It has been demonstrated that postmortem MDCT, or virtual
|
|
|
- Barnard Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
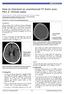
1 Published April 5, 2012 as /ajnr.A2966 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.B. Smith G.E. Lattin Jr P. Berran H.T. Harcke Common and Expected Postmortem CT Observations Involving the Brain: Mimics of Antemortem Pathology BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Postmortem imaging with CT or MR is emerging as an effective technique to augment forensic autopsy. Expected findings on postmortem imaging of the brain may mimic pathologic processes in the living brain, leading to potential misdiagnosis. The purpose of this study is to describe the array of CT findings that can be expected to be present within the brain after death. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A retrospective review was performed using an anonymized data base of 33 postmortem head CTs with no evidence of trauma to the face or scalp. Head CTs were assessed for 1) loss of gray white differentiation, 2) effacement of the ventricles and cisterns, 3) postmortem intravascular blood distribution, 4) presence of intracranial or intravascular air, and 5) an irregular appearance of the falx. Imaging findings were correlated with autopsy findings. RESULTS: Visualization of the basal ganglia was noted in 30 (91%) subjects, and the cortical ribbon was appreciated in 14 (42%). The ventricles and cisterns were effaced in 19 (58%) cases. An expected postmortem blood distribution was seen in 27 (82%) instances. Intravascular air was present in 14 cases (42%). A lumpy falx was present in 20 cases (61%). In 4 cases of subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage noted on autopsy, but not on CT, retrospective review confirmed that a true discrepancy between the radiology and pathology findings persisted. CONCLUSIONS: Recognition of expected postmortem patterns is required before pathology can be accurately diagnosed. A limitation of CT virtual autopsy is the possibility of missing small blood collections. ABBREVIATIONS: MDCT multidetector CT It has been demonstrated that postmortem MDCT, or virtual autopsy, is complementary to forensic autopsy. 1-3 As virtual autopsy gains more widespread utilization, an understanding of the imaging findings that reflect the normal decomposition process is essential to prevent misinterpretation of normal postmortem radiologic findings as pathologic processes. The goal of this article is to characterize the expected imaging findings in the postmortem brain in the 72 hours after death and to describe the pitfalls in imaging interpretation that could lead to an incorrect diagnosis. Materials and Methods BRAIN ORIGINAL RESEARCH Received September 14, 2011; accepted after revision November 9. From the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Department of Radiologic Pathology (A.B.S., G.E.L., H.T.H.), Washington, DC; Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (A.B.S., G.E.L., H.T.H.), Bethesda, Maryland; Armed Forces Medical Examiner System (P.B.), Rockville, Maryland. Paper previously presented as an educational exhibit at: Annual Meeting of the Radiologic Society of North America, November 28 December 3, 2010; Chicago, Illinois. The views herein are those of the authors and not of the US Department of Defense, US Army, or US Air Force. Please address correspondence to Alice B. Smith, MD, Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Uniformed Services University, 4301 Jones Bridge Rd, Bethesda, MD 20814; alsmith@usuhs.mil Fig 1. The lumpy falx. Axial noncontrast CT image demonstrates irregularity along the falx (arrows). This is related to high attenuation within the venous structures and not subarachnoid hemorrhage. More peripherally located venous structures also demonstrate high attenuation (arrowhead) Patients A retrospective review was performed using an anonymized data base of 33 postmortem head CT scans from autopsied cases with no evidence of trauma to the face or scalp and an intact calvaria. The 33 cases were divided as to cause of death, with 24 cases associated with traumatic (penetrating) injury to areas other than the head or brain and 9 cases associated with nontraumatic causes not related to intracranial pathology (cardiac-related pathology). Imaging findings were cataloged and correlated with intracranial autopsy findings. The time from death to imaging was within 72 hours. Subjects had been maintained in a cooled environment as soon after death as possible, but times varied. However, all were in the early stages of decomposition, as judged by absence of settling or liquefaction of the brain. Data on sex and age were not available, other than all subjects were between 18 and 65 years of age. Copyright 2012 by American Society of Neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
