correlated). 4. It prevents excessive cardiac dilatation.
|
|
|
- Noreen Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy of Pericardium Functions of Pericardium Pericardial disease 1. Fibrous layer 2. Serous layer: Filled with ~ 50 ml Epicardium: visceral layer that covers the heart Parietal pericardium: reflection of epicardium that covers the fibrous layer 1. It protects and lubricates the heart. 5. Distribution and equalization of hydrostatic forces on heart. 2. It minimizes friction with surroundings. 6. Diastolic coupling (diastolic pressure in two ventricles is 3. It holds it in a fixed anatomical position. correlated). 4. It prevents excessive cardiac dilatation. 7. It retards spread of infection and malignancy from surroundings. 8. It holds proximal portions of the great vessels. Pericardial Diseases Congenital absence of pericardium. Pericardial cyst. Syndromes of pericarditis Syndromes of pericarditis Etiology of of Pericarditis 7 I s: Idiopathic Infection Infarction Irradiation Immunological Iatrogenic Infiltration Pathology Presentation DD of Pericardial Rub 1. Dry 2. Constrictive 3. Adherent Infectious Post- myocardial infarction (worse prognosis) Malignant Uraemic Myxoedema Chylopericardium Autoimmune Viral (Echo, Mumps, Herpes, HIV) Bacterial (Staphylococcus, Streps) Tuberculous Acute myocardial infarction (early) Dressler s syndrome (late Primary tumours of the heart (mesothelioma) Metastatic pericarditis (breast, leukaemia,) Collagen vascular (rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic fever, SLE) Drug- induced (hydralazine, isoniazid) Post- radiation Post- surgical Post- pericardiotomy syndrome Post- traumatic Familial Idiopathic The most common cause is Idiopathic ( mostly unrecognized Viral Pathology ( Fibrinous) : bread- and- butter Diagnostic Triad: (SSI) à Chest pain+ Friction rub + ECG changes ± General constitutional symptoms FHMA (Fever, headache, malaise, anorexia) Items Symptom Chest pain (SOCRATES) Sign Friction Rub (hallmark of acute pericarditis) (PQRS) S Site Retrosternal / parasternal O Onset Over hours C Character Soreness/ ache / sharp R Radiation Shoulder / scapula / back A Association Pleuritic pain / SOB T Timing Duration / course / pattern 4. Effusion with or without tamponade. 5. Effusive- constrictive (effusion + constriction). Fungal (Histoplasmosis, Candida) Protozoal (Amoeba) Comment E Exacerbation / Lying flate / inspiration / cough / swallowing / sitting up / leaning forward Alleviating S Severity Moderate Item P Pitch High- pitched ( press with diaphragm), sitting, leaning forward, inspiration increases it Q Quality Superficial, leathery,, transient (fleeting), gallop- like, very loud rubs can be palpable R Radiation No or little radiation S Site Pulmonary area, lower left sternal edge T Timing 3 components (ventricular systole, diastole, atrial systole) nb It sounds like two pieces of sandpaper rubbed against one another. Transient, fleeting. Does not disappear on holding up respiration (DD pleurisy) Scratching Crackling (making a snapping sound) Creaking (squeak, making a harsh sound) Crunchy (making a crackly sound) Grating (making a harsh or abrasive noise) Scraping Squeaky (making short, high sound) ECG PR segment Knuckle- shaped depression & ST segment Saddle- shaped elevation PR- segment depression is virtually pathognomonic for acute pericarditis CXR Associated pleural effusion Echo/Doppler Associated pericardial effusion Echocardiography is neither sensitive nor specific for the diagnosis of acute pericarditis. Pleural rub: Stop breathing ( pleural ceases but pericardial remains). Both are heard in o Viral pleuropericarditis. o Post- myocardial infarction (Dressler's) syndrome Other causes of Lots of Noise: (SYSTOLO- DIASTOLIC MURMUR) o PDA murmur. o To- and- fro murmur of AR o Murmur of combined AS and AR. o VSD with AR. o Severe MR with high- flow diastolic rumble. 1. Symptomatic: Analgesia for pain 2. Specific: o Steroids for rheumatic diseases o Colchicine for recurrent, idiopathic form o Anti- TB with steroids
2 Hemodynamics of Pericardial Effusion Symptoms & Signs Pericardial Effusion Type Fluid Causes Transudation Water Generalized anasarca as heart failure Exudation Serofibrinous Inflammatory (all causes of pericarditis) Hemorrhagic Serous + blood TB, AMI, uremia, malignancy Suppurative Pus Pyogenic infections Hemopericardium Pure blood Trauma, rupture heart (AMI), rupture dissecting aortic aneurysm Chylopericardium Chylous Thoracic duct obstruction or injury 1. Depends on amount and rate of accumulation 2. Massive, slowly accumulating may cause no effects. 3. Small, rapidly accumulating causes an increase in intrapericardial pressure which interferes with cardiac filling causing cardiac tamponade. 4. It compresses the right side more. 1. Pain: of pericarditis or dull ache due to pericardial distension. 