrcio Ribeiro, Marta Pratcorona, Claudia Erpelinck-Verschueren, Veronika Rockova, Mathijs Sanders,
Hypercholesterolemia and FH Public Policy, Success Stories
 Hypercholesterolemia and FH Public Policy, Success Stories Pedro Mata MD, PhD Spanish FH Foundation Iberoamerican FH Network www.colesterolfamiliar.org Spanish FH Foundation www.colesterolfamiliar.org
Hypercholesterolemia and FH Public Policy, Success Stories Pedro Mata MD, PhD Spanish FH Foundation Iberoamerican FH Network www.colesterolfamiliar.org Spanish FH Foundation www.colesterolfamiliar.org
Genetic Testing and Analysis. (858) MRN: Specimen: Saliva Received: 07/26/2016 GENETIC ANALYSIS REPORT
 GBinsight Sample Name: GB4411 Race: Gender: Female Reason for Testing: Type 2 diabetes, early onset MRN: 0123456789 Specimen: Saliva Received: 07/26/2016 Test ID: 113-1487118782-4 Test: Type 2 Diabetes
GBinsight Sample Name: GB4411 Race: Gender: Female Reason for Testing: Type 2 diabetes, early onset MRN: 0123456789 Specimen: Saliva Received: 07/26/2016 Test ID: 113-1487118782-4 Test: Type 2 Diabetes
Supplementary materials and methods
 Supplementary materials and methods Targeted resequencing RNA probes complementary in sequence to the coding exons (+ 2bp) of target genes were designed using e-array (https://earray.chem.agilent.com/earray/)
Supplementary materials and methods Targeted resequencing RNA probes complementary in sequence to the coding exons (+ 2bp) of target genes were designed using e-array (https://earray.chem.agilent.com/earray/)
Hypercholesterolemia: So much cholesterol, so many causes
 Hypercholesterolemia: So much cholesterol, so many causes Student group names kept anonymous Department of Biology, Lake Forest College, Lake Forest, IL 60045, USA Hypercholesterolemia is a disease characterized
Hypercholesterolemia: So much cholesterol, so many causes Student group names kept anonymous Department of Biology, Lake Forest College, Lake Forest, IL 60045, USA Hypercholesterolemia is a disease characterized
Department of Internal Medicine and Molecular Science, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan. 4
 146 Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis Original Articles Vol. 11, No. 3 Clinical Features of Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Japan in a Database from 1996 1998 by the Research Committee of the
146 Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis Original Articles Vol. 11, No. 3 Clinical Features of Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Japan in a Database from 1996 1998 by the Research Committee of the
analysis in hereditary breast/ovarian cancer families of Portuguese ancestry
 Clin Genet 2015: 88: 41 48 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12441 The role of targeted
Clin Genet 2015: 88: 41 48 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12441 The role of targeted
Targeted sequencing of refractory myeloma reveals a high incidence of mutations in CRBN and Ras pathway genes
 Targeted sequencing of refractory myeloma reveals a high incidence of mutations in CRBN and Ras pathway genes KM Kortüm 1,8 *, EK Mai 3,4 *, NH Hanafiah 3 *, CX Shi 1, YX Zhu 1, L Bruins 1, S Barrio 1,
Targeted sequencing of refractory myeloma reveals a high incidence of mutations in CRBN and Ras pathway genes KM Kortüm 1,8 *, EK Mai 3,4 *, NH Hanafiah 3 *, CX Shi 1, YX Zhu 1, L Bruins 1, S Barrio 1,
Genetic Dyslipidemia and Cardiovascular Diseases
 Sultan Qaboos University Genetic Dyslipidemia and Cardiovascular Diseases Fahad AL Zadjali, PhD Fahadz@squ.edu.om We care 1 2/14/18 DISCLOSURE OF CONFLICT No financial relationships with commercial interests
Sultan Qaboos University Genetic Dyslipidemia and Cardiovascular Diseases Fahad AL Zadjali, PhD Fahadz@squ.edu.om We care 1 2/14/18 DISCLOSURE OF CONFLICT No financial relationships with commercial interests
N. Setia, 1 I. C. Verma, 1 B. Khan, 2 and A. Arora Introduction
 Cardiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 658526, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/658526 Review Article Premature Coronary Artery Disease and Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Need for Early Diagnosis
Cardiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 658526, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/658526 Review Article Premature Coronary Artery Disease and Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Need for Early Diagnosis
