Symptomatic mitral myxomatous
|
|
|
- Jasper Richards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Symptomatic mitral myxomatous transformation in the elderly P. COLLINS, R. E. COTTON, and R. S. DUFF Departments of Cardiology and Pathology, City Hospital, Nottingham Thorax (1976), 31, 765. Collns, P., Cotton, R. E., and Duff, R. S. (1976). Thorax, 31, Symptomatic mitral myxomatous transformation in the elderly. The clinical and pathological features of four patients with intractable heart failure, due to myxomatous change in the mitral valve, are described. It is suggested that this change may represent a response of ageing connective tissue to mechanical stress. The integrity of the mitral valve can be impaired by a variety of pathological processes; the clinical picture depends upon the suddenness with which mitral incompetence develops and the adequacy of the circulatory adjustments (Raftery, Oakley, and Goodwin, 1966). Residual rheumatic heart disease is found in the elderly, although less commonly than in the general population; and of those with mitral valve disease two-thirds have dominant regurgitation (Caird, 1963). However, mitral incompetence should not be labelled as rheumatic without supporting evidence, as a proportion of cases result from other causes. Myxomatous (mucoid) degeneration of the mitral valve is one such condition, in which there is disruption of the normal collagenous architecture of the valve and its replacement by gelatinous material which stains metachromatically. This results in thickened, nodular, voluminous cusps which may prolapse into the left atrium during ventricular systole (Bittar and Sosa, 1968). The clinical importance of this change in the elderly became apparent following the description of two such patients in 1958 by Fernex and Fernex. Pomerance (1969) reported this change in 1% of adult necropsies, with an average age incidence of 73-6 years, but thought it to be of little clinical significance. The purpose of this paper is to describe four elderly patients who had severe and fatal mitral incompetence shown to be due to gross myxomatous change in their mitral valves. CASE REPORTS CASE 1 A 76-year-old woman was admitted to hospital with orthopnoea and interscapular pain of five days' duration. She was dyspnoeic, sweating, and cyanosed; the heart was irregular, with a ventricular rate of 104/min; the blood pressure was 140/70 mmhg. The jugular venous pressure was raised 2 cm. Auscultation revealed a protodiastolic gallop, and a harsh apical pansystolic murmur accompanied by a thrill. Rales were heard throughout both lung fields. The electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with supraventricular ectopic beats and left anterior heart block (Fig. 1). The chest radiograph showed a slight increase in the transverse diameter of the heart, without undue prominence of the left atrium in the straight film. Despite treatment with intravenous and oral frusemide, together with digitalis, she died four days after admission. At necropsy the heart weighed 340 g. There was slight dilatation of the left atrium and early left ventricular hypertrophy. The papillary muscles of the left ventricle were normal and there was no suspicion of infarction or scarring of the left ventricular myocardium. The coronary arteries showed mild atheroma but there was no occlusion. The mitral valve cusps were thickened, nodular, and opalescent. The anterior cusp was voluminous and was ballooned into the left atrium (Fig. 2). The chordae were intact. Histology of the valve cusps showed gross myxomatous change. CASE 2 A 65-year-old woman had acute dyspnoea for one week and central chest pain for some hours before admission to hospital. She was breathless, sweating, and cyanosed; the heart was regular at 120/min, and the blood pressure 160/ 90 mmhg. The jugular venous pressure was raised 4 cm and there was pitting oedema of the ankles. There was an apical pansystolic murmur, 765
2 I.. j i2 i./. :1f9, 766 P. Collins, R. E. Cotton, and R. S Dufy It L... i.s X....^... LfkJA"YT FIG. 1. The ECG of case 1 showing sinus rhythm with supraventricular extrasystoles and left anterior heartblock. accompanied by a thrill, and a protodiastolic gallop. Rales were heard throughout both lung fields. The electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm, clockwise rotation, left axis deviation, and left ventricular hypertrophy. ST segment depression was present in the standard limb leads and V5. The chest radiograph showed a moderate increase in heart size without prominence of the left atrium in the straight film. She was treated with digoxin and frusemide but died on the third day after admission. At necropsy the heart weighed 460 g and showed dilatation of the left atrium and biventricular hypertrophy. There was no macroscopic evidence of myocardial infarction or of myocardial fibrosis. The mitral valve cusps were nodular, rll'*. thickened, and opalescent. The posterior cusp was prolapsed into the left atrium. Rupture of one group of its chordae had occurred adjacent to their insertion on the papillary muscle (Fig. 3). Histology of the valve revealed gross myxomatous change. There was no evidence of significant coronary artery disease. A 67-year-old man was sent into hospital CASE 3 with cardiac failure and a history of exertional dyspnoea over the preceding three years. He was breathless and cyanosed; the heart was irregular with a ventricular rate of around 95/ min, and the blood pressure 120/80 mmhg. The jugular venous pressure was raised to the angle of the jaw and there was gross pitting oedema