2. Dyspnea & orthopnea: relieved by sitting up and leaning forwards. 3. Compression of surroundings: Symptoms Cough (trachea) Dysphagia (esophagus) Hoarseness of voice (LRLN 1. General: FHMA 2. Local: (Heart) Inspection: precordial bulge in children Palpation: invisible and impalpable apex Percussion: o Increase area of cardiac dullness o Dullness in 2nd left space disappeared by sitting up (shifting dullness) Signs o Dullness outside apex o Dullness to the right of sternum o Stony dullness at lower end of sternum o Wide bare area Auscultation: o Faint and distant heart sounds o Sinus tachycardia 3. Local: (left lung) Ewart,s sign (dullness & bronchial breathing below inferior angle of left scapula) Complications 1. Cardiac tamponade. 2. Constrictive pericarditis. X- ray heart and chest. Globular or flask- shaped heart. ECG (low voltage, ST- T wave changes, electrical alternans). Echocardiography. Chemical & bacteriological study of pericardial fluid. Blood tests: viral markers, autoimmune markers, CRP, etc. X- Ray Heart and Chest Cardiomegaly Flask- shaped heart (narrow base) Acute right costo- phrenic angle Sharply defined, immobile border Normal lung vessels Decreased pulsations of cardiac borders with fluoroscopy Echocardiography Diagnostic Bedside Detect amount Guide aspiration Follow progress
3 Definition Cardiac Tamponade (Compression) Medical emergency caused by accumulation of fluid in an amount sufficient to cause serious obstruction to diastolic ventricular filling. Amount: < 200 ml when collects rapidly > 2000 ml when collects slowly causing pericardial stretching. Cardiac tamponade results in: Low COP & congestion in systemic and pulmonary veins. Pathologic Physiology Symptom and sign Clinical Diagnosis Echocardiography All symptoms of pericardial effusion. Low COP symptoms. Symptoms of systemic venous congestion. Symptom Beck,s triad: Falling arterial pressure + rising venous pressure + small, quiet heart. Seen only with acutely developing tamponade as cardiac trauma or rupture. All signs of pericardial effusion. Low COP signs: small pulse volume, hypotension, tachycardia. Signs of systemic congestion: Marked neck vein congestion Enlarged tender liver Ascites precox Sign Edema of lower limbs Pulsus paradoxus : decrease in SBP > 10 mm Hg with normal inspiration. Kaussmaul s sign = inspiratory filling of neck veins. Prominent X- descent with diminutive or absent y descent. Tetrad 1. Tachycardia 3. Distended neck veins 2. Dyspnea/tachypnea 4. Clear lungs 1. Decrease SBP Beck s triad 2. Distended neck veins 3. Distant heart sounds (Small, quiet heart) 4. Seen only with acutely developing tamponade as cardiac trauma or rupture. Tamponade is a clinical diagnosis. It shows location of effusion. Swinging heart (Like watch pendulum). RV collapse in diastole. RA collapse. It identifies the best access route for drainage. Total electrical alternans (involving P- QRS- T) is pathognomonic of cardiac tamponade. ECG Lead II in Tamponade Pre- and post- pericardiocentesis DDX Marked Cardiomegaly. Constrictive Pericarditis. 1. Specific treatment of underlying etiology. 2. Pericardiocentesis: Diagnostic/Therapeutic ( in cardiac tamponade, it is urgent) 3. Surgical: pericardiectomy or pericardio- pleural window
4 Definition Postpericardial Injury Syndrome (PPIS) Recurrent pericarditis or pericardial effusion that results from injury of the pericardium or underlying myocardium. Synonyms and causes 1. Post- pericardiotomy 2. Post- myocardial infarction syndrome (Dressler's Syndrome) 3. Traumatic (blunt, sharp, or iatrogenic) pericarditis 1. Following myocardial injury or AMI, myocardial antigens are exposed and/or released, and, in some cases, an immune complex can form. Mechanism 2. This immune activation triggers a local inflammatory reaction, and may involve remote organs such the pleura and synovia, due to molecular mimicry and immune cross- reactions. 3. The time needed for the immune reaction to develop may account for the observed latency period of 2 to 3 weeks between the AMI and the onset of DS. Clinical features Post- Infarction Pericarditis 1. Prior injury of the pericardium, myocardium, or both 2. A latent period (2-10 weeks) between the injury and the development of pericarditis or pericardial effusion 3. A tendency for recurrence 4. Responsiveness to NSAIDs and corticosteroids Usual early form Within a week. 20% of transmural myocardial infarction. Pericardial irritation by adjacent infarcted myocardium. NSAIDs: ibuprofen (increase coronary blood flow) / ASA. Steroids 5. Fever, leukocytosis, and ESR (and other markers of inflammation) 6. Pericardial and sometimes pleural effusion, with or without a pulmonary infiltrate 7. Alterations in the populations of lymphocytes in peripheral blood Late (delayed) autoimmune rxn (Dressler's Syndrome): 2 weeks- few months after infarction. Similar to postcardiotomy syndrome. Definition Etiology Pathologic Physiology Symptoms General Signs Cardiac Signs Constrictive pericarditis Thickening, fibrosis, fusion of visceral with the parietal pericardium and finally calcification which constricts the heart. It imprisons the heart. Most cases are idiopathic. Recurrent viral, bacterial, uremic. Post- cardiac surgery. Radiation. Connective tissue diseases Healing TB pericarditis ( a common cause in the past). 