Results of geometric ballistocardiography
|
|
|
- Gordon Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Results of geometric ballistocardiography D. Jezbera, J. Kříž, J. Rajsner, F. Studnička, P. Šeba Abstract Results of application of differential geometry on ballistocardiographic signals is presented. Three measurements are discussed blood pressure monitoring, pulse wave velocity monitoring and arrhythmias monitoring. Patients were measured using piezoelectric foil sensors placed under the mattress of clinical bed. Data from sensors was compared with the data from ECG and blood pressure monitor to determine the possibility of unobtrusive measurements. Few volunteers who suffer from atrial fibrillation were measured and the occurrence of arrhythmias was examined. Keywords arrhythmia, ballistocardiography, blood pressure, pulse wave velocity, unobtrusive I. INTRODUCTION EEKINGfor new unobtrusive methods of measurement of Shuman biosignals has big importance in modern medicine [1]. The blood pressure is typically measured using the inflatable strap on the arm, which pushes on the arteries. Physician can hear the pulse wave in the artery using the stethoscope and then the systolic blood pressure is set equal to the pressure in the strap at which the pulse wave stops propagating through the veins. More precise measurement can be done by injecting the pressure sensor directly in the arteries (typically into the radial artery). This sensor can continuously monitor the blood pressure over time (i.e. blood pressure variability - BPV). The first method is obtrusive, since inflating strap on the arm can cause discomfort to the patient and affect the results. Second method is invasive and can cause various harm to the patient. It is needed to find other methods of blood pressure monitoring which are unobtrusive. For this purpose we used piezoelectric foil sensors which were put under the mattress so they are in no direct contact with the patient. A signal measured by piezoelectric foil sensors is called the ballistocardiogram (BCG). The signal corresponds with small mass movements of the whole body, generated by the forces of heart contraction and by the blood evicted to large arteries (the principle of action and reaction) [2]. These movements are transferred through the mattress to the sensors. Since the blood pressure directly corresponds with the forces that are moving with the whole body [3], the amplitude of the signals must correspond with the amplitude of the blood pressure in This work was supported by the project of specific research at Faculty of Science, University of Hradec Králové, grant No. 2012/2112. F. Author is with the Department of Medical Biophysics, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, PO BOX 38, Šimkova 870, Hradec Králové, , Czech republic. S., T., F., F. Authors, arewith the Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Hradec Králové, Rokitanského 62, Hradec Králové, , Czech republic. ( filip.studnicka@uhk.cz). the beat-to-beat precission. Difficulty with BCG signal is that it strongly depends on the position of the patient on the bed and it generates a lot of artifacts caused e. g. by patient's movement or when the hospital personnel is moving around the bed. For the precise BPV measurement it is needed that the patient does not change its position on the bed. Human cardiovascular system is a branching graph consisting of aorta, aorta branching, arteries, etc., on which the pulse wave generated by the heart contraction is propagating. There is a strong correlation between the variability of the blood pressure and the pulse wave velocity [4], so time-based experiments were performed by [5]. According to the Moens- Korteweg [5] equation the pulse wave velocity (PWV) is determined by the arterial elasticity and its diameter. If we assume, that the elasticity does not change significantly during the experiment, the changes of PWV can be considered being caused by the changes of the aortal blood pressure. Relation between the blood pressure and PWV (called the Moens-Korteweg equation) is presented in [1] and [5]: where BP represents the blood pressure, PWV is the pulse wave velocity and a, b, c and d are constants dependent on the human physiology. So the relation between the pulse wave velocity and the blood pressure is exponential. Atrial fibrillation is a special type of arrhythmia. It is caused usually by problems with electrical conductivity on the heart muscle. It is very common among people over 60 years age. It is by itself dangerous only when untreated, the arrhythmia can generate precipitate which can harm the patient. Big problem with atrial fibrillation is that a lot of patients do not know that they suffer from it since it can be proven only using ECG. Unobtrusive continuous monitoring of patients in the hospital without ECG monitors can discover atrial fibrillation among patients and can save their lives. II. EXPERIMENTAL SETUP, DESCRIPTION OF HARDWARE Patients were measured on clinical bed equipped with six piezoelectric foil sensorswhich were close connected to charge amplifier. Each sensor with amplifier was stuck on a plastic ledge with length about 60 cm. These ledges were located in parallel under the mattress equidistantly 30 cm (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2). ISSN:
2 of the patients made them unable to move, so the BCG signal was affected only by the hospital personnel moving around the bed and sometimes performing basic medical actions. III. THEORY OF MEASUREMENT Fig. 1: Scheme of the measurement hardware. Fig. 2: Ledges with sensors. Signal from sensors was led to 20 bit analog-to-digital converter and then via optical fibers to receiver, which was connected to personal computer by means of USB. The usage of optical fibers guarantees galvanic isolation from the computer. The sampling frequency used was 1 khz. The measurement was done in the Resuscitation Department of the IKEM Cardiology Centre in Prague. Two diseased patients were measured on clinical beds. Both patients had their blood pressure measured using the pressure sensor stuck into radial artery and were also measured using ECG monitor. The pressure sensor and the ECG were connected to the standard hospital monitor, from which the analog signal was led to AD converter (as well as piezoelectric foil sensors) to ensure time synchronization of the signals. Each measurement lasted for 15 minutes. The health condition A. Blood pressure variablity From the BCG measurement, six signals were obtained. To achieve stronger correlation, so called euclidean monitoring function was calculated (see [6], [7] and [8]). Then typical peaks, corresponding with the cardiac cycle were found and their amplitude measured. The signal from the blood pressure sensor was analyzed and the peaks in the signal (see Fig. 3) were found. The amplitude of those peaks directly corresponds with the systolic blood pressure. Unfortunately, the autozero function of the AD converter resets the mean value of the signal to zero in random intervals. This phenomenon made us unable to derive direct equation to convert between the blood pressure (in Torr) and the amplitude of the signal (in mv). Thus auxiliary units were used in each next step of the signal processing. To ensure that the amplitude of the peaks is compared up to beat-to-beat precision, the threshold for the time diference between the peaks in pressure and monitoring function was set to 300\,ms. This time difference occurs due to unsharp edge of the peaks in monitoring function and also because of the variability in the mechanical response to the heartbeat. After calculation of the amplitudes, two time series were made. First time series was the series of amplitudes of the blood pressure (i.e. BPV) and second time series was the series of amplitudes of the monitoring function. %The derivatives of those two curves were calculated and then the sign of the derivative for each heart beat was derived. If the sign of the derivative is the same for both time series, it means, that the monitoring function can give us the information about the changes in the blood pressure. B. Pulse wave velocity Position of R-waves in ECG diagram were found and the time difference between corresponding (with beat-to-beat precision) peaks in blood pressure and monitoring function were compared with the amplitude of the corresponding peak of blood pressure. These times are often called pulse arrival times (PAT) [3] since it is the quantity which tells us how long does it take for the pulse to arrive to some specific point with the time of R-wave set to zero. From the Moens-Korteweg equation, the dependence of the quantity on the amplitude of blood pressure should belinear. ISSN:
3 Fig. 3: Comparison between the raw signals of ECG, blood pressure and monitoring function. Blue circles denote the position of R-wave, red circles denotes position of blood pressure maxima, black circles denotes peaks in monitoring function. C. Arrhythmias monitoring Occurrence of atrial fibrillation is associated with the decrease of blood pressure. During the phenomena the atria do not contract properly so less blood is ejected into the chambers. Also the P-wave in ECG signal is not present. Analysing the data from ECG and blood pressure it is possible to find the occurrence of arrhythmia and to compare the signals with the monitoring function. atrial fibrillation. Corresponding reaction such as pause in the heart cycle and increase or decrease of blood pressure can be also determined from the monitoring function. Using piezoelectric sensors it is thus possible to easily detect atrial fibrillation which is very important for the patients who do not know about their arrhythmias. Sex Male Age 82 years Weight 65 kg Height 170 cm Surgery aortic valve replacement for pig s valve Time after 3 days surgery Health condition Total no. of heartbeats No. of 302 heartbeats analysed Table 1: Patient 1. irregular heart action, atrial fibrillation, double aortocoronary bypass, ischemic heart disease 1114 IV. RESULTS The comparison between the amplitudes of blood pressure and monitoring function are on Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. It was not possible to use all the heart beats because the hospital personnel often performed some basic medical actions, which affects the amplitude of the monitoring function. Only heartbeats with