Phylogenesis of the respiratory system
|
|
|
- Hester Stephens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phylogenesis of the respiratory system 1. The totality of processes providing intake of oxygen into the organism, its usage and expelling of the carbon dioxide gas into the external medium is a) respiration b) shallow breathing c) internal breathing d) external breathing Comment [R1]: Comment [R2R1]: Comment [R3R2]: Comment [R4R3]: Comment [R5R4]: Comment [R6R5]: 2. Types of breathing a) internal, external b) internal, shallow c) external shallow d) intestinal, shallow 3. The exchange of gases between an organism and the environment taking place in the respiratory organs is a) shallow breathing b) intestinal breathing c) internal breathing d) external breathing 4. The exchange of gases between a cell and tissue fliud is a) shallow breathing b) intestinal breathing c) internal breathing d) external breathing 5. Name the types of external breathing a) shallow, external b) tissue, internal c) ectodermal, mesodermal d) shallow, intestinal
2 6. Name the origin of the shallow breathing a) ectodermal, mesodermal b) endodermal c) ectodermal d) mesodermal 7. Name the derivatives of the shallow breathing in Vertebrates a) gills, lung sacs, trachea b) gills, trachea c) lung sacs, lungs d) gills, trachea, lungs 8. Name the characteristic of the shallow breathing a) it is performed through the skin surface b) it is performed through the fragment of the alimentary tube c) takes place in bronchi d) it is performed in the upper respiratory tracts 9. Name the origin of the intestinal breathing a) ectodermal, mesodermal b) endodermal c) ectodermal d) mesodermal 10. Name the characteristic of the intestinal breathing a) it is performed through the skin surface b) it is performed through the fragment of the alimentary tube c) takes place in bronchi d) it is performed in the upper respiratory tracts 11. The derivatives of the intestinal breathing a) lungs of Vertebrates b) lungs of Amphibia c) gills, lung sacs of Mammals
3 d) gills, lung sacs of Invertebrates 12. Name the organ homologous to the lung of Amphibia a) float of the dipnoan fish b) gills of Invertebrates c) lungs of Reptiles d) trachea of Vertebrates 13. Respiratory organs of Amphibia a) trachea b) gills, lung sacs c) sac-like lungs with some short septa d) spongoid lungs 14. Peculiarities of structure of lungs of Amphibia a) thin-walled sac-like lungs with many short septa b) dense, spongoid lungs c) thin-walled sac-like lungs with some short septa d) cellular lungs 15. The amount of oxygen that enters through the lungs of Amphibia a) 100% b) 60-70% c) 30-40% d) all amount enters through the skin 16. Differentiation of the pneumatic tracts of Amphibia a) trachea, two bronchi b) bronchial tube c) trachea d) poorly differentiated 17. Respiratory organs of Reptiles a) sac-like lungs
4 b) cellular lungs c) alveolar lungs d) trachea 18. Peculiarities of structure of lungs of Reptiles a) thin-walled sac-like with some short septa b) dense, spongoid c) divided into chambers by septa (cellular) d) alveolar 19. The amount of oxygen that enters through the lungs of Reptiles а) 100% b) 60-70% c) 30-40% d) all amount enters through the skin 20. Differentiation of the pneumatic tracts of Reptiles a) trachea, two bronchi b) bronchial tube c) trachea d) poorly differentiated 21. Respiratory organs of Birds a) sac-like lungs b) cellular lungs c) alveolar lungs d) spongoid lungs 22. Peculiarities of structure of lungs of Birds a) thin-walled sac-like with some short septa b) dense, spongoid consisting of the tube bronchi c) divided into chambers by septa (cellular) d) alveolar, bronchial tree is present
5 23. Name the structures of the Bird s respiratory organs where the gas exchange takes place a) lung sacs b) parabronchi c) bronchi d) brochioles 24. Double respiration in Birds is a) gas exchange taking place in trachea and bronchi b) gas exchange taking place in bronchi and alveoli c) gas exchange taking place in the upper respiratory tracts and lungs d) gas exchange taking place during inhalation and exhalation 26. Name the animal class for which the phenomenon of double respiration is peculiar a) Birds b) Mammals c) Reptiles, Birds d) Amphibia 27. Respiratory organs of Mammals a) sac-like lungs b) cellular lungs c) alveolar lungs d) spongoid lungs 28. Peculiarities of structure of lungs of Mammals a) thin-walled sac-like with some short septa b) dense, spongoid consisting of the tube bronchi c) divided into chambers by septa (cellular) d) alveolar, bronchial tree is present
6 29. Name the structures of the Mammals respiratory organs where the gas exchange takes place a) bronchial tree b) parabronchi c) alveoli d) bronchioles 30. The surface of Mammalians lungs in... times larger than the body surface a) 2 b) c) 1000 d) The ventilation of Mammalians lungs goes with the help of a) skin b) bronchi, pleura c) diaphragm d) intercostal muscles, diaphragm 32. One of the basic trends of the evolution of the human respiratory system is a) appearance of lung sacs b) enlargement of the gas exchange surface c) diaphragm hypoplasia d) appearance of the internal respiration 33. One of the basic trends of the evolution of the human respiratory system is a) appearance of lung sacs b) appearance of the internal respiration c) appearance of trachea d) differentiation of the respiratory tracts