1. Rigid pericardium interferes with filling in late but not in early diastole. 2. Filling is reduced abruptly when the elastic limit of the pericardium is reached. 3. Nb: in cardiac tamponade, the filling is impeded throughout diastole. Resembles CHF, but not due to heart failure. Low COP symptoms. Symptoms of systemic venous congestion. Pulmonary congestive symptoms are not prominent. Acute pulmonary edema never occurs. Pulse Small volume Pulsus paradoxus Atrial fibrillation Neck veins /Abdomen Marked congestion Kussmaul,s sign Marked X- descent Deep Y- descent (Friedreich s sign) 1. Systolic retraction of apex beat and parasternal area. 2. Pericardial Knock 3. Weak heart sounds. 4. Small, quiet heart Enlarged tender liver Ascites precox Edema lower limbs Pericardial Knock Definition Sharp, loud, high- pitched, early diastolic sound. Sudden distension of ventricles against thick, rigid pericardium. Genesis It coincides with early diastolic filling. It is considered as loud S3. Causes Constrictive pericarditis. Complications Cardiac cirrhosis Atrial fibrillation Protein loosing enteropathy Marked proteinuria/ nephrotic syndrome 1. ECG: low- voltage, negative or flat T- waves, P mitrale. 2. CXR: normal or small- sized heart, calcified pericardium best seen in lateral view, clear lungs. 3. Echocardiography: 2D and Doppler (restrictive pattern). 4. MRI & CTS :pericardial thickening > 5 mm thickness. 5. Cardiac catheterization: equal pressure in all cardiac chambers, deep Y descent, square- root sign) 6. Angiography Pericardiectomy is the only definitive treatment. Medical: Salt restriction Diuretics Digitalis for AF and heart failure Anti- TB + steroids for TB
5
Pericardial diseases
 Pericardial diseases Anatomy of the pericardium Consists of parietal and visceral membranes. The space between them(pericardial space is normally filled by a lymph like fluid. The fluid s normal quantity
Pericardial diseases Anatomy of the pericardium Consists of parietal and visceral membranes. The space between them(pericardial space is normally filled by a lymph like fluid. The fluid s normal quantity
THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART
 THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate
THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate
PERICARDIAL DIAESE. Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University
 PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
Pericardial disease. Se-Jung Yoon Cardiology division NHIS Ilsan hospital
 Pericardial disease Se-Jung Yoon Cardiology division NHIS Ilsan hospital Normal pericardial effusion Normal pericardium Normal pericardium Pericardial Layers: Visceral layer Parietal layer Fibrous pericardium
Pericardial disease Se-Jung Yoon Cardiology division NHIS Ilsan hospital Normal pericardial effusion Normal pericardium Normal pericardium Pericardial Layers: Visceral layer Parietal layer Fibrous pericardium
An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
Miscellaneous Cardiology Topics pregnancy - congenital - myocarditis - pericardial disease. Pregnancy and Cardiovascular Disease MCQ
 Miscellaneous Cardiology Topics pregnancy - congenital - myocarditis - pericardial disease Maan Jokhadar, MD, FACC Emory Center for Advanced Heart Failure Therapy Emory Adult Congenital Heart Center Pregnancy
Miscellaneous Cardiology Topics pregnancy - congenital - myocarditis - pericardial disease Maan Jokhadar, MD, FACC Emory Center for Advanced Heart Failure Therapy Emory Adult Congenital Heart Center Pregnancy
10/16/2014. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular
 Hypertrophic (IHSS) Diagnosis Chest x ray cardiomegaly Electrocardiography LV hypertrophy, ST segment T was changes, Q waves in inferior & precordial leads Atrial & ventricular dysrhythmias Hypertrophic
Hypertrophic (IHSS) Diagnosis Chest x ray cardiomegaly Electrocardiography LV hypertrophy, ST segment T was changes, Q waves in inferior & precordial leads Atrial & ventricular dysrhythmias Hypertrophic
Cardiac Examination. Pediatrics Clinical Examination
 Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
Integrative Clinical Hemodyamics
 Integrative Clinical Hemodyamics James A. Goldstein, MD Director, Research & Education Division of Cardiology William Beaumont Hospital Disclosure Information Integrative Clinical Hemodyamics James A.
