Head Injury Management Guidelines For St Mary s Major Trauma Centre
|
|
|
- Shona Rosalyn Short
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Head Injury Management Guidelines For St Mary s Major Trauma Centre Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Referral Process, Admission and Resuscitation... 2 The Trauma Tree Pathway:... 2 Neurosurgery Registrar Presence at Trauma Calls... 3 Times to CT and theatre... 3 Acute Head Injuries Outside of the Trauma Tree Pathway... 3 Chronic Subdurals and Non Urgent Head Injuries:... 3 Non- Trauma Neurosurgery Cases within St Mary s:... 4 Documentation of Referrals... 4 Documentation in Notes... 4 Emergency Head Injury Management in Resus... 5 Use of Mannitol / Hypertonic Saline... 5 Warfarin Reversal... 5 Imaging... 6 Emergency Head Injury Management in Theatres... 6 Specific surgical principals:... 7 Emergency Head Injury Management on ITU... 7 Emergency Head Injury Management on the Major Trauma Ward... 8 Documentation:... 8 General Information:... 8 DVT prevention:... 8 Seizures prevention:... 8 Discharge / Follow Up:... 8 Audit and M&M:... 9 Paediatrics:... 9 Trials... 9 Initial version written 16/02/2011 Updated 12/04/2013 Up- to- date version: 1
2 Introduction This document outlines the main principals of care that we should provide for patients suffering Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). The principals of assessment and management are the same as the guidelines produced by NICE (which can be found here: IN addition, patients will be dealt with as defined in the MTC Operational Policy and Clinical Pathways documents. This document highlights specifically some of the local issues. All decisions to admit, not admit, to operate or not to operate and most management decisions should be made by the Consultant in charge of the patients care or the Consultant on call. If there are any doubts then please contact the relevant Consultant. Referral Process, Admission and Resuscitation The majority of patients will be admitted via the standard trauma tree pathway as described below (the trauma tree for London s Ambulance Service is in Appendix 1.1 and explains why most head injured patients will come directly to us). However, we also provide care for the trauma patients that come outside of this pathway as explained. The Trauma Tree Pathway: This mechanism has been set out in great detail by the London Trauma Office (LTO). In brief, based on mechanism of injury, London Ambulance Crews will triage patients to the most appropriate centre hence they may bypass local units to bring a head injury directly to St Mary s. They are then trauma called. 2
3 In some circumstances, the Ambulance crew may take them direct to a local hospital who then refer them to the Trauma team leader at St Marys. He/She will normally inform the Neurosurgeon that a head injury is expected. If possible, please call back the original referrer and obtain more information and images through IEP. If the call comes directly to Neurosurgery, then it is essential that the Consultant and the trauma team leader are both informed. All transfers of acutely unwell TBI patients are time critical and hence this must be stated at the time of transport request. On arrival the patient should be re- trauma called and treated as if they have come directly to St Mary s ED. Neurosurgery Registrar Presence at Trauma Calls It is a requirement that a Neurosurgical registrar is present at all trauma calls (and it is a requirement to sign in). We have agreed that if there is no head / spinal injury, the neurosurgery registrar is to be released as soon as possible. The resus process follows standard ATLS principals. If a CT scan demonstrates head / spinal injury then it is a LTO requirement that the Trauma Team leader informs the Neurosurgery Consultant on call within 90 minutes and this is documented in the notes. If the Trauma team Leader does not speak to the Consultant, then the registrar must do (and document it). This later communication is more common and is more appropriate. Either way, a discussion with the Neurosurgery Consultant should be documented within 90 minutes of arrival. Times to CT and theatre LTO expect us to achieve times to CT scan of < 30 minutes and times to theatre of <1 hour. These are difficult to achieve hence rapid diagnosis and communication is required. The patient is then transferred to theatres / ITU / the MTU as clinically indicated. Acute Head Injuries Outside of the Trauma Tree Pathway It is common practice for neurosurgeons to receive referrals directly, especially if the mechanism of injury has not been appreciated. Under such circumstances the trauma pathway may should still be activated by informing the TTL. The TTL may not call a trauma call if the patient is clearly well. Chronic Subdurals and Non Urgent Head Injuries: St Mary s has a limited capacity as a Major Trauma Centre and therefore non- urgent cases, in most circumstances, should be admitted to Charing Cross Hospital. Such cases should always be discussed with the Consultant on Call (he/ she is on call for both sites). It is important to be helpful to try to coordinate a response to try to make life easier for the referring hospital. If the patient is to be admitted to St Marys the trauma team leader and the trauma consultant of the week should be informed. 3
4 Non- Trauma Neurosurgery Cases within St Mary s: We have an ethical responsibility to provide acute neurosurgical care to Non- trauma cases while they await a bed at Charing Cross or other general neurosurgical facility. Such patients should be dealt with on an individual basis with close discussion between the Neurosurgery and ITU Consultant. As soon as a bed is available at Charing Cross Hospital they should be transferred. Documentation of Referrals All patients, whether admitted through St Mary s Emergency Department or from other hospitals should have their history and examination documented in our referral system. This is currently done electronically using An alternative website can be found at If the referral comes from outside Imperial, then you can ask the referring hospital to fill in the online form. If from within our Emergency Department, this should be completed by the registrar attending the trauma call. This generates an . It is vital that an is also sent back acknowledging receipt and stating a plan. Documentation in Notes Brain Injuries commonly involve accidents or assaults and hence notes will often be scrutinised. Hence, it is more important than ever that good note keeping occurs. The following are essential: Name; Grade; Date; Time; Bleep No. Summary of History and Examination. Name of Consultant with whom discussed and a clear plan. 4