Heterozygous FH is caused by mutations in the LDLR gene
 Phenotypic Variation in Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia A Comparison of Chinese Patients With the Same or Similar Mutations in the LDL Receptor Gene in China or Canada Simon N. Pimstone, Xi-Ming
Phenotypic Variation in Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia A Comparison of Chinese Patients With the Same or Similar Mutations in the LDL Receptor Gene in China or Canada Simon N. Pimstone, Xi-Ming
Dominantly inherited type IIa dyslipoproteinemia is genetically
 R3531C Mutation in the Apolipoprotein B Gene Is Not Sufficient to Cause Hypercholesterolemia Jean-Pierre Rabès, Mathilde Varret, Martine Devillers, Philippe Aegerter, Ludovic Villéger, Michel Krempf, Claudine
R3531C Mutation in the Apolipoprotein B Gene Is Not Sufficient to Cause Hypercholesterolemia Jean-Pierre Rabès, Mathilde Varret, Martine Devillers, Philippe Aegerter, Ludovic Villéger, Michel Krempf, Claudine
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a prevalent and
 Discriminative Ability of LDL-Cholesterol to Identify Patients With Familial Hypercholesterolemia A Cross-Sectional Study in 26 406 Individuals Tested for Genetic FH Roeland Huijgen, MD; Barbara A. Hutten,
Discriminative Ability of LDL-Cholesterol to Identify Patients With Familial Hypercholesterolemia A Cross-Sectional Study in 26 406 Individuals Tested for Genetic FH Roeland Huijgen, MD; Barbara A. Hutten,
CHAPTER IV RESULTS Microcephaly General description
 47 CHAPTER IV RESULTS 4.1. Microcephaly 4.1.1. General description This study found that from a previous study of 527 individuals with MR, 48 (23 female and 25 male) unrelated individuals were identified
47 CHAPTER IV RESULTS 4.1. Microcephaly 4.1.1. General description This study found that from a previous study of 527 individuals with MR, 48 (23 female and 25 male) unrelated individuals were identified
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF FH CHILDREN. O. GUARDAMAGNA Dipartimento di Scienze della Sanità Pubblica e Pediatriche UNIVERSITA DI TORINO
 DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF FH CHILDREN O. GUARDAMAGNA Dipartimento di Scienze della Sanità Pubblica e Pediatriche UNIVERSITA DI TORINO DISCLOSURES Kowa MSD Pfizer Astrazeneca Synageva/Alexion OUTLINE Background
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF FH CHILDREN O. GUARDAMAGNA Dipartimento di Scienze della Sanità Pubblica e Pediatriche UNIVERSITA DI TORINO DISCLOSURES Kowa MSD Pfizer Astrazeneca Synageva/Alexion OUTLINE Background
LIPOPROTEINE ATEROGENE E ANTI-ATEROGENE ATEROGENE
 LIPOPROTEINE ATEROGENE E ANTI-ATEROGENE ATEROGENE Sebastiano Calandra Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche Università di Modena e Reggio Emilia Incidence Rate/1000 200-150 - 100-50 - Women 0 Men
LIPOPROTEINE ATEROGENE E ANTI-ATEROGENE ATEROGENE Sebastiano Calandra Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche Università di Modena e Reggio Emilia Incidence Rate/1000 200-150 - 100-50 - Women 0 Men
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Ku CA, Hull S, Arno G, et al. Detailed clinical phenotype and molecular genetic findings in CLN3-associated isolated retinal degeneration. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online
Supplementary Online Content Ku CA, Hull S, Arno G, et al. Detailed clinical phenotype and molecular genetic findings in CLN3-associated isolated retinal degeneration. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online
chr6: _ del HFE NM_ ,744 bp deletion Deletion of entire HFE gene 2
 Table S1. Details of pathogenic and possibly pathogenic variants identified in the HH genes HFE, HFE2, HAMP, TFR2 and SLC40A1 from published reports. Variants have been classified as either 1, possibly
Table S1. Details of pathogenic and possibly pathogenic variants identified in the HH genes HFE, HFE2, HAMP, TFR2 and SLC40A1 from published reports. Variants have been classified as either 1, possibly
Appendix F Simon Broome Diagnostic criteria for index individuals and relatives
 Appendix F Simon Broome Diagnostic criteria for index individuals and relatives 1 SIMON BROOME DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR INDEX INDIVIDUALS (PROBANDS) 2 2 GENDER- AND AGE-SPECIFIC LDL-C CRITERIA FOR THE DIAGNOSIS