Integrative Clinical Hemodyamics James A. Goldstein, MD Director, Research & Education Division of Cardiology William Beaumont Hospital Disclosure Information Integrative Clinical Hemodyamics James A.
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Cath Lab Essentials: Pericardial effusion & tamponade
 Cath Lab Essentials: Pericardial effusion & tamponade Pranav M. Patel, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief, Division of Cardiology Director, Cardiac Cath Lab & CCU University of California, Irvine Division of Cardiology
Cath Lab Essentials: Pericardial effusion & tamponade Pranav M. Patel, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief, Division of Cardiology Director, Cardiac Cath Lab & CCU University of California, Irvine Division of Cardiology
Inflammatory Cardiovascular Diseases
 Inflammatory Cardiovascular Diseases Presented By: Cynthia Webner, BSN, RN, CCRN-CMC www.cardionursing.com CNEA 2009 1 Pericarditis Inflammatory process involving the visceral or parietal pericardium Multiple
Inflammatory Cardiovascular Diseases Presented By: Cynthia Webner, BSN, RN, CCRN-CMC www.cardionursing.com CNEA 2009 1 Pericarditis Inflammatory process involving the visceral or parietal pericardium Multiple
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Case Presentation- Pericarditis Author(s): Kwaku Nyame License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Case Presentation- Pericarditis Author(s): Kwaku Nyame License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of
TAMPONADE CARDIAQUE. Dr Cédrick Zaouter TUSAR 15 décembre 2015
 TAMPONADE CARDIAQUE Dr Cédrick Zaouter TUSAR 15 décembre 2015 OUTLINE History Incidence Definition Pathophysiology Aetiologies Investigations - Echocardiography Treatment of cardiac tamponade Pericardial
TAMPONADE CARDIAQUE Dr Cédrick Zaouter TUSAR 15 décembre 2015 OUTLINE History Incidence Definition Pathophysiology Aetiologies Investigations - Echocardiography Treatment of cardiac tamponade Pericardial
We are now going to review the diagnosis and management of pericardial collections and tamponade
 We are now going to review the diagnosis and management of pericardial collections and tamponade FEEL COURSE PAGE 1 Paying particular attention to the difference between a collection and cardiac tamponade
We are now going to review the diagnosis and management of pericardial collections and tamponade FEEL COURSE PAGE 1 Paying particular attention to the difference between a collection and cardiac tamponade
CARDIOLOGY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF CARDIOLOGY (2018)
 CARDIOLOGY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF CARDIOLOGY (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation in
CARDIOLOGY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF CARDIOLOGY (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation in
Cardiac tamponade and Pericardiocentesis Made Easy
 Cardiac tamponade and Pericardiocentesis Made Easy www.cardiconcept.com Etiology of pericardial diseases. Non Infectious cause Infectious cause European Heart Journal (2015) 36, 2921 2964 Recommendations
Cardiac tamponade and Pericardiocentesis Made Easy www.cardiconcept.com Etiology of pericardial diseases. Non Infectious cause Infectious cause European Heart Journal (2015) 36, 2921 2964 Recommendations
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
Acute Coronary Syndromes Unstable Angina Non ST segment Elevation MI (NSTEMI) ST segment Elevation MI (STEMI)
 Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3
 Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
Pericarditis and Myocarditis. Sheba Medical Center Cardiology Department Carlyn Wallis
 Pericarditis and Myocarditis Sheba Medical Center Cardiology Department Carlyn Wallis Outline Pericarditis Normal function of the pericardium Pathophysiology + Etiology Clinical Presentation Differential
Pericarditis and Myocarditis Sheba Medical Center Cardiology Department Carlyn Wallis Outline Pericarditis Normal function of the pericardium Pathophysiology + Etiology Clinical Presentation Differential
Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile. Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption
 Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption Chief Complaint - SOB - When asked: Increasing difficulty
Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption Chief Complaint - SOB - When asked: Increasing difficulty
Heart sounds and murmurs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct
 Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ
 CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT. Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center
 MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Mitral Valve Regurgitation Mitral Valve Stenosis Mitral Valve Prolapse MITRAL REGURGITATION
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Mitral Valve Regurgitation Mitral Valve Stenosis Mitral Valve Prolapse MITRAL REGURGITATION
