Case N 1. Dyspnea and cough. Right thoracic paint. AFB in sputum not yet available. Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
|
|
|
- Baldwin Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
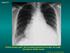
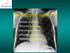
1 Case N 1 Dyspnea and cough. Right thoracic paint. AFB in sputum not yet available Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
2 Case N 1 CXR: Right abundant pleural effusion. Notice the typical concave aspect of the superior edge of the opacity (yellow arrows). Nodular infiltrate of the left superior lobe with cavity (red arrow). Tuberculosis is highly probable. The AFB should be positive in sputum because of the left cavity full of tb bacilli in communication with airways. Pleural punction is necessary for analysis ( confirmation of serofibrinous exsudative and lymphocitic reaction) and evacuation of the fluid for prevention of pleural sequela Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
3 Case N 2 Woman, 40 years old, asthenia weight loss, cough and left thoracic paint for few weeks. No sputum available. Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
4 Case N 2 Left pleural effusion. Notice the «pushing back» of the mediastinum. Probable left hilar and mediastinal adenopathies. Notice that aortic arch and descending aorta are not visible (contact with adenopathies?).bilateral diffuse nodules visible in the lung field. Probable TB. HIV context?. But carcinomatous miliary with metastatic pleural effusion is also possible. Cytology and pleural biopsy is essential for diagnosis. Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
5 Case N 3 Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
6 Case N 3 Pleural opacity of the left field, with concavity of the superior limit and pushing back of the mediastinum (no retraction= no associated atelectasis). The association with alveolar pictures and infiltrate of the right lung suggests TB. Pleural punction and biochemical and bacteriological of the fluid with Sputum analysis (AFB) is necessary for diagnosis confirmation. If possible, in case of sero-fibrinous or sero-hematic fluid, pleural biopsy with special needle should be performed, if pathologic laboratory is available. Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
7 Case N 4 Dyspnea and cough. Right thoracic paint, with disapperance of pulmonary sounds, on the right side.past history of smoking.
8 Case N 4 Chest X ray: abundant right pleural effusion. Notice the attraction of the heart and trachea on the same side than the pleural effusion, suggesting underlying atelectasis. Also notice a right mass visible in the pulmonary area, above the pleural effusion. Lymphocitic exsudative fluid. Final diagnosis is not TB. Bronchial cancer with pleural extension and underlying atelectasis
9 Case N 5 Cough and left thoracic paint for few weeks. AFB neg. In sputum
10 Case N 5 Left pleural effusion.the chest Xray is not technically correct: No normal details visible in the lung area, because of an inadequat penetration / contrast. Ther is a small retro clavicular infiltrate, higly indicative of TB infiltrate, with TB pleural effusion
11 Case N 6 Chronic exercice dyspnea with fever for several weeks. Non productive cough,and weigh loss Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
12 Case N 6 CXR:Abundant right pleural effusion. Notice the pushing back of the trachea and mediastinum: It is not an atelectasis because no retraction. Pleural punction is necessary for evacuating fluid and bateriological and bochemical analysis. If possible, in case of sero-fibrinous or serohematic fluid, pleural biopsy with special needle should be performed, if pathologic laboratory is available.if sero fibrinous fluid the most probable diagnosis is TB in high incidence TB country. Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
13 Case N 7 Woman, fever cough and left thoracic paint for several weeks. No improvment with antibiotics.. AFB negative Probable pleural effusion with attraction of the mediastinum: probable associated atelectasis
14 Case N 7 After evacuation of pleural fluid : atelectasis of the middle lobe. Notice the small infiltrate of the right axillar infiltrate. TB pleural effusion (positive pleural biopsy for tb granuloma)
15 Case N 8 Chronic exercice dyspnea for many monthes with non productive cough. AFB negative. Weigh loss and nocturnal sweet Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
16 Case N 7 Retracted opacity of the whole right lung. Notice the attraction of the trachea and the heart. This suggests a right lung atelectasis not a pleural effusion. The association with infiltrate of the left apex with localised pleural thickness is indicative of TB. The radiological aspect suggests TB sequela, because of retraction and chronic evolution, but clinical context, the notion of past complete TB treatment and sputum analysis for AFB is very important for the diagnosis of sequela or active TB Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
17 Case N 8 Woman, right thoracic pain and fever. Non productive cough.no respiratory sounds on the right side.
18 Case N 8 Chesr X ray: well limited opacity with round superior limit, edge matching with the thoracic wall: encysted pleurisy (TB, infectious non tb, or purulent ). It is necessary to make punction to go farer in diagnosis and treatment
19 Case N 8 Chest X ray after first punction Good evolution after repeted punctions(sero fibrinous effusion ) physiotherapy and anti TB treatment: Encysted tuberculous pleurisy.