5 Emergency Head Injury Management in Resus Management should follow standard ATLS principles, however, two specific areas should be highlighted: Airway management: ATLS states that head injured patients of GCS <8 should be intubated. While true, many greater than GCS 8 will also need to be intubated for airway management during CT scanning. Physiological management: Optimising Intracranial Pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure is vital in resus. The following parameters should be controlled: Maintain Oxygenation (100% O2 or 15 l via non- rebreathe mask) EtCO2 = 4.5kPa Keep normothermic (or slightly cool) If intubated, ensure full paralysis and analgesia If spine cleared, keep head end elevated degrees. If appropriate, and ICP monitor can be placed in resus. ICP can then also be optimised. Use of Mannitol / Hypertonic Saline These osmotic diuretics can be used when imminent herniation is demonstrated. Classically this involves a dilating pupil on the ipsilateral side to the injury. There are a number of studies that demonstrate mild benefit of hypertonic saline over mannitol, especially in the hypovolaemic patient and where a more prolonged effect is desired. A standard dose of hypertonic saline is 6mls/Kg of 5% to a max of 350mls. For mannitol, a standard dose is: 1 1.4g/Kg. (100g of 20% for a 70Kg man) Warfarin Reversal If a head injured patient has been on Warfarin, careful consideration should be given to reversing this. If there is any deterioration in conscious level there is no need to wait for a CT scan. If the patients is brought in by London HEMS, then a near patient INR will have usually been done and Octiplex already given. If not, then we should administer Octiplex. Details of how to obtain this are on the Code Red card within resus. If there are any delays, please inform the TTL or Neurosurgery Consultant on call. Note, if a full dose of Octiplex is given, there is no need to wait for an INR before starting surgery. 5
6 In less urgent cases FFP can be given but check INR pre- op when using this. Imaging A standard plain CT scans are usually adequate for most intracranial injuries. To avoid missing carotid or vertebral dissections, the Memphis modified criteria should be used to decide upon CTA: Screening protocol criteria Basilar skull fracture with involvement of the carotid canal Basilar skull fracture with involvement of petrous bone Cervical spine fracture Neurological exam not explained by brain imaging Horner s syndrome LeFort II or III fracture pattern Neck soft tissue injury (seatbelt sign or hanging or haematoma) MRI: We have pre- booked MRI slots each day. These are at: Monday: 10:00 Tuesday: 10:30 Wednesday: 14:00 Thursday: 14:15 Friday: 14:30 Saturday: 10:00-14:00 (give as much notice as possible) Outside of normal working hours, MRI is only possible at Charing Cross. Discuss this with the on call consultant before arranging. Emergency Head Injury Management in Theatres The following are golden rules for cases going to theatre: 6
7 1) The Consultant on Call is informed (if the 1 st on is not contactable, then contact the second on. Failing that, call Mark Wilson directly ( ) 2) The patient is booked in and has a hospital number (for blood cross match purposes) 3) A WHO correct site surgery form is completed and the side of the patient marked 4) A Consent form is completed (usually Consent form 4) 5) Imaging must be displayed in theatres Additional Information: Between 8am and 5pm, a Consultant Neurosurgeon is always present in the building, though may allow the neurosurgery Registrar to operate without direct supervision if both are comfortable. If at any point a neurosurgery registrar feels they need additional support they should inform the Consultant immediately. Specific surgical principals: The type of surgery and decisions such as whether to leave bone flaps in our out is at the discretion of the consultant in charge of the case. There are however certain principals of neurotrauma care that should be targeted: 1. Rapid decompression of expanding extra- axial haematoma LTO require such cases to be in theatre within 1 hour of arrival. 2. Surgical decompression for refractory ICP should probably be within a trial (such as Rescue- ICP see trials below) 3. Ensure haemostais prior to closure Emergency Head Injury Management on ITU All neurotrauma patients must be seen everyday by a Neurosurgery / NeuroITU consultant and this must be documented. Separate ITU Head Injury Guidelines have been created by the intensivists. In brief, the principals of good ITU Care of Head Injured patients are: 1. All patients who have had a head injury who cannot be weaned from sedation and assessed should have ICP monitoring. 2. Stepwise increases in medical management should aim to maintain ICPs of < 25mmHg. 3. CPP targets are to be defined (if appropriate) by both the neurosurgeon and neurointensivist looking after the patient in question. Clear thought should be given when CPPs are targeted. ITU at St Mary s has an electronic documentation system. It is often difficult on the ward round to document things as you go along as there are usually to many people and too few computers. As such we recorded our notes and plan on the proforma sheet (appendix 3). In addition, it would be ideal to make an electronic note when able. Add hoc notes should be recorded electronically 7
8 Emergency Head Injury Management on the Major Trauma Ward All patients must be seen everyday by a Consultant Neurosurgeon and this must be documented. Documentation: Each day a note should be made about the patients condition and a plan for the next 24 hours. This should ideally be documented on the proforma (appendix 1). This can also be downloaded from General Information: Head Injury Protocol: Please see Appendix 2 for clinical guidelines for Head Injury Management DVT prevention: DVT prophylaxis must always be considered. TEDS / Flowtrons should be provided (and checked) as standard. Tinzaparin is appropriate in many patients, but this must be checked with the neurosurgeon in charge of the case. In patients with acute bleeds, then Tinzaparin would not be appropriate. It is at the discretion of the Neurosurgery Consultant, evaluating each patient on an individual basis as to when the benefits of Tinzeparin outweigh the risks. Most cranial injuries can be started on Tinxaparin 72 hours post injury. Seizures prevention: Anyone who has a seizure should start antiepileptics Anyone else for whom a seizure would be detrimental or whos CT scan demonstrates a lesion which is highly likely to be eleptogenic (e.g. depressed skull fracture or temporal lobe haematoma) should be on phenytoin for 1 week. 15 mg/kg IV loading followed by mgod oral (titrate to levels). Discharge / Follow Up: All patients who are discharged following a head injury should be offered a follow- up appointment in Mark Wilson s clinic on Tuesday morning. sharon.hinds@imperial.nhs.uk to arrange. In addition, some patients (discuss with Consultant involved) should be followed up by David Sharp in his clinic. The forms to fax to arrange this are on the shared drive and on the shelves in the Trauma office. Alternatively download the pdf from 8
9 Audit and M&M: We have a Regular M&M meeting on the Second Thursday of each month directly after the Trauma meeting (2pm). Paediatrics: We have a duty to provide emergency care in life threatening (e.g. Extradural, imminent coning) to all patients including children and should undertake this as per SBNS guidelines. We should also be able to assess CT scans and wake children with no significant intracranial injury when appropriate. We should not however undertake care of more prolonged head injury management (e.g. contusions requiring ICP monitor) and these children should be refered to Great Ormond Street. At present, all children with head injuries requiring neurosurgical input should be discussed with GOSH. Separate guidelines specifically for the head injury management of children are available. Trials We are involved in a number of clinical trials at Imperial. These include: Rescue ICP (for refractory ICP) Eurotherm (an ITU study) - And we are enrolling in Crash Clearly, the consultant in charge if the patients care should make the decision as to whether a patient is suitable for a specific trial. 9