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Objectives. Highlight typical feature of TB pericarditis. How to make a diagnosis. How to treat TB pericarditis
 Dr. Conteh Objectives Highlight typical feature of TB pericarditis How to make a diagnosis How to treat TB pericarditis New evidence for adjunctive corticosteroid Introduction TB pericarditis occurs in
Dr. Conteh Objectives Highlight typical feature of TB pericarditis How to make a diagnosis How to treat TB pericarditis New evidence for adjunctive corticosteroid Introduction TB pericarditis occurs in
Pericardial effusion, Cardiac Tamponade, and echo guided pericardiocentesis
 KSC 2017 Echo5- Myocardial and Pericardial disease Pericardial effusion, Cardiac Tamponade, and echo guided pericardiocentesis Ji-Hyun Jung Division of Cardiology Sejong Hospital KSC 2017 The 61 th Annual
KSC 2017 Echo5- Myocardial and Pericardial disease Pericardial effusion, Cardiac Tamponade, and echo guided pericardiocentesis Ji-Hyun Jung Division of Cardiology Sejong Hospital KSC 2017 The 61 th Annual
efferent fibers from t.. Heart Surface anatomy and heart sounds -Dry lecture -Gray s 169,
 A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
2/7/ LEAD ECG CASE STUDIES Lisa Riggs MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN-K CASE #1 WHAT ELSE WOULD YOU ASSESS? WHAT S YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
 12 LEAD ECG CASE STUDIES Lisa Riggs MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN-K CASE #1 31 y/o male is a direct admit from the physician s office with c/o chest pain and SOA WHAT ELSE WOULD YOU ASSESS? WHAT S YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
12 LEAD ECG CASE STUDIES Lisa Riggs MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN-K CASE #1 31 y/o male is a direct admit from the physician s office with c/o chest pain and SOA WHAT ELSE WOULD YOU ASSESS? WHAT S YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Dr.Kasturi Bhagawati Emergency Medicine Department
 Dr.Kasturi Bhagawati Emergency Medicine Department 16-04-2015 Introduction Chest trauma is often sudden and dramatic. Cardiac injuries can be catastrophic. Accounts for 25% of all trauma deaths 10% of
Dr.Kasturi Bhagawati Emergency Medicine Department 16-04-2015 Introduction Chest trauma is often sudden and dramatic. Cardiac injuries can be catastrophic. Accounts for 25% of all trauma deaths 10% of
Περικαρδίτιδα στην καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια
 ΣΕΜΙΝΑΡΙΑ ΟΜΑΔΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑΣ, ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΑ 2015 Περικαρδίτιδα στην καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια Γεώργιος Λάζαρος Α Πανεπιστηµιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν. Αθηνών I declare that I have no conflict of interest
ΣΕΜΙΝΑΡΙΑ ΟΜΑΔΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑΣ, ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΑ 2015 Περικαρδίτιδα στην καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια Γεώργιος Λάζαρος Α Πανεπιστηµιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν. Αθηνών I declare that I have no conflict of interest
OTOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD & NECK SURGERY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM
 OTOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD & NECK SURGERY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD & NECK SURGERY (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice
OTOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD & NECK SURGERY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD & NECK SURGERY (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice
Year 1 Peer Based Learning 2018 Cardiovascular System
 Please note this learning resource has been produced by the GUMS Academic Team. It is possible that there are some minor errors in the questions/answers, and other possible answers that are not included
Please note this learning resource has been produced by the GUMS Academic Team. It is possible that there are some minor errors in the questions/answers, and other possible answers that are not included
See below for descriptions of the waveform
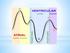 The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
PLASTIC SURGERY AND BURNS SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM
 PLASTIC SURGERY AND BURNS SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM OF PLASTIC SURGERY AND BURNS (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation in the general
PLASTIC SURGERY AND BURNS SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM OF PLASTIC SURGERY AND BURNS (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation in the general
INTERNAL MEDICINE SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE (2016)
 INTERNAL MEDICINE SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE (206) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation
INTERNAL MEDICINE SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE (206) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Pericardial Disease: Case Examples. Echo Fiesta 2017
 Pericardial Disease: Case Examples Echo Fiesta 2017 2014 2014 MFMER MFMER 3346252-1 slide-1 Objectives Have a systematic approach to evaluation of constriction 2014 MFMER 3346252-2 CASE 1 2013 MFMER 3248567-3
Pericardial Disease: Case Examples Echo Fiesta 2017 2014 2014 MFMER MFMER 3346252-1 slide-1 Objectives Have a systematic approach to evaluation of constriction 2014 MFMER 3346252-2 CASE 1 2013 MFMER 3248567-3
Valvular Heart Disease Mitral Stenosis
 Valvular Heart Disease Mitral Stenosis A 75 year old woman with loud first heart sound and mid-diastolic murmur Chronic dyspnea Class 2/4 Fatigue Recent orthopnea/pnd Nocturnal palpitation Pedal edema
Valvular Heart Disease Mitral Stenosis A 75 year old woman with loud first heart sound and mid-diastolic murmur Chronic dyspnea Class 2/4 Fatigue Recent orthopnea/pnd Nocturnal palpitation Pedal edema
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
PEDIATRICS SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF PEDIATRICS ( )
 PEDIATRICS SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF PEDIATRICS ( ) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation in the
PEDIATRICS SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF PEDIATRICS ( ) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and provide consultation in the
Pericarditis. Marquette University. James F. Ginter Aurora Cardiovascular Services
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Physician Assistant Studies, Department 4-23-2012 Pericarditis James F. Ginter Aurora Cardiovascular
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Physician Assistant Studies, Department 4-23-2012 Pericarditis James F. Ginter Aurora Cardiovascular
Normal Pericardial Physiology
 Normal Pericardial Physiology Normal pericardium contains 20-30 ml of lymphoid fluid lubricating function that facilitates normal myocardial rotation and translation during each cardiac cycle in that the
Normal Pericardial Physiology Normal pericardium contains 20-30 ml of lymphoid fluid lubricating function that facilitates normal myocardial rotation and translation during each cardiac cycle in that the
Pericardial Diseases/Tamponade Illustrative Cases
 Pericardial Diseases/Tamponade Illustrative Cases Jae K. Oh, MD Echo Hawaii 2017 2012 MFMER 3200268v3(2010)-1 Case #1 47 year old man Chest pain Not exertional Normal Examination 2016 MFMER slide-2 1 47
Pericardial Diseases/Tamponade Illustrative Cases Jae K. Oh, MD Echo Hawaii 2017 2012 MFMER 3200268v3(2010)-1 Case #1 47 year old man Chest pain Not exertional Normal Examination 2016 MFMER slide-2 1 47
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly
 Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY (2018)
 OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and
OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY SAUDI BOARD PROGRAM SAUDI BOARD FINAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY (2018) I Objectives a. Determine the ability of the candidate to practice as a specialist and
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Chest Pain. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal. Department of Medicine
 Chest Pain Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine BACKGROUND Approx 5% of all ED visits 15 % - AMI 25-30 % - Unstable angina 50-55 % - Other conditions Atypical presentations common 2% of patients
Chest Pain Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine BACKGROUND Approx 5% of all ED visits 15 % - AMI 25-30 % - Unstable angina 50-55 % - Other conditions Atypical presentations common 2% of patients
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV
 Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
SPOTLIGHT ON PERICARDIAL DISEASE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk SPOTLIGHT ON PERICARDIAL DISEASE Author : DAN FORSTER Categories : Vets Date : February 16, 2009 DAN FORSTER discusses the
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk SPOTLIGHT ON PERICARDIAL DISEASE Author : DAN FORSTER Categories : Vets Date : February 16, 2009 DAN FORSTER discusses the
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
This is a common cause of chronic pericardial
 clinical Study Tuberculous Pericardial Effusion GS SAINANI, RAJESH G SAINANI Abstract Tuberculous pericardial effusion is common in Afro-Asian countries. Since, the introduction of HIV infection, the incidence
clinical Study Tuberculous Pericardial Effusion GS SAINANI, RAJESH G SAINANI Abstract Tuberculous pericardial effusion is common in Afro-Asian countries. Since, the introduction of HIV infection, the incidence
The pericardial sac is composed of the outer fibrous pericardium
 Pericardiectomy for Constrictive or Recurrent Inflammatory Pericarditis Mauricio A. Villavicencio, MD, Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Thoralf M. Sundt, III, MD Anatomy and Preoperative Considerations The pericardial