20 Case N 8 January 2006 February 2006 Scan evolution of the previous case
21 Case N 9 Woman 40 years old, no medical past history, fever and chills with quick onset.
22 Case N 9 CXR: right superior acute lobar pneumonia and left inferior pneumonia with pleural effusion. Notice on the lateral view the disappearance of the left diaphragm (positive silhouette signwith pneumonia and pleural effusion).acute infectious non tb pneumonia is the most probable diagnosis, and antibiotic treatment must be quickly egaged (amoxicillin) In an other clinical context (sub acute or chronical evolution, HIV positive, no improvment with amoxicillin,) one should consider tuberculous pneumonia diagnosis
23 Case N 9 No improvment after antibiotic treatment: increasment of the left pleural effusion
24 Case N 9 Scan view of the previous case: encysted purulent pleural effusion
25 Case N 9 Improvment after thoracic drainage
26 Case N 10 Acute dyspnea, and right thoracic pain with fever and purulent sputum
27 Case N 10 Chest X ray J1: round alveolar picture with small pleural effusion. The clinical and radiological features suggest an acute round infectious pneumonia with pleural reaction
28 Case N 10 J4 after 4 days of amoxicillin. Increasment of dyspnea and worsening condition Loculated purulent pleural effusion.
29 Case N 10 J8 after thoracic drainage and antibiotic. Recovery with no more dyspnea and no more fever. Notice that sometimes pneumococcic pneumonia can be complicated with purulent pleural effusion with quick evolution and life threatening infectious complication. In this case, antibiotic is not suffisant, pleural drainage of the purulent effusion is absolutely necessary
30 Case N 11 Man, 76 years old, fever and worsening condition for Three weeks..no improvment after antibiotic Chest X ray: well limited opacity with round superior limit, edge matching with the thoracic wall: encysted pleural effusion. It is necessary to make punction to go farer in diagnosis and treatment: in this case it was a purulent effusion
31 Case N 11 Improvment after thoracic drainage (J4)
32 Case N 11 Improvment after thoracic drainage (J8)
33 Case N 12 Man, 63 years old. Cough and increasing dyspnea for 2 monthes. Past history of smoking. Flatness and decreasing of respiratory sounds on the right side.
34 Case N 12 Chest X ray: right abundant pleural effusion. Intersticial and alveolar pictures seen in the upper right lobe. Notice micronodules in the left lung. The mediastinum and heart are attracted on the right side, suggesting associated atelectasis of the right inferiror and middle lobe. Tuberculosis is possible. But in this case, it was a bronchial cancer, with pleural extension an metastatic controlateral extension.
35 Case N 12 Magnified view an scanner of the previous slide
36 Case N 13 Man,dyspnea and worsening condition. Past history of prostatic cancer. Chest x ray: abundant pleural effusion pushing back mediastinum. Punction; sero fibrinous fluid
37 Case N 13 Chest x ray of the previous case after drainage and hormonal treatment. Notice the round opacities around the thoracic wall: residual encysted pleural effusion
38 Case N 13 Scan view of the previous case: encysted pleurisy (red arrows)
39 Case N 13 Chest X ray of the previous case after 6 monthes of hormonal treatment.
40 Case N 14 Man 46 years old, cough and exercice dyspnea, tachycardia, and past history of anterior thoracic paint. ECG: myocardial ischemic signs.auscultation: crepitant rales.
41 Case N 14 CXR: cardiomegaly with left ventricle enlargment. Encysted pleural effusion in the minor fissura (red arrow). Enlargment of pulmonary arteries and alveolar diffuse pictures, with perihilar predominance: Acute. left cardiac failure, with alveolar oedema, in cardiac ischemic context. Pleural encysted effusion in scissura are frequent in left cardiac failure
42 Case N 14 Same patient after treatment: diuretic TNT and CEI. Notice the cardiac and left ventricle enlargment and the 2 right scissura well visible on the lateral view.
43 Case N 15 Man, tobacco user. Fever and cough..afb negative
44 Case N 15 Chest x ray: round opacity. Cavity on the superior part of the opacity with fluid level. Ovoïd opacity near thoracic wall: encysted pleural effusion. TB is possible, but AFB are negative which is a strong argument against this diagnosis because in case of TB, cavities are very rich in TB bacillli and sputum examinations are usually positive Finally 2 diagnosis are possible: bronchial cancer with pleural extension and bacterial abcess with pleural reaction (purulent or sero fibrinous). The 2nd hypothesis is more probable because of clinical context..
