Patient Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
|
|
|
- David Leslie Montgomery
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK7026 Version: 5 Review date: 30th June 2021
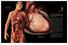
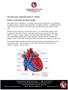
2 The Normal Heart The Heart is made up of four chambers: the upper two chambers are called the atrium and the lower two are known as ventricles. Muscular walls, called septum, divide the heart into two sides. On the right side of the heart, the right atrium and ventricle work to pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs; on the left side, the left atrium and ventricle combine to pump oxygenated blood to the body. Page 1
3 The usual form of treatment Often in a newborn the PDA may close on its own without any intervention. If the PDA continues after the newborn period it will generally never close on its own. Medical or surgical closure is recommended in such cases to prevent future risk of endocarditis (inflammation of the lining of the heart). Medication may be given to aid closure of the ductus such as Indomethacin. Medications are only successful in newborn infants. If this does not work closure is often achieved by surgery where the PDA is tied off (ligated). In older children if the ductus is small, a coil may be placed within the vessel which will expand to block the blood flow. If the ductus is larger, a flexible device can be placed within the ductus as a plug. Risks, discomforts of treatment and alternatives The risk of complications with any of these treatments is low, determined mostly by how ill the child is prior to treatment. All benefits and risks of treatment will be discussed with you by your specialist. Specific problems regarding treatment or surgery can not be discussed here as every child s problem needs to be assessed and treated individually. Page 2
4 Page 3 Medications For your Infant:
5 Nature and reasons for the condition When a baby is still in the mother s womb a baby s lungs are not needed to supply oxygen because the baby receives oxygen via the mother s lungs and the placenta. Since baby s lungs do not provide any oxygen, there is no need for energy to be expanded pumping blood to the lungs. The ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel that is present in all babies while still in the womb that allows blood to bypass the pathway to the lungs; it allows blood to flow from the pulmonary artery to the aorta. When the baby is born and the unbumbilical cord is cut, the lungs are now needed to supply oxygen. Therefore the lungs expand, their blood vessels relax to accept more flow and the ductus arteriosus usually closes within the first few hours of life. On occasion, however the ductus arteriosus does not close on its own and this is referred to as a patent ( patent meaning open) ductus arteriosus or (PDA). While this condition is seen more frequently in premature babies, it may also appear in full term infants. Signs & Symptoms: The symptoms of PDA depend on the size of the ductus and how much blood flow it carries. After birth, the pressures and resistance are much tighter in the aorta than the pulmonary artery, so if a ductus arteriosus is present, blood will flow from the aorta into the pulmonary artery. This extra blood flow into the lungs can overload the lungs and put an additional burden on the heart to pump this extra blood. This situation may not be well tolerated in a premature baby who already has problems related to immaturity of the lungs themselves. These babies may need more support from the ventilator and have symptoms of congestive heart failure. A newborn with a PDA may appear to have: Fast breathing Breathlessness Increase in work of breathing More respiratory infections Infants gets tired easily Poor weight gain e.g. (failure to thrive) If the PDA is very small there may be no symptoms at all and the only way to detect the PDA is to listen to the heart for a heart murmur. Page 4
6 Page 5 Notes
7 Medicines used to treat heart problems Many infants will not require any medications at all. For those who do here are just a few on the more common medicines. Frusemide & Hydrochlorothiazide These are diuretics (water medicine) which make the kidneys pass more urine. Infants and children on these drugs loose sodium, chloride and potassium (different salts in the blood stream) and water. When the heart is not working very well, water and salt accumulate in the body, liver and the lungs, making particularly the lungs rather heavy. When these drugs are given, the lungs become somewhat lighter, easier to expand and, less energy is used in breathing thus helping the infant to breathe. Spironolactone/Amiloride These are weaker diuretics (water medicine) which make the kidneys pass more urine. They hold on to potassium (salt) and are often used with other diuretics. Captopril & Hydralazine These drugs dilate (open) the blood vessels and as a result reduce blood pressure. They can be used to restore normal blood pressure. They can also be used in those infants and children with normal blood pressure and a weak heart. By reducing the blood pressure this reduces the work of the heart. Propranolol This reduces the rate and force of contraction of the heart muscle. It is useful in treating fast heart rates, high blood pressure and also relieving spasm of heart muscle with other more complicated heart problems. Page 6