10 Appendix 1: Date and Time: Admitting Consultant Summary Hospital No: Patient Name: Date of Admission Ward Round Consultants Day Neuro Vitals FiO2 PaO2/SaO2 Temperature GCS (EVM=Total) ICP Pupils Right Left EV D Day Limb Neuro RA LA RL LL CT Scan CSF C - Spine Cleared Maintain Collar T/Lsp Other Injuries CVS HR: BP: RS ABDO Bloods Hb Na+ WCC K+ Plts Ur INR/APPT Creat Phenytoin CRP Micro Other Notes Plan CHECK TED/Flotron s Fragmin Pabrinex /DTs Signature Print Bleep 10
11 Appendix 2 BASIC HEAD INJURY PROTOCOL Patient Admitted Standard ATLS Management Fulfils NICE criteria for Intubation Yes No Intubate Fulfils NICE criteria for CT Nil significant on CT Neuro- Obs as per NICE guidleines CT demonstrates intracranial pathology requiring immediate craniotomy CT demonstrates tight brain Theatre immediately Insert ICP monitor Post op Insert ICP monitor Follow High ICP protocol Home: Most patients with servere brain injuires will have comples discharge/rehab plans. For minor head injuries, discharge must be with head injury advice and with someone appropriate High ICP (>25) Low ICP (<25) Follow up: In Head Injury clinic (MW or DS) Document plan for length of sedation and plan if ICP increases 11
10. Severe traumatic brain injury also see flow chart Appendix 5
 10. Severe traumatic brain injury also see flow chart Appendix 5 Introduction Severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death in children in the UK, accounting for 15% of deaths in 1-15
10. Severe traumatic brain injury also see flow chart Appendix 5 Introduction Severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death in children in the UK, accounting for 15% of deaths in 1-15
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
Standardize comprehensive care of the patient with severe traumatic brain injury
 Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Iowa Methodist Medical Center Des Moines Management of Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (GCS < 9) ADULT Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Iowa Methodist Medical Center Des Moines Management of Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (GCS < 9) ADULT Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma
Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
UHSM ED Pathway ELDERLY FALL / COLLAPSE
 UHSM ED Pathway ELDERLY FALL / COLLAPSE Patient name / Pathway for patients who require assessment in ED after a fall or collapse Note: - It can be used if the patient has also sustained a minor head injury
UHSM ED Pathway ELDERLY FALL / COLLAPSE Patient name / Pathway for patients who require assessment in ED after a fall or collapse Note: - It can be used if the patient has also sustained a minor head injury
Case 1. Case 5/30/2013. Traumatic Brain Injury : Review, Update, and Controversies
 Case 1 Traumatic Brain Injury : Review, Update, and Controversies Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD 32 year old male s/p high speed MVA Difficult extrication Intubated at scene Case BP 75 systolic / palp GCS 3
Case 1 Traumatic Brain Injury : Review, Update, and Controversies Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD 32 year old male s/p high speed MVA Difficult extrication Intubated at scene Case BP 75 systolic / palp GCS 3
Head injuries. Severity of head injuries
 Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Traumatic Brain Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
North West London Trauma Network Spinal Pathway and Protocols
 North West London Trauma Network Spinal Pathway and Protocols 1. Spinal Clearance in the Trauma Patient Inclusions: All trauma patients who are not alert and orientated, unable to cooperate (including
North West London Trauma Network Spinal Pathway and Protocols 1. Spinal Clearance in the Trauma Patient Inclusions: All trauma patients who are not alert and orientated, unable to cooperate (including
HEAD INJURY. Dept Neurosurgery
 HEAD INJURY Dept Neurosurgery INTRODUCTION PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION MANAGEMENT - INVESTIGATIONS - TREATMENT INTRODUCTION Most head injuries are due to an impact between the head and another
HEAD INJURY Dept Neurosurgery INTRODUCTION PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION MANAGEMENT - INVESTIGATIONS - TREATMENT INTRODUCTION Most head injuries are due to an impact between the head and another
Traumatic Brain Injury:
 Traumatic Brain Injury: Changes in Management Across the Spectrum of Age and Time Omaha 2018 Trauma Symposium June 15, 2018 Gail T. Tominaga, M.D., F.A.C.S. Scripps Memorial Hospital La Jolla Outline Background
Traumatic Brain Injury: Changes in Management Across the Spectrum of Age and Time Omaha 2018 Trauma Symposium June 15, 2018 Gail T. Tominaga, M.D., F.A.C.S. Scripps Memorial Hospital La Jolla Outline Background
Traumatic Brain Injury Protocol
 Traumatic Brain Injury Protocol Section 1. Pre-PICU Management Sources: Guidelines for Pre-Hospital Management of Traumatic Brain Injury 2000: BrainTrauma Foundation New York. Recommendations for the Transfer
Traumatic Brain Injury Protocol Section 1. Pre-PICU Management Sources: Guidelines for Pre-Hospital Management of Traumatic Brain Injury 2000: BrainTrauma Foundation New York. Recommendations for the Transfer
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
Paediatric Neurosurgical Emergencies. Kate Parkins Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Alder Hey
 Paediatric Neurosurgical Emergencies Kate Parkins Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Alder Hey Level of consciousness AVPU GCS D Neurological Assessment Pupillary reaction to light Limb movements History
Paediatric Neurosurgical Emergencies Kate Parkins Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Alder Hey Level of consciousness AVPU GCS D Neurological Assessment Pupillary reaction to light Limb movements History
CORE STANDARDS STANDARDS USED IN TARN REPORTS
 CORE STANDARDS Time to CT Scan BEST PRACTICE TARIFF SECTION 4.10 MAJOR TRAUMA 7 If the patient is admitted directly to the MTC or transferred as an emergency, the patient must be received by a trauma team
CORE STANDARDS Time to CT Scan BEST PRACTICE TARIFF SECTION 4.10 MAJOR TRAUMA 7 If the patient is admitted directly to the MTC or transferred as an emergency, the patient must be received by a trauma team
A Study to Describe Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Optimization Practice among ICU Patients of Tertiary Hospital of South India
 International Journal of Caring Sciences January-April 2018 Volume 11 Issue 1 Page 296 Original Article A Study to Describe Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Optimization Practice among ICU Patients of Tertiary
International Journal of Caring Sciences January-April 2018 Volume 11 Issue 1 Page 296 Original Article A Study to Describe Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Optimization Practice among ICU Patients of Tertiary