patient lying still and no other disturbance were used. Similar patterns can be observed at various times. The correlation coefficients between the time series are 82\% for the first patient and 70\% for the second patient. The dependence of blood pressure on PWV for patient 1 is on Fig. 6. On the x-axis is the quantity $\frac{1}{p_xm_x}$, where $p_x$ is the time difference between the peak in blood pressure and R-wave in ECG and $m_x$ is the time difference between the peak in monitoring function and R- wave in ECG (see Fig. 3). The peak in monitoring function occurs later than the peak in blood pressure as it is shown on Fig. 3. This peak in monitoring function can be assigned to the movement of the whole body due to pulse absorption in the cardiovascular system. It can be seen that the autozero function reset the data three times thus making three different linear dependencies, which can be clearly distinguished. Because of this autozero function, only qualitative conclusions can be made. The dependence of blood pressure on PWV for patient 2 is on Fig. 7. On the x-axis is for comparison only the quantity $\frac{1}{p_x}$. Again, two autozero resets occured and two linear dependencies can be distinguished. Examples of arrhythmia occurrences are on Fig. 8and Fig. 9. It is clearly possible to determine the occurrence of Fig.4: Comparison between the maxima of monitoring function (black) and blood pressure (red) - Patient 1, on the x- axis is the number of heartbeats. Sex Male Age 88 years Weight 82 kg Height 168 cm Surgery aortic valve replacement for pig s valve Time after surgery 90 minutes Health condition hypertension, chronical obstruction of lungs Total no. of heartbeats 970 No. of heartbeats 659 analysed Table 2: Patient 2. ISSN:
4 Fig.5: Comparison between the maxima of monitoring function (black) and blood pressure (red) - Patient 2, on the x- axis is the number of heartbeats. Fig. 8: Detection of atrial fibrillation Patient 1. Fig. 6: The dependence of blood pressure on PWV Patient 1. Fig. 7: The dependence of blood pressure on PWV Patient 2. Fig. 9: Detection of atrial fibrillation Patient 1. V. CONCLUSION Two patients were measured using piezoelectric foil sensors placed under the mattress of the clinical bed. Data from the sensors were processed and compared with data from blood pressure sensor stucked in the radial artery of the patients. It is shown, that blood pressure variability can be measured unobtrusively using piezoelectric foil sensors with sufficient precision to monitor e.g. the immediate effect of medicine on blood pressure, but only with patient lying still on the bed. The analysis of pulse wave velocity was made using the comparison between the signals from blood pressure sensor and piezoelectric foil sensors. It is shown, that both types of signals satisfy Moens-Korteweg equation. Because these sensors can also record the position similar to R-wave, it is possible, to use piezoelectric foil sensors to monitor the changes of pulse wave velocity.finally the occurrence of atrial fibrillation was found and compared with the monitoring function. It is shown that atrial fibrillation can be also detected using piezoelectric sensors. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors are very grateful to the company Linet, Ltd. and the Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine in Prague. ISSN:
5 REFERENCES [1] E.Pinheiro, Theory and developments in an unobtrusive cardiovascular system representation: Ballistocardiography,The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, vol.4, 2010, pp [2] C. Barón, Balistocardiografo: historia de un instrumento para medir en forma indirecta el desempeno del corazon, Revista Colombiana de Cardiologia, vol.16, no.1, [3] E.Pinheiro, Non-intrusive device for real-time circulatory system assesment with advanced signal processing capabilities, Measurement Science Review, vol.10, no.5, [4] P.K.Sullivan, Passive physiological monitoring (P2M) system, U.S.Patent B1, January 10, [5] Y. Liu, C. C.Y. Poon, Y.-T. Zhang, A Hydrostatic Calibration Method for the Design of Wearable PAT-based Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices, 30th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, August 20-24, 2008 [6] J.Kříž, P. Šeba, Force plate monitoring of human hemodynamics, Nonlinear Biomedical Physics, vol. 2, no. 1, [7] F.Studnička, P. Šeba, D.Jezbera, J.Kříž, Continuous monitoring of heart rate using accelerometric sensors,35th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Conference Publications, pp , Prague, [8] D. Jezbera, J. Kříž, F. Studnička, P. Šeba, Geometric Ballistography- Vital Functions Monitoring, Recent advances in Energy, Environment, Biology and Ecology, WSEAS Transactions on Biology and Biomedicine, pp , ISSN:
Blood Pressure Determination Using Analysis of Biosignals
 Blood Pressure Determination Using Analysis of Biosignals RADIM ČÍŽ 1, MILAN CHMELAŘ 2 1 Department of Telecommunications Brno University of Technology Purkyňova 118, 612 00 Brno CZECH REPUBLIC cizr@feec.vutbr.cz,
Blood Pressure Determination Using Analysis of Biosignals RADIM ČÍŽ 1, MILAN CHMELAŘ 2 1 Department of Telecommunications Brno University of Technology Purkyňova 118, 612 00 Brno CZECH REPUBLIC cizr@feec.vutbr.cz,