7 34. One of the basic trends of the evolution of the human respiratory system is a) appearance of the additional organs of respiration b) appearance of the internal respiration c) diaphragm hypoplasia d) appearance of gills 35. Name the malformations of the human respiratory system due to phylogenetic reasons a) trachea-lung respiration b) broncho-pulmonary cysts c) double respiration d) gills respiration 36. Name the malformations of the human respiratory system due to phylogenetic reasons a) double respiration b) gills respiration c) hypoplasia of a lung d) Botallo s duct patency 37. Name the malformations of the human respiratory system due to phylogenetic reasons a) hypoplasia of a diaphragm b) Botallo s duct patency c) double respiration d) trachea-lung respiration 38. Name the malformations of the human respiratory system due to phylogenetic reasons a) oesophagotracheal fistulas b) trachea-lung respiration c) double respiration d) gills respiration
8 39. Cavities in lungs that are limited with a connective tissue membrane a) broncho-pulmonary cysts b) oesophagotracheal fistulas c) hypoplasia of a lung d) hypoplasia of a diaphragm 40. Maldevelopments of trachea and oesophagus a) broncho-pulmonary cysts b) oesophagotracheal fistulas c) hypoplasia of a lung d) hypoplasia of a diaphragm Phylogenesis of the circulatory system 1. Name the first organisms with the circulatory system a) Fishes b) Arthropoda c) Lancelet d) Annelides 2. Name one of the reasons of the circulatory system appearance a) aromorphosis b) heteromorphosis c) appearance of coelom d) ground way of living 3. Name one of the reasons of the circulatory system appearance a) heteromorphosis b) appearance of the local respiratory organs c) ground way of living d) aromorphosis 4. The circulatory system of Lancelet is
9 a) closed b) unclosed c) 3-chamber heart d) 2-chamber heart 5. The characteristic of the circulatory system of Lancelet a) 3-chamber heart b) unclosed c) 2-chamber heart d venosus f) abdominal aorta and sinus unction as a heart 6. The quantity of bronchial arteries in the Lancelet s circulatory system a) 10 b) 100 c) 6 d) 7 7. Peculiarities of structure of bronchial arteries of the Lancelet s circulatory system a) they are reduced b) start from sinus venosus c) they are branched into capillaries d) they are not branched 8. The characteristic of the circulatory system of Fishes a) unclosed, 2-chamber he c) 2-chamber heart d) closed, heart is absent 9. Name the chambers of Fishes heart a) 2 atrium and a ventricle b) an atrium and 2 ventricles c) an atrium and a ventricle d) 2 atrium and 2 ventricles
10 10. Peculiarities of structure of gill arteries of the Fishes circulatory system a) reduced b) start from sinus venosus c) branched into capillaries d) not branched 11. Name the quantity of pairs of gill arteries of the Fishes circulatory system, laid in embryogenesis a) 100 b) 10 c) 8 d) Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Fishes circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis remain as sublingual and submaxillary and 4 th pairs c) 6 th and 7 th pairs d) 3 rd, 4 th, 5 th, 6 th 13. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Fishes circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the gill arteries and 4 th pairs c) 6 th and 7 th pairs d) 3 rd, 4 th, 5 th, 6 th 14. Name the Class of animals, in which the renal portal first appeared a) Lancelet b) Fishes c) Amphibia
11 d) Reptiles 15. Name the Class of animals, in which the pulmonary circulation first appeared a) Lancelet b) Fishes c) Amphibia d) Reptiles 16. The characteristic of the circulatory system of Amphibia a) unclosed, 2-chamber heart b) 3-chamber heart c) 2-chamber heart d) closed, heart is absent 17. Name the chambers of Amphibia s heart a) 2 atrium and a ventricle b) an atrium and 2 ventricles c) an atrium and a ventricle d) 2 atrium and 2 ventricles 18. Contents of blood in carotid arteries of Amphibia a) venous b) mixed c) partly mixed d) arterial 19. Contents of blood in arches of aorta of Amphibia a) venous b) mixed c) 95% arterial d) arterial 20. Contents of blood in dermo-pulmonary of Amphibia a) venous b) mixed
12 c) partly mixed d) arterial 21. Name the quantity of pairs of gill arteries of the Amphibia s circulatory system, laid in embryogenesis a) 100 b) 10 c) 7 d) Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Amphibia s circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the carotid arteries 23. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Amphibia s circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the arches of aorta 24. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Amphibia s circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the dermopulmonary arteries
13 25. Name the vessels the carotid duct in embryogenesis connects a) aorta arches b) carotid arteries c) aorta arches and dermo-pulmonary arteries d) aorta arches and carotid arteries 26. Name the vessels the Botallo s duct in embryogenesis connects a) aorta arches b) carotid arteries c) aorta arches and dermo-pulmonary arteries d) aorta arches and carotid arteries 27. The characteristic of the circulatory system of Reptiles a) closed, 2-chamber heart b) 3-chamber heart, ventricle is separated with incomplete septum c) unclosed, heart is absent d) 3-chamber heart, ventricle is separated with complete septum 28. Name the chambers of Reptiles heart a) 2 atrium and a ventricle b) an atrium and 2 ventricles c) an atrium and a ventricle d) 2 atrium and a ventricles with incomplete septum 29. Contents of blood in the right aorta arch of Reptiles a) venous b) mixed c) partly mixed d) arterial 30. Contents of blood in the left aorta arch of Reptiles a) venous
14 b) mixed c) partly mixed d) arterial 31. Contents of blood in the pulmonary arteries of Reptiles a) venous b) mixed c) partly mixed d) arterial Comment [R7]: 32. Name the quantity of pairs of gill arteries of the Reptiles circulatory system, laid in embryogenesis a) 100 b) 10 c) 7 d) Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Reptiles circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the carotid arteries 34. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Reptiles circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the arches of aorta
15 35. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Amphibia s circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the pulmonary arteries 36. The characteristic of the circulatory system of Birds a) 4-chamber heart, left arch of aorta b) 3-chamber heart c) 3-chamber heart, ventricle is separated with incomplete septum d) 4-chamber heart, right arch of aorta 37. Name the vessels of the Birds heart that start from ventricles a) right arch of aorta and pulmonary artery b) left arch of aorta and pulmonary artery c) right and left archs of aorta d) right and left archs of aorta and pulmonary artery 38. Name the quantity of pairs of gill arteries of the Birds circulatory system, laid in embryogenesis a) 100 b) 10 c) 7 d) Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Birds circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the carotid arteries
16 40. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Birds circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the right arch of aorta 41. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Birds circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the pulmonary arteries 42. The characteristic of the circulatory system of Mammalia a) 4-chamber heart, left arch of aorta b) 3-chamber heart c) 3-chamber heart, ventricle is separated with incomplete septum d) 4-chamber heart, right arch of aorta 43. Name the vessels of the Mammalia s heart that start from ventricles a) right arch of aorta and pulmonary artery b) left arch of aorta and pulmonary artery c) right and left archs of aorta d) right and left archs of aorta and pulmonary artery
17 44. Name the quantity of pairs of gill arteries of the Mammalia s circulatory system, laid in embryogenesis a) 100 b) 10 c) 7 d) Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Mammalia s circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the carotid arteries 46. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Mammalia s circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the left arch of aorta 47. Name the pairs of gill arteries of the Mammalia s circulatory system, that by the end of embryogenesis form the pulmonary arteries
18 48. One of the basic trends of the evolution of the human circulatory system is а) appearance of heart and its chambers differentiation b) the increased number of the gill arteries c) appearance of the carotid duct d) appearance of the Botallo s duct 49. One of the basic trends of the evolution of the human circulatory system is а) appearance of the carotid duct b) reduction and modification of the gill arches c) the increased number of the gill arteries d) appearance of the Botallo s duct 50. One of the basic trends of the evolution of the human circulatory system is а) appearance of the Botallo s duct b) appearance of the carotid duct c) appearance and differentiation of the pulmonary circulation d) the increased number of the gill arteries 51. Congenital failure of the main heart vessels when the left and the right arches of aorta develop a) aortic ring b) Botallo s duct patency c) development the right arch of aorta d) general arterial trunck 52. Congenital cardio-vascular system failure when the vessel connecting the aorta arch with the pulmonary artery remains a) aortic ring b) Botallo s duct patency c) development the right arch of aorta
19 d) general arterial trunck 53. Congenital cardio-vascular system failure when instead of the left arch of aorta the right one develops a) aortic ring b) Botallo s duct patency c) development the right arch of aorta d) general arterial trunck 54. Congenital cardio-vascular system failure when the spiral septum between the left arch of aorta and the pulmonary artery doesn t develop a) aortic ring b) Botallo s duct patency c) development the right arch of aorta d) general arterial trunck 55. Congenital cardio-vascular system failure when the aorta starts from the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk from the left one a) transposition of aorta and pulmonary artery b) Botallo s duct patency c) development the right arch of aorta d) general arterial trunck
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION
 Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Circulatory and Respiratory System. By: Kendall Taomoto, Czaresse Piano, and Lynn Luu
 Circulatory and Respiratory System By: Kendall Taomoto, Czaresse Piano, and Lynn Luu Content Standards 34.5 Gas exchange occurring in the respiratory system 34.1 Open and Closed circulatory systems linking