45 Case N 15 Previous case. Radiological evolution after antibiotic and pleural drainage( serofibrinous fluid)) Final diagnosis: bacterial non tb abcess with pleural reaction
46 Case N 16 Dyspnea and anterior thoracic paint.
47 Case N 16 Notice the left pleural effusion, associated with enlargment of the cardiac silhouette. This enlargment is nearly symetric between the left edge (incompletely seen) and the right one. The heart looks like a «callebasse». This is highly indicative of a pericardial effusion, associated with pleural effusion. In a context of country with high incidence of TB, the most probable diagnosis is pleural and pericardial tuberculous effusion. Diagnosis of pericardial effusion will be easily confirmed by trans thoracic echography
48 Case N 17 Man, chronic dyspnea for several monthes. Decrease of repiratory noise on the Righy side Past hystory of TB treatment. No precision about type and duration Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
49 Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg Case N 17 Technically not perfect: not strict front view: the vertical line of the spinal processes is not in the middle of the 2 internal limits of the clavicles. Nevertheless it seems that there is a retraction of the right lung with a right pleural thickness, and calcified nodules of the right inferior lobe. This suggests TB sequelae. But AFB in sputum must be found negative before diagnosis of sequela
50 Case N 18 Severe asthenia, dyspnea and cough. Auscultation: decreasing of left respiratory sounds
51 Case N 18 Diffuse opacity of the left lung like ground glass attenuation. It is not a lung opacity.it is a pleural thickness which overlap the lung; this pleural opacity is more dense in the axillar and area and lateral cul de sac, because of tangential incidence of the X ray beam. Associated alveolar picture othe superior and inferior right lobe. One important detail is that this patient is very tired and dyspneic. This CXR has probably been taken in supine position. The left picture strongly suggests a pleural effusion in supine position. Pleural punction: serofibrinous fluid.. The association with controlateral alveolar picture suggests TB. AFB must actively searched in sputum. Supine position must be indicated on the CXR by the radiological technician.
52 Case N 19 Dyspnea, cough, AFB negative in sputum. Past history of TB 6 years ago with treatment. One does not know the treatment duration and modality.
53 Case N 19 This chest X ray suggests TB sequellaes: retractile right pleural thickness (no fluid oserved at echography) calcified nodule, and calcified bilateral hilar nodes, and repeted negative sputums
54 Case N 20 Left thoracic paint increasing for 2 monthes and worsening condition With asthenia and weight loss
55 Case N 20 Mesothelioma; Notice the pleural effusion and the pleural irregular thickness in the left axillar and apex pleural area, suggesting tumor process.it can suggest primary pleural cancer (mesothelioma ) or metastatic process TB pleural effusion is also possible in such CXR. If possible pleural biopsy could facilitate the diagnosis.
56 Case N 20 Same patient after one year of evolution; the pleural tumor process has increased Of course no improvment with tb treatyment which has been instaured on the beginning of the evolution
57 Case N 21 Woman, right lateral thoracic paint, weight loss and asthenia.no cough, no fever, no sputum
58 Case N 21 Right inferior, non systematised and non homogenous opacity. The important detail is the disappearance of the middle arch of the 9th rib. This strongly suggests malignant tumor, probably metastatic. TB pulmonary or pleural infection does not destroy thoracic wall : TB is very improbable
59 Case N 21 Previous case: notice the disappearance of the middle arch of the 9th rib wich is more visible on a specific x ray for bone density with oblic incidence.
60 Case N 22 Man,70 years old, heavy smoker. Worsening condition for few monthes with left scapular and back pain.
61 Case N 22 Chest X ray: big round and homogenous opacity in the left upper lobe. No cavity in the opacity; This is not consistent for TB diagnosis (no cavity in a mass bigger than 3 cm) or for acute infectious disease (no infectious clinical context). Take notice of the disapearance of the posterior arch of the 2nd 3rd and 4th rib: This strongly suggests a malignant tumor wich has destroyed a part of the thoracic wall. TB is impossible in this case (no excavation ans oteolysis of the ribs, which is not compatible with tuberculous pneumonia ).