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth. Objectives 11/7/2017
 Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
Acute Neurosurgical Emergency Transfer [see also CATS SOP neurosurgical]
![Acute Neurosurgical Emergency Transfer [see also CATS SOP neurosurgical] Acute Neurosurgical Emergency Transfer [see also CATS SOP neurosurgical]](/thumbs/87/96512765.jpg) Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Acute Neurosurgical Emergency Transfer [see also CATS SOP neurosurgical] Document Control Information Author D Lutman Author Position Head of Clinical
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Acute Neurosurgical Emergency Transfer [see also CATS SOP neurosurgical] Document Control Information Author D Lutman Author Position Head of Clinical
Neuroprotective Effects for TBI. Craig Williamson, MD
 Neuroprotective Effects for TBI Craig Williamson, MD Neuroprotection in Traumatic Brain Injury Craig Williamson Clinical Assistant Professor Neurocritical Care Fellowship Director Disclosures I will discuss
Neuroprotective Effects for TBI Craig Williamson, MD Neuroprotection in Traumatic Brain Injury Craig Williamson Clinical Assistant Professor Neurocritical Care Fellowship Director Disclosures I will discuss
Best-evidence Review of Acute Care for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 Pragmatic Evidence-based Review Best-evidence Review of Acute Care for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Reviewer Mark Ayson MBChB DPH Date Report Completed August 2011 Important Note: It is not
Pragmatic Evidence-based Review Best-evidence Review of Acute Care for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Reviewer Mark Ayson MBChB DPH Date Report Completed August 2011 Important Note: It is not
8/29/2011. Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000. Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000
 Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Medicines Protocol HYPERTONIC SALINE 5%
 Medicines Protocol HYPERTONIC SALINE 5% HYPERTONIC SALINE 5% v1.0 1/4 Protocol Details Version 1.0 Legal category POM Staff grades Registered Paramedic Registered Nurse Specialist Paramedic (Critical Care)
Medicines Protocol HYPERTONIC SALINE 5% HYPERTONIC SALINE 5% v1.0 1/4 Protocol Details Version 1.0 Legal category POM Staff grades Registered Paramedic Registered Nurse Specialist Paramedic (Critical Care)
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
CP80 Version: V01. Acute Oncology Management Service Date approved: 8 th May 2015 Date ratified: 1 st June 2015 Review date: 1 st June 2017
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) AND PATHWAY FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION (MSCC) WITHIN THE CHRISTIE (Refer to the Manchester Cancer Network MSCC Pathway flowchart)
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) AND PATHWAY FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION (MSCC) WITHIN THE CHRISTIE (Refer to the Manchester Cancer Network MSCC Pathway flowchart)
Analgesia for chest trauma - RVI
 Analgesia for chest trauma - RVI Northern Network Initial Management Patients with blunt chest trauma will be managed in a standard fashion within the context of the well established trauma systems at
Analgesia for chest trauma - RVI Northern Network Initial Management Patients with blunt chest trauma will be managed in a standard fashion within the context of the well established trauma systems at
PATHWAY MANAGEMENT OF METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION (MSCC) THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE
 PATHWAY MANAGEMENT OF METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION (MSCC) THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: Dr V. Misra Version: Accountable Committee: V3 MSCC Network
PATHWAY MANAGEMENT OF METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION (MSCC) THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: Dr V. Misra Version: Accountable Committee: V3 MSCC Network
SOUTH THAMES CHILDREN S CANCER NETWORK GROUP. REFERRAL PROTOCOLS AND DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING PROTOCOLS October 2014
 SOUTH THAMES CHILDREN S CANCER NETWORK GROUP REFERRAL PROTOCOLS AND DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING PROTOCOLS October 2014 Contents 1. Leukaemia Referral, Diagnostic and Staging Guidelines 2. Lymphoma Referral,
SOUTH THAMES CHILDREN S CANCER NETWORK GROUP REFERRAL PROTOCOLS AND DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING PROTOCOLS October 2014 Contents 1. Leukaemia Referral, Diagnostic and Staging Guidelines 2. Lymphoma Referral,
Head injury in children
 Head injury in children Michael Kim, MD Department of Emergency Medicine University of Wisconsin- Madison #1 cause of death and disability Bimodal distribution 62,000 hospitalization 564,000 ED visits
Head injury in children Michael Kim, MD Department of Emergency Medicine University of Wisconsin- Madison #1 cause of death and disability Bimodal distribution 62,000 hospitalization 564,000 ED visits
Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba. Department of Neurological Surgery
 Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba Department of Neurological Surgery Early decompressive craniectomy in severe head injury with intracranial hypertension Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD,
Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba Department of Neurological Surgery Early decompressive craniectomy in severe head injury with intracranial hypertension Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD,
Clinical Guideline for the care of children with Hydrocephalus or blocked ventricular shunt
 Clinical Guideline for the care of children with Hydrocephalus or blocked ventricular shunt Version: 1.1 Approval Committee: Date of Approval: Ratification Group (eg Clinical network): CSRG "[Format dd-mmm-yyyy]"
Clinical Guideline for the care of children with Hydrocephalus or blocked ventricular shunt Version: 1.1 Approval Committee: Date of Approval: Ratification Group (eg Clinical network): CSRG "[Format dd-mmm-yyyy]"
Trauma CT Scanning Protocol
 Northern Trauma Network Trauma CT Scanning Protocol Background Whole body CT (WBCT) has assumed a pivotal position in trauma management. UK trauma is typically described as blunt and blind i.e. blunt trauma
Northern Trauma Network Trauma CT Scanning Protocol Background Whole body CT (WBCT) has assumed a pivotal position in trauma management. UK trauma is typically described as blunt and blind i.e. blunt trauma
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Neurosurgery Student Clerkship Guide 2017 2018 Introduction Welcome to LSUHSC New Orleans neurosurgery rotation. Our department is dedicated
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Neurosurgery Student Clerkship Guide 2017 2018 Introduction Welcome to LSUHSC New Orleans neurosurgery rotation. Our department is dedicated
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Goals. Objectives
 Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
Vertebroplasty Balloon kyphoplasty What has NICE said? Who can have vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty? Why has NICE said this?