3 Symptomatic mitral myxomatous transformation in the elderly FIG. 2. Case 1. The mitral valve shows ballooning of the anterior leaflet (left), which appears coarsely nodular and thickened. The posterior leaflet (right) shows similar nodularity and thickening but to a lesser degree. FIG. 3. Case 2. The posterior cusp of m.tral valve is nodular and thickened due to myxomatous change. The arrow points to the site of chordal rupture. 767
4 768 of the legs. Auscultation revealed an apical pansystolic murmur and a third heart sound. Highpitched rhonchi were heard throughout both lungs. The electrocardiogram showed atrial fibrillation, clockwise rotation, and left axis deviation. The T waves were inverted in leads I, II, and V5 to V7. The cardiac failure did not respond to intensive treatment with digoxin and frusemide, and death occurred on the eleventh day. At necropsy the heart was enlarged (600 g) and generally dilated and showed biventricular hypertrophy. The myocardium showed no evidence of fibrosis or infarction. The coronary arteries were atheromatous but there was no coronary artery occlusion. The mitral valve cusps were thickened, nodular, and opalescent but were not ballooned, and their chordae were intact (Fig. 4). There was considerable dilatation of the mitral annulus which FIG. 4. Case 3. The mitral valve leaflets have the characteristic thickened, nodular appearance of myxomatous change, but in this patient the mitral incompetence was considered to be due to dilatation of the mitral annulus. P. Collins, R. E. Cotton, and R. S Dufi admitted four fingers. Histology of the valve apparatus showed myxomatous change. CASE 4 A man of 71 gave a history of dyspnoea and ankle oedema of sudden onset three months previously. He was admitted to another hospital where he was found to have congestive heart failure and mitral incompetence. He recovered sufficiently to be discharged after three weeks. Subsequently he was admitted to the Nottingham City Hospital with a recurrence of symptoms and a history of a recent fall, which had resulted in several fractured ribs. On admission he was dyspnoeic and cyanosed; the heart was irregular at 105/min; blood pressure 120/80 mmhg. The jugular venous pressure was raised, and he had ankle oedema. There was an apical pansystolic murmur accompanied by a thrill. The lung bases were dull to percussion. The electrocardiogram showed atrial fibrillation but little else of note. The chest radiograph showed marked cardiac enlargement and bilateral pleural effusions. Despite treatment with digoxin and frusemide he died on the third day after admission. At necropsy the heart was considerably enlarged (860 g). The left atrial appendage contained antemortem thrombus. The left atrium was dilated and there was biventricular hypertrophy. The myocardium, although hypertrophied, was otherwise normal. The coronary arteries were moderately atheromatous but there was no occlusion. The mitral valve cusps were thickened, nodular, and opalescent. The posterior cusp was prolapsed into the left atrium, and a number of its chordae were ruptured. In addition, there was an anomalous insertion of the chordae on to the inferior surfaces of the cusps. Histology of the valve apparatus showed myxomatous change. The lungs showed multiple areas of infarction. DISCUSSION In none of the above patients was there a past history of rheumatic fever nor was there any postmortem evidence of chronic rheumatic heart disease, bacterial endocarditis or significant coronary artery or myocardial disease. There was no family history of cardiac disease, and none of the patients was known to have had cardiac trouble in adult life before the terminal illness. None of them showed the obvious features of Marfan's syndrome. Focal mitral myxomatous change in the elderly has been recognized for many years (Dewitzky,
5 Symptomatic mitral myxomatous transformation in the elderly 1910; Felsenreich and von Weisner, 1915; Bohmig and Kruckeberg, 1934). This localized form is not uncommon and is thought to increase in incidence with advancing years. It is more common in the posterior than the anterior cusp and is mainly confined to the distal half of the valve fibrosa (Pomerance, 1967). Focal myxomatous change per se appears to have no haemodynamic significance. The earliest reports of gross and symptomatic mitral myxomatous change have shown an association with the Marfan syndrome, often with involvement of the tricuspid and pulmonary valves (Weill, 1932; Tobin, Bay, and Humphreys, 1947; Tung and Liebow, 1952; McKusick, 1955; Sinclair, Kitchin, and Turner, 1960; Berenson and Geer, 1963; Shankar et al., 1967). Read, Thal, and Wendt (1965) designated nine cases of valvular myxomatous change as the 'floppy valve syndrome'. His patients had an age range of 15 to 49 years. Many had features or a family history of Marfan's syndrome, of which he considered this condition to be a forme fruste. Pomerance (1965) described the necropsy findings in patients over the age of 75, and compared those who had heart failure before death with those who had clinically normal hearts. Six per cent of those in failure had mitral myxomatous (mucoid) change compared with 3% in the control group. However, all those in heart failure had multiple pathological lesions which could have been significant. There is little doubt that in many patients myxomatous mitral valve changes do not produce either clinical