8 If you have any further questions please contact your child s consultant via their secretary via the hospital switchboard. The secretaries are available Monday to Friday 9.00 am to 5.00 pm If you need to contact the Department outside of these hours please phone either: Ward 3F Ward 4F Whiston Hospital Warrington Road, Prescot, Merseyside, L35 5DR Telephone:
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) A Parent Information Leaflet What is the Ductus Arteriosus? What is the Ductus Arteriosus? The Ductus Arteriosus is a small muscular blood vessel that joins the pulmonary
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) A Parent Information Leaflet What is the Ductus Arteriosus? What is the Ductus Arteriosus? The Ductus Arteriosus is a small muscular blood vessel that joins the pulmonary
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
 Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 This information sheet explains about the congenital (present at birth) heart condition
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 This information sheet explains about the congenital (present at birth) heart condition
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR)
 Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR) WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0876 Version: 5 Review date: June 2020 How does the urinary system work? The urinary system consists of the
Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR) WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0876 Version: 5 Review date: June 2020 How does the urinary system work? The urinary system consists of the
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
HOW TO HELP YOUR DOG WITH HEART FAILURE......and enjoy more time together
 HOW TO HELP YOUR DOG WITH HEART FAILURE......and enjoy more time together Heart failure Understanding heart failure in your dog The heart is a pump that transports blood, which is rich in oxygen and nutrients,
HOW TO HELP YOUR DOG WITH HEART FAILURE......and enjoy more time together Heart failure Understanding heart failure in your dog The heart is a pump that transports blood, which is rich in oxygen and nutrients,
and the beat goes on: developing a heart and vascular system
 HEARTCHAPTER1.qxp 7/15/05 10:22 AM Page 4 this integrated system of heart, blood, and vessels is known as the cardiovascular system. CHAPTER 1 and the beat goes on: developing a heart and vascular system
HEARTCHAPTER1.qxp 7/15/05 10:22 AM Page 4 this integrated system of heart, blood, and vessels is known as the cardiovascular system. CHAPTER 1 and the beat goes on: developing a heart and vascular system
SPECIFIC HEART DEFECTS
 A. Acyanotic Defects 1. Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD): SPECIFIC HEART DEFECTS Which side of the heart is stronger? Left This is when there is an opening between the left and right ventricle (in the septum)
A. Acyanotic Defects 1. Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD): SPECIFIC HEART DEFECTS Which side of the heart is stronger? Left This is when there is an opening between the left and right ventricle (in the septum)
Nephrotic Syndrome. Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0862 Version: 5 Review date: 30 June 2020 HELEN WINSTON
 Nephrotic Syndrome WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0862 Version: 5 Review date: 30 June 2020 Nature and reasons for the condition Nephrotic syndrome is a condition where
Nephrotic Syndrome WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0862 Version: 5 Review date: 30 June 2020 Nature and reasons for the condition Nephrotic syndrome is a condition where
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
PDA in Pets There s Nothing Affectionate About Patent Ductus Arteriosus
 PDA in Pets There s Nothing Affectionate About Patent Ductus Arteriosus People are frequently born with heart defects. They often require intricate and specialized surgeries to help correct them. So too
PDA in Pets There s Nothing Affectionate About Patent Ductus Arteriosus People are frequently born with heart defects. They often require intricate and specialized surgeries to help correct them. So too
Nit-Occlud. Coil System for PDA Closure PATIENT EDUCATIONAL BROCHURE
 Nit-Occlud PDA Coil System for PDA Closure PATIENT EDUCATIONAL BROCHURE A Patient s Educational Brochure to Non-Surgical Closure of the Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Using the Nit-Occlud PDA Inside This
Nit-Occlud PDA Coil System for PDA Closure PATIENT EDUCATIONAL BROCHURE A Patient s Educational Brochure to Non-Surgical Closure of the Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Using the Nit-Occlud PDA Inside This
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0875 Version: 5 Review date: June 2020 Notes Page 1 Nature and Reasons for Condition Urinary tract infections
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0875 Version: 5 Review date: June 2020 Notes Page 1 Nature and Reasons for Condition Urinary tract infections
Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do?
 Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Septal Defects. How does the heart work?
 Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Understanding your child s heart. Patent ductus arteriosus
 Understanding your child s heart Patent ductus arteriosus 15 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions running through your
Understanding your child s heart Patent ductus arteriosus 15 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions running through your
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (Type of Heart Birth Defect) Basics OVERVIEW Patent refers to open ; ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel between the aorta (main artery of the body) and the pulmonary artery (main
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (Type of Heart Birth Defect) Basics OVERVIEW Patent refers to open ; ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel between the aorta (main artery of the body) and the pulmonary artery (main
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
The Tell Tale Heart. Introduction to the Heart. Name
 The Tell Tale Heart CIBT Student Laboratory Exercise Name Introduction to the Heart The main function of the heart is to keep blood constantly moving throughout the body. In mammals the heart is a large
The Tell Tale Heart CIBT Student Laboratory Exercise Name Introduction to the Heart The main function of the heart is to keep blood constantly moving throughout the body. In mammals the heart is a large
Heart Disorders. Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8. Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders
 Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology. Emma Walker 7 th May 2016
 Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia
 Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
Ummeenatrbilaoiasetptiwmsaiiri
 atrial This This atrial CIRCULATORY CHANGES My My pressure In the foetus the left atrial is low as relatively Ummeenatrbilaoiasetptiwmsaiiri ze@fgffmftheyubsidtritupyeiirieminfyifjjtajefjjieiminylntentiiiarmmnitnteimiiiinc1udingfromthepl9centaj
atrial This This atrial CIRCULATORY CHANGES My My pressure In the foetus the left atrial is low as relatively Ummeenatrbilaoiasetptiwmsaiiri ze@fgffmftheyubsidtritupyeiirieminfyifjjtajefjjieiminylntentiiiarmmnitnteimiiiinc1udingfromthepl9centaj
Adult Congenital Heart Disease (A.C.H.D) Study Pack. [Type text]
![Adult Congenital Heart Disease (A.C.H.D) Study Pack. [Type text] Adult Congenital Heart Disease (A.C.H.D) Study Pack. [Type text]](/thumbs/87/96023874.jpg) Adult Congenital Heart Disease (A.C.H.D) Study Pack ACHD Study Pack Contents Page numbers Contents 2 Pack Contents 3 4 Introduction and how the pack works 5 7 The foetal heart 8 9 Atrial Septal Defects
Adult Congenital Heart Disease (A.C.H.D) Study Pack ACHD Study Pack Contents Page numbers Contents 2 Pack Contents 3 4 Introduction and how the pack works 5 7 The foetal heart 8 9 Atrial Septal Defects
Closing your Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
 Closing your Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what a PDA is why it should be closed what to expect with this procedure what follow-up care
Closing your Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what a PDA is why it should be closed what to expect with this procedure what follow-up care
Heart Disease in Dogs: An Overview
 Heart Disease in Dogs: An Overview Heart disease in dogs is a commonly diagnosed condition. A dog s heart, lungs, and blood vessels combine to form his circulatory system. The heart is the central player
Heart Disease in Dogs: An Overview Heart disease in dogs is a commonly diagnosed condition. A dog s heart, lungs, and blood vessels combine to form his circulatory system. The heart is the central player
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Eisenmenger syndrome. Long term care and information for patients
 Long term care and information for patients 4 Recovering from a heart attack Recovering from a heart attack 4 is a form of congenital heart disease in which the pressure in the pulmonary (lung) arteries
Long term care and information for patients 4 Recovering from a heart attack Recovering from a heart attack 4 is a form of congenital heart disease in which the pressure in the pulmonary (lung) arteries
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle
 ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle In this activity, you will follow the flow of blood through the heart. Your heart has two jobs to do, and its two sides have separate responsibilities: The left side pumps oxygen-enriched
ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle In this activity, you will follow the flow of blood through the heart. Your heart has two jobs to do, and its two sides have separate responsibilities: The left side pumps oxygen-enriched
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
 Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Understanding your child s heart. Coarctation of the aorta
 Understanding your child s heart Coarctation of the aorta 2 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions running through your
Understanding your child s heart Coarctation of the aorta 2 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions running through your
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
The Living Environment Units 18, 19, and 20 Human Body Test
 The Living Environment Units 18, 19, and 20 Human Body Test Please read the following directions. This test comprises ten (10) questions of which you will choose and answer only five (5) questions. If
The Living Environment Units 18, 19, and 20 Human Body Test Please read the following directions. This test comprises ten (10) questions of which you will choose and answer only five (5) questions. If
HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT
 BOOK 4 HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT SECTION 3 EXERCISE AND FITNESS IN HUMANS THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The human nervous system consists of: the central nervous system (CNS) the brain and spinal
BOOK 4 HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT SECTION 3 EXERCISE AND FITNESS IN HUMANS THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The human nervous system consists of: the central nervous system (CNS) the brain and spinal
Cardiovascular system Physiology Sheet (1)
 Cardiovascular system Physiology Sheet (1) In any patient the most important thing is the cardiorespiratory system, if any patient comes to you with a car accident for example the first thing that you
Cardiovascular system Physiology Sheet (1) In any patient the most important thing is the cardiorespiratory system, if any patient comes to you with a car accident for example the first thing that you
Transurethral Prostatectomy (TURP) for Benign Disease
 Transurethral Prostatectomy (TURP) for Benign Disease Whiston Hospital Warrington Road, Prescot, Merseyside, L35 5DR Telephone: 0151 426 1600 St Helens Hospital Marshall Cross Road, St Helens, Merseyside,
Transurethral Prostatectomy (TURP) for Benign Disease Whiston Hospital Warrington Road, Prescot, Merseyside, L35 5DR Telephone: 0151 426 1600 St Helens Hospital Marshall Cross Road, St Helens, Merseyside,
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
PUBLIC SUMMARY OF RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) CANDESARTAN/HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE ORION 8 MG/12.5 MG, 16 MG/12.5 MG, 32 MG/12.5 MG, 32 MG/25 MG ORION
 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) CANDESARTAN/HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE ORION 8 MG/12.5 MG, 16 MG/12.5 MG, 32 MG/12.5 MG, 32 MG/25 MG ORION CORPORATION DATE: 17-04-2015, VERSION 2 VI.2 Elements for
PUBLIC SUMMARY OF RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) CANDESARTAN/HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE ORION 8 MG/12.5 MG, 16 MG/12.5 MG, 32 MG/12.5 MG, 32 MG/25 MG ORION CORPORATION DATE: 17-04-2015, VERSION 2 VI.2 Elements for
Development of the Heart *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Cardiac Emergencies in Infants. Michael Luceri, DO
 Cardiac Emergencies in Infants Michael Luceri, DO October 7, 2017 I have no financial obligations or conflicts of interest to disclose. Objectives Understand the scope of congenital heart disease Recognize
Cardiac Emergencies in Infants Michael Luceri, DO October 7, 2017 I have no financial obligations or conflicts of interest to disclose. Objectives Understand the scope of congenital heart disease Recognize
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012
 The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
A. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis. B. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis.