62 Case N 22 Magnified view of the previous slide.: the 2nd, 3rd and 4th posterior arch of the ribs have diseappered
63 Case N 23 Young child with respiratory failure. Bulky mass in the left lung, pushing off the mediastinum. Notice the destruction of the third rib, medium arch, which confirms the diagnosis of probable malignant tumor Courtesy Dr L. Kalisa-Rwanda
64 Case N 24 Man, 23 years old, right thoracic paint and dyspnea with quick onset No lung disease past history
65 Case N 24 CXR: right pneumothorax. Notice the position of the mediastinum which is pushed on the opposite side at expiration.
66 Case N 25 Fever cough dyspnea for several weeks. Left thoracic paint and increasing dyspnea with quick onset
67 Case N 25 Association of right superior lobe infiltrate and left pneumothorax. Tuberculosis (no producting cough, so AFB neg ) TB treatment must be instaured and thoracic tube must be quickly introduce in the left pleural cavity with continuous aspiration to try to bring back the lung to the thoracic wall. If the pneumothorax is long standing with important lung destruction and with important fistula between lung and pleural cavity, the drainage will not be efficient. That is why in case of tuberculous pneumothorax, thoracic drainage must be realised as soon as possible
68 Case N 26 Man 60 years old. Worsening condition,with asthenia and weight loss for many monthes. Purulent right pleural effusion with AFB in fluid.
69 Case N 26 Chest X ray: chronic tuberculous hydropneumothorax, caused by tuberculous cavity in sub pleural area, which has ruptured in pleural cavity. Thoracic continuous drainage will be probably not efficient because old and important ltb lesions in the right lung. The pronostic is bad even with TB treatment, unless if thoracic surgery is possible ( thoracoplasty)
70 Case N 27 Fever, cough and dyspnea.
71 Case N 27 Chest xray: complex opacity of the left lung with fluid level. Encysted pleurisy or pulmonary abcess? Lateral view gives the answer: the dimension of the fluid level is not the same on the front view and the lateral view:. the fluid level is in the pleural cavity: encysted purulent pleurisy with pyopneumothorax. Pleural drainage is necessary for recovery.
72 Case N 27 Scan view of the previous case: encysted pleural effusion with fluid level
73 Case N 28 Fever right thoracic pain and abundant purulent sputum.
74 Case N 28 Chest X ray: round bulky excavated picture: Bacterial non tb abcess. Notice the same dimension of the fluid level on the front and the lateral view: the opacity is in the lung (different from the case n 27). The opacity is in the lung and grows like a sphere. So the dimension of the section materialised by the fluid level has the same dimension on the front view and the lateral view.
75 Case N 29 Man, 5O years old, fever cough, with quick onset, and left thoracic paint
76 Case N 29 CXR: encysted pleural effusion with 2 different collection. Ponction: purulent fluid: encysted purulent pleural effusion
77 Case N 28 Improvment after thoracic drainage with left inferior thoracic sequella
78 Case N 30 Man,80 years old, heavy smoker, right scapular paint and worsening condition CXR: Right thoracic opacity with destruction of posterior arch of the 3rd 4th and 5th rib. This opacity is not a lung opacity neither pleural one : it is a parietal opacity: probable parietal extension of a bronchial cancer. In this case the diagnostic of TB is highly improbable: no excavation in this bulky opacity, rib destruction.. Notice 2 others round opacities in the inferior lobe suggesting metastasis.
Case N 1. Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds. Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania
 Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Man 70 years old, chronic chonic exercice dyspnea, and past history of HTA. Acute and severe dyspnea, with non purulent sputum.
 Chapter 7 Man 70 years old, chronic chonic exercice dyspnea, and past history of HTA. Acute and severe dyspnea, with non purulent sputum. Auscultation: crepitant bilateral rales. Chest Xray: cardiomegaly
Chapter 7 Man 70 years old, chronic chonic exercice dyspnea, and past history of HTA. Acute and severe dyspnea, with non purulent sputum. Auscultation: crepitant bilateral rales. Chest Xray: cardiomegaly
Man, 65 years old, heavy smoker, cough, dyspnea and weight loss. AFB negative in sputum. Is TB possible?
 Chapter 10 Man, 65 years old, heavy smoker, cough, dyspnea and weight loss. AFB negative in sputum. Is TB possible? The opacity of the left upper lobe is not cavited and looks like a tissular mass, not
Chapter 10 Man, 65 years old, heavy smoker, cough, dyspnea and weight loss. AFB negative in sputum. Is TB possible? The opacity of the left upper lobe is not cavited and looks like a tissular mass, not
I particularly want to thank: -Pr Pierre L Her who has been my nearest partner in this adventure which began in Cambodia many years ago.