abnormality or disturbance of cardiac function. However, our patients illustrate that at the other end of the spectrum this lesion can produce severe mitral incompetence which may be rapidly fatal. The mechanism of mitral incompetence in our patients was ruptured chordae (two), prolapse of a deformed cusp (one), and dilatation of the mitral annulus (one). Others have found associated loss of valve substance, shortening of the chordae, nodularity of the cusps, and bacterial endocarditis. The pathogenesis of mitral myxomatous change is uncertain; some authors regard it as an ageing phenomenon (Fernex and Femex, 1958), whereas Pomerance (1969) considered it to be a nonspecific change resulting from a variety of possible aetiological factors. It therefore seems that patients who have this change may be divided into two groups: (1) a younger group who have Marfan's syndrome or L 769 its forme fruste, and (2) a group of morphologically normal but older persons. Clearly, in the first group, this change cannot represent an ageing phenomenon but is presumed to be related to a developmental anomaly of the mesoderm. The mitral valve is the commonest site at which myxomatous change occurs in both groups of patients. It is also the valve which is subject to the most haemodynamic stress. One factor in the pathogenesis of myxomatous change may be the response of ageing valvular connective tissue to mechanical stress, and its premature appearance in patients who have Marfan's syndrome may reflect an increased susceptibility due to an inherent defect of connective tissue. There were no clinical features in our patients that enable this change to be distinguished during life from other causes of mitral incompetence, nor did we find specific electrocardiographic changes such as those described in relation to the mitral valve abnormalities of Marfan's syndrome (Bowers, 1969). However, this condition should be considered in the differential diagnosis of mitral incompetence in the elderly, especially if this is thought to be of recent onset and of severe degree. REFERENCES Berenson, G. S. and Geer, J. C. (1963). Heart disease in the Hurler and Marfan syndromes. Archives of Internal Medicine, 111, 58. Bittar, N. and Sosa, J. A. (1968). The billowing mitral valve leaflet. Circulation, 38, 763. Bohmig, R. and Kruckeberg, B. (1934). Untersuchungen uber die diagnostischen Schwierigkeiten bei chronischen Veranderungen der Mitralklappe. Beitrage zur pathologischen Anatomie und zur allgemeinen Pathologie, 94, 163. Bowers, D. (1969). Primary abnormalities of the mitral valve in Marfan's syndrome: electrocardiographic findings. British Heart Journal, 31, 676. Caird, F. I. (1963). Heart disease in old age. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 39, 408. Dewitzky, W. (1910). Ueber den Bau die Entstehung verschiedener Formen der chronischen Veraenderungen in den Herzklappen. Virchows Archiv fdr pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und far klinische Medizin, 199, 273. Felsenreich, G. and von Wiesner, R. (1915). Ueber Veranderungen an funktionstuchtigen Herzklappen. Frankfurter Zeitschrift fuir Pathologie, 18, 1. Fernex, M. and Fernex, C. (1958). La d6g6ndrescence mucoide des valvules mitrales; ses repercussions fonctionelles. Helvetica Medica Acta, 25, 694. McKusick, V. A. (1955). The cardiovascular aspects of Marfan's syndrome; a heritable disorder of connective tissue. Circulation, 11, 321.
6 770 Pomerance, A. (1965). Pathology of the heart with and without cardiac failure in the aged. British Heart Jotrnal, 27, 697. Pomerance, A. (1967). Ageing changes in human heart valves. British Heart Journal, 29, 222. Pomerance, A. (1969). Ballooning deformity (mucoid degeneration) of atrioventricular valves. British Heart Journal, 31, 343. Raftery, E. B., Oakley, C. M., and Goodwin, J. F. (1966). Acute subvalvar mitral incompetence. Lancet, 2, 360. Read, R. C., Thal, A. P., and Wendt, V. E. (1965). Symptomatic valvular myxomatous transformation, (the floppy valve syndrome). Circulation, 32, 897. Shankar, K. R., Hultgren, M. K., Lauer, R. M., and Diehl, A. M. (1967). Lethal tricuspid and mitral P. Collins, R. E. Cotton, and R. S Duf regurgitation in Marfan's syndrome. A merican Journal of Cardiology, 20, 122. Sinclair, R. J. G., Kitchin, A. H., and Turner, R. W. D. (1960). The Marfan syndrome. Quarterly Journal of Medicine, 29, 19. Tobin, J. R., Bay, E. B., and Humphreys, E. M. (1947). Marfan's syndrome in the adult. Archives of Internal Medicine, 80, 475. Tung, H. L. and Liebow, A. A. (1952). Marfan's syndrome. Laboratory Investigation, 1, 382. Weill, G. (1932). Ectopie des cristallins et malformations generales. Annales d'oculistique, 169, 21. Requests for reprints to: Dr. P. Collins, The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield 1. Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from on 16 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
By the end of this session, the student should be able to:
 Valvular Heart disease HVD By Dr. Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab VHD- Objectives By the end of this session, the student should be able to: Define and classify valvular heart disease. Enlist the causes of acquired
Valvular Heart disease HVD By Dr. Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab VHD- Objectives By the end of this session, the student should be able to: Define and classify valvular heart disease. Enlist the causes of acquired
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should.