EXPERIMENTS WITH BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING USING ECG AND PPG
 EXPERIMENTS WITH BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING USING ECG AND D. Špulák 1, R. Čmejla 1, V. Fabián 2 Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, 1 Department of Circuit Theory 2
EXPERIMENTS WITH BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING USING ECG AND D. Špulák 1, R. Čmejla 1, V. Fabián 2 Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, 1 Department of Circuit Theory 2
Continuous Monitoring of Blood Pressure Based on Heart Pulse Analysis
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Continuous Monitoring of Blood Pressure Based on Heart Pulse Analysis To cite this article: Valerie Tan et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1049 012062
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Continuous Monitoring of Blood Pressure Based on Heart Pulse Analysis To cite this article: Valerie Tan et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1049 012062
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure
 Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
LATEST TRENDS on SYSTEMS (Volume I) New Seismocardiographic Measuring System with Separate QRS Detection. M. Stork 1, Z. Trefny 2
 New Seismocardiographic Measuring System with Separate QRS Detection M. Stork 1, Z. Trefny 2 1 Department of Applied Electronics and Telecommunications University of West Bohemia, P.O. Box 314, 30614 Plzen,
New Seismocardiographic Measuring System with Separate QRS Detection M. Stork 1, Z. Trefny 2 1 Department of Applied Electronics and Telecommunications University of West Bohemia, P.O. Box 314, 30614 Plzen,
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG)
 PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
Medical Electronics Dr. Neil Townsend Michaelmas Term 2001 ( The story so far.
 Medical Electronics Dr Neil Townsend Michaelmas Term 2001 (wwwrobotsoxacuk/~neil/teaching/lectures/med_elec) Blood Pressure has been measured (in some way) for centuries However, clinical interpretation
Medical Electronics Dr Neil Townsend Michaelmas Term 2001 (wwwrobotsoxacuk/~neil/teaching/lectures/med_elec) Blood Pressure has been measured (in some way) for centuries However, clinical interpretation
A bioimpedance-based cardiovascular measurement system
 A bioimpedance-based cardiovascular measurement system Roman Kusche 1[0000-0003-2925-7638], Sebastian Hauschild 1, and Martin Ryschka 1 1 Laboratory of Medical Electronics, Luebeck University of Applied
A bioimpedance-based cardiovascular measurement system Roman Kusche 1[0000-0003-2925-7638], Sebastian Hauschild 1, and Martin Ryschka 1 1 Laboratory of Medical Electronics, Luebeck University of Applied
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
CARDIAC CYCLE CONTENTS. Divisions of cardiac cycle 11/13/13. Definition. Badri Paudel GMC
 CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
Heart Abnormality Detection Technique using PPG Signal
 Heart Abnormality Detection Technique using PPG Signal L.F. Umadi, S.N.A.M. Azam and K.A. Sidek Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic University
Heart Abnormality Detection Technique using PPG Signal L.F. Umadi, S.N.A.M. Azam and K.A. Sidek Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic University
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
Circulatory system of mammals
 Circulatory system of mammals Explain the cardiac cycle and its initiation Discuss the internal factors that control heart action Blood flows through the heart as a result of pressure differences Blood
Circulatory system of mammals Explain the cardiac cycle and its initiation Discuss the internal factors that control heart action Blood flows through the heart as a result of pressure differences Blood
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control. Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics
 BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Pumps A pump is a device that accepts fluid at a low pressure P 1 and outputs the
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Pumps A pump is a device that accepts fluid at a low pressure P 1 and outputs the
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Special Lecture 10/28/2012
 Special Lecture 10/28/2012 HYPERTENSION Dr. HN Mayrovitz Special Lecture 10/28/2012 Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) - Definitions ABP Review Indirect Oscillographic Method Resistance (R), Compliance (C)
Special Lecture 10/28/2012 HYPERTENSION Dr. HN Mayrovitz Special Lecture 10/28/2012 Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) - Definitions ABP Review Indirect Oscillographic Method Resistance (R), Compliance (C)
ENT 318/3 Artificial Organs
 ENT 318/3 Artificial Organs Modeling of cardiovascular system and VAD Lecturer Ahmad Nasrul bin Norali 1 What is modeling and why we need it? In designing product, sometimes we have to make sure that the
ENT 318/3 Artificial Organs Modeling of cardiovascular system and VAD Lecturer Ahmad Nasrul bin Norali 1 What is modeling and why we need it? In designing product, sometimes we have to make sure that the
