AJNT. Original Article. Comparison between Doppler Ultrasound and Biopsy Findings in Patients with Suspected Kidney Transplant Rejection.
|
|
|
- Avice Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
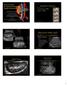
1 Jan;3(1):23-8 Original Article AJNT Comparison between Doppler Ultrasound and Biopsy Findings in Patients with Suspected Kidney Transplant Rejection Osama A Osman a*, Bernice Griffith b, Sally Classick C a. RDMS; RVT INOVA health system. b. Assistant professor of radiology; INOVA Fairfax Hospital, USA. c. Ultrasound supervisor; INOVA Fairfax Hospital, USA. Abstract Introduction: The role of Doppler ultrasound in diagnosing kidney allograft rejections is controversial. Our goal in this study was to investigate the utility of Doppler-measured resistive index (RI) as a screening tool for kidney transplant rejection. Methods: We retrospectively studied a random sample of 188 kidney transplanted patients who had Dopplerultrasound examination followed within two weeks by transplant biopsy. We evaluated the specificity and sensitivity of Doppler ultrasound in diagnosing rejection at different RI thresholds, using the reported biopsy findings as the gold standard. Results: The RI values of the study population had a mean value of 0.7 ± 0.11 (mean ± SD) and a range of There was no significant difference in the mean RI between patients with biopsy proven rejection and patients without rejection (0.68±0.09 versus 0.71±0.12, P = 0.16). The sensitivity and specificity of Dopplermeasured RI in diagnosing rejection was highly variable depending on the chosen cut-off value, ranging between % and % respectively. Acceptable specificity was only achieved at the expense of very low sensitivity. Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and interstitial edema (IE) were associated with higher RI values than other pathological entities, while very low RI values had high specificity and low sensitivity for transplanted renal artery stenosis (TRAS). Conclusion: Doppler-measured RI lacks accuracy in diagnosing transplanted kidney rejection, resulting in poor utility of this test as a screening tool for rejection. * Corresponding author; 3245 Rio Dr #711, Falls Church, VA 22041, USA. E mail: osammyoa@yahoo.com Keywords: Doppler Ultrasound; Rejection; Resistive Index (RI); Transplant kidney The authors declared no conflict of interest Introduction The first renal transplantation was performed in 1954 and since then the kidney tops the list of organs transplanted. However, despite of all the advances in kidney transplantation, clinicians still deal with relatively frequent dilemmas of allograft dysfunction and usually resort to ultrasound as a first line investigative tool. The role of gray-scale ultrasonography in the management of renal dysfunction is still limited despite the dramatic improvement in the image quality that occurred over the last 20 years [1]. The information obtained from gray-scale ultrasonography remains largely anatomic. Other parameters like the increased cortical echogenicity seen in gray-scale ultrasonography have a poor sensitivity (62%) and specificity (58%) in detecting kidney diseases [2, 3]. The introduction of Doppler-ultrasound promised to improve the clinical utility of ultrasound in patients with renal dysfunction. Many publications support the utility of Doppler-ultrasound in the management of both native and transplanted kidney dysfunction [4-11]. On the other hand, opinions and data arguing against the utility of Doppler-ultrasound in differentiating various kidney diseases also exist [12-14]. Tublin et al argued that Doppler ultrasound s ability to detect different renal pathologies is based on the assumption that changes in the intrarenal arterial waveforms accurately reflect the subtle changes in renal vascular resistances (RVR) that occur with renal disease [1]. These changes are generally quantified using the so called Doppler ultrasounds resistive index (RI), which is equal to the difference between the peak systolic velocity and end diastolic velocity divided by the peak systolic velocity (figures 1-3). 25
2 Osman, Griffith and Classick Figure 1: Calculation of RI from the spectral waveform Krumme et al studied the RI of 110 stable renal allografts, and found a mean value of 0.70 ± 0.07 (mean ± SD), with a range of [15]. During rejection, the changes that lead to an increase in RVR and RI probably occur as a direct result of the impedance of blood flow caused by external pressure exerted on blood vessels by expanding interstitium, infiltration by inflammatory cells, edema or the process of fibrosis. Changes that occur in the vascular wall itself as a response to the injury e.g. intimal thickening or lumen narrowing by thrombus might also lead to direct change in the RVR. In acute cellular rejection there is marked interstitial infiltration with mononuclear cells and occasionally eosinophils, and disruption of the tubular basement membranes (tubulitis) by the infiltrating cells [16]. This infiltration together with the associated edema is speculated to be behind the change in the RVR that leads to elevated RI. While, and due to its direct effect on the kidney vasculature, vascular rejection might have a direct effect on RVR and RI. Data from models of chronic kidney diseases may be extrapolated for a better understanding of the situation in chronic rejection and chronic allograft nephropathy. Professor El Nahas reported that when the endothelial cell is injured, it loses its mature anticoagulant, antiinflammatory and anti-proliferative phenotype and acquires new pro-coagulant, pro-inflammatory and mitogenic characteristics [17]. This marks the initiation of the chronic inflammatory process. The chronicity of the process aids the overlapping of inflammation and scaring. This dual pathological process, ongoing inflammation and scaring, is speculated to be behind the increase in the renal vascular resistance that leads to elevated RI. However, unlike the acute rejection process, RI may or may not be elevated in chronic rejection. Kelcz et al noted that patients with chronic rejection (as well as cyclosporine toxicity) were unlikely to have RI higher than 0.80 [18]. It is generally agreed that RI is the single most reliable Doppler ultrasound parameter in detecting kidney allograft rejection [19]. However, the variability of data concerning the reliability of Doppler-calculated RI in detecting transplanted kidney rejection represents the main motivation behind conducting our study. Meyer et al concluded that Duplex Doppler ultrasound, although less invasive, is neither sufficiently sensitive nor specific in the diagnosis of acute rejection [12]. While Hollenbeck et al reported that an elevated RI has a sensitivity of 90% in detecting rejection [20]; Allen et al reported a lower sensitivity of 76 %, using a cut point of 0.75 [21]. Furthermore, Dupont et al reported that at RI cut-point of 0.9, the test had specificity for acute rejection of 89%, but a sensitivity of just 6% [14]. Figure 2: Spectral Doppler waveform obtained at the level of the interlobar artery of a stable kidney transplant with a calculated RI of 0.60 Figure 3: Spectral Doppler waveform of a transplanted kidney affected by acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and interstitial edema, with a calculated RI of