2 Fig 2. Increased vascular attenuation. A, Sagittal reformation from a noncontrast CT reveals high attenuation within the sagittal (arrow) and straight sinuses (arrowhead). The irregular appearance of the sagittal sinus is related to the cortical veins draining into the sinus. B, Axial noncontrast CT through the level of the circle of Willis reveals increased attenuation within the arteries. The beam-hardening artifact is related to the grommets on the human remains pouch. Imaging Protocol All imaging was performed on a LightSpeed 16 Xtra (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, Wisconsin). The subjects remained in human remains pouches for the imaging. Whole body (head to toe) images were acquired helically in the axial plane, with a section thickness of 1.2 mm and a section interval of 1.3 mm, enabling reformations (ma 480 KV 120). In addition, axial 2.5-mm-section-thickness images of the head were also obtained with the CT gantry angled parallel to the orbitalmeatal line. Imaging immediately preceded autopsy in all cases. A board-certified forensic pathologist performed the autopsies. Imaging Review The images were evaluated by a board-certified neuroradiologist with forensic radiology experience, a forensic radiologist with more than 10 years experience in the field of forensic radiology, and a boardcertified general radiologist with experience in forensic radiology. The evolving field of forensic radiology requires assessing imaging findings in a way that differs from assessing images from a living patient, so collaboration among radiologists with different areas of expertise was important. For their initial interpretation, the radiologists were blinded to the autopsy results. Evaluation of the imaging was performed using an Advantage workstation (software version 4.2_07; GE Healthcare). The imaging findings were then correlated Fig 3. Visualization of the basal ganglia. Axial CT using narrow window and level (50W 35 L) allows for visualization of both the basal ganglia and thalami. with autopsy findings to confirm that the observation was not the result of a pathologic process. The focus of the image review was to document brain findings that would be pathologic in a living patient but that would become an expected observation after death as decomposition ensues. Five criteria were selected. Brain CT scans were assessed for 1) loss of gray white differentiation, 2) effacement of the ventricles and cisterns, 3) blood distribution pattern, 4) presence of intracranial or intravascular air, and 5) an irregular or lumpy appearance of the falx (Fig 1). The radiologists applied the same criteria used in assessing the living brain, and images were manipulated for optimal window and level. Gray white differentiation was judged by whether the basal ganglia or cortical ribbon was visible. Visualization of the gray white differentiation was enhanced using narrow window and level (stroke window) ranges W and L. A recurring blood distribution pattern in the postmortem brain was recognized and termed normal. It was described as increased attenuation involving the circle of Willis and dural venous sinuses (Fig 2). For intravascular air and irregular falx cases, presence versus absence was noted, with no attempt made at quantification. Results Visualization of the basal ganglia was noted in 30 (91%) cases (Fig 3), and the cortical ribbon was appreciated in 14 (42%). The ventricles and cisterns were effaced in 19 (58%) subjects. Normal postmortem blood distribution was seen in 27 (82%) instances. Intravascular air was present in the brain in 14 cases (42%). A lumpy falx was present in 20 cases (61%). The findings are summarized in the Table. In 6 cases, differences between the radiologic and pathologic findings were present. After review of the autopsy findings and careful correlation with the images, there was consensus agreement that subarachnoid hemorrhage was recognized on the MDCT in 2 of these 6 cases. Thus, the images and autopsy were in agreement. In 4 cases, retrospective review confirmed that a true discrepancy between the radiology and pathology findings persisted in regard to detection of blood on the brain surface. In these cases where discrepancy persisted, it was concluded that MDCT did not demonstrate abnormality, despite knowledge of the location of the hemorrhage (sub- 2 Smith AJNR
3 Postmortem Imaging Findings Loss of G W Case Type Differentiation Effaced Ventricles/Cisterns Expected PM Blood Distribution PM Intracranial Air Trauma Visible BG 22/24 Yes 15/24 Yes 19/24 12/24 12/24 Loss of G W 7/24 Normal 8/24 SAH 4/24 Dilated 1/24 Natural cause of death Visible BG 8/9 Yes 4/9 Yes 8/9 2/9 8/9 Loss of G W 7/9 Normal 5/9 Note: Loss of G W differentiation evaluated by whether BG visible and whether remaining G W visible. Expected PM blood distribution dense circle of Willis, cavernous sinus, tentorium, transverse sinus, sagittal sinus. PM Intracranial Air air in the arteries, veins, or diploic spaces. Lumpy Falx nodular appearance to falx seen in PM imaging. BG indicates basal ganglia; G W, gray white; PM, postmortem. Lumpy Falx Fig 4. Bilateral subdural hemorrhage not seen on CT. A, Photograph from autopsy in which the left aspect of the dura has been reflected to the right, revealing the left-sided subdural hematoma that is adherent to the dura. Note that viewing the brain from above changes right left orientation from the convention used on CT. B, Noncontrast CT coronal reformat from the same subject does not demonstrate subdural hemorrhage. No evidence of hemorrhage was seen on the original axial images or the sagittal reformation. arachnoid in 3 cases, and bilateral subdural hematomas in 1) (Fig 4). Fig 5. Cerebral autolysis. Noncontrast CT reveals low cerebral attenuation, with loss of the gray white differentiation, and sulcal and cisternal effacement. Discussion Correlation of postmortem images and autopsy has significant medicolegal implications. One concern is that settling of blood in the venous sinuses and cortical veins can be confused with subarachnoid or subdural hemorrhage. Pathologists recognize that normal postmortem decomposition never leads to subarachnoid or subdural hemorrhage. Our findings indicate that small collections can be both overlooked and undetectable with CT imaging, even when using reformations, which has been shown to improve detection in living patients. 