Long-term Sleep Monitoring System and Long-term Sleep Parameters using Unconstrained Method
 Long-term Sleep Monitoring System and Long-term Sleep Parameters using Unconstrained Method Jaehyuk Shin, Youngjoon Chee, and Kwangsuk Park, Member, IEEE Abstract Sleep is a most important part of a human
Long-term Sleep Monitoring System and Long-term Sleep Parameters using Unconstrained Method Jaehyuk Shin, Youngjoon Chee, and Kwangsuk Park, Member, IEEE Abstract Sleep is a most important part of a human
Outline. Electrical Activity of the Human Heart. What is the Heart? The Heart as a Pump. Anatomy of the Heart. The Hard Work
 Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
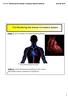 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION
 66 EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is meant by cell? UNIT I PHYSIOLOGY AND TRANSDUCERS The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood
66 EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is meant by cell? UNIT I PHYSIOLOGY AND TRANSDUCERS The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood
Estimation of Systolic and Diastolic Pressure using the Pulse Transit Time
 Estimation of Systolic and Diastolic Pressure using the Pulse Transit Time Soo-young Ye, Gi-Ryon Kim, Dong-Keun Jung, Seong-wan Baik, and Gye-rok Jeon Abstract In this paper, algorithm estimating the blood
Estimation of Systolic and Diastolic Pressure using the Pulse Transit Time Soo-young Ye, Gi-Ryon Kim, Dong-Keun Jung, Seong-wan Baik, and Gye-rok Jeon Abstract In this paper, algorithm estimating the blood
5.2. MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE
 5.2. MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE Purpose of experiment To examine a person s blood pressure. Tasks of experiment To record the pressure changes in the vascular system: using the traditional method measure
5.2. MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE Purpose of experiment To examine a person s blood pressure. Tasks of experiment To record the pressure changes in the vascular system: using the traditional method measure
Atrial Fibrillation. Why It s Important. Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23. Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com. Page 1
 Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
EVALUATION OF NONINVASIVE PULSE TRANSIT TIME METHODOLOGIES FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HYPERTENSION DANIEL JOHN BADGER. A thesis submitted to the
 EVALUATION OF NONINVASIVE PULSE TRANSIT TIME METHODOLOGIES FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HYPERTENSION by DANIEL JOHN BADGER A thesis submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick Rutgers, The State University of New
EVALUATION OF NONINVASIVE PULSE TRANSIT TIME METHODOLOGIES FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HYPERTENSION by DANIEL JOHN BADGER A thesis submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick Rutgers, The State University of New
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Method, Technology and Validity
 Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system
 Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
JAMES R. KNIGHT
 JAMES R. KNIGHT knightjr@ah.org James is currently the supervisor of clinical engineering at Sonora Regional Medical Center. He is the chairman of the CMIA Training & Education Committee. He also develops
JAMES R. KNIGHT knightjr@ah.org James is currently the supervisor of clinical engineering at Sonora Regional Medical Center. He is the chairman of the CMIA Training & Education Committee. He also develops
Author's copy - produced at Lamar University
 BLOOD PRESSURE ESTIMATION USING PHOTOPLETHYSMOGRAPHY WITH TELEMEDICINE APPLICATION (Centered, double spaced if more than one line, all capitals) (2 inches from title to A Thesis ) A Dissertation Presented
BLOOD PRESSURE ESTIMATION USING PHOTOPLETHYSMOGRAPHY WITH TELEMEDICINE APPLICATION (Centered, double spaced if more than one line, all capitals) (2 inches from title to A Thesis ) A Dissertation Presented
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Carotid and radial pulse feature analysis with EMFi sensor
 Carotid and radial pulse feature analysis with EMFi sensor Jarmo Alametsä 1, Ari Palomäki 2, Jari Viik 1 1 Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland, 2 Kanta Häme Central Hospital, Hämeenlinna,
Carotid and radial pulse feature analysis with EMFi sensor Jarmo Alametsä 1, Ari Palomäki 2, Jari Viik 1 1 Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland, 2 Kanta Häme Central Hospital, Hämeenlinna,
POWER EFFICIENT PROCESSOR FOR PREDICTING VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIA BASED ON ECG
 POWER EFFICIENT PROCESSOR FOR PREDICTING VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIA BASED ON ECG Anusha P 1, Madhuvanthi K 2, Aravind A.R 3 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Prince Shri Venkateshwara
POWER EFFICIENT PROCESSOR FOR PREDICTING VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIA BASED ON ECG Anusha P 1, Madhuvanthi K 2, Aravind A.R 3 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Prince Shri Venkateshwara