 This leaflet has been provided to help answer some of the questions that you, or those who care for you, may have about vertebroplasty and/or balloon kyphoplasty. Vertebroplasty is a medical procedure
This leaflet has been provided to help answer some of the questions that you, or those who care for you, may have about vertebroplasty and/or balloon kyphoplasty. Vertebroplasty is a medical procedure
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient. Barts and The London NHS Trust
 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
excellence in care Procedure Neuroprotection For Review Aug 2015
 Neuro Projection HELI.CLI.14 Purpose This procedure outlines the management principles of patients being retrieved with traumatic brain injury (TBI), spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage (including subarachnoid
Neuro Projection HELI.CLI.14 Purpose This procedure outlines the management principles of patients being retrieved with traumatic brain injury (TBI), spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage (including subarachnoid
Trauma resuscitation in the Elderlyfrom a physiological perspective
 6 November 2017 Trauma resuscitation in the Elderlyfrom a physiological perspective Joseph Mathew Consultant, Emergency/ 6 November 2017 2 http://www.who.int/ageing/publications/global_health.pdf 6 November
6 November 2017 Trauma resuscitation in the Elderlyfrom a physiological perspective Joseph Mathew Consultant, Emergency/ 6 November 2017 2 http://www.who.int/ageing/publications/global_health.pdf 6 November
A bout million patients present to UK hospitals
 420 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Application of the Canadian CT head rules in managing minor head injuries in a UK emergency department: implications for the implementation of the NICE guidelines H Y Sultan, A Boyle,
420 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Application of the Canadian CT head rules in managing minor head injuries in a UK emergency department: implications for the implementation of the NICE guidelines H Y Sultan, A Boyle,
Pediatric Head Trauma August 2016
 PEDIATRIC HEAD TRAUMA AUGUST 2016 Pediatric Head Trauma August 2016 EDUCATION COMMITTEE PEER EDUCATION Quick Review of Pathophysiology of TBI Nuggets of knowledge to keep in mind with TBI Intracranial
PEDIATRIC HEAD TRAUMA AUGUST 2016 Pediatric Head Trauma August 2016 EDUCATION COMMITTEE PEER EDUCATION Quick Review of Pathophysiology of TBI Nuggets of knowledge to keep in mind with TBI Intracranial
TRAUMA CHART. SW London & Surrey Trauma Network Trauma Documentation. Trauma Team. Pre-alert details
 SW London & Surrey Trauma Network Trauma Documentation Pre-alert details Ambulance Call Sign: Age: Mechanism: Injury: Date: Call received by: Male / Female Time: St George s Hospital East Surrey Hospital
SW London & Surrey Trauma Network Trauma Documentation Pre-alert details Ambulance Call Sign: Age: Mechanism: Injury: Date: Call received by: Male / Female Time: St George s Hospital East Surrey Hospital
Traumatic Brain Injury Pathways for Adult ED Patients Being Admitted to Trauma Service
 tic Brain Injury Pathways for Adult ED Patients Being Admitted to Service Revision Team Tyler W. Barrett, MD, MSCI Elizabeth S. Compton, NP Bradley M. Dennis, MD Oscar D. Guillamondegui, MD, MPH Michael
tic Brain Injury Pathways for Adult ED Patients Being Admitted to Service Revision Team Tyler W. Barrett, MD, MSCI Elizabeth S. Compton, NP Bradley M. Dennis, MD Oscar D. Guillamondegui, MD, MPH Michael
R Adams Cowley Founder of the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center and Maryland EMS System in Baltimore, Maryland.
 R Adams Cowley 1917 -- 1991 Founder of the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center and Maryland EMS System in Baltimore, Maryland. ...That the primary purpose of medicine was to save lives, that every critically
R Adams Cowley 1917 -- 1991 Founder of the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center and Maryland EMS System in Baltimore, Maryland. ...That the primary purpose of medicine was to save lives, that every critically
Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury
 Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury Current TBI Guidelines Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD Department of Neurosurgery Guidelines for the management of traumatic brain injury Journal of Neurotrauma
Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury Current TBI Guidelines Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD Department of Neurosurgery Guidelines for the management of traumatic brain injury Journal of Neurotrauma
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEAD INJURIES IN REMOTE AND RURAL ALASKA
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEAD INJURIES IN REMOTE AND RURAL ALASKA Approximately 800 patients with head injuries die or are hospitalized in the state of Alaska each year 1. In addition, thousands
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEAD INJURIES IN REMOTE AND RURAL ALASKA Approximately 800 patients with head injuries die or are hospitalized in the state of Alaska each year 1. In addition, thousands
Expert Group Meeting-Trauma
 Why was Trauma Summit needed? There are no clear guidelines/algorithms to assist acute management of trauma patients in the Indian setting. One of our visions is to assist young doctors in acute care medicine
Why was Trauma Summit needed? There are no clear guidelines/algorithms to assist acute management of trauma patients in the Indian setting. One of our visions is to assist young doctors in acute care medicine
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES
 TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
Head injuries in children. Dr Jason Hort Paediatrician Paediatric Emergency Physician, June 2017 Children s Hospital Westmead
 Head injuries in children Dr Jason Hort Paediatrician Paediatric Emergency Physician, June 2017 Children s Hospital Westmead Objectives Approach to minor head injury Child protection issues Concussion
Head injuries in children Dr Jason Hort Paediatrician Paediatric Emergency Physician, June 2017 Children s Hospital Westmead Objectives Approach to minor head injury Child protection issues Concussion
Accompanied to walk Yes No Accompanied to walk Yes No Side of Fracture
 Fracture Neck Of Femur / Fast Track Criteria: Admission where femoral neck fracture is the primary diagnosis Accident & Emergency Assessment (To be completed by A/E Nurse and/or A/E doctor) Patient label
Fracture Neck Of Femur / Fast Track Criteria: Admission where femoral neck fracture is the primary diagnosis Accident & Emergency Assessment (To be completed by A/E Nurse and/or A/E doctor) Patient label
SUBJECT: Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL, INC. Passion for excellence. Compassion for people. Effective Date: December 1, 2005 Proposed By: Samuel Picone III, MD, Trauma Medical Director Approval and Dates: Dr. Bunch,
ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL, INC. Passion for excellence. Compassion for people. Effective Date: December 1, 2005 Proposed By: Samuel Picone III, MD, Trauma Medical Director Approval and Dates: Dr. Bunch,
H Alex Choi, MD MSc Assistant Professor of Neurology and Neurosurgery The University of Texas Health Science Center Mischer Neuroscience Institute
 H Alex Choi, MD MSc Assistant Professor of Neurology and Neurosurgery The University of Texas Health Science Center Mischer Neuroscience Institute Memorial Hermann- Texas Medical Center Learning Objectives
H Alex Choi, MD MSc Assistant Professor of Neurology and Neurosurgery The University of Texas Health Science Center Mischer Neuroscience Institute Memorial Hermann- Texas Medical Center Learning Objectives
Quality Surveillance Team. Major Trauma Services Quality Indicators
 Quality Surveillance Team Major Trauma Services Quality Indicators 1 MAJOR TRAUMA QUALITY INDICATORS Introduction These quality indicators have been commissioned by the National Clinical Director for Major
Quality Surveillance Team Major Trauma Services Quality Indicators 1 MAJOR TRAUMA QUALITY INDICATORS Introduction These quality indicators have been commissioned by the National Clinical Director for Major
Evaluation and Stabilization of the Athlete with Possible Spine Injury
 Evaluation and Stabilization of the Athlete with Possible Spine Injury Jeffrey H. Bohmer, MD, FACEP Emergency Physician Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital June 12, 2015 Introduction Goals: 1.