Appendix F Simon Broome Diagnostic criteria for index individuals and relatives 1 SIMON BROOME DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR INDEX INDIVIDUALS (PROBANDS) 2 2 GENDER- AND AGE-SPECIFIC LDL-C CRITERIA FOR THE DIAGNOSIS
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B HEC1A PTEN +/+ HEC1A PTEN -/- 16 HEC1A PTEN -/- 22 PTEN RAD51 % Cells with RAD51 foci 40 -IR +IR 30 20 10 * *! TUBULIN 0 HEC1A PTEN+/+ HEC1A PTEN-/- 16 HEC1A PTEN-/- 22 C D 1.0
Supplementary Figure 1 A B HEC1A PTEN +/+ HEC1A PTEN -/- 16 HEC1A PTEN -/- 22 PTEN RAD51 % Cells with RAD51 foci 40 -IR +IR 30 20 10 * *! TUBULIN 0 HEC1A PTEN+/+ HEC1A PTEN-/- 16 HEC1A PTEN-/- 22 C D 1.0
Familial hypercholesterolaemia
 Familial hypercholesterolaemia Jaimini Cegla MRCP FRCPath PhD Consultant in Chemical Pathology and Metabolic Medicine Hammersmith Hospital Lipid Clinic 20 April 2017 An unrecognised, potentially fatal,
Familial hypercholesterolaemia Jaimini Cegla MRCP FRCPath PhD Consultant in Chemical Pathology and Metabolic Medicine Hammersmith Hospital Lipid Clinic 20 April 2017 An unrecognised, potentially fatal,
Re-classification of variants: Implications from the cardiac perspective
 Re-classification of variants: Implications from the cardiac perspective Karen McGuire Oxford Medical Genetics Laboratories, Churchill Hospital, Old Road, Oxford, OX3 7LE. Re-classification New evidence
Re-classification of variants: Implications from the cardiac perspective Karen McGuire Oxford Medical Genetics Laboratories, Churchill Hospital, Old Road, Oxford, OX3 7LE. Re-classification New evidence
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation
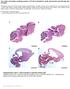 The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Huijgen, R. (2012). Familial hypercholesterolemia:
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Huijgen, R. (2012). Familial hypercholesterolemia:
Sample Test Report. Mayo Clinic GeneGuide. Report. Consumer Name DOB: 00/00/0000
 Mayo Clinic GeneGuide Report Consumer Name DOB: // Table Of Contents Mayo Clinic GeneGuide Genetic Test Results Demographics and Ordering Information 3 How to Use This Report 4 Carrier Screening - No variants
Mayo Clinic GeneGuide Report Consumer Name DOB: // Table Of Contents Mayo Clinic GeneGuide Genetic Test Results Demographics and Ordering Information 3 How to Use This Report 4 Carrier Screening - No variants
Cascade Screening for FH: the U.S. experience
 Cascade Screening for FH: the U.S. experience Paul N. Hopkins, MD, MSPH Professor of Internal Medicine Cardiovascular Genetics University of Utah Disclosures Consultant Genzyme, Amgen, Regeneron Research
Cascade Screening for FH: the U.S. experience Paul N. Hopkins, MD, MSPH Professor of Internal Medicine Cardiovascular Genetics University of Utah Disclosures Consultant Genzyme, Amgen, Regeneron Research
LIPID CLUB Rome, 2014
 LIPID CLUB Rome, 2014 June the 6h 6th Hyperlipidaemia in FH Children Ornella Guardamagna University of Torino DICLOSURES Medpace Kowa DSMB member MSD, Pfizer, Synageva Investigator in industry funded trials
LIPID CLUB Rome, 2014 June the 6h 6th Hyperlipidaemia in FH Children Ornella Guardamagna University of Torino DICLOSURES Medpace Kowa DSMB member MSD, Pfizer, Synageva Investigator in industry funded trials
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies
 Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society
A total of 2,822 Mexican dyslipidemic cases and controls were recruited at INCMNSZ in
 Supplemental Material The N342S MYLIP polymorphism is associated with high total cholesterol and increased LDL-receptor degradation in humans by Daphna Weissglas-Volkov et al. Supplementary Methods Mexican
Supplemental Material The N342S MYLIP polymorphism is associated with high total cholesterol and increased LDL-receptor degradation in humans by Daphna Weissglas-Volkov et al. Supplementary Methods Mexican
Focus on FH (Familial Hypercholesterolemia) Joshua W. Knowles, MD PhD for PCNA May, 2013
 Focus on FH (Familial Hypercholesterolemia) Joshua W. Knowles, MD PhD for PCNA May, 2013 Conflicts CMO for The FH Foundation Pre-talk quiz What is cascade screening? 1. screening all family members 2.
Focus on FH (Familial Hypercholesterolemia) Joshua W. Knowles, MD PhD for PCNA May, 2013 Conflicts CMO for The FH Foundation Pre-talk quiz What is cascade screening? 1. screening all family members 2.
PCSK9 inhibition in homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia
 PCSK9 inhibition in homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia Slide deck kindly supplied as an educational resource by Dr Evan A Stein MD PhD Director Emeritus Metabolic & Atherosclerosis Research Center
PCSK9 inhibition in homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia Slide deck kindly supplied as an educational resource by Dr Evan A Stein MD PhD Director Emeritus Metabolic & Atherosclerosis Research Center
Identification and management of familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) - An overview
 Identification and management of familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) - An overview National Collaborating Centre for Primary Care and Royal College of General Practitioners NICE Guideline CG 71 (August
Identification and management of familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) - An overview National Collaborating Centre for Primary Care and Royal College of General Practitioners NICE Guideline CG 71 (August
ABSENCE OF APO B R3500Q MUTATION AMONG KELANTANESE MALAYS WITH HYPERLIPIDAEMIA
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2000 (16-21) ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSENCE OF APO B R3500Q MUTATION AMONG KELANTANESE MALAYS WITH HYPERLIPIDAEMIA Win Mar Kyi, Mohd. Nizam Isa*,
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2000 (16-21) ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSENCE OF APO B R3500Q MUTATION AMONG KELANTANESE MALAYS WITH HYPERLIPIDAEMIA Win Mar Kyi, Mohd. Nizam Isa*,
Colclough et al., Human Mutation 1
 Region Colclough et al., Human Mutation 1 Supp. Table S1. List of HNF1A mutations Nucleotide Change NM_000545.5 Promoter and 5 UTR Mutations Protein Effect NM_000545.5 Three letter amino acid description
Region Colclough et al., Human Mutation 1 Supp. Table S1. List of HNF1A mutations Nucleotide Change NM_000545.5 Promoter and 5 UTR Mutations Protein Effect NM_000545.5 Three letter amino acid description
Familial Hypercholesterolemia What a cardiologist should know
 Institut für Klinische Chemie Arnold von Eckardstein Familial Hypercholesterolemia What a cardiologist should know Etiology of Hypercholesterolemia monogenic: (rare): e.g. familial hypercholesterolemia
Institut für Klinische Chemie Arnold von Eckardstein Familial Hypercholesterolemia What a cardiologist should know Etiology of Hypercholesterolemia monogenic: (rare): e.g. familial hypercholesterolemia
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM The LDL Receptor, LDL Uptake, and the Free Cholesterol Pool
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM The, LDL Uptake, and the Free Cholesterol Pool I. Michael Brown and Joseph Goldstein A. Studied families with familial hypercholesterolemia. B. Defined the relationship
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM The, LDL Uptake, and the Free Cholesterol Pool I. Michael Brown and Joseph Goldstein A. Studied families with familial hypercholesterolemia. B. Defined the relationship
From Biology to Therapy The biology of PCSK9 in humans Just LDL-cholesterol or more? May 24th. Dr. Gilles Lambert
 Dr. Gilles Lambert Associate Professor in Cell Biology University of Nantes Medical School Group Leader, Laboratory of Nutrition and Metabolism, University Hospital of Nantes From Biology to Therapy The
Dr. Gilles Lambert Associate Professor in Cell Biology University of Nantes Medical School Group Leader, Laboratory of Nutrition and Metabolism, University Hospital of Nantes From Biology to Therapy The
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Parkinson disease 8, automsomal dominant OMIM number for disease 607060 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Parkinson disease 8, automsomal dominant OMIM number for disease 607060 Disease
Familial hypercholesterolemia in Morocco: first report of mutations in the LDL receptor gene
 J Hum Genet (2003) 48:199 203 DOI 10.1007/s10038-003-0010-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mariame El Messal Æ Karima Aı t Chihab Rachid Chater Æ Joan Carles Vallve Æ Faı za Bennis Aı cha Hafidi Æ Josep Ribalta Æ Mathilde
J Hum Genet (2003) 48:199 203 DOI 10.1007/s10038-003-0010-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mariame El Messal Æ Karima Aı t Chihab Rachid Chater Æ Joan Carles Vallve Æ Faı za Bennis Aı cha Hafidi Æ Josep Ribalta Æ Mathilde
Long-term exposure to Myozyme results in a decrease of anti-drug antibodies in lateonset Pompe disease patients
 Long-term exposure to Myozyme results in a decrease of anti-drug antibodies in lateonset Pompe disease patients Elisa Masat 1, Pascal Laforêt 1,2, Marie De Antonio 3, Guillaume Corre 4, Barbara Perniconi
Long-term exposure to Myozyme results in a decrease of anti-drug antibodies in lateonset Pompe disease patients Elisa Masat 1, Pascal Laforêt 1,2, Marie De Antonio 3, Guillaume Corre 4, Barbara Perniconi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation Weizhen Ji, Jia Nee Foo, Brian J. O Roak, Hongyu Zhao, Martin G. Larson, David B.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation Weizhen Ji, Jia Nee Foo, Brian J. O Roak, Hongyu Zhao, Martin G. Larson, David B.
Genotype phenotype correlation in a cohort of Portuguese patients comprising the entire spectrum of VWD types: impact of NGS
 Coagulation and Fibrinolysis 17 Genotype phenotype correlation in a cohort of Portuguese patients comprising the entire spectrum of VWD types: impact of NGS Teresa Fidalgo 1 ; Ramon Salvado 1 ; Irene Corrales
Coagulation and Fibrinolysis 17 Genotype phenotype correlation in a cohort of Portuguese patients comprising the entire spectrum of VWD types: impact of NGS Teresa Fidalgo 1 ; Ramon Salvado 1 ; Irene Corrales
De Leeneer et al., Human Mutation 1
 De Leeneer et al., Human Mutation 1 Supp. Table S1A. Overview of the genes included in the workflow Ensembl Gene ID Ensembl Transcript ID Associated Gene Name ENSG00000198691 ENST00000370225 ABCA4 NM_000350.2
De Leeneer et al., Human Mutation 1 Supp. Table S1A. Overview of the genes included in the workflow Ensembl Gene ID Ensembl Transcript ID Associated Gene Name ENSG00000198691 ENST00000370225 ABCA4 NM_000350.2
ALANINE:GLYOXYLATE AMINOTRANSFERASE (AGXT) GENE (PRIMARY HYPEROXALURIA TYPE 1) MUTATION DATA BASE
 ALANINE:GLYOXYLATE AMINOTRANSFERASE (AGXT) GENE (PRIMARY HYPEROXALURIA TYPE 1) REFERENCE SEQUENCES: c.dna: NM_000030 g.dna: NG_008005.1 MUTATION DATA BASE Nomenclature: HGVS guidelines (http://www.hgvs.org/rec.html)
ALANINE:GLYOXYLATE AMINOTRANSFERASE (AGXT) GENE (PRIMARY HYPEROXALURIA TYPE 1) REFERENCE SEQUENCES: c.dna: NM_000030 g.dna: NG_008005.1 MUTATION DATA BASE Nomenclature: HGVS guidelines (http://www.hgvs.org/rec.html)
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
 NSC892314B002270 898 1 907 31 9010 23 1 Molecular Study of Type III Hyperlipoproteinemia in Taiwan β β ε E Abstract β Type III hyperlipoproteinemia (type III HLP; familial dysbetalipoproteinemia ) is a
NSC892314B002270 898 1 907 31 9010 23 1 Molecular Study of Type III Hyperlipoproteinemia in Taiwan β β ε E Abstract β Type III hyperlipoproteinemia (type III HLP; familial dysbetalipoproteinemia ) is a
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10833 Supplementary Table 1: Clinical information for 48 whole exome sequencing samples Sample ID Age Gender tumor location Death OS (months) Recurrence PFS
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10833 Supplementary Table 1: Clinical information for 48 whole exome sequencing samples Sample ID Age Gender tumor location Death OS (months) Recurrence PFS
Running title: Huijgen et al.; Discriminative ability of LDL-C in FH
 Discriminative Ability of LDL-Cholesterol to Identify Patients with Familial Hypercholesterolemia: A Cross-Sectional Study in 26,406 Individuals Tested for Genetic FH Running title: Huijgen et al.; Discriminative
Discriminative Ability of LDL-Cholesterol to Identify Patients with Familial Hypercholesterolemia: A Cross-Sectional Study in 26,406 Individuals Tested for Genetic FH Running title: Huijgen et al.; Discriminative
Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer
 Liao X et al. PIK3CA Mutation in Colorectal Cancer. Page 1 Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer Exon Domain Nucleotide change* Amino acid change* cases 9 Helical c.1621t>a p.e541t
Liao X et al. PIK3CA Mutation in Colorectal Cancer. Page 1 Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer Exon Domain Nucleotide change* Amino acid change* cases 9 Helical c.1621t>a p.e541t
Molecular Diagnostic Testing by eyegene: Analysis of Patients With Hereditary Retinal Dystrophy Phenotypes Involving Central Vision Loss
 Genetics Molecular Diagnostic Testing by eyegene: Analysis of Patients With Hereditary Retinal Dystrophy Phenotypes Involving Central Vision Loss Akhila Alapati, 1 Kerry Goetz, 2 John Suk, 1 Mili Navani,
Genetics Molecular Diagnostic Testing by eyegene: Analysis of Patients With Hereditary Retinal Dystrophy Phenotypes Involving Central Vision Loss Akhila Alapati, 1 Kerry Goetz, 2 John Suk, 1 Mili Navani,
Supplemental Material can be found at:
 Supplemental Material can be found at: methods An improved method on to functionally characterize novel and known LDLR mutations Maria Romano, *, Maria Donata Di Taranto, Peppino Mirabelli, *, Maria Nicoletta
Supplemental Material can be found at: methods An improved method on to functionally characterize novel and known LDLR mutations Maria Romano, *, Maria Donata Di Taranto, Peppino Mirabelli, *, Maria Nicoletta
Novel NPHS1 gene mutations in a Chinese family with congenital nephrotic syndrome
 c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Novel NPHS1 gene mutations in a Chinese family with congenital nephrotic syndrome FENGJIE YANG, YAXIAN CHEN, YU ZHANG, LIRU QIU, YU CHEN and JIANHUA ZHOU Department
c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Novel NPHS1 gene mutations in a Chinese family with congenital nephrotic syndrome FENGJIE YANG, YAXIAN CHEN, YU ZHANG, LIRU QIU, YU CHEN and JIANHUA ZHOU Department
Molecular Genetic Background of an Autosomal Dominant Hypercholesterolemia in the Czech Republic