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular
 Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Stationary regime for Standing Wave Central Pattern Generator
 Stationary regime for Standing Wave Central Pattern Generator Roberto Martin-del-Campo & Edmond Jonckheere Presenter: Roberto Martin-del-Campo 3 rd IEEE Global Conference on Signal & Information Processing
Stationary regime for Standing Wave Central Pattern Generator Roberto Martin-del-Campo & Edmond Jonckheere Presenter: Roberto Martin-del-Campo 3 rd IEEE Global Conference on Signal & Information Processing
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp , , , I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System
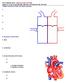 P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
Assessment of Reliability of Hamilton-Tompkins Algorithm to ECG Parameter Detection
 Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Istanbul, Turkey, July 3 6, 2012 Assessment of Reliability of Hamilton-Tompkins Algorithm to ECG Parameter
Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Istanbul, Turkey, July 3 6, 2012 Assessment of Reliability of Hamilton-Tompkins Algorithm to ECG Parameter
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Robust Detection of Atrial Fibrillation for a Long Term Telemonitoring System
 Robust Detection of Atrial Fibrillation for a Long Term Telemonitoring System B.T. Logan, J. Healey Cambridge Research Laboratory HP Laboratories Cambridge HPL-2005-183 October 14, 2005* telemonitoring,
Robust Detection of Atrial Fibrillation for a Long Term Telemonitoring System B.T. Logan, J. Healey Cambridge Research Laboratory HP Laboratories Cambridge HPL-2005-183 October 14, 2005* telemonitoring,
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012
 The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class IV
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
The Automated Defibrillator: A Biomedical Engineering Success Story. Dr. James A. Smith
 The Automated Defibrillator: A Biomedical Engineering Success Story Dr. James A. Smith A Aorta VCS Superior Vena Cava RA Right Atrium RV Right Ventricle LV Left Ventricle The Heart Beating Heart: Video
The Automated Defibrillator: A Biomedical Engineering Success Story Dr. James A. Smith A Aorta VCS Superior Vena Cava RA Right Atrium RV Right Ventricle LV Left Ventricle The Heart Beating Heart: Video
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) Volume 2, Issue 10, April 2013
 ECG Processing &Arrhythmia Detection: An Attempt M.R. Mhetre 1, Advait Vaishampayan 2, Madhav Raskar 3 Instrumentation Engineering Department 1, 2, 3, Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune, India Abstract
ECG Processing &Arrhythmia Detection: An Attempt M.R. Mhetre 1, Advait Vaishampayan 2, Madhav Raskar 3 Instrumentation Engineering Department 1, 2, 3, Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune, India Abstract
11/18/13 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN. Origin of Bioelectric Signals
 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
Testing the Accuracy of ECG Captured by Cronovo through Comparison of ECG Recording to a Standard 12-Lead ECG Recording Device
 Testing the Accuracy of ECG Captured by through Comparison of ECG Recording to a Standard 12-Lead ECG Recording Device Data Analysis a) R-wave Comparison: The mean and standard deviation of R-wave amplitudes
Testing the Accuracy of ECG Captured by through Comparison of ECG Recording to a Standard 12-Lead ECG Recording Device Data Analysis a) R-wave Comparison: The mean and standard deviation of R-wave amplitudes
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
External Oscillatory Blood Pressure - EOBPTM
 External Oscillatory Blood Pressure - EOBPTM Development of Novel Principle To Measure Blood Pressure Mindaugas Pranevicius, M.D., Osvaldas Pranevicius, M.D., Ph.D. Pranevicius Biotech Inc., Forest Hills,
External Oscillatory Blood Pressure - EOBPTM Development of Novel Principle To Measure Blood Pressure Mindaugas Pranevicius, M.D., Osvaldas Pranevicius, M.D., Ph.D. Pranevicius Biotech Inc., Forest Hills,
Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations
 ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
ECG Acquisition System and its Analysis using MATLAB
 ECG Acquisition System and its Analysis using MATLAB Pooja Prasad 1, Sandeep Patil 2, Balu Vashista 3, Shubha B. 4 P.G. Student, Dept. of ECE, NMAM Institute of Technology, Nitte, Udupi, Karnataka, India
ECG Acquisition System and its Analysis using MATLAB Pooja Prasad 1, Sandeep Patil 2, Balu Vashista 3, Shubha B. 4 P.G. Student, Dept. of ECE, NMAM Institute of Technology, Nitte, Udupi, Karnataka, India
Cardiac Cycle MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Dual-Cuff Method Improves Accuracy of Blood Pressure and Hemodynamics Determination
 Dual-Cuff Method Improves Accuracy of Blood Pressure and Hemodynamics Determination JIRI JILEK 1, MILAN STORK 2 1 Carditech, Culver City, California, USA jilekj@usa.net 2 Dept. of Applied Electronics and
Dual-Cuff Method Improves Accuracy of Blood Pressure and Hemodynamics Determination JIRI JILEK 1, MILAN STORK 2 1 Carditech, Culver City, California, USA jilekj@usa.net 2 Dept. of Applied Electronics and