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome
 Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
The Adolescent and Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program
 The Adolescent and Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University D- Transposition of the Great Vessels D- transposition of the great
The Adolescent and Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University D- Transposition of the Great Vessels D- transposition of the great
TRAINING NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS
 TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
What to Expect at Seattle Children s Hospital
 Patient and Family Education Heart Failure What to Expect at Seattle Children s Hospital This booklet is meant to help you understand heart failure and the care your child receives in the heart failure
Patient and Family Education Heart Failure What to Expect at Seattle Children s Hospital This booklet is meant to help you understand heart failure and the care your child receives in the heart failure
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA
 Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
CongHeartDis.doc. Андрій Миколайович Лобода
 CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
Update on mangement of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Dr. Trinh Thi Thu Ha
 Update on mangement of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants Dr. Trinh Thi Thu Ha Outline 1. Overview of PDA 2. Timing of screening PDA? 3. When to treat PDA? Timing of ductal closure Prenatal
Update on mangement of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants Dr. Trinh Thi Thu Ha Outline 1. Overview of PDA 2. Timing of screening PDA? 3. When to treat PDA? Timing of ductal closure Prenatal
Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영
 When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
PDA: Closure Using Coils and Devices: Indications, Technique & Outcome
 PDA: Closure Using Coils and Devices: Indications, Technique & Outcome Daniel Levi, MD, FSCAI Associate Professor of Pediatrics UCLA Biomedical Engineering Mattel Children s Hospital at UCLA, Division
PDA: Closure Using Coils and Devices: Indications, Technique & Outcome Daniel Levi, MD, FSCAI Associate Professor of Pediatrics UCLA Biomedical Engineering Mattel Children s Hospital at UCLA, Division
Spleen. Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum. Vessel walls. Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels. Artery elastic tissue
 Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Skeletal muscle. Flow increases and decreases with each muscular contraction - as a result of compression of the blood vessels by contracted muscle
 Regional blood flow Skeletal muscle Extreme increases during exercises Flow increases and decreases with each muscular contraction - as a result of compression of the blood vessels by contracted muscle
Regional blood flow Skeletal muscle Extreme increases during exercises Flow increases and decreases with each muscular contraction - as a result of compression of the blood vessels by contracted muscle
Mitral Valve Disease (MVD)
 Mitral Valve Disease (MVD) What is the mitral valve? The heart contains 4 valves within it. Each valve is present to allow unidirectional flow and to prevent flow backwards. The mitral valve is the valve
Mitral Valve Disease (MVD) What is the mitral valve? The heart contains 4 valves within it. Each valve is present to allow unidirectional flow and to prevent flow backwards. The mitral valve is the valve
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Atrioventricular Valve Endocardiosis Basics
 Atrioventricular Valve Endocardiosis Basics OVERVIEW Atrioventricular valve refers to the heart valves between the top chamber (known as the atrium ) and the bottom chamber (known as the ventricle ) of
Atrioventricular Valve Endocardiosis Basics OVERVIEW Atrioventricular valve refers to the heart valves between the top chamber (known as the atrium ) and the bottom chamber (known as the ventricle ) of
Cyanotic spells in Tetralogy of Fallot
 Cyanotic spells in Tetralogy of Fallot Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains
Cyanotic spells in Tetralogy of Fallot Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains
Understanding your child s heart. Pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect
 Understanding your child s heart Pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect 13 About this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have
Understanding your child s heart Pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect 13 About this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have
Understanding your child s heart. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
 Understanding your child s heart Hypoplastic left heart syndrome 8 bout this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news and have lots of questions running
Understanding your child s heart Hypoplastic left heart syndrome 8 bout this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news and have lots of questions running
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pulse Oximetry Screening in Newborns to Enhance the Detection Of Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Frequently Asked Questions
 Pulse Oximetry Screening in Newborns to Enhance the Detection Of Critical Congenital Heart Disease Frequently Asked Questions Current Recommendation: The current recommendation from the Canadian Cardiovascular
Pulse Oximetry Screening in Newborns to Enhance the Detection Of Critical Congenital Heart Disease Frequently Asked Questions Current Recommendation: The current recommendation from the Canadian Cardiovascular
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Cardiomyopathy Consequences. function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease in which the heart muscle
 Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Kofinas Perinatal Providing Care to the Unborn
 Alexander D. Kofinas, MD Director, Kofinas Perinatal Associate Professor, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology Cornell University, College of Medicine Patient instructions for the use of Indomethacin and
Alexander D. Kofinas, MD Director, Kofinas Perinatal Associate Professor, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology Cornell University, College of Medicine Patient instructions for the use of Indomethacin and
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
GraspIT AQA GCSE Organisation Questions
 A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Papworth Hospital NHS Trust INTRODUCTION. Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan INTRODUCTION
 Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Blood Vessels. veins. valve. to the heart. capillaries from the heart. arteries. Visual 25-1
 Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System
 The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