 What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
Pathology of the heart in the tenth decade
 J. clin. Path. (968),, 37-3 Pathology of the heart in the tenth decade ARIELA POMERANCE' From the Department of Histopathology, Central Middlesex Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of the heart was
J. clin. Path. (968),, 37-3 Pathology of the heart in the tenth decade ARIELA POMERANCE' From the Department of Histopathology, Central Middlesex Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of the heart was
Valvular Heart Disease
 Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
CURRENT SURVEY MAX ZOOB. M.D., M.R.C.P. Consultant Cardiologist, Regional Cardiac Unit, Brook Hospital, London, S.E. 18
 Postgrad. med. J. (March 1969) 45, 180-185. CURRENT SURVEY Non-rheumatic mitral incompetence and papillary muscle dysfunction Summary Non-rheumatic mitral incompetence may be caused by a variety of conditions
Postgrad. med. J. (March 1969) 45, 180-185. CURRENT SURVEY Non-rheumatic mitral incompetence and papillary muscle dysfunction Summary Non-rheumatic mitral incompetence may be caused by a variety of conditions
Marfan s Disease: Tricuspid and Mitral Valve Insufficiency with a Normal Aortic root
 Case Reports Marfan s Disease: Tricuspid and Mitral Valve Insufficiency with a Normal Aortic root Jacques Heibig, MD, FACC, FCCP,* Charles Robinson, MD, FRCP(C) and Mohammed E. Fawzy, MB, MRCP* * Consultant
Case Reports Marfan s Disease: Tricuspid and Mitral Valve Insufficiency with a Normal Aortic root Jacques Heibig, MD, FACC, FCCP,* Charles Robinson, MD, FRCP(C) and Mohammed E. Fawzy, MB, MRCP* * Consultant
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT. Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center
 MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Mitral Valve Regurgitation Mitral Valve Stenosis Mitral Valve Prolapse MITRAL REGURGITATION
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Mitral Valve Regurgitation Mitral Valve Stenosis Mitral Valve Prolapse MITRAL REGURGITATION
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm!
 Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Mitral Valve Disease. Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna
 Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
Two semilunar valves. Two atrioventricular valves. Valves of the heart. Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve
 The Heart 3 Valves of the heart Two atrioventricular valves Two semilunar valves Right atrioventricular or tricuspid valve Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve
The Heart 3 Valves of the heart Two atrioventricular valves Two semilunar valves Right atrioventricular or tricuspid valve Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Acute aortic dissection and medial degeneration
 T7horax (1976), 31, 49. Acute aortic dissection and medial degeneration in patients with 'floppy' mitral valves ROXANE McKAY and MAGDI H. YACOUB The Cardiothoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Middlesex
T7horax (1976), 31, 49. Acute aortic dissection and medial degeneration in patients with 'floppy' mitral valves ROXANE McKAY and MAGDI H. YACOUB The Cardiothoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Middlesex
THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS
 BY From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College, and Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda Received May 11, 1959 Endomyocardial fibrosis is an important cause of heart failure in this part of Africa. The
BY From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College, and Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda Received May 11, 1959 Endomyocardial fibrosis is an important cause of heart failure in this part of Africa. The
Historical perspective R1 黃維立
 Degenerative mitral valve disease refers to a spectrum of conditions in which morphologic changes in the connective tissue of the mitral valve cause structural lesions that prevent normal function of the
Degenerative mitral valve disease refers to a spectrum of conditions in which morphologic changes in the connective tissue of the mitral valve cause structural lesions that prevent normal function of the
OUTPUT IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
 TRICUSPID INCOMPETENCE AND RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTPUT IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE BY PAUL KORNER* AND JOHN SHILLINGFORDt From the Department of Medicine, Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Received
TRICUSPID INCOMPETENCE AND RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTPUT IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE BY PAUL KORNER* AND JOHN SHILLINGFORDt From the Department of Medicine, Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Received
Mitral incompetence after repair of ostium
 Thorax (1965), 20, 40. Mitral incompetence after repair of ostium primum septal defects A. R. C. DOBELL, D. R. MURPHY, G. M. KARN, AND A. MARTINEZ-CARO From the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the