Circulatory and Respiratory System By: Kendall Taomoto, Czaresse Piano, and Lynn Luu Content Standards 34.5 Gas exchange occurring in the respiratory system 34.1 Open and Closed circulatory systems linking
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Circulatory and Respiratory
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
10.1 The Pulmonary-Circulatory System
 pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Respiration & Circulation
 Respiration & Circulation Objectives Describe the purpose of the respiratory system List & describe the structures of the respiratory system Describe the respiratory cycle, frequency, and factors that
Respiration & Circulation Objectives Describe the purpose of the respiratory system List & describe the structures of the respiratory system Describe the respiratory cycle, frequency, and factors that
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Spleen. Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum. Vessel walls. Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels. Artery elastic tissue
 Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Circulation and Respiration
 Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Circulation: Chapter 25. Cardiac Output. The Mammalian Heart Fig Right side of the heart
 Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Circulation and Gas Exchange
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
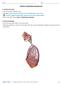 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
CHAPTER 26. Circulation and Gas Exchange
 CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Oxygen in, CO2 out circulation and respiration How animals
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Oxygen in, CO2 out circulation and respiration How animals
circ./gas ex. gas exchange chapter 44
 circ./gas ex. chapter 44 gas exchange Gas exchange (respiration?) provides O removes CO respiratory medium atmosphere is ~1% O (by volume). Pi of O = ~160mmHg Pi of CO = ~0.3 mmhg Dalton s Law higher altitudes
circ./gas ex. chapter 44 gas exchange Gas exchange (respiration?) provides O removes CO respiratory medium atmosphere is ~1% O (by volume). Pi of O = ~160mmHg Pi of CO = ~0.3 mmhg Dalton s Law higher altitudes
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe
 Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to
 1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
Chapter 42. Circulation and Gas Exchange
 Chapter 42 Circulation and Gas Exchange Overview: Trading Places Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level by crossing the plasma membrane
Chapter 42 Circulation and Gas Exchange Overview: Trading Places Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level by crossing the plasma membrane
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Nasal Cavity. The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the. (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!)
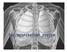 Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Animal Organs. SNC2P Biology
 Animal Organs SNC2P Biology The Hierarchy of Structure Level 5 Organism (many different organ systems working together Level 4 System (one or more organs that work together to perform a body function)
Animal Organs SNC2P Biology The Hierarchy of Structure Level 5 Organism (many different organ systems working together Level 4 System (one or more organs that work together to perform a body function)
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Oxygen in, CO2 out circulation and respiration How animals
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Oxygen in, CO2 out circulation and respiration How animals
Functions of the Circulatory System
 Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
3/26/2013. General Properties of Circulatory Systems. Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Circulation and Gas Exchange Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion time is proportional to the square of the distance Diffusion is only efficient
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Circulation and Gas Exchange Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion time is proportional to the square of the distance Diffusion is only efficient
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Class XI Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Biology
 Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Organogenesis Part 2. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm
 Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45536 1 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m45536 1 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p.
 NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Topic Page: Circulatory system
 Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Fig Gastrovascular cavity. Pharynx 2 mm. (b) A closed circulatory system. Heart. Interstitial fluid Blood Small branch vessels in each organ
 Chapter 4: Circulation and Gas Exchange AP Biology 13 1 Gas Exchange Unicellular organisms - gas exchange occurs directly with the environment Multicellular organisms - direct gas exchange is not possible
Chapter 4: Circulation and Gas Exchange AP Biology 13 1 Gas Exchange Unicellular organisms - gas exchange occurs directly with the environment Multicellular organisms - direct gas exchange is not possible
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