3 Doppler ultrasound in kidney transplant rejection Table 1: Clinical, Doppler ultrasound and biopsy findings of the study population (N=188) Characteristic Details Number (%) Gender Male 122 (64.9%) Female 66 (35.1%) Ethnicity White 89 (47.3%) Black 67 (35.7%) Other minorities 32 (17%) Source of graft Living donor 75 (40%) Deceased donor 133 (60%) Immunosuppressant used Findings suggestive of TRAS Peri-transplant fluid collection In this study, we compared ultrasound and biopsy findings in patients with suspected transplanted kidney rejection at INOVA Fairfax Hospital, Virginia USA, aiming to evaluate the utility of Doppler ultrasound in detecting kidney allograft rejection. Methods Tacrolimus 142 (75.5%) Cyclosporine 40 (21.3%) Sirolimus 6 (3.2%) Reported 19 (10.1%) Not reported 169 (89.9%) Present 14 (7.4%) Absent 174 (92.6) Biopsy findings Biopsy proven rejection 72 (38.3%) CAN 43 (22.9%) Interstitial fibrosis 34 (18.1%) Drug toxicity 14 (7.4%) Acute tubular necrosis 10 (5.3%) Interstitial nephritis 6 (3.2%) Interstitial edema 3 (1.6%) No biopsy findings 17 (9%) BANFF classification No rejection 116 (61.7%) IA 34 (18.1%) IB 19 (10.1%) IIA 7 (3.7%) IIB 1 (0.5%) Borderline rejection 11 (5.9%) TRAS: transplanted renal artery stenosis; CAN: chronic allograft nephropathy The main objective of this study was to determine the sensitivity and specificity of the Doppler-measured RI in detecting transplanted kidney rejection. Only patients who had kidney transplant biopsy within two weeks of a Doppler ultrasound study were included in the study. Out of our kidney-transplant patients pool at Fairfax Hospital Virginia who fulfilled the inclusion criteria, we randomly selected a sample of 188 patients and retrospectively compared the reported Doppler ultrasound findings and kidney allograft biopsy findings. All the Doppler ultrasound studies were done using HDI 5000 or iu22, Phillips-ATL Ultrasound, Bothell, Washington (USA), ultrasound systems equipped with multi-hertz Curvilinear, 3-5 MHz and 4-7 MHz, ultrasound transducers. SPSS version 16.0 for Windows was used for the statistical analysis. We evaluated different cut-off values for the RI (0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8 and 0.9) by dichotomizing patients into two groups around each cut-off value; those with RI > the cut-off value, were considered to be the test positive and those with RI the cut-off value were considered the test negative. The reported biopsy finding was considered the gold standard test. Sensitivity was calculated as the test true positive cases divided by the sum of the test true positive and the test false negative cases. Specificity was calculated as the test true negative cases divided by the sum of the test true negative and false positive cases. Accuracy was calculated as the sum of the test true positive and the test true negative cases divided by the total number of patients. Continuous data are presented as mean ± SD and compared using t-test or one-way ANVOVA as appropriate. Categorical data are presented as frequencies and percentages and compared using X 2 and Fisher exact test. Results The study included 188 patients. The overall characteristics of the study population are shown (Table 1). The RI values of the study population had a normal distribution, with a mean value of 0.7 ± 0.11 (mean ± SD) and a range of There was no significant difference in the mean RI between patients taking tacrolimus, cyclosporine and sirolimus (0.69±0.12, 0.71±0.01 and 0.7±0.05 respectively, P = 0.8). There was no significant difference in the mean RI between patients reported to have peri-transplant fluid collection and patients without fluid collection (0.74±0.12 versus 0.69±0.11, P=0.9). There was no significant difference in the mean RI between patients with findings suggestive of transplanted renal artery stenosis (TRAS) and patients without such findings (0.7±0.17 versus 0.7±0.11, P = 0.97). However, we found that patients who have very low RI are more likely to have TRAS with a specificity of 99%, a sensitivity of 16%, and an accuracy of 91% at an RI cut-off value of 0.5. There was no significant difference in the mean RI between patients with and without biopsy proven rejection (0.68±0.09 versus 0.71±0.12, P = 0.16). However, the RI was found to be significantly different between different categories of graft biopsy findings other than rejection, with acute tubular necrosis (ATN) 27
4 Osman, Griffith and Classick Table 2: Mean RI values for different categories of graft biopsy findings other than rejection (P = 0.001) Number Mean RI SD Rejection Acute tubular necrosis Interstitial fibrosis Interstitial nephritis Interstitial edema Drug toxicity Chronic allograft nephropathy No biopsy findings Table 3: sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of RI in diagnosing kidney transplant rejection at different RI thresholds Cut-off value for RI Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Accuracy (%) and interstitial edema (IE) having higher RI values than other categories (Table 2). The sensitivity of RI in diagnosing rejection decreased and its specificity increased with increasing RI thresholds (Table 3). Using an RI threshold of 0.5 resulted in high sensitivity (98.6%) at the cost of very low specificity (2.6%), while using an RI threshold of 0.9 resulted in high specificity (92.2%) at the cost of very low sensitivity (4.1%). Discussion The mean RI value in our study was found to be similar to what has been reported by Krumme et al [15], although they did their study on patients with stable renal function while our sample was comprised mainly of patients with worsening graft function. The lack of difference in the mean RI between patients with and without biopsy proven rejection correlates with the data reported by Dupont et al who stated that the average RI in the rejection group was not higher than in controls [14]. When we considered histopathological findings other than allograft rejection, we observed that ATN and IE had a relatively higher mean RI (>0.8) compared to other categories. However, these findings should be considered with caution due to the reported overlapping between these pathological entities, as some patients were reported to have IE with ATN and some reported to have ATN with interstitial nephritis. Many different values were reported in literature for the sensitivity of Doppler ultrasound in diagnosing transplanted kidney rejection. It is apparent from this study that the Doppler sensitivity is greatly affected by the chosen RI threshold. Sensitivity was found to be 98% at an RI threshold of 0.5; as this threshold was increased, sensitivity dropped sharply reaching a value of 4.1% at an RI threshold of 0.9. The same findings were reported by Dupont et al [14], which would explain the variability found in the literature. Despite the high sensitivity achieved with a low RI threshold of 0.5, the value of Doppler ultrasound as a screening tool for rejection remains poor. This is due to the fact that at such a low RI threshold, test specificity is very low (2.6%), with a high false positive rate of 97.5%. The poor utility of Doppler ultrasound as a screening tool for rejection is reflected by a test accuracy of only %. The low accuracy of Doppler-measured RI in detecting rejection may be attributed to many factors. Overlapping of pathological processes often exists. The observed RI can be the net resultant effect of this overlap rather than the absolute effect of any single process. Thus the effect 28