Thorax (1965), 20, 40. Mitral incompetence after repair of ostium primum septal defects A. R. C. DOBELL, D. R. MURPHY, G. M. KARN, AND A. MARTINEZ-CARO From the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Possible link with isolated aortic stenosis
 British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1006-1011 Minor congenital variations of cusp size in tricuspid aortic valves Possible link with isolated aortic stenosis F. E. M. G. VOLLEBERGH AND A. E. BECKER From the
British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1006-1011 Minor congenital variations of cusp size in tricuspid aortic valves Possible link with isolated aortic stenosis F. E. M. G. VOLLEBERGH AND A. E. BECKER From the
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic
 Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
A Case Showing Atrial Dissociation and Other Various Kinds of Arrhythmias
 A Case Showing Atrial Dissociation and Other Various Kinds of Arrhythmias Shigeru KAWAGOE, M.D., Keiichi HASHIMOTO, M.D., Hirokazu HAYAKAWA, M.D., and Eiichi KIMURA, M.D. SUMMARY A case is reported in
A Case Showing Atrial Dissociation and Other Various Kinds of Arrhythmias Shigeru KAWAGOE, M.D., Keiichi HASHIMOTO, M.D., Hirokazu HAYAKAWA, M.D., and Eiichi KIMURA, M.D. SUMMARY A case is reported in
Ostium primum defects with cleft mitral valve
 Thorax (1965), 20, 405. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Ostium primum defects are common; by 1955, 37 operated cases had been reported by
Thorax (1965), 20, 405. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Ostium primum defects are common; by 1955, 37 operated cases had been reported by
Mitral Regurgitation in a Patient with the Madan Syndrome
 Mitral Regurgitation in a Patient with the Madan Syndrome I BERNARD SEGAL, M.D.,* HRATCH KASPARIAN, M.D.,** AND WILLIAM LIKOFF, M.D., F.C.C.P,t N 1896, MARFAN DESCRIBED THE GROSS skeletal manifestations
Mitral Regurgitation in a Patient with the Madan Syndrome I BERNARD SEGAL, M.D.,* HRATCH KASPARIAN, M.D.,** AND WILLIAM LIKOFF, M.D., F.C.C.P,t N 1896, MARFAN DESCRIBED THE GROSS skeletal manifestations
Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New?
 Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New? Chronic degenerative valvular disease is the most common cardiovascular disease in small animals, and is also
Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New? Chronic degenerative valvular disease is the most common cardiovascular disease in small animals, and is also
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Semiology of the Heart in the 21 st century
 Semiology of the Heart in the 21 st century Workshop Rodrigo Salgado Dept of Radiology Antwerp University Hospital - Belgium Question The cardiothoracic index a. Is something I always mention, because
Semiology of the Heart in the 21 st century Workshop Rodrigo Salgado Dept of Radiology Antwerp University Hospital - Belgium Question The cardiothoracic index a. Is something I always mention, because
Abstract Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog
 Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation: Etiology and Natural History of Disease and Triggers for Intervention
 Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation: Etiology and Natural History of Disease and Triggers for Intervention John N. Hamaty D.O. FACC, FACOI November 17 th 2017 I have no financial disclosures Primary Mitral
Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation: Etiology and Natural History of Disease and Triggers for Intervention John N. Hamaty D.O. FACC, FACOI November 17 th 2017 I have no financial disclosures Primary Mitral
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS AND HYPERTENSION
 MITRAL STENOSIS AND HYPERTENSION IAN R. BY GRAY From University College Hospital Received April 15 1953 Hypertension is often found in cases of mitral stenosis but reports of the frequency of the association
MITRAL STENOSIS AND HYPERTENSION IAN R. BY GRAY From University College Hospital Received April 15 1953 Hypertension is often found in cases of mitral stenosis but reports of the frequency of the association
'circular shunt'1. CASE 1 Shortly after birth a 36-hour-old, full-term infant girl showed cyanosis and dyspnoea. Physical
 Pulmonary atresia with left ventricularright atrial communication: basis for 'circular shunt'1 Thorax (1966), 21, 83. KENNETH L. JUE, GEORGE NOREN, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Departments of Paediatrics
Pulmonary atresia with left ventricularright atrial communication: basis for 'circular shunt'1 Thorax (1966), 21, 83. KENNETH L. JUE, GEORGE NOREN, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Departments of Paediatrics
Valvular Heart Disease in Clinical Practice
 Valvular Heart Disease in Clinical Practice Michael Y. Henein Editor Valvular Heart Disease in Clinical Practice 123 Editor Michael Y. Henein Consultant Cardiologist Umea Heart Centre Umea University
Valvular Heart Disease in Clinical Practice Michael Y. Henein Editor Valvular Heart Disease in Clinical Practice 123 Editor Michael Y. Henein Consultant Cardiologist Umea Heart Centre Umea University
I (312) Mitral Regurgitation What Should You Know?