Evaluation and Stabilization of the Athlete with Possible Spine Injury Jeffrey H. Bohmer, MD, FACEP Emergency Physician Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital June 12, 2015 Introduction Goals: 1.
UAMS MEDICAL CENTER TRAUMA and CRITICAL CARE SERVICES MANUAL. SUPERSEDES: New PAGE: 1 of 5. RECOMMENDATION(S): Drs. Bill Beck/J.R.
 SUPERSEDES: New PAGE: 1 of 5 Purpose: To provide recommendations for the treatment and management of patients with traumatic brain injury. Definitions: Severe TBI - Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of 3 to 8 without
SUPERSEDES: New PAGE: 1 of 5 Purpose: To provide recommendations for the treatment and management of patients with traumatic brain injury. Definitions: Severe TBI - Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of 3 to 8 without
Any closer to evidence based practice? Asma Salloo Chris Hani Baragwantah Academic Hospital University of Witwatersrand
 Any closer to evidence based practice? Asma Salloo Chris Hani Baragwantah Academic Hospital University of Witwatersrand Evidence Pathophysiology Why? Management Non-degenerative, Non-congenital insult
Any closer to evidence based practice? Asma Salloo Chris Hani Baragwantah Academic Hospital University of Witwatersrand Evidence Pathophysiology Why? Management Non-degenerative, Non-congenital insult
Candidate number BOOK TWO. NSW Fellowship Course - SAQ trial paper
 BOOK TWO QUESTION 10 (20 marks) DOUBLE QUESTION You are the consultant in a regional Emergency Department. A 5 year old girl re-presents having been discharged 7 hours ago. She was assessed during the
BOOK TWO QUESTION 10 (20 marks) DOUBLE QUESTION You are the consultant in a regional Emergency Department. A 5 year old girl re-presents having been discharged 7 hours ago. She was assessed during the
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF)
 Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF) About your condition The pressure from your bulging disc(s) might be causing your pain, numbness or weakness.
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF) About your condition The pressure from your bulging disc(s) might be causing your pain, numbness or weakness.
UPDATE OF NEUROCRITICAL CARE PHARMACOTHERAPY. Vera Wilson, PharmD, BCPS Emergency Services Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Johnson City Medical Center
 UPDATE OF NEUROCRITICAL CARE PHARMACOTHERAPY Vera Wilson, PharmD, BCPS Emergency Services Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Johnson City Medical Center DISCLOSURE STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL INTEREST I, Vera Wilson,
UPDATE OF NEUROCRITICAL CARE PHARMACOTHERAPY Vera Wilson, PharmD, BCPS Emergency Services Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Johnson City Medical Center DISCLOSURE STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL INTEREST I, Vera Wilson,
Rhonda Dixon, DVM Section Head, Emergency and Critical Care Sugar Land Veterinary Specialty and Emergency
 Rhonda Dixon, DVM Section Head, Emergency and Critical Care Sugar Land Veterinary Specialty and Emergency Traumatic Brain Injury Causes Pathophysiology Neurologic assessment Therapeutic Approach Status
Rhonda Dixon, DVM Section Head, Emergency and Critical Care Sugar Land Veterinary Specialty and Emergency Traumatic Brain Injury Causes Pathophysiology Neurologic assessment Therapeutic Approach Status
Intraoperative contralateral extradural hematoma during evacuation of traumatic acute extradural hematoma: A case report with review of literature
 Intraoperative contralateral extradural hematoma during evacuation of traumatic acute extradural hematoma: A case report with review of literature Anand Sharma 1, Arti Sharma 2, Yashbir Dewan 1 1 Artemis
Intraoperative contralateral extradural hematoma during evacuation of traumatic acute extradural hematoma: A case report with review of literature Anand Sharma 1, Arti Sharma 2, Yashbir Dewan 1 1 Artemis
Trauma Registry Documentation December 16, 2014
 Trauma Registry Documentation December 16, 2014 The State of Florida now requires ALL Acute Care hospitals to submit data to the statetrauma Registry. Although Baptist Health hospitals are NOT Trauma Centers
Trauma Registry Documentation December 16, 2014 The State of Florida now requires ALL Acute Care hospitals to submit data to the statetrauma Registry. Although Baptist Health hospitals are NOT Trauma Centers
:: Closed Head Injury in Adults
 ADULT TRAUMA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Initial Management of :: Closed Head Injury in Adults Suggested citation: Dr Duncan Reed 2007, Adult Trauma Clinical Practice Guidelines, Initial Management of
ADULT TRAUMA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Initial Management of :: Closed Head Injury in Adults Suggested citation: Dr Duncan Reed 2007, Adult Trauma Clinical Practice Guidelines, Initial Management of
PRE-HOSPITAL PATIENT CARE PROTOCOLS BASIC LIFE SUPPORT/ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT
 PRE-HOSPITAL PATIENT CARE PROTOCOLS BASIC LIFE SUPPORT/ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT Board Approved June 2007 Revised December 2009 Revised July 2011 Revised June 2015 435 Hunter Street Fredericksburg, VA 22401
PRE-HOSPITAL PATIENT CARE PROTOCOLS BASIC LIFE SUPPORT/ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT Board Approved June 2007 Revised December 2009 Revised July 2011 Revised June 2015 435 Hunter Street Fredericksburg, VA 22401
Traumatic Brain Injury
 Traumatic Brain Injury Mark J. Harris M.D. Associate Professor University of Utah Salt Lake City USA Overview In US HI responsible for 33% trauma deaths. Closed HI 80% Missile / Penetrating HI 20% Glasgow
Traumatic Brain Injury Mark J. Harris M.D. Associate Professor University of Utah Salt Lake City USA Overview In US HI responsible for 33% trauma deaths. Closed HI 80% Missile / Penetrating HI 20% Glasgow
Can we abolish skull x-rays for head injury?
 ADC Online First, published on April 25, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2004.053603 Can we abolish skull x-rays for head injury? Matthew J Reed, Jen G Browning, A. Graham Wilkinson & Tom Beattie Corresponding author:
ADC Online First, published on April 25, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2004.053603 Can we abolish skull x-rays for head injury? Matthew J Reed, Jen G Browning, A. Graham Wilkinson & Tom Beattie Corresponding author:
Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach
 Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach Dr. Sunit Dr Sunit, Apollo children's hospital Blah blah Lots of head injury Lot of ill children Various methods of injury Various mechanisms of brain damage
Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach Dr. Sunit Dr Sunit, Apollo children's hospital Blah blah Lots of head injury Lot of ill children Various methods of injury Various mechanisms of brain damage
INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE -!!
 INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE - Significance raised ICP main cause of death in severe head injury main cause of morbidity in moderate and mild head injury main target and prognostic indicator in the ITU setting
INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE - Significance raised ICP main cause of death in severe head injury main cause of morbidity in moderate and mild head injury main target and prognostic indicator in the ITU setting
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly
 MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 127 30 TH MARCH 2009 Kavitha Raghavan, King s College Hospital, London Richard Waddington, Kingston Hospital, Surrey Correspondence
MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 127 30 TH MARCH 2009 Kavitha Raghavan, King s College Hospital, London Richard Waddington, Kingston Hospital, Surrey Correspondence
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Incidence of Trauma in Childhood Leading cause of death and disability in children older than one year all over the world Structured approach Primary survey and resuscitation
European Resuscitation Council Incidence of Trauma in Childhood Leading cause of death and disability in children older than one year all over the world Structured approach Primary survey and resuscitation
02/GMS/0030 ADULT EPILEPSY SERVICE CCP for General Medical and Surgical POOLE HOSPITAL NHS FOUNDATION TRUST
 Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Leads 02/GMS/0030 ADULT EPILEPSY SERVICE CCP for General Medical and Surgical Provider Lead POOLE HOSPITAL NHS FOUNDATION TRUST Period 1 April 2013 to 31
Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Leads 02/GMS/0030 ADULT EPILEPSY SERVICE CCP for General Medical and Surgical Provider Lead POOLE HOSPITAL NHS FOUNDATION TRUST Period 1 April 2013 to 31
Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Protocol
 Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Protocol PROTOCOL I. Objective II. Definition of Severe TBI III. Patient Care: Parameters IV. Patient Care: Management Timeline (First 7 days of TBI) V. Nursing Care: Communication
Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Protocol PROTOCOL I. Objective II. Definition of Severe TBI III. Patient Care: Parameters IV. Patient Care: Management Timeline (First 7 days of TBI) V. Nursing Care: Communication
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (ANAESTHESIOLOGY) FINAL EXAMINATION - MARCH Time : p.m p.m.
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (ANAESTHESIOLOGY) FINAL EXAMINATION - MARCH 2016 Date :- 10 th March 2016 LONG ESSAY QUESTIONS Answer any three questions. Answer each question
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (ANAESTHESIOLOGY) FINAL EXAMINATION - MARCH 2016 Date :- 10 th March 2016 LONG ESSAY QUESTIONS Answer any three questions. Answer each question
Report of the Welsh Neuroscience External Expert Review Group. All Wales Recommendations
 Report of the Welsh Neuroscience External Expert Review Group All Wales Recommendations Main Recommendations 1. The workforce delivering all aspects of care to people with acute and long term neurological
Report of the Welsh Neuroscience External Expert Review Group All Wales Recommendations Main Recommendations 1. The workforce delivering all aspects of care to people with acute and long term neurological
Spinal injury. Structure of the spine
 Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
PEER REVIEW VISIT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM)
 PEER REVIEW VISIT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM) Regional Trauma Network Trauma Centre Trauma Service RMTN Network Organisation Measures (T13-1C-1) - 2013/14 Peer Review Visit Date 29th April 2014 Compliance
PEER REVIEW VISIT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM) Regional Trauma Network Trauma Centre Trauma Service RMTN Network Organisation Measures (T13-1C-1) - 2013/14 Peer Review Visit Date 29th April 2014 Compliance
Cranio-cervical decompression. Information for patients Neurosurgery
 Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
HEAD INJURY MODULE ASSESSMENT OF HEAD INJURY
 HEAD INJURY MODULE Introduction Head injury is common in both adult and paediatric populations. In all-comers with head injury, () 90% present with normal or near-normal consciousness, and mortality is
HEAD INJURY MODULE Introduction Head injury is common in both adult and paediatric populations. In all-comers with head injury, () 90% present with normal or near-normal consciousness, and mortality is
Trust Guideline for the Pituitary Tumour / other Pituitary Emergency
 A Clinical Guideline For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: AMU, Accident and emergency and all other clinical areas All Medical staff Management of patients with suspected pituitary tumours
A Clinical Guideline For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: AMU, Accident and emergency and all other clinical areas All Medical staff Management of patients with suspected pituitary tumours
Pathology Service User Guide Haematology
 Pathology Service User Guide Haematology St Richard s This section of the Pathology Service User Guide includes: Anticoagulant Therapy Information about the Anticoagulant Clinic Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Pathology Service User Guide Haematology St Richard s This section of the Pathology Service User Guide includes: Anticoagulant Therapy Information about the Anticoagulant Clinic Low Molecular Weight Heparin
SAFE PAEDIATRIC NEUROSURGERY A Report from the SOCIETY OF BRITISH NEUROLOGICAL SURGEONS
 SAFE PAEDIATRIC NEUROSURGERY 2001 A Report from the SOCIETY OF BRITISH NEUROLOGICAL SURGEONS SAFE PAEDIATRIC NEUROSURGERY 2001 INTRODUCTION In 1997 the SBNS agreed to the setting up of a task force to
SAFE PAEDIATRIC NEUROSURGERY 2001 A Report from the SOCIETY OF BRITISH NEUROLOGICAL SURGEONS SAFE PAEDIATRIC NEUROSURGERY 2001 INTRODUCTION In 1997 the SBNS agreed to the setting up of a task force to
Low risk upper GI bleeding pathway
 Low risk upper GI bleeding pathway Background Low risk upper GI bleeding may be safely managed without an emergency admission to NUH following presentation to the ED. NUH uses the Glasgow Blatchford score
Low risk upper GI bleeding pathway Background Low risk upper GI bleeding may be safely managed without an emergency admission to NUH following presentation to the ED. NUH uses the Glasgow Blatchford score
Chapter 31. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Head Trauma
 Chapter 31 Head Trauma Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced
Chapter 31 Head Trauma Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced
MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION
 CLINICAL POLICY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION DOCUMENT REF: PCLASCORD (Version No. 1.4) Name and designation of policy author(s) Approved by (committee, group, manager)
CLINICAL POLICY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION DOCUMENT REF: PCLASCORD (Version No. 1.4) Name and designation of policy author(s) Approved by (committee, group, manager)
NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM
 NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM Chairperson Professor Dr Zamzuri Idris Head of Department Members Associate Professor Dato Dr
NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM Chairperson Professor Dr Zamzuri Idris Head of Department Members Associate Professor Dato Dr