4 It has been previously demonstrated that a limitation of CT virtual autopsy is the possibility of missing very small collections of blood. Yen et al 5 evaluated postmorten brains with traumatic injury and found that CT had a sensitivity of 73% for the detection of subdural hemorrhage. In their study, the cases where the subdural hemorrhage was missed occurred when the blood layer in the forensic autopsy was less than 3 mm in thickness. 5 This correlated with what was found in our study, and the etiology of the subarachnoid and subdural hemorrhage was presumed to be related to trauma, even though there was no obvious external or calvarial evidence of traumatic head injury. In these cases, the subjects had evidence of penetrating injury to other body regions. There was no evidence that subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage was related to decomposition. Other imaging findings depend on the rate of decomposition, which is variable, depending on factors including ambient temperature, body weight and size, and humidity. 6 Cerebral autolysis is present, to some degree, in bodies autopsied after 24 hours. Imaging findings of this phenomenon include blurring or loss of the gray white junction, decrease in cerebral attenuation, and effacement of the sulci and ventricles (Fig 5). 6 Our visualization of cortical ribbon in 42% and basal AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
4 Fig 6. Hematocrit effect. A, Axial noncontrast CT reveals high attenuation within the posterior aspect of the sagittal sinus but low attenuation within the anterior aspect of the sinus (arrow). Beam-hardening artifact is caused by the grommets on the body bag. B, Sagittal reformation demonstrates the fluid fluid level in the sagittal sinus (arrow). Fig 7. Hyperattenuating vein. Axial (A) and coronal reformat (B) noncontrast CT demonstrates a hyperattenuating vein in the left tempoparietal region (arrows). This should not be mistaken for subarachnoid hemorrhage. ganglia in 91% confirm the need for proper windowing to see the deep gray matter. The expected postmortem blood distribution is attributed to postmortem hypostasis. Livor mortis, or postmortem hypostasis, results in increased attenuation within the dependent aspects of blood vessels. A hematocrit effect with fluid levels may be seen in the larger vessels (Fig 6). This results from the higher attenuation erythrocytes layering in the dependent portion of the vessel. One study reported that this phenomenon may be seen on imaging within 2 hours after death. 7 In a body that has remained in the supine position since death, high attenuation may be seen in the posterior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, and transverse sinuses. 6 Increased arterial attenuation is secondary to hemoconcentration, and this finding should not be mistaken for subarachnoid hemorrhage. The venous structures will also demonstrate increased attenuation due to hemoconcentration, and this should not be mistaken for dural sinus thrombosis unless there are additional findings to suggest acute thrombosis, such as venous infarction. 6 Frequently, a prominent hyperattenuating vein was noted in the temporoparietal region (Fig 7). This may be unilateral and should not be confused with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Putrefactive gas may be seen, to variable degrees, within the arterial and venous structures, and it is typically symmetrically distributed (Fig 8) 6 ; however, positioning of the head to one side or the other may result in more air on the nondependent side. It should not be mistaken for a pathologic gas collection, such as an air embolus, and is frequently missed on forensic autopsy. 5 It should be noted that finding air in the postmortem brain is directly related to air in the vascular system in general, so variability is linked to decomposition in the torso. We do not believe vascular air in the brain is an isolated occurrence. The lumpy falx appearance is secondary to the hyperattenuating cortical veins abutting the falx. Understanding that these vessels may be misinterpreted as subarachnoid hemorrhage is important. In a study by Yen et al, 5 close to 20% of cases were falsely diagnosed with subarachnoid hemorrhage on postmortem imaging. 4 Smith AJNR