 Mitral Regurgitation What Should You Know? Table of Contents What is Mitral Regurgitation? 3 What are the Symptoms? 4 What are the risks? 5 Who Gets Mitral Regurgitation? 6 Diagnosing Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral Regurgitation What Should You Know? Table of Contents What is Mitral Regurgitation? 3 What are the Symptoms? 4 What are the risks? 5 Who Gets Mitral Regurgitation? 6 Diagnosing Mitral Regurgitation
SAMPLE HLTEN610A. TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank. Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment
 TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
How to Diagnose Heart Failure
 How to Diagnose Heart Failure Patrick J Gallagher 12 th November 2014 Sudden Cardiac Death Davies Criteria 1. Acute coronary event ± infarction 2. Coronary narrowing + healed infarction 3. Coronary narrowing
How to Diagnose Heart Failure Patrick J Gallagher 12 th November 2014 Sudden Cardiac Death Davies Criteria 1. Acute coronary event ± infarction 2. Coronary narrowing + healed infarction 3. Coronary narrowing
Unruptured Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm, With Dissection into the
 Case Report Unruptured Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm, With Dissection into the Interventricular Septum Udora NC, Ejim EC *, Okoye JU Department of Medicine, University of Nigeria, Teaching Hospital, Ituku-
Case Report Unruptured Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm, With Dissection into the Interventricular Septum Udora NC, Ejim EC *, Okoye JU Department of Medicine, University of Nigeria, Teaching Hospital, Ituku-
Significance and prognosis of an isolated late systolic murmur: a 9- to 22-year follow-up'
 British Heart_Journal, I974, 36, 525-532. Significance and prognosis of an isolated late systolic murmur: a 9- to 22-year follow-up' Howard Allen, Alan Harris, and Aubrey Leatham From St. George's Hospital,
British Heart_Journal, I974, 36, 525-532. Significance and prognosis of an isolated late systolic murmur: a 9- to 22-year follow-up' Howard Allen, Alan Harris, and Aubrey Leatham From St. George's Hospital,
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Shea, M.D., 2008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Shea, M.D., 2008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease
 Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease TIRONE E. DAVID, MD ; SEMIN THORAC CARDIOVASC SURG 19:116-120c 2007 ELSEVIER INC. PRESENTED BY INTERN 許士盟 Mitral valve
Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease TIRONE E. DAVID, MD ; SEMIN THORAC CARDIOVASC SURG 19:116-120c 2007 ELSEVIER INC. PRESENTED BY INTERN 許士盟 Mitral valve
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
8/31/2016. Mitraclip in Matthew Johnson, MD
 Mitraclip in 2016 Matthew Johnson, MD 1 Abnormal Valve Function Valve Stenosis Obstruction to valve flow during that phase of the cardiac cycle when the valve is normally open. Hemodynamic hallmark - pressure
Mitraclip in 2016 Matthew Johnson, MD 1 Abnormal Valve Function Valve Stenosis Obstruction to valve flow during that phase of the cardiac cycle when the valve is normally open. Hemodynamic hallmark - pressure
MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE IN
 181 MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE IN THE ELDERLY* MAXWELL L. GELFAND, M.D. New York University Medical Center New York, New York M ITRAL valve prolapse, a frequent cause of valvular disease, is known by many other
181 MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE IN THE ELDERLY* MAXWELL L. GELFAND, M.D. New York University Medical Center New York, New York M ITRAL valve prolapse, a frequent cause of valvular disease, is known by many other
Presentation, symptoms and signs of heart failure
 3 Presentation, symptoms and signs of heart failure What will I learn? In this section you will learn: Who is at risk of heart failure The symptoms of heart failure The signs of heart failure The importance
3 Presentation, symptoms and signs of heart failure What will I learn? In this section you will learn: Who is at risk of heart failure The symptoms of heart failure The signs of heart failure The importance
FIBROSIS INTRACARDIAC CALCIFICATION IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL
 INTRACARDIAC CALCIFICATION IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS BY K. SOMERS AND A. W. WILLIAMS From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College Medical School, P.O. Box 2072, Kampala, Uganda Received August 29,
INTRACARDIAC CALCIFICATION IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS BY K. SOMERS AND A. W. WILLIAMS From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College Medical School, P.O. Box 2072, Kampala, Uganda Received August 29,
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
Congenital Heart Disease Cases
 Congenital Heart Disease Cases Sabrina Phillips, MD FACC FASE Mayo Clinic Congenital Heart Disease Center 2013 MFMER slide-1 No Disclosures 2013 MFMER slide-2 1 CASE 1 2013 MFMER slide-3 63 year old Woman
Congenital Heart Disease Cases Sabrina Phillips, MD FACC FASE Mayo Clinic Congenital Heart Disease Center 2013 MFMER slide-1 No Disclosures 2013 MFMER slide-2 1 CASE 1 2013 MFMER slide-3 63 year old Woman
TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK -
 Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
RESULTING FROM BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS
 Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 415. SURGICAL CORRECTION OF MITRAL INCOMPETENCE RESULTING FROM BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS BY B. G. BARRATT-BOYES From Green Lane Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand Received March 27,
Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 415. SURGICAL CORRECTION OF MITRAL INCOMPETENCE RESULTING FROM BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS BY B. G. BARRATT-BOYES From Green Lane Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand Received March 27,
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
Mitral Valve Disease. Chapter 29
 Chapter 29 Mitral Valve Disease Thomas R. Griggs Mitral valve leaflets consist of thin, pliable, fibrous material. The two leaflets anterior and posterior open by unfolding against the ventricular wall
Chapter 29 Mitral Valve Disease Thomas R. Griggs Mitral valve leaflets consist of thin, pliable, fibrous material. The two leaflets anterior and posterior open by unfolding against the ventricular wall
Heart Disorders. Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8. Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders
 Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers MANAGEMENT
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers MANAGEMENT
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ
 CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 229-234 Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis A. M. LEAK,' M. W. MILLAR-CRAIG,2 AND BARBARA M. ANSELL1 From the 'Juvenile Rheumatism Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 229-234 Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis A. M. LEAK,' M. W. MILLAR-CRAIG,2 AND BARBARA M. ANSELL1 From the 'Juvenile Rheumatism Unit,
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1982) 58, 257-263 PAPERS Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation resulting from myocardial infarction ROBERT M. DONALDSON M.R.C.P.
Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1982) 58, 257-263 PAPERS Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation resulting from myocardial infarction ROBERT M. DONALDSON M.R.C.P.
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
DISCLOSURE. Echocardiography in Systemic Diseases: Questions. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None 5/7/2018
 Echocardiography in Systemic Diseases: Questions Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echocardiography Associate
Echocardiography in Systemic Diseases: Questions Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echocardiography Associate
Mitral Valve Disease, When to Intervene
 Mitral Valve Disease, When to Intervene Swedish Heart and Vascular Institute Ming Zhang MD PhD Interventional Cardiology Structure Heart Disease Conflict of Interest None Current ACC/AHA guideline Stages
Mitral Valve Disease, When to Intervene Swedish Heart and Vascular Institute Ming Zhang MD PhD Interventional Cardiology Structure Heart Disease Conflict of Interest None Current ACC/AHA guideline Stages
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Differentiation of Ventricular Tachycardia from Junctional Tachycardia with Aberrant Conduction
 Differentiation of Ventricular Tachycardia from Junctional Tachycardia with Aberrant Conduction The Use of Competitive Atrial Pacing By ROBERT M. EASLEY, JR., M.D., AND SIDNEY GOLDSTEIN, M.D. SUMMARY A
Differentiation of Ventricular Tachycardia from Junctional Tachycardia with Aberrant Conduction The Use of Competitive Atrial Pacing By ROBERT M. EASLEY, JR., M.D., AND SIDNEY GOLDSTEIN, M.D. SUMMARY A
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Valve Analysis and Pathoanatomy: THE MITRAL VALVE
 : THE MITRAL VALVE Marc R. Moon, M.D. John M. Shoenberg Chair in CV Disease Chief, Cardiac Surgery Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO Secretary, American Association for Thoracic Surgery
: THE MITRAL VALVE Marc R. Moon, M.D. John M. Shoenberg Chair in CV Disease Chief, Cardiac Surgery Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO Secretary, American Association for Thoracic Surgery
RUPTURED AORTIC VALVE WITH MYCOTIC
 RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Saluki heart pathology study
 Heart conditions by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, Autumn-Winter 2001 For the last decade I have been involved in Saluki heart research. Ouroriginalgoalwastoexaminethe incidence
Heart conditions by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, Autumn-Winter 2001 For the last decade I have been involved in Saluki heart research. Ouroriginalgoalwastoexaminethe incidence
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
CH; Multiple-choice questions. Cardiology questions for the MRCP (UK) examination QUESTION 4. Mark Appleby, Derek Rowlands QUESTION 1 QUESTION 3
 Postgrad MedJ7 1998;74:643-648 ) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1998 Multiple-choice questions Yorkshire Heart Centre, Leeds LS1 3EX, UK M Appleby Manchester Heart Centre, Manchester M13 9WL,
Postgrad MedJ7 1998;74:643-648 ) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1998 Multiple-choice questions Yorkshire Heart Centre, Leeds LS1 3EX, UK M Appleby Manchester Heart Centre, Manchester M13 9WL,
Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias
 Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias caused by: 1.Ectopic focus: Extrasystole or premature beat. If discharge is occasional. Can be: Atrial Extrasystole Vevtricular Extrasystole 2.Cardiac Arrhythmia
Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias caused by: 1.Ectopic focus: Extrasystole or premature beat. If discharge is occasional. Can be: Atrial Extrasystole Vevtricular Extrasystole 2.Cardiac Arrhythmia
Heart sounds and murmurs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct
 Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Case 1. Case 2. Case 3
 Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
PROGRESS IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY. Congenital Mitral Stenosis and Mitral Insufficiency
 PROGRESS IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY Congenital Mitral Stenosis and Mitral Insufficiency GEORGE W. B. STARKEY, M.D.* Boston, Massachusetts CONGENITAL MITRAL STENOSIS AND mitral insufficiency are rare, particularly
PROGRESS IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY Congenital Mitral Stenosis and Mitral Insufficiency GEORGE W. B. STARKEY, M.D.* Boston, Massachusetts CONGENITAL MITRAL STENOSIS AND mitral insufficiency are rare, particularly
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
DISSECTING ANEURYSM OF THE INTERVENTRICULAR SEPTUM*
 DISSECTING ANEURYSM OF THE INTERVENTRICULAR SEPTUM* Bernheim (1910, 1915) first drew attention to the occurrence of right heart failure as a result of mechanical obstruction produced by bulging of a hypertrophied
DISSECTING ANEURYSM OF THE INTERVENTRICULAR SEPTUM* Bernheim (1910, 1915) first drew attention to the occurrence of right heart failure as a result of mechanical obstruction produced by bulging of a hypertrophied
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
What is Your Diagnosis?