5 Doppler ultrasound in kidney transplant rejection of one pathological process can be masked or altered by the effect of another. Also, blood flow through the kidneys forms a closed circuit that starts at the renal artery and ends at the renal vein. Any pathological process acting at any point of this continuum will affect the hemodynamics of the blood flowing through the entire circuit. By convention and for standardization, Doppler sampling for RI measurement is taken at the level of the interlobar and arcuate arteries. Proximally acting pathologies like renal artery stenosis tends to increase resistance to blood flow. If the Doppler sampling is taken immediately before or at the stenotic segment, high blood-flow velocities can be detected. The energy loss at the point of stenosis will lead to a decrease in the blood pressure and thus dampen down the blood flow in the distal vessel past the point of stenosis. This dampening will result in very weak upstroke leading to the formation of the so-called Tardus Parvus waveform and a very low RI. Pathological processes that affect the renal parenchyma distal to the arcuate artery tend to increase the pressure at the sampling point leading to a high RI. When rejection (acts distally and tends to increase the RI) occurs concomitantly with renal artery stenosis (acts proximally and tends to decrease the RI) the net result is often a falsely low RI thus masking the effect of rejection on the RI. As a matter of fact, we found that a very low RI (<0.5) can be considered a strong clue pointing towards the presence of TRAS with a specificity of 99% and an accuracy of 90%, but very low sensitivity at 16 %. In addition, the variations in RI cannot be solely due to the pathological processes involving the transplanted kidney. While deprived of neuronal control, the renal vascular bed remains under hormonal control mechanisms besides its autoregulation. The effect of humeral or pharmacological factors on renal RI during episodes of rejection cannot be ruled out. In addition, the state of the circulation, the presence of fever and variability in heart rate are all factors that might affect the amount of blood flowing through the transplanted kidney and accordingly alter the RI value. Mostbeck et al stated that an increase in heart rate decreases the RI [22]. In addition, Pozniak et al stated that bradycardia and general hypotension also affect the RI value [23]. Many transplant patients are under antihypertensive medications that can lower blood pressure and heart rate, at least from the pathological hypertensive range to the normal range. This pharmacological effect may be equivalent to hypotension, and may lead to variations in RI values. Inter-patient variation may also lead to alterations in the RI value. Recipient age, donor age and graft age all lead to significant variations in the baseline value of RI. Krumme et al reported a statistically significant correlation between RI value and recipient age [15]. In this study, other factors that might contribute to variability include ethnicity, gender and the source of the graft. In addition, the Doppler-measured RI values in this study have been measured by different sonographist, due the retrospective nature of the study. Hence, the chance for inter-observer error is high. Conclusion There was no significant difference in the mean RI value between patients with and without biopsy proven rejection. The sensitivity and specificity of Doppler-measured RI in diagnosing rejection is highly variable depending on the chosen cut-off value. Acceptable specificity is only achieved at the expense of very low sensitivity, resulting in poor utility of this test as a screening tool for rejection. Very high RI values were found to be associated with edematous allograft conditions such as IE and ATN, while very low RI values had high specificity and low sensitivity for TRAS. References 1. Tublin ME, Tessler FN, Murphy ME. Correlation between renal vascular resistance, pulse pressure, and the resistive index in isolated perfused rabbit kidneys. Radiology. 1999;213(1): Platt JF, Rubin JM, Bowerman RA, Marn CS. The inability to detect kidney disease on the basis of echogenicity. Am J Roentgenol 1988;151(2): Quaia E, Bertolotto M. Renal parenchymal diseases: is characterization feasible with ultrasound? Eur Radiol. 2002;12(8): Mostbeck GH, Zontsich T. Ultrasound of the kidney: obstruction and medical diseases. Eur Radiol. 2001;11(10): Platt JF. Doppler ultrasound of the kidney. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1997;18(1): Platt JF, Ellis JH. Renal duplex Doppler ultrasonography: a noninvasive predictor of kidney dysfunction and hepatorenal failure in liver disease. Hepatology. 1994;20(2): Platt JF, Rubin J M. Acute renal obstruction: evaluation with intrarenal duplex Doppler and conventional US. Radiology. 1993;186(3): Platt JF. Duplex Doppler evaluation of native kidney dysfunction: obstructive and nonobstructive disease. Am J Roentgenol. 1992;158(5):
6 Osman, Griffith and Classick 9. Platt JF, Ellis JH. Renal transplant pyelocaliectasis: role of duplex Doppler US in evaluation. Radiology. 1991;179(2): Brkljacic B, Drinkovic I. Intrarenal duplex Doppler sonographic evaluation of unilateral native kidney obstruction. J Ultrasound Med. 1994;13(3): Gottlieb RH, Luhmann KT. Duplex ultrasound evaluation of normal native kidneys and native kidneys with urinary tract obstruction. J Ultrasound Med. 1989;8(11): Meyer M, Paushter D. The use of duplex Doppler ultrasonography to evaluate renal allograft dysfunction. Transplantation. 1990;50(6): Mostbeck GH, Kain R. Duplex Doppler sonography in renal parenchymal disease. Histopathologic correlation. J Ultrasound Med. 1991;10(4): Dupont PJ, Dooldeniya M. Role of duplex Doppler sonography in diagnosis of acute allograft dysfunctiontime to stop measuring the resistive index? Transpl Int. 2003;16(9): Krumme B, Grotz W, Kirste G, Schollmeyer P, Rump LC. Determinants of intrarenal Doppler indices in stable renal allografts. J Am Soc Nephrol May;8(5): Solez K, Axelsen R A. International standardization of criteria for the histologic diagnosis of renal allograft rejection: the Banff working classification of kidney transplant pathology. Kidney Int. 1993;44(2): El Nahas M. Kidney remodelling and scarring: the plasticity of cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18(10): Kelcz F, Pozniak MA. Pyramidal appearance and resistive index: insensitive and nonspecific sonographic indicators of renal transplant rejection. Am J Roentgenol. 1990;155(3): Jakobsen JA, Brabrand K. Doppler examination of the allografted kidney. Acta Radiol. 2003;44(1): Hollenbeck M, Hilbert N. Increasing sensitivity and specificity of Doppler sonographic detection of renal transplant rejection with serial investigation technique. Clin Investig. 1994;72(8): Allen KS, Jorkasky DK, Arger PH, Velchik MG, Grumbach K, Coleman BG, Mintz MC, Betsch SE, Perloff LJ.Renal allografts: prospective analysis of Doppler sonography. Radiology Nov;169(2): Mostbeck GH, Gössinger HD, Mallek R, Siostrzonek P, Schneider B, Tscholakoff D. Effect of heart rate on Doppler measurements of resistive index in renal arteries. Radiology. 1990;175: Pozniak MA, Kelcz F, Stratta RJ, Oberley TD. Extraneous factors affecting resistive index. Invest Radiol. 1988;23:
Prediction of Tubulo Interstitial Injuries by Doppler Ultrasound in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Value of Resistive Index and Atrophic Index
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 8, August 2015 1 Prediction of Tubulo Interstitial Injuries by Doppler Ultrasound in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Value
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 8, August 2015 1 Prediction of Tubulo Interstitial Injuries by Doppler Ultrasound in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Value
Case 8038 Renal allograft complicated with renal artery stenosis
 Case 8038 Renal allograft complicated with renal artery stenosis Santiago I, Canelas A, Pinto AP Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2009, Nov. 30 Patient: 61 year(s), male Clinical History A 61-year-old
Case 8038 Renal allograft complicated with renal artery stenosis Santiago I, Canelas A, Pinto AP Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2009, Nov. 30 Patient: 61 year(s), male Clinical History A 61-year-old
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries. Duplex Ultrasound. In the Beginning
 Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection
 Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
Early assessment of renal resistance index after kidney transplant can help predict long-term renal function
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 2916 2920 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl203 Advance Access publication 5 August 2006 Original Article Early assessment of renal resistance index after kidney transplant can help
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 2916 2920 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl203 Advance Access publication 5 August 2006 Original Article Early assessment of renal resistance index after kidney transplant can help