5 Fig 8. Vascular air. Axial noncontrast CT images demonstrate air within both the arterial and venous structures, which is relatively symmetrically distributed. In addition, air is seen within the subcutaneous tissues (arrows). Major limitations of this study relate to the absence of specific timing from death to autopsy and the nature of preservation. Consequently, we are not able to determine the order in which brain changes occur and how they may interrelate. It would be very helpful to know whether postmortem brain findings might be linked to time of death, but this would require a carefully controlled study in which serial CT imaging is conducted on cases where time of death is known and environmental circumstances can be controlled. Conclusions The gold standard for postmortem forensic evaluation is the forensic autopsy, but virtual autopsy is proving to be a useful adjunct. A limitation of CT virtual autopsy is the possibility of missing very small collections of blood. The normal array of CT findings that are expected to be present in the brain after death are pathologic in the antemortem brain. For example, increased attenuation within the vasculature may be mistaken for hemorrhage or thrombosis. Recognition of postmortem patterns caused by decomposition is required before pathology can be accurately diagnosed. Disclosures: H. Theodore Harcke UNRELATED: Royalties: Elsevier, Comments: Royalty payment for textbook written in 2010 (title: Essentials of Forensic Imaging). References 1. Levy AD, Abbott RM, Mallak CT, et al. Virtual autopsy: preliminary experience in high-velocity gunshot wound victims. Radiology 2006;240: Thali MJ, Jackowski C, Oesterhelweg, et al. VIRTOPSY - the Swiss virtual autopsy approach. Leg Med (Tokyo) 2007;9: Thali MJ, Yen K, Schweitzer, et al. Virtopsy, a new imaging horizon in forensic pathology: virtual autopsy by postmortem multislice computed tomography (MSCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) a feasibility study. J Forensic Sci 2003;48: Wei SC, Ulmer S, Lev MH, et al. Value of coronal reformations in the CT evaluation of acute head trauma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31: Yen K, Lovblad K-O, Scheurer E, et al. Post-mortem forensic neuroimaging: correlation of MSCT and MRI findings with autopsy results. Forensic Sci Int 2007;173: Levy AD, Harcke HT, Mallak CT. Postmortem imaging: MDCT features of postmortem change and decomposition. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 31: Shiotani S, Kohno M, Ohashi N, et al. Postmortem intravascular high-density fluid level (hypostasis): CT findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2002;26: AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Overview of physiological post-mortem alterations in totalbody imaging of 100 in-hospital deceased patients
 Overview of physiological post-mortem alterations in totalbody imaging of 100 in-hospital deceased patients Poster No.: C-1234 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Wagensveld, W. Oosterhuis,
Overview of physiological post-mortem alterations in totalbody imaging of 100 in-hospital deceased patients Poster No.: C-1234 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Wagensveld, W. Oosterhuis,
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma
 July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1
 POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
Subdural Hygroma versus Atrophy on MR Brain Scans: "The Cortical Vein Sign"
 Subdural Hygroma versus Atrophy on MR Brain Scans: "The Cortical Vein Sign" Kerry W. McCiuney, 1 Joel W. Yeakley, 1 Marc J. Fenstermacher, 1 Samuel H. Baird, 1 and Carmen M. Bonmati 1 PURPOSE: To determine
Subdural Hygroma versus Atrophy on MR Brain Scans: "The Cortical Vein Sign" Kerry W. McCiuney, 1 Joel W. Yeakley, 1 Marc J. Fenstermacher, 1 Samuel H. Baird, 1 and Carmen M. Bonmati 1 PURPOSE: To determine
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Director of MRI and Neuroradiology Section, department of Diagnostic Imaging, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center
 Sigal Tal MD Director of MRI and Neuroradiology Section, department of Diagnostic Imaging, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center Fields of interest: Neuroradiology & Forensic imaging Clinical fellowships in Neuroradiology
Sigal Tal MD Director of MRI and Neuroradiology Section, department of Diagnostic Imaging, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center Fields of interest: Neuroradiology & Forensic imaging Clinical fellowships in Neuroradiology
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of
 L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of Radiology RSNA Annual Meeting 2016 Trainee call readiness
L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of Radiology RSNA Annual Meeting 2016 Trainee call readiness
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.2.RD10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents. Rishikant Sinha 1, Ahmad Rizwan Karim 2
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.2.RD10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents. Rishikant Sinha 1, Ahmad Rizwan Karim 2
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
 Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol
 MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is defined as the extravasation of
 Published January 22, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4223 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Evaluation of Virtual Noncontrast Images Obtained from Dual- Energy CTA for Diagnosing Subarachnoid Hemorrhage X.Y. Jiang, S.H.