 What is Your Diagnosis? A STORM R Dulgheru, Liege, Belgium Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. Case presentation 52 years old male Ongoing oppressive chest
What is Your Diagnosis? A STORM R Dulgheru, Liege, Belgium Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. Case presentation 52 years old male Ongoing oppressive chest
ADVANCES IN MITRAL VALVE DISEASE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ADVANCES IN MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Author : Gemma Hopkins Categories : Vets Date : June 1, 2009 Gemma Hopkins relates an informative
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ADVANCES IN MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Author : Gemma Hopkins Categories : Vets Date : June 1, 2009 Gemma Hopkins relates an informative
DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS Author : Mike Martin Categories : Vets Date : November 7, 2011 Mike Martin offers advice
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS Author : Mike Martin Categories : Vets Date : November 7, 2011 Mike Martin offers advice
ACUTE LEFT AURICULAR FAILURE
 ACUTE LEFT AURICULAR FAILURE BY CRIGHTON BRAMWELL AND A. MORGAN JONES From the Cardiographic Department, Manchester Royal Infirmary Received April 1, 1944 Various hypotheses have been advanced to account
ACUTE LEFT AURICULAR FAILURE BY CRIGHTON BRAMWELL AND A. MORGAN JONES From the Cardiographic Department, Manchester Royal Infirmary Received April 1, 1944 Various hypotheses have been advanced to account
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy. Lavanya Rai Manipal
 Peripartum Cardiomyopathy Lavanya Rai Manipal Definition - PPCM - Dilated cardiomyopathy of unknown cause resulting in cardiac failure that occurs in the peripartum period in women without any preexisting
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy Lavanya Rai Manipal Definition - PPCM - Dilated cardiomyopathy of unknown cause resulting in cardiac failure that occurs in the peripartum period in women without any preexisting
Secundum atrial septal defect associated with a cleft mitral valve'
 British Heart Journal, I973, 35, I3I5-I320. Secundum atrial septal defect associated with a cleft mitral valve' Daniel J. Goodman, and E. William Hancock From Cardiology Division, Stanford University School
British Heart Journal, I973, 35, I3I5-I320. Secundum atrial septal defect associated with a cleft mitral valve' Daniel J. Goodman, and E. William Hancock From Cardiology Division, Stanford University School
Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
Management of Congenital Aortic Stenosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 201. Management of Congenital Aortic Stenosis JOHN M. REID, ERIC N. COLEMAN, and JOHN G. STEVENSON From the University Department of Child Health; the Department
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 201. Management of Congenital Aortic Stenosis JOHN M. REID, ERIC N. COLEMAN, and JOHN G. STEVENSON From the University Department of Child Health; the Department
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: papillary muscle Trabeculae Carneae chordae tendineae
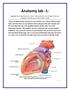 Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Δημήτρης Τσιάπρας MD FESC ΩΝΑΣΕΙΟ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΧΕΙΡΟΥΡΓΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ
 Δημήτρης Τσιάπρας MD FESC ΩΝΑΣΕΙΟ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΧΕΙΡΟΥΡΓΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Αποφυγή ισομετρικής άσκησης Χημειοπροφύλαξη Β-αναστολέα επί αισθήματος παλμών Συζήτηση περί πιθανότητας χειρουργικής επιδιόρθωσης στον κατάλληλο
Δημήτρης Τσιάπρας MD FESC ΩΝΑΣΕΙΟ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΧΕΙΡΟΥΡΓΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Αποφυγή ισομετρικής άσκησης Χημειοπροφύλαξη Β-αναστολέα επί αισθήματος παλμών Συζήτηση περί πιθανότητας χειρουργικής επιδιόρθωσης στον κατάλληλο
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Morphometric study on posterior papillary muscles of human tricuspid valve
 Morphometric study on posterior papillary muscles of tricuspid valve Original Research Article ISSN: 2394-0026 (P) Morphometric study on posterior papillary muscles of human tricuspid valve Harsha B.R.
Morphometric study on posterior papillary muscles of tricuspid valve Original Research Article ISSN: 2394-0026 (P) Morphometric study on posterior papillary muscles of human tricuspid valve Harsha B.R.