 Physiol. Res. 66 (Suppl. 1): S47-S54, 2017 REVIEW Molecular Genetic Background of an Autosomal Dominant Hypercholesterolemia in the Czech Republic L. TICHÝ 1, L. FAJKUSOVÁ 2, P. ZAPLETALOVÁ 1, L. SCHWARZOVÁ
Physiol. Res. 66 (Suppl. 1): S47-S54, 2017 REVIEW Molecular Genetic Background of an Autosomal Dominant Hypercholesterolemia in the Czech Republic L. TICHÝ 1, L. FAJKUSOVÁ 2, P. ZAPLETALOVÁ 1, L. SCHWARZOVÁ
Identification and characterization of LDL receptor gene mutations in hyperlipidemic Chinese
 Identification and characterization of LDL receptor gene mutations in hyperlipidemic Chinese Jui-Hung Chang,* Ju-Pin Pan,, Der-Yan Tai,** Ai-Chun Huang,* Pi-Hung Li,* Hui-Ling Ho,* Hui-Ling Hsieh,* Shiu-Ching
Identification and characterization of LDL receptor gene mutations in hyperlipidemic Chinese Jui-Hung Chang,* Ju-Pin Pan,, Der-Yan Tai,** Ai-Chun Huang,* Pi-Hung Li,* Hui-Ling Ho,* Hui-Ling Hsieh,* Shiu-Ching
Dr. Ayman Mohsen Mashi, MBBS Consultant Hematology & Blood Transfusion Department Head, Laboratory & Blood Bank King Fahad Central Hospital, Gazan,
 Dr. Ayman Mohsen Mashi, MBBS Consultant Hematology & Blood Transfusion Department Head, Laboratory & Blood Bank King Fahad Central Hospital, Gazan, KSA amashi@moh.gov.sa 24/02/2018 β-thalassemia syndromes
Dr. Ayman Mohsen Mashi, MBBS Consultant Hematology & Blood Transfusion Department Head, Laboratory & Blood Bank King Fahad Central Hospital, Gazan, KSA amashi@moh.gov.sa 24/02/2018 β-thalassemia syndromes
Hearing Loss Imaging Thyroid function tests TFT (age at test)
 Clinical Information on patients. Unclassified variants are denoted in brackets. EVA is enlarged vestibular aqueducts - Indicates no information. means asian. Patient TFT (age at test) 25215 c.1001+1g>a
Clinical Information on patients. Unclassified variants are denoted in brackets. EVA is enlarged vestibular aqueducts - Indicates no information. means asian. Patient TFT (age at test) 25215 c.1001+1g>a
Inhibition of PCSK9: The Birth of a New Therapy
 Inhibition of PCSK9: The Birth of a New Therapy Prof. John J.P. Kastelein, MD PhD FESC Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medical Center / University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Disclosures Dr. Kastelein
Inhibition of PCSK9: The Birth of a New Therapy Prof. John J.P. Kastelein, MD PhD FESC Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medical Center / University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Disclosures Dr. Kastelein
Use of panel tests in place of single gene tests in the cancer genetics clinic
 Clin Genet 2015: 88: 278 282 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12488 Short Report se of panel tests in place of single gene tests in the cancer genetics clinic
Clin Genet 2015: 88: 278 282 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12488 Short Report se of panel tests in place of single gene tests in the cancer genetics clinic
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
ATP III (Adult Treatment Panel III) CLASSIFICATION C IN ADULTS
 LABORATORY AND RISK FACTORS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS S R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty RISK FACTORS FOR CHD Clinical Risk Factors Laboratory Risk Factors MAJOR CLINICAL RISK
LABORATORY AND RISK FACTORS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS S R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty RISK FACTORS FOR CHD Clinical Risk Factors Laboratory Risk Factors MAJOR CLINICAL RISK
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a common autosomal,
 Clinical Expression of Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Clusters of Mutations of the LDL Receptor Gene That Cause a Receptor-Defective or Receptor-Negative Phenotype S. Bertolini, A. Cantafora, M. Averna,
Clinical Expression of Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Clusters of Mutations of the LDL Receptor Gene That Cause a Receptor-Defective or Receptor-Negative Phenotype S. Bertolini, A. Cantafora, M. Averna,
LE IPERCHILOMICRONEMIE FAMILIARI
 LE IPERCHILOMICRONEMIE FAMILIARI Livia Pisciotta Di.M.I.-Università di Genova HYPERCHYLOMICRONEMIA SYNDROME Ø Hypertriglyceridemia (>10 mmol/l, >877 mg/dl) Ø Fasting chylomicronemia Ø Recurrent abdominal
LE IPERCHILOMICRONEMIE FAMILIARI Livia Pisciotta Di.M.I.-Università di Genova HYPERCHYLOMICRONEMIA SYNDROME Ø Hypertriglyceridemia (>10 mmol/l, >877 mg/dl) Ø Fasting chylomicronemia Ø Recurrent abdominal
UW359 Ovary 3c 3 Serous Recurrent 68 BRCA1 816delGT BRCA1 del exon 1-2. UW417 Ovary 3c 3 Serous Primary 38 BRCA1 1675delA
 Supplementary Table 1. Cases with deleterious germline mutations, somatic HR mutations, and somatic PTEN mutations. ID Site Stage Grade Histology Tumor Age Germline mutation(s) a Somatic HR mutation(s)
Supplementary Table 1. Cases with deleterious germline mutations, somatic HR mutations, and somatic PTEN mutations. ID Site Stage Grade Histology Tumor Age Germline mutation(s) a Somatic HR mutation(s)
Author's personal copy