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen. Jonathan Swanson, MD
 Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Transducer Selection. Renal Artery Duplex Exam. Renal Scan. Renal Scan Echogenicity. How to Perform an Optimal Renal Artery Doppler Examination
 How to Perform an Optimal Renal Artery Doppler Examination Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging
How to Perform an Optimal Renal Artery Doppler Examination Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on an waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on a waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience. Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy
 BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical
 Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical techniques Review normal appearance Discuss US diagnosis of
Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical techniques Review normal appearance Discuss US diagnosis of
Erin Kane, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman BIDMC Radiology Core Clerkship March 2009
 Erin Kane, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman BIDMC Radiology Core Clerkship March 2009 Agenda Patient OH: Initial presentation Kidney transplantation: Menu of tests Routine imaging for kidney donors Selected
Erin Kane, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman BIDMC Radiology Core Clerkship March 2009 Agenda Patient OH: Initial presentation Kidney transplantation: Menu of tests Routine imaging for kidney donors Selected
Pathological back-ground of renal transplant pathology and important mile-stones of the Banff classification
 Banff 1 Banff Pathological back-ground of renal transplant pathology and important mile-stones of the Banff classification Department of Nephrology, Japanese Red Cross Nagoya Daini Hospital Morozumi Kunio,
Banff 1 Banff Pathological back-ground of renal transplant pathology and important mile-stones of the Banff classification Department of Nephrology, Japanese Red Cross Nagoya Daini Hospital Morozumi Kunio,
No financial or commercial relationships to disclose
 Deanna New, RVT No financial or commercial relationships to disclose IAC REQUIREMENTS: The main duty of a sonographer is to make the physician or radiologists job easier by capturing images and doing
Deanna New, RVT No financial or commercial relationships to disclose IAC REQUIREMENTS: The main duty of a sonographer is to make the physician or radiologists job easier by capturing images and doing
Impact of Sickle Cell Disease in Renal Arteries Blood Flow Indices Using Ultrasonography
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(2): 9-13 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170502.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Impact of Sickle
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(2): 9-13 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170502.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Impact of Sickle
US of Renovascular Hypertension. Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc Associate Professor Director, Thoracoabdominal Imaging
 US of Renovascular Hypertension Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc Associate Professor Director, Thoracoabdominal Imaging Disclosures Nothing Relevant Unrelated grant funding Siemens US Toshiba US Objectives
US of Renovascular Hypertension Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc Associate Professor Director, Thoracoabdominal Imaging Disclosures Nothing Relevant Unrelated grant funding Siemens US Toshiba US Objectives
AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of Renal Artery Duplex Sonography
 AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of Renal Artery Duplex Sonography 2008 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) is a multidisciplinary
AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of Renal Artery Duplex Sonography 2008 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) is a multidisciplinary
Renal transplantation: Sonography and Doppler assessment of transplanted kidneys in adult Sudanese patients
 Renal transplantation: Sonography and Doppler assessment of transplanted kidneys in adult Sudanese patients Moawia Gameraddin 1,2, Awadia Gareeballah 3, Bushra A. Malik 4, Mohammed Yousef 5, Safa Siddig
Renal transplantation: Sonography and Doppler assessment of transplanted kidneys in adult Sudanese patients Moawia Gameraddin 1,2, Awadia Gareeballah 3, Bushra A. Malik 4, Mohammed Yousef 5, Safa Siddig
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation. Dr.E Nemati. Professor of Nephrology
 Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
Goals. Access flow and renal artery stenosis evaluation by Doppler ultrasound. Reimbursement. WHY use of Doppler Ultrasound
 Access flow and renal artery stenosis evaluation by Doppler ultrasound Adina Voiculescu, MD Interventional Nephrology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston Instructor at Harvard Medical School Understand
Access flow and renal artery stenosis evaluation by Doppler ultrasound Adina Voiculescu, MD Interventional Nephrology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston Instructor at Harvard Medical School Understand
Intrarenal Resistive Index after Renal Transplantation
 The new england journal of medicine original article Intrarenal Resistive Index after Renal Transplantation Maarten Naesens, M.D., Ph.D., Line Heylen, M.D., Evelyne Lerut, M.D., Ph.D., Kathleen Claes,
The new england journal of medicine original article Intrarenal Resistive Index after Renal Transplantation Maarten Naesens, M.D., Ph.D., Line Heylen, M.D., Evelyne Lerut, M.D., Ph.D., Kathleen Claes,
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary
 Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Understanding the Doppler RI:
 Understanding the Doppler RI: Impact of Renal Arterial Distensibility on the RI in a Hydronephrotic Ex Vivo Rabbit Kidney Model Michael E. Murphy, PhD, Mitchell E. Tublin, MD The aim of this study was
Understanding the Doppler RI: Impact of Renal Arterial Distensibility on the RI in a Hydronephrotic Ex Vivo Rabbit Kidney Model Michael E. Murphy, PhD, Mitchell E. Tublin, MD The aim of this study was
The renal resistive index is a non-invasive indicator of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhotics
 Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2016), 3, 23 27 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The renal resistive index is a non-invasive indicator of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhotics Mohsin Aslam, S. Ananth Ram,
Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2016), 3, 23 27 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The renal resistive index is a non-invasive indicator of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhotics Mohsin Aslam, S. Ananth Ram,
What Do We Know? Disclosure Statement: 3/11/2015. Deep abdominal imaging
 Marsha M. Neumyer, BS, RVT, FSVU, FSDMS, FAIUM International Director Vascular Diagnostic Educational Services Vascular Resource Associates Harrisburg, PA Disclosure Statement: CME Calendar QR Code Marsha
Marsha M. Neumyer, BS, RVT, FSVU, FSDMS, FAIUM International Director Vascular Diagnostic Educational Services Vascular Resource Associates Harrisburg, PA Disclosure Statement: CME Calendar QR Code Marsha
Reversed Diastolic Flow in the Renal Transplant: Perioperative Implications Versus Transplants Older Than 1 Month
 Abdominal Imaging Original Research Lockhart et al. Reversed Diastolic Flow in Renal Transplant Abdominal Imaging Original Research Mark E. Lockhart 1 Charles G. Wells 2 Desiree E. Morgan 1 Naomi S. Fineberg
Abdominal Imaging Original Research Lockhart et al. Reversed Diastolic Flow in Renal Transplant Abdominal Imaging Original Research Mark E. Lockhart 1 Charles G. Wells 2 Desiree E. Morgan 1 Naomi S. Fineberg
DISCLOSURE TEST YOUR WAVEFORM IQ. Partial volume artifact. 86 yo female with right arm swelling, picc line. AVF on left? Dx?