Published January 22, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4223 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Evaluation of Virtual Noncontrast Images Obtained from Dual- Energy CTA for Diagnosing Subarachnoid Hemorrhage X.Y. Jiang, S.H.
Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis.
 Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Poster No.: R-0005 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Poster No.: R-0005 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Postmortem CT of the aorta: to be or not to be the fatal lesion
 Postmortem CT of the aorta: to be or not to be the fatal lesion Poster No.: C-0575 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Akashi, T. Murakami, M. Uetani, T. Murase, T. Yamamoto, K. Ikematsu;
Postmortem CT of the aorta: to be or not to be the fatal lesion Poster No.: C-0575 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Akashi, T. Murakami, M. Uetani, T. Murase, T. Yamamoto, K. Ikematsu;
Virtual Autopsy: Abdominal Postmortem MDCT JR Dryden, MD 1 ; E O Neal 1 ; M King 2 ; MH Lee 1 ; RS Montgomery 1 ; RM Marks, MD 1,3
 Virtual Autopsy: Abdominal Postmortem MDCT JR Dryden, MD 1 ; E O Neal 1 ; M King 2 ; MH Lee 1 ; RS Montgomery 1 ; RM Marks, MD 1,3 1. Naval Medical Center San Diego, Department of Radiology 2. Naval Medical
Virtual Autopsy: Abdominal Postmortem MDCT JR Dryden, MD 1 ; E O Neal 1 ; M King 2 ; MH Lee 1 ; RS Montgomery 1 ; RM Marks, MD 1,3 1. Naval Medical Center San Diego, Department of Radiology 2. Naval Medical
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke. Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV
 The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
Dating Neurological Injury
 Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Forensic Radiology Original Research
 Aghayev et al. Postmortem MDCT and MRI of Fatal Hemorrhage Forensic Radiology Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Emin Aghayev 1 Martin Sonnenschein 2 Christian Jackowski
Aghayev et al. Postmortem MDCT and MRI of Fatal Hemorrhage Forensic Radiology Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Emin Aghayev 1 Martin Sonnenschein 2 Christian Jackowski
Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:787 791, May 2004 Case Report Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination Charles B. L. M. Majoie, Marcel van Straten,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:787 791, May 2004 Case Report Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination Charles B. L. M. Majoie, Marcel van Straten,
Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report
 NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD
 Neuroradiology NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
Neuroradiology NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD
 NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Neuroradiology Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms 1 Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Neuroradiology Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms 1 Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography.