 Clinica Chimica Acta 412 (2011) 920 924 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinica Chimica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinchim Plasma HDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels
Clinica Chimica Acta 412 (2011) 920 924 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinica Chimica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinchim Plasma HDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels
Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification
 Variant Effect Prediction Training Course 6-8 November 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification Andreas Laner / Anna Benet-Pagès 1 Content 1. Background... 3 2. Aim
Variant Effect Prediction Training Course 6-8 November 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification Andreas Laner / Anna Benet-Pagès 1 Content 1. Background... 3 2. Aim
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Huijgen, R. (2012). Familial hypercholesterolemia:
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia: the Dutch approach Huijgen, R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Huijgen, R. (2012). Familial hypercholesterolemia:
The Molecular Genetic Background of Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Data From the Slovak Nation-Wide Survey
 Physiol. Res. 66: 75-84, 2017 The Molecular Genetic Background of Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Data From the Slovak Nation-Wide Survey D. GABČOVÁ 1, B. VOHNOUT 2,3, D. STANÍKOVÁ 1,4, M. HUČKOVÁ 1, M.
Physiol. Res. 66: 75-84, 2017 The Molecular Genetic Background of Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Data From the Slovak Nation-Wide Survey D. GABČOVÁ 1, B. VOHNOUT 2,3, D. STANÍKOVÁ 1,4, M. HUČKOVÁ 1, M.
Screening for dyslipidemias in children and adolescents
 Screening for dyslipidemias in children and adolescents Nataša Bratina, Urh Grošelj Dept. of Pediatric Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism; University Children s Hospital, UMC Ljubljana Why to screen,
Screening for dyslipidemias in children and adolescents Nataša Bratina, Urh Grošelj Dept. of Pediatric Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism; University Children s Hospital, UMC Ljubljana Why to screen,
Expression of an LDL receptor allele with two diverent mutations (E256K and I402T)
 J Clin Pathol: Mol Pathol 2000;53:31 36 31 Institute of Laboratory Medicine, Department of Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital, S-221 85 Lund, Sweden U Ekström M Abrahamson P Nilsson-Ehle Department
J Clin Pathol: Mol Pathol 2000;53:31 36 31 Institute of Laboratory Medicine, Department of Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital, S-221 85 Lund, Sweden U Ekström M Abrahamson P Nilsson-Ehle Department
Treatment of severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia LDL Apheresis
 Treatment of severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia LDL Apheresis Identifying and Treating Severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia October 14-15, 2017 Dubai, UAE Dr. Khalid Al-Waili, MD, FRCPC, DABCL Senior
Treatment of severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia LDL Apheresis Identifying and Treating Severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia October 14-15, 2017 Dubai, UAE Dr. Khalid Al-Waili, MD, FRCPC, DABCL Senior
Request for Prior Authorization for PCSK9 inhibitor therapy Website Form Submit request via: Fax
 Request for Prior Authorization for PCSK9 inhibitor therapy Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 PCSK9 is a protein that reduces the hepatic removal of low-density
Request for Prior Authorization for PCSK9 inhibitor therapy Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 PCSK9 is a protein that reduces the hepatic removal of low-density
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Mandelker D, Zhang L, Kemel Y, et al. Mutation detection in patients with advanced cancer by universal sequencing of cancer-related genes in tumor and normal DNA vs guideline-based
Supplementary Online Content Mandelker D, Zhang L, Kemel Y, et al. Mutation detection in patients with advanced cancer by universal sequencing of cancer-related genes in tumor and normal DNA vs guideline-based
Endocrine Surgery. Characteristics of the Germline MEN1 Mutations in Korea: A Literature Review ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Korean Journal of INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-1703 (Print) ISSN 2287-6782 (Online) Korean J Endocrine Surg 2014;14:7-11 The Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery Characteristics of the Germline MEN1 Mutations in Korea: A Literature
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-1703 (Print) ISSN 2287-6782 (Online) Korean J Endocrine Surg 2014;14:7-11 The Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery Characteristics of the Germline MEN1 Mutations in Korea: A Literature
Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk COPYRIGHT. J. Peter Oettgen, MD
 Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk J. Peter Oettgen, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Preventive Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk J. Peter Oettgen, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Preventive Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
p.arg119gly p.arg119his p.ala179thr c.540+1g>a c.617_633+6del Prediction basis structure
 a Missense ATG p.arg119gly p.arg119his p.ala179thr p.ala189val p.gly206trp p.gly206arg p.arg251his p.ala257thr TGA 5 UTR 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 UTR Splice Site, Frameshift b Mutation p.gly206trp p.gly4fsx50 c.138+1g>a
a Missense ATG p.arg119gly p.arg119his p.ala179thr p.ala189val p.gly206trp p.gly206arg p.arg251his p.ala257thr TGA 5 UTR 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 UTR Splice Site, Frameshift b Mutation p.gly206trp p.gly4fsx50 c.138+1g>a
Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Spring 2015
 Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
The role of mipomersen therapy in the treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia
 Reviews: Clinical Trial Outcomes The role of mipomersen therapy in the treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia Clin. Invest. (2012) 2(10), 1033 1037 Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder
Reviews: Clinical Trial Outcomes The role of mipomersen therapy in the treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia Clin. Invest. (2012) 2(10), 1033 1037 Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder
Supplementary material PCNT point mutations and familial intracranial aneurysms
 Supplementary material PCNT point mutations and familial intracranial aneurysms Oswaldo Lorenzo-Betancor, MD, PhD 1, Patrick R. Blackburn, PhD 2,3, Emily Edwards, CCRP 4, Rocío Vázquez-do-Campo, MD 4,
Supplementary material PCNT point mutations and familial intracranial aneurysms Oswaldo Lorenzo-Betancor, MD, PhD 1, Patrick R. Blackburn, PhD 2,3, Emily Edwards, CCRP 4, Rocío Vázquez-do-Campo, MD 4,
Supplemental Table 1. The list of variants with their respective scores for each variant classifier Gene DNA Protein Align-GVGD Polyphen-2 CADD MAPP
 Supplemental Table 1. The list of variants with their respective scores for each variant classifier Gene DNA Protein Align-GVGD Polyphen-2 CADD MAPP Frequency Domain Mammals a 3 S/P b Mammals a 3 S/P b
Supplemental Table 1. The list of variants with their respective scores for each variant classifier Gene DNA Protein Align-GVGD Polyphen-2 CADD MAPP Frequency Domain Mammals a 3 S/P b Mammals a 3 S/P b
LIPOPROTIEN APHERESIS. Bruce Sachais, MD, PhD Executive Medical Director New York Blood Center
 LIPOPROTIEN APHERESIS Bruce Sachais, MD, PhD Executive Medical Director New York Blood Center OUTLINE Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) Diagnosis Treatment options Lipoprotein apheresis Procedures Expected
LIPOPROTIEN APHERESIS Bruce Sachais, MD, PhD Executive Medical Director New York Blood Center OUTLINE Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) Diagnosis Treatment options Lipoprotein apheresis Procedures Expected
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
MUTATIONS IN THE APOLIPOPROTEIN B GENE, HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA, AND THE RISK OF ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE
 MUTATIONS IN THE APOLIPOPROTEIN B GENE, HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA, AND THE RISK OF ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE ASSOCIATION OF MUTATIONS IN THE APOLIPOPROTEIN B GENE WITH HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA AND THE RISK OF ISCHEMIC
MUTATIONS IN THE APOLIPOPROTEIN B GENE, HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA, AND THE RISK OF ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE ASSOCIATION OF MUTATIONS IN THE APOLIPOPROTEIN B GENE WITH HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA AND THE RISK OF ISCHEMIC
review Genetically modified mice for the study of apolipoprotein B Edward Kim 1 and Stephen G. Young
 review Genetically modified mice for the study of apolipoprotein B Edward Kim 1 and Stephen G. Young Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, San Francisco, CA 94141-9100, and Cardiovascular Research
review Genetically modified mice for the study of apolipoprotein B Edward Kim 1 and Stephen G. Young Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, San Francisco, CA 94141-9100, and Cardiovascular Research
Research Article Identification of Novel ARSA Mutations in Chinese Patients with Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
 International Journal of Genomics Volume 2018, Article ID 2361068, 9 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2361068 Research Article Identification of Novel ARSA Mutations in Chinese Patients with Metachromatic
International Journal of Genomics Volume 2018, Article ID 2361068, 9 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2361068 Research Article Identification of Novel ARSA Mutations in Chinese Patients with Metachromatic