Pericardiectomy for Constrictive or Recurrent Inflammatory Pericarditis Mauricio A. Villavicencio, MD, Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Thoralf M. Sundt, III, MD Anatomy and Preoperative Considerations The pericardial
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Pericardial effusion with emphasis on the electrocardiographic aspects By Andrés Ricardo Pérez-Riera MDPhD
 Pericardial effusion with emphasis on the electrocardiographic aspects By Andrés Ricardo Pérez-Riera MDPhD ECG In pericarditis Pericardial effusion Pericardium The pericardium is a double sheet made up
Pericardial effusion with emphasis on the electrocardiographic aspects By Andrés Ricardo Pérez-Riera MDPhD ECG In pericarditis Pericardial effusion Pericardium The pericardium is a double sheet made up
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions
 POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
Palpable Pulsus Paradoxus in the Setting of Malignant Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade Akshay Pendyal, MD
 Palpable Pulsus Paradoxus in the Setting of Malignant Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade Akshay Pendyal, MD University of Colorado Department of Internal Medicine None Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Palpable Pulsus Paradoxus in the Setting of Malignant Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade Akshay Pendyal, MD University of Colorado Department of Internal Medicine None Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University
 Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University in St. Louis Goal o To review the imaging criteria of
Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University in St. Louis Goal o To review the imaging criteria of
Chronic Pericarditis with Effusion
 Chronic Pericarditis with Effusion By PAUL S. BARKER, M. D., AND FRANKLIN D. JOHNSTON, M. D. Pericarditis with effusion is sometimes a chronic disease, an exception to the general rule that it is acute
Chronic Pericarditis with Effusion By PAUL S. BARKER, M. D., AND FRANKLIN D. JOHNSTON, M. D. Pericarditis with effusion is sometimes a chronic disease, an exception to the general rule that it is acute
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should.
 What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy
 2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
Outline. Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials
 Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
MI Acute occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery is the cause of 40% to 50% of all MIs. *
 MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Oncologic Emergencies
 Oncologic Emergencies Peter Bjerkerot RN, OCN 1339 Normandy Drive Atlanta, GA 30306-2574 404.754.5952 WebPage http://boyrn.com peter.bjerkerot@mindspring.com Full Disclosure Statement Celgene Nurse Advisory
Oncologic Emergencies Peter Bjerkerot RN, OCN 1339 Normandy Drive Atlanta, GA 30306-2574 404.754.5952 WebPage http://boyrn.com peter.bjerkerot@mindspring.com Full Disclosure Statement Celgene Nurse Advisory
A Case of Impending Cardiac Tamponade Caused by Effusive Constrictive Pericarditis
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550038 Volume 2, Issue 5 Case Report A Case of Impending Cardiac Tamponade Caused by Effusive Constrictive Pericarditis Catalina Sanchez-Alvarez
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550038 Volume 2, Issue 5 Case Report A Case of Impending Cardiac Tamponade Caused by Effusive Constrictive Pericarditis Catalina Sanchez-Alvarez
FIBROSIS INTRACARDIAC CALCIFICATION IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL
 INTRACARDIAC CALCIFICATION IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS BY K. SOMERS AND A. W. WILLIAMS From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College Medical School, P.O. Box 2072, Kampala, Uganda Received August 29,
INTRACARDIAC CALCIFICATION IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS BY K. SOMERS AND A. W. WILLIAMS From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College Medical School, P.O. Box 2072, Kampala, Uganda Received August 29,
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS. Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP
 APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
Semiology of the Heart in the 21 st century
 Semiology of the Heart in the 21 st century Workshop Rodrigo Salgado Dept of Radiology Antwerp University Hospital - Belgium Question The cardiothoracic index a. Is something I always mention, because
Semiology of the Heart in the 21 st century Workshop Rodrigo Salgado Dept of Radiology Antwerp University Hospital - Belgium Question The cardiothoracic index a. Is something I always mention, because
LeMone & Burke Ch 30-32