Electrocardiography Biomedical Engineering Kaj-Åge Henneberg
 Electrocardiography 31650 Biomedical Engineering Kaj-Åge Henneberg Electrocardiography Plan Function of cardiovascular system Electrical activation of the heart Recording the ECG Arrhythmia Heart Rate
Electrocardiography 31650 Biomedical Engineering Kaj-Åge Henneberg Electrocardiography Plan Function of cardiovascular system Electrical activation of the heart Recording the ECG Arrhythmia Heart Rate
The correlation of AVA measured by transthoracic, transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac CT
 The correlation of AVA measured by transthoracic, transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac CT R.Petr, H.Linkova, J.Knot, E.Paskova, J.Daniel, M.Labos Cardiocenter of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady
The correlation of AVA measured by transthoracic, transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac CT R.Petr, H.Linkova, J.Knot, E.Paskova, J.Daniel, M.Labos Cardiocenter of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Lab Activity 24 EKG. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 24 EKG Reference: Dubin, Dale. Rapid Interpretation of EKG s. 6 th edition. Tampa: Cover Publishing Company, 2000. Portland Community College BI 232 Graph Paper 1 second equals 25 little boxes
Lab Activity 24 EKG Reference: Dubin, Dale. Rapid Interpretation of EKG s. 6 th edition. Tampa: Cover Publishing Company, 2000. Portland Community College BI 232 Graph Paper 1 second equals 25 little boxes
The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph
 AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
Non-Invasive Method of Blood Pressure Measurement Validated in a Mathematical Model
 Non-Invasive Method of Blood Pressure Measurement Validated in a Mathematical Model Instrumentation and Control Department, JSS Academy of Technical Education, Noida (U.P.), India Abstract- The non-invasive
Non-Invasive Method of Blood Pressure Measurement Validated in a Mathematical Model Instrumentation and Control Department, JSS Academy of Technical Education, Noida (U.P.), India Abstract- The non-invasive
ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE. CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS
 ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The ECG sensor measures electrical potentials produced by the heart (Electro- cardiogram).
ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The ECG sensor measures electrical potentials produced by the heart (Electro- cardiogram).
Development of Non-Restraint Blood Pressure Measurement Method Utilizing PWV
 Development of Non-Restraint Blood Pressure Measurement Method Utilizing PWV Yasunari Asakura School of Integrative and Global Majors, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan Email: asakura@ golem.kz.tsukuba.ac.jp
Development of Non-Restraint Blood Pressure Measurement Method Utilizing PWV Yasunari Asakura School of Integrative and Global Majors, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan Email: asakura@ golem.kz.tsukuba.ac.jp
Science in Sport. 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read. The Electrocardiogram. ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE. Sensors: Loggers: Logging time: 10 seconds
 Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
current, and acting like
 Heart 10 IV. HEART PHYSIOLOGY - How the heart beats. How the heart depolarizes the myocardium, which leads to a contraction. A) INTRINSIC CONTROL - Heart controls its own rhythm. HOW? The presence of gap
Heart 10 IV. HEART PHYSIOLOGY - How the heart beats. How the heart depolarizes the myocardium, which leads to a contraction. A) INTRINSIC CONTROL - Heart controls its own rhythm. HOW? The presence of gap
Continuous Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Using Pulse Transit Time and Photoplethysmogram Intensity Ratio
 Continuous Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Using Pulse Transit Time and Photoplethysmogram Intensity Ratio Xiao-Rong Ding, Student Member, IEEE, Yuan-Ting Zhang, Fellow, IEEE, Jing Liu, Wen-Xuan Dai,
Continuous Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Using Pulse Transit Time and Photoplethysmogram Intensity Ratio Xiao-Rong Ding, Student Member, IEEE, Yuan-Ting Zhang, Fellow, IEEE, Jing Liu, Wen-Xuan Dai,
Measuring Heart Rate and Blood Oxygen Levels for Portable and Wearable Devices
 Measuring Heart Rate and Blood Oxygen Levels for Portable and Wearable Devices By Zhang Feng, Senior Medical Applications Engineer Marten Smith, Medical Marketing Manager Medical Products Group Microchip
Measuring Heart Rate and Blood Oxygen Levels for Portable and Wearable Devices By Zhang Feng, Senior Medical Applications Engineer Marten Smith, Medical Marketing Manager Medical Products Group Microchip
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
Temporal Analysis and Remote Monitoring of ECG Signal
 Temporal Analysis and Remote Monitoring of ECG Signal Amruta Mhatre Assistant Professor, EXTC Dept. Fr.C.R.I.T. Vashi Amruta.pabarekar@gmail.com Sadhana Pai Associate Professor, EXTC Dept. Fr.C.R.I.T.