PEER REVIEW VISIT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM)
 PEER REVIEW VISIT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM) Regional Trauma Network Trauma Centre Trauma Service RMTN Manchester Collaborative MTC Greater Manchester Major Trauma Centre Collaborative Network Organisation
PEER REVIEW VISIT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM) Regional Trauma Network Trauma Centre Trauma Service RMTN Manchester Collaborative MTC Greater Manchester Major Trauma Centre Collaborative Network Organisation
CARE PATHWAY FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG PERSONS WITH FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA, NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS OR SUSPECTED CENTRAL VENOUS LINE INFECTIONS
 CARE PATHWAY FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG PERSONS WITH FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA, NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS OR SUSPECTED CENTRAL VENOUS LINE INFECTIONS This Care Pathway has been developed by a multidisciplinary team. It
CARE PATHWAY FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG PERSONS WITH FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA, NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS OR SUSPECTED CENTRAL VENOUS LINE INFECTIONS This Care Pathway has been developed by a multidisciplinary team. It
Traumatic Brain Injury
 General Information Traumatic Brain Injury What you need to know Complicated condition with high variability in etiology, severity, distribution of injury, and pattern of functional impairment (Klyce,
General Information Traumatic Brain Injury What you need to know Complicated condition with high variability in etiology, severity, distribution of injury, and pattern of functional impairment (Klyce,
Chapter 39 Trauma in the Elderly
 Chapter 39 Trauma in the Elderly Episode Overview 1) 5 Risk Factors for falls in the elderly? 2) What anatomic and physiologic changes in the elderly patient are important for the management of trauma
Chapter 39 Trauma in the Elderly Episode Overview 1) 5 Risk Factors for falls in the elderly? 2) What anatomic and physiologic changes in the elderly patient are important for the management of trauma
Canadian Stroke Best Practices Initial ED Evaluation of Acute Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) Order Set (Order Set 1)
 Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care: All patients presenting to an emergency department with suspected stroke or transient ischemic attack must have an immediate clinical evaluation
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care: All patients presenting to an emergency department with suspected stroke or transient ischemic attack must have an immediate clinical evaluation
ICP. A Stepwise Approach. Stephan A. Mayer, MD Professor, Neurology & Neurosurgery Director, Neurocritical Care, Mount Sinai Health System
 ICP A Stepwise Approach Stephan A. Mayer, MD Professor, Neurology & Neurosurgery Director, Neurocritical Care, Mount Sinai Health System ICP: Basic Concepts Monroe-Kellie doctrine: skull = fixed volume
ICP A Stepwise Approach Stephan A. Mayer, MD Professor, Neurology & Neurosurgery Director, Neurocritical Care, Mount Sinai Health System ICP: Basic Concepts Monroe-Kellie doctrine: skull = fixed volume
Traumatic Brain Injury Pathway, GCS 15 Closed head injury
 Traumatic Brain Injury Pathway, GCS 15 Closed head injury Plus Any One of the Following Mild TBI 2010 Consensus Definition of TBI from CDC, NINDS, NIDDR, VA, DVBIC, DCoE Plus Any One of the Following New
Traumatic Brain Injury Pathway, GCS 15 Closed head injury Plus Any One of the Following Mild TBI 2010 Consensus Definition of TBI from CDC, NINDS, NIDDR, VA, DVBIC, DCoE Plus Any One of the Following New
Early Treatment of TBI A Prospective Study from Austria
 Early Treatment of TBI A Prospective Study from Austria Walter Mauritz MD, PhD Dept. of Anaesthesiology & Critical Care Trauma Hospital XX, 1200 Vienna, Austria International Neurotrauma Research Organisation,
Early Treatment of TBI A Prospective Study from Austria Walter Mauritz MD, PhD Dept. of Anaesthesiology & Critical Care Trauma Hospital XX, 1200 Vienna, Austria International Neurotrauma Research Organisation,
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome
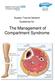 Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
The Walton Centre. NHS Foundation Trust. Patient Information. Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 The Walton Centre NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Stereotactic Radiosurgery Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) is a non-invasive treatment of brain tumours (benign and malignant), arteriovenous malformations
The Walton Centre NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Stereotactic Radiosurgery Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) is a non-invasive treatment of brain tumours (benign and malignant), arteriovenous malformations
Paediatric Emergency Prompt Cards
 Paediatric Emergency Prompt Cards Introduced July 2016 Prompt cards are designed to be used by any member of the resus team If you have any comments or suggestions, please contact helen.collyer-merritt@sash.nhs.uk
Paediatric Emergency Prompt Cards Introduced July 2016 Prompt cards are designed to be used by any member of the resus team If you have any comments or suggestions, please contact helen.collyer-merritt@sash.nhs.uk
Major Trauma Dashboard Measures. SUPPORT DOCUMENT April 2016 TO BE READ IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE MT DASHBOARD
 Major Trauma Dashboard Measures SUPPORT DOCUMENT April 2016 TO BE READ IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE MT DASHBOARD Introduction This document addresses key questions relevant to the Major Trauma Dashboard and
Major Trauma Dashboard Measures SUPPORT DOCUMENT April 2016 TO BE READ IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE MT DASHBOARD Introduction This document addresses key questions relevant to the Major Trauma Dashboard and
Refractory Seizures. Dr James Edwards EMCORE May 30th 2014
 Refractory Seizures Dr James Edwards EMCORE May 30th 2014 Refractory Seizures Seizures are a common presentation to the ED and some patients will have multiple seizures or have a reduced level of consciousness
Refractory Seizures Dr James Edwards EMCORE May 30th 2014 Refractory Seizures Seizures are a common presentation to the ED and some patients will have multiple seizures or have a reduced level of consciousness
11. Spinal cord injury
 11. Spinal cord injury Introduction Always think spinal (vertebral) and/or spinal cord injury (SCI) in children with trauma. Remember SCIWORA cord injury may be present without abnormalities on routine
11. Spinal cord injury Introduction Always think spinal (vertebral) and/or spinal cord injury (SCI) in children with trauma. Remember SCIWORA cord injury may be present without abnormalities on routine
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2008, Volume 10, Number 8:
 Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2008, Volume 10, Number 8: 516-520. CLINICAL PEARL The Hazards of Stopping a Brain in Motion: Evaluation and Classification of Traumatic
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2008, Volume 10, Number 8: 516-520. CLINICAL PEARL The Hazards of Stopping a Brain in Motion: Evaluation and Classification of Traumatic