 LeMone & Burke Ch 30-32 2 Right side- Low oxygenation Low pressure Light workload Goes toward the lungs Left side High oxygenation Thick walled high pressure Heavier workload Carries oxygenation blood
LeMone & Burke Ch 30-32 2 Right side- Low oxygenation Low pressure Light workload Goes toward the lungs Left side High oxygenation Thick walled high pressure Heavier workload Carries oxygenation blood
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC
 Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Etiology, Classification & Management. Sheba Medical Center Cardiology Department Matthew Wright St. George s University of London
 Etiology, Classification & Management Sheba Medical Center Cardiology Department Matthew Wright St. George s University of London Introduction World Health Organization (1995): Diseases of myocardium (heart
Etiology, Classification & Management Sheba Medical Center Cardiology Department Matthew Wright St. George s University of London Introduction World Health Organization (1995): Diseases of myocardium (heart
High Yield Associations Cardio for Step 1. Amanda Krauss, Adee Elhamdani
 High Yield Associations Cardio for Step 1 Amanda Krauss, Adee Elhamdani EKGs Irregularly irregular with no p waves and inconsistent RR intervals High Yield new onset MC risk factors Regular PP intervals
High Yield Associations Cardio for Step 1 Amanda Krauss, Adee Elhamdani EKGs Irregularly irregular with no p waves and inconsistent RR intervals High Yield new onset MC risk factors Regular PP intervals
Inflammatory Heart Disease
 Inflammatory Heart Disease Pericarditis inflammation of the pericardium Causes: may result from bacterial, viral or fungal infection can be assoc. w/ systemic diseases such as autoimmune disorders, rheumatic
Inflammatory Heart Disease Pericarditis inflammation of the pericardium Causes: may result from bacterial, viral or fungal infection can be assoc. w/ systemic diseases such as autoimmune disorders, rheumatic
Pleural Effusion. Exudative pleural effusion - Involve an increase in capillary permeability and impaired pleural fluid resorption
 Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
Pericardial Diseases 2015 Update
 Pericardial Diseases 2015 Update BRUCE W. USHER, MD PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CARDIOLOGY DIVISION MEDICAL UNIVERSITY SOUTH CAROLINA CHARLESTON, SOUTH CAROLINA GUIDELINES: PERICARDIAL DISEASES Ø European Society
Pericardial Diseases 2015 Update BRUCE W. USHER, MD PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CARDIOLOGY DIVISION MEDICAL UNIVERSITY SOUTH CAROLINA CHARLESTON, SOUTH CAROLINA GUIDELINES: PERICARDIAL DISEASES Ø European Society
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Valvular Heart Disease
 Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
CASE PRESENTATION. By: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Supervised By: DR.ABDULHAK AL_NUAIMI
 CASE PRESENTATION By: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Supervised By: DR.ABDULHAK AL_NUAIMI Name :Manal A. AGE : 22 years Marital status : married Occupation : housewife حي العامل Mosul Residence : DOA : 10 th,
CASE PRESENTATION By: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Supervised By: DR.ABDULHAK AL_NUAIMI Name :Manal A. AGE : 22 years Marital status : married Occupation : housewife حي العامل Mosul Residence : DOA : 10 th,
Cardiology. Objectives. Chapter
 1:44 M age 1121 Chapter Cardiology Objectives art 1: Cardiovascular natomy and hysiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia nalysis (begins on p. 1127) fter reading art 1 of this chapter, you should be able
1:44 M age 1121 Chapter Cardiology Objectives art 1: Cardiovascular natomy and hysiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia nalysis (begins on p. 1127) fter reading art 1 of this chapter, you should be able
Essentials of Pericardial Diseases
 Essentials of Pericardial Diseases 1 Nikolaos Skubas MD, 2 Manuel Fontes MD The pericardial diseases result in cardiovascular perturbations ranging from asymptomatic electrocardiographic findings (in pericarditis
Essentials of Pericardial Diseases 1 Nikolaos Skubas MD, 2 Manuel Fontes MD The pericardial diseases result in cardiovascular perturbations ranging from asymptomatic electrocardiographic findings (in pericarditis
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Chest Pain
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Tracheal normal sound heard over trachea loud tubular quality high-pitched expiration equal to or slightly longer than inspiration
 = listening for sounds produced in the body over chest to ID normal & abnormal lung sounds all BS made by turbulent flow in the airways useful in making initial D & evaluating effects of R 4 characteristics
= listening for sounds produced in the body over chest to ID normal & abnormal lung sounds all BS made by turbulent flow in the airways useful in making initial D & evaluating effects of R 4 characteristics
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