Temporal Analysis and Remote Monitoring of ECG Signal Amruta Mhatre Assistant Professor, EXTC Dept. Fr.C.R.I.T. Vashi Amruta.pabarekar@gmail.com Sadhana Pai Associate Professor, EXTC Dept. Fr.C.R.I.T.
CHAPTER 4 ESTIMATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE USING PULSE TRANSIT TIME
 64 CHAPTER 4 ESTIMATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE USING PULSE TRANSIT TIME 4.1 GENERAL This chapter presents the methodologies that are usually adopted for the measurement of blood pressure, heart rate and pulse
64 CHAPTER 4 ESTIMATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE USING PULSE TRANSIT TIME 4.1 GENERAL This chapter presents the methodologies that are usually adopted for the measurement of blood pressure, heart rate and pulse
Heart. Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat
 Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
V. Marozas 1, S. Daukantas 1, A. Petrėnas 1, A. Sološenko 1, D. Stankevičius 1, B. Paliakaitė 1, D. Jegelevičius 1, A. Lukoševičius 1, E.
 V. Marozas 1, S. Daukantas 1, A. Petrėnas 1, A. Sološenko 1, D. Stankevičius 1, B. Paliakaitė 1, D. Jegelevičius 1, A. Lukoševičius 1, E. Kaldoudi 2 1 Biomedical Engineering Institute, Kaunas University
V. Marozas 1, S. Daukantas 1, A. Petrėnas 1, A. Sološenko 1, D. Stankevičius 1, B. Paliakaitė 1, D. Jegelevičius 1, A. Lukoševičius 1, E. Kaldoudi 2 1 Biomedical Engineering Institute, Kaunas University
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System
 Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Keywords: Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Interface System (ANFIS), Electrocardiogram (ECG), Fuzzy logic, MIT-BHI database.
 Volume 3, Issue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Detection
Volume 3, Issue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Detection
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Biomedical Instrumentation
 University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Biomedical Instrumentation Electrical stimulation prof.dr.sc. Ratko Magjarević December 2015 Electrical stimulation The effect of electric
University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Biomedical Instrumentation Electrical stimulation prof.dr.sc. Ratko Magjarević December 2015 Electrical stimulation The effect of electric
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG for Hypertension Management
 Application of ICG for Hypertension Management 1mA @ 100 khz Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Non-invasive Beat-to-beat Hemodynamic Monitoring Diastole Systole Aortic valve is closed No blood flow in the aorta
Application of ICG for Hypertension Management 1mA @ 100 khz Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Non-invasive Beat-to-beat Hemodynamic Monitoring Diastole Systole Aortic valve is closed No blood flow in the aorta
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse
 Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II. Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
A Simple Portable ECG Monitor with IOT
 A Simple Portable ECG Monitor with IOT R. H. Sayyed 1, Maqdoom Farooqui 2, A. R. Khan 3 and Gulam Rabbani 4 Asso. Prof, Department of Electronic Science, Abeda Inamdar Sr. College, Pune, India 1 Principal,
A Simple Portable ECG Monitor with IOT R. H. Sayyed 1, Maqdoom Farooqui 2, A. R. Khan 3 and Gulam Rabbani 4 Asso. Prof, Department of Electronic Science, Abeda Inamdar Sr. College, Pune, India 1 Principal,
1 Non-invasive measurement of arterial pressure
 Non-invasive measurement of arterial pressure I. Background A. Circulatory systems Human circulation takes place in a closed system that consists of two subsystems, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation,
Non-invasive measurement of arterial pressure I. Background A. Circulatory systems Human circulation takes place in a closed system that consists of two subsystems, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation,
Determination of Blood Pressure and Hemodynamics from Oscillometric Waveforms
 Determination of Blood Pressure and Hemodynamics from Oscillometric Waveforms J. Jilek*, M. Stork** *Carditech, Culver City, California, USA **Department of Applied Electronics and Telecommunications University
Determination of Blood Pressure and Hemodynamics from Oscillometric Waveforms J. Jilek*, M. Stork** *Carditech, Culver City, California, USA **Department of Applied Electronics and Telecommunications University