 Deborah Rubens University of Rochester Rochester, NY DISCLOSURE Neither I nor my immediate family have a financial relationship with a commercial organization that may have a direct or indirect interest
Deborah Rubens University of Rochester Rochester, NY DISCLOSURE Neither I nor my immediate family have a financial relationship with a commercial organization that may have a direct or indirect interest
The Evaluation of Renal Hemodynamics with Doppler Ultrasonography
 The Evaluation of Renal Hemodynamics with Doppler Ultrasonography Mahir Kaya Department of Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Atatürk University, Erzurum Turkey 1 1. Introduction Gray-scale renal
The Evaluation of Renal Hemodynamics with Doppler Ultrasonography Mahir Kaya Department of Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Atatürk University, Erzurum Turkey 1 1. Introduction Gray-scale renal
DOPPLER ULTRASONOGRAPHY: A TOOL FOR NEPHROLOGISTS SINGLE CENTRE EXPERIENCE. Milovanceva-Popovska M., Dzikova S.
 Prilozi, Odd. biol. med. nauki, MANU, XXIX, 1, s. 107 128 (2008) Contributions, Sec. Biol. Med. Sci., MASA, XXIX, 1, p. 107 128 (2008) ISSN 0351 3254 UDK : 616.61-073.432.19 DOPPLER ULTRASONOGRAPHY: A
Prilozi, Odd. biol. med. nauki, MANU, XXIX, 1, s. 107 128 (2008) Contributions, Sec. Biol. Med. Sci., MASA, XXIX, 1, p. 107 128 (2008) ISSN 0351 3254 UDK : 616.61-073.432.19 DOPPLER ULTRASONOGRAPHY: A
Management of Rejection
 Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Renal Pathology- Transplantation. Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic
 Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
Can renal Doppler sonography replace diuretic radionuclide renography in infants with hydronephrosis?
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2006; 48: 221-227 Original Can renal Doppler sonography replace diuretic radionuclide renography in infants with hydronephrosis? Knut Liepe 1, Heike Taut-Sack 2 Departments
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2006; 48: 221-227 Original Can renal Doppler sonography replace diuretic radionuclide renography in infants with hydronephrosis? Knut Liepe 1, Heike Taut-Sack 2 Departments
Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis
 Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Etiology Fibromuscular
Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Etiology Fibromuscular
James E. Cooper, M.D. Assistant Professor, University of Colorado at Denver Division of Renal Disease and Hypertension, Kidney and PancreasTransplant
 James E. Cooper, M.D. Assistant Professor, University of Colorado at Denver Division of Renal Disease and Hypertension, Kidney and PancreasTransplant Program Has no real or apparent conflicts of interest
James E. Cooper, M.D. Assistant Professor, University of Colorado at Denver Division of Renal Disease and Hypertension, Kidney and PancreasTransplant Program Has no real or apparent conflicts of interest
The Banff Classification for Diagnosis of Renal Allograft Rejection: Updates from the 2017 Banff Conference
 The Banff Classification for Diagnosis of Renal Allograft Rejection: Updates from the 2017 Banff Conference Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Statement of Disclosure Mark
The Banff Classification for Diagnosis of Renal Allograft Rejection: Updates from the 2017 Banff Conference Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Statement of Disclosure Mark
Statement of Disclosure
 Statement of Disclosure Mark Haas serves as a paid consultant on pathology adjudication committees for two industry-sponsored clinical trials: Shire ViroPharma Treatment of Acute ABMR AstraZeneca Treatment
Statement of Disclosure Mark Haas serves as a paid consultant on pathology adjudication committees for two industry-sponsored clinical trials: Shire ViroPharma Treatment of Acute ABMR AstraZeneca Treatment
Evaluation of Colour Duplex Ultrasound Scanning in Diagnosis of Renal Artery Stenosis, Compared to Angiography: A Prospective Study on 53 Patients
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 14, 305-309 (1997) Evaluation of Colour Duplex Ultrasound Scanning in Diagnosis of Renal Artery Stenosis, Compared to Angiography: A Prospective Study on 53 Patients M. Mollo,
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 14, 305-309 (1997) Evaluation of Colour Duplex Ultrasound Scanning in Diagnosis of Renal Artery Stenosis, Compared to Angiography: A Prospective Study on 53 Patients M. Mollo,
A Study on the Value of Measuring Resistive Index of the Intrarenal Arterial Blood Flow for diagnosing the Acute Unilateral Obstructive Uropathy
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 A Study on the Value of Measuring Resistive Index of the Intrarenal Arterial Blood Flow for diagnosing the Acute Unilateral Obstructive Uropathy Abstract
Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 A Study on the Value of Measuring Resistive Index of the Intrarenal Arterial Blood Flow for diagnosing the Acute Unilateral Obstructive Uropathy Abstract
Acute dysfunction of renal transplants: Contrast ultrasound assessment
 Acute dysfunction of renal transplants: Contrast ultrasound assessment Poster No.: C-1340 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: A. Afaq, E. L. Leen, C. Harvey; London/UK
Acute dysfunction of renal transplants: Contrast ultrasound assessment Poster No.: C-1340 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: A. Afaq, E. L. Leen, C. Harvey; London/UK
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Utility of Doppler Ultrasound as the Primary Imaging Modality in Renal Graft Dysfunction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 2, June: 201-207, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Utility of Doppler Ultrasound as the Primary Imaging Modality in Renal Graft Dysfunction MOHAMED S. EL-SHARKAWY,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 2, June: 201-207, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Utility of Doppler Ultrasound as the Primary Imaging Modality in Renal Graft Dysfunction MOHAMED S. EL-SHARKAWY,
ASDIN 7th Annual Scientific Meeting DISCLOSURES TECHNICAL CONSIDERATIONS TECHNICAL CONSIDERATIONS UTILITY OF ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATING ACCESS
 DISCLOSURES UTILITY OF ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATING ACCESS DYSFUNCTION None Vandana Dua Niyyar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, Emory University UTILITY OF ULTRASOUND IN ACCESS
DISCLOSURES UTILITY OF ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATING ACCESS DYSFUNCTION None Vandana Dua Niyyar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, Emory University UTILITY OF ULTRASOUND IN ACCESS
Acute renal failure (ARF) in the transplanted kidney represents a
 Acute Renal Failure in the Transplanted Kidney Kim Solez Lorraine C. Racusen Acute renal failure (ARF) in the transplanted kidney represents a high-stakes area of nephrology and of transplantation practice.