 A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography. Poster No.: C-1787 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Ahmed 1, G. Avery
A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography. Poster No.: C-1787 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Ahmed 1, G. Avery
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
POSTMORTEM IMAGING INTERPRETATION GUIDELINE 2015 IN JAPAN
 POSTMORTEM IMAGING INTERPRETATION GUIDELINE 2015 IN JAPAN Editor: Japan Radiological Society and Study Group of Japan Health and Labor Sciences Research 2015 Guideline for Postmortem Image Interpretation
POSTMORTEM IMAGING INTERPRETATION GUIDELINE 2015 IN JAPAN Editor: Japan Radiological Society and Study Group of Japan Health and Labor Sciences Research 2015 Guideline for Postmortem Image Interpretation
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition
 637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
Transverse Dural Sinus Thrombosis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Transverse Dural Sinus Thrombosis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Child with headache and otomastoiditis. Diagnosis Dural venous thrombosis secondary to mastoiditis Discussion The cerebral
Transverse Dural Sinus Thrombosis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Child with headache and otomastoiditis. Diagnosis Dural venous thrombosis secondary to mastoiditis Discussion The cerebral
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke
 Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review
 Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
Dating Neurological Injury
 Dating Neurological Injury Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Dating Neurological Injury Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign
 Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels
 CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
The Role of Multidetector CT Venography in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis
 Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 4(2): 284-289, 2009 2009, INSInet Publication The Role of Multidetector CT Venography in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis 1 Mohamed Abdel
Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 4(2): 284-289, 2009 2009, INSInet Publication The Role of Multidetector CT Venography in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis 1 Mohamed Abdel
MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2:59 514, March 1999 MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis William K. Erly, Richard J. Bellon, Joachim F. Seeger, and Raymond F. Carmody BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2:59 514, March 1999 MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis William K. Erly, Richard J. Bellon, Joachim F. Seeger, and Raymond F. Carmody BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Cranial Postoperative Site: MR Imaging Appearance
 27 Cranial Postoperative Site: MR Imaging Appearance Charles F. Lanzieri1 Mark Larkins2 Andrew Mancall 1 Ronald Lorig 1 Paul M. Duchesneau 1 Scott A. Rosenbloom 1 Meredith A. Weinstein 1 The ability to
27 Cranial Postoperative Site: MR Imaging Appearance Charles F. Lanzieri1 Mark Larkins2 Andrew Mancall 1 Ronald Lorig 1 Paul M. Duchesneau 1 Scott A. Rosenbloom 1 Meredith A. Weinstein 1 The ability to
Discrepancies in interpretation of night-time emergency computed tomography scans by radiology residents
 Research Discrepancies in interpretation of night-time emergency computed tomography scans by radiology residents Acta Radiologica Open 7(10) 1 6! The Foundation Acta Radiologica 2018 Article reuse guidelines:
Research Discrepancies in interpretation of night-time emergency computed tomography scans by radiology residents Acta Radiologica Open 7(10) 1 6! The Foundation Acta Radiologica 2018 Article reuse guidelines:
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage as a Complication of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
 Mitali Madhusmita et al CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10036-1183 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage as a Complication of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis 1 Mitali Madhusmita, 2 Archana Bhate, 3 Anannya Mukherji ABSTRACT
Mitali Madhusmita et al CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10036-1183 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage as a Complication of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis 1 Mitali Madhusmita, 2 Archana Bhate, 3 Anannya Mukherji ABSTRACT
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke
 Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
Case Report Anoxic Brain Injury Presenting as Pseudosubarachnoid Hemorrhage in the Medical Intensive Care Unit
 Hindawi Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2017, Article ID 9071482, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9071482 Case Report Anoxic Brain Injury Presenting as Pseudosubarachnoid Hemorrhage in the Medical
Hindawi Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2017, Article ID 9071482, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9071482 Case Report Anoxic Brain Injury Presenting as Pseudosubarachnoid Hemorrhage in the Medical
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Blood Supply. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Blood Supply Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Review Sessions with Dr. Riedl Tuesdays 4-5pm in MCB 3-146 (the main lab room) The first exam is coming soon!
Blood Supply Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Review Sessions with Dr. Riedl Tuesdays 4-5pm in MCB 3-146 (the main lab room) The first exam is coming soon!