 Introduction and advices for users: CXR interpretation in TB/HIV high burden settings Clinical and radiological cases for training to positive and differential diagnosis Here are collected 144 clinical
Introduction and advices for users: CXR interpretation in TB/HIV high burden settings Clinical and radiological cases for training to positive and differential diagnosis Here are collected 144 clinical
Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy
 Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Pleural effusion: Findings of fluid between
Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Pleural effusion: Findings of fluid between
Pleural syndrome. Tubercular pleurisy
 Pleural syndrome. Tubercular pleurisy Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) Pleurisy: Findings of fluid between visceral
Pleural syndrome. Tubercular pleurisy Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) Pleurisy: Findings of fluid between visceral
Key messages. CXR interpretation in TB/HIV setting. Training course
 Key messages CXR interpretation in TB/HIV setting Training course Normal CXR Front view and lateral view Good notions of technical conditions to obtain a good CXR Good knowledge of criteria for quality
Key messages CXR interpretation in TB/HIV setting Training course Normal CXR Front view and lateral view Good notions of technical conditions to obtain a good CXR Good knowledge of criteria for quality
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Interstitial syndrome
 Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
Interstitial Syndrome Ground glass attenuation miliary and nodular images Linear images
 Interstitial Syndrome Ground glass attenuation miliary and nodular images Linear images Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology
Interstitial Syndrome Ground glass attenuation miliary and nodular images Linear images Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology
Pulmonary TB aspects
 Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Cardio-vascular syndrome. Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
 Cardio-vascular syndrome Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Left pulmonary artery Right pulmonary artery OFCP Left
Cardio-vascular syndrome Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Left pulmonary artery Right pulmonary artery OFCP Left
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Radiological syndroms. Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome
 Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Alveolar condensation syndrome
 Alveolar condensation syndrome Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) Lobule: morphological unit. Dimension: 10 to
Alveolar condensation syndrome Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) Lobule: morphological unit. Dimension: 10 to
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
CARDIO-VASCULAR SYNDROME
 CARDIO-VASCULAR SYNDROME Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) OFCP Right pulmonary artery Left pulmonary artery
CARDIO-VASCULAR SYNDROME Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) OFCP Right pulmonary artery Left pulmonary artery
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
X-Rays. Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady
 X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai
 Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
and localized ground glass opacities, or bronchiolar focal or multifocal micronodules;
 E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Let s Talk TB A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year
 A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Thoracic Imaging: A Case of Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Unknown Primary
 January 28, 2009 Thoracic Imaging: A Case of Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Unknown Primary Kristina Mirabeau-Beale, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda Introduce Patient RS Discuss
January 28, 2009 Thoracic Imaging: A Case of Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Unknown Primary Kristina Mirabeau-Beale, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda Introduce Patient RS Discuss
FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS
 FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS PART I QUALITY ASSESSMENT 1 PATIENT-DEPENDENT FACTORS 3 REVIEW OF IMPORTANT ANATOMY 7 LUNGS AND PLEURA 11 DIAPHRAGMS 13 BONES AND SOFT TISSUES 14 A BRIEF LOOK
FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS PART I QUALITY ASSESSMENT 1 PATIENT-DEPENDENT FACTORS 3 REVIEW OF IMPORTANT ANATOMY 7 LUNGS AND PLEURA 11 DIAPHRAGMS 13 BONES AND SOFT TISSUES 14 A BRIEF LOOK
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3
 Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Objectives. What is a Chest X Ray? CXR Workshop. Definition (diagnostic tool/internal PE) Types. Cost
 Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Approach to CXR. Terminology. 1.Identification. Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow. Correct patient Correct date and time Correct examination
 Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity.
 Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Radiology of the respiratory disease
 Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Web Chapter 3. Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT
 Web Chapter 3 Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT Sarabjeet Singh, MD Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD *Eugene J. Mark, MD *James Stone, MD James H. Thrall, MD Department of Radiology and *Department
Web Chapter 3 Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT Sarabjeet Singh, MD Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD *Eugene J. Mark, MD *James Stone, MD James H. Thrall, MD Department of Radiology and *Department
Role of imaging (images) in my practice. Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases
 Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Signs in Chest Radiology
 Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
TUBERCULOSIS. By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi
 TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
Acute pneumonia Simple complement
 Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
X-rays. Dr Will Dooley
 X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
100 Chest X Rays for Study Group. by Dr. Suneet Khurana
 100 Chest X Rays for Study Group by Dr. Suneet Khurana Approach to - Chest X Ray (shadow of the viscera on a photographic plate) Gas appears Black Fat appears Dark Grey Water Appears as Light Grey Bone
100 Chest X Rays for Study Group by Dr. Suneet Khurana Approach to - Chest X Ray (shadow of the viscera on a photographic plate) Gas appears Black Fat appears Dark Grey Water Appears as Light Grey Bone
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria
 American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
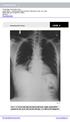 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
Radiological Features of Mycobacterium tuberculosis TUBERCULE BACILLUS TUBERCULE BACILLUS DIAGNOSIS. Guy Richards. PATHOGENESIS of TUBERCULOSIS
 Radiological Features of Guy Richards Department of critical care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa TUBERCULE BACILLUS Discovery
Radiological Features of Guy Richards Department of critical care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa TUBERCULE BACILLUS Discovery
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results
 AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p
 Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
Pleural Effusion. Exudative pleural effusion - Involve an increase in capillary permeability and impaired pleural fluid resorption
 Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer
 Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS. Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP
 APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
Interactive Lecture. Lecture 7 - Interactive. Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease. Editing File. Done By. Color Coding Important Notes Extra
 Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Lung Cancer Resection
 Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Complicated echinococcal cyst to Biopsy or not to biopsy. V. Rusanov MR Kramer Pulmonary Institute, Rabin medical center
 Complicated echinococcal cyst to Biopsy or not to biopsy V. Rusanov MR Kramer Pulmonary Institute, Rabin medical center Case 1 84 y.o. Male, Iraq descend, past smoker 40 PY Medical History- HTN, Rheumatoid
Complicated echinococcal cyst to Biopsy or not to biopsy V. Rusanov MR Kramer Pulmonary Institute, Rabin medical center Case 1 84 y.o. Male, Iraq descend, past smoker 40 PY Medical History- HTN, Rheumatoid
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Imaging of Respiratory Disorders: M2 Pathology correlated with Radiology
 Imaging of Respiratory Disorders: M2 Pathology correlated with Radiology by (c) Dr Goh Poh Sun MBBS(Melb), FRCR(UK), FAMS(Singapore), MHPE(Maastricht) Senior Consultant Radiologist and Associate Professor
Imaging of Respiratory Disorders: M2 Pathology correlated with Radiology by (c) Dr Goh Poh Sun MBBS(Melb), FRCR(UK), FAMS(Singapore), MHPE(Maastricht) Senior Consultant Radiologist and Associate Professor
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Introduction to Chest CT Interpretation. Objectives 8/28/2017
 Introduction to Chest CT Interpretation Deborah Stein ACNP BC, CCRN NP Education Specialist Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care Medicine August 28, 2017 Objectives Basic Principles Thoracic Anatomy
Introduction to Chest CT Interpretation Deborah Stein ACNP BC, CCRN NP Education Specialist Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care Medicine August 28, 2017 Objectives Basic Principles Thoracic Anatomy
Elderly Man with Dyspnoea
 Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Pneumonia, Pleurisy, Lung cancer
 Pneumonia, Pleurisy, Lung cancer Pneumonia is an infection of lung parenchyma, which leads to inflammation and exudates filling air spaces with fluid (consolidation). This leads to reduced lung compliance
Pneumonia, Pleurisy, Lung cancer Pneumonia is an infection of lung parenchyma, which leads to inflammation and exudates filling air spaces with fluid (consolidation). This leads to reduced lung compliance
X-Rays. Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM
 X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order. Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital
 Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference
 Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Pulmonary Nodules & Masses
 Pulmonary Nodules & Masses A Diagnostic Approach Heber MacMahon The University of Chicago Department of Radiology Disclosure Information Consultant for Riverain Technology Minor equity in Hologic Royalties
Pulmonary Nodules & Masses A Diagnostic Approach Heber MacMahon The University of Chicago Department of Radiology Disclosure Information Consultant for Riverain Technology Minor equity in Hologic Royalties
Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the
 Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (Thromb Haemost 2010; 103.4) Case 1 You are paged by an emergency room physician, who
Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (Thromb Haemost 2010; 103.4) Case 1 You are paged by an emergency room physician, who
Case Scenario 1. The patient agreed to a CT guided biopsy of the left upper lobe mass. This was performed and confirmed non-small cell carcinoma.
 Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Radiological staging of lung cancer. Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh
 Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP. October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18
 Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