Acute Renal Failure in the Transplanted Kidney Kim Solez Lorraine C. Racusen Acute renal failure (ARF) in the transplanted kidney represents a high-stakes area of nephrology and of transplantation practice.
The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography
 Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29755 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moes, Dirk Jan Alie Roelof Title: Optimizing immunosuppression with mtor inhibitors
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29755 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moes, Dirk Jan Alie Roelof Title: Optimizing immunosuppression with mtor inhibitors
Renal. Prof John Buscombe
 Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
HD Scanning: Velocities and Volume Flow
 HD Scanning: Velocities and Volume Flow Non-Invasive Lab Symposium West Orange, NJ April 27, 2018 Volume Flow Cindy Sturt, MD, FACS, RVT 500,000 Americans on dialysis 20-25% annual mortality 65% 5 year
HD Scanning: Velocities and Volume Flow Non-Invasive Lab Symposium West Orange, NJ April 27, 2018 Volume Flow Cindy Sturt, MD, FACS, RVT 500,000 Americans on dialysis 20-25% annual mortality 65% 5 year
Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries
 Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries Greg Curry Vascular Ultrasound Workshop Aug 2017 The Examination Technique Pathophysiology Role of US then and now Background Live Scanning Ultrasound Population: 20% Hypertensive
Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries Greg Curry Vascular Ultrasound Workshop Aug 2017 The Examination Technique Pathophysiology Role of US then and now Background Live Scanning Ultrasound Population: 20% Hypertensive
Carotid artery occlusion: Positive predictive value of duplex sonography compared with arteriography
 Carotid artery occlusion: Positive predictive value of duplex sonography compared with arteriography Jonathan D. Kirsch, MD, Louis R. Wagner, MD, E. Meredith James, MD, J. William Charboneau, MD, Douglas
Carotid artery occlusion: Positive predictive value of duplex sonography compared with arteriography Jonathan D. Kirsch, MD, Louis R. Wagner, MD, E. Meredith James, MD, J. William Charboneau, MD, Douglas
Renal Doppler Hospital Based Study and Review of Literature
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Hospital Based Study and Review of Literature Jahangeer Ahmad Bhat 1, Murassa Shamshad 2, Aresalan Malik 1, Iqbal Bhat 3, Iqbal Dar 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Study was done
ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Hospital Based Study and Review of Literature Jahangeer Ahmad Bhat 1, Murassa Shamshad 2, Aresalan Malik 1, Iqbal Bhat 3, Iqbal Dar 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Study was done
The value of different resistance parameters in distinguishing biopsy-proved dysfunction of renal auografts
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (995) 0: 527-52 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation The value of different resistance parameters in distinguishing biopsy-proved dysfunction of renal auografts
Nephrol Dial Transplant (995) 0: 527-52 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation The value of different resistance parameters in distinguishing biopsy-proved dysfunction of renal auografts
Ultrasound in Acute Kidney Injury. Pamela Parker Ultrasound Specialty Manager
 Ultrasound in Acute Kidney Injury Pamela Parker Ultrasound Specialty Manager Aims What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? Discuss the implications of AKI for USS Revisit Resistive Index (RIs) Why? The FACTS
Ultrasound in Acute Kidney Injury Pamela Parker Ultrasound Specialty Manager Aims What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? Discuss the implications of AKI for USS Revisit Resistive Index (RIs) Why? The FACTS
Indications: following: embolization. artery that has diseases 5. The evaluation. of suspected. such entities. a cold hand. biopsy
 Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Incidence of Rejection in Renal Transplant Surgery in the LVHN Population Leading to Graft Failure: 6 Year Review
 Incidence of Rejection in Renal Transplant Surgery in the LVHN Population Leading to Graft Failure: 6 Year Review Jessica Ludolph 1 Lynsey Biondi, MD 1,2 and Michael Moritz, MD 1,2 1 Department of Surgery,
Incidence of Rejection in Renal Transplant Surgery in the LVHN Population Leading to Graft Failure: 6 Year Review Jessica Ludolph 1 Lynsey Biondi, MD 1,2 and Michael Moritz, MD 1,2 1 Department of Surgery,
GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL
 GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Carotid Duplex Ultrasound SECTION: Vascular Ultrasound ORIGINATOR: Deborah L. Richert, BSVT, RDMS, RVT DATE: October 15, 2015
GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Carotid Duplex Ultrasound SECTION: Vascular Ultrasound ORIGINATOR: Deborah L. Richert, BSVT, RDMS, RVT DATE: October 15, 2015
Postoperative AV Fistula Evaluation. Postoperative examination protocol. Postoperative AVF Protocol. Hemodialysis Access Surveillance
 Hemodialysis Access Surveillance Postoperative AV Fistula Evaluation Failure of maturation Stenosis Perigraft mass/fluid collection Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular
Hemodialysis Access Surveillance Postoperative AV Fistula Evaluation Failure of maturation Stenosis Perigraft mass/fluid collection Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular
Radial Artery Assessment for Coronary Artery Bypass
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Radial Artery Assessment for Coronary Artery Bypass This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Radial Artery Assessment for Coronary Artery Bypass This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2016
 STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Vascular Sonography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Vascular Sonography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
Disclosure Statement:
 Marsha M. Neumyer, BS, RVT, FSVU, FSDMS, FAIUM International Director Vascular Diagnostic Educational Services Vascular Resource Associates Harrisburg, PA Disclosure Statement: CME Calendar QR Code Marsha
Marsha M. Neumyer, BS, RVT, FSVU, FSDMS, FAIUM International Director Vascular Diagnostic Educational Services Vascular Resource Associates Harrisburg, PA Disclosure Statement: CME Calendar QR Code Marsha
Ultrasound Imaging of The Posterior Circulation
 Ultrasound Imaging of The Posterior Circulation Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RDMS-RVT Clinical Manager General Ultrasound/Neurovascular Laboratory Cleveland
Ultrasound Imaging of The Posterior Circulation Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RDMS-RVT Clinical Manager General Ultrasound/Neurovascular Laboratory Cleveland
Kidney Summary. Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA
 Kidney Summary Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Key Issues to Address re: the Classification 1. Incorporation of i-ifta + tubulitis into the TCMR classification - Defining
Kidney Summary Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Key Issues to Address re: the Classification 1. Incorporation of i-ifta + tubulitis into the TCMR classification - Defining
Sonographic Evaluation of an Immature Brescia-Cimino Fistula
 696792JDMXXX10.1177/8756479317696792Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyChappell research-article2017 Case Study Sonographic Evaluation of an Immature Brescia-Cimino Fistula Journal of Diagnostic Medical