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Endovascular Thrombolysis in Deep Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
 Endovascular Thrombolysis in Deep Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Michael P. Spearman, Charles A. Jungreis, Joseph J. Wehner, Peter C. Gerszten, and William C. Welch Summary: We present two cases of acute thrombosis
Endovascular Thrombolysis in Deep Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Michael P. Spearman, Charles A. Jungreis, Joseph J. Wehner, Peter C. Gerszten, and William C. Welch Summary: We present two cases of acute thrombosis
Published August 16, 2012 as /ajnr.A3243
 Published August 16, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3243 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Shinohara M. Sakamoto H. Takeuchi T. Uno T. Watanabe T. Kaminou T. Ogawa Subarachnoid Hyperattenuation on Flat Panel Detector Based
Published August 16, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3243 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Shinohara M. Sakamoto H. Takeuchi T. Uno T. Watanabe T. Kaminou T. Ogawa Subarachnoid Hyperattenuation on Flat Panel Detector Based
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging has been reported to be a sensitive and specific method in the diagnosis of disease of the sub-
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence
 A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography
 Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
How to Read a Head CT. Andrew D. Perron, MD, FACEP. Head CT. Head CT. Head CT. Head CT. EM Residency Program Director
 Blood Can Be Very Bad How to Read a Head CT EM Residency Program Director (or How I learned to stop worrying and love computed tomography ) Department of Emergency Medicine Maine Medical Center Portland,
Blood Can Be Very Bad How to Read a Head CT EM Residency Program Director (or How I learned to stop worrying and love computed tomography ) Department of Emergency Medicine Maine Medical Center Portland,
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management
 Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
TABLES. Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging. Conclusions. Author (Year) Classification Process/Evid ence Class
 TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
Evaluation of the Effect of Hemoglobin or Hematocrit Level on Dural Sinus Density Using Unenhanced Computed Tomography
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.3349/ymj.213.54.1.28 pissn: 513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(1):28-33, 213 Evaluation of the Effect of Hemoglobin or Hematocrit Level on Dural Sinus Density
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.3349/ymj.213.54.1.28 pissn: 513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(1):28-33, 213 Evaluation of the Effect of Hemoglobin or Hematocrit Level on Dural Sinus Density
Virtual Navigator study: Subset of preliminary data about cerebral venous circulation
 Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 Bartels E, Bartels S, Poppert H (Editors): New Trends in Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics an Update. Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 journal
Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 Bartels E, Bartels S, Poppert H (Editors): New Trends in Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics an Update. Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 journal
Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection in Adults: Evaluation with MDCT
 Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection in Adults: Evaluation with MDCT e-poster: 349 Congress: 2WCTI 2009 Type: Educational poster Topic: Pulmonary circulation Authors: MeSH: Bhatti W, Maldjian
Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection in Adults: Evaluation with MDCT e-poster: 349 Congress: 2WCTI 2009 Type: Educational poster Topic: Pulmonary circulation Authors: MeSH: Bhatti W, Maldjian
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment
 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
B. CT protocols for the spine
 B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Times Have Changed! Forensic Radiology A New Challenge for Radiology and Forensic Pathology
 Special Articles Review Flach et al. Forensic Radiology Special Articles Review Patricia M. Flach 1,2,3 Michael J. Thali 1 Tanja Germerott 4 Flach PM, Thali MJ, Germerott T Keywords: postmortem CT, postmortem
Special Articles Review Flach et al. Forensic Radiology Special Articles Review Patricia M. Flach 1,2,3 Michael J. Thali 1 Tanja Germerott 4 Flach PM, Thali MJ, Germerott T Keywords: postmortem CT, postmortem
l' ".'"` va" Fig. 1 Patient 1. Precontrast computed tomographic scans demonstrating areas of increased attenuation
 136 -. i 'sit'' -k tz#. / e, = r + -e l' ".'"` va" "t 'hua th ;] fteqhiv.r'" ' Fig. 1 Patient 1. Precontrast computed tomographic scans demonstrating areas of increased attenuation in the region of the
136 -. i 'sit'' -k tz#. / e, = r + -e l' ".'"` va" "t 'hua th ;] fteqhiv.r'" ' Fig. 1 Patient 1. Precontrast computed tomographic scans demonstrating areas of increased attenuation in the region of the
The radiodensity of cerebrospinal fluid and vitreous humor as indicator of the time since death
 Forensic Sci Med Pathol (2016) 12:248 256 DOI 10.1007/s12024-016-9778-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The radiodensity of cerebrospinal fluid and vitreous humor as indicator of the time since death Desirée H. J. L.
Forensic Sci Med Pathol (2016) 12:248 256 DOI 10.1007/s12024-016-9778-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The radiodensity of cerebrospinal fluid and vitreous humor as indicator of the time since death Desirée H. J. L.
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