696792JDMXXX10.1177/8756479317696792Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyChappell research-article2017 Case Study Sonographic Evaluation of an Immature Brescia-Cimino Fistula Journal of Diagnostic Medical
Doppler Ultrasound of the Kidney
 Doppler Ultrasound of the Kidney Chang-Kyu Sung Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNU-SMG Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Doppler ultrasound (US) is a very useful
Doppler Ultrasound of the Kidney Chang-Kyu Sung Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNU-SMG Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Doppler ultrasound (US) is a very useful
Vascular Sonography Examination
 Vascular Sonography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Vascular Sonography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
Vascular Sonography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Vascular Sonography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
How to assess the hemodynamic importance of a renal artery stenosis. Felix Mahfoud, MD Saarland University Hospital Homburg/Saar, Germany
 How to assess the hemodynamic importance of a renal artery stenosis Felix Mahfoud, MD Saarland University Hospital Homburg/Saar, Germany How to assess renal artery stenosis severity 1. Non-invasive assessments
How to assess the hemodynamic importance of a renal artery stenosis Felix Mahfoud, MD Saarland University Hospital Homburg/Saar, Germany How to assess renal artery stenosis severity 1. Non-invasive assessments
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline
 Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Impact of ultrasound examination shortly after kidney transplantation
 Eur Surg (2017) 49:140 144 DOI 10.1007/s10353-017-0467-z Impact of ultrasound examination shortly after kidney transplantation Christoph Schwarz Jakob Mühlbacher Georg A. Böhmig Marin Purtic Eleonore Pablik
Eur Surg (2017) 49:140 144 DOI 10.1007/s10353-017-0467-z Impact of ultrasound examination shortly after kidney transplantation Christoph Schwarz Jakob Mühlbacher Georg A. Böhmig Marin Purtic Eleonore Pablik
Renal doppler assessment in differentiating obstructive from non-obstructive hydronephrosis in children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Renal doppler assessment in differentiating obstructive from non-obstructive hydronephrosis in children Nadzri Misni, Dr Rad (UKM)*, Erica Yee Hing, Dr Rad (UKM)*, Hamzaini Abdul Hamid,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Renal doppler assessment in differentiating obstructive from non-obstructive hydronephrosis in children Nadzri Misni, Dr Rad (UKM)*, Erica Yee Hing, Dr Rad (UKM)*, Hamzaini Abdul Hamid,
Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy. Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA
 Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA Renal Transplant Biopsies Tissue Processing Ideal world process as
Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA Renal Transplant Biopsies Tissue Processing Ideal world process as
Renal transplantation is widely accepted as the treatment
 Review Article Sonographic Evaluation of Renal Allograft JS Sandhu, P Sandhu*, K Saggar* Abstract Sonography has become an integral part of the care of renal allograft recipients. It is a simple, inexpensive
Review Article Sonographic Evaluation of Renal Allograft JS Sandhu, P Sandhu*, K Saggar* Abstract Sonography has become an integral part of the care of renal allograft recipients. It is a simple, inexpensive
Diagnosis of Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS)
 May 2001 Diagnosis of Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Kurt Fink, Harvard Medical School, Year III Epidemiology Hypertension -Affects 60 million Americans Essential HTN >95% of cases Secondary HTN 1-5% of cases
May 2001 Diagnosis of Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Kurt Fink, Harvard Medical School, Year III Epidemiology Hypertension -Affects 60 million Americans Essential HTN >95% of cases Secondary HTN 1-5% of cases
Renal artery stenosis
 Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
이학종분당서울대학교병원. Ultrasound in Urinary Colic
 이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
Pediatric Imaging Original Research
 Interlobar Artery Parameters with Duplex Doppler Sonography Pediatric Imaging Original Research A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 186:828 832 0361 803X/06/1863 828 American Roentgen Ray
Interlobar Artery Parameters with Duplex Doppler Sonography Pediatric Imaging Original Research A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 186:828 832 0361 803X/06/1863 828 American Roentgen Ray
Doppler ultrasound as noninvasive diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease
 Doppler ultrasound as noninvasive diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease Poster No.: C-0246 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Ballester Valles, F. Aparici-Robles; Valencia/ES Keywords:
Doppler ultrasound as noninvasive diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease Poster No.: C-0246 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Ballester Valles, F. Aparici-Robles; Valencia/ES Keywords:
Doppler Ultrasound Findings in the Hepatic Artery Shortly After Liver Transplantation
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay García-riado et al. Hepatic rtery fter Liver Transplantation Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay FOUS ON: Ángeles García-riado 1 Rosa Gilabert nnalisa erzigotti
Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay García-riado et al. Hepatic rtery fter Liver Transplantation Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay FOUS ON: Ángeles García-riado 1 Rosa Gilabert nnalisa erzigotti
Doppler ultrasound measurements of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects.
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 4, 464-468 DOI: Doppler ultrasound measurements of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects. Mehmet Zekai Pekkafalı, Kemal Kara Gulhane Military Medicine
Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 4, 464-468 DOI: Doppler ultrasound measurements of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects. Mehmet Zekai Pekkafalı, Kemal Kara Gulhane Military Medicine
Postnephrectomy Changes in Doppler Indexes of Remnant Kidney in Unrelated Kidney Donors
 Kidney Transplantation Postnephrectomy Changes in Doppler Indexes of Remnant Kidney in Unrelated Kidney Donors Abolfazl Bohlouli, 1 Mohammad Kazem Tarzamni, 2 Afshar Zomorrodi, 1 Sedigeh Abdollahifard,
Kidney Transplantation Postnephrectomy Changes in Doppler Indexes of Remnant Kidney in Unrelated Kidney Donors Abolfazl Bohlouli, 1 Mohammad Kazem Tarzamni, 2 Afshar Zomorrodi, 1 Sedigeh Abdollahifard,
Radiologic Importance of a High- Resistive Vertebral Artery Doppler Waveform on Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography
 CME Article Radiologic Importance of a High- Resistive Vertebral Artery Doppler Waveform on Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography Esther S. H. Kim, MD, MPH, Megan Thompson, Kristine M. Nacion, BA, Carmel Celestin,
CME Article Radiologic Importance of a High- Resistive Vertebral Artery Doppler Waveform on Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography Esther S. H. Kim, MD, MPH, Megan Thompson, Kristine M. Nacion, BA, Carmel Celestin,
Image Formation (10) 2 Evaluation and Selection of Representative Images (10)
 STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Vascular Sonography The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists
STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Vascular Sonography The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Malignant Breast Masses Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 4-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad
 ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
Impact of Subclinical Rejection on Transplantation
 Trends in Transplantation 2007;1:56-60 Impact of Subclinical Rejection on Transplantation David N. Rush for the Winnipeg Transplant Group Transplant Manitoba Adult Kidney Program, University of Manitoba,
Trends in Transplantation 2007;1:56-60 Impact of Subclinical Rejection on Transplantation David N. Rush for the Winnipeg Transplant Group Transplant Manitoba Adult Kidney Program, University of Manitoba,
Color Doppler Imaging Evaluation of Proximal Vertebral Artery Stenosis
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Hua et al. Color Doppler Imaging of Proximal Vertebral Artery Stenosis Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Yang Hua 1 Xiu-Feng
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Hua et al. Color Doppler Imaging of Proximal Vertebral Artery Stenosis Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Yang Hua 1 Xiu-Feng
Measure #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE:
Measure #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE:
Carotid Abnormalities Coils, Kinks and Tortuosity David Lorelli M.D., RVT, FACS Michigan Vascular Association Conference Saturday, October 20, 2012
 Carotid Abnormalities Coils, Kinks and Tortuosity David Lorelli M.D., RVT, FACS Michigan Vascular Association Conference Saturday, October 20, 2012 Page 1 Table of Contents Carotid Anatomy Carotid Duplex
Carotid Abnormalities Coils, Kinks and Tortuosity David Lorelli M.D., RVT, FACS Michigan Vascular Association Conference Saturday, October 20, 2012 Page 1 Table of Contents Carotid Anatomy Carotid Duplex
Quality ID #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE
Quality ID #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE
SELECTED ABSTRACTS. All (n) % 3-year GS 88% 82% 86% 85% 88% 80% % 3-year DC-GS 95% 87% 94% 89% 96% 80%
 SELECTED ABSTRACTS The following are summaries of selected posters presented at the American Transplant Congress on May 5 9, 2007, in San Humar A, Gillingham KJ, Payne WD, et al. Review of >1000 kidney
SELECTED ABSTRACTS The following are summaries of selected posters presented at the American Transplant Congress on May 5 9, 2007, in San Humar A, Gillingham KJ, Payne WD, et al. Review of >1000 kidney
Colour Doppler sonography to screen for renal artery stenosistechnical
 2385 Colour Doppler sonography to screen for renal artery stenosistechnical points to consider B. Krumme and L. C. Rump University Hospital Freiburg, Department of Internal Medicine, Freiburg, Germany
2385 Colour Doppler sonography to screen for renal artery stenosistechnical points to consider B. Krumme and L. C. Rump University Hospital Freiburg, Department of Internal Medicine, Freiburg, Germany
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
Immediate Postoperative Sonography of Renal Transplants: Vascular Findings and Outcomes
 Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Horrow et al. Sonography of Renal Transplants Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Mindy M. Horrow 1 fshin Parsikia 2 Radi Zaki 2 Jorge Ortiz 2 Horrow MM, Parsikia,
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Horrow et al. Sonography of Renal Transplants Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Mindy M. Horrow 1 fshin Parsikia 2 Radi Zaki 2 Jorge Ortiz 2 Horrow MM, Parsikia,
SCORING OF i-ifta: POTENTIAL RULES & ROLE IN CHRONIC TCMR
 SCORING OF i-ifta: POTENTIAL RULES & ROLE IN CHRONIC TCMR Parmjeet Randhawa, MD Professor of Pathology The Thomas E Starzl Transplantation Institute University of Pittsburgh . I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR FINANCIAL
SCORING OF i-ifta: POTENTIAL RULES & ROLE IN CHRONIC TCMR Parmjeet Randhawa, MD Professor of Pathology The Thomas E Starzl Transplantation Institute University of Pittsburgh . I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR FINANCIAL
RADIOLOGY HEAD & NECK IMAGING. Iranian Journal of. Hadi Rokni Yazdi 1*, Safoura Faraji 2, Farokhlegha Ahmadi 3, Reza Shahmirzae 4
 HEAD & NECK IMAGING Iran J Radiol. 2012;9(1):12-16. DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.6730 Iranian Journal of RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGYwww.iranjradiol.com Color Doppler Indices of Orbital Arterial Flow in End-Stage Renal
HEAD & NECK IMAGING Iran J Radiol. 2012;9(1):12-16. DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.6730 Iranian Journal of RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGYwww.iranjradiol.com Color Doppler Indices of Orbital Arterial Flow in End-Stage Renal
The Effect of Poststenotic Vessel Wall Compliance
 The Effect of Poststenotic Vessel Wall Compliance upon the Pulsus Tardus Phenomenon Ronald O. Bude, M.D. Jonathan M. Rubin, M.D., Ph.D. Joel F. Platt, M.D. and Ronald S. Adler, M.D., Ph.D. ANN ARBOR, MICHIGAN
The Effect of Poststenotic Vessel Wall Compliance upon the Pulsus Tardus Phenomenon Ronald O. Bude, M.D. Jonathan M. Rubin, M.D., Ph.D. Joel F. Platt, M.D. and Ronald S. Adler, M.D., Ph.D. ANN ARBOR, MICHIGAN
Clinical pathological correlations in AKI
 Clinical pathological correlations in AKI Dr. Rajasekara chakravarthi Director - Nephrology Star Kidney Center, Star Hospitals Renown clinical services India Introduction AKI is common entity Community
Clinical pathological correlations in AKI Dr. Rajasekara chakravarthi Director - Nephrology Star Kidney Center, Star Hospitals Renown clinical services India Introduction AKI is common entity Community
Vascular Ultrasound: Current state, current needs, future directions
 Vascular Ultrasound: Current state, current needs, future directions Laurence Needleman, MD Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University Disclosures
Vascular Ultrasound: Current state, current needs, future directions Laurence Needleman, MD Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University Disclosures
The Force is in the cfdna. Roy D. Bloom MD University of Pennsylvania
 The Force is in the cfdna Roy D. Bloom MD University of Pennsylvania Disclosures Advisor: Veloxis, CSL Behring Royalties: UpToDate Research support: CareDx, Veloxis, Shire Nephrocentric presentation Road
The Force is in the cfdna Roy D. Bloom MD University of Pennsylvania Disclosures Advisor: Veloxis, CSL Behring Royalties: UpToDate Research support: CareDx, Veloxis, Shire Nephrocentric presentation Road
Abdominal Doppler. Cases of Where, Why, and How
 Abdominal Doppler Cases of Where, Why, and How Jill D. Trotter, BS, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Director, Diagnostic Medical Sonography Program Vanderbilt University/Vanderbilt Medical Center Nashville, Tennessee
Abdominal Doppler Cases of Where, Why, and How Jill D. Trotter, BS, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Director, Diagnostic Medical Sonography Program Vanderbilt University/Vanderbilt Medical Center Nashville, Tennessee
Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab
 TRANSPLANTATION Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab Khadijeh Makhdoomi, 1,2 Saeed Abkhiz, 1,2 Farahnaz Noroozinia, 1,3
TRANSPLANTATION Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab Khadijeh Makhdoomi, 1,2 Saeed Abkhiz, 1,2 Farahnaz Noroozinia, 1,